Content
- 1 The best varieties of honeysuckle in the Urals
- 2 Correct planting of honeysuckle
- 3 Features of the care and cultivation of the Ural honeysuckle
- 4 Fertilizers required by the plant
- 5 Reproduction of honeysuckle
- 6 Preparing for planting honeysuckle outdoors
- 7 Planting process
- 8 Diseases and pests of honeysuckle
- 9 Reproduction methods
- 10 Honeysuckle varieties
- 11 Types of honeysuckle
- 12 How to propagate honeysuckle
- 13 When to plant honeysuckle outdoors
- 14 How to choose a place to plant honeysuckle
- 15 Plant care honeysuckle
- 16 Watering the honeysuckle
- 17 Fertilizers for honeysuckle
- 18 Pruning honeysuckle
For a long time, this plant grew only in the territories of Siberia and was considered a wild plant. Many people who lived in the Urals did not want to plant honeysuckle in their gardens for many reasons.
First, they believed that honeysuckle is a shrub that defies cultivation. Secondly, people underestimated the benefits of this plant. Thirdly, it was believed that it would not survive the large frosts that are typical for the Urals.
However, despite all these reasons, one of the gardeners decided to plant this shrub with dark blue fruits on his territory and got an excellent result. He realized that honeysuckle is a frost-resistant plant, the fruits of which are rich in vitamins and have many medicinal properties. After this experiment, there was a horticultural explosion, as a result of which this berry appeared in most people in their territories.
Honeysuckle has certain characteristics that are associated with its appearance. Among these features are the following
- the plant has several subspecies, which have their own external characteristics;
- honeysuckle fruits - tasty and healthy blue berries;
- honeysuckle is a branched shrub that reaches a height of about two and a half meters;
- the trunk of the plant is not strong enough, the stems of which can be easily broken by hand;
- the leaves of the plant are juicy green in color, oblong oval;
- flowers are bright orange funnel-shaped.

The best varieties of honeysuckle in the Urals
Each plant always has its own subspecies. And honeysuckle is no exception. Among all its subspecies, the best in the Urals are
- Amazon is a frost-resistant honeysuckle variety characterized by an early ripening period (mid-June). The berries of this variety are quite tasty, juicy and sweet, they begin to crumble early, so they must be picked on time. However, the yield from one bush is small - about one and a half kilograms.
- Viola is one of the most frost-resistant fruits of the Ural honeysuckle. The fruits of this variety are large enough and have a sweetish taste, but with a slight bitterness. The harvest of the variety is very large, about four kilograms per bush, the berries begin to crumble in June, so they must be picked early.
- Cinderella is a beloved variety of honeysuckle, which is distinguished by its large berries and strawberry aroma. The bone of this variety itself is not high, but it gives a medium-sized crop (about two kilograms per bush). Cinderella, like many varieties of the Ural honeysuckle, is quite frost-resistant, it can withstand frosts down to -50 degrees Celsius.
- Maria is another frost-resistant honeysuckle variety, which is distinguished by its large and tasty berries. This variety yields a fairly good harvest (about 1.5 - 2 kilograms) and begins to bear fruit early (around June).
- Elizabeth is a variety of honeysuckle, the main features of which are large fruits, good harvest, frost resistance, large shrubs, increased immunity to pests and diseases.
- Gorlinka is a versatile variety that is good in all respects. Its main features are frost resistance, low yield, large fruits with a good sweet taste and small shrubs.
- Amphora is a variety of honeysuckle that is perfect for growing in the northern regions of Russia, including the Urals. The fruits of this variety are not bad, but there is a bitter taste in the taste, the plants give a bountiful harvest, which is up to three kilograms per bush. Amphora berries are great for harvesting for the winter and freezing.
- Bakchar's pride is a wonderful variety of honeysuckle, which is distinguished by a special form of berries. The fruits of this variety are sweet and sour, suitable for long distance transportation. The plant easily tolerates various diseases and pests.
- Chelyabinka is a variety of honeysuckle, ideal for the Urals. It has the ability to produce good yields, increased frost resistance and large spreading bushes. The plant bears fruit late, but you can spend a lot of time and effort on it.

Correct planting of honeysuckle
Correct planting is the key to the success of the plant, an important process that requires adherence to all the rules. Honeysuckle, although an unpretentious plant, which is characterized by increased frost resistance and immunity to diseases, nevertheless requires compliance with certain conditions when planting it, among which the main ones are
- the best time to plant honeysuckle is late spring or early summer;
- prepared soil - thoroughly dug up soil with all the necessary mineral fertilizers introduced into it;
- holes dug for planting with various pebbles, gravel or drainage introduced there;
- planting pits must also be filled with compost in order for it to saturate the soil with all the substances necessary for the plant;
- abundant watering after planting and mulching (for this you can use sawdust, needles, peat, grass or moss).

Features of the care and cultivation of the Ural honeysuckle
Nursing and growing are important stages in the growth and development of every plant. In order for a person to get a bountiful harvest of honeysuckle berries, he needs to constantly monitor the condition of his bush, it is necessary to water, feed, cut and heal on time for all diseases and pests. Honeysuckle has certain requirements for caring for it, among which the main ones are
Watering
Watering the plant must be done very carefully, since honeysuckle does not tolerate waterlogging, but loves moist soil. Honeysuckle should not be watered often, the main periods for watering are the flowering time and the ripening time of the fruits. If you do not do these two important watering, then you can either lose some part of the crop, or the plant will get sick or die.
Loosening and mulching the soil
Loosening and mulching are the stages associated with caring for the soil of the plant, which must be done regularly, otherwise the plant will lose the necessary nutrients and will soon die.
Loosening of the soil must be done correctly, without damaging the plant. Loosening is done regularly to maintain good soil condition and help it get more oxygen.
Mulching is an equally important process that must be carried out constantly, because thanks to this process, the plant receives the necessary mineral and organic fertilizers, which come from the soil to the plant and form its body.For mulching, it is advisable to use sawdust, peat or a certain type of moss.
Correct pruning of honeysuckle
Pruning is the process of getting rid of parts that are unnecessary to the plant. It is very important as it helps the entire plant to grow and develop. Honeysuckle, like any plant, requires proper pruning, so you need to constantly monitor the condition of the crown of the plant.
Pruning of honeysuckle should be done in the third year of the plant's life, do not create a dense web of shoots, which prevents the plant from growing calmly and correctly. It is necessary to prune mercilessly, shortening the shoots to twenty centimeters, so you will give the fruits and flowers more room for development and ripening. The most important part of pruning is pruning the lower shoots, which stimulates the plant to grow and produce nice, large flowers, and then healthy juicy fruits.
Preparing honeysuckle for the Ural winter
Getting ready for winter is an important, but fairly simple step in the life of a honeysuckle. You just need to do the following with the plant: cut off unnecessary branches and shoots, as they can become breeding grounds for diseases; the plant itself is spud and mulched so that pests do not appear in the soil that can spoil the plant in winter.

Fertilizers required by the plant
Each plant requires a certain amount of fertilizer of various types and components. Honeysuckle is no exception in this case, since this plant is very fond of various fertilizers, among which the main ones are
- nitrogen, which is necessary for the soil of the plant;
- potassium, which is involved in the formation of the plant organism;
- phosphoric, which maintains the good appearance of the plant;
- organic fertilizers, which are necessary to saturate the soil with various mineral components.
Reproduction of honeysuckle
Reproduction is an important step that helps the gardener or gardener get more plants for a beautiful garden or for a large number of crops. For the correct reproduction of a plant, you need to know all the basic rules, otherwise you will lose not only the result you are striving for, but also the strength, time and energy that were spent on this matter. So, let's look at the breeding features of honeysuckle
- reproduction occurs by cuttings or layering;
- shoots for reproduction are harvested in advance;
- the best time for breeding is spring;
- choose the best seedlings without any damage;
- everything must be done carefully and carefully so as not to destroy the plant.
In the article we will tell you about an unusual plant: how to plant it correctly and how to care for it.
Honeysuckle is a shrub that is prized primarily for its decorative effect. In decorative varieties, the fruits are not edible. But thanks to their beautiful appearance, they won the hearts of many gardeners. The shrub perfectly complements the beauty of the suburban area.
Proper planting and care of honeysuckle is the key to an attractive appearance and a good harvest.
Preparing for planting honeysuckle outdoors
The honeysuckle family includes shrubs of various configurations: high, low, woody, liana-like. They are grown both for decorative purposes and for harvesting berries.
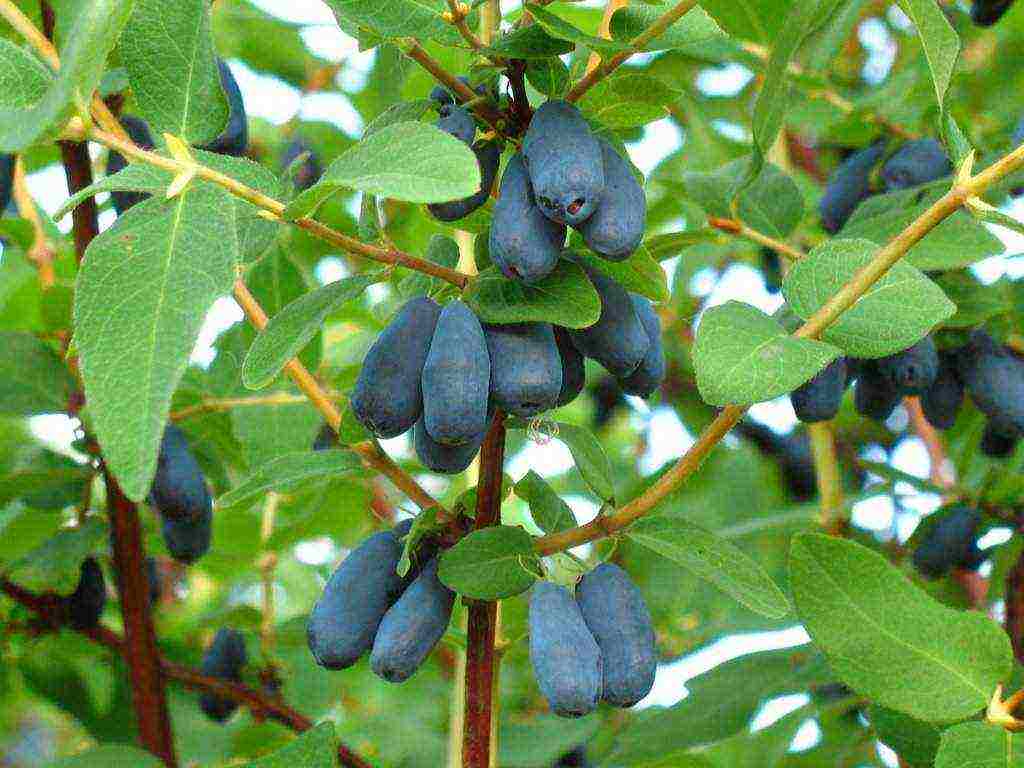

The fruits of edible honeysuckle and Kamchatka honeysuckle are suitable for eating, Tatar honeysuckle is inedible. Planting and caring for honeysuckle should be carried out in accordance with the agricultural practices of the culture.
Landing dates
The culture on your site can be planted in autumn and spring. But the most suitable time of the year will still be autumn. In spring, the plant is planted in May, and in autumn in early October.
Landing in the open field is carried out before bud break. If planted later, the plant may not take root, and its resistance to various diseases also decreases. In areas where cold weather sets in faster, planting is carried out in August (Arctic and eastern Siberia).For central Russia, the right time will be the end of September and the beginning of October.

According to statistics, fewer seedlings take root in the spring than in the fall. The reason is that plants planted at such a time are more sick and develop poorly. Before planting, you need to choose a comfortable place for the culture and prepare both the bush itself and the soil.
For transplanting honeysuckle from one place to another, it is recommended to use the transfer method together with a large lump of earth.
Choosing a place for a shrub
Edible honeysuckle is a very thermophilic plant. The place under the bush should be well lit by the sun. The acidic soil of honeysuckle is not suitable. This negatively affects growth and fruiting. Loose, organic-rich soils are most suitable for honeysuckle. Does not tolerate shrubs close to groundwater. From this, the roots begin to rot.
You should also protect the plant from the winds, as they can drop already ripe fruits to the ground. The right place is the key to a good harvest.
The shrub can withstand slight shading. Lack of moisture adversely affects the plant: the growth of shoots decreases, the quality of the crop decreases. Potatoes and vegetables are good precursors for honeysuckle.
The place must be cleared of weeds. You can use herbicides to destroy them.
"There are two main conditions to consider when choosing a location for honeysuckle: good lighting and sufficient soil moisture."
Soil preparation
Correct planting should be done in well-fertilized soil. Mineral and organic fertilizers are used. Thanks to the nutrients, the plant will quickly take root and gain strength before fruiting. The planting site begins to be prepared in the fall. The soil is fertilized with fresh manure, and this is not recommended in the spring.
Selection and preparation of planting material
When buying a seedling, ask the seller to tell you everything about the bush you like. It is advisable to purchase planting material in specialized stores. In this case, you will be sure that the plant is absolutely healthy and of the variety you need.
Tips for choosing planting material:
- You need to buy a 2-year-old plant. Its height should reach 30-40 cm.
- The branch should bend, not have any damage.
- Sometimes the bark of seedlings may peel off. This is completely normal.
- A well-developed bush should have buds on the branches. Their absence suggests that the culture is not entirely healthy.
- It is recommended to grow honeysuckle of different varieties in the country. Not all plants of this species can sufficiently pollinate each other.
- In the future, it will be possible to independently propagate the honeysuckle.
Choosing a healthy seedling is not easy. A biennial plant should have three or four elastic branches, a well-developed root system. Before purchasing, it is advisable to check the earthen lump for mold. If there is no mold, the plant is quite healthy and will quickly take root in the summer cottage.
Before planting, planting material should be prepared: carefully examine, cut off broken branches and roots. Very long roots should be shortened to 30 cm, the main thing is not to damage the kidneys during preparation.
Planting process
After preparing the soil and planting material, the plant is planted.
- A few days before planting, holes are dug 40 × 40 × 40 in size. The distance between the holes should be one and a half meters for low-growing bushes and two to three meters for tall ones.
- In the hole, it is necessary to provide a drainage layer of expanded clay, crushed stone or broken ceramic bricks.
- Each hole must be filled with a mixture of natural soil with fertilizers (compost, superphosphate and ash). For sandy soil, you need to take more compost.
- Fill each hole well with water.
- An earthen mound is formed in the center of the hole and a seedling is placed on its top.Its root system must be gently spread evenly on all sides of the hole.
- Then the roots should be sprinkled with soil.
- After planting, the holes should be poured abundantly with water again so that the earth settles a little.
- The soil around the seedling is mulched so that moisture is retained in the soil.
Outdoor care for honeysuckle
Honeysuckle needs constant care: watering, feeding, pruning, weeding and loosening the soil around the bush, preventive measures and treatment for pests and diseases.

And garden honeysuckle will delight you with its appearance, and give good harvests for many years.
Watering
The initial care for garden honeysuckle is watering. It should be abundant, and the soil under the plant itself should always be moist.
You can water not only at the root, but the whole plant as a whole. Spray watering is carried out in the morning and in the evening - to protect the plant from burns.
Top dressing
From early spring to autumn, honeysuckle needs regular feeding. Every two weeks, you need to apply a new portion of fertilizer. Many are wondering how to fertilize. The first feeding is carried out with a nitrogen-containing complex - due to it, the plant will quickly gain vegetative mass.
Most importantly, nitrogen fertilization before flowering. An excess of this substance reduces the frost resistance of the crop. As soon as the plant fades, nitrogen-phosphorus feeding is carried out with the calculation of 25 g of nitrophoska per 10 liters of such feeding. 3-5 liters of solution are poured under each bush.
In autumn, potash salt is used as a fertilizer in an amount of 15 g / m2. But the frequency of such feeding is only once every three years. It is recommended to fertilize the soil with plant compost and humus.
Pruning features
Garden honeysuckle berries are formed only on young shoots, therefore it is recommended to rejuvenate the bush every 3-6 years. The procedure consists in removing all old and weak shoots.
To completely rejuvenate a very old crop, all branches should be cut to the root. With abundant watering, regular feeding, new shoots on the bush will appear soon. The bush will also restore fruiting.
In addition to rejuvenation, they prune old, dry, broken branches and shoots growing inside the bush in the autumn. It is necessary to thin out the bush so that sunlight better gets into its very thickets.
The young plant does not need to be pruned for the first three years after planting.
Fruiting honeysuckle
With the onset of warmth, each of us dreams of quickly eating berries grown in our own garden. But most of the berries ripen only in the second half of June. Honeysuckle fruits will delight before all garden berries.
While residents of the southern regions of Russia are already feasting on, in the middle lane the fruits are still quite green. In the north, the fruits ripen at the end of June.
Edible honeysuckle has dark blue fruits with a waxy coating. Most often they are oblong in shape. From one adult bush, you can collect about 2 kg of berries. Honeysuckle begins to bear fruit 3-4 years after planting.
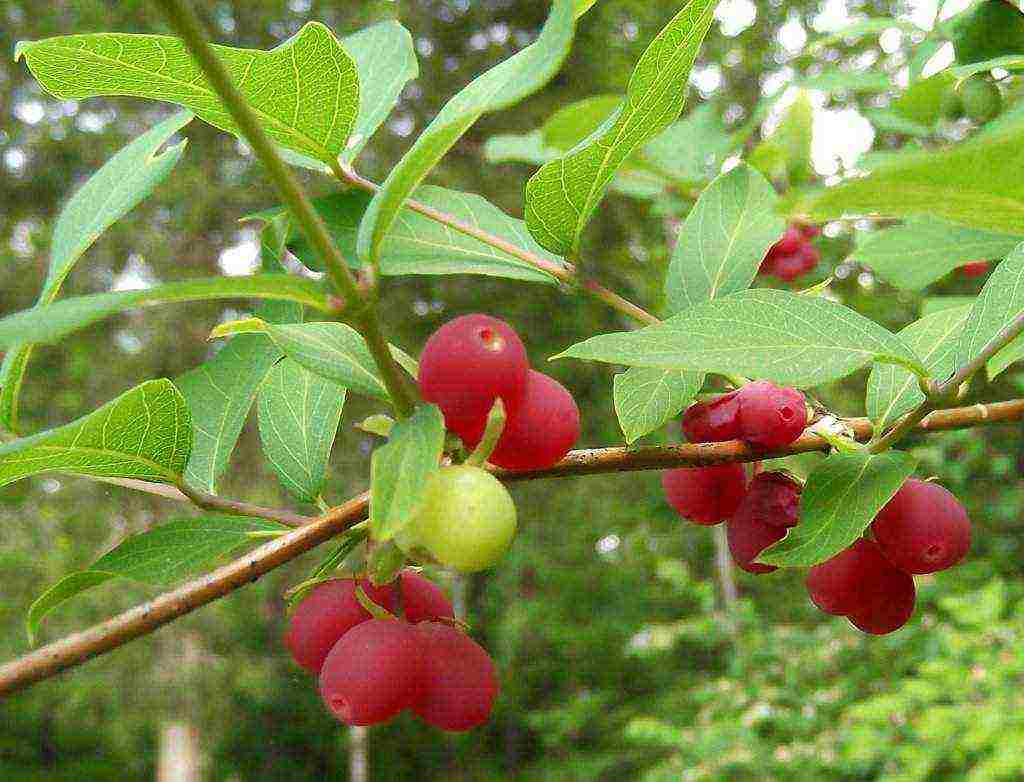

Up to 6-8 years, the yield of the bush will increase. The berry taste resembles a cross between blueberries and blueberries. The fruits can be sweet, sour, or sweet and sour. The palatability of the berry is influenced by the varietal characteristics laid down and the weather conditions under which they ripened.
Ripe fruits begin to fall off very quickly and therefore it is necessary to harvest quickly. If the berries turn dark blue, they are ripe. The ripeness of the fruit is also determined by the color of the pulp inside: if it is red, then it’s time to harvest.
Useful properties of berries
Honeysuckle berries contain vitamins C, P, also iodine, magnesium, iron. Often the edible fruits of honeysuckle are used in folk medicine as a variety of decoctions and infusions. In terms of vitamin C content, honeysuckle berries are not inferior to lemon and strawberries - recognized favorites. Fresh berries are also good at quenching thirst.

People with diseases of the cardiovascular system, anemia, hypertension are recommended to consume the fruits regularly. A large amount of vitamins makes it possible to use them for recovery from serious illnesses and when following a diet.
Edible honeysuckle is used to prevent gastritis and stomach ulcers. A good diuretic berry.
Diseases and pests of honeysuckle
Timely measures taken to prevent diseases and pests will help grow a healthy plant.
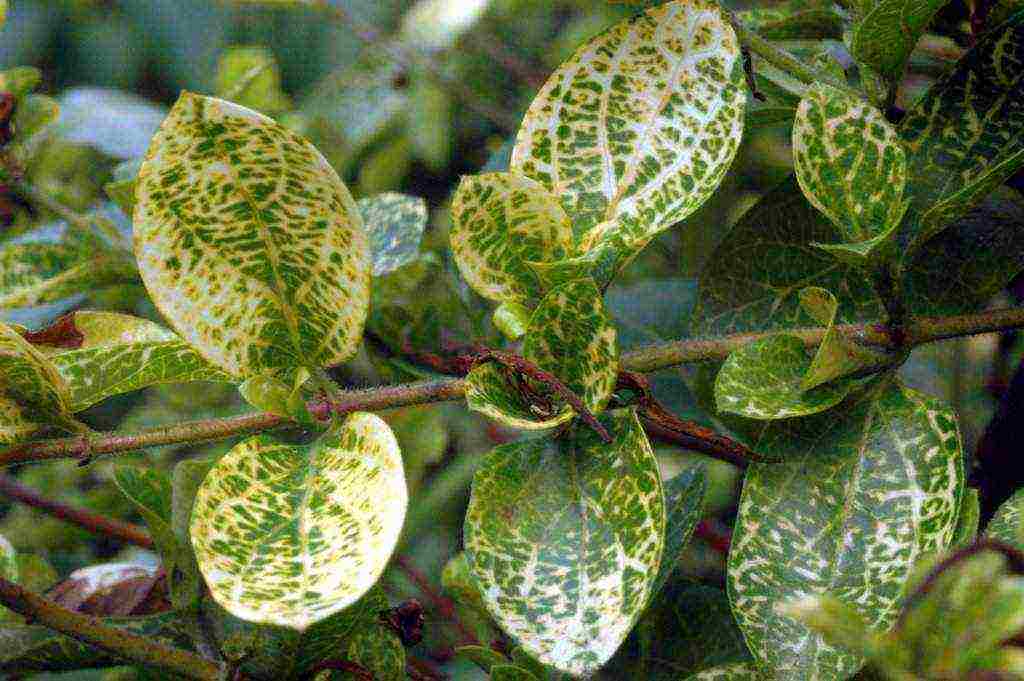

The spread of various diseases is associated with an increase in interest from gardeners in this culture. Most often, infected planting material is already acquired. Pest control is very difficult. The most important rule is to comply with all agrotechnical growing conditions.
Diseases
Powdery mildew. Fungal disease. Modern fungicides will help.
Symptoms: The leaves are covered with a white tomentose bloom on both sides of the leaf. Gradually, the affected tissues darken and dry out. Leaves fall off prematurely, which reduces the plant's ability to tolerate cold temperatures. The affected shoots must be removed, since the infection remains under the bark for a long time.
Ascochitous spot of honeysuckle. The leaves are covered with blackish blurry spots. The greenery gradually dries out, crumbles ahead of time, thereby lowering the frost resistance of the shrub. Fallen leaves must be burned, because the infection still persists in them.
As a preventive measure, the bushes are sprayed in the spring and after flowering with a Bordeaux mixture.
Light gray spotting. The leaves are covered with numerous rounded spots. Such leaves darken and fall off.
Pests
Red-footed shtitnik. A large bug, its body size reaches 13-17 mm. The top is painted brown with a bronze tint and numerous small dots, the bottom is strewn with rusty-red black dots. Drinks the juice of trees and shrubs.
In the spring, it is recommended to carry out preventive treatment of bushes (before and after flowering) with drugs such as fufanon, kemifos, actellik.
Narrow-bodied honeysuckle. An insect with a shiny green body. The size of the beetle is 7-8 mm. Active flight of the pest is observed during the flowering period of honeysuckle. Gnaws leaves from the edges.
The female insect lays eggs on shoots and cuttings of leaves. New larvae make their way under the bark of the plant and remain there until the onset of spring. Damaged shoots die off over time. To destroy the pest, the bushes must be sprayed with the drug "Fufanon".
Aphid. One of the few pests that live in the crown of the plant. Honeysuckle leaves suffer the most from aphids. The insect feeds on the sap of the plant. When damaged, the leaves change color - they become pale and become covered with brown spots.
Most often, in order to reduce harm from insects, shrubs are treated with a solution of laundry soap, infusions of herbs (chamomile, calendula). Also on sale there are various drugs that destroy the pest: "Entobacterin", "Fitoverm", "Biotlin".
Five-fingered fingerwing. Its caterpillars attack unripe berries. The pest eats away the pulp of the fruit, from which they dry up and fall to the ground ahead of time. The drug "Pyrethroid" will help get rid of the enemy.
Reproduction methods
You can propagate honeysuckle:
- layering;
- cuttings;
- dividing the bush.
In addition to vegetative methods, it is also possible to grow a new plant from seeds. Each method has its own pros and cons.
Propagation by cuttings
- This type of reproduction of honeysuckle has a number of advantages.
- Each new cut retains the characteristics of the mother plant.
- With this method, you can harvest the crop in a year. For example, when propagated by seeds, honeysuckle begins to bear fruit only in the third year after planting.
- It is best to harvest cuttings in the summer (period after flowering and before the berries ripen).With earlier harvesting, they may not take root (approximately 60% of the planting material).
Propagation by green cuttings
A strong shoot is suitable for the cutting. From it you need to take 12 cm in length. A good cutting should be 0.5 cm in diameter with two internodes.
New cuttings should be immediately planted in a prepared container. Soil of sand and peat in a ratio of 3: 1 is pre-moistened. Room humidity should be 85%, temperature - 25 degrees Celsius. The most suitable place would be a foil greenhouse or greenhouse.
Subject to all the necessary growing recommendations, the cutting will take root 10 days after being placed in a container. To harden the cuttings, it is necessary to regularly ventilate the greenhouse - ventilate for 20-40 minutes, each time increasing the time and number of ventilations.

Planted cuttings must be watered, weeded, loosened and sprayed in hot weather.
There is also a way of propagation by lignified cuttings. The cutting procedure is similar to that of a green cutting. They differ from each other only in terms of harvesting planting material.
Lignified cuttings are cut in early October, when the leaves have completely fallen from the bush. They are placed in thick paper with sawdust or sand and stored in a dark cool room in the spring. Not all such cuttings take root. But you can use growth stimulants so that the rooted shoot begins to develop faster.
Reproduction by layering
Layers can be either vertical or horizontal. For reproduction with horizontal layers, it is necessary to dig up and level the ground around the plant. The procedure is carried out in June. Lower young shoots are laid on the ground in 1 cm deep grooves prepared in advance.
Then they must be secured with a hairpin (a wooden one is better) and sprinkle all the shoots with a five-centimeter layer of earth. The next spring, the young plant is separated from the mother.

The process of reproduction by vertical layers is preferable to the previous one, but it is possible only for plants not older than 3-5 years. The base of the bush is covered with a layer of loose earth (20 cm). Throughout the summer, the plant must be regularly watered and hilled. Next year, the land will need to be excavated, the shoots should be cut off and planted in a new place.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
It is considered the easiest way. It makes it possible to get several strong seedlings from one adult plant at once. This procedure is carried out in the fall, when all the leaves fall off the honeysuckle.
For new bushes, holes are prepared: fertilizers are applied to them and filled with water. Before planting, seedlings should be shortened by one third to speed up strengthening. To divide the bush, take a bush from 5 to 7 years old.
Saplings from older plants may not take root. The shrub is dug up, divided into three parts and planted.
Honeysuckle varieties
Almost 50 types of honeysuckle are grown on the territory of Russia, but only the fruits of 15 varieties are suitable for consumption. Ornamental varieties have a curly bush shape. The plant begins to bloom in the second half of May. Most varieties feel great in central Russia.
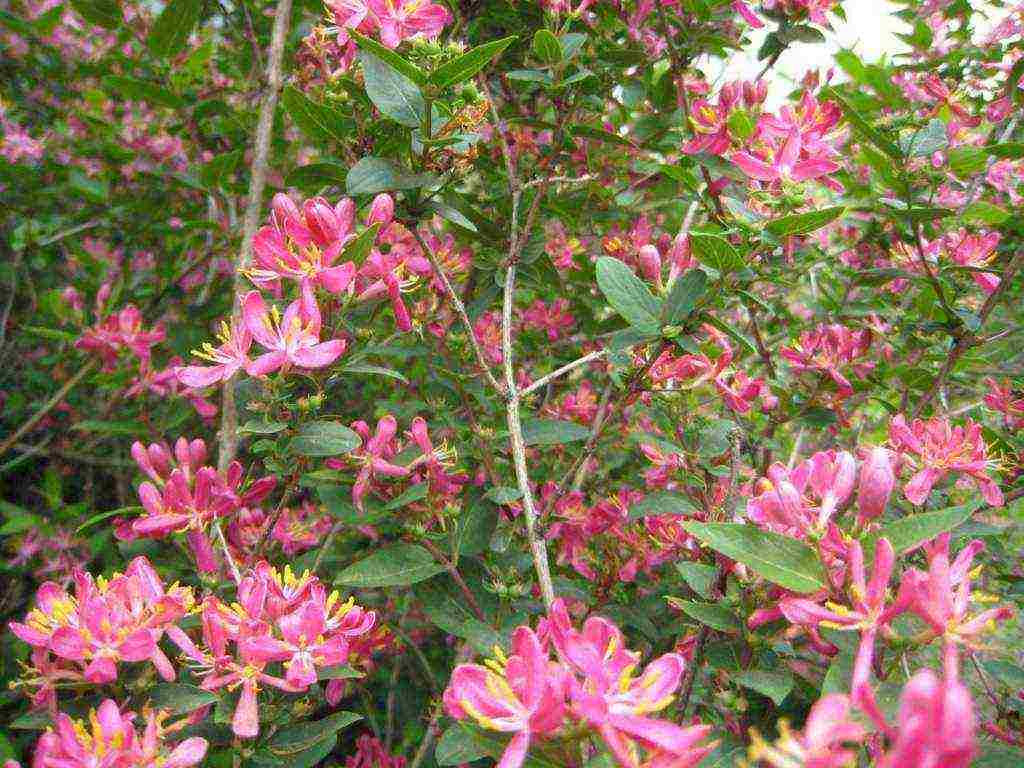

For cultivation in the Moscow region, varieties are also perfect: "chosen one", "nymph", "moraine", "silginka". Edible species include: blue, Caucasian, Altai, honeysuckle, Kamchatka honeysuckle.
Description of species
Honeysuckle honeysuckle. The view is very popular. Comes from southern Europe. Climbing shrub. It is a melliferous crop. The branches are large (5 cm). They have a very pleasant aroma. The inside of the flower is yellow, the outside is covered with purple stripes. The berries are red-orange.
At the age of four, the first flowers begin to appear. The flowering period is 20 days. Honeysuckle of this variety grows quickly in moist and fertile soil. Life expectancy is approximately 30 years.Used to decorate buildings, arches, fences.
Curly honeysuckle. It grows in the natural conditions of Europe and Asia. Plant height up to 5 meters, flowers are two-colored. There are decorative forms. For example, late curly honeysuckle has fallen in love with many gardeners due to its long flowering period (from the beginning to the end of summer).
In the early days, the flowers are red, but gradually lose their original appearance. The plant should be covered for the winter. For this, the shoots are removed from the supports and sprinkled on top with dry leaves and spruce branches.
Tatar honeysuckle. The shrub height can reach three meters. It begins to bloom in late spring with graceful white or pink flowers. Unpretentious to growing conditions, tolerates low temperatures well.
Albert's honeysuckle. It is a small shrub (1.2 m) with thin shoots and barely visible leaves. The flowers have a delicate aroma. It perfectly tolerates a lack of moisture, has increased winter hardiness, and is often used by landscape designers to decorate rocky gardens and alpine slides.
Alpine honeysuckle. The plant is very compact, it grows only a meter. The flowers do not have any smell. The fruits are red with a shiny bloom. The dwarf form Nana can be found in the gardens of Europe.
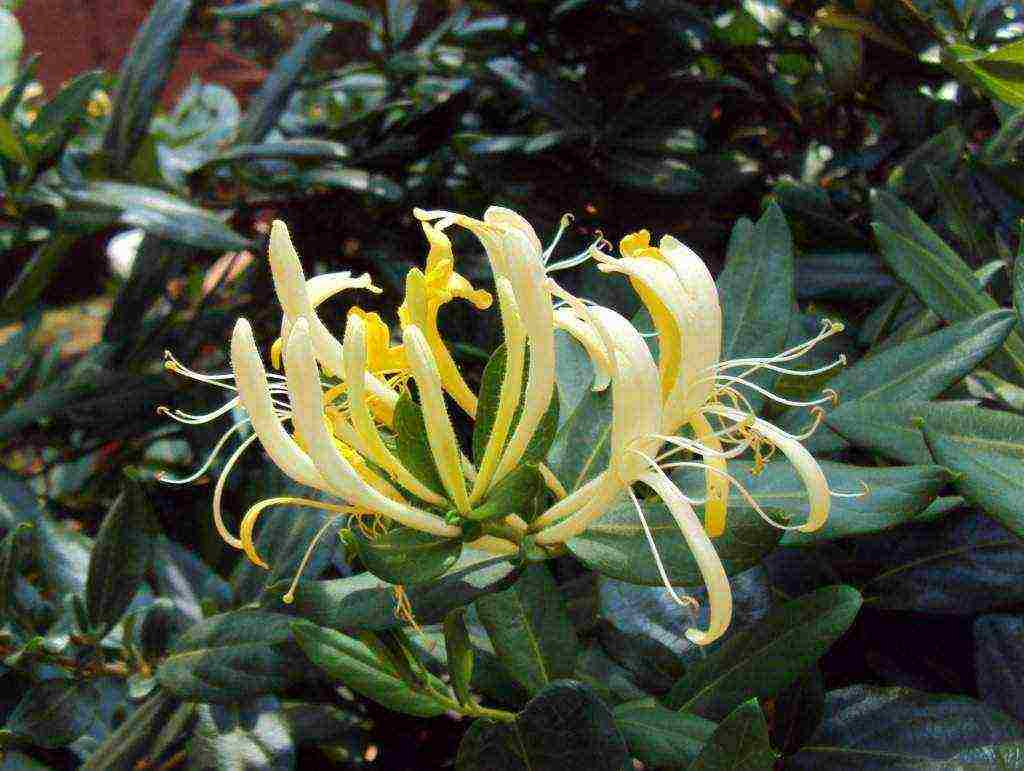

Golden honeysuckle. For the first time, the variety was grown in the further east, where it still grows. Honey plant. Blooms in May, and closer to August, the first red berries appear. The shrub height varies from 2 to 4 meters. Does not need to create special conditions for personal care. Winter hardy.
Korolkov's honeysuckle. The bush is up to 3 m. The first time it blooms and bears fruit with the onset of three years of age. Refers to late varieties. The flowering period is mid to late June and lasts two weeks. The flowers are pink.
Rough honeysuckle. They are distinguished by their orange-yellow flowers. They bloom in early summer. Abundant flowering. Then bright red fruits appear in their place. Unpretentious to care. The plant can be propagated both by cuttings and by seeds.
American honeysuckle. Hybrid variety. The shape of the bush is curly. The variety has very beautiful flowers: yellow inside, purple outside. A very thermophilic plant. Needs additional shelter for the winter.
Description of varieties
Honeysuckle "nymph". The variety has a long growing season. Bred by St. Petersburg breeders. The berries are very large (3 cm long and weigh up to 1.2 g). The taste is sweet and sour, the seeds are almost invisible on the bush.
The fruits are dark blue with a waxy bloom. Up to 1.5 kg of berries can be harvested from one adult bush. Almost do not crumble like other varieties. You can enjoy the fruits at the end of June.
The bush of the plant is oval. Has a wonderful decorative look. The crop can be used as a hedge.
Honeysuckle "blue bird". Early ripe variety. Bred in Siberia. The variety is especially popular in Belarus. Besides him, the popular varieties there are "blue spindle", "daughter of a giant", "Pavlovskaya".
The bushes are highly developed, with a massive dense oval crown. The berries are sweet and medium in size. When ripe, they do not crumble.
The variety can withstand low temperatures and is immune to disease. Poorly self-pollinated. It is recommended to plant other varieties with it for pollination.
Attention! “You cannot plant only one specific variety in your summer cottage, there should be several of them. This is because honeysuckle is a poor self-pollinator. You run the risk that the plant will only bloom, but not bear fruit. "
You can pick up several crops at once that will feel great in your climate zone. The variety of forms of this plant allows it to be used in various compositions as an addition to other garden crops. Feel free to experiment.
Honeysuckle is exactly the plant that should be in the garden.This is an excellent decoration of the site, and varieties with edible fruits will delight you with tasty, healthy and, most importantly, early berries. What the doctor prescribed against spring beriberi.
They began to grow and cultivate garden honeysuckle quite recently, but summer residents immediately fell in love with this culture. There are many types of honeysuckle, but they can all be roughly divided into two broad categories: edible and decorative. In this article, we will discuss the best varieties of honeysuckle, tell you how to grow it in order to always get a rich harvest and a beautiful garden.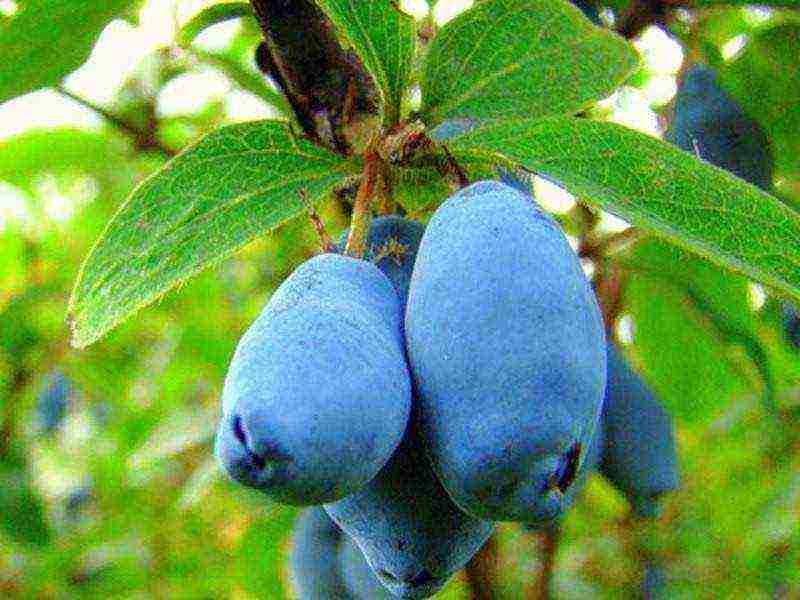
Types of honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is an ornamental curly honeysuckle that stands out for its beauty. The plant weaves along low supports, no more than 2 m. The curly shrub is covered with oblong leaves, which have a deep green tint outside, and their dove-blue color on the inside.
Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
Blue bird - this unique variety is bred from the Kamchatka variety of shrubs. An excellent honeysuckle for growing, as it is not susceptible to a variety of pests, but at the same time it gives a large yield. The first berries on the bushes ripen 3 years after planting.
The blue spindle is a type of honeysuckle that ripens early. The crown of the bush is rather rare, its branches are massive and well developed, the height of the plant does not exceed 1 m. The whole bush is dotted with oblong leaves, dark green in color.
Gourmet is a variety of honeysuckle with excellent fruits. The bush is quite compact, its crown is rounded. The whole plant is covered with beautiful foliage, they are oval in shape, and their color is dark green. The fruits are small enough, their weight does not exceed 0.7 g. They have a pleasant juicy pulp, with a sour-sweet taste that is absolutely free of bitterness.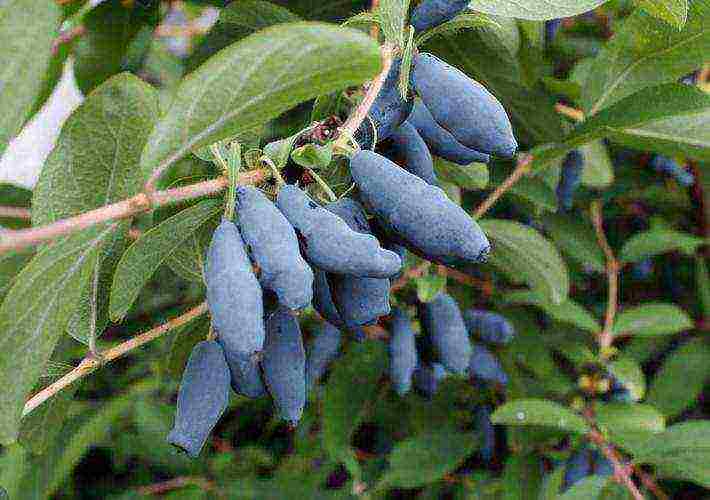
Amphora is derived from Kamchatka varieties, therefore it tolerates severe frosts and is suitable for growing in the northern regions of the country. The bush is not tall, only about 1.5 m, its crown is round. The whole plant is densely covered with dense foliage, dark green in color.
How to propagate honeysuckle
The main breeding method for honeysuckle is the vegetative method of green cuttings. The best time for its application is the beginning of ripening of the berries at the time of their staining blue. In the conditions of the southern region, this technique can be carried out already at the beginning of the second decade of May, and in a hot summer, cuttings begin earlier than in a cold one. Growing annual shoots or parts thereof 8-12 cm long with 2-3 buds are used as green cuttings. The survival of green cuttings is facilitated by harvesting them "with a heel" - a piece of wood from an annual branch. For this, the shoot is not cut off, but broken out at its base. The prerequisites for green cuttings are protected soil and the possibility of watering; rooting is better done in conditions of "artificial fog", under a film, a bottle.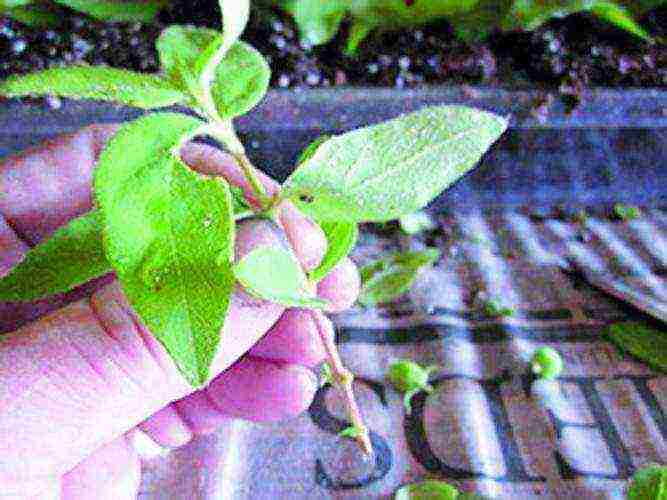
The second way of reproduction of honeysuckle is lignified cuttings. But in this case, the yield of planting material is much less, about 30%. Strong annual shoots with a diameter of 6-10 mm are used for cuttings. They are cut at the end of March and before the beginning of the growing season, stored in the refrigerator for planting. Before planting, the branches are cut into cuttings up to 20 cm long. As soon as the weather permits, in early April they are planted in a nursery, greenhouse or greenhouse. When breeding and caring for honeysuckle, daily watering is necessary. Roots appear in 40-45 days. Rooted cuttings are grown next year. For successful survival, seedlings should have 2-3 branches 20-30 cm long, roots - at least 3-4 pieces 20 cm long.
When to plant honeysuckle outdoors
If the planting of honeysuckle was carried out correctly, then the first harvest of berries can be harvested in two years. And although honeysuckle is a rather picky plant, proper care guarantees its healthy appearance and abundant fruiting.So, you should know that honeysuckle seedlings in the first year after planting need regular watering, and before the first wintering, they must be additionally insulated with a layer of mulch of 10-15 cm. When choosing seedlings, give preference to 2-year-old specimens that already have several branches and reach a height of 30-40 cm. Be sure to inspect each bush. Its branches should be flexible, without visible damage.
Peeling bark is normal for this plant. A healthy seedling has a branched root system and growth buds on the branches. Experienced gardeners recommend immediately purchasing different varieties of honeysuckle, since they are all pollinated in different ways.
For planting honeysuckle in open ground, planting pits are preliminarily prepared, which have a size of 40x40x40 cm and are located 1.5 - 2 meters apart. A nutritious mixture of organic and mineral fertilizers such as OMU "Universal" is poured onto their bottom, onto which the straightened roots of the seedling are lowered. Then they are covered with loose earth so that the root collar is deepened by 5 cm.
The soil around the planted honeysuckle is compacted and watered with a bucket of water. After the moisture is completely absorbed, the soil around the bush is mulched with organic matter. It is strictly forbidden to prune the honeysuckle immediately after planting, as this leads to a delay in growth and development.
How to choose a place to plant honeysuckle
The main criterion for choosing a planting site for honeysuckle is the availability of good lighting. Of course, the bush is able to survive in the shade, but then the yield will be minimal, and the decorative varieties will bloom poorly. More light is needed for a bountiful harvest and lush flowering of honeysuckle.
Avoid elevated areas where there is a threat of drafts. Honeysuckle's shoots are tender and brittle and can break easily in strong winds.
Curly decorative varieties of honeysuckle are recommended to be planted around arbors or near an arch, so that the shoots have support for further growth. Lower edible varieties can be planted either in a group in one corner of the plot, or as a hedge in one row along the fence or border of the plot.
Plant care honeysuckle
The better the growing conditions, the more beautiful the bushes and the greater the yield. For the first 3 years, the plant needs only timely watering and weeding from weeds and the use of mulch. The first 3 years after planting, honeysuckle grows slowly, since all the energy is directed to the growth of the root system, then the growth of the ground part is significantly enhanced.
Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
Watering the honeysuckle
Honeysuckle loves water, so if the summer is dry, then abundant watering is indispensable. It is better to use water warm, settled in a barrel. After watering, the soil is loosened, but very carefully, since the root system develops superficially and it is easy to damage it. Weeds are removed as needed. If the ground around the shrub is covered with a layer of mulch, then loosening and weeding is not carried out.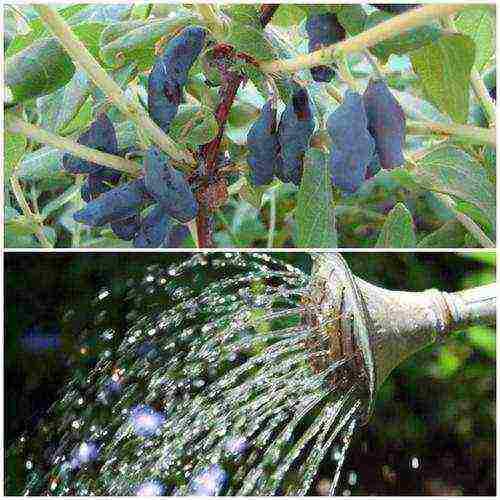
Fertilizers for honeysuckle
Organic fertilizers have a long lasting effect. Therefore, they can be applied once every 3-4 years. Manure is applied at the end of May or at the beginning of June. Consumption of organic fertilizers per bush - 7-10 kg.
To increase the availability of water and mineral elements 1-3 times during the growing season, the soil is loosened and weeded. In the spring, starting from mid-April, you can safely add nitrogen fertilizers (10-15 g per 1 sq. M).
During this period, the plant undergoes intensive growth of roots and shoots. It is important to add this top dressing before flowering. After flowering, the plant can be fed with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
When planting a young bush of honeysuckle, a phosphorus supplement (10–15 g per 1 sq. M. Superphosphate) is applied for the growth and strengthening of the roots.
Potash dressing is applied every 2-3 years in the fall in the amount of 15 g per 1 sq. m. After pruning the shrub, you can add a double dose of mineral elements.
Pruning honeysuckle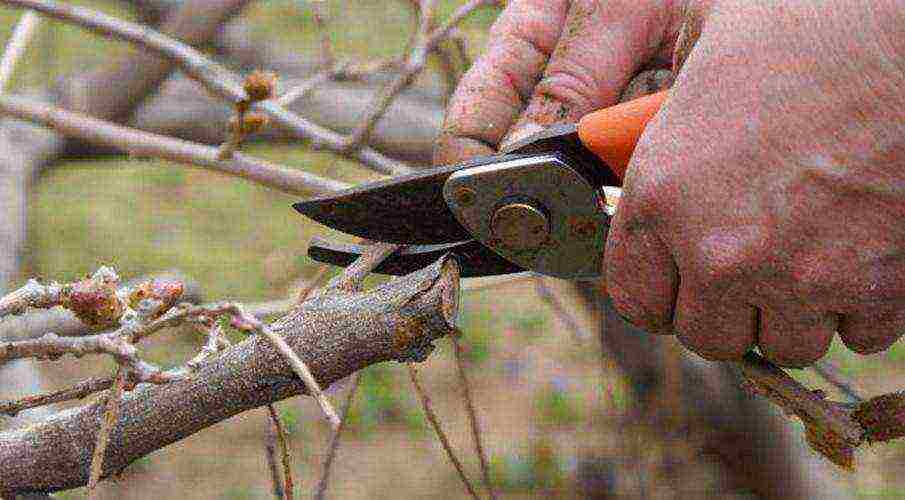
Honeysuckle pruning consists of the following steps:
- All dry and broken branches should be pruned. You need to cut off to the living part of the branch or below the break point. You don't need to delete the entire branch. It is necessary to remove only the broken or dried part of it. All branches that are inclined to the ground must be completely removed. They impede light and airing of the bush, and ripe berries will lie on the ground. Such branches can be left on if you want to propagate honeysuckle. To do this, you can bury the branch with earth. The next year, this branch will take root and get a "gratis" seedling.
- It is necessary to leave no more than 8-15 strong branches in the bush, depending on the age of the bush and the strength of its growth. First you need to remove the gnarled, curved branches, and then the so-called tops. These are long branches without branches, with a small umbrella of branches at the very top.
- It is necessary to remove on the remaining strong branches, shoots that go inside the crown of the bush. The more sunlight falls into the middle of the bush, the greater the yield, and the berry will not become smaller.
- If the bush is old and has not been pruned for a long time, you can carry out anti-aging pruning of honeysuckle. To do this, in autumn or early spring, you need to cut off all branches at a height of 30-40 cm. Strong young shoots will grow in the first year. The next year they will give a crop and after fruiting, no more than 15 of the strongest branches should be left on the bush.
Honeysuckle is a unique plant that is increasingly found in gardens and parks. The shrub is planted as a decorative hedge, and edible varieties, and as a berry crop. The fruits are universal, they are used to prepare jellies, jams, liqueurs and liqueurs, they are frozen and dried. All parts of the plant are widely used in folk medicine for the prevention and treatment of various diseases.
What is honeysuckle?
Honeysuckle is a perennial ornamental and berry shrub with a lush crown. The name (Lonicera) "honeysuckle" owes to the famous physicist and botanist Adam Lonicera, who lived in the 14th century. More common in the northern hemisphere, in areas with a temperate climate. The plant can have either a straight stem or a creeping or curly stem. Regardless of the species, it blooms early, filling the air with a charming aroma, which attracts a large number of bees.
back to contents ↑ Where and what it is used for
Every year, honeysuckle conquers more and more garden and vegetable garden plots. There is something to love about her! It blooms in May one of the first, pleases with delicate buds with an almond-honey smell, and the fruits ripen earlier than other plants.
They appreciate it for its ease of care, stable yields, especially in areas with late spring and short summer, where nature does not indulge in a special variety of fruits. It easily tolerates severe winters, and even during flowering, frost at -5 does not affect a good harvest, which is unacceptable for other fruits.
Decorative curly varieties are used for vertical gardening of arbors, pergolas and arches. From plants with a lush and dense crown, fragrant hedges are formed, blooming almost until the very frost.
Culinary specialists love berries for their peculiar taste, aroma and a large amount of pectin substances, thanks to which a dense jelly is obtained from it, are used as a harmless dye. It is good in jam, in compote, you can dry it, freeze it, grind it with sugar, make liqueurs and wine, and what a delicious filling for pies it turns out!
It is widely used in folk medicine in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, anemia, hypertension, skin diseases, respiratory system and others. Honeysuckle has healing not only berries, which give a head start to lemon in terms of vitamin C content, but also all parts: leaves, bark, flowers.
back to content ↑ Plant varieties
Most often, honeysuckle, which has edible berries, is planted in gardens.Favorite varieties of Russians: Pavlovskaya, Borel, Blue Spindle, Amphora, Gzhelka, Vasyugan, Gerda, Titmouse, Nymph Sineglazka, Blue Bird, Bochkarskaya, Leningrad giant, Cinderella, Kamchadalka and Chernichka. If you wish, you can easily find a detailed description and reviews of each of them. There are varieties of newer selection, but they can fail in a frosty winter, and these have already been tested over the years by several generations of gardeners. The varieties differ in the ripening period of the crop, the height of the bushes and the shape of the branches, and the taste of berries.
back to content ↑ Undersized
- Gourmand is a compact bush, the yield is high, but the berries are not very large, weighing about 0.7 g. Fruits without bitterness, are characterized by low crumbling. Suitable for hedges. Plant next to her "Nymph" and "Nizhegorodskaya early" for pollination.
- Omega - also refers to undersized varieties with a rounded crown, but the berries are larger and reach a weight of up to 1 g, they cannot “boast” of high yields, but the berries practically do not crumble. Fruits without bitterness, sweet and sour, the plant is planted as a hedge.
back to contents ↑ Medium-sized
- Nymph is a compact bush with an oval crown and dark green leaves. The berries are large, 3 cm each, and weigh up to 1.2 g, with careful care, each bush pleases with a harvest of 1.5 kg. The berries have a pleasant sweetish taste, slightly sour. Plant next to Violet, Omega, Blue Spindle for pollination.
- Leningrad giant - the name speaks both of the place of selection and the size of the fruits. The seeds of the Kamchatka endemic were used as the starting material for breeding. The berries ripen early, can reach a size of up to 4 cm, but more often - 3 cm, have a dense skin, the yield of the bush reaches 3 kg. A feature of the variety, in addition to the size of the berries, is their arrangement - in bunches, which speeds up the harvest. The fruit tastes without sourness and bitterness, it does not crumble from the bushes for a long time.
back to content ↑ Tall
- Volkhova is a bush with an oval dense crown, tall with thick shoots. It got its name from the river flowing in the Leningrad region, where it was bred. It belongs to varieties with an average ripening period, the fruits appear by mid-June. The berries reach a length of 1.7 cm, and the weight of one is up to 0.8 g, they have a rather dense skin, and the taste is sweet. Harvest up to one and a half to two kilograms per bush. Scattering is insignificant, pollinated by bumblebees, planted next to other varieties, for example: Lazurnaya, Pavlovskaya. It tolerates severe frost.
- Tatar honeysuckle is an ornamental shrub, grows up to 2.5 meters, frost-resistant, drought-resistant, when cutting, you can set the crown to any shape. A plant of 3-4 years old begins to bloom from May-June, bright berries begin to ripen in July-September, they are inedible. Suitable as a decorative hedge.
- Honeysuckle is the most common fragrant honeysuckle in landscape design, its curly stem can reach 6 meters. In translation, it means "goat leaf", it grows up to a size of 10 cm in length and 4 cm in width. Beautiful large flowers of pink or cream color with a delicate aroma that intensifies in the evening. Alcohol tincture is made of them, and a decoction is made from the leaves, with which they rinse the throat with sore throat and wash the head with hair loss, it also helps with colic.
Video plot
back to content ↑ Types
Honeysuckle berries, regardless of the species, ripen earlier than other fruit crops. Some bloom at the same time, but give fruits later. Berries of different types of plants in terms of ripening can vary by a month and a half.
Early
- Titmouse is a relatively young variety, bred in Moscow in 1998 by A.G. Kuklina and A.K. Skvortsov, employees of the Main Botanical Garden. It is distinguished by abundant fruiting, does not crumble, and withstands light frosts during flowering without consequences for the harvest. Berries without bitterness, aromatic, weighing up to 1 g, sweet and sour taste, elongated with a characteristic whitish bloom. The harvest begins in the second or third decade of June.
- Strawberry is another early ripening honeysuckle variety, bred by the South Ural Research Institute of Fruit and Vegetable Growing. High-yielding bushes with strong shoots, up to 2 meters high, resistant to freezing, prefer partial shade or sun, and are not capricious in their care. Berries weighing up to 2 g, when ripe, hold for a long time on the branches, very sweet with a strawberry aroma.
back to contents ↑ Late
- The dove is an edible variety with good yields. From an adult bush, under favorable conditions, you can collect about 2 kg of fruit. The berries are elongated, weigh up to 1.6 g, dark blue in color with a characteristic whitish bloom, thin skin and delicate fragrant pulp. The taste is sweet and sour with a spicy light bitterness, appear by the end of June or early July, do not crumble from the bush for a long time.
- Serotina - curly honeysuckle, decorative, blooms with beautiful fragrant flowers, then they turn into red fruits. It begins to bloom in June-August, and continues even until September-October, if the drying inflorescences are removed in time and the fruits are not allowed to form. The aroma is subtle, reminiscent of linden, by the evening the fragrance is felt stronger.
- Liana - can reach 3-4 meters in height, with an annual growth of up to a meter, planted with a support. For the winter, the shoots are carefully freed from the support, laid out on the ground, covered with spruce branches and sprinkled with a thick layer of dry leaves.
- Volkhova - edible honeysuckle. Variety with an average yield: up to 1.5 kg per bush. Berries with a strong skin weighing up to 0.8 g, reach a length of up to 1.7 cm, do not taste bitter, fragrant, have a very delicate aftertaste reminiscent of strawberries. She is not capricious in her care, frost-resistant, loves partial shade and regular root watering.
back to content ↑ How to plant and care for honeysuckle
Honeysuckle refers to unpretentious crops, but it still requires some attention. She prefers moist, well-warmed, fertile soil, but the lower branches should be in the shade. Bushes must be protected from the wind. Any soil is suitable, except sandy. Do not plant in areas where groundwater is close to the surface.
RECOMMENDED! The plant prefers a soil pH of 5.5-6.5, therefore, about a month before planting in a permanent place, produce acidic soils by adding 1 sq. 200 g of lime.
If the seedling has an open (without a clod of earth) root system, then it is better to plant it in early autumn. At this time, the growth of shoots in plants stops, a dormant period begins. If the seedling has closed roots, then during the entire growing season.
The bushes, if not cut off, reach their maximum growth by the age of seven, the average length is about 2 m.At this time, it is recommended to thin out, cut out dried branches lying on the ground and broken. Honeysuckle is not a currant, it does not require strict pruning, but it does not tolerate frequencies either.
Each adult bush can reach a diameter of up to 2 meters, and up to 15 skeletal brushes can grow on it.
back to table of contents ↑ Step-by-step landing plan
- 4 days before planting, dig square holes (40x40x40 cm) with a distance between them of 1.5-2 m for small varieties, and 2.5-3 m for tall ones.
- Place any drainage layer in the hole (crushed stone, shards, expanded clay, broken brick, etc.).
- Fill the holes with fertile soil mixed with two buckets of compost, a kilogram of ash and 50 g of superphosphate. For sandy compost soil, about 3 buckets are taken with the addition, if desired, of 4-5 kg of clay per 1 square meter.
- It is good to spill the holes with rain or settled water.
- Pour an earthen cone in the center of the hole, place the seedling carefully on the top, carefully straighten the roots.
- Carefully sprinkle the roots with earth in small portions, leave the neck free. Pour a large amount of water into the hole so that the poured earth settles. Add more soil if necessary.
- Mulch the soil around the trunk to retain moisture in depth and attract earthworms to loosen the soil.
Only dry stems and twigs located inside the crown should be pruned after planting, since traditional pruning delays the development of the seedling and the onset of its fruiting.
IMPORTANT! In the first year, it is necessary to water it regularly, and for the winter to cover the area of the roots with a layer of mulch (at least 15 cm).
back to contents ↑ Proper care
The crop can be harvested in a couple of years, however, it will be small. But this is temporary, and over the years, depending on the variety, it will reach 2 kg per bush. Honeysuckle is a picky plant, it practically does not get sick and, with proper care, will delight you with a stable harvest for up to 30 years or more.
In the fall, you need to thin out the crown from the dried branches that shade the plant. In the spring, add organic matter under each bush, and when the snow begins to melt, feed it with nitrogen. With the appearance of flowers, and then fruits, water the bushes with an aqueous solution of ash. Avoid the formation of a crust along the trunk, the soil should be airy and allow the roots to breathe. Loosening should be done carefully, as the root system is close to the surface, and watered "at the root".
Video recommendations
back to content ↑ How to propagate honeysuckle
The easiest way to propagate honeysuckle at home is to cut 30 cm tops from the bush with shears in the spring, put the "bouquet" in water and plant it about a month later, when the roots appear. For their faster appearance, special agents can be added to the water. Young plantings will give the first harvest in three years.
You can also breed honeysuckle with seeds, but this method is laborious, and it takes a lot of time. Another disadvantage is that there is no guarantee of the safety of varietal qualities. Honeysuckle also reproduces by cuttings and division of adult bushes. To obtain good yields, several varieties should be planted side by side for mutual pollination.
A distinctive feature of honeysuckle from other berry crops is that it grows only until the beginning of summer, and then "goes into hibernation." Therefore, it can be transplanted (with a clod of earth) from July until frost. In the spring, she wakes up early, even before the soil thaws completely, and already does not tolerate transplanting well.
back to content ↑ Disease and pest control
Honeysuckle has good "immunity", the plant rarely gets sick. The main enemies are aphids and honeysuckle. To get rid of them, it is enough to treat the shrubs with special preparations immediately after harvesting.
In winter, plants can be harmed by mice. Spraying the bushes with 3% copper sulfate makes the branches "tasteless" for rodents, and serves as the prevention of fungal diseases.
The benefits and harms of honeysuckle
Honeysuckle can be considered a universal product, it helps with various diseases. Its berries, rich in trace elements, vitamin C and many others, ripen before anyone else and help the body in the fight against spring vitamin deficiency.
back to content ↑ Useful properties
The berries of the plant are not only tasty, but also healthy, their juice helps to alleviate the condition of patients with burns and ulcers, and the broth will help keep blood pressure normal, only you should not drink it before bedtime, as it has a strong diuretic effect.
A decoction made from flowers and leaves can be used to treat colds. Honeysuckle will help with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, it can fight ulcers and gastritis, eliminate capillary fragility, clean blood vessels and rejuvenate the body. And rubbed with sugar, it will become a vitamin supplement for the body during the autumn-winter period.
back to content ↑ Harm and contraindications
There are no serious contraindications for honeysuckle berries, you should not overeat it, and should not be given to young children. Rarely, some people may experience individual intolerance, which is manifested by itching, redness, skin rashes, muscle cramps, and indigestion. The golden rule is that everything needs a measure.
IMPORTANT! It is necessary to distinguish between edible and inedible honeysuckle.You can eat black or dark blue berries, red and orange are poisonous!
back to contents ↑ Honeysuckle jam in a slow cooker
Try honeysuckle jam with red currant juice and tea rose petals in a pressure or multicooker.
Ingredients:
- Honeysuckle - 1 kg;
- Sugar - 1 kg;
- Petals - 200 g;
- Currant juice - 200 ml.
How to cook:
- Set the "Frying" mode and cook the syrup from the juice and sugar.
- Honeysuckle has an exquisite taste; pink petals will help to add interesting shades to it. Pour honeysuckle into the syrup, wrap the petals in cheesecloth, put in a slow cooker, close the lid.
- Turn off the heating after 5 minutes, leave the lid closed, let the jam simmer for another hour.
- Pour into small jars, close the lids tightly. Check the tightness: carefully, so as not to burn yourself, turn the can over, if there are no bubbles, everything is fine. Cover the jam, let cool.
It turns out an amazingly beautiful jam: a dark blue mass of jelly, in which, like bright sparks, red honeysuckle berries. The scent of a rose, after opening the lid, still did not leave anyone indifferent. How nice it is on a winter evening, over a cup of fragrant tea with this magic jam, to remember the summer.
Loading …
We are looking forward to the arrival of spring, the appearance of the first greens, berries and fruits in the garden, but they are still far away. This is where honeysuckle will come to the rescue, which begins to bloom as soon as the snow melts, and in June will present you with fragrant and healthy berries for care and maintenance.
Rate the article:
(votes -
, rating:
out of 5)


