Content
- 1 Selection of varieties and seeds
- 2 Landing dates
- 3 Preparing the soil for beets
- 4 Site selection, crop rotation
- 5 Seed preparation
- 6 Planting beets in open ground
- 7 Beet care
- 8 Watering and feeding
- 9 Optimal planting density
- 10 Harvesting and storage
- 11 Diseases and pests of beets
- 12 Variety selection
- 13 Preparing a site for beets
- 14 Seed treatment
- 15 Planting beets in open ground
- 16 Beet care
- 17 Diseases and pests of beets
- 18 Which variety to choose
- 19 Landing
- 20 Beet care
- 21 Disease and pest control
- 22 Harvesting and storage
- 23 Video: growing beets in the open field
- 24 Variety selection
- 25 Video "Sorts"
- 26 Site selection and preparation of beds
- 27 Seed preparation and planting procedure
- 28 Outdoor care
- 29 Harvesting and storage
- 30 Video "Growing and Care"
To grow sweet and healthy table beets, suitable for long-term storage, you need to know the intricacies of the agricultural technology of this vegetable. Anyone who masters this science is guaranteed a varied vitamin menu for the whole winter.
Selection of varieties and seeds
Beets are unpretentious and ready to grow in all latitudes, except perhaps permafrost. You can opt for localized varieties or experiment with new hybrids with increased endurance.
The ripening period of beets depends on the variety and ranges from 80 to 130 days. You can adjust the ripening time by planting beets under a greenhouse or seedlings, pre-germinating seeds.
The most popular varieties suitable for growing in all climates:
Valenta - early ripening variety with sweet, dark red flesh, cold-resistant, dormant, disease-resistant.
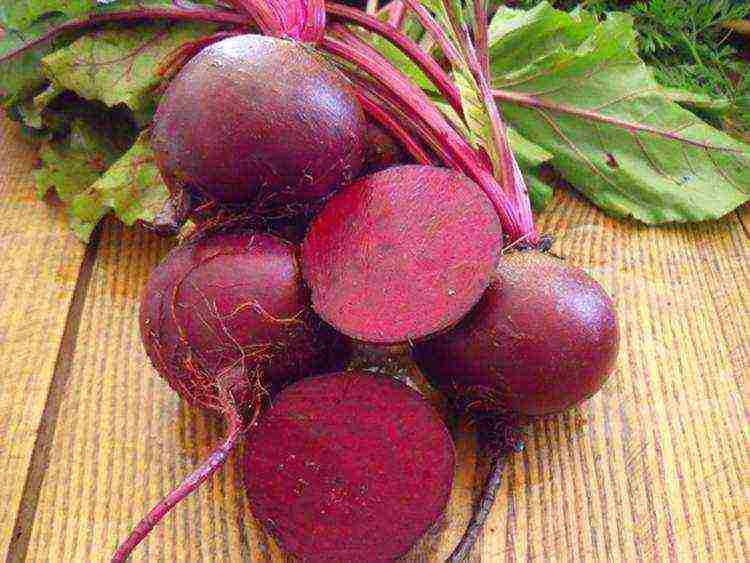

Ataman - medium late variety, cylindrical fruits weighing 300 g, burgundy, sweet with uniform pulp, very well stored.
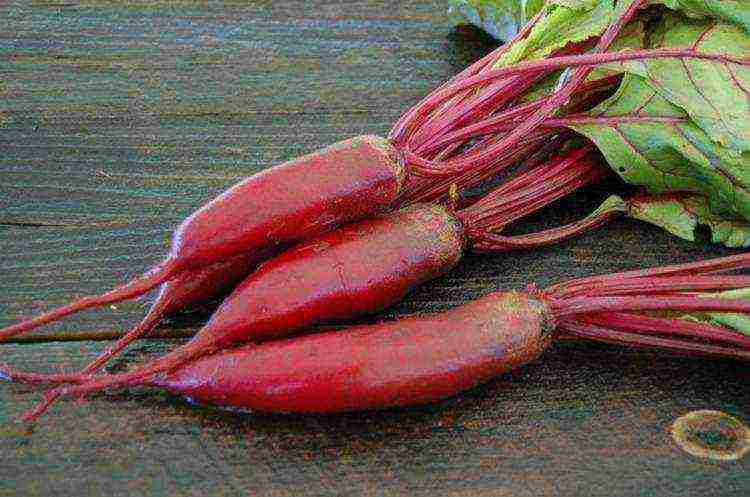

Cylinder - a mid-late variety with an elongated bright red fruit weighing up to 500 g, strong immunity and good keeping quality.
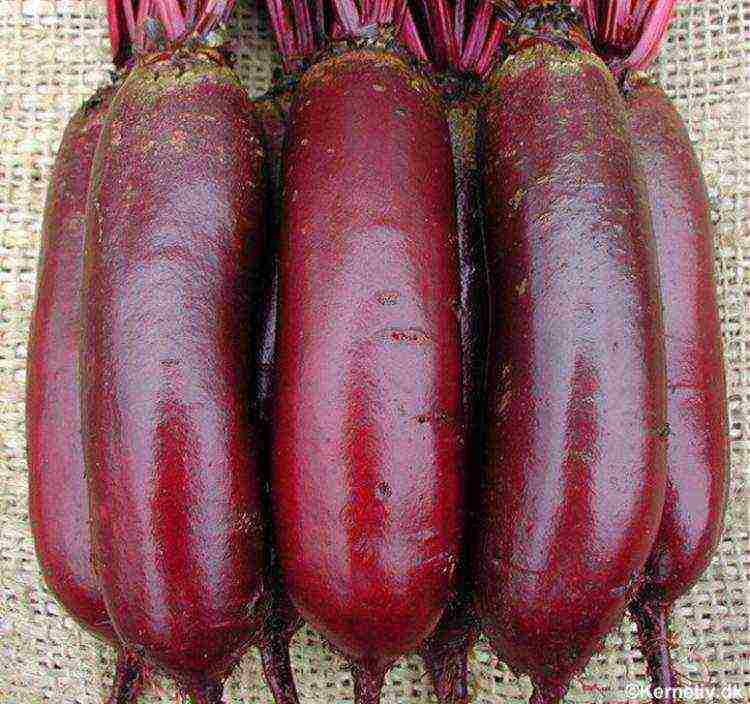

Winter - medium early cold-resistant variety, resistant to most diseases, round fruits weighing 200 - 400 g with burgundy pulp.
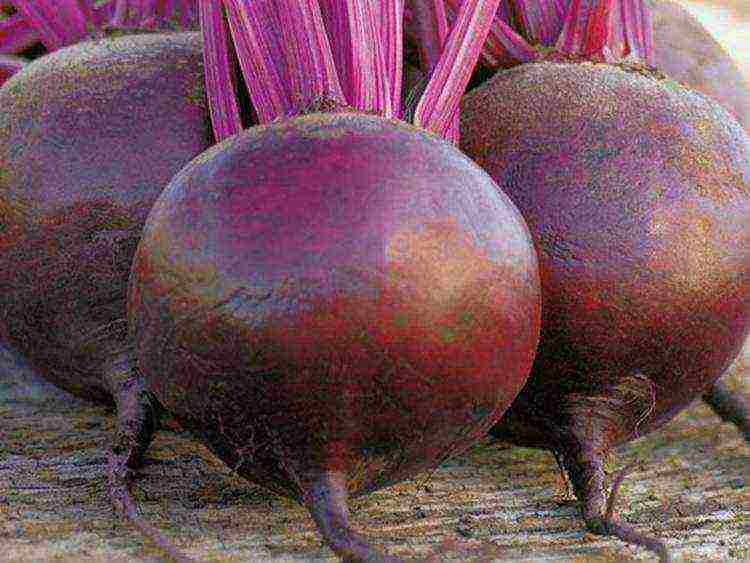

Red hero - medium-early high-yielding variety, cylindrical dark red fruits with thin skin and uniform pulp weighing 200-550 g.

Red ice - mid-early variety, bright red fruits, with structural pulp, low weight - 200-300 g, well stored.

Bikores - mid-season high-yielding variety, bright red fruits weighing 200-350 g, lax.

If you plan to eat all-season beets from your garden, then you need to plant both early and late varieties of beets.
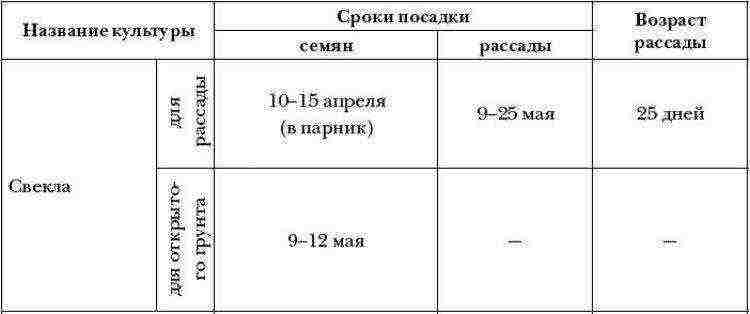
Landing dates
Most often, beets are planted in the spring, when the air warms up to 15-18 C. You can do this a little earlier, in April, planting non-germinated seeds under a greenhouse.
If the spring is too cold, you can shift the planting date to a later time by choosing early ripening beets.
Winter beets are sown with dry seeds before the onset of frost. For this, only specially oriented varieties are chosen. Sowing sites are covered. They start growing in early spring and provide a summer beet crop. Root vegetables ripened in the summer are not subject to long-term storage.
Preparing the soil for beets
The soil is dug up in the fall after careful harvesting of the previous harvest. Organic components (compost or manure) are applied as deeply as possible - by 30-35 centimeters.You can organize some semblance of a warm bed, but with a thin layer of organic matter, so that it has time to decompose by the time the beet root grows to it.
The acidity of the earth is reduced by scattering dolomite flour, crushed eggshells or wood ash.
Mineral additives - superphosphate and potassium sulfate - are best applied in the fall, so that they have time to dissolve in the soil. They are scattered dry over the garden bed before digging at the rate of no more than 0.3 kg. one square meter of land.
The root crop develops better in loose soil. In the spring, it is good to re-dig the bed and mulch it with peat or rotted sawdust.

Site selection, crop rotation
The rules for choosing a place for beets:
- beets love space, the less often the root crops are planted from each other, the more space they have for building rounded barrels;
- if there is no need for large plantations of this root crop, beets can be planted by the border method on potatoes, cucumbers, beans, next to herbs or onions;
- beets need frequent irrigation, but stagnant water will lead to decay, which means that the bed must be broken up next to the irrigation source in a well-drained area;
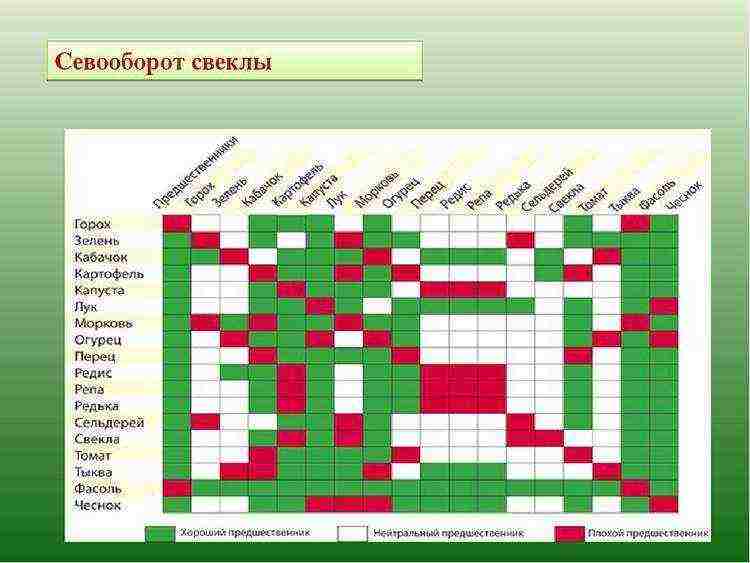
- beets are not planted twice in a row in one place, they observe the crop rotation very carefully;
- the preceding plants for this vegetable are onions, garlic, potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, carrots, zucchini;
- it is undesirable to plant beets after cabbage and for the second year in a row in one place.
If you have to squeeze any crops in the garden by planting them on poor soil, then this can be safely done with beets. You can ensure its growth by good loosening of the soil, timely watering and fertilization.
Seed preparation
Beet seeds before planting:
- check for germination - pour it into a glass with salt water, mix and remove the floating ones;
- quenched by alternating hot water and cold, keeping in each temperature regime for several hours;
- disinfected by keeping for 12 hours in a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- stimulated by soaking in a growth promoter.
- germinate if the seeds are prepared for growing beet seedlings.
For podzimny planting, you need to limit yourself only to testing for germination and disinfection - excessively swollen seeds can germinate in the winter and die.

Planting beets in open ground
Beet seeds are large compared to most horticultural crops. Sowing will not be difficult.
Beets are sown into grooves 3-5 centimeters deep with a distance of 5 centimeters from each other and 20 centimeters between rows.
Winter crops are buried 10 centimeters so that the seeds do not die.
When planting beets in open ground with seedlings, the interval is set at least 20 centimeters.
Beet care
The process of growing beets includes watering, feeding, loosening and mandatory thinning.
Beets do not require close attention at all if they grow in good soil and with proper watering. But if the plant lacks nutrition, this will adversely affect the taste or lead to diseases.
- Phomosis of fruits and leaves of beets develops with a lack of boron and is expressed in the appearance of lightened spots on the foliage, it is also fraught with curvature and the appearance of cavities in the root crop.
- Cercosporosis is threatened by excessive moisture in the beds.
- Excess nitrogen in the soil will result in the bitter earthy taste of beets.

Watering and feeding
After germination, you need to water the beets often - once every two to three days, alternating watering with shallow loosening so as not to damage the roots. You do not need to huddle this root crop. But it is good to form a boletus between the rows of beets, through which water will flow. In case of soil erosion, a thin layer of humus is poured on top.
Loosening can be replaced by mulching. A layer of chopped dried grass between the rows will help to retain moisture.

A one-time application of mineral fertilizers before planting is sufficient for beets. It makes sense to carry out additional feeding only if the plants noticeably lag behind in growth.
As a preventive dressing, periodic watering of beets with diluted herbal infusions or yeast fertilizers is suitable.
Two or three times per season, you can water the beets with salted water at the rate of one tablespoon per 10 liters of water. Or use complex fertilizers according to the instructions, for example, Macbor.
Root crops accumulate nitrates more actively than other crops. When growing beets, it is better to opt for natural fertilizers.
Optimal planting density
An important point in caring for beets is thinning. It is carried out in several stages so that the owner has the opportunity to evaluate the growing roots and choose the best ones. Before each thinning, it is necessary to pour the beets well.
When the first pair of leaves appears, the weakest plants are removed. Later, when thinning, diseased specimens are removed, too thickened good roots can be transplanted to a new place or used for food as greenery.
From the initial distance between plants of 5 centimeters, as a result, it is necessary to go to an interval of 15-20 centimeters.
Harvesting and storage
Beets are harvested in the fall before the onset of cold weather, when the leaves on the plant wilted. When harvesting, it is necessary to act carefully, prying large layers of earth with a shovel and taking out root crops one by one.
The earth is carefully shaken off the fruit, and it is better not to cut off the remaining corolla of leaves - just remove the wilted stems.
Medium-sized root vegetables with intact skin are stored in a dry room at a temperature of 2 to 5 C.
Diseases and pests of beets
The main pests of any root crops are moles, bear and rodents. Beet fleas, wireworms and slugs are also dangerous. In addition, plants are affected by various rot, nematodes.
These troubles should be dealt with, first of all, by observing the hygiene of the personal plot - high-quality cleaning, thorough deep digging and preventive treatment of plantings with natural disinfectants - wood ash, tobacco dust, hot pepper powder.
These root crops are famous for their unpretentiousness and constancy. They are well stored in basements and vegetable pits, preserving nutrients until spring. Be sure to find a spot on your site for beets.
Beets are one of the favorite garden crops and can be found in almost every garden plot. The secret of a good harvest of beets lies in the correct choice of varieties, timely planting and good care.
Growing beets in the open field
Variety selection
There are quite a few varieties of table beet used in cooking. Experienced gardeners recommend planting several varieties of different ripening periods. At the same time, the harvest is removed in two terms, early varieties for use in summer, mid-season and late ones - for canning and storage.
The most popular varieties:
- early - Libero, Incomparable A 463, Vinaigrette Jelly;
Beetroot Vinaigrette Marmalade
- mid-season - Smuglyanka, Negritanka, Larka;
Beetroot
- later - Cylinder, Ataman.
Beet Ataman
In addition, when buying, you should pay attention to the purpose of the variety - for fresh consumption and cooking, for canning, for storage. The shape and color of the root crop is a matter of taste, but it has been noticed that varieties with uniform pulp without rings are more juicy.
Varieties with uniform flesh without rings are more juicy
Preparing a site for beets
Beets love warmth and bright light, so they need a sunny area with nutritious and loose soil. It grows well on peat soils, sandy loams and loams with high fertility. In order to ensure a high yield, it is better to prepare the area for beets in the fall.
Good predecessors of this culture are:
- tomatoes and peppers;
- cucumbers, pumpkins and zucchini;
- greens, legumes, cereals;
- onion garlic.
Land preparation
It is not recommended to plant beets after:
- potatoes;
- all types of cabbage, radish;
- carrots, celery and parsnips.
Beets grow worst of all on the plots where their closest relatives were grown: chard, fodder, sugar and table beets.
The site is dug at the end of the garden season or in early spring on a shovel bayonet with the fertilizers indicated in the table.
It is important not to exceed the recommended doses of mineral fertilizers, otherwise the root crops will turn out to be loose, with voids and cracks. You can replace fertilizers with organic matter: rotted manure that has lain in the herd for at least two years, humus, ash.
The beds are best done just before planting.
It is better to do the beds just before planting, so more moisture will remain in the soil, and the seeds will germinate faster. The soil is loosened and leveled with a rake, if it has time to dry out, you need to water it well, after which you can start sowing.
Seed treatment
Beet seeds
Beetroot seeds are shriveled drupes and are fairly large in size, so they can be easily planted at appropriate intervals. Commercial seeds are often treated with stimulants and fungicides and are easily recognized by their bright pink or greenish color. Such seeds do not need processing, it can even harm. They are sown dry without preparation in moist soil.
Beet seeds treated with stimulants and fungicides
The color of untreated beet seeds is brownish, sometimes sandy with a greenish tinge. Before planting, it is recommended to prepare them in the way described below.
- Soak the seeds in room temperature water for several hours. The floating seeds are thrown away, they usually germinate late, give small roots of irregular shape.
- Drain the water and immerse the seeds, wrapped in gauze, in a solution of Epin, Zircon or another germination stimulator. They are kept in solution from half an hour to 4 hours, focusing on the instructions for using the drug.
- Remove the stimulant from the solution and place in a warm place for 12-24 hours. During this time, the seeds swell, some of them peck, after which you can start planting.
Beet seed processing
Planting beets in open ground
In order for the beets to please you with a good harvest, it is important to correctly determine the planting dates. Single shoots appear at a soil temperature of 5-7 degrees, but massive and friendly shoots can be achieved only when the ground warms up to a temperature of 13-16 degrees at a depth of 8-10 cm.
This usually does not happen until mid-May. It was pointless to plant beets in open ground before - being in cold, damp soil, the seeds can rot, and the emerging plants will then go into the arrow.
Beets are usually planted no earlier than mid-May.
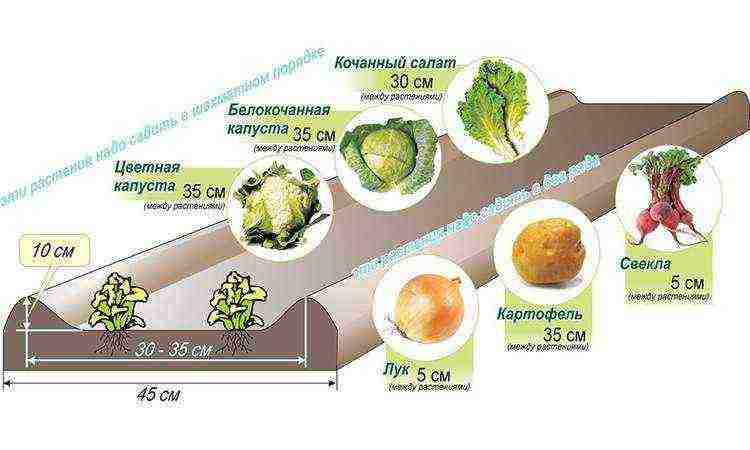
On the prepared beds, grooves are marked with a depth of about 2 cm. It is convenient to make them using a board, pressing it with its end into the loosened soil - the bed of the grooves will be dense, and the planting depth will be the same. By choosing a board of the desired width, you can also use it to mark the distance between the rows. It should be:
- 10-15 cm for small root crops intended for summer consumption or pickling;
- 20-30 cm for varieties with large roots for winter storage.
The grooves are poured from a watering can, preventing erosion, and left until the water is absorbed. Seeds are laid out on the bottom of the grooves, maintaining an interval of 4 to 10 cm, depending on the size and purpose of the selected variety. From above they are covered with soil or well-rotted humus and watered.
Planting beets
For large planting volumes, you can make a template, as in the figure, while the distances between the plants will always be the same.
Sowing template for beets at the same distance
Video - The subtleties of planting beets in open ground
Beet care
Beets are unpretentious and drought-resistant, but they can only give a high yield with good care and adherence to agricultural technology.
- In dry and hot weather, beets are regularly watered from a watering can by sprinkling. It is better to use water that is settled and heated in the sun. At the same time, the leaves are refreshed, the plants perceive the feeding better, and grow faster.
In dry and hot weather, beets are regularly watered from a watering can by sprinkling
- Beets must be loosened regularly to prevent the appearance of a hard soil crust. It is better to do this in the morning after watering. The depth of loosening is no more than 3-4 cm, otherwise there is a risk of damaging the roots.
- Mulching will help reduce the frequency of watering and loosening, and also reduce weeds. Sawdust, straw, humus are used as mulch.
Mulching will help reduce the frequency of watering and loosening
- It is necessary to weed the beets regularly from the emergence of shoots to the closure of the leaves, after which weeds are not afraid of it.
- In the phase of two true leaves, the plants are thinned out, leaving a gap of 3-5 cm between them. The second thinning is carried out when the roots reach 1.5-2 cm in diameter, while leaving enough space between them for the selected variety. Plucked plants can be used to make soups and salads.
In the phase of two true leaves, the plants are thinned out
- Frequent feeding of beets with properly prepared soil is usually not required. On poor soils in the first weeks after germination, you can water the seedlings with infusion of mullein or chicken droppings.
- It is recommended two or three times during the growing season to feed the plants with a complex fertilizer containing trace elements: potassium, boron, copper, molybdenum. Dusting with ashes is also helpful, and will also help with pest control.
It is recommended to feed the plants with complex fertilizer two or three times during the growing season.
Diseases and pests of beets
With good care, beets rarely get sick and are affected by pests, but for a full harvest it is important not to miss the first signs of the disease.
| Fomoz | Fungal disease, accompanied by the appearance of spots on the lower leaves and dry rot of the core of the root crop. The reason is a lack of boron, it is necessary to feed with boric acid | |
| Cercosporosis |
Cercosporosis of beet |
It affects plant leaves, impairs the growth and development of root crops. The reason is a lack of potassium, it is necessary to feed with potassium chloride or ash |
| Downy mildew, downy mildew | It can be identified by a gray-purple bloom on the underside of the tops, then they begin to dry out or rot. The plant must be sprayed with fungicides, it is better to do this prophylactically in the phase of 2-3 leaves | |
| Corneed | An infectious disease affecting seedlings. At the same time, the leg becomes thin, turns black, and soon the plant dies. Disease occurs when there is a lack of aeration on heavy damp soils | |
| Fusarium | Occurs in dry weather with insufficient watering. Leaf cuttings darken, root crops crack with the formation of a white bloom at the site of damage | |
| Brown rot | It appears, on the contrary, at high humidity and excess nitrogen. It manifests itself as a brown or gray bloom on root crops. When rot appears, the fruits are removed, and the site is not used for growing root crops for 4-5 years |
Compliance with all recommendations will allow not only to get a good harvest, but also to keep it until the next season, while the roots will be juicy, tasty and healthy.
Video - How to grow beautiful, healthy and tasty beets
It is simply impossible to imagine borsch, herring under a fur coat or vinaigrette without beets, they are delicious and extremely useful. In this article, you will learn all the secrets of growing root crops in the open field.

Outdoor beets
- Beets are a light-loving vegetable, therefore, it will not be possible to get a good harvest by organizing beds in the shade;
- Seeds germinate at temperatures above 5 degrees, so before planting, make sure that the soil is warm enough, otherwise you risk provoking the shooting process;
- The quantity and quality of the crop largely depends on proper watering. Despite the fact that the vegetable grows even in dry conditions, it is recommended to water it 2-3 times a week for excellent growth;
- Do not forget to feed and protect from pests in a timely manner.
Which variety to choose
Several varieties of vegetables are known:
- Canteen... We use it for cooking. It can be round, flat and cylindrical. There are pink, light and wine-burgundy. Red ball and bohemia are considered the best for growing outdoors, they can be harvested in 10-11 weeks. Egyptian flat, Bona and Detroit ripen a little longer (16-17 weeks). Cylinder is a late variety and can be tasted after 19 weeks.

Table beet
- Sugar... It is used, as is clear, for the production of sugar. They are grown mainly in the southern regions. The already mentioned variety of Detroit, as well as Bohemia, Bon and Stall, are considered bright representatives of this category.

Sugar beet
- Stern... People do not eat food, they grow it mainly for feeding livestock. Root crops are quite large, round, oval and conical in shape.

Fodder beet
Landing
The plant is planted in open ground at an average daily temperature of at least 5 degrees. Planting with insufficient heating threatens the appearance of peduncles and low quality of root crops. The optimal time for planting is the May holidays, when the earth is still wet.
Soil preparation
The vegetable grows well in light, fertile, nitrogen-rich soil. Areas suitable for its cultivation where cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants or onions used to grow. It is not worth arranging beds where chard, carrots and / or cabbage were located last year.
It is advisable to prepare the place in late March - early April. Each square meter must be fertilized with a mixture, for the preparation of which you will need: 35 g of superphosphate, 20 g of ammonium sulfate and such an amount of ammonium nitrate, 15 g of potassium chloride. For greater fertility, it is not forbidden to make each square of the site a couple of kilograms of humus. The acidic soil needs to be neutralized by pouring one and a half kilos of fluff lime per m2.

A bed with lime for beets
In early May, you need to start sowing, after digging up the ground and organizing the beds.
Planting seeds
Success largely depends on the quality of the selected seeds. Remember that they should be firm and not squashed, without an unpleasant odor. It is better to purchase them from trusted sellers.
Before planting, the seeds must be prepared - soaked in cold water for 20 hours or in warm water for literally half an hour. Attention: seeds in granules should not be soaked, since the procedure will nullify the entire effect of granulation. After they can be sent into the ground, not deep - literally 1-2 cm.

Beet seeds
The germination process can be accelerated by bubbling, in other words, soaking in water saturated with oxygen. A special apparatus is used for this purpose, but a conventional aquarium compressor is also suitable. The procedure takes from 12 to 18 hours; at the first signs of germination, move the seeds to well-moistened soil. The larger the gap between the seedlings, the larger the root crop will be, but you should not strive to grow 1 kg vegetables, since their taste will not be as pleasant as that of medium-sized fruits. The optimum distance between seeds is 5, and between rows is 25 centimeters.
If the groundwater level is high on the site, then the beds will have to be raised or organized on the ridges.
Planting seedlings
Planting seedlings will allow you to harvest much earlier than when sowing seeds. For this purpose, choose early varieties from what we have suggested above.Depending on the region of your residence, it should be sown in March-April.
A large box or tray is suitable for growing seedlings. Take care of a good drainage layer and a suitable potting mix. Spread the seeds evenly over the surface of the prepared soil, sprinkle with a little earth on top and water. Move to a warm place. During seed germination, make sure that the soil is not waterlogged, otherwise they will rot, you should not dry it out either.
Shorten the center root of the seedling by a third before planting in open ground. In order for young seedlings to grow stronger, water them with a humate solution for the first couple of weeks and protect them from direct sunlight. Well, when the size of the root crop is about a walnut, thin out to an interval of 8-10 cm between them.

Planting beet seedlings
Planting winter beets
There are also gardeners who plant a vegetable in the winter. In this case, the earth needs to be dug up to a quarter of a meter, and after each square of the plot, fertilize with organic matter (1/2 bucket / m2), potassium chloride and superphosphate, at the rate of 30 g per unit area, and sow the roots. The seeding rate is 2-3 grams per square meter. In the spring, when the snow melts, do not forget to fertilize the beds with urea.

Mulching a bed with beet hay
Winter beets need mulching. It will protect crops from frost, so stock up on fresh sawdust and other material suitable for this purpose.
Beet care
Beets are not particularly picky crops, however, in order to harvest a good harvest, follow the watering rules, fertilize them in a timely manner and protect them from parasites.
Watering
When watering, it is important to find a middle ground. High humidity threatens that the plant will rot, and overdrying is fraught with the fact that the fruits will be small.
How to tell if a root crop needs water? Just try to stick your finger into the ground, if it is only a couple of centimeters dry, then refrain from watering.
Immediately after planting, it is very important not to overmoisten the soil. In June, it is enough to pour one and a half buckets per square meter a couple of times a week. If such an irrigation regime is not suitable for some reason, then it is allowed to moisten the ground 2 times a month, but then at least 6 buckets will be required for each unit of area.

Watering young beets
Loosen up after watering to prevent or destroy existing soil crust that makes it difficult to aerate the roots.
Thinning
Beet seeds are inflorescences, in which there are several pieces at once. That is why they germinate quite densely. In order for the root crops to be of a good size, thinning should be performed already in the first stages of development. Some gardeners throw out the removed plants, but if they are planted in another place, they will take root well.

Beet thinning and transplanting
When the first leaves appear, care must be taken that the weeds do not clog the young shoots. Therefore, make sure that there are no weeds in the beet bed. Before sprouting, spraying with tractor kerosene will help to fight excess vegetation (about 50 grams per square meter will be required). Then use a solution of sodium nitrate for this purpose. But after the beets gain strength, the grass will not harm it in any way.
Fertilizer
Beets need good fertilization, they prefer organic matter and ash, and with a lack of nutrients, they grow poorly.
The first portion of nitrogen fertilizers should be applied after the first thinning, 10 g per m2. As soon as the tops begin to close in the aisles, it is necessary to make a second top dressing. For this procedure, prepare a cocktail of 8 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium chloride for each unit of area.
Even though beets love feeding, don't overdo it. In particular, excessive nitrogen fertilization leads to the accumulation of nitrates in the root crop.

Mineral fertilizers for beets
Disease and pest control
Beets rarely get sick, and pests rarely infect them. Nevertheless, you need to know the symptoms of diseases in order to eliminate them in a timely manner.
The most common diseases include:
- Fomoz... It manifests itself as brown or yellowish concentric spots on the lower leaves of the rosette, then black dots appear. The reason is the lack of boron. If the listed symptoms are found, feed brown (3 grams / m2) and sprinkle with a solution, for the preparation of which 1/2 teaspoon of boric acid must be diluted in a bucket of cold water.
- Cercosporosis... The fact that the plant is sick is indicated by small light spots on the upper side of the leaves and a light gray bloom on the lower. Timely feeding the plant with potassium chloride will help preserve it.
- Peronosporosis... At the beginning of the disease, a gray-purple bloom appears on the underside of the leaves, then they wrap up, lose color and dry in dry weather, and rot in wet weather. Soaking seeds in Apron before sowing and regular spraying with fungicides at the beginning of the growing season will help prevent this ailment.
- Corneed... Young plants turn black, thin out and die. To prevent this, do not neglect fertilizing with brown and loosening. Peat mulching will also be an excellent helper.
- Fusarium and brown rot... The lower leaves wither, the petioles turn black at the base, the fruits crack and fill with a white substance - these are the signs of the disease. The reason is the high content of nitrogen and moisture. Top dressing with boron solution and liming is effective in the fight.
When yellow rounded spots appear on the tops, it is appropriate to talk about a lack of potassium and excessive acidity of the soil. Lime milk will help to solve this problem, for the preparation of which you need 200 g of fluffy lime and 80 g of potassium chloride to dissolve in 10 liters of water and water the plant with the resulting solution. Red tops report sodium deficiency and, again, acidic earth. Sprinkle ash over the beds and sprinkle with salt water.
Beets are also attacked by pests, including:
- mining flies;
- bear;
- beet aphid;
- scoops;
- fleas;
- shield beetles.
Weeding regularly will help prevent pests. If this measure turned out to be ineffective, then spraying with an infusion of onion peels will save you from aphids. Iskra and Karbofos solutions will kill flies. "Powdering" the bushes with ash or tobacco dust will scare the flea beetles. Well, treatment with bitoxibacillin or gomelin will help to cope with the scoop.
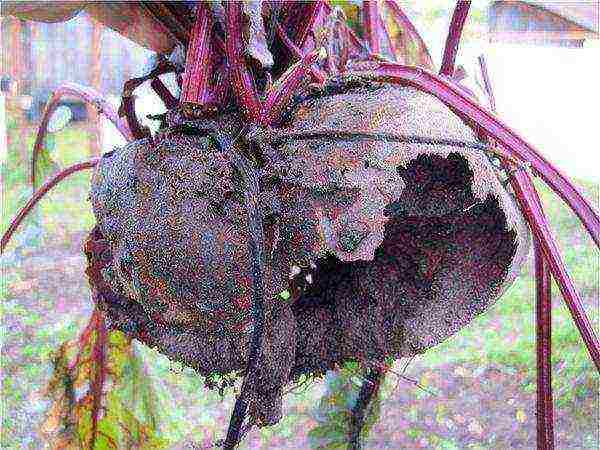

A root crop destroyed by a bear
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting is required before the first frost. It is recommended to store beets at a temperature of 3 to 5 degrees. In a cellar, basement or earthen hole, root crops will lie until summer, retaining maximum benefits for the body.
Video: growing beets in the open field
We often use beets in our first courses and winter salads. If we start to cook it for vinaigrette, "fur coat" and other salads, then summer is over, and we are starting to use vegetables intended for long-term storage. This tasty, healthy, nutritious vegetable is found in every country house,
growing beets
in the open field it is not difficult, at the same time, you need to know certain features in order to always get a rich harvest. This root crop, originally from the Mediterranean coast, is so fond of us that it is now cultivated in all regions of our country, regardless of the difference in weather and climatic conditions and soil.
Variety selection
Distinguish between table, sugar and fodder beets. Canteen, leaf and root, may differ in terms of ripening, shape of fruits, color of root pulp. You can grow any in the country, it is only important to know the characteristics of the variety.
Early ripening beets are planted for summer use, they fully ripen two to three months after sowing, but they start eating them much earlier. It is better to grow medium-late and late varieties for long-term storage, which ripen from three to five months. Throughout the winter, there are usually roots that were harvested after full ripening, but for such a long time, beets may not grow in all regions. Therefore, it is advisable to choose a variety, knowing how long it needs to grow, and the duration of the warm season in a particular area.
Early varieties, such as "Cold-resistant", "Egyptian", "Red ball", "Bordeaux 237", "Nobol", need to ripen from 60 to 90 days from the moment of sowing. Young roots begin to be used for food if their diameter exceeds 1.5 cm, this is the time when dense shoots are thinned out, and roots and leaves can already be eaten. Young, succulent leaves are often used together with other garden herbs for salads, okroshka or soups.
Mid-early varieties ripen from 90 to 130 days. Beetroot varieties "Detroit", "Mulatka", "Bona", "Bohemia" are more resistant in comparison with the early ones. She does not suffer from temperature changes, withstands drought, and is less susceptible to diseases. After complete ripening, it can be stored for a long time. It is these varieties that are chosen for consumption in winter in those regions where September brings real cold, where later varieties simply cannot ripen.
Late-ripening beets should grow from 130 to 150 days from the moment of sowing, of course, five months of heat is not everywhere, therefore such varieties are not grown in the north. Among the most popular late varieties, gardeners choose Cylinder and Renova.
Video "Sorts"
From the video you will learn about the best varieties of beets for growing.
Site selection and preparation of beds
Beets, which are not too troublesome to plant and care in the open, loves open, sunny places. So she needs to find a bed that is not shaded so that she can get maximum solar heat all day. Every year, beets are planted in a new place, otherwise the harvest may not be seen at all, and the whole season is in vain to fight diseases and pests. It is not advisable to plant it after all types of cabbage, radish, rapeseed, carrots. Experts disagree about potatoes, but this vegetable grows best where tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, onions, eggplants, legumes or cereals were previously grown. As you can see, the choice is large enough so that you can change the place every year - this is a very important condition for trouble-free growing.
Beets do not like heavy, acidic soils, as well as stagnant water, but they can somehow maintain their existence even there. But a vegetable grown on light, air-permeable soils can even be slightly alkaline, and if it also receives the right amount of moisture regularly, it will certainly present a delicious juicy, slightly crunchy root vegetable. It is best to choose (or create) a plot with fertile sandy loam or loamy non-acidic soil, such conditions will guarantee a good harvest. Often, gardeners plant a beet curb along the paths in the beds with cabbage or carrots. This neighborhood will provide vegetables with the necessary nutrition and watering, since the needs are much the same.
Sowing is done most often in the spring, when the earth has definitely warmed up to +10 degrees, but the place is being prepared in the fall. After harvesting, the garden bed is completely freed from plant residues, dug deep into the bayonet of a shovel, simultaneously removing the roots of perennial weeds. If the soil is even slightly acidic, you need to correct the ph by adding lime, dolomite flour, or at least wood ash. In the fall, they fill the soil with fertilizers - they must add humus or compost, complex mineral fertilizers containing, in addition to the obligatory nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, some more iron, boron, copper, magnesium, molybdenum, manganese.
But beets are sensitive to an overdose of fertilizers, too generous mineral fertilizing can lead to the accumulation of nitrates, root crops will get voids or cracks. You cannot fertilize root crops with fresh manure, only humus that has stood for at least two years.
Thus, the prepared soil is watered and left to rest until spring, to absorb fertilizers. Autumn sowing is carried out before winter, not earlier than November, so that the seeds do not sprout, but are preserved until the onset of heat, while simultaneously being hardened by frost.
They will sprout earlier than spring sowing, will give stronger shoots, unless they germinate during an unplanned thaw, which will inevitably lead to their subsequent freezing.
Seed preparation and planting procedure
The seeds of beets are peculiar, several are hidden under one shell, up to five sprouts can form during germination, which is why they are laid in the ground, one in each nest. Strange large drupes should have a sandy brown color or slightly greenish, if the purchased seeds are colored bright pink or bluish green, this means that they have been treated with fungicides and growth stimulants, they no longer need to be prepared for sowing, they are placed directly dry into the ground.
Untreated seeds need to be prepared for sowing. To do this, they are first soaked in warm water, thrown out, those that remain are wrapped in gauze or collected in a linen bag and poured with a growth stimulator solution ("Epin", "Zircon") for the time indicated on the package. Such a solution can be prepared by yourself. For a liter of warm water, take 2 g of boric acid, 4 g of nitroammophoska, 5 g of superphosphate, 1 teaspoon of baking soda, a little wood ash. Seeds are poured with this solution for half an hour. Then for another day the seeds are kept in conditions of heat and moisture.
The nashed seeds are placed in the prepared furrows in the garden bed, at a distance of about 10 cm from each other. The grooves are easy to make with the end of the board - the board is placed sideways on the prepared bed and slightly pressed, deepening to two centimeters. Then they retreat 20-30 cm and make the next groove. This is very convenient: the bottom becomes even, dense, the rows are parallel, the distance between the rows is the same. They are lightly watered from a watering can just before sowing.
The seeds are covered with soil, watered, and then mulched a couple of centimeters high with peat or compost. Sowing is carried out when the air and soil temperature is not lower than +10 degrees. If sown earlier, the seedlings will appear, maybe a little later, but such plants do not form a root crop, they usually grow large leaves and rush to discard the peduncle.
In regions with a short summer, it is more convenient to grow beets using the seedling method; they are planted in a garden bed, too, at an earth temperature of at least +10 degrees. And before that, they germinate under a film or at home. If the seeds were sown in boxes, then with the appearance of the leaves, they are dived into separate cups or break through a couple of times before planting in the garden, and the torn sprouts are transplanted to another place. Seedlings are planted in a permanent place after the appearance of three leaves, it is advisable to simply move the sprouts together with the earthen lump, so it is good if they grew already in separate cups. This transfer together with the native land reduces stress and speeds up the process of adaptation to a new place.
Outdoor care
After the appearance of a couple of leaves, the plants are looked after as usual: they are weeded, watered, loosened, fed, protected from pests and diseases. From sowing to the closing of the leaves, a bed with beets needs to be weeded all the time - weeds not only take nutrients from vegetables, but provoke various diseases. After the closure of the beet leaves above the ground, the weeds practically do not grow under them.
For uniform development, root crops must receive a sufficient amount of moisture, therefore, the plants need to be watered regularly, and better water warmed up in the sun should be used. Young plants are usually watered once a week in the evening, and in the morning you need to loosen the ground around to prevent an earthen crust from forming. Adult plants are watered less often, but it all depends on the weather - hot, dry weather requires more frequent watering, while rains or cloudy weather postpone watering. If in doubt, you can always check with your hand how dry the soil is to decide if watering is needed. To water and loosen the soil less often, you can mulch the bed with peat or just hay, cut grass.
At first, plants actively consume nitrogen, they need it for growth, and later, when forming root crops, they need more potassium, phosphorus, and boron. Therefore, after the leaves appear, the garden bed can be watered with a solution of mullein infusion or bird droppings, only they need to be diluted eightfold (manure) or twelvefold (litter). Some are sprinkled with nettle infusion or urea. Beets respond well to foliar dressing, in the summer they are watered from a watering can over the leaves with a solution of boric acid, for which they dissolve 2 g of boric acid with 10 liters of water. In summer, salt water is poured over the leaves, dissolving 1 tablespoon in 10 liters of water. Gardeners who grow vegetables on depleted soils feed them every two to three weeks. But experts warn that an excess of fertilizer can lead to cracking of root crops, the formation of voids. In addition, beets are prone to accumulation of nitrates, which we then consume, harming ourselves. So all feeding should be done on a second thought.
Be that as it may, the closer autumn is, the less often you need to water and feed the plants. Two to three weeks before harvesting, watering is stopped altogether. This is especially true for late varieties that are intended for long-term storage. Early ripening beets are watered as needed and plucked when needed.
Not so many diseases lie in wait for beets in the garden. With a lack of boron, phomaosis may develop. Peronosporosis can deprive the crop, at the first symptoms (curling of leaves, the appearance of a bloom with a purple tint), before the formation of root crops, it can be treated with copper-containing preparations or special fungicides. With waterlogging, stagnation of water in heavy soil, root cannon may occur. Attacks by beet and miner flies, scoops, beet aphids or flea beetles are possible. An infusion of onion peels can save them from them. Dusting plants with wood ash and tobacco dust will be a good prevention.
Harvesting and storage
Early beets are plucked when the roots are larger than 6 cm in diameter, but can be eaten earlier. But the late varieties, which are going to be stored in winter, are harvested when the leaves turn yellow, dry, and fall to the ground. If the leaves begin to dry, in a week you need to choose a crop.
On a dry fine day, the beets are pried with a pitchfork, taken out, and left to dry in the garden. Then they are cut or torn off by hand (this method is considered less painful), leaving at least 2.5 cm of petioles, shaken off the remnants of the earth, sorted.
Those beets that will be stored for a long time are dried in the fresh air under a roof or in a ventilated room. And then they are already transferred to a place where it will be stored at a humidity of 90% and a temperature of 0 to +2 degrees. Root crops are stored in wooden or even plastic boxes, for better preservation they are powdered with chalk or simply sprinkled with sand.
Video "Growing and Care"
From the video you will learn all the secrets of fruitful beet growing.


