Content
- 1 Variety selection
- 2 Preparing a site for beets
- 3 Seed treatment
- 4 Planting beets in open ground
- 5 Beet care
- 6 Diseases and pests of beets
- 7 Preparing the beds for sowing beets
- 8 Beet sowing timing and seed preparation
- 9 Summer beetroot care
- 10 Harvesting and storing beets
- 11 Beet varieties with photos
- 12 Pests and diseases
- 13 Soil and bed preparation
- 14 Fertilization
- 15 Landing dates
- 16 Seed preparation
- 17 Sowing technique
- 18 Care
- 19 Diseases
- 20 Pests
- 21 Soil preparation and sowing seeds
- 22 Summer beet care
- 23 Beet pests and diseases
- 24 How and when to store beets
Beets are one of the favorite garden crops and can be found in almost every garden plot. The secret of a good harvest of beets lies in the correct choice of varieties, timely planting and good care.
Growing beets in the open field
Variety selection
There are quite a few varieties of table beet used in cooking. Experienced gardeners recommend planting several varieties of different ripening periods. At the same time, the harvest is removed in two periods, early varieties for use in summer, mid-season and late ones - for canning and storage.
The most popular varieties:
- early - Libero, Incomparable A 463, Vinaigrette Jelly;
Beetroot Vinaigrette Marmalade
- mid-season - Smuglyanka, Negritanka, Larka;
Beetroot
- later - Cylinder, Ataman.
Beet Ataman
In addition, when buying, you should pay attention to the purpose of the variety - for fresh consumption and cooking, for canning, for storage. The shape and color of the root crop is a matter of taste, but it has been noticed that varieties with uniform pulp without rings are more juicy.
Varieties with uniform flesh without rings are more juicy
Preparing a site for beets
Beets love warmth and bright light, so they need a sunny area with nutritious and loose soil. It grows well on peat soils, sandy loams and loams with high fertility. In order to ensure a high yield, it is better to prepare the area for beets in the fall.
Good predecessors of this culture are:
- tomatoes and peppers;
- cucumbers, pumpkins and zucchini;
- greens, legumes, cereals;
- onion garlic.
Land preparation
It is not recommended to plant beets after:
- potatoes;
- all types of cabbage, radish;
- carrots, celery and parsnips.
Beets grow worst of all on the plots where their closest relatives were grown: chard, fodder, sugar and table beets.
The site is dug at the end of the garden season or in early spring on a shovel bayonet with the fertilizers indicated in the table.
It is important not to exceed the recommended doses of mineral fertilizers, otherwise the root crops will turn out to be loose, with voids and cracks. You can replace fertilizers with organic matter: rotted manure that has lain in the herd for at least two years, humus, ash.
The beds are best done just before planting.
It is better to do the beds just before planting, so more moisture will remain in the soil, and the seeds will germinate faster. The soil is loosened and leveled with a rake, if it has time to dry out, you need to water it well, after which you can start sowing.
Seed treatment
Beet seeds
Beetroot seeds are shriveled drupes and are fairly large in size, so they can be easily planted at appropriate intervals. Commercial seeds are often treated with stimulants and fungicides and are easily recognized by their bright pink or greenish color. Such seeds do not need processing, it can even harm. They are sown dry without preparation in moist soil.
Beet seeds treated with stimulants and fungicides
The color of untreated beet seeds is brownish, sometimes sandy with a greenish tinge. Before planting, it is recommended to prepare them in the way described below.
- Soak the seeds in room temperature water for several hours. The floating seeds are thrown away, they usually germinate late, give small roots of irregular shape.
- Drain the water and immerse the seeds, wrapped in gauze, in a solution of Epin, Zircon or another germination stimulator. They are kept in solution from half an hour to 4 hours, focusing on the instructions for using the drug.
- Remove the stimulant from the solution and place in a warm place for 12-24 hours. During this time, the seeds swell, some of them peck, after which you can start planting.
Beet seed processing
Planting beets in open ground
In order for the beets to please you with a good harvest, it is important to correctly determine the planting dates. Single shoots appear at a soil temperature of 5-7 degrees, but massive and friendly shoots can be achieved only when the earth warms up to a temperature of 13-16 degrees at a depth of 8-10 cm.
This usually does not happen until mid-May. It was pointless to plant beets in open ground before - being in cold, damp soil, the seeds can rot, and the emerging plants will then go into the arrow.
Beets are usually planted no earlier than mid-May.
On the prepared beds, grooves are marked with a depth of about 2 cm. It is convenient to make them using a board, pressing it with its end into the loosened soil - the bed of the grooves will be dense, and the planting depth will be the same. By choosing a board of the desired width, you can also use it to mark the distance between the rows. It should be:
- 10-15 cm for small root crops intended for summer consumption or pickling;
- 20-30 cm for varieties with large roots for winter storage.
The grooves are poured from a watering can, preventing erosion, and left until the water is absorbed. Seeds are laid out on the bottom of the grooves, maintaining an interval of 4 to 10 cm, depending on the size and purpose of the selected variety. From above they are covered with soil or well-rotted humus and watered.
Planting beets
For large planting volumes, you can make a template, as in the figure, while the distances between the plants will always be the same.
Sowing template for beets at equal spacing
Video - The subtleties of planting beets in open ground
Beet care
Beets are unpretentious and drought-resistant, but they can only give a high yield with good care and adherence to agricultural technology.
- In dry and hot weather, beets are regularly watered from a watering can by sprinkling. It is better to use water that is settled and heated in the sun. At the same time, the leaves are refreshed, the plants perceive the feeding better, and grow faster.
In dry and hot weather, beets are regularly watered from a watering can by sprinkling
- Beets must be loosened regularly to prevent the appearance of a hard soil crust. It is better to do this in the morning after watering. The depth of loosening is no more than 3-4 cm, otherwise there is a risk of damaging the roots.
- Mulching will help reduce the frequency of watering and loosening, and also reduce weeds. Sawdust, straw, humus are used as mulch.
Mulching will help reduce the frequency of watering and loosening
- It is necessary to weed the beets regularly from the emergence of shoots to the closure of the leaves, after which weeds are not afraid of it.
- In the phase of two true leaves, the plants are thinned out, leaving a gap of 3-5 cm between them.The second thinning is carried out when the roots reach 1.5-2 cm in diameter, while leaving enough space between them for the selected variety. Plucked plants can be used to make soups and salads.
In the phase of two true leaves, the plants are thinned out
- Frequent feeding of beets with properly prepared soil is usually not required. On poor soils in the first weeks after germination, you can water the seedlings with infusion of mullein or chicken droppings.
- It is recommended two or three times during the growing season to feed the plants with a complex fertilizer containing trace elements: potassium, boron, copper, molybdenum. Dusting with ashes is also helpful, and will also help with pest control.
It is recommended to feed the plants with complex fertilizer two or three times during the growing season.
Diseases and pests of beets
With good care, beets rarely get sick and are affected by pests, but for a full harvest it is important not to miss the first signs of the disease.
| Fomoz | Fungal disease, accompanied by the appearance of spots on the lower leaves and dry rot of the core of the root crop. The reason is a lack of boron, it is necessary to feed with boric acid | |
| Cercosporosis |
Cercosporosis of beet |
It affects plant leaves, impairs the growth and development of root crops. The reason is a lack of potassium, it is necessary to feed with potassium chloride or ash |
| Downy mildew, downy mildew | It can be identified by a gray-purple bloom on the underside of the tops, then they begin to dry out or rot. The plant must be sprayed with fungicides, it is better to do this prophylactically in the phase of 2-3 leaves | |
| Corneed | An infectious disease affecting seedlings. At the same time, the leg becomes thin, turns black, and soon the plant dies. Disease occurs when there is a lack of aeration on heavy damp soils | |
| Fusarium | Occurs in dry weather with insufficient watering. Leaf cuttings darken, root crops crack with the formation of a white bloom at the site of damage | |
| Brown rot | It appears, on the contrary, at high humidity and excess nitrogen. It manifests itself as a brown or gray bloom on root crops. When rot appears, the fruits are removed, and the site is not used for growing root crops for 4-5 years |
Compliance with all recommendations will allow not only to get a good harvest, but also to keep it until the next season, while the roots will be juicy, tasty and healthy.
Video - How to grow beautiful, healthy and tasty beets
For most gardeners, beets are included in the mandatory list of crops that they grow on their backyard plots. This is not a capricious vegetable, but nevertheless, knowledge of some rules of agricultural technology will allow you to avoid mistakes and get a good harvest of the vegetable. The timing of sowing, thinning and caring for beets in the summer will be discussed in this article.
Preparing the beds for sowing beets

The place where the table beet will be grown must be determined in the fall and properly processed. The site is dug to the depth of a shovel bayonet with the introduction of organic fertilizers: half a bucket of ready-made compost or humus per 1 sq. m. From mineral fertilizers make superphosphate 30 g / m2 and ammonium nitrate 20-30 g / m2. Acidic soils are limed by adding fluff lime, dolomite flour or wood ash.
Fresh manure should not be applied under beets - this causes an increased concentration of nitrates in root crops and their deformation.
The area intended for sowing should be well lit, because beets are light-requiring plants.
The best predecessors are cucumbers, carrots, onions, potatoes. It is not advisable to sow it after tomatoes, cabbage and the beets themselves.
Keeping crop rotation increases yields and minimizes the likelihood of plant disease.
Beet sowing timing and seed preparation

Beets are not sown too early. The soil should warm up to at least 10 ° C, usually in early May.Focusing on this period, pre-sowing seed treatment and soaking are carried out.
The seed material of the beet is a small and rather dense nodule, in which there are two, three, and sometimes more seeds. This means that one tuber will give several sprouts.
For seedlings to appear earlier, the seeds are treated with growth stimulants (Epin, Zircon), and kept in a damp cloth in a warm place for two to three days. Swollen or already hatched seeds must be sown in moist soil.
- To do this, grooves are cut in the garden at a distance of 25 cm from each other and watered from a watering can with a narrow spout.
- Then the seeds are laid out, leaving a gap of 5-7 cm between them.
- Crops can be covered with light mulch or covered with plastic wrap, this will keep the bed moist and increase the temperature of the soil.
Often, gardeners spend the winter sowing of beets in order to have an early vegetable on their table. However, it should be borne in mind that such root crops are suitable only for fresh consumption in the summer-autumn period. It will not be possible to save them until spring.
Autumn sowing
It is carried out just before the onset of frost, approximately at the end of October. But the bed is prepared in advance, filled with organic and mineral fertilizers, cut grooves and covered with either plastic wrap or covering non-woven material. This will protect the soil from leaching of nutrients and from germination of weeds. Separately, dry soil is harvested to fill the grooves with seeds and bring it into a dry room. At the right time, beets are sown, increasing the seeding rate.
The beds must be mulched with all available materials: peat, sawdust, compost, straw chaff or all the same covering material.
Spring care
Behind podzimny crops begins with mulch harvesting and careful loosening of the soil. Further chores will be associated with thinning, fertilizing, watering and removing weeds.
Growing beets along the edge of the garden: video
Summer beetroot care
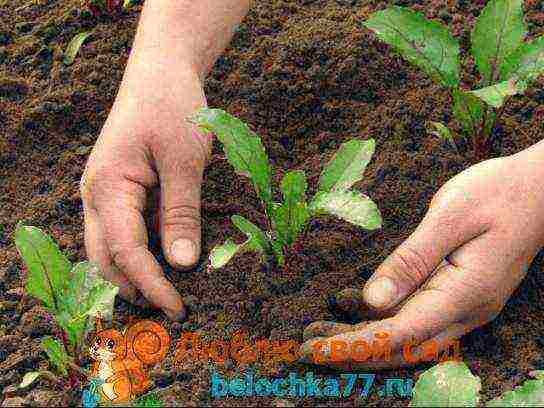

Caring for the beet beds appears along with the beet sprouts. It is important not to miss the moment the sprouts appear and remove the plastic wrap if the gardener resorted to this method of maintaining moisture and heat.
Due to the characteristic feature of the seeds, to give several shoots from one nodule, beet shoots are thickened, therefore, after the appearance of the first true leaves, they need to be thinned.
Before work, the garden bed should be watered so that the process of detaching the roots is less painful. Excess plants can be transplanted to a new location or filled in voids in the same bed, instead of non-germinated seeds.
Beets tolerate transplanting well in spring.
After thinning, the first feeding of the beets is carried out. These must be nitrogen-containing substances. After about a month, the feeding is repeated, but already with mineral fertilizers - phosphorus and potassium.
The introduction of nitrogen fertilizers during the formation of the root crop reduces its quality and worsens the keeping quality of the vegetable in winter.
Watering for beets should be sparse, but abundant (about 20 l / m2). Excessive moisture reduces the quality of the beets and causes diseases. 2-3 weeks before harvesting, the moistening of the beet beds is completely stopped, since the roots that are oversaturated with moisture are worse stored.
Planting carrots in spring
Harvesting and storing beets
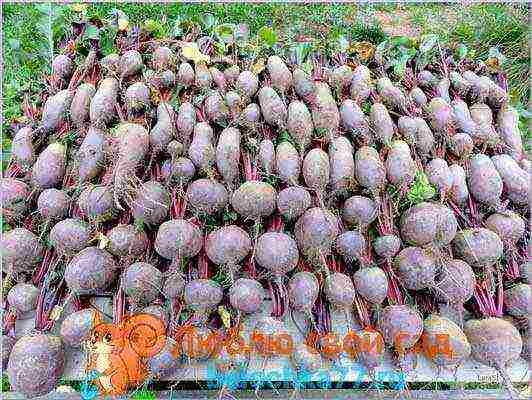

Harvesting of root crops must be carried out at the end of the first autumn month, before frost occurs. The beets are dug in with a pitchfork and, grabbing the tops of the beet with a hand, are removed from the soil. If the site has been well cared for and the soil is loose, then additional tools may not be required for harvesting. Root crops are simply pulled out of the soil by hand and laid out on the garden bed to dry. Then the tops are cut off, leaving stumps of 2-3 cm. Some gardeners recommend twisting it by hand.
Roots dried and peeled from the ground are placed in boxes and covered with river sand - this will preserve the juiciness of the vegetable.
You can spread the beets on the surface of the potatoes, they will also remain juicy due to the fact that they will take away excess moisture from a neighbor.
The harvested crop is stored in a cellar or vegetable store, if any.
How to grow large beets: video
Beet varieties with photos
In order to correctly navigate in choosing a variety for growing beets in a summer cottage, you need to know that they are divided into early, mid-season and late. Early varieties mature in less than three months, but are much worse stored. Therefore, they are grown for consumption in summer, autumn and for all kinds of preparations for the winter. For long-term storage, it is better to grow mid-season and late varieties of beets.
Detroit
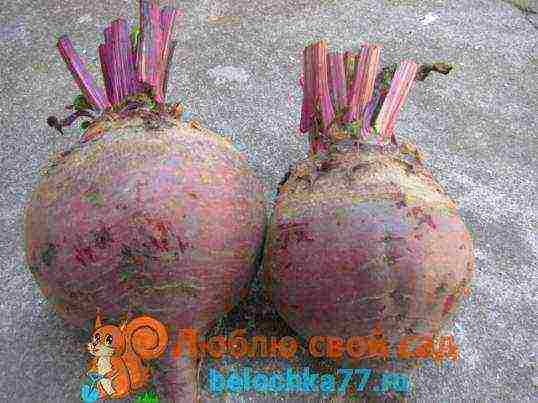

An early variety that easily tolerates minor spring frosts. The root vegetable is small in size and has a beautiful red flesh color. The color is even, without rings characteristic of beets. Full ripening of the vegetable occurs 110 days after sowing the seeds. Selectively, fruits are eaten much earlier.
Bordeaux 237

A variety that is very popular among gardeners. Almost round, medium-sized fruit with dark red flesh. It tolerates spring frosts well. Can be sown before winter.
Egyptian flat

A very interesting variety. Root vegetables can weigh more than 500 grams and are juicy and delicious. The variety is drought-resistant and can do without rain and abundant watering for a long time.
The pulp is burgundy, with small rings. In the bins of the gardener, it can well retain its taste for more than 7 months.
Cylinder
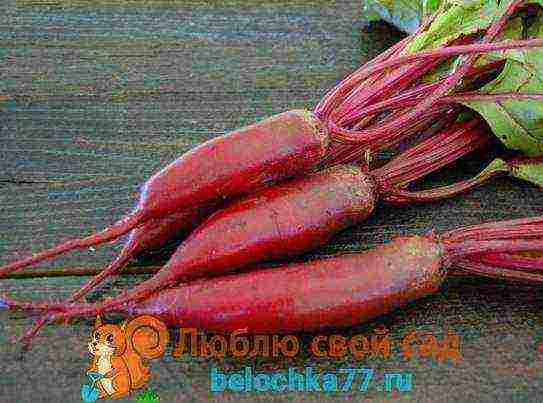

The variety is characterized by an elongated root crop. Its length can be 15-20 cm, and its diameter is about 7-10 cm. The pulp is juicy and sweet, dark red in color, without rings. Cylinder beets are immune to most diseases and have good keeping quality in winter.
Renova

This variety also has cylindrical fruits with dark purple colored flesh. It can be stored well for more than six months without losing its taste.
Beet varieties with photo and name
Pests and diseases
Beet disease

Growing table beets at their summer cottage, the gardener aims to obtain a healthy and high-quality harvest. So that there are enough root crops for summer consumption, for conservation, and for winter storage. How nice it is to get a dense and juicy vegetable out of the cellar knowing that it has been grown by our own labor and without all kinds of chemical growth accelerators.
But it is not always easy to care for beets, they are also exposed to diseases and pests that damage the root system, root crops and vegetable tops.
Control and prevention measures:
- observance of crop rotation
- growing disease resistant varieties
- pre-sowing treatment of the site and seeds
- compliance with the rules of care for crops
There are few pests and diseases in beets, and if compliance with all prevention points did not help, and they still appeared, you need to take measures to eliminate them.
Corneed
At the initial stage of beet development, that is, during the period of germination and disclosure of cotyledonous leaves, the plant may be threatened by a root beet. Most often, this complex disease is preceded by waterlogging of the soil, its heavy composition, sudden changes in temperature and the entry of seedlings under return frosts.
- Seedlings change their natural green color to a darker one,
- the spine rots
- the plant falls and dies.
But even if the sprout survives, it will lag behind in growth and development and will not give a full harvest.
If a problem is found, care must be taken to improve the structure of the soil. Add components that improve air permeability: humus, sawdust, compost, fine straw chaff.
For prevention, liming of the site and pre-sowing disinfection of seeds are carried out.Fitosporin or Previkur is suitable for these purposes.
Cercosporosis
A disease such as cercosporosis is carried by spores, and sometimes it can be found on the seed. Wet and warm weather encourages its active reproduction. The peak of the development of the disease occurs in June and July. Cercosporiasis affects beet petioles and leaves; brown spots with dark edging are formed on them.
If the disease occurs at the initial stage of beet growth, then its development is significantly reduced and the root crop is practically not formed.
Preventive measures:
seed treatment before sowing with Fitosporin.
Control measures:
spraying beet beds with Bordeaux liquid or fungicide solution.
Fomoz
At the end of the growing season, when the roots have already gained strength, the beets undergo a disease called phomosis. Due to the fact that the vegetable will soon be harvested, gardeners often pay little attention to brown spots on the leaves, which gradually move to the petioles.
- The tops dries up, and the disease enters the root crop.
- The pulp turns black, becomes hard and unsuitable for food.
- Phomosis is especially pronounced during storage of the crop.
Disease prevention measures:
- compliance with crop rotation,
- disinfection of seeds.
In order to prevent the development of the disease in the next summer season, all plant residues must be destroyed.
Beet pests
Medvedka

Inhabiting the area where beets are sown, it can be harmful at all stages of plant development. An adult and its offspring eat seeds, gnaw shoots and rhizomes of beetroot.
The bear lives underground, so deep tillage in the fall and before sowing will protect and destroy the settlements of this pest. The use of insecticides is acceptable.
Beet fleas
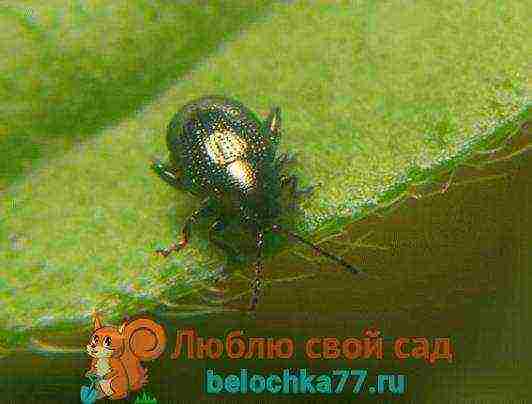

They feed on the pulp of leaf plates. As a result, holes appear on them, this weakens the development of young plants.
The main rule for the prevention and control of the pest is to keep the beet beds clean. In addition, the site is pollinated with ash or tobacco dust.
Beet fly

It hibernates in the ground, and with the arrival of heat it goes outside and lays eggs on the back of the leaves. The emerging larvae actively eat the pulp of young leaves, which inhibits the plant.
Control and prevention measures include:
- weed removal
- removal of damaged leaves
- treatment of the site with the drug "Inta-vir"
Beet bug
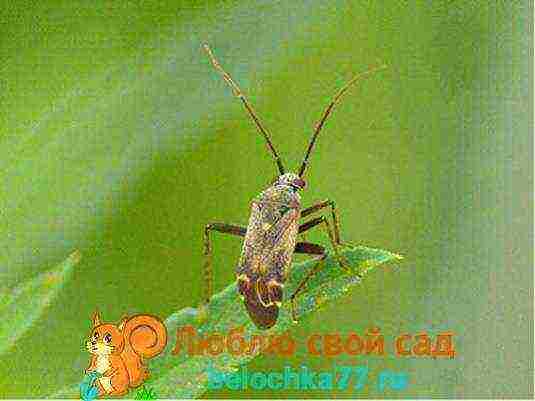

Half a centimeter in size, eats leaves per day five times its own weight. The pest multiplies very quickly and can cause significant damage to beet crops. Damaged young plants wither and die. In adults, leaves begin to dry, which leads to a decrease in yield.
Control measures include:
- deep digging of soil
- regular weed removal
- treatment of the site with insecticides
To get a good harvest of beets at their summer cottage, the gardener does not need too much effort. But as a result, he will be rewarded with fragrant borscht, beautiful and tasty vinaigrette and unchanged herring “under a fur coat”.
Beetroot (beetroot) is one of the most popular root crops grown in household plots. There are two ways to plant beets: seeds and seedlings. There is no fundamental difference between them. The yield mainly depends on the structure and fertility of the soil, and many varieties of beets are quite loyal to weather conditions. If you correctly make a ridge, then you can get high-quality fruits both in a drought and in a rainy summer.
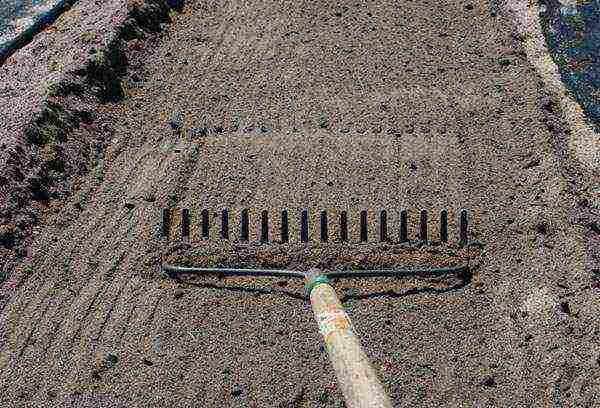

Soil and bed preparation
When choosing a place for beets, you should pay attention to what crops occupied the planned area last season. Planting this root vegetable is categorically not recommended after cabbage, but after potatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin and greens, the beet will grow well. Carrots, peas and onions are neutral precursors.When grown on an industrial scale, beets are planted after winter wheat and rye.
The beets are planted in a well-illuminated place for a long time. There should be no dense bushes, spreading trees, fence, walls nearby. It is advisable to choose a high part of the site that is not flooded by torrential rains.
It is worth considering the basic requirements for the soil for beets.
- Acidity in the range of 6.2-7.5. If there is a lot of colza, wild sorrel and horsetail on the site, then the soil is acidic. Root vegetables will be small, ugly in shape. Lime or dolomite flour must be added. When preparing a ridge for beets, moderate liming is possible in the year of planting.
- The optimal soil is loose, rich in organic matter (loamy, sandy loam, black soil). Growing beets in too clayey soil without special preparation and sanding is a waste of time and effort. The fruit will be fibrous, tough, and bitter.
- The depth of the arable soil layer is from 25 to 30 cm.
Under favorable conditions, root crops develop quickly, and an accelerated accumulation of sugar occurs.
Advice
Excessive lime content in the soil leads to a decrease in the ability of beets to assimilate micro- and macroelements. It is important to respect the dosage.

Fertilization
Beets are demanding on the content of micro and macro elements in the soil. For reference: 1 ton of root crops extracts from the ground up to 7 kg of nitrogen, about 3 kg of phosphorus and up to 9 kg of potassium. While the root system is still weak, the plant especially needs phosphorus, then intensive absorption of other nutrients begins.
It is optimal to prepare a ridge for beets in the fall, adding rotted manure, compost (about 15-20 kg per 1 m2) and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers to the soil. Mineral dressings can be embedded in the soil before planting. Of the complex additives, NPK 13-12-19 or CAS are usually used.
For winter sowing of beets, the following complex of fertilizers (per 1 m2) is applied to the soil:
- half a bucket of manure, humus or compost;
- 30 g of potassium chloride (chlorine ions prevent the accumulation of nitrates);
- 30 g superphosphate.
Advice
Beets are very fond of organic matter, but the introduction of fresh or semi-rotted manure before planting will lead to a deterioration in the taste and presentation of the fruit.
In preparation for planting, the soil is carefully dug to a depth of about 30 cm, all clods are broken, the surface is leveled and slightly compacted. Many gardeners plant beets along the ridges - long, high ridges like potato ones. Thus, the root crop is better ventilated, receives more sun, and is protected from rot and souring. This is especially true for heavy soils. If the soil is fertile and loose, then carpet can be planted.
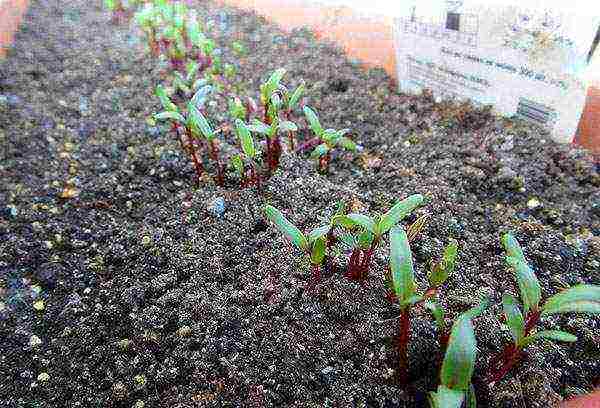

Landing dates
Beet seeds can germinate at temperatures of 3-4 ° C, but the process will take about 25 days. At 6-7 ° C, seedlings will appear already on the 10-15th day, and when the temperature stabilizes to 11-18 ° C, the period will be only a week. There is no point in sowing beets until the soil at a depth of 6 cm warms up at least to 7-8 ° C, since the probability of death of seedlings from frost is high (the sprouts will not tolerate -1 ° C).
Planting beets in the spring in different regions is carried out at their own time:
- North Caucasus - 1 decade of April;
- Central Black Earth Region - 3rd decade of April;
- north of the Central Black Earth Region, Non-Black Earth Region, Volga Region, Bashkortostan and Altai - 1 decade of May.
Long-term storage late beets are sown in the second decade of May, you can plant them until June 10. Such varieties will have enough time before frost to fully mature, and they are stored much better than early and mid-season ones.
The terms are given roughly, for each year they may vary depending on weather conditions.
You can sow beets in a greenhouse or in boxes about a month and a half before planting in open ground. The scheme of embedding into the substrate: 4 x 4 cm. This method is suitable for regions with unstable weather.The maturation period of root crops with the seedling method of cultivation will accelerate by 2-3 weeks.
You can plant beets with seeds in the fall. There are special varieties for this, since ordinary species will begin to shoot and will not produce a crop. Sowing beets in autumn is beneficial for regions with cool, short summers. The sowing date comes when stable frosts begin, the soil is covered with a crust. In the Urals or Siberia, the right time is November. There are no general recommendations on how long to sow beets in the winter. It is important not to miss the last period before the earth "grabs" (3-4 ° C below zero). According to popular observations, the optimal time is the moment when the leaves are completely shed by the cherries.
It should be noted that autumn planting beets are not suitable for long-term storage.
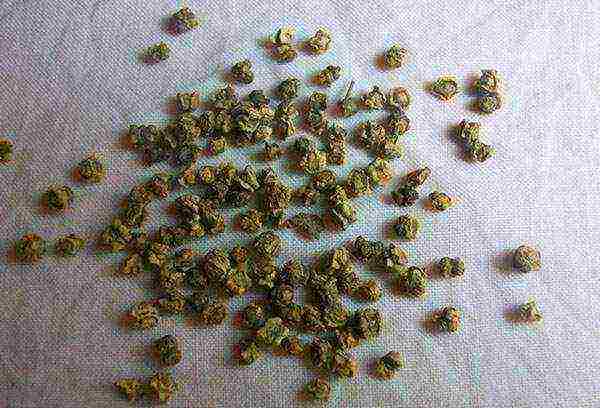

Seed preparation
Beet seeds are fruit lumps, in which several seeds are collected (from 2 to 6 pieces). For this reason, many novice gardeners are surprised when, with a neat schematic sowing of seed-egg capsules, heap shoots suddenly appear from the garden bed.
Beet seeds planted in spring will hatch faster if prepared. The easiest way is to soak for a day in a solution of one of the following products (for 1 liter of warm water):
- a quarter teaspoon of boric acid and half a teaspoon of nitrophoska or nitroammophoska;
- 1 teaspoon superphosphate;
- a teaspoon of baking soda;
- a tablespoon of wood ash.
A day later, the seeds are washed, wrapped in a damp cloth and kept at room temperature for 3-4 days, not allowing the bundle to dry out.
When planting in autumn, you do not need to soak the seeds.
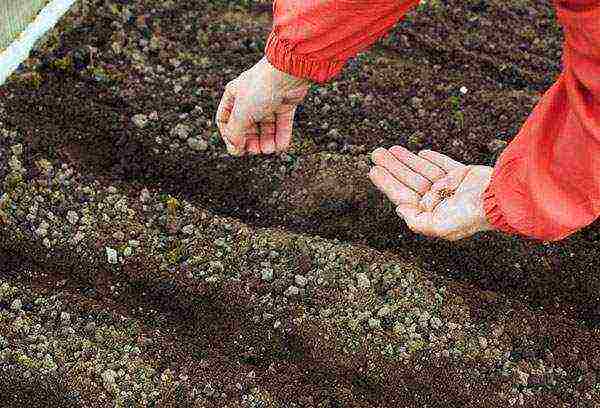

Sowing technique
Immediately before the spring planting of the beets, the ridge is loosened about 5 cm deep and leveled. Sowing or planting seedlings is necessary either in cloudy weather, or in the evening, so that the soil does not wind up and the seedlings do not die from the hot sun.
Planting beets in open ground with seeds is carried out according to the following rules:
- rows are made at a distance of at least 30 cm;
- on loam, beet seedlings are embedded in grooves 2-3 cm deep;
- on sandy and sandy loam soils - 3-4 cm.
In dry weather, the ridge is spilled with water in advance (in an hour or two), in rainy weather it is enough to moisten the grooves. After 3-4 days, it is recommended to loosen the soil with a spring or wire rake. After such a procedure, the beets grow more amicably.
When shoots appear, they must be carefully thinned out. This procedure is carried out twice: in the phase of two true leaves, leaving a distance of 3-4 cm between the seedlings, then in the phase of 3-4 leaves. The average gap between beet sprouts in the end should be 10-20 cm. How much to leave depends on the variety, usually the step is indicated on the seed package.
Advice
If you leave too large gaps between the plants, then the roots will grow large, difficult to heat treatment.
Excess beet sprouts should not be thrown away. If before the procedure it is good to spill the earth, and pry the seedlings with a special spatula (you can use a spoon handle), then the roots will not be damaged. The seedlings will quickly take root in another place, and the shape of the fruit will not suffer in the future, as is the case with carrots.
Podzimny sowing of beets is carried out in dry soil. The seeds are placed in grooves 4 cm deep and covered with a loose substrate (you can mix soil with sand). Then the soil is lightly compacted, the bed is mulched and covered with dry leaves or spruce branches. In the spring, the shelters are removed, the soil is spilled with nitrogen fertilizer, and a film is laid on top until the first shoots appear.
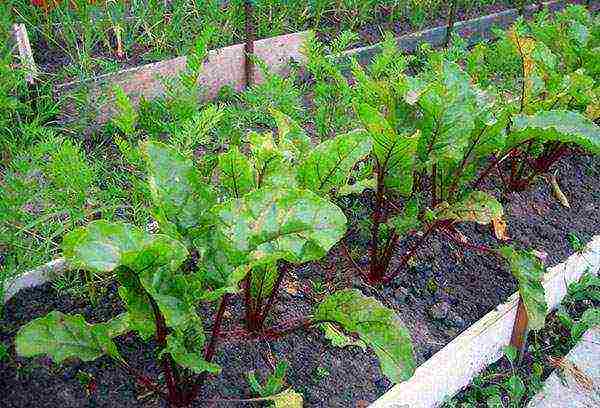

Care
The main care for young beet sprouts is to moisturize and loosen. A crust must not be allowed to form on the soil. Loosening is done carefully, while the plants are small, you can do this with an ordinary old fork.Beets are responsive to this procedure, therefore it is recommended to carry it out until the foliage closes.
Top dressing
The first feeding of beets with mineral fertilizers (nitrogen) is carried out after thinning, the second (complex) - after closing the tops.
Nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus are the main elements needed by beets. If there are no complex mineral fertilizers at hand, then ash, previously mixed with compost, can be added to the soil. Consumption: 3 glasses of clean ash per 1m2.
Advice
It is better to apply nitrogen fertilizers for beets in several portions and not to abuse them, since their excess contributes to the accumulation of nitrates in root crops. Fractional application reduces the negative effect by 2 times. The best form is urea (10 g per 1 m2).
The second top dressing of beets (when the fruit is about the size of a walnut) consists of potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. Consumption: 8 g of superphosphate, 10 g of potassium chloride per 1 m2. Nitrogen is no longer used.
If there is not enough boron in the soil, then the beets react by rotting the core. The deficiency of copper and molybdenum also negatively affects, which can be replenished with foliar feeding (in the 10-leaf phase). For this, liquid micronutrient fertilizers are used, which contain boron in organomineral form and manganese in chelated form.
If the beets develop slowly, rounded yellow spots appear on the tops, then there are signs of a lack of potassium and too acidic soil. In this case, watering with milk of lime will help. Recipe: 200 g of fluffy lime, 80 g of potassium chloride, diluted in 10 liters of water. The solution should be enough for 10 running meters of landings (along the line).
In case of reddening of the beet tops (sodium deficiency), it is necessary to sprinkle the ridge with ash and sprinkle with salt water (1 glass of salt per 10 liters). This procedure will also increase the sugar content of the root vegetables.
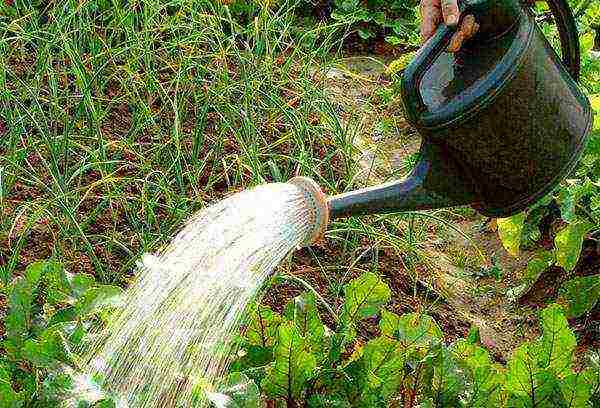

Watering
The watering regime for beets depends on the weather. In the first month and a half of plant development, the soil should not be allowed to dry out. Young beets are very fond of evening sprinkling. After this procedure, the tops freshen up and acquire a high turgor.
If the summer is not too hot, then growing beets outdoors will not be a hassle. After the tops are closed in the aisles, the moisture will erode more slowly, and the root crop is already able to get food from the deeper layers of the soil.
Watering beets stops about a month before harvesting.
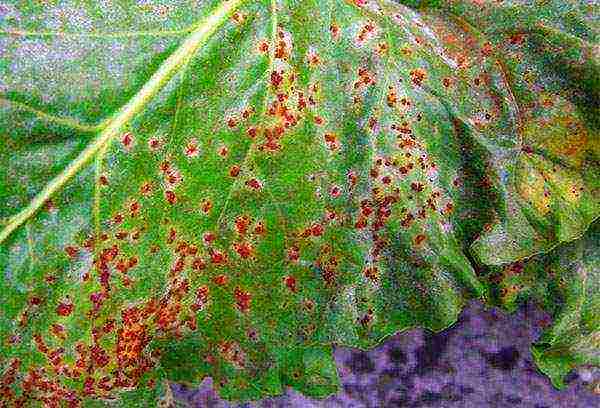
Diseases
Competent agricultural technology minimizes the likelihood of beet diseases caused by soil quality. Increased acidity is the cause of root defects, such as:
- scab in the form of cracks and growths on fruits;
- phomosis (zonal spotting on the leaves) - the disease can also be the result of a lack of boron;
- blackening of the pulp;
- root-eater, "black leg" (at the seedling stage);
- voids in the root crop.
However, all of the above can also occur due to an excess of nitrogen or with unbalanced feeding, therefore, fertilizer must be applied correctly.
Fungal diseases can develop: peronosporosis, cercosporosis, manifested by drying of the tops. Only treatment with fungicides (HOM, Fundazol, Carbendazim, copper oxychloride) can help.

Pests
Growing beets in the country can be unsuccessful for years if wheatgrass grows around the garden and the soil is acidic. This is the most comfortable habitat for the larvae of the click beetle - wireworms. It is they who are able to turn any root vegetable literally into a sieve.
It is possible to reduce the number of these pests of beets only by regularly used control methods:
- select yellow worms manually when digging:
- bury potato tubers in traps;
- exterminate wheatgrass, calcify the soil;
- periodically use special equipment (for example, "Provotox" granules).
Leaf and root beet aphids can also cause damage. Regular spraying with Green Soap solution, Pyrethrum will help to destroy the pest.
Beet fleas eat away the leafy pulp.In the fight against them, ash, tobacco dust, pollination with Hexachloran is effective.
If white winding passages appear on the leaves of the beet, it means that the larva of the miner moth lives in them. With a small scale of damage, the leaves break off and are destroyed. In case of mass infection, treatment with the drugs "Fufanon", "Bi-58 New" is used.
In most cases, growing beets in private plots is not a big deal. If there are few weeds, and soil cultivation in spring and autumn is done correctly, then the risk of attack by pests is minimal. Crop rotation is also an effective protection measure.
Many gardeners plant both late and early beets in the plots, providing themselves with a fresh harvest and a supply of root crops for the winter. This is an unpretentious plant, the seeds of which sprout quickly enough, the seedlings are patient to adverse weather conditions, and to get a good harvest, it is enough to competently prepare the garden bed.
 To grow a tasty root crop with good yields, you will need to know some of the intricacies of planting and caring for beets in the open field. The culture is two years old, but with improper cultivation, the formation of a peduncle will begin, while the root crop will not work or it will be small and ugly. Cultivated varieties that form round heads and elongated cylindrical fruits. Beets are table, fodder and sugar beets. The color of a table root vegetable can be not only burgundy, sometimes varieties with a different color are found. There are leafy beet varieties.
To grow a tasty root crop with good yields, you will need to know some of the intricacies of planting and caring for beets in the open field. The culture is two years old, but with improper cultivation, the formation of a peduncle will begin, while the root crop will not work or it will be small and ugly. Cultivated varieties that form round heads and elongated cylindrical fruits. Beets are table, fodder and sugar beets. The color of a table root vegetable can be not only burgundy, sometimes varieties with a different color are found. There are leafy beet varieties.
Soil preparation and sowing seeds
 Beets like fertile light soil with a neutral reaction. Therefore, the cultivation garden is prepared in the fall. The best predecessors will be crops that are demanding on soil fertility. It can be onions, cucumbers, tomatoes. Do not sow beets after cruciferous crops because they have common pests. The bed must have been limed in previous years. Before sowing, superphosphate and potassium chloride are additionally introduced into the soil. For fertility, a sufficient humus content is important, which is created with the introduction of compost or humus.
Beets like fertile light soil with a neutral reaction. Therefore, the cultivation garden is prepared in the fall. The best predecessors will be crops that are demanding on soil fertility. It can be onions, cucumbers, tomatoes. Do not sow beets after cruciferous crops because they have common pests. The bed must have been limed in previous years. Before sowing, superphosphate and potassium chloride are additionally introduced into the soil. For fertility, a sufficient humus content is important, which is created with the introduction of compost or humus.
Fresh manure is not added to the garden bed for root crops. Beets absorb nitrogen fertilizers well and store them in root crops. Therefore, an excess of nitrogen in the soil is unacceptable.
The soil is loosened deeply and cut into furrows with a distance of 25 cm. The seeds are laid out at a distance of 9-10 cm. From above they are sprinkled to a depth of 2 cm, the soil is moistened. Seedlings will appear in a week if pre-sowing seed treatment is carried out.
 Beet seeds are collected in nodules and are located on top in a common shell, which must be destroyed to accelerate seed germination. They are soaked in an ash solution, in stimulants, followed by germination. For this, the seed is kept wet for a day or two. During this time, the seeds swell, and their germination in the ground is faster.
Beet seeds are collected in nodules and are located on top in a common shell, which must be destroyed to accelerate seed germination. They are soaked in an ash solution, in stimulants, followed by germination. For this, the seed is kept wet for a day or two. During this time, the seeds swell, and their germination in the ground is faster.
 Up to five seedlings can emerge from the nodule. Therefore, after germination, the plants should be thinned out, leaving one strong sprout from the glomerulus. There are single-sprout beet seeds and this information is written on the package. How to plant beets, at what distance, depends on further care. If you need to use young leaves and nodules, beets are sown more often in order to thin out and use early production.
Up to five seedlings can emerge from the nodule. Therefore, after germination, the plants should be thinned out, leaving one strong sprout from the glomerulus. There are single-sprout beet seeds and this information is written on the package. How to plant beets, at what distance, depends on further care. If you need to use young leaves and nodules, beets are sown more often in order to thin out and use early production.
Summer beet care

To grow tasty root vegetables with good yields, you must follow simple care rules:
- sowing at the optimum time;
- proper watering of plants;
- weed and pest control;
- plant feeding.
If the beets are intended for obtaining marketable products for winter storage, you should not rush to sowing. The soil should be warmed up by 10 degrees, the seedlings should not fall under a cold snap, otherwise the beets will shoot themselves. Therefore, sowing begins when stable warmth for young seedlings is guaranteed.
 In each region, warmth comes at different times. Therefore, for Ukraine, sowing can be in April, in the Moscow region in mid-May, in Eastern Siberia at the very end of May. When growing beets, there are several features that will help you grow a tender root vegetable.
In each region, warmth comes at different times. Therefore, for Ukraine, sowing can be in April, in the Moscow region in mid-May, in Eastern Siberia at the very end of May. When growing beets, there are several features that will help you grow a tender root vegetable.
Only beets need to be fed with ordinary table salt. At the same time, it becomes softer and sweeter. The explanation for the phenomenon lies in the origin of the plant. In the Mediterranean, for centuries it was blown by the sea, saturated with salt air, and it became physiologically necessary for a plant.
After thinning the plant, it is watered with the addition of fertilizer for the fastest development of the rosette. How to feed the beets for growth is chosen according to the circumstances. This can be herbal infusion with nettle, potassium nitrate, or urea. Any of the presented fertilizers contain nitrogen.

After 6-7 developed leaves appear, foliar feeding with microelements should be carried out, the most important of which for beets will be boron. If, after applying nitrogen, the beets grow poorly, then they decide to feed them after analyzing the acidity of the soil. It is possible that an acidic environment interferes with the assimilation of elements. The first aid in this case will be the introduction of ash.
The lack of boron in the soil must be replenished. Signs of a lack of an element will be beet fomoz - the formation of black spots on the root crop. Preventive spraying with a solution of 5 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water will save root crops from flaws.
 After the fruit has formed the size of a walnut, a second feeding is done with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. How to feed the beets in July is chosen based on the requirements of the development of the plant. From the moment the root crop begins to form, any fertilizing with the inclusion of nitrogen compounds should be excluded. Fertilizer Agricola-4 can be considered an example of such a balanced feeding. In this case, fertilizing is carried out without spraying, from the spout closer to the plants, without wetting the leaf blade. Any top dressing is performed on wet soil after watering.
After the fruit has formed the size of a walnut, a second feeding is done with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. How to feed the beets in July is chosen based on the requirements of the development of the plant. From the moment the root crop begins to form, any fertilizing with the inclusion of nitrogen compounds should be excluded. Fertilizer Agricola-4 can be considered an example of such a balanced feeding. In this case, fertilizing is carried out without spraying, from the spout closer to the plants, without wetting the leaf blade. Any top dressing is performed on wet soil after watering.
 Sometimes the question arises of how to water beets outdoors. The root crop does not develop well with uneven soil moisture. Abundant watering of dry soil can lead to cracking of root crops. Therefore, water-charging irrigation is required by sprinkling with the supply of up to 20 liters of water per square one time. In between, weekly watering is required, which is stopped 2 weeks before harvesting.
Sometimes the question arises of how to water beets outdoors. The root crop does not develop well with uneven soil moisture. Abundant watering of dry soil can lead to cracking of root crops. Therefore, water-charging irrigation is required by sprinkling with the supply of up to 20 liters of water per square one time. In between, weekly watering is required, which is stopped 2 weeks before harvesting.
Beet pests and diseases
 Healthy beet leaves have a shiny surface without spots. The appearance of uncharacteristic chlorotic manifestations, dry spots indicates that it is time to carry out foliar treatment with fungicidal preparations. The best will be prevention using Fitosporin or Bordeaux mixture with a concentration of 1%.
Healthy beet leaves have a shiny surface without spots. The appearance of uncharacteristic chlorotic manifestations, dry spots indicates that it is time to carry out foliar treatment with fungicidal preparations. The best will be prevention using Fitosporin or Bordeaux mixture with a concentration of 1%.
Pests inflict great damage on beets:
- beet fleas;
- nematodes and wireworms;
- winter and cabbage scoops.
The control of these pests includes methods of mechanical sampling of pests from the ground, biological and chemical methods of control. The use of repellents on developing crops is the best prophylaxis. Using soil stimulants will allow microorganisms to rebalance themselves without the use of chemicals. Therefore, the regular use of drugs such as Radiance and EM-1 Baikal will help increase the immunity of plants to pests and diseases. In addition, a film is created on the leaves, which prevents the penetration of spores and punctures.
How and when to store beets
 The most valuable are medium-sized root crops. That is why you should not rush with the spring sowing of seeds. The larger the beets grow, the coarser their fiber. Remove the beets before frost, since the root crop does not tolerate sub-zero temperatures and will be unsuitable for storage. And the biology of the plant is such that the grown root rises above the surface. Therefore, the beets are harvested early.
The most valuable are medium-sized root crops. That is why you should not rush with the spring sowing of seeds. The larger the beets grow, the coarser their fiber. Remove the beets before frost, since the root crop does not tolerate sub-zero temperatures and will be unsuitable for storage. And the biology of the plant is such that the grown root rises above the surface. Therefore, the beets are harvested early.
 The vegetable is freed from the stalks without a knife, by twisting the tops. The cut with a knife dries for a long time and more juice leaves the root crop than with uneven twisting. The earth dries out and is gently scraped off the surface without disturbing the thin skin. Damaged fruits are not suitable for storage. You can store beets in a box of sand and just on top of the potatoes. It picks up excess moisture from the cellar.
The vegetable is freed from the stalks without a knife, by twisting the tops. The cut with a knife dries for a long time and more juice leaves the root crop than with uneven twisting. The earth dries out and is gently scraped off the surface without disturbing the thin skin. Damaged fruits are not suitable for storage. You can store beets in a box of sand and just on top of the potatoes. It picks up excess moisture from the cellar.
Beet planting video


