Content
- 0.1 Planting a climbing rose with an open root system
- 0.2 Planting a climbing rose with a closed root system
- 0.3 Watering
- 0.4 Top dressing
- 0.5 Mulching
- 0.6 Loosening
- 0.7 Removal of dead buds and root shoots
- 0.8 Garter of a climbing rose to a support
- 0.9 Climbing rose pruning
- 1 General information
- 2 Rose planting and care in the open field
- 3 Planting roses in open ground in spring
- 4 Watering roses
- 5 Fertilizers for roses
- 6 When to replant roses
- 7 Pruning roses
- 8 Preparing roses for the winter
- 9 Rose home care at home
- 10 Propagation of roses by seeds
- 11 Reproduction of roses by cuttings in summer
- 12 Propagation of roses by cuttings in potatoes
- 13 How to propagate a rose with cuttings from a bouquet
- 14 Propagation of roses by cuttings in a package
- 15 Reproduction of roses in the Burito way
- 16 Reproduction of roses in the Trannoy way
- 17 Propagation of roses by grafts
- 18 Reproduction of roses by dividing the bush is possible only for non-grafted species
- 19 Diseases and pests
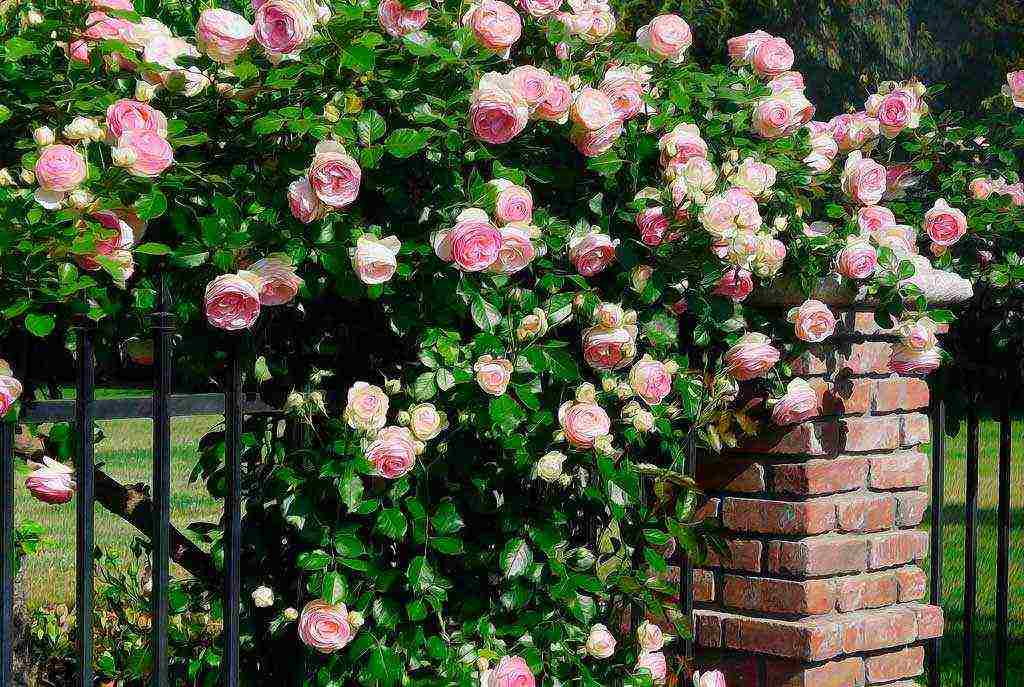

No matter how beautiful and fragrant the garden flowers are, they cannot compete with the beautiful rose. The popularity of roses all over the world is only growing every year, because breeders are constantly developing new varieties and even species. In recent years, interest in climbing roses has increased. This is most likely due to the emergence of many new varieties that combine the best characteristics of the multi-flowered and large-flowered varieties.
Gardeners have learned to grow climbing roses in their backyards. But they often complain that these beauties behave capriciously and do not live up to the expectations placed on them. The thing is that you need to care for climbing roses a little differently than for an ordinary garden rose. In addition, the support is of great importance - it must be made of the right material and positioned in the right place.
The correct planting of climbing roses is the key to their healthy growth and long-term abundant flowering. These beauties can live on the site for more than 20 years, therefore, they need to be placed thoughtfully. Roses are hardy plants, but the care of climbing roses must be correct and systematic.
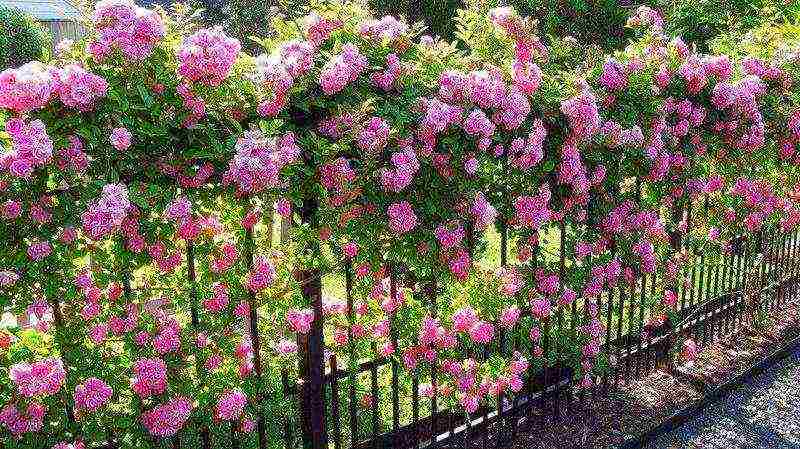

Dates of planting a climbing rose with an open root system in regions with a cold, damp climate and poor soils, they occur in early to mid-May, when the soil temperature will be 10-12 ° C, but before bud break.
In the southern regions, the climbing rose is planted in the fall, until mid-October. Within 2 weeks, the plant will be able to form new root shoots. In winter, the young rhizome will harden, and with the onset of spring it will develop simultaneously with the ground part and form a strong bush.
In the middle lane, you can plant a plant in late October, when the Indian summer ends, or in late April-early May, when the soil temperature is 10-12 ° C, but before bud break.
The above is the best time to plant a climbing rose. But, if necessary, the plant can be planted both in spring and autumn in all regions. The main thing is to ensure that during the planting of a climbing rose, the soil is not already or is still frozen or waterlogged.
Advice! To understand if the soil is waterlogged, you need to squeeze a handful of earth in your fist. If, after you unclenched your palm, the lump does not lose its shape, and after hitting the ground it crumbles, but does not spread, then everything is in order.
Container climbing roses (closed-root) can be planted throughout the season.

Today, in stores and at fairs, you can buy climbing rose seedlings with an open or closed root system.
Climbing roses with open roots should be planted immediately in the ground. When choosing, pay attention to the presence of lignified shoots - there should be at least two of them.Such a shoot must be ripe (bend with a crunch), otherwise the rose may not withstand wintering. The bush as a whole should look healthy, have well-developed roots, strong, without dried out fragments. The length of the shoots should be at least 60-70 cm.
Climbing roses with a closed root system are sold in containers, so you cannot immediately assess the condition of the roots. Carefully inspect the shoots, they should look healthy, not very elongated, if they have a light green color, then it is better to refrain from buying.
The elongation of the shoots and their light shade indicate improper storage of seedlings - either in excessive heat or in insufficient lighting. Such a rose will be weak, painful, unlikely to survive the winter. Close attention should also be paid to the grafting sites; a properly grafted cutting should have callus tissue at the "joint" site, which promotes fusion. If the graft site is peeling and looks unhealthy, then with such a rose you will only have problems.

Climbing roses have their own requirements for growing conditions:
- The area where the flowers will grow should be well lit most of the day. The plant tolerates light shading well in the second half of the day, but at first it will bloom badly in a deep shade, it will hurt, it will become difficult to care for it, and over time it will die without a transplant.
- Climbing roses are undemanding to soil. Slightly acidic, humus-rich, well-drained loams are most suitable for them, but they will grow on almost any soil. Where climbing roses should not be planted is on incredibly acidic or alkaline soils. On poor and very dense clay soils, you need to add organic matter. And to improve soil drainage for climbing roses, sometimes it is enough to loosen the soil twice before planting.
- Climbing roses absolutely do not tolerate wetlands. You cannot plant them where the water table rises above 1.5 m. If you have just such a site, before growing climbing roses, you need to make a raised flower bed or terrace for them.
- You can not plant climbing roses where roses have been growing for more than 10 years before - the soil there is depleted and infected with pathogens and pests. If there is no alternative, the upper soil layer at a depth of half a meter must be replaced.
- Climbing roses are fond of lowland, open areas blown by a strong wind. In order for them not to get sick, you need space.

The soil for planting in the spring is prepared in the fall, in other cases - a month before the planned procedure.
The site for the rose garden must first be dug to a depth of 50-70 cm, this is especially important for heavy clay soils. Small stones in the soil can be left, but the roots of the weeds must be carefully selected and discarded.
It is necessary to add to the earthen mixture, per 1 square meter: 1 kg of wood ash, a pound of bone meal and 100 g of superphosphate. On poor soils for digging, add 10 kg of organic matter (manure, humus or peat compost) per 1 sq. m. In very acidic soil, also add 500 g of dolomite flour or lime per square meter. Coarse sand is introduced into the clay soil.
On chalky soils or in those places where roses have grown for more than 10 years in a row, planting pits 60x60 cm deep are dug 45 cm deep.They are filled with a planting mixture consisting of equal parts of sod land and peat with the addition of a half-liter jar of bone meal for two buckets of mixture.

All the stages of the pre-planting preparation of a climbing rose described below are applied both in spring and in autumn. By the way, roses planted in spring will lag slightly in development (for example, delay flowering by about 10 days) and will require increased attention than those planted in autumn.
Before planting in spring, a seedling with an open root system is shortened by 2 buds, an average of 30 cm in length.In autumn, the stems are not pruned; after planting, they are shortened in the spring, after the leaves bloom. The roots are cut to a living white tissue, on average - up to 30 cm, and sprinkled with crushed charcoal for disinfection.
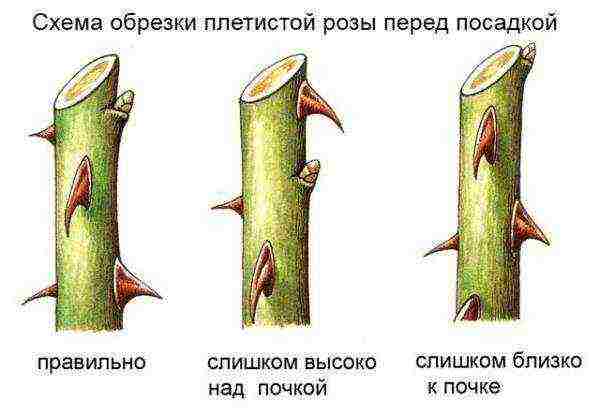 |
It happens that purchased climbing roses with a bare root cannot be planted immediately, they need to be saved somehow. To do this, dig a V-shaped hole, lay out labeled plants along one side. The deepening is covered with soil, it is slightly compacted.
Immediately before planting, the roots of the plants are soaked in water for a couple of hours. For better adaptation, growth stimulants are added to the water: "Kornevin", "Heteroauxin", "Etamon" or "Phosphobacterin", 3 tablets of which are preliminarily diluted in 0.5 water. If the stems of the plant are shriveled, the climbing rose bush is immersed in water entirely.
Instead of soaking, the plant can be dipped for an hour in a creamy mash made of clay and 1/10 of fresh manure, with the addition of growth stimulants (see above).
Important! When planting a climbing rose, the roots should not remain open for a minute - cover them with burlap or cellophane.

Whether the cultivation and subsequent care of the climbing rose will be simple depends largely on the correct planting. First of all, keep in mind that if several plants are supposed to be planted, the distance between them should be at least 1.5 meters. Otherwise, climbing roses will simply interfere with each other, caring for them will be difficult. Other plants should not be planted closer than half a meter from the rose bush.
Planting a climbing rose with an open root system
Dig a hole 50 cm from the support or wall with a bevel in the opposite direction from it. The standard planting hole is 60 cm deep and 40 cm wide. Adjust its dimensions according to the shape and size of the plant's root system.
Pour several handfuls of planting mixture on the bottom of the hole (how to prepare it is described in the chapter on preparing the soil for planting), lay the roots of the climbing rose in the opposite direction from the support. Make sure that all the roots are directed downwards and do not bend upwards! Sprinkle them with two shovels of soil, carefully compact it.
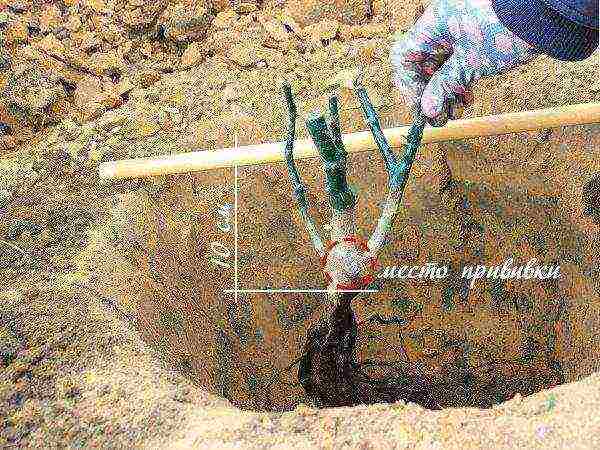 |
When immersing a seedling in the soil, make sure that the root collar is also deepened by 10 cm - this will protect it from frost in the cold season and allow the plant to take root. When planting, make sure that the root system is straightened and that air voids do not form when covered with earth. The roots are gently straightened, covered with soil, slightly compacted with your hands.
Important! Sealing the landing fossa always start from the edge and work your way towards the center. Don't push hard!
Fill the hole completely, squeeze the soil again and water the climbing rose abundantly. Even if the ground was damp when planting a climbing rose, you will need at least a bucket of water per plant. When it is absorbed, add the planting mixture.
Even if you are planting climbing roses in the spring, add a small mound of earth to cover part of the stem. Now it only remains to tie the branches to the support.
In some cases, gardeners cover newly planted bushes with plastic wrap - this technique contributes to better adaptation of plants in a new place. It is up to you to decide whether to do it or not, if the weather conditions in your region push you to create greenhouse conditions for climbing roses, then do not forget to lift the film daily and gradually increase the airing time every day. After stable warm weather is established, remove the film and cover the ground around the bushes with leaf humus, peat, chopped bark or straw.
Planting a climbing rose with a closed root system
The container climbing rose can be planted throughout the season.
Dig a planting hole that is 10 cm larger than the container of the rose on all sides.Place a layer of planting mixture on the bottom (see above). Carefully, trying not to disturb the earthen ball, remove the climbing rose from the container and set it in the center of the hole so that the top of the earthen ball is flush with the edges of the planting hole.
Fill the empty space with planting mixture, carefully compact it. Water the plant abundantly, and when the water is completely absorbed, top up the soil.
 |
Advice! To make it easier to get the plant out of the container without breaking the earthen ball, water the climbing rose abundantly.
The first time after planting, the plant needs to be watered abundantly and often, and if you planted them in the spring, then shade in the first days. You can just cover them with newspapers at noon.

Climbing roses need to be watered, fed and loosened regularly. True, in recent years, mulching of the soil around plants has become very popular, which does not allow for frequent cultivation, but helps to retain moisture and protects against weeds.
Watering
Climbing roses, especially grafted ones, have a powerful root system. Old plants can go without watering for a long time, even in the hottest dry summer. But it's still better if you water them as the soil dries out.
It is best to water the plants in the evening or early in the morning at the root. Getting on the leaves, moisture can cause fungal diseases, especially often the climbing rose suffers from powdery mildew. Better yet, if you have the means to sit down and the ability to install drip irrigation.
What you can't do is water the plant often and little by little. You will moisten the top layer of the soil, the moisture from which will quickly evaporate, and the main roots that feed the plant will suffer from a lack of water. Water sparingly, but in large quantities. Pour at least 15 liters of water under the climbing rose.
Don't be fooled that everything is fine if the old rose bush looks attractive and blooms continuously in hot weather. The plant will take revenge on you next season - in the spring it will not come out of the dormant period, it will give a weak growth and poor flowering. In addition, a climbing rose that was poorly watered the previous summer has flowers that are usually smaller than they can be under normal conditions.
Important! A newly planted plant is often watered until it takes root.
Top dressing
If climbing roses are not fed, they will grow and bloom, but this will affect the growth rate of shoots and the quality of flowering. A plant that has not received the necessary nutrients will give a weak increase (and for climbing varieties this is unacceptable), it will be more susceptible to diseases and may even lose its remontability for the season (the ability to bloom again).
Root dressing Root feeding of climbing roses is done up to 7 times a season. Immediately after opening, they are fed with ammonium nitrate, two weeks later, the feeding is repeated. During the budding period, the plant is given a full range of mineral fertilizers, and it is better to take a special one intended for roses.
Immediately before the first wave of flowering climbing roses, which is usually the most lush and massive and requires a lot of energy from the plant, feed the bushes with infusion of mullein or bird droppings, diluted 1:10 or 1:20, respectively.
After the first wave of flowering, which usually ends at the end of July, climbing roses are fed with full mineral fertilizer, and at this the fertilizing containing nitrogen stops. If the plant assimilates nitrogen further, the growth of shoots will continue, they will not have time to ripen by winter and will freeze too much. Sometimes a climbing rose with immature shoots dies in winter.
Starting in August, you need to give the plant two more top dressing. Previously, potassium monophosphate came to the rescue - in addition to saturating the climbing rose with phosphorus and potassium, it helps the shoots ripen, strengthens the root system, helps the plant prepare for winter and survive it safely.Today there are new fertilizers on sale that do not contain nitrogen, when buying, consult with the seller, which is best for your conditions.
Important! If, when planting a climbing rose, you filled the soil well with organic matter, in the spring and summer the plant under the root can not be fed. But two autumn dressings with nitrogen-free fertilizers are best done.
Foliar dressing Foliar dressing is called fast. It is carried out directly on the crown of the plant from a garden sprayer. Experienced gardeners do such treatments every two weeks from the moment the leaves of climbing roses open until the end of summer.
Root dressing works for a long time, but does not reach the leaves and buds immediately, and the foliar dressing is immediately supplied to the soft tissues of the plant, its effect is felt by a climbing rose on the same day. In addition, microelements vital for a perennial plant are better absorbed precisely with foliar feeding.
It is best to apply at the same time a complex mineral fertilizer, highly soluble in water, a chelate complex and "Epin." Everything is poured into one container and mixed well. To do this, just leave some empty space in it and shake it well.
Important! Epin and chelates tend to foam. It is best to add them when the bottle is already filled with water. Of course, it will take longer to shake it later, but you will not wait for the foam to settle.
The beauty of foliar dressing of climbing roses is that at the same time they can be used to treat plants from pests and diseases, simply by adding the desired drug along with fertilizers, if this is not prohibited in the instructions.
Important! Oxides of metals, such as copper-containing preparations, ferrous sulfate, etc. do not combine with anything; plants need to be treated with them separately!
Foliar treatments of climbing roses should be carried out carefully and only early in the morning or in cloudy weather.
Mulching
Mulching allows you to preserve moisture in the ground, inhibits the growth of weeds and can serve as an additional top dressing for the plant. The soil can be mulched with peat, well-rotted manure, grass cuttings, leaf humus or crushed tree bark.
Loosening
Loosening is designed to protect against weeds and to improve soil aeration, that is, to give oxygen access to the plant roots. You cannot loosen the ground under climbing roses deeper than a couple of centimeters, otherwise you risk damaging the thin sucking roots.
Removal of dead buds and root shoots
In order for remontant climbing roses to bloom better, you need to remove wilted flowers in a timely manner. They need to be removed with a secateurs, making a cut over the second or third sheet. In a young plant, only a very short section of the shoot is removed.
If a climbing rose blooms once a season and has beautiful fruits, they are left on the bush. Before sheltering the plant for the winter, the fruits must also be removed.
Root shoots are shoots growing from the stock, not from a grafted varietal plant. If you do not remove them in a timely manner, they will simply drown out the bush. In order to remove root shoots, it is not enough to cut it off at ground level - this way it will grow back even better over time. You need to dig out the root a little and cut off the excess shoot at the very root collar of the plant, and this should be done as early as possible.
It is very easy to distinguish root shoots - usually it differs greatly from the cultivated plant both in color and in the shape of the leaves.
Garter of a climbing rose to a support
A climbing or climbing rose has long, flexible shoots that often need support. Although large-flowered varieties of climbing roses do not always need support. If the plant has powerful erect stems, which, having reached a certain length, droop, and there is enough space on the site, you can not tie them up.They can be used to form a beautiful hedge in a large area that does not require much maintenance.
So that you can familiarize yourself with this topic in detail, we have dedicated a separate article to it: “Climbing rose supports«.
Climbing rose pruning
Pruning climbing roses is one of the most important steps in plant care. The appearance of the plant and the abundance of its flowering depend on timely and correctly cut shoots. An improperly pruned climbing rose may not bloom at all.
The purpose of pruning is to remove old shoots in a timely manner, which stimulates flowering and the formation of new stems of the plant. New stems also need to be regulated, otherwise we will get a ball of thin branches intertwined with each other, and we will wait for flowering for years.
This topic is vast, so we dedicated a separate article to it: “Climbing rose pruning«.

Prevention and control of diseases and pests is one of the important aspects of caring for a climbing rose.
Spider mites, aphids, leafworms, thrips, rose sawfly - a list of the most active parasites of climbing roses.
At the initial stage aphids can be removed from the branches manually, after putting on garden gloves, but as soon as she feels like a full owner, you will need the help of chemicals. Insecticides "Sharpei", "Aktara", "Inta-Vir", as well as the good old "Karbofos" are guaranteed to help you cope with this problem.
If you want to try traditional methods of dealing with aphids, then grate laundry soap (1 tbsp. l.) and dissolve it in 1 liter of water. Irrigate rose bushes with this solution for a week, then remove all affected fragments - it should help.
Spider mite loves heat and drought, a silvery coating on foliage is a sign of the presence of an intruder. Old methods of struggle with the help of thick tobacco infusion or wormwood broth give very good results. Contact ascaricide "Neoron" is one of the best means of protecting roses from spider mites. One ml of the drug is dissolved in a liter of water, after which the bushes are irrigated. Sometimes it is enough to treat roses twice with this preparation for the tick to give up its positions. Bio-insecticide "Fitoverm" also proved to be excellent in this matter.
According to the reviews of experienced gardeners, the drug "Aktara" works great against rose sawfly... Preparations "Aktellik" and "Phosbecid" (15 ml per 10 liters of water) also show a good result, which extends not only to the sawfly, but also to other "lovers" of climbing roses.
By the way, spring and autumn spraying with Bordeaux liquid is a good prevention of pest infestation for climbing roses.
Among the diseases of climbing roses, the most dangerous are: bacterial cancer, gray mold, powdery mildew, coniotirium (burned bark).
There are no cures for some diseases (bacterial cancer), however, taking prevention seriously will minimize the risk of disease. Disinfection of the root system in a solution of 3% copper sulfate (before planting), removal of suspicious fragments and rapid irrigation of wound sites with the same copper sulfate are the most often recommended preventive measures.
Defeat by Coniotirium can be found in the spring, as soon as the protective cover is removed from the roses. In this case, it is necessary to immediately cut off diseased branches (with the capture of healthy fragments) and burn them. Until the buds awaken, the plant can be treated with three percent iron sulfate, the ground around the bush must be watered too. The same Bordeaux liquid or the drug "Abiga-Peak" can also be involved in the case while the buds have not yet blossomed.
To combat other diseases of roses, the usual scheme works - the removal of the affected areas and their subsequent burning, abundant irrigation of the plant with a solution of ferrous sulfate (3%), copper sulfate (2%) or Bordeaux liquid (3%).Such spraying is often carried out in three stages (with a weekly interval), but sometimes, especially at an early stage, one treatment may be enough.

Shelter for wintering is carried out in two ways: by untiing and bending to the ground or fixing on a support.
An unsupported shelter for the winter The bush is untied from the support. At a slight angle, it is bent to the ground and covered with spruce branches.
From above, they are wrapped in fiberglass, which allows the plant to breathe and does not allow water to pass through. The soil under the plant is covered with dry soil and mulched with fallen leaves.
Shelter of a climbing rose on a support The bush is covered with spruce branches directly on the support, wrapped with agrofibre or burlap and fixed with twine.
Experienced gardeners recommend covering several bushes at the same time. This contributes to a greater concentration of dry air between the plants and their better warming, which helps the roses overwinter without loss.

 The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO Sady Rossii
The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years. In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NPO Sady Rossii
 In the spring, many gardeners are actively planting roses with cuttings. Of course, you can plant and grow roses not only with the help of cuttings. It is quite possible to grow a rose from seeds. Still, most flower growers prefer cuttings.
In the spring, many gardeners are actively planting roses with cuttings. Of course, you can plant and grow roses not only with the help of cuttings. It is quite possible to grow a rose from seeds. Still, most flower growers prefer cuttings.
Planting rose cuttings in open ground is usually done in spring. In regions with a warm climate, you can plant cuttings of roses at the very beginning of spring, for example, in the first decade of April. However, in the conditions of the Russian Central Lane, it is best to land at the end of spring, when the threat of night frosts has already passed. If you hurry with planting, the cuttings of the rose may simply die from an unexpected cold snap.
 If weather forecasters promise that spring will be warm and early, you can plan to plant rose cuttings around the time when spring is already in full swing. The ideal option is the long May holidays and weekends, from May 1st to May 9th. But sometimes spring in the Middle Lane is quite capricious. Sometimes it can snow unexpectedly even in May.
If weather forecasters promise that spring will be warm and early, you can plan to plant rose cuttings around the time when spring is already in full swing. The ideal option is the long May holidays and weekends, from May 1st to May 9th. But sometimes spring in the Middle Lane is quite capricious. Sometimes it can snow unexpectedly even in May.
Therefore, those who are worried about the safety of young cuttings can postpone planting even until the end of May - beginning of June. It all depends on the region, on the nature of the local spring and on the specifics of the site on which the landing is carried out. If a successful, well-lit place with fertile soil is chosen for planting, the plant will immediately enter into intensive growth. Then the florist will not have to regret that the planting was postponed until the very end of spring.
The main benefits of cuttings
 Roses can be planted from seeds or cuttings. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Plus growing from seed lies in the fact that the gardener knows exactly which variety he is buying: the package gives exact information about the name of the variety and the optimal conditions for its cultivation. When the plant is grown from seed, it can be kept at home in a flower pot for the first time. Then they gradually accustom them to fresh air and in the spring, when the soil warms up well, they are planted in open ground.
Roses can be planted from seeds or cuttings. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Plus growing from seed lies in the fact that the gardener knows exactly which variety he is buying: the package gives exact information about the name of the variety and the optimal conditions for its cultivation. When the plant is grown from seed, it can be kept at home in a flower pot for the first time. Then they gradually accustom them to fresh air and in the spring, when the soil warms up well, they are planted in open ground.
Cuttings, bought on the market or taken from other growers, there is no packaging and, accordingly, there is no brief information about the plant: the name of the variety, photograph, recommendations for care. A beginner gardener who is still poorly versed in all the variety of varieties can easily be deceived.In the best case, they might sell him the wrong variety of roses that he wanted. Therefore, it is best to purchase cuttings in specialized stores and nurseries.
The main advantages are as follows:
 Disembarkation is carried out during the warm season - at the end or in the middle of spring, when the soil is already warm, and the night frosts have been safely forgotten;
Disembarkation is carried out during the warm season - at the end or in the middle of spring, when the soil is already warm, and the night frosts have been safely forgotten;- With proper care, they grow very quickly and stretch upward, while a rose planted from a seed grows and develops several times slower;
- Planting technology is much easierthan the technology of growing these flowers from seed;
- Roses grown from cuttings, in comparison with plants grown from seeds, are more resistant to aggressive external influences. They are more hardy and resistant to sudden changes in temperature, as well as to pests and parasites.
What does a novice gardener need to know?
Landing in this manner is a fairly straightforward operation. However, before planting, the florist needs to imagine basic sequence of actions... It will be as follows:
- You need to decide on the place... It should be well lit. Many growers plant rose bushes around the perimeter of the site so that the overgrown bushes subsequently play the role of a kind of hedge;
- Land intended for landing must be dig up and loosen thoroughly rake. Debris and stones must be removed from the ground. You also need to visually inspect the soil for the presence of pests and parasites;
- You can fertilize the ground a little... For this purpose, it is best to use non-aggressive industrial fertilizers, and natural organic fertilizers - ash or eggshells. Eggshells contain a lot of calcium, and ash is rich in potassium and repels pests and parasites;
- It is necessary to outline a place for planting each individual cuttings;
 Followed by dig a hole for the seedlings;
Followed by dig a hole for the seedlings;- The next stage is directly landing. Wearing protective gloves so as not to prick on the thorns, the florist carefully takes the seedling intended for planting and plants it in the newly dug hole;
- Then you need gently surround the seedling with earth on all sides with a shovel or a small hoe. This operation is somewhat similar to hilling potatoes;
- After planting the cuttings need to water... After two to three hours, the watered soil can be gently loosened without touching the seedlings, so that the liquid does not stagnate in the ground.
 If the planting has been done correctly, the cuttings will soon enter a phase of active growth and begin to grow rapidly. Those growers who already have roses on the site may not acquire new cuttings, but propagate already growing bushes. This method seems to be the most reliable. A gardener who uses his own planting material can be one hundred percent sure of its quality and authenticity.
If the planting has been done correctly, the cuttings will soon enter a phase of active growth and begin to grow rapidly. Those growers who already have roses on the site may not acquire new cuttings, but propagate already growing bushes. This method seems to be the most reliable. A gardener who uses his own planting material can be one hundred percent sure of its quality and authenticity.
It is best to plant at about four to five o'clock in the evening, when the soil is well warmed up, but there is no longer the midday heat. Planting cuttings of roses early in the morning is not recommended due to the fact that the ground has not yet warmed up. In addition, there is often fog in the morning, and roses do not like high humidity. Also, do not plant them late at night, when the ground is already starting to cool. If the day is not hot but sunny, you can plant flowers at noon and after lunch. However, if the sun bakes like summer, it is better to wait until the evening with planting. The ideal day for planting is a warm spring day without rain or wind.
 Roses can also be planted in a common flower garden, among other flowers. You can also plant bushes around the perimeter of the site. The most important thing is that the roses get enough sunlight. In the northern regions of Russia, it is best to plant winter-hardy varieties of roses specially bred for these places, for example, the Canadian climbing rose.
Roses can also be planted in a common flower garden, among other flowers. You can also plant bushes around the perimeter of the site. The most important thing is that the roses get enough sunlight. In the northern regions of Russia, it is best to plant winter-hardy varieties of roses specially bred for these places, for example, the Canadian climbing rose.
Canadian roses tolerate frost well and easily adapt to any climatic conditions.In the southern regions, you can plant any varieties of roses, the main thing is that the planting material is of high quality. The choice of seedlings for planting is a very crucial stage. If a novice florist does not dare to make a choice, it is best to take a more experienced colleague to the market or nursery.
How to choose cuttings of roses for planting in spring
When choosing a material for planting, a florist should be guided by the following rules:
- A good quality cut should be straight, twisted and deformed seedlings of irregular shape are unsuitable for planting;
 The presence of a whitish or light gray bloom on the cuttings - a sign of mold or fungal infection. Most often, they are affected by a fungus if they were grown in unsuitable conditions, for example, in a room with high air humidity. Such cuttings are also not worth purchasing. Firstly, the stalk will quickly die, and, secondly, it can infect the rest of the plants with the fungus;
The presence of a whitish or light gray bloom on the cuttings - a sign of mold or fungal infection. Most often, they are affected by a fungus if they were grown in unsuitable conditions, for example, in a room with high air humidity. Such cuttings are also not worth purchasing. Firstly, the stalk will quickly die, and, secondly, it can infect the rest of the plants with the fungus;- The presence of dry brown leaves twisted into a tube on the rose from which the stalk is taken indicates that dangerous pests and parasites have chosen this bush. Of course, you should refrain from buying;
- Qualitative planting material should have an even, resilient stem ... The rose from which the shoots are taken must have a well-developed root system.
You should not purchase cuttings for planting from random people. You also need to be very careful when ordering planting material in specialized online stores for gardeners and gardeners. Many growers exchange seedlings by mail, but this is also not the best option, because during the transfer, the stalk may die.
Care of young cuttings
Young cuttings, just planted in place, require careful maintenance. Primarily, young shoots require:
 Intensive watering combined with loosening;
Intensive watering combined with loosening;- Bright sunlight;
- Top dressing with mineral fertilizers intended for garden flowers;
- Preventive treatment against pests and parasites.
 Later, when the stalk turns into a sprawling rose bush, another important event will need to be included in the list of basic care measures - pruning... If you neglect pruning, rose bushes quickly take on a neglected, unpresentable look. Correct pruning is especially important for winter-hardy climbing roses, for example, Canadian roses.
Later, when the stalk turns into a sprawling rose bush, another important event will need to be included in the list of basic care measures - pruning... If you neglect pruning, rose bushes quickly take on a neglected, unpresentable look. Correct pruning is especially important for winter-hardy climbing roses, for example, Canadian roses.
It happens that not all seedlings take root. This is usually caused by improper planting technology. For example, a hole was dug too deep or the grower forgot to water the plant after planting it. However, this also happens for other reasons. It is possible that the stalk that did not take root was initially infected with parasites or fungal infection. If one or more of the planted cuttings have died some time after planting, the grower should visually inspect the rest of the cuttings and check if they are healthy.
Planting roses by cuttings: practical recommendations
 Planting roses using cuttings is the most common way of planting these plants in conditions of the Russian Central zone... Before planting, a novice florist should get himself the most complete picture of this variety. If the variety is characterized by increased frost resistance, you can safely plant it early, for example, in early April. If the rose, on the contrary, is afraid of temperature changes, it is better not to rush to plant it.
Planting roses using cuttings is the most common way of planting these plants in conditions of the Russian Central zone... Before planting, a novice florist should get himself the most complete picture of this variety. If the variety is characterized by increased frost resistance, you can safely plant it early, for example, in early April. If the rose, on the contrary, is afraid of temperature changes, it is better not to rush to plant it.
It is also necessary to know exactly the basic needs of each variety for moisture, feeding and sunlight. Those varieties that are more attracted to the light than others are best planted in an open area or on a hill. And those varieties that calmly perceive the shade can be planted in small groups along the perimeter of the garden plot.
Planting roses with cuttings is an exciting experience. The main thing is proper care, and the toga rose will soon delight the grower with its wonderful aroma.
> > > > > >
Rose is a plant belonging to the Rosehips. In the wild, these flowers mainly grow in the temperate climate of the Northern Hemisphere, but in our central Russia, roses are grown when planting and nursing in the open field, as well as at home.
General information
Roses are very attractive and are not only used as ordinary garden plants or houseplants. They are used in gardening, rose petal jam, and rose oil.
Growing up, roses form bushes with their shoots, the height of which differs depending on the type of plant. Some types of roses reach 30 cm in height, while others grow more than two and a half meters.
The branches of the plant are divided into uterine and annual stems. The shape of the leaf differs depending on the type of flower.
Peduncle size also varies from species to species. It can be short, or it can grow almost a meter. Rose flowers come in various shapes and colors, the size varies from a couple of centimeters in diameter to 15-20 cm. The number of petals in flowers is also different, from 5 to 120 pieces.
The colors of roses are of all possible colors - pink, black, white, even blue roses are bred. And the pinnacle of breeders' achievements are varieties that change color during flowering.
There is no way to describe the huge variety of roses. Among cultivated roses, park and garden roses are distinguished; it is also worth remembering indoor varieties. Most often, bush roses, climbing, miniature, floribunda and grandiflora roses are grown.
But the rather popular Chinese rose is actually hibiscus, and the desert rose is adenium.
A lot of varietal roses have been bred and it would take a very long time to list even a small fraction of varieties.
to the table of contents
Rose planting and care in the open field
Roses are quite demanding plants, so planting and caring for them requires knowledge of the characteristics of this flower.
Planting roses is best done in the fall, but no later than mid-season. It is also advised to purchase material for planting in the autumn, since in the spring they are often sold that were left over from last year.
Rosehips are photophilous and the place of cultivation for them should be chosen unshaded, but if you have climbing roses, it is better that the midday sun does not bake them. Drafts and northerly winds are bad for plants, and do not plant flowers in places where groundwater rises high to the surface.
To plant roses, you need to drain the soil, which should be slightly acidic (about 6 pH), fertility is not so important, but it affects the beauty of flowering, so fertile substrates are welcome.
Before planting roses, the seedlings are shortened to 20 cm and placed in water for a couple of hours. A hole for a rose is dug about 50 cm in, and the depth is made 10 cm deeper than its roots.
The soil from the pit must be mixed with compost. For three lobes of land, one share of compost is taken. It is also worth mixing a little ash into the substrate, and pouring a bucket of water with a tablet of heteroauxin into the hole.
The rose is planted so that the grafting site sinks four centimeters into the soil, and for climbing roses - ten centimeters.
The flower must be placed in the hole and carefully covered with the substrate, trampling it down as the hole is filled. Young plants need to be hilled 15 cm and shaded for 15 days. Climbing roses spud 20 cm.
The distance between the landing sites must be at least one meter.
Not far from the bushes, you need to warm up a small shaft from the soil so that the water does not spread during watering.
If groundwater is too high on your site, then you need to make an elevated flower bed for the roses, otherwise the roots will often rot.
Also, if the soil where you want to plant the plants is very clayey, then you need to dig it up with sand.
to the table of contents
Planting roses in open ground in spring
Young roses may not stand up to very cold winters and therefore, if you live in regions that are too frosty, plant flowers in the spring. The best period at this time is mid-April and almost all of May.
The planting process in spring is almost the same as in autumn. Right before planting, the seedlings need to be dipped in a clay mash, and after planting, the site is covered with mulch.
If there is a threat of frost, then the stems must be covered with a film, which must be removed for some time every day for airing. The time without film must be gradually increased, since the plants are hardened in this way. The film is completely removed when the frost is probably gone.
During the first year after planting, roses undergo a formation period. At this time, the main thing is to pinch the stems to improve bushiness. It is also important in the first half of the summer to remove the flower buds as soon as they begin to appear. In the second period of summer, the buds are also removed, but after formation. If you have a climbing rose, then it needs to be supported.
to the table of contents
Watering roses
It is not necessary to water the flowers often, but only as needed, when the soil dries up. Regular watering is needed only for the first year, which needs to be watered every couple of days.
During the growing season, watering is carried out a little more often so that the green mass develops better. And at the end of summer, watering, on the contrary, is reduced. It is preferable to carry out the procedure in the morning. Do not use cold water.
You need to water the bushes carefully, because water can erode the soil, it is best to use drip irrigation.
to the table of contents
Fertilizers for roses
As for fertilizer, the first years do not need to be fed at all. Further, fertilizers must be applied in this way.
In the spring, during the stage of active growth, a double dose of fertilizer is applied, then feeding is carried out during the appearance of buds, at the end of flowering and before the stems begin to grow stiff.
In the spring, for fertilization, take 20 grams of ammonium sulfate for each square meter of soil. After a couple of weeks, this fertilization is repeated. During the formation of buds, feeding is carried out using 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 30 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium salt per square meter.
At the end of flowering, the plant is fed with a complex fertilizer, and in the fall with potassium salt with superphosphate, about 30 grams per square meter. Among organic fertilizers, chicken droppings, ash, and manure are perfect. No fertilization is carried out during the flowering period.
For adult roses, fertilization is possible only with organic matter, but do not overdo it, otherwise the plant may give dense foliage, but not bloom.
to the table of contents
When to replant roses
Over time, roses grow and lose their beauty and when this happens, they need to be transplanted. Repotting is best done in April or October, but spring is still preferred.
Before starting the transplant, the bush is cut to 20 cm, and all the leaves are torn off. The bush must be removed from the soil along with an earthen lump. To facilitate its movement, the roots are laid on a piece of cloth. You can plant a rose with this fabric, it will rot over time.
Climbing roses are transplanted much less often, usually only if a bad place is chosen for growing and if the plant dies in the old place. When transplanting this variety of roses, you need to be more careful, since their roots are more sensitive than others.
to the table of contents
Pruning roses
In the spring, summer and fall, you need to prune the bushes. Spring pruning is carried out to form the shape of a bush, in summer it is carried out to clean the bushes from unnecessary buds, dull flowers, fruits. In the fall, bad stems are removed from the plant.
Pruning is carried out until the buds are swollen. Only strong branches should be left, of which the young are preferred.
Older plants need to be pruned more carefully, as they are worse at restoring the crown, the same applies to flowers planted on poor soil.After the operation, the cut sites must be treated with garden varnish.
In autumn, these rose hips do not require watering and special supervision, in addition to weeding and loosening the soil.
to the table of contents
Preparing roses for the winter
Before winter, they need to be spud with a mixture of peat and sand. Hilling is carried out with the onset of the first frost, and the site is covered with a film to prevent precipitation from falling on them.
Before wintering, leaves are cut off from plants and burned. It is also advisable to treat the bushes with a 1% solution of copper sulfate. When the night temperature drops to -6ºC, roses are warmed with spruce branches.
To prevent rodents from disturbing your plants in winter, you need to scatter poison baits around the flower bed.
If you covered the area with insulation and oilcloth, then from time to time it will need to be ventilated so that the bushes do not bump.
Climbing roses must be removed from the supports before winter and lowered to the ground. Old roses do not fit well and therefore, it will be necessary to bend them to the ground gradually. This procedure must be carried out at positive temperatures, otherwise the bushes will break. Before wintering, a climbing rose is pinned in the soil, and insulated in the same way as an ordinary one.
to the table of contents
Rose home care at home
If you want to have a room rose, then remember that they do not like cold water and too hot temperatures in the summer.
When buying a plant, you should not rush to transplant it; first you need to wait for the rose to get used to the new conditions.
During the period of growing green mass, you need to water the rose well, and during the rest of the time, watering is carried out a little less often, but make sure that the water does not stagnate in the pot.
A rose transplant is carried out by transshipment in the waxing moon phase. It is necessary to carry out the operation if the plant has filled the entire pot, if the soil in the container with the plant is depleted or the plant has aged and needs to be rejuvenated.
We recommend fertilizing indoor roses with a mullein once every 15 days, and during the flowering period every 7 days. If the plant is sick or has been recently transplanted, feeding is not necessary, and it is also better not to fertilize the flowers in gloomy and cold weather.
In summer, moving it to the balcony will benefit a room rose. You can start to take out the flower after the night temperature becomes warm. At first, the rose needs to be kept in the shade so that it adapts, and then it is moved to diffused light.
For the winter, the stems need to be cut so that there are 4 buds on each branch. Pruning can also be done in the spring, before the plant begins to develop. In winter, the flower is watered every three days and sprayed.
Roses are very sensitive to drafts and plant protection with a paper cylinder would be a good solution to this problem (cylinder height is about half a flower).
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by seeds
Reproduction of roses is carried out by seeds and vegetatively. Seed propagation is usually used only for wild roses, and not all of them can produce full-fledged seeds.
The material is taken at the stage when the fruit turns red. This usually happens in August or a little earlier.
Then stratification is carried out in wet sand at a temperature of about 3 ºC. With the onset of spring, the seeds are treated with stimulants for better root formation and sown to a depth of two centimeters, and then covered with humus mulch.
When a pair of true leaves appears in sprouted roses, they are transplanted so that the seedlings are at a distance of 7 cm from each other, and the gap between the rows is 20 cm. In the summer, the area with young roses must be fertilized with mineral fertilizer.
Until next August, you need to take care of the bushes, and then they are taken as a stock.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses by cuttings in summer
Usually, the best results are obtained by propagation by cuttings, which can be carried out in different ways.
For a simple, natural way to root shoots in summer, you need to cut the stems in the evening or early in the morning.Slightly woody shoots or those that are about to bloom or have recently faded are preferred.
You can find out that the stem is ready for breeding by breaking off a thorn on it. If it breaks off easily, then you can use the shoot as a cutting.
The length of the cuttings should be about 14 cm, and each of them should have a pair of leaves and buds without flowers. Excess leaves are plucked.
The incision is treated with an agent for stimulating root growth and placed in water to which pieces of rose leaf are added.
Cuttings are planted directly into the ground, having previously treated the pits for planting with a solution of potassium permanganate.
The branches need to be covered with jars that will serve as greenhouses for them. Young cuttings are very sensitive and the daytime temperature must not drop below 25 ºC and the night temperature 19ºC until rooting has taken place.
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by cuttings in potatoes
An interesting way is to root cuttings in potatoes. To do this, in the spring, you need to dig a shallow trench, about 15 cm, and fill it 5 cm with sand.
Twenty-centimeter cuttings are stuck into potatoes, from which you need to cut out all the eyes, and then they will simply be thrown into your little ditch with sand. At first, the seedlings can be kept under glass jars.
It is important to constantly water the cuttings, and once every 5 days, water it with sweetened water (2 tea boats of sugar per glass of water).
to the table of contents
How to propagate a rose with cuttings from a bouquet
If you were presented with a bouquet of domestic roses, then they can be used for propagation. Imported flowers will not work as they are treated with preservatives.
All flowers, thorns, buds are removed from the cuttings, and the leaves are removed from below and shortened from above. The stem itself is cut to 20 cm. Then it is simply placed in distilled water, which is changed until roots appear.
Further procedures do not differ from those described above for conventional cuttings.
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by cuttings in a package
The finished cuttings are placed in a bag with moist soil, inflated and tied well, and then placed on the windowsill. In about a month, roots should form and the cuttings can be planted.
Transplanting cuttings is done before winter, if you want to plant cuttings in spring or later, you have received the desired cutting and it seems difficult to keep it.
Just dig the shoot into the soil and arrange a dry shelter for it so that the cold does not reach it, and plant the cuttings in the spring.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses in the Burito way
Burito's method is completely unreliable, since root formation does not occur even in 50% of cases. But sometimes it does happen.
The cuttings should be treated with a root-growth agent and then placed in a damp newspaper in a dark, warm place (about 17 ° C). You will have a chance that after 15 days the cuttings will form roots, but let's be honest - this chance is scanty.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses in the Trannoy way
To reproduce with this type, you need to cut off the top of the shoot with a limp flower and a few small leaves. Further, it is observed until the kidneys from below begin to swell. This indicates that the stem is ready for growing.
At this time, the cuttings need to be cut to 20 cm, remove all the leaves except the top two and plant in a well-lit area, several copies at once in one hole. Cover the cuttings with a large plastic container, which is not removed until the cold weather. Seedlings will sometimes need to be watered and loosened up in the soil next to them.
This method is also quite unreliable, but still better than the previous one.
to the table of contents
Propagation of roses by grafts
They need to be grafted onto young rose hips. The dog rose and its varieties are considered the best for this, but others can be used. The vaccine is usually done in the middle of summer.
To do this, remove the lateral stems from the stock and clean its root collar from the soil.A T-shaped incision is made on it in which the cutting is placed. Check the kidney after 20 days. If it is swollen, then everything is fine, but if it turns black, then the grafting failed. Before wintering, grafted roses are spud 5 cm above the grafting level.
In the spring, the earth is raked, and the plant on which the grafting was carried out is cut one centimeter above the grafting site. When the flower begins to grow, it will need to be pinched over the third leaf.
to the table of contents
Reproduction of roses by dividing the bush is possible only for non-grafted species
For such reproduction, it is necessary in the spring, even before the buds begin to bloom, dig up a rose and cut it in such a way that on each division there is a part of the root and a shoot. The places of the cuts are powdered with coal and then parts of the bush are simply planted like ordinary roses.
To propagate a rose by layering, in early spring you need to make an annular cut on the stem that grows from the root collar, and then bend it into the hole, fix it and sprinkle it with moist soil. Further, the soil will need to be moistened until autumn, when the cuttings take root. It will be possible to separate the cub from the mother next spring.
to the table of contents
Diseases and pests
The worst pests for roses are aphids and spider mites... In the early stages, aphids can be fought by simply cutting off the leaves or crushing the aphids, you can also wash the leaves with soap, but if this does not help, you need to buy an insecticide "for roses and grapes" in a specialized store.
WITH spider mite you can fight with an infusion of wormwood or tobacco, but if the pest has spread too much, it is better to buy a means to combat it. This pest affects the rose if it grows in dry conditions and lacks moisture.
Also, the rose can be attacked thrips, cicadas, rose sawfly, but if you take proper care of the plant, they will not appear.
One of the diseases dangerous for the rose is bacterial cancer, which can be recognized by the growths that gradually harden. This disease cannot be cured and the plant will die.
Examine the material before purchasing, and also carry out pest control before planting with a three percent Bordeaux liquid. If you notice growths on the plant, try removing the leaves and treating the cuts with copper sulfate, but there is no guarantee that you will have time to help the flower.
Coniotirium it is a disease that affects the bark of plants. It appears as brown spots that darken over time and “ring” the stem. These shoots must be cut off and burned immediately. Also, if this ailment is found, before winter it is necessary to stop fertilizing the rose with nitrogen, and replace it with potassium dressing.
Powdery rose represents white spots. Sick areas should be immediately removed and burned, and the plant should be treated with iron (3%) or copper (2%) vitriol.
Brown spots on the leaves and the falling off of the latter indicate black spot... To prevent the development of the disease, you need to fertilize the rose with potassium-phosphorus dressings in the fall, as well as treat the plant and the area where it is grown with Bordeaux liquid (3%).
Also, the rose can get sick gray mold, after which the plant is most often burned. But, if the fungus has not taken effect, then you can try to cure it with a Bordeaux solution diluted in water (100 grams per bucket). In this way, a diseased plant will need to be processed 3-4 times every seven days.
- If your rose is not blooming, then you may just have acquired a weak plant or a variety that rarely blooms. This also happens if the flower lacks light or nutrients. The lack of flowering can be caused by freezing in winter. But the most dangerous reason for the lack of flowering, in which the rose loses its varietal properties, is the wildness of the plant.
- If you notice shoots with small leaves and an abundance of thorns, then immediately cut them off (usually such stems appear from the very bottom of the bush).If you do not fight them, then over time these shoots capture the entire bush and it runs wild.
- The leaves of roses can fall off if they are struck by pests or a disease, and besides this, the reason is often hidden in the roots of the plant. The root can rot, and there are also cases of damage by bears or May beetle larvae, mice and moles.
- In addition to diseases, the leaves of a rose can turn yellow from an elementary lack of nutrients such as nitrogen, iron and manganese, as well as potassium.
With a lack of nitrogen, the leaves turn yellow alternately. First, this happens with the bottom layer, which falls off after yellowing. Further, such a fate awaits the middle leaves, and then the whole bush. With a lack of potassium, the leaves begin to turn yellow from the edge, and then dry out. With a lack of trace elements, the veins on the leaves of the plant begin to turn yellow. Another cause of yellowness is excess moisture in the soil.
to the table of contents
 The rose has many worshipers, but few people decide to plant it in their garden, assuming that it needs special care. But the rose is not so whimsical as it is commonly believed. You just need to follow the rules of its breeding.
The rose has many worshipers, but few people decide to plant it in their garden, assuming that it needs special care. But the rose is not so whimsical as it is commonly believed. You just need to follow the rules of its breeding.
Today, rose seedlings are sold in abundance. However, it is not a fact that the plant will take root and will be of the promised color and size, as we wanted. Therefore, I would like to know how not to make a mistake and choose the right rose seedlings, based on the fact that not all roses winter well in the conditions of the Moscow region and the northern regions (see on a separate page).
Roses grow successfully in one place for up to 10 years. For their successful cultivation, it is very important to choose the right place for planting. It is best suited sunny places, sheltered from the winds, with fertile, but not waterlogged soil with an acidity close to neutral. It can be planted in spring or autumn. They are planted in a hole up to 1 m deep, filling it with compost or other rotted organic fertilizer. When planting seedlings, it is necessary to ensure that the grafting site is 5 cm underground. Roses do not like alkaline soil and die when the water table is high. Before planting, they are cut at a height of 15-20 cm. Then the plants are watered and hilled.
After planting, special attention should be paid to agrotechnical care, since many diseases are aggravated by improper agricultural techniques (excessive fertilization, dryness or waterlogging, sharp temperature fluctuations). Agrotechnical techniques and the timing of their implementation depend on natural conditions. And the number of irrigations depends on the duration of the growing season, the amount of precipitation, the proximity of groundwater, temperature conditions, the structure of the soil (how much it is able to retain and retain moisture). Roses are watered starting in spring, about once a week. In the fall, watering is stopped. Sprinkler irrigation is not recommended as it increases the susceptibility to disease.
Throughout the growing season, roses are followed by careful maintenance, spring pruning, forming bushes, loosening the soil around the bushes, watering, feeding, weeding, mulching, pest control, preparation for winter and shelter. When pruning, you can select suitable shoots for grafting. - see "Roses from a cutting".
 Pruning roses is a simple operation, but it requires knowledge of some rules. The main pruning is carried out in spring at a height of 20-25 cm, with the exception of climbing and park species, in which only old shoots are removed.
Pruning roses is a simple operation, but it requires knowledge of some rules. The main pruning is carried out in spring at a height of 20-25 cm, with the exception of climbing and park species, in which only old shoots are removed.
Shoots are cut with a sharp pruner at an angle of 45 degrees, to healthy wood, 5-6 cm above the developed bud. The surface of the cut should be smooth, without cracks and burrs, be sure to cover it with garden pitch. Pruned to a bud located on the outside of the shoot, so as not to shade the center of the bush. Sometimes in strong rose plants, 2-3 shoots grow from one bud after pruning. Leave one, the rest must be removed. All weak, thin, crossing, diseased, dead shoots are cut to the level of soil or healthy wood.
The number of shoots is left on the bush, at which air exchange and good illumination of the bush can be ensured. In this case, the development of fungal diseases such as powdery mildew, black spot, rust and others that arise in stagnant air is excluded.
The formation of bushes requires special attention in the first summer after planting. All small spreading inside, thickening the plant shoots, as well as growing from the grafting site or the root collar (in own-rooted ones) are cut into a ring, strongly growing ones are pinched. In June, the formative pruning is finished so as not to cause the growth of new shoots, which, having not had time to ripen, freeze slightly, often causing the roses to get sick.
During the summer, for greater decorativeness and longer abundant flowering, it is necessary to remove faded flowers. In grafted roses, wild rose hips are promptly removed to the base, which is especially abundant in the first summer, and should be less in subsequent years.
In subsequent years, summer pruning consists in shortening individual, too violently growing shoots, especially in bushes of large-flowered roses and crowns of a standard rose. However, the most important task of summer pruning is to induce the plant to bloom again. In order for the bush to give the maximum number of flowers that a particular variety is capable of producing, you need to correctly carry out summer pruning. You can't just remove a faded rose flower with a simple pinch, that is, tore off one flower and that's all - this is a big mistake, because a new shoot with a flower will appear very high. It will be elongated, thin and easily bendable. It is necessary to remove the flower even before the petals completely fall off, as soon as the flower loses its attractiveness. You need to cut the flower lower, then the new shoot in this place will grow strong and will hold on tightly (when pruning, leave the stumps above the eye 6-8 mm).
 Roses need constant care, as well as loosening the soil around the plants (to a depth of 5-10 cm), especially in a hot period, after prolonged rains, when a solid crust forms. As a result, all weeds are destroyed, air easily penetrates into the loosened soil, the earth warms up well, besides, loosening saves water. Deep loosening is dangerous for the rose, since even minor damage to the roots will harm the plant. Usually, loosening begins in May and ends in July-August to avoid encouraging the plant to grow further.
Roses need constant care, as well as loosening the soil around the plants (to a depth of 5-10 cm), especially in a hot period, after prolonged rains, when a solid crust forms. As a result, all weeds are destroyed, air easily penetrates into the loosened soil, the earth warms up well, besides, loosening saves water. Deep loosening is dangerous for the rose, since even minor damage to the roots will harm the plant. Usually, loosening begins in May and ends in July-August to avoid encouraging the plant to grow further.
When caring for roses, mulching is used by sprinkling the surface of the earth with peat, humus, peat compost. Such bedding with a layer of up to 10 cm allows you to reduce the amount of irrigation and loosening, improves the physical and chemical properties of the soil, the living conditions of soil microorganisms. Therefore, in the spring, immediately after the spring work, you need to pour mulching material between the rose bushes, it is better to do this work before the buds open. If the bedding spoils the decorative appearance, later it will be possible to embed it into the soil by loosening.
An important quality of roses is their resistance to low temperatures. However, when choosing a variety for unfavorable soils and slopes, you need to take into account the characteristics of roses. Especially should be protected large-flowered, multi-flowered varieties, which should be spud and covered with plastic wrap for the winter.
For winter, rose bushes are carefully bent to the ground, covered with dry material (peat, spruce branches, leaves, sawdust), and an old oilcloth (cellophane film) is placed on top. Then the snow will reliably cover the bushes. In early spring, when it gets a little warmer, the winter cover is gradually removed. Roses are fully opened only after the soil has thawed. Cut off dried branches and, if necessary, shorten the shoots. The variety is chosen taking into account the planting site - a garden bed, a flower bed, a balcony or a pot.
Roses are perennial crops that are grown outdoors.With such cultivation, great attention is paid to both preventive measures and the protection of plants from diseases and pests. The selection of varieties with increased disease resistance is of great importance in the cultivation of roses.
 Nutrition is an important part of caring for roses. It should be remembered that roses do not like acidic soil, they require constant application of organic fertilizers, a sufficient amount of a variety of nutrients. Calcium is needed to neutralize acidic soils: dolomite flour, chalk, slaked lime, wood ash, and organic fertilizer, a deoxidizer, are used.
Nutrition is an important part of caring for roses. It should be remembered that roses do not like acidic soil, they require constant application of organic fertilizers, a sufficient amount of a variety of nutrients. Calcium is needed to neutralize acidic soils: dolomite flour, chalk, slaked lime, wood ash, and organic fertilizer, a deoxidizer, are used.
Nitrogen promotes plant growth, roses need it after pruning (in early May), during the formation of new shoots, in preparation for re-flowering. The last term for applying nitrogen is the beginning of August (fertilizers causing growth: urea, liquid organic fertilizing, "Effekton - Ts", "Effekton - DC".
Phosphorus is essential for the maturation of strong shoots. Influences the intensity and quality of flowering. It is brought in from June to September inclusive (single or double superphosphate)
Potassium is necessary during budding and flowering, as well as in preparing roses for winter. Potassium is easily washed out of the soil, it is introduced from June to October in the form of potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate), potassium chloride.
Trace elements (magnesium, iron, boron, manganese) are required during the entire growing season. The lack of iron in the soil causes chlorosis, the lack of boron and manganese reduces plant immunity. Apply "Agricola for flowering plants" (granular mineral fertilization) and "Agricola - Rose", any complete fertilizer (always contains trace elements) and wood ash.
In the first year after planting, when filling the soil with fertilizers, there is no need for top dressing. In subsequent years, roses need regular nutrition. Mineral fertilizers, primarily nitrogen in the form of ammonium nitrate, are applied in early spring after the removal of the shelter and pruning. After fertilization, the soil is dug to a depth of 10 cm. Further feeding is timed to the phases of plant growth and development - the beginning of flowering, new growth of shoots.
It is a common mistake to add fresh manure or bird droppings to the soil for planting roses in the spring. For young seedlings, this is simply destructive. Organic fertilizers are best given to plants in liquid form.
1 liter of mushy mullein (cow dung) or bird droppings is diluted with 10 liters of water. Poultry droppings should ferment in a barrel for up to 10 days, only after that it is used, once again diluting at the rate of 0.5-1 liter of the prepared solution per 10 liters of water. Watered only under the bushes so that flies do not start. After feeding with such unpleasantly smelling nutrients from above, you need to "powder" the soil with wood ash or chalk, then loosen it to a depth of 5-6 cm.
Usually in spring, roses get good nutrition from mulching carried out in late autumn, early November. Usually, decomposed cow dung or peat-manure humus, or simply well-prepared peat, or vegetable humus are poured onto the bushes. These organic substances are an excellent source of humus. Thanks to this nutrition, the rose forms a root system more intensively in the spring, and if it is fed with nitrogen at this time (about 1 tablespoon of urea / carbamide), then the results will be excellent.
The approximate dose of fertilizers per 1 square meter: ammonium nitrate 20 grams, superphosphate 30 grams, potassium salt 10 grams. In the summer, liquid fertilizing with a mullein is effective. Top dressing with nitrogen fertilizers ends at the end of July. In August, for better ripening of the shoots, potash and phosphorus fertilizers are applied. For the same purpose, watering is limited.


