Content [show]
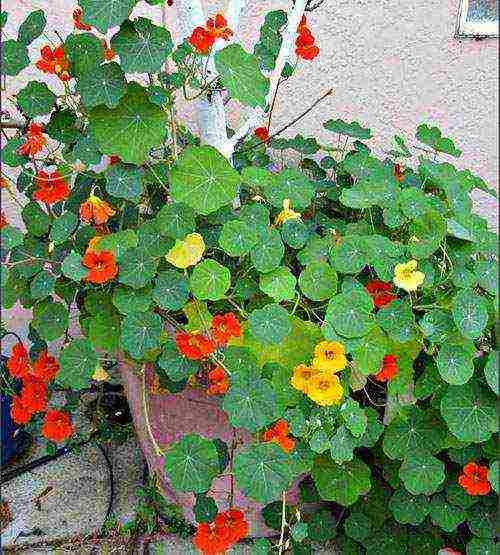 Climbing or bush nasturtiums are one of the most memorable flowering annuals, pleasing to the eye from the first half of summer until frost. If nasturtium has taken root on the site, planting and caring for it in the open field does not take a lot of time from the summer resident. The plant is unpretentious, responsive to care, willingly and abundantly blooms. Experienced gardeners use nasturtium to protect their beds from pests, and gourmets know how to turn unripe seeds, young leaves and delicate flower corollas into an exquisite dish.
Climbing or bush nasturtiums are one of the most memorable flowering annuals, pleasing to the eye from the first half of summer until frost. If nasturtium has taken root on the site, planting and caring for it in the open field does not take a lot of time from the summer resident. The plant is unpretentious, responsive to care, willingly and abundantly blooms. Experienced gardeners use nasturtium to protect their beds from pests, and gourmets know how to turn unripe seeds, young leaves and delicate flower corollas into an exquisite dish.
For several decades, nasturtiums disappeared from flower beds and front gardens, but today they are again finding admirers and worthy places in summer cottages, in parks, on terraces and loggias.
Dates of planting nasturtium in the ground in spring
 In nature, there are almost 90 species of nasturtiums, which in the native conditions of the subtropics of the American continent have the form of not only annuals, but also perennials.
In nature, there are almost 90 species of nasturtiums, which in the native conditions of the subtropics of the American continent have the form of not only annuals, but also perennials.
In the middle lane, even the most frost-resistant varieties are not warm enough for wintering, so nasturtium is grown as an ornamental summer plant, planting seeds or seedlings in the garden.
How to organize planting of nasturtium in open ground, when to plant flowers in different regions?
Nasturtium seeds begin to germinate when the air and soil warms up to 18–20 ° C. If the seedlings fall under frost, there is a danger of freezing, therefore they plan to plant nasturtium in the ground in the spring, paying attention to the weather conditions of the region. The farther south, the earlier the right moment comes.
In the middle lane, seed placement in open ground is carried out in the middle or at the end of May. In Siberia, where planting and caring for nasturtium in the open field is postponed for 7-10 days, for early flowering it is better to use not sowing in flower beds, but planting grown seedlings.
Planting in open ground with seeds and caring for nasturtium
 For nasturtiums, sunny, quiet areas with drained light soil are preferred.On poor soils, the plant looks depressed, its leaves become smaller and brighter, flowers appear later and not as massively as on well-fertilized moist soils. At the same time, the culture has a negative attitude towards the introduction of fresh organic matter.
For nasturtiums, sunny, quiet areas with drained light soil are preferred.On poor soils, the plant looks depressed, its leaves become smaller and brighter, flowers appear later and not as massively as on well-fertilized moist soils. At the same time, the culture has a negative attitude towards the introduction of fresh organic matter.
Dig up a place for sowing, carefully breaking up the clods. The change is embedded in the soil to a depth of about 2 cm, and on lighter substrates, the holes are made somewhat deeper.
If planting nasturtium and care in the open field is complicated by the high density of the soil, it is better to add peat and sand to it in advance.
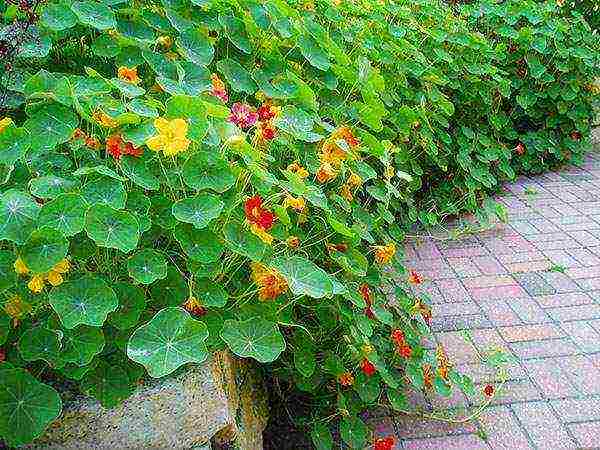
Furrows or holes for large seeds are made at a distance of 25 cm for bush varieties and with an interval of up to 40 cm for climbing, highly growing varieties. Experienced gardeners advise sowing 2-4 seeds in one hole. Curly nasturtium can quickly form a lush green crown for vertical gardening.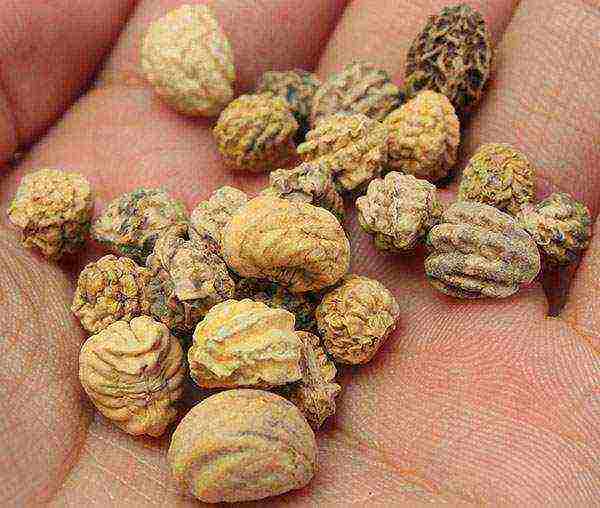
Rapidly growing and lushly flowering plants help to separate outbuildings from the yard in the shortest possible time, to plant trees in a gazebo, or to create a comfortable shady corner in a sunny area.
When planting nasturtium and leaving in the open field, a trellis made of stretched cord or net helps to give the plant an upright position, to monitor the condition of the lashes.
After filling the ridges, the soil is slightly compacted and watered. Seedlings of nasturtium appear in 7-10 days. They are quite friendly and strong. So that the sprouts do not suffer from recurrent cold weather, they can be covered with non-woven material at night.
Taking care of nasturtium after planting outdoors
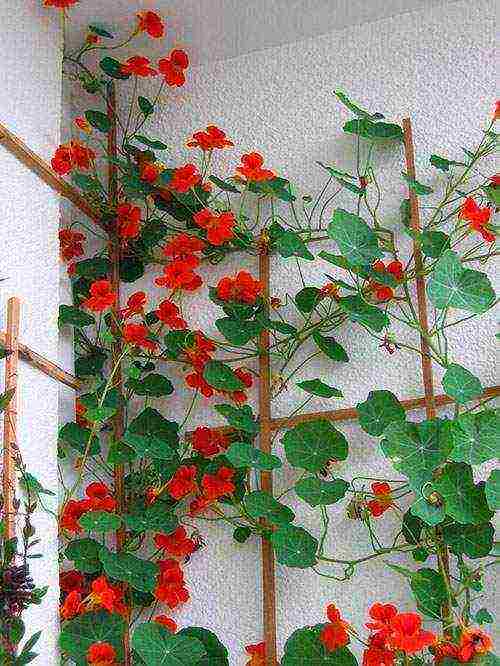 Throughout the warm season, nasturtiums are watered, making sure that the soil under the plants is free of weeds and loose. From a lack of moisture, especially in hot weather, the casting of nasturtium turns yellow, the buds fall off, the already blossoming corollas fade faster. For irrigation, settled water heated in the sun is used.
Throughout the warm season, nasturtiums are watered, making sure that the soil under the plants is free of weeds and loose. From a lack of moisture, especially in hot weather, the casting of nasturtium turns yellow, the buds fall off, the already blossoming corollas fade faster. For irrigation, settled water heated in the sun is used.
Shrub nasturtiums bloom 25-30 days after sowing. Climbing varieties, regardless of the timing of planting and caring for nasturtium in the open field, open the buds another 10-15 days later. To make the flowering lush and last until the first frost, the plants are fed monthly using complex mixtures. At the beginning of growth, fertilizers for nasturtium may have an increased concentration of nitrogen and potassium. But then an excess of nitrogen causes a rapid build-up of green mass and a delay in the appearance of buds. Therefore, from June, top dressing should contain more phosphorus and potassium.
By autumn, the flowering of nasturtium gradually dies down, but does not stop. Therefore, green plants remain on the site until the cold weather.
Then the stems are harvested, the site is dug up and spilled with phytosporin or other means to improve the quality of the soil.
Planting nasturtium seeds for seedlings and caring for seedlings
 For those who do not want to wait a whole month for yellow, orange, white and red flowers of nasturtium to appear on their beds, you can sow seeds in April and grow seedlings of this unpretentious flower at home.
For those who do not want to wait a whole month for yellow, orange, white and red flowers of nasturtium to appear on their beds, you can sow seeds in April and grow seedlings of this unpretentious flower at home.
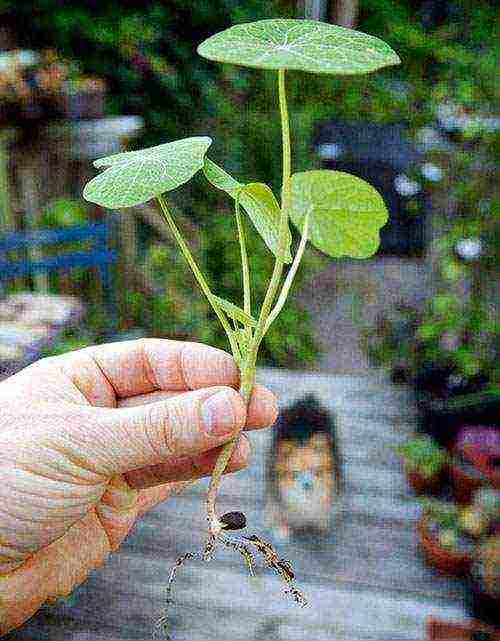
Sowing is carried out in peat pots to a depth of about 1 cm.This is important, since nasturtium does not tolerate transplanting well and during planting, it is necessary to preserve both the earthen ball and all the roots formed.
After planting, the surface is compacted and watered. In the future, you need to moisten the soil regularly, preventing the entire volume of the pot from drying out. When the seeds hatch, the seedlings are provided with good light and temperatures in the order of 18–20 ° C. This will allow the nasturtium to form a sturdy plant with a few true leaves. The transfer of seedlings to a flower bed or to a balcony box is planned for May.
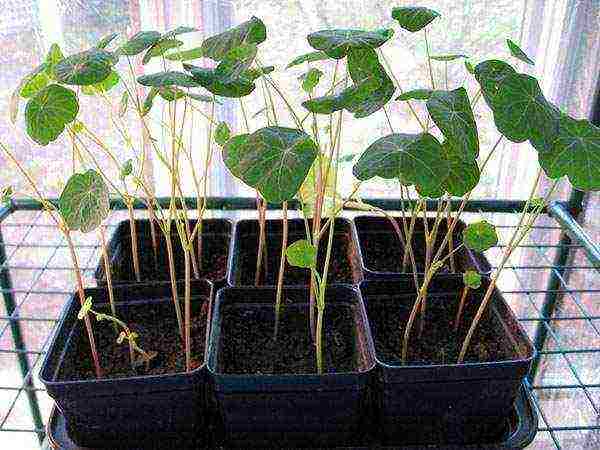 Sowing with seeds, planting nasturtium in open ground, and caring for an ornamental plant throughout the summer will not be able to complicate summer residents even with the most modest experience. The flower is as unpretentious as it is decorative and useful. Bright clumps of nasturtium near cabbage beds will help distract aphids and cabbage butterflies.Potatoes and eggplants are less attacked by the Colorado potato beetle.
Sowing with seeds, planting nasturtium in open ground, and caring for an ornamental plant throughout the summer will not be able to complicate summer residents even with the most modest experience. The flower is as unpretentious as it is decorative and useful. Bright clumps of nasturtium near cabbage beds will help distract aphids and cabbage butterflies.Potatoes and eggplants are less attacked by the Colorado potato beetle.
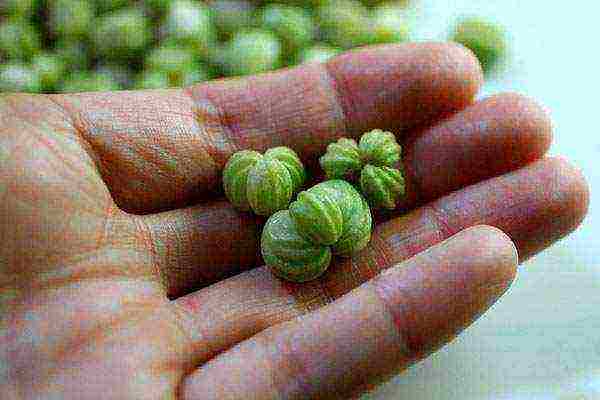 The unusual plant is used not only as an ornamental and phytosanitary culture. Irregularly shaped green nasturtium seed pods in the marinade acquire a spicy taste and are served as a snack. And flowers and leaves are a crunchy vitamin supplement for early low-calorie salads.
The unusual plant is used not only as an ornamental and phytosanitary culture. Irregularly shaped green nasturtium seed pods in the marinade acquire a spicy taste and are served as a snack. And flowers and leaves are a crunchy vitamin supplement for early low-calorie salads.
Video about planting nasturtium
Nasturtium appeared in Europe thanks to the Jesuit monks in the middle of the 16th century, and already in the 18th century, Europeans knew not only about the wonderful decorative, but also about the excellent taste and medicinal properties of this plant. The name comes from the Latin word for 'small trophy' due to the helmet-like shape of some parts of the flower.
The name Capuchin stuck in Germany: the peculiar shape of the spur served as the basis for this. Hood and capuchin are brothers words. In our gardens, it appeared simultaneously with potatoes and corn, and has long been the leader in popularity among garden flowers for many decades. Nasturtium made our grandmothers and great-grandmothers happy with their flowering. She is happily bred in the flower beds of kindergartens and schools, since it is an unpretentious flower, therefore, care does not present any difficulties and is minimized, even a schoolchild is available.
Nasturtium - a vibrant color palette for your garden
Nasturtium, capuchin (Tropaeolum) - this genus includes about 90 species of herbaceous perennial plants, native to Central and South America, the Mediterranean. Plants are unpretentious, with magnificent flowers of various shades from yellow to red, grown as annuals in the form of compact bushes or vines. The stem is creeping or curly up to 3 m long. The root system is pivotal, located in the upper layers of the soil.
Leaves are large, alternate, thyroid or palmate, juicy on long petioles, green or red. The flowers are large, single, bisexual, on long stalks, located in the leaf axils. Blooms from late June until the first frost. The fruit is three-celled, consists of single-seeded fruitlets with a tuberous surface and a spongy light yellow-green shell.
Growing and caring for nasturtium outdoors
Nasturtiums are grown outdoors in pots, flower girls, and flower beds. Curly and creeping species - in hanging baskets, on supports. It grows very quickly - the nasturtium hedge serves as an excellent screen all summer long. Prefers well-lit, drained areas, loamy soils.
On over-fertilized lands, it develops powerful stems and leaves to the detriment of flowering. During flowering, regular watering is required. With a lack of moisture, it grows poorly, does not bloom for a long time. They are fed every 3 weeks with a moderate amount of complex mineral fertilizers. The culture does not tolerate fresh organic fertilizers, lime, excess nitrogen fertilizers, as well as waterlogging.
Withered flowers, damaged and diseased plants are promptly removed. This stimulates the formation of new buds. Not resistant to low temperatures: flowers cannot stand even light frost.
Growing nasturtium from seeds When to plant in soil and seedlings

Nasturtium seeds photo
Planting nasturtium seeds in the ground
Annual species are grown from seeds. They can be sown in open and protected ground from the end of March to the beginning of April. A garden bed is prepared, thoroughly loosening the soil and filling the furrows every 20-25 cm. Rather large seeds of nasturtium are planted to a depth of 2-3 cm and the furrows are closed with the back of the rake. The distance between seeds should be at least 8-10 cm in order to get full-fledged seedlings for planting in a permanent place.
After sowing, it will not be superfluous to cover the bed with a film, placing arcs, or build an earthen rampart around the perimeter, pressing the film with a stone or brick to the ground. When seedlings appear, it will be necessary to ensure that the temperature inside the greenhouse does not rise above 25 ° C, water on time.Because high temperatures, scorching sunlight and lack of moisture are no less destructive than negative temperatures. When warm days come, the film is removed during the day, protecting the plants only at night in case of sudden frosts.

Nasturtium growing from seeds when to plant Photos of seedlings
You can plant nasturtium in the ground at once to a permanent place, hoping that the distance between the bushes should be left decent: about 40-50 cm. Do not spare space, otherwise the plants will oppress each other, become poorly developed and little decorative. Planting nasturtium in open ground immediately on a flower bed is carried out only when the night frosts recede: the seeds will quickly sprout and be damaged by frost if they are not protected. Depending on the region, this could be late May - early June.
Growing nasturtium from seed for seedlings at home
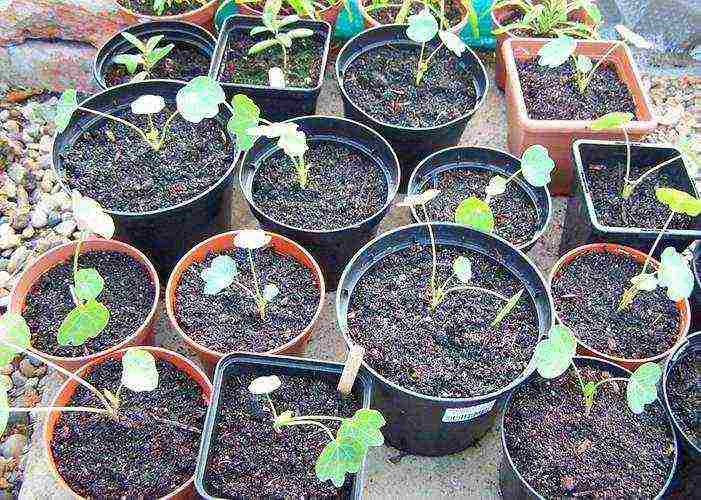

How to plant nasturtium seeds for seedlings photo
Nasturtium seedlings are sown with the onset of April 1-2 seeds in peat pots or tablets. You can use loose soil for flower plants by filling them with ordinary seedling cups. The depth of the planting is 1 cm. After planting, it is necessary to water it, put the cups on the south window, where there will be enough light and heat. You can cover the seeds with a film to create a greenhouse environment, but when seedlings appear, it should be removed. Seedlings appear in 10-12 days. If two seeds were planted, a more powerful sprout is chosen, and the weak plant is cut off. Grown plants are planted in May in fertile, well-loosened and watered soil, without disturbing the earthen coma, at a distance of 40-50 cm.
Curly varieties can be planted a little more often - up to 35 cm, but this is if they grow on a vertical support. Directly in the open ground, seeds pre-soaked during the day are sown from mid-May. Cold snap is detrimental to nasturtium, so it is better to cover the plants at first with a film or non-woven material.
How to collect nasturtium seeds
Nasturtium usually produces abundant self-seeding, which, under favorable conditions, will germinate the next year. The seeds are harvested after flowering, they remain viable for at least 4 years. They are removed from the most liked copies. Mature seeds are brown in color. After collecting them, they are dried and stored in paper bags. Perennial species are planted in the spring (5-7 plants per 30-45 cm container at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other) and put on a well-lit windowsill.
Wintering of perennial nasturtium and storage of tubers
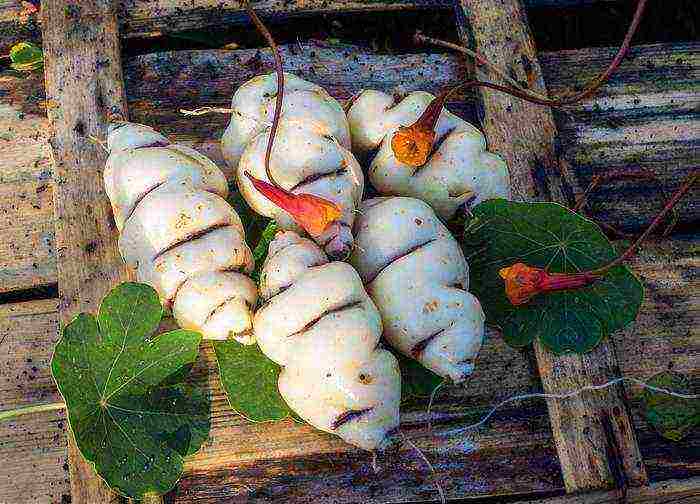

Preparing nasturtium for winter photo tubers
In the fall, the bushes are cut to the ground. And in cold climates, the tubers are dug up and stored in a cool place in a box with dry peat.

Reproduction of nasturtium tubers photo
Perennial species are propagated by dividing tubers in March. After that, they are laid out for germination or immediately planted in pots with nutritious soil, and after the onset of warm days, they are taken out into the street. Perennial species of this tropical beauty have just begun to conquer the market, while little known.
Propagation of nasturtium by cuttings
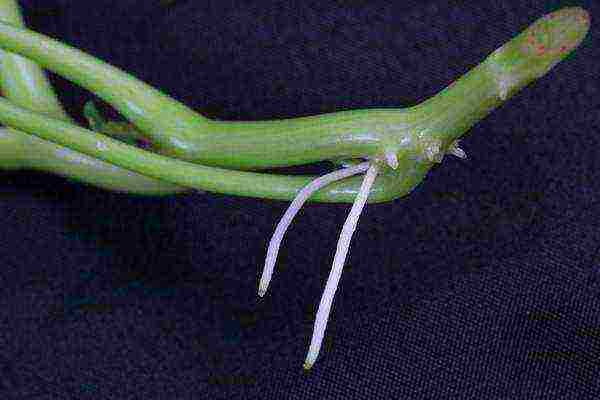
Cutting of nasturtium photo
Nasturtium can be grafted. This method is used when breeding terry varieties. Cuttings are rooted in wet sand or a glass of water, after processing them with root. They plant 1 cuttings in a glass; when transplanted into open ground, they do not violate the earthen coma. The main breeding method for nasturtium is still seed. It is the simplest, most readily available, and is widely used.
Pests and diseases
It is affected by gray rot, rot, mosaic. If changes are found in the form of a mosaic pattern, wilting of the lower leaves, small brown spots, the damaged parts of the plant should be removed.
It will not be superfluous to additionally process the plantings with special preparations. Usually, diseases develop actively in damp weather and with thickened, poorly ventilated plantings.Observe the recommended sowing distance. This is one of those cases when it is better to plant less often, and then your flower garden will not be afraid of many diseases.
Pests of nasturtium are aphids, spider mites and cruciferous fleas. Chemicals can be used to combat them. If you eat the plant for food, use traditional methods - daily pollination of plants with a mixture of ash and tobacco dust or spraying with vinegar (1 glass of 9% vinegar or 2 tablespoons of vinegar essence in a bucket of water). Ash can be scattered around the bushes.
Nasturtium helps to increase the yield of vegetables. She distracts insect pests, which willingly choose capuchin for laying their eggs. Therefore, by growing nasturtium near vegetable beds, you will protect them from whiteflies, cabbage butterflies, Colorado potato beetles. You can combine planting by mixing nasturtium with vegetables or making decorative curtains from it. Nasturtium is one of the most sought-after flowers of many gardeners. It is unpretentious, blooms for a long time and pleases the eye with a magnificent outfit, serves as protection from many insects.
Useful properties of nasturtium
Nasturtium is successfully used by folk medicine for vasodilation, in order to improve the blood supply to the heart muscle, as an antitussive agent, as an antiseptic for diseases of the genitourinary system, as normalizing metabolic processes. It is useful for the elderly. Due to the content of carotene and sulfur in it, which are preventive substances for sclerosis. It is used in food as a source of vitamins, increasing the biological value of ordinary dishes.
Leaves, buds, flowers and unripe fruits have a pleasant pungent taste, reminiscent of watercress. Leaves and flowers are used in salads, sandwiches, soups, sauces, side dishes. Unripe fruits, buds are pickled separately or mixed with other vegetables. The unpretentious flower has long won the hearts of amateur ceta growers. It does not require special care, grows quickly and blooms for a long time, is able to turn even the most dull corners of the garden into a colorful landscape.
The variety of colors, the availability of planting material will satisfy the needs of any gardener. Curly shapes serve as an excellent decoration for hedges, yard buildings, as well as those places that need to be hidden from prying eyes. Bush forms are suitable for decorating flower beds, borders, mixborders. In terms of the complexity of breeding, it is available to the most inexperienced growers. Planting and caring for nasturtium can be trusted even by a child.
Types of nasturtium with description and photo
There are varieties of nasturtium with bushy and climbing forms, with simple, double, semi-double flowers. There are variegated varieties. It is used as an ornamental flower crop for carpet planting, for vertical gardening. Leaves, buds, unripe fruits are used as an aromatic additive in cooking.
Large nasturtium Tropaeolum majus

Large nasturtium Tropaeolum majus photo
Annual, curly, uplifting species. It is characterized by thyroid light green, red or yellow flowers with a spur. Leaves are long-petiolate, rounded, uneven, green or with a purple tint. Most often, the ‘Glym’ variety is bred with semi-double flowers painted in orange tones. On the basis of this species, many varieties have been bred, bred in personal plots.
Foreign nasturtium Tropaeolum peregrinum

Foreign nasturtium Tropaeolum peregrinum photo
Curly nasturtium from the Canary Islands, perennial form with irregular yellow flowers with a fringed edge and thyroid leaves. If the winter is warm, it winters well in the open field.
Tuberous nasturtium Tropaeolum tuberosum

Tuberous nasturtium Tropaeolum tuberosum photo
A climbing tuberous plant with gray-green five-lobed leaves, which is grown in the mountainous regions of Peru, Chile, Bolivia. In the absence of support, it forms a soil cover.It has large pear-shaped tubers and is an important starchy product.
It has been cultivated since ancient times by the Indians. Yellow-orange flowers 4-5 cm long with a red spur appear later than in other species. The tubers are large, yellow with a marbled pattern. Cultivated as an annual. In autumn, tubers are removed from the ground, ventilated in the open air, and stored like dahlias.
Nasturtium is suitable for inexperienced summer residents and gardeners, or for owners of poorly developed plots. The flower is unpretentious, easy to grow, and its beauty is not inferior to other more "thoroughbred" brothers. In this article, you will find out when to plant nasturtium in 2018, familiarize yourself with favorable and unfavorable days, the rules for choosing a place for planting and the main methods of growing.
Brief description of the variety (with photo)
 Delicate nasturtium
Delicate nasturtium
Nasturtium (Tropaeolum) is a herbaceous or semi-shrub type plant. In the harsh climate of the Urals, Siberia and temperature extremes in the Middle Volga region, nasturtium is grown by flower growers as an annual, and no more than 10 varieties out of 50 available are used to decorate the beds.
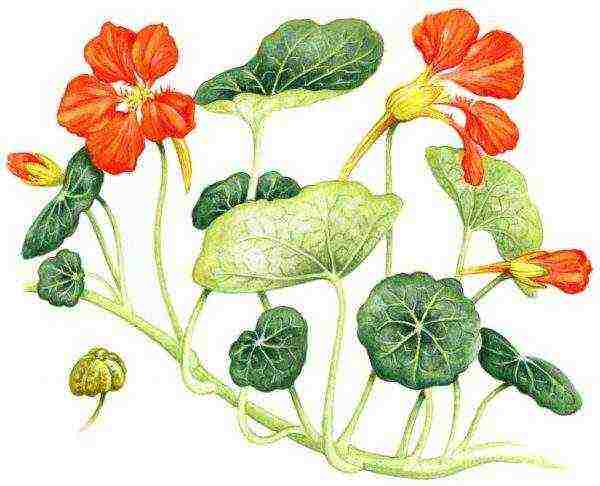 The approximate structure of nasturtium
The approximate structure of nasturtium
The stalks of nasturtium are usually fleshy and juicy, with sufficient watering they branch well, creep or curl (up to 2 m), depending on the variety. The leaves are covered with a waxy bloom and are arranged in a checkerboard pattern, have a rounded or thyroid shape, the edges are solid, they are attached to the stems with a long petiole.
 Green nasturtium fruit
Green nasturtium fruit
The flowers have an unobtrusive pleasant aroma, the shape is often irregular, the peduncles are long and solitary, located in the axils of the leaves. The color of the petals is usually bright red or different shades of yellow and orange.
The fruit consists of three identical parts.
Ripe seeds are round-kidney-shaped, wrinkled, medium-sized (10-40 seeds per 1 g), remain viable for 4 to 5 years.
Traditionally, there are 5 types of nasturtium:
- Shield-bearing nasturtium
- Large nasturtium
- Foreign nasturtium
- Cultural nasturtium
Table 1. Comparative characteristics of the main types of nasturtium
|
Species name |
The size | Description of the species (color and size of flowers, leaf shape) |
Seeds |
Representatives of the species |
|
Shield-bearing nasturtium |
Annual, creeping stems up to 4 mu |
Leaves are deep green in color, very fragile. Flowers up to 6 cm, rich or dark red. |
Suitable for collection |
Lucifer |
|
Small nasturtium |
Annual, up to 35 cm. |
The leaves are thyroid, with thin petioles. Flowers are small, velvety, often with dark spots, color - all shades of yellow. | The seeds ripen well and are suitable for self-breeding. |
Black corduroy, Cherry rose. |
|
Large nasturtium |
Annual, in mild climates - perennial. Shrub forms grow up to 20-30 cm, and climbing ones - up to 3 m. |
Thyroid leaves of various colors: light green, dark green, burgundy. Flowers with a diameter of no more than 5 cm, the color varies from pale pink to deep red. |
The seeds ripen well. |
Brown flare, Yeti, Salmon flare, Spitfaye. |
|
Foreign nasturtium |
Curly grassy, up to 3.6 m |
The leaves are strongly dissected, the flowers are up to 4 cm, bright yellow in color with delicate petals. |
Seeds in Russia usually do not ripen |
Canary liana, Birdie, |
|
Cultural nasturtium |
Hybrid of large and thyroid nasturtium, annual; Dwarf - from 15 to 25 cm, compact up to 55 cm, curly (creeping) up to 4 m. |
Leaves are thyroid, green or purple. Flowers are double or simple, up to 5 cm in diameter in various shades of yellow and red. |
Buy seeds in stores |
Gleming Mahagani, Moonlight, Golden Globe. |
All parts of nasturtium are edible except for the roots. Pregnant women and people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are strictly prohibited from eating nasturtium - it irritates the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
When to plant nasturtium in 2018
Since most gardeners in their sowing work are guided by the lunar calendar, we present for your convenience a summary table for planting annual flowering plants for seedlings and in the ground.
When to plant nasturtium in 2018: auspicious and forbidden days according to the lunar calendar:
| January | February | March | April |
May |
June |
|
| Auspicious days | 1, 19, 20, 26, 27, 28, 29 |
1, 2, 3, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26 |
1, 3, 4, 20, 21, 22, 23, 28, 29, 30 |
1, 18, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25, 26, 29 |
6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14 |
4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11 |
| Forbidden days |
2, 16, 17, 18, 31 |
15, 16, 17 |
2, 16, 17, 18, 31 |
15, 16, 17, 30 |
15, 29 |
6, 13, 28 |
The answer to the question "When and how to plant nasturtium?" For Siberia and the Urals, growing nasturtium through seedlings is more suitable. Seeds of nasturtium are sown for seedlings, usually a month before its intended planting in open ground.
Soil preparation
Nasturtium grows successfully in moist and moderately fertile soils with a slightly acidic reaction, but experienced summer residents claim that with proper care, nasturtium will grow in clay soil. It is better to choose a place for a garden bed that is sunny or with openwork partial shade.
Gardeners recommend planting nasturtium next to cabbage beds: it will distract pests from it.
Growing nasturtium: basic methods
In Russia, there are three ways of growing nasturtium: by seeds in open ground, through seedlings and cuttings. The first of them is the most popular, since it does not require preliminary manipulations with seedlings; it is widely used in the territories of Russia with a temperate climate.
The seedling method is less common, since, on the one hand, nasturtium is unpretentious, on the other, there are certain problems with moving it into open ground. However, it should be noted that this method is justified in areas of continental and sharply continental climate. Reproduction of nasturtium by cuttings is much less common, but some gardeners still turn to this method. You can talk about the features and disadvantages of each of the methods for growing nasturtium.
Sowing nasturtium seeds in open ground
Regardless of the chosen cultivation method, the seeds must be prepared for planting: soak in water at a temperature of + 50 ° C for 24 hours until they swell, or place them in a damp cotton cloth.
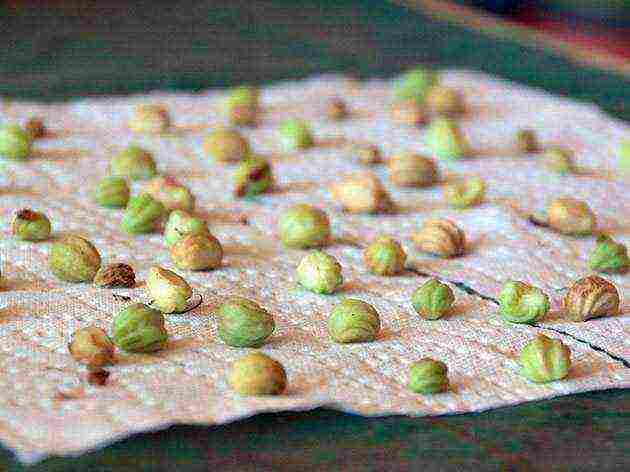 Preparing seeds for planting
Preparing seeds for planting
Seeds of nasturtium are sown in moist open ground when the likelihood of a return of night frosts disappears. 2-3 seeds are placed in the holes to a depth of 2 cm, planting distance: from 20 to 30 cm for bush varieties of nasturtium, from 40 to 50 cm for climbing ones. Sprinkle with earth on top and press a little. Subsequently, the soil must be periodically loosened and moistened regularly. After the first shoots appear, nasturtium can be fed with Nitroammophos at the rate of 1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water, half a liter for each plant. Be sure to water the soil abundantly before fertilizing!
 Sowing nasturtium seeds in open ground
Sowing nasturtium seeds in open ground
Nasturtium begins to bloom thirty days after the first shoots appear.
Self-collected seeds during germination are likely to lose some of the characteristics of the variety, so it is better to buy them in specialized stores.
Growing nasturtium through seedlings
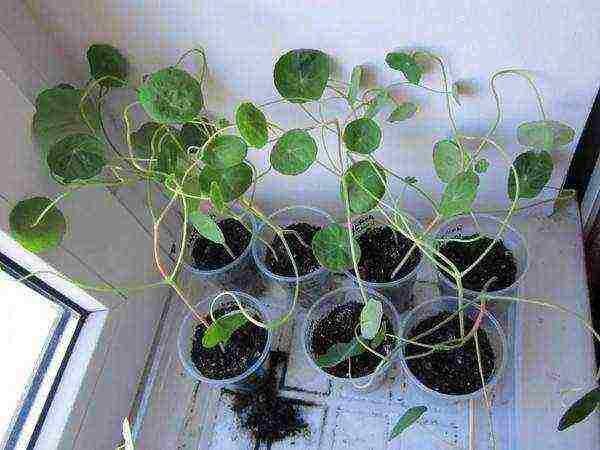 Nasturtium seedlings ready for open field transplantation
Nasturtium seedlings ready for open field transplantation
Growing nasturtium through seedlings is suitable for gardeners living in harsh climatic regions for which an earlier flowering of the variety is important. Therefore, it is better to start sowing nasturtium seeds for growing seedlings at least two weeks before planting it in open ground. Recommendations for the depth of the seeds and their distance from each other are the same as when growing this flower directly in the open field.
Do I need to dive for nasturtium?
It is categorically impossible to dive nasturtium seedlings because of its weak root system. That is why it is better to grow seedlings in peat pots, from which all packaging films must be removed before moving into open ground.
For the same reason, experienced gardeners advise growing nasturtium from cuttings or by sowing seeds directly into the open ground, so as not to injure the delicate root system of the flower once again.
Propagation of nasturtium by cuttings
 Cutting of nasturtium
Cutting of nasturtium
Cuttings of nasturtium are first rooted in water, then in wet sand. This method is of little use in Russia due to the plant's inability to winter. Therefore, some flower growers transplant especially beautiful specimens of nasturtium into pots for home wintering on a light and cool windowsill. In the spring it will already be possible to carry out cuttings.
Features of caring for nasturtium
In general, nasturtium is characterized as an unpretentious plant, however, a number of recommendations should be followed when growing it:
- Watering. Crops and first shoots should be watered regularly with warm, settled water. As soon as the first buds appear, irrigation is carried out only as the soil dries out.
- Light is equally important to nasturtium at all stages of growth.
- Top dressing. As is the case with other flowering plants, excessive feeding will lead to the growth of the green part and the oppression of the flowering plant. To form colorful flower beds and flower arrangements, nasturtium is grown with a shortage of organic fertilizers. Some gardeners start fertilizing the soil already at the stage of seed germination, others - 14 days after planting the cuttings. Basically, nasturtium should be fertilized before flowering at intervals of 10 days. For example, 30 g "Agricola Rose" or nitrophoska per 10 liters of water. Fertilizers containing phosphorus will increase the number of buds on the bush.
- Pruning and weeding of nasturtium is carried out according to the standard scheme: dry inflorescences and weeds are removed as they appear (if seed collection is not planned). This stimulates flowering well. Be sure to save a few buds on the bush of your favorite nasturtium variety to get seed for the next year. After flowering and harvesting the seeds, the nasturtium tops are either burned or sent to compost pits or mulch.
Diseases and pests
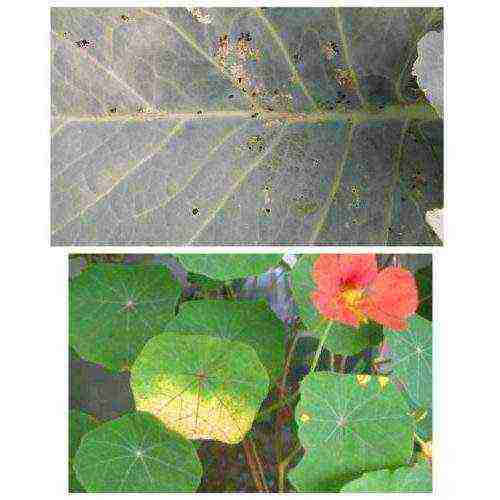 Some diseases of nasturtium
Some diseases of nasturtium
Diseases to which nasturtium is most often affected:
- leaf spot
- rust,
- bacterial damage
- pests.
Among the reasons for the deterioration of the state of nasturtium are:
- Lack of light
- Excessive watering
- Lack of fertilizer
These factors often cause yellowing of nasturtium leaves.
If the plant is sick, it is better to immediately remove it and burn it. The garden tools used to carry out the work must be disinfected. Gardeners recommend watering the soil with a manganese solution or other specialized agent, and it is better to treat the neighboring plantations with a fungicide.
If the reason for the yellowing of the leaves is a violation of the care regimen, then restore it and do not neglect preventive measures against pests (aphids, spider mites, fleas, etc.) To do this, treat the nasturtium with a mixture of wood ash with tobacco dust, or with purchased chemicals. In the fight against caterpillars, treating the plant with mustard diluted in water (1 tbsp per 1 l) will help.
How to Collect Nasturtium Seeds?
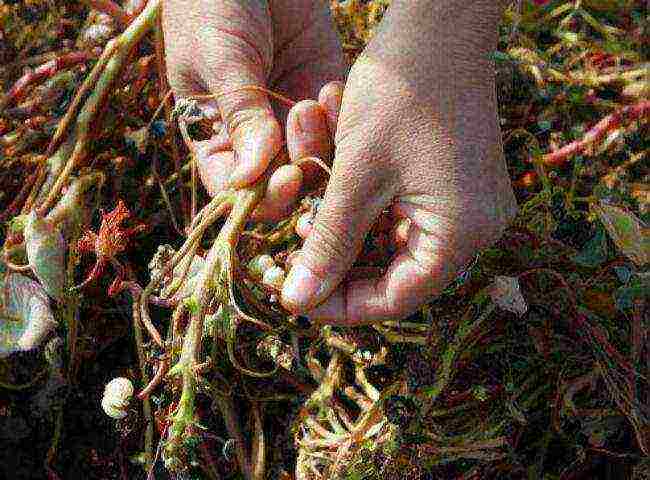 Collecting nasturtium seeds
Collecting nasturtium seeds
Recall that the seeds of foreign nasturtium do not have time to ripen in the Russian climate, so they cannot be collected for the seed version.
Ripe seeds are harvested after the end of flowering of the plant and always before the onset of the first frost. They are easily separated from the pedicel, while changing color from light green to whitish. Do not let them fall to the ground. It is better to store seeds for self-seeding of nasturtium in paper bags in a cool and dark place.
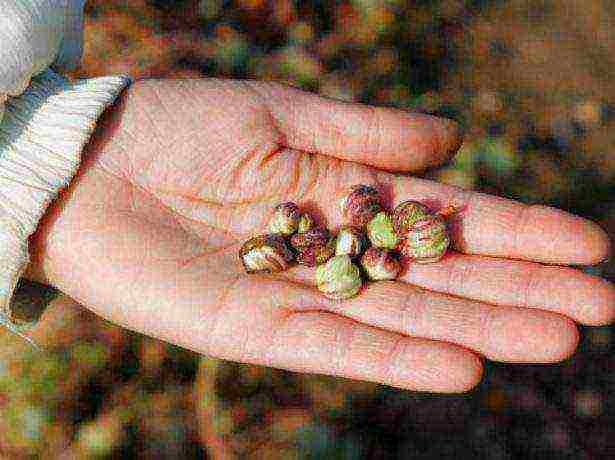 Nasturtium fruit
Nasturtium fruit
Some uses for different varieties of nasturtium in landscape design
Thanks to the combination of contrasting greenery and bright spots of nasturtium inflorescences, it looks great in various compositions. Low-growing varieties decorate curbs, Japanese gardens and alpine slides.
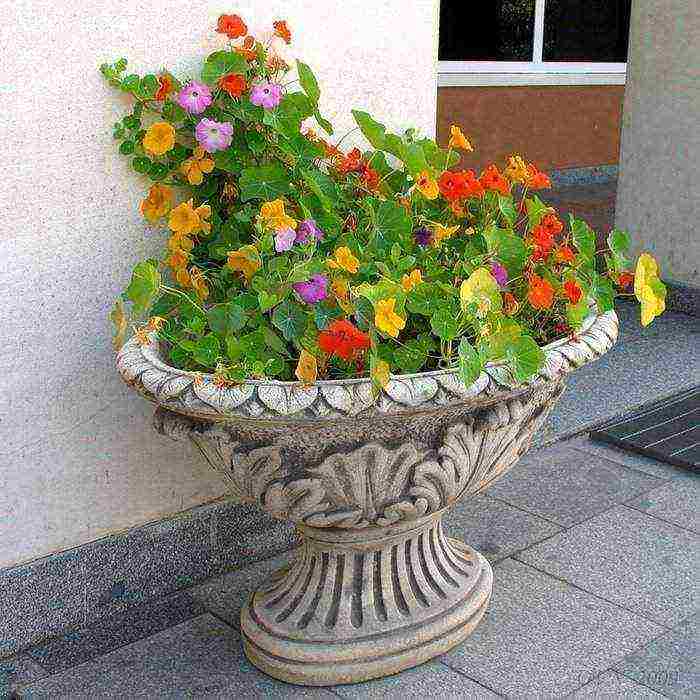 Nasturtium in a flowerpot
Nasturtium in a flowerpot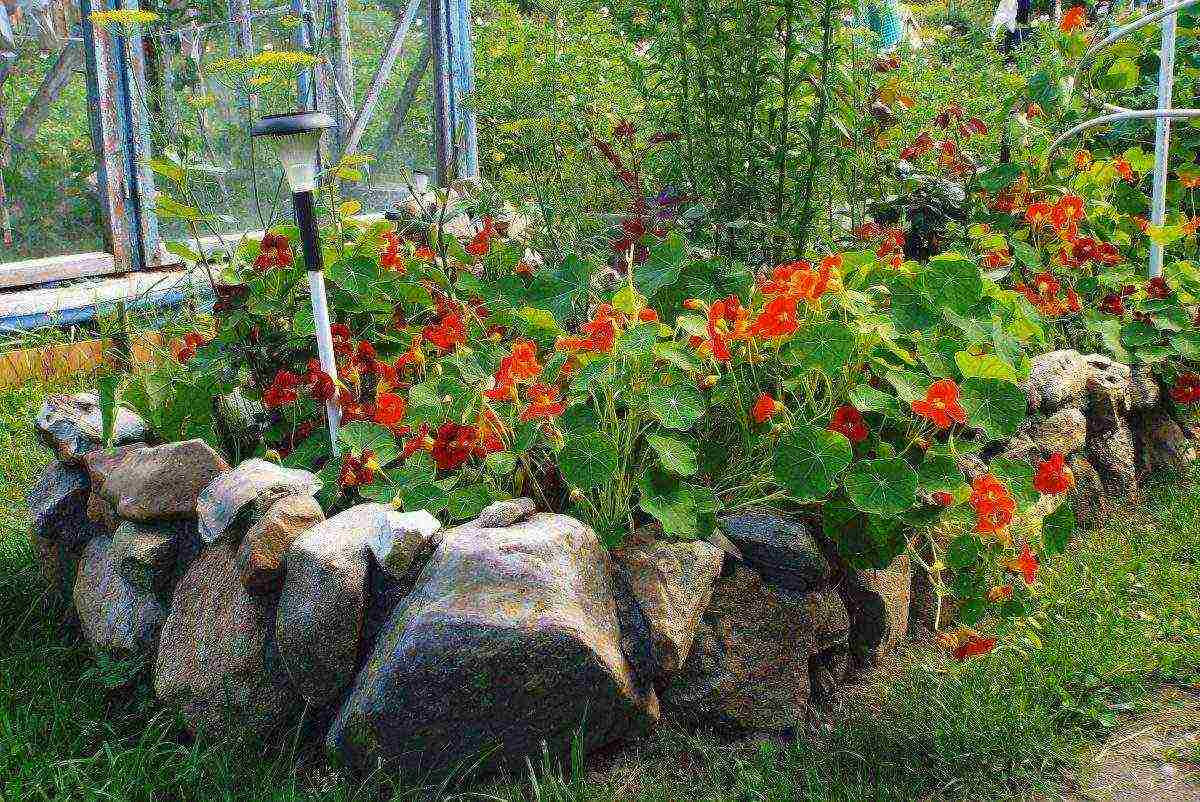 Nasturtium in stone composition
Nasturtium in stone composition Decorating the veranda with undersized nasturtium
Decorating the veranda with undersized nasturtium
Weaving nasturtium is perfect for decorating gazebos, balconies, house walls and arches.
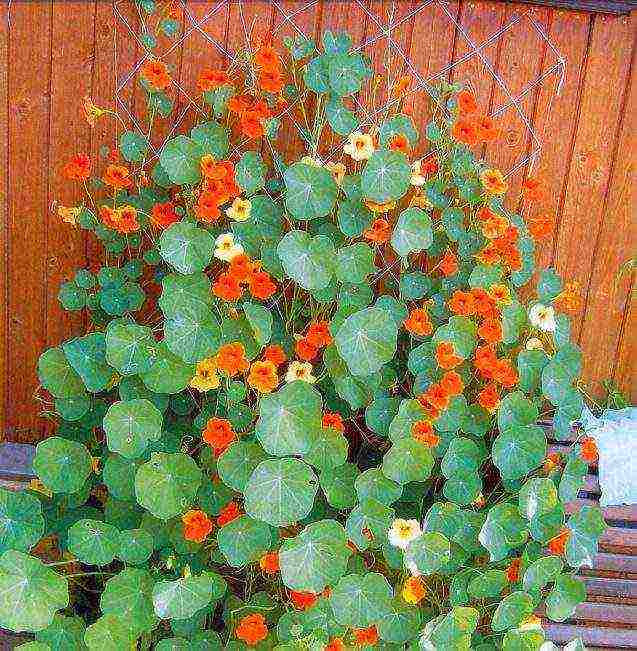 Fence decoration with climbing nasturtium
Fence decoration with climbing nasturtium
Remember, flowers grown with love are guaranteed to decorate your garden!
growing from seeds, varieties,
planting and care in the open field
 Nasturtium (or capuchin), belongs to the Nasturtium family, and is a herb that has about 90 species. The plant is originally from America, but it has reliably settled in our latitudes, since it is distinguished by unpretentiousness, in-demand healing properties and taste characteristics. Nasturtium with its long flowering is able to decorate any, even the most sophisticated garden. Nasturtiums are more often vines with a succulent stem, but there are also semi-shrubs in the genus. The leaves are lobed, alternate, entire, palmate or thyroid. Flowers - simple, double and semi-double - irregular, fragrant, zygomorphic, bisexual, axillary, consisting of five (sometimes more) petals, the same sepals, tube with nectar in the form of a funnel. The color of the flowers is most often red or yellow. The fruit consists of three wrinkled kidney-shaped lobes, in each of which rounded-kidney-shaped seeds ripen. Both flowers and stems of nasturtium have medicinal properties and are also used in cooking.
Nasturtium (or capuchin), belongs to the Nasturtium family, and is a herb that has about 90 species. The plant is originally from America, but it has reliably settled in our latitudes, since it is distinguished by unpretentiousness, in-demand healing properties and taste characteristics. Nasturtium with its long flowering is able to decorate any, even the most sophisticated garden. Nasturtiums are more often vines with a succulent stem, but there are also semi-shrubs in the genus. The leaves are lobed, alternate, entire, palmate or thyroid. Flowers - simple, double and semi-double - irregular, fragrant, zygomorphic, bisexual, axillary, consisting of five (sometimes more) petals, the same sepals, tube with nectar in the form of a funnel. The color of the flowers is most often red or yellow. The fruit consists of three wrinkled kidney-shaped lobes, in each of which rounded-kidney-shaped seeds ripen. Both flowers and stems of nasturtium have medicinal properties and are also used in cooking.
Nasturtium - species and varieties
In the wild, at home, perennial nasturtiums grow. But in our climatic conditions, a tropical beauty cannot remain in the ground for the winter, therefore it is grown as an annual. Of the cultivated species of nasturtium, the following are most often grown:
Foreign or Canary nasturtium
 This vine is native to South America. Its light green stems reach a length of 3.5 m and very quickly braid arbors and trellises. It blooms from mid-summer to frost with bright yellow small flowers with corrugated petals and green spurs. Leaves are medium-sized, five- or seven-partite. The seeds in the middle lane do not have time to mature naturally.
This vine is native to South America. Its light green stems reach a length of 3.5 m and very quickly braid arbors and trellises. It blooms from mid-summer to frost with bright yellow small flowers with corrugated petals and green spurs. Leaves are medium-sized, five- or seven-partite. The seeds in the middle lane do not have time to mature naturally.
Large nasturtium
 Very branched, bare, fragile stems reach a length of 250 cm. If the variety is erect, and not creeping, then the stem grows up to 70 cm in height. Blooms profusely from June to autumn frosts. It reproduces well by self-sowing, the seeds do not lose their germination up to 4 years. The leaves are asymmetrical, large, rounded, thyroid, the surface is light green, the underside is gray-gray, the petioles are long, about 8 cm in diameter. The species is represented by dozens of varieties, including compact bush forms. The most popular varieties:
Very branched, bare, fragile stems reach a length of 250 cm. If the variety is erect, and not creeping, then the stem grows up to 70 cm in height. Blooms profusely from June to autumn frosts. It reproduces well by self-sowing, the seeds do not lose their germination up to 4 years. The leaves are asymmetrical, large, rounded, thyroid, the surface is light green, the underside is gray-gray, the petioles are long, about 8 cm in diameter. The species is represented by dozens of varieties, including compact bush forms. The most popular varieties:
✿ King Theodore - the flowers are bright red
✿ Peach Melba - cream flowers, in the center - red spots
✿ Salmon Baby - semi-double flowers, salmon color
✿ ladybug - apricot-colored flowers with burgundy spots in the middle.
Cultural nasturtium
 It combines hybrids of shield-bearing nasturtium and large nasturtium. Flowers: from light yellow to orange-red, simple or double, fragrant, up to 5 cm in diameter, one in the axils of the leaves. Blooms profusely from June to frost. Stems are densely leafy, leaves are green or purple, thyroid. Varieties of this species differ in shape and height: there are compact varieties of nasturtium (up to 50 cm in height), there are creeping, with shoots up to 4 m long, or dwarf ones - 15-20 cm in height. Popular varieties:
It combines hybrids of shield-bearing nasturtium and large nasturtium. Flowers: from light yellow to orange-red, simple or double, fragrant, up to 5 cm in diameter, one in the axils of the leaves. Blooms profusely from June to frost. Stems are densely leafy, leaves are green or purple, thyroid. Varieties of this species differ in shape and height: there are compact varieties of nasturtium (up to 50 cm in height), there are creeping, with shoots up to 4 m long, or dwarf ones - 15-20 cm in height. Popular varieties:
✿ Vesuvius - erect bush up to 30 cm tall, becomes semi-creeping as it grows. The leaves are large, rounded, dark green. The flowers are simple, up to 5 cm in diameter, salmon-pink with an orange tint, a dark red spot on the two upper petals with strokes around. The calyx is yellow.
✿ Wirlibird Orange - forms many flowers of pastel color with thin stripes.
✿ Garnet Jam - upright bush, compact, up to 30 cm tall. The leaves are large, rounded, light green.The flowers are double, rather large, up to 6 cm in diameter, garnet-red with an orange tint. The top two petals have brown streaks. The calyx is bright yellow.
✿ Gleming Mahagani - bush up to 40 cm tall. The flowers are red, double.
✿ Golden Globe - bush compact, spherical, erect, 25 cm high, up to 40 cm in diameter. The leaves are rounded, light green. The flowers are double, large, up to 6.5 cm in diameter, golden yellow, without spots. The calyx is yellow.
✿ Globe of Fire - upright bush up to 45 cm tall. Leaves are light green. The flowers are double, large, up to 7 cm in diameter, bright orange. The upper two petals have dark brown streaks. The calyx is dark yellow.
✿ Kaiserin von India - upright bush up to 25 cm tall, compact, spherical. The leaves are small, dark green with a purple bloom, gray-gray underneath. The flowers are simple, up to 4.5 cm in diameter, dark red with brown-red strokes at the base of the two upper petals. The calyx is orange-red outside.
✿ Moon Light - lashes up to 180 cm high. The flowers are pale yellow.
✿ Peach Melba - bush up to 25 cm tall. The flowers are creamy, with a red pattern on the petals.
✿ Type top Alaska - bush up to 20 cm tall. The flowers are yellow.
✿ Foyeoglantz - creeping bush up to 25 cm tall. The leaves are large, light green. The flowers are large, up to 6 cm in diameter, double, fiery orange with dark red strokes on the two upper petals. The calyx is orange-red.
✿ Henina Grasshof - double flowers, red.
Small nasturtium
 Herbaceous plant, used as an annual. Stems are thin, branched, grooved, 15-35 cm tall. Flowers: small, about 3 cm in diameter, yellow with dark spots. Leaves: small, rounded, thyroid, on long and very thin petioles. The upper three petals are velvety pointed along the edge. The spurs are short, cylindrical, somewhat curved. Blooms from June to October. The seeds ripen well. The most popular varieties:
Herbaceous plant, used as an annual. Stems are thin, branched, grooved, 15-35 cm tall. Flowers: small, about 3 cm in diameter, yellow with dark spots. Leaves: small, rounded, thyroid, on long and very thin petioles. The upper three petals are velvety pointed along the edge. The spurs are short, cylindrical, somewhat curved. Blooms from June to October. The seeds ripen well. The most popular varieties:
✿ Cherry rose - grows up to 30 cm in height, blooms with bright red double flowers
✿ Black Velvet - the same 30 cm in height, simple flowers up to 6 cm in diameter, so dark burgundy that they are almost black. This variety is sometimes called "Black Lady".
Shield-bearing nasturtium
 creeping dwarf shrub, dark green, juicy and fragile shoots of which reach 4 m in length. The leaves are thyroid, dark green. Flowers of a juicy dark red hue. Blooms from June to October, the seeds ripen perfectly. The most common variety is Lucifer... These are erect bushes up to 25 cm tall, the shoots are light green, the leaves are large, dark green with a dark red tint. The flowers are simple, up to 6 cm in diameter, red-orange.
creeping dwarf shrub, dark green, juicy and fragile shoots of which reach 4 m in length. The leaves are thyroid, dark green. Flowers of a juicy dark red hue. Blooms from June to October, the seeds ripen perfectly. The most common variety is Lucifer... These are erect bushes up to 25 cm tall, the shoots are light green, the leaves are large, dark green with a dark red tint. The flowers are simple, up to 6 cm in diameter, red-orange.
Nasturtium growing from seed
 Large seeds of nasturtium are sown directly in open ground in mid or late May, when the last frost has passed. In holes up to two centimeters deep, located at a distance of 25-30 cm from each other, nasturtium seeds are placed in a nesting way - 3-4 pieces per hole. If there is a possibility of nighttime drops in temperature, cover the sown area with plastic wrap or other covering material and use only warm water for irrigation. Seedlings will appear in a couple of weeks.
Large seeds of nasturtium are sown directly in open ground in mid or late May, when the last frost has passed. In holes up to two centimeters deep, located at a distance of 25-30 cm from each other, nasturtium seeds are placed in a nesting way - 3-4 pieces per hole. If there is a possibility of nighttime drops in temperature, cover the sown area with plastic wrap or other covering material and use only warm water for irrigation. Seedlings will appear in a couple of weeks.
Nasturtium seedling cultivation
Growing nasturtium seedlings allows for earlier flowering. For growing seedlings, peat cups or cups with a retractable bottom are used. In May, seeds are sown in them, 2-3 pieces at a depth of 2 cm. The temperature in the room with seedlings should be 20-22 ºC. Seedlings will appear in a couple of weeks. Make sure that the seedlings have enough light, because the lack of lighting makes them stretch, and after landing on the site, they get sick for a long time and do not bloom. The root system of nasturtium is weak, and the leaf surface is quite large, therefore, in order not to injure the roots, the seedlings are not dived and transplanted into the soil along with an earthen clod, right in a glass.
Planting nasturtium in open ground
 When to plant nasturtium. Planting of nasturtium is carried out in the first decade of June. Set aside a well-lit and wind-protected area in your garden, since nasturtium does not bloom as abundantly in the shade as it does in good light. The soil on the site should be slightly acidic, with good drainage, light and fertile.On organic-rich soils, the plants turn luxuriantly green, but they do not want to bloom; on too poor soils, the flowering of nasturtium is not so beautiful, the leaves are small, and the stems look bare. On stagnant moist soils, nasturtium rots.
When to plant nasturtium. Planting of nasturtium is carried out in the first decade of June. Set aside a well-lit and wind-protected area in your garden, since nasturtium does not bloom as abundantly in the shade as it does in good light. The soil on the site should be slightly acidic, with good drainage, light and fertile.On organic-rich soils, the plants turn luxuriantly green, but they do not want to bloom; on too poor soils, the flowering of nasturtium is not so beautiful, the leaves are small, and the stems look bare. On stagnant moist soils, nasturtium rots.
How to plant nasturtium. In early June, you can plant seedlings in open ground. Planting seedlings is carried out together with an earthen clod, and if you sowed seeds in peat pots, then right together with the pots to avoid breaking or breaking fragile roots. Depending on the variety of nasturtium, the distance between the specimens should be 20-40 cm. At first, it is advisable to cover the planting at night. Nasturtiums will bloom in a month and a half.
Nasturtium - outdoor care
 Caring for nasturtium consists in weeding the area and watering the plants. If you mulch the garden bed after planting, then you will not have to deal with weeds. At the very beginning of growth, regular and abundant watering is very important, but when the nasturtium blooms, water the site only when the soil dries up: if the soil is wet all the time, the plant will turn magnificently green, but there will be few flowers. It is necessary to remove dried flowers in a timely manner, unless you need seeds, but to collect seeds for the next year, it is enough to leave only a few ovaries to ripen. The nasturtium is fed weekly with potassium-phosphorus fertilizer until it blooms. Nasturtium nitrogen fertilizers are not required. After the nasturtium has faded, watering is gradually reduced until it stops. Since nasturtium is grown mainly as an annual plant, then it is necessary to treat it with the onset of autumn as with an annual, namely: dig up the site, burn the tops, having previously collected the seeds, if there is such a need.
Caring for nasturtium consists in weeding the area and watering the plants. If you mulch the garden bed after planting, then you will not have to deal with weeds. At the very beginning of growth, regular and abundant watering is very important, but when the nasturtium blooms, water the site only when the soil dries up: if the soil is wet all the time, the plant will turn magnificently green, but there will be few flowers. It is necessary to remove dried flowers in a timely manner, unless you need seeds, but to collect seeds for the next year, it is enough to leave only a few ovaries to ripen. The nasturtium is fed weekly with potassium-phosphorus fertilizer until it blooms. Nasturtium nitrogen fertilizers are not required. After the nasturtium has faded, watering is gradually reduced until it stops. Since nasturtium is grown mainly as an annual plant, then it is necessary to treat it with the onset of autumn as with an annual, namely: dig up the site, burn the tops, having previously collected the seeds, if there is such a need.
Reproduction of nasturtium
In addition to the seed method, for the propagation of nasturtium, a vegetative method is also used - cuttings. The cuttings are rooted in wet sand or water. Most often, terry varieties of nasturtiums or new varieties are propagated in this way, the seeds of which are difficult to find in flower shops. The vegetative method allows you to preserve the species and varietal characteristics during reproduction.
Nasturtium - diseases and pests
 Nasturtium is not only beautiful but also very useful. In addition, it somehow instills fear in Colorado beetles, whiteflies, aphids, cabbage and other insect pests. But diseases of nasturtium sometimes affect, first of all, such as bacterial wilting, which is expressed in the weakening of the lower leaves, and then the wilting of the entire plant. Or gray rot, manifested by dry brown spots on the leaves. From time to time, brown or black rust spots or variegated mosaic stains appear on the leaves of nasturtium. In case of defeat by these diseases, infected specimens must be removed and burned, and healthy plants must be treated with special preparations that destroy pathogens.
Nasturtium is not only beautiful but also very useful. In addition, it somehow instills fear in Colorado beetles, whiteflies, aphids, cabbage and other insect pests. But diseases of nasturtium sometimes affect, first of all, such as bacterial wilting, which is expressed in the weakening of the lower leaves, and then the wilting of the entire plant. Or gray rot, manifested by dry brown spots on the leaves. From time to time, brown or black rust spots or variegated mosaic stains appear on the leaves of nasturtium. In case of defeat by these diseases, infected specimens must be removed and burned, and healthy plants must be treated with special preparations that destroy pathogens.
How to collect nasturtium seeds
If you feel like breeding, you can harvest nasturtium seeds yourself. As the flowers wither, the seeds ripen. It must be remembered that the seeds of all types of nasturtium have time to ripen before frost, the only exception is foreign nasturtium. When the seeds ripen, they turn from green to whitish and, easily separating from the peduncle, fall to the ground. Therefore, be careful and try to have time to collect them before they crumble. Ripe seeds are stored in cardboard boxes. Seeds of foreign nasturtium are harvested unripe and ripened at home.
WHERE TO BUY NASTURTIA SEEDS
 The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years.In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NGO "Gardens of Russia"
The Scientific and Production Association "Sady Rossii" has been introducing the latest achievements in the selection of vegetable, fruit, berry and ornamental crops into the wide practice of amateur gardening for 30 years.In the work of the association, the most modern technologies are used, a unique laboratory for microclonal reproduction of plants has been created. The main tasks of NPO Sady Rossii is to provide gardeners with high-quality planting material for popular varieties of various garden plants and novelties of world selection. Delivery of planting material (seeds, onions, seedlings) is carried out by Russian post. We are waiting for you for shopping: NGO "Gardens of Russia"


