Content
- 1 Features of a juniper (shrub)
- 2 Juniper planting
- 3 How to care for the garden
- 4 Reproduction of juniper
- 5 Wintering juniper in the country
- 6 The main types and varieties of junipers with a photo
- 6.1 Common juniper (Juniperus communis)
- 6.2 Juniper virginiana (Juniperus virginiana), or "pencil tree"
- 6.3 Juniper horizontal or prostrate (Juniperus horizontalis)
- 6.4 Juniper Cossack (Juniperus sabina)
- 6.5 Chinese Juniper (Juniperus chinensis)
- 6.6 Rocky juniper (Juniperus scopulorum)
- 6.7 Scaly juniper (Juniperus squamata)
- 6.8 Juniper medium (Juniperus x media)
- 7 Juniper properties
- 8 Beneficial features
- 9 Description
- 10 Peculiarities
- 11 Varieties and types of tree juniper
- 12 Shrub juniper
- 13 Juniper: planting and care
- 14 Juniper: reproduction
- 15 Plant propagation
- 16 Care
- 17 Landing rules
- 18 Diseases and pests

- Type: conifers
- Full-bloom Period: May
- Height: 1.5-30m
- Green color
- Perennial
- Hibernates
- Shady
- Drought resistant
Unlike the southern and tropical regions, in the northern latitudes, conifers have a special place in the garden landscape - in the off-season and in winter, only they are able to revive the garden with their colors. Evergreen conifers are usually "garden soloists" due to the rich color of the needles, ranging from dark emerald to silvery gray and golden. Junipers, which have a wide range of crown shades and successfully complement the “all-season” garden, are no exception - a garden designed to be attractive at any time of the year. Planting and caring for a juniper is not an easy process - knowing the nuances allows you to grow an ephedra of high decorativeness, which fits favorably into landscape design.
- Choosing a variety of juniper for planting
- Sapling planting technology
- Growing juniper from seeds
- How to apply fertilizers correctly
- Winter care
- Location on the flowerbed: 8 beautiful patterns
- Types and varieties of juniper
Spherical, pyramidal, conical, weeping or creeping - the shape of the crown of a juniper can be any, which expands the possibilities of landscape design in the formation of compositions that are expressive in their geometry. By combining only conifers, you can compose an original garden, bright in originality and style: landscape or regular, avant-garde or classical, ethnic or modernist.

A rock garden created by combining juniper with other types of conifers will look great at any time of the year.
Coniferous plants gracefully decorate the garden, creating a calm and elegant landscape. Large cone-shaped or columnar junipers will be good in single or group planting, acting as the center of the landscape composition. A single juniper looks catchy in the form of a topiary. A single large plant is always a dominant feature in garden design, which is desirable to surround with smaller plants.
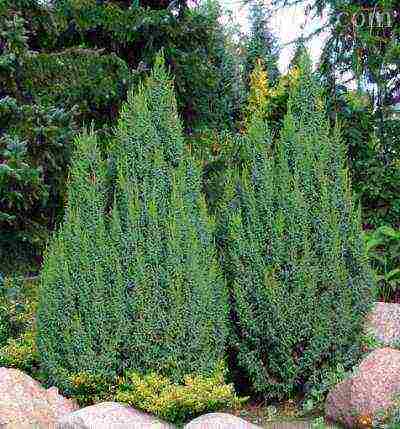

A group planting of a scaly juniper of the Loderi variety with its conical crown will advantageously complement the composition of rockery
Junipers with a geometric crown look good in regularly planned gardens, creating viewpoints and emphasizing the correct outline of the flower beds.In landscape gardens, cone-shaped and spherical junipers perfectly coexist with less "officious" perennial plants, and varieties spreading in shape will give a border, a rock garden or a reservoir of expressiveness.
They are often used in planting hedges (molded, free-growing) and mixborders, decorating the foreground of alpine slides and ridges, to delineate the boundaries of lawns or flower beds.

By combining molded and unshaped junipers with an exotic crown, you can create a spectacular rockery
Dwarf junipers in the form of compact bonsai and topiary are indispensable when laying a garden in an oriental style - they will advantageously decorate a stony composition and branching paths, advantageously combined with ground cover and low-growing plants: saxifrages, loosestrife, stonecrop, carnations, phloxes and cereals.
Junipers with a beautiful crown color:
- bluish-silver rocky juniper of the Blue Arrow variety,
- bluish blue Meyeri and Blue Carpet,
- gray-gray rock variety Skyrocket,
- horizontal juniper of some species (Andorra Compact, Blue Chip) turns purple in winter,
- Pfitzeriana Aurea's sprawling golden-tone juniper looks great against the backdrop of the lawn.
The spectacular crown of junipers does not require frequent pruning, but varieties that grow in the form of a hedge are cut regularly: in the middle of summer and in spring, removing dry and some lateral branches that protrude beyond the formed crown. If the juniper grows in the garden like a bonsai, then the haircut is performed in April-May and in October-November.
Choosing a variety of juniper for planting
When choosing a type of juniper for planting in the garden, you must have complete information about its characteristics: winter hardiness, plant size in adult form, crown shape and color, growing conditions and care. Junipers, which are brought to us from Western European nurseries, can be both sufficiently resistant to the severe winters characteristic of central Russia, and non-resistant, successfully growing without shelter only in the southern regions.
After acquiring a new coniferous plant (even frost-resistant), experienced gardeners recommend covering it for the first winter with spruce branches or burlap, tying up the branches in order to avoid sunburn of the needles and damage to the crown from snow.

The juniper of the medium grade Gold Coast, with golden needles, is an impressive contrast to the more emerald greens.
Employees of the botanical gardens of Russia have identified juniper varieties that are suitable and unsuitable for cultivation in domestic latitudes.
Winter hardy species of juniper (Juniperus):
- ordinary (J. Communis),
- Cossack (J. Sabina),
- scaly (J. Squmata),
- horizontal (J. Horizontalis),
- Siberian (J. Sibirica),
- Chinese (J. Chinensis),
- solid (J. Rigida),
- virginian (J. Virginiana).
Non-resistant types of juniper:
- Turkestan (J. Turkestanica),
- inclined (J. Procumbens),
- Zeravshan (J. Seravshanica),
- red (J. Oxycedrus).
Successful rooting and growth of a juniper largely depends on the quality of the purchased seedlings. When purchasing planting material, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Plants with an open root system are best avoided.
- It is advisable to purchase a juniper in a container or with an earthen lump wrapped in burlap.
- The root system and branches should show an increase in the current year.
- There should be no cracks on the trunk of the plant.
- Fresh shoots should be flexible and unbreakable.
- The color of the crown should be uniform, without brownish blotches and white flakes at the base of the needles.
- It is recommended that you choose those plants that have been grown in a container, not outdoors, and then simply transplanted into a container.
Junipers with an open root system are planted in early spring or autumn, and seedlings with an earthen ball are planted throughout the entire period from spring to autumn. For the northern regions, planting in spring is optimal - so the seedling will have time to take root in order to more successfully endure the winter.

Combining junipers with different colors of needles, you can form a hedge that is unusual in color and shape
Sapling planting technology
Due to their decorativeness, junipers are a good choice for a young garden, when a group of several conifers is able to fill the voids in the landscape immediately after planting and form an attractive composition. For planting light-loving junipers, an open, well-lit area of the garden is selected, with loamy or sandy loamy light soil - nutritious and sufficiently moist.

Living molded hedge made of silver-blue juniper will become a catchy element of garden landscaping
If the soil is clayey and heavy, then a mixture of garden soil, peat, sand and coniferous soil (loose soil with needles, collected under spruce or pine trees in the forest) is added to the planting hole. At the same time, the soil is preliminarily drained, falling asleep on the bottom of the planting pit broken brick or sand. Junipers grow well on lean soils, they can easily tolerate drought, but stagnant moisture in the soil is destructive for them.
The most successful soil mixture for planting juniper: 2 parts of sod land, 2 parts of humus, 2 parts of peat, 1 part of sand. It is also advisable to add 150 g of Kemira-universal and 300 g of nitrophoska to the mixture, as well as epin after planting (for optimal survival) under each seedling.

Horizontal junipers with a spread-out crown fit well into the design of the area near the pond
The dimensions of the planting hole depend on the size of the root system of the juniper, for example, for large species they dig a hole of about 60 × 80 cm.The plant is planted quickly so that the root system does not have time to dry out, but carefully so as not to damage the earthen ball or young roots. After planting in open ground, the juniper is watered abundantly and covered from direct sunlight.
The density of the placement of junipers on the site depends on the landscape composition - whether it will be a hedge, specimen or group planting. For junipers, the distance between seedlings when planting is selected in the range from 0.5 to 2 m. For a small garden, it is better to stay on compact species of juniper.
Growing juniper from seeds
When collecting juniper seeds for sowing, it is important to observe the time intervals - it is better to prepare not quite ripe seeds at the end of summer than finally ripe seeds in the fall. This will make it more likely to germinate. The collected planting material must be sown immediately, but you need to be prepared for the fact that, due to the hard shell, the juniper seeds will sprout only 2-3 years after sowing.

A group planting of Chinese junipers will revitalize the garden during the off-season and winter
You can plant a juniper dug in the forest on the site, having previously indicated the orientation of the parts of the world on its trunk in order to maximally simulate the features of its growth in the natural environment during transplantation. The lump of "native" land should be large, with a preserved top layer of humus.
How to apply fertilizers correctly
Subject to the selection of juniper varieties that are resistant to domestic climatic conditions, care for young plants is minimal - junipers almost do not get sick and are not affected by pests, do not require intensive feeding and spraying. In the future, it is enough only to ensure the watering of the juniper in dry years and 2-3 times per season to support it with nitrogen or complex fertilizers.

Different varieties of junipers have differently colored needles, but the needles of a bluish-blue hue look especially beautiful
In no case should you fertilize conifers with bird or cow humus - this burns the roots of the juniper, and the plant dies. Also, you cannot loosen the soil around the junipers - due to the fact that the root system of conifers belongs to the surface type, the nutrition of the trunk will deteriorate, and the plant will begin to wither. For a juniper, it is enough to mulch the soil with coniferous soil harvested in the forest.
Winter care
In winter, the formed crowns of junipers can disintegrate under the weight of snow, and some branches can break.To avoid such troubles, the crowns of molded junipers are tied in advance in the fall. Certain types of junipers are sensitive to changes in day and night temperatures in early spring, active winter and spring sun and require shelter in February-March. Needle burns lead to a change in the green color of the crown of the conifers to a brown-yellow hue and, consequently, to the loss of decorativeness of the juniper.

Plumosa horizontal juniper acts as a ground cover plant for a rock garden
If the buds of the ephedra remain alive during a sunburn, then the young shoots gradually cover the burnt places, but if the buds have died, then the branches affected by frost must be cut off to healthy wood and treated with garden pitch.
In order for the juniper needles to retain their brightness in winter, the plant must be regularly watered, fertilized in spring and at the end of summer with granulated baits, and sprayed with micronutrient fertilizers on the needles.
Gardeners practice these types of juniper shelter for the winter:
- Snow. An excellent option for miniature and creeping forms - simply throw snow on the branches of the ephedra. But in case of heavy snowfall, it is recommended to make a protective frame.
- Lapnik. They are fixed on the branches in tiers, moving from the bottom to the top of the juniper.
- Non-woven and woven fabrics. Ephedra are wrapped in spunbond, burlap, kraft paper (in two layers), light cotton cloth and tied with a rope, leaving the lower part of the crown open. The film cannot be used - the plant will rot.
- Screen. Installed from the maximum illuminated side of the plant.
Lutrasil is not suitable for sheltering a juniper - it lets in the sun's rays, and a shelter from cardboard boxes is also not entirely successful. In the experience of gardeners, metallized insulation, used for laying laminate flooring, is excellent as a shelter for ephedra. To do this, in October (while the ground is still not frozen), pegs are driven in around the juniper, and the plant itself is wrapped in a substrate in November.

The horizontal Bar Harbor juniper with a rounded crown effectively complements the solitary deciduous planting
Frost-resistant types of juniper that do not burn in the sun: Cossack, medium varieties (Hetzi, Old Gold, Mint Julep), Chinese Gold Star, Pendula and Pfitzeriana varieties. Subspecies of common juniper are badly burned in the winter and spring sun.
Location on the flowerbed: 8 beautiful patterns 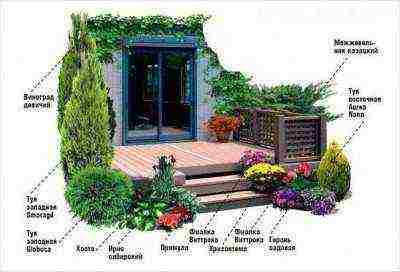
Juniper Cossack is one of the most frost-resistant varieties, ideal for planting in central Russia

Hiberic's columnar juniper acts as a focal point in the flower bed

Several types of juniper can be combined on a flower bed: rocky, horizontal, Chinese - any combination will be successful

1. Thuja western "Holmstrup". 2. Barberry Thunberg "Red Chief". 3. Mountain pine "Mops". 4. Juniper medium "Old Gold". 5. Juniper Cossack "Tamariscifolia". 6. Ground cover perennials (bryozoan, stonecrop)
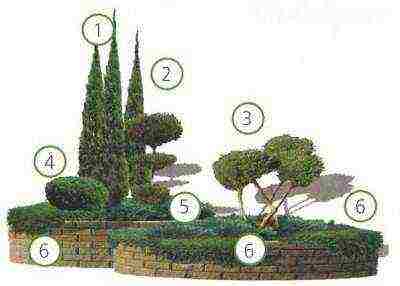
1. Rocky juniper "Blue Arrow". 2. Juniper rocky molded "Skyrocket". 3. Juniper scaly molded "Meyeri". 4. Mountain pine "Mops". 5. Juniper horizontal "Blue Chip". 6. Juniper leaning "Nana"

1. Chinese juniper "Blaauw" or "Blue Alps". 2. Thuja western "Stolwijk" or "Rheingold". 3. Thuja eastern "Aurea Nana". 4. Canadian spruce "Conica". 5. Thuja western "Tiny Tim" or "Little Champion". 6. Mountain pine "Gnom". 7. Colorado spruce "Glauca Globosa" or European "Nidiformis". 8. Juniper horizontal "Blue Chip" or "Prince of Wales". 9. Juniper horizontal "Wiltonii". 10. Dammer's cotoneaster. 11. Ground cover roses. 12. Flowers: petunia, subulate phlox, aubrieta, thyme, verbena. 13. Spirea "Snowmound"
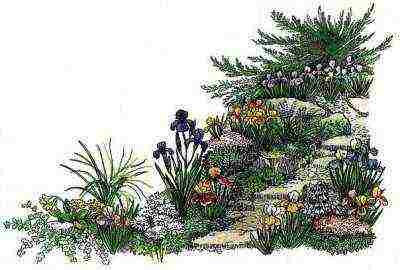
Juniper with an original crown plays the role of an accent on an alpine slide

1. Molded Cossack juniper. 2. Siebold's sedum. 3. The sedum is caustic. 4. Iris dwarf. 5. Garden iris (bearded, medium-sized). 6. Ear primrose. 7. Iberis is evergreen. 8. Sod meadow. 9. The hybrid was rejuvenated. 10. Soddy saxifrage. 11. Muscari tufted. 12. Spoon-leaf bell
Types and varieties of juniper
The decorativeness of the planting of junipers significantly depends on the correctly selected variety - its dimensions, taking into account the growth, the shape of the crown, the color and texture of the needles.Varieties belonging to the same species of juniper can vary significantly in their external characteristics - this is also worth considering.
Juniper scaly:
- Meyeri. Height 1 m, growth rate 10 cm per year. The needles are silver-blue. Mixborders and bonsai.
- Blue Carpet. Height 0.6 m, diameter 2-2.5 m. Creeping branchy crown. The needles are silver-blue. Unpretentious, growing rapidly. The lower tier of landscape compositions.
Juniper medium:
- Old Gold. Height 0.4 m, diameter 1 m. Wide rounded crown of yellow-gold color. Single planting on the lawn, in the rock gardens.
- Mint Julep. Height 1.5 m, diameter 2-3 m. Sprawling crown with curved branches and scaly green needles. Group planting, alpine slides, tamping of tall shrubs.
- Gold Star. Height 1 m, diameter 2.5 m. A low-growing shrub with a spreading crown and needles of a golden-green tone. Low cut or loose hedges, decorating gutters and drainage wells.
- Pfitzeriana compact. Height 0.8 m, diameter 1.5-2 m. Sprawling crown, needle-shaped green needles. Grows quickly, tolerates haircuts well. Curbs, clumps of evergreens with different colors of needles, molded and unshaped hedges, the organization of the lower tier in large-scale landscape compositions.
Red cedar:
- Hetz. Height 1 m, diameter 2-2.5 m. Growth 30 cm per year. Sprawling, rounded crown with scaly silvery-blue needles. Tolerates haircuts well. Single and group boarding.
- Canaerti. Height 5-7 m, diameter 2-3 m. Annual growth 30 cm. Columnar crown with dark green needles. Solitaire, bands, hedges.
- Gray Oul. Height 1 m, diameter 2.5 m. Growth 20 cm per year. Sprawling crown with scaly silvery-blue needles and purple shoots. Shaped compositions.
Juniper horizontal:
- Blue Chip. Height 0.4 m, diameter 2 m. A low-growing dwarf shrub with needle-shaped needles of a bluish-blue tone. Rock gardens, heather gardens, retaining walls.
- Blue Forest. Height 0.3 m, diameter 1.5. Creeping ground cover crown with blue needles. Strengthening the slopes, lower tiers of rock gardens, container planting.
- Andorra compact. Height 0.4 m, diameter 1.5 m. Flat-round cushion-shaped crown with blue-gray scaly needles. Low curbs, decorating the slopes and tiers of the garden.
- Andorra compact Veriegata. Height 0.4 m, diameter 1.5 m. Cushion-shaped crown with radiant shoots and bright green needles with whitish blotches on the tips of the branches. Mixed groups, rocky gardens.
- Wiltoni. Height 0.1 m, diameter 2 m. Branched ground cover crown with silver-emerald needles. Large groups, rock gardens, juniper lawns.
Juniper Chinese:
- Strickta. Height 2.5 m, diameter 1.5 m. Cone-shaped crown with greenish-blue needles. Single and group planting, growing in flowerpots.
- Obelisk. Height 3 m, diameter 1.2-1.5 m. Columnar crown with bluish-green needles.
- Monarch. Height 2 m, diameter 1.5 m. Asymmetric columnar crown. Single and group landings.
- Kurivao Gold. Height 2 m, diameter 2 m. Spreading openwork crown of rounded shape with green needles and young shoots of a golden hue. Single planting, mixed and coniferous groups, rock gardens.
Rocky juniper Skyrocket. Height 3 m, diameter 0.7 m. Annual growth 10-20 cm. Pyramidal crown with short bluish-green needles. Vertical accent in rock gardens, alley plantings, lawns, contrasting compositions and hedges.
Common juniper Hibernica. Height 3-5 m, diameter 1-1.2 m. Columnar crown with bluish-steel prickly needles. Solitaire on lawns, group plantings and compositions with deciduous species.
Juniper Cossack. Height 1 m, diameter 2 m. Sprawling crown with herbaceous green needles. Hedges, single and group plantings.
The variety of colors and shapes of junipers allows you to create spectacular landscape compositions, combining them with other coniferous and deciduous species of shrubs or trees, as well as flowers and other garden plants.
The horizontal juniper is also called creeping. This plant not only has beneficial properties, its bushes are very often used by gardeners to decorate their garden.This shrub can be easily cut, and with proper care it grows and has a beautiful crown. Its crown is green with a bluish tinge, while the bush itself seems to creep along the ground, hence its name. This bush is not tall, at the age of 10 years it reaches only one meter, and sometimes even less. But on the other hand, its diameter can be from 2 to 2.5 meters. The photo below shows what an adult creeping juniper looks like.

One of the features of the horizontal, as well as any other juniper, is that it secretes enzymes such as phytoncides. This is a substance that disinfects the plant itself, it kills any infections, fungi, harmful insects, thus protecting itself. For a juniper, this is a defense mechanism, but for a person, it is just a godsend. The fact is that this enzyme not only kills the infection on the plant itself, but even cleans the air around it. Therefore, if you plant it in your garden, your air will be clean, and you can walk in your garden without fear of getting sick, for example, during the period of viral infections in the fall. The more bushes of this wonderful plant in your garden, the less likely you are to get sick. For example, the Ministry of Health recommends that all TB dispensaries plant a juniper on their territory. Thus, by purifying the air, it does not give the possibility of re-infection with Koch's sticks for patients who have already been treated.
Juniper is a coniferous plant, its crown pleases with its colors all year round, because it is an evergreen plant. Its shades are different, it all depends on the variety of juniper. When pruning branches, do not throw them away, as they can be used to decorate your apartment or for medical purposes. Its essential oils are medicinal, it is possible to brew decoctions from the branches and treat various diseases, such as disorders of the gastrointestinal system, it has a calming effect and removes toxins.
How to choose the right one and plant this beautiful plant at home? In what way to plant a juniper, the main thing is what kind of care does it need? You can find answers to all these questions in this article.
Juniper can be planted with seeds or cuttings. If you do not want to wait long, you can purchase an already grown bush in the market or in gardeners and just plant it correctly at home. In any case, whichever way you would not like, only know the correct care, the choice of a planting site will be the key to a healthy juniper bush.
If you have chosen a horizontal juniper for planting in your garden, be aware that this is one of the varieties of juniper that easily tolerates any frost. For the winter, it does not need to be covered, the only thing that needs to be done is to build a frame to protect the branches from snow. It is better to do this only for those regions where blizzards rage in winter, where a very large amount of snow falls. Due to the large amount of snow, the branches of this bush can simply break off, and in the spring they will not have the aesthetic appearance that you would like.
If you decide to plant this plant, choose a sunny and open area for it, it does not like darkening.
When choosing seedlings, pay attention to several details, firstly, the seedling must be at least 3 years old, so it will take root better. Secondly, you cannot buy it without land around the root, if you saw that the seller is giving you a seedling without land, and its roots have been peeled off or at least chipped off, you know that such a seedling will not survive. Its root system is very fragile, it is very easy to damage it, therefore, experienced gardeners sell seedlings along with the soil around the seedling. Below in the photo you can see how to choose the right seedlings.
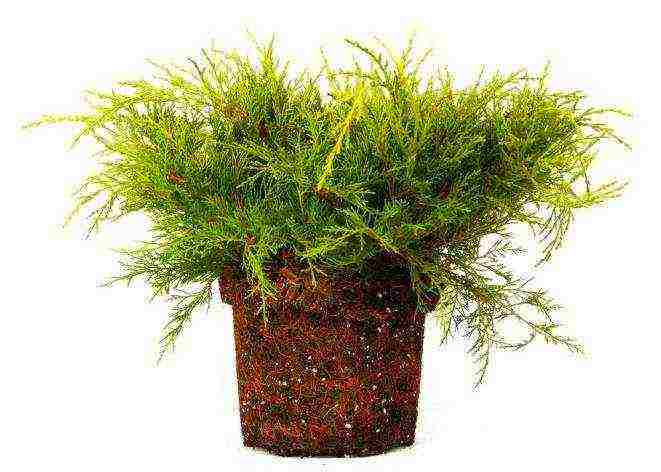

The correct choice of seedling.

Wrong choice of seedling.
The plant should be planted in late spring, late April or early May. There is no need to choose a special soil, as this plant grows in any soil.The only thing you can do for it is to add fertilizer to the soil. Whether it is peat or manure, there are always some fertilizing rules to follow. If you chose peat for fertilization, then prepare the soil in advance, lay the peat in a thick layer on the soil, cover with foil and keep it there for at least a week. Then mix with the soil and the whole area is ready for planting.
If you chose manure, in no case use fresh manure, it must lie for at least two weeks, rot before you start using it. It is better to dilute manure with warm water, for 10 liters of water you need two kg of manure. Then just pour it into the holes a little at a time before planting the plant there.
Holes need to be dug twice the size of the plant root itself. If your garden soil is too clayey and unfavorable for many plants, don't worry, juniper grows in any soil. BUT, for more confidence, you can make just such an admixture and fill the hole with it. Take peat, regular soil from your garden, and soil from a coniferous forest. Coniferous soil should be mixed with needles, this will be a kind of fertilizer. Mix the earth in equal proportions, but the peat should be 4 times less than the earth itself.
Don't forget about drainage as well. You can buy it in a store or make it yourself at home from broken bricks. Lay out the bottom of the hole with broken brick randomly, so that there is air between the bricks. Then pour the fertilizer, if you decide to use manure, if not, then take an admixture with peat. Be sure to water the hole and plant your plant. The peculiarity of this plant is that it is not afraid of drought, but high humidity, on the contrary, is fatal for it. Therefore, after planting, do not water the plant often, it is enough to water it once a week, or even once every 10 days. When watering, it is imperative to spray the crown of the bush, but do not overfill the plant itself. The best way to water is by sprinkling. You can do this either with a hose and special nozzles, or with a watering can with a nozzle.
It is recommended to do mulching around the planted cutting, the best raw material for this is sawdust from coniferous trees, or ordinary needles, small needles from any coniferous trees. Spread the sawdust around the cutting in a small layer 5-8 cm. Thus, when watering, excess moisture will be absorbed by the sawdust. And the sawdust itself, when rotted, will become an excellent fertilizer for your plant.
If you are planting several juniper bushes, then remember that the distance between them should be at least three meters. The horizontal juniper grows more than 2.5 meters wide, therefore, the distance between plants is very important. Similarly, you cannot plant it near trees, buildings and other objects that will interfere with the growth of the plant.
If you decide to plant horizontal juniper yourself from seeds, you need to know a few rules for planting the seeds of this plant.
Firstly, it is better to collect seeds not in the fall, as is customary, but at the end of summer. Then the seeds have not yet dried, but they are already beginning to ripen gradually. At the end of summer, the seeds are not dry, but they are already ready to be planted. When sowing seeds, you need to be patient, as they sprout 1-2 years after sowing. If they still do not come off, then the seeds were unusable. If they do, then the young sprouts will need care. Care will be the same as for cuttings.
Regardless of the long wait for the seeds to sprout, you can plant juniper cuttings. They can be bought at a specialty store, from gardeners, or found in the forest. You can also dig up young junipers in the forest.
Remember, if you are digging a young bush and want to transplant it into your garden, try to recreate the conditions as close as possible to its familiar environment.For example, mark on the trunk of a bush, parts of the world, which side it used to grow to the south, and which to the north. And plant in exactly the same position at home. This is very important, since, due to the change of cardinal points, the plant weakens and it is difficult to adapt to a new place. When digging up the plant, try to dig up more soil along with the roots. Do not clean the earth itself, but transport it home with the earthy clod. "Native land" will give the plant an opportunity to better take root.
The stalk must be prepared in advance in the greenhouse, when it grows up and gets stronger, only then can it be transplanted into the garden. A stalk can be taken at any time of the year, it does not matter for the future plant. After you have cut a cutting, put it in the water and wait for it to take root, it is best to take a few cuttings, as sometimes not all cuttings take root. Then plant the cutting in the ground and cover with foil. Until the cuttings get stronger, they need to be constantly sprayed with water, see that direct sunlight does not fall on them, otherwise they will wither.
Excellent advice on preparing the soil for planting cuttings or juniper seeds. It is necessary to make a soil mixture from coniferous soil, peat, sand and sawdust. Take coniferous soil in the same forest where you dug the cutting, dig the ground 8-10 cm deep in order to capture not only the top layer with needles, but also the layer where rotted needles are already present, they will create top dressing for your plant. You will also need sawdust, shavings, dry fallen needles from any coniferous trees. Mix coniferous soil with garden soil, add peat, while peat should be four times less than earth.
After that, start planting the cutting. This should be done in the same way as when planting an ordinary adult juniper. Dig a hole, lay out drainage, plant a cutting and cover with the prepared soil mixture. Sprinkle the soil around the cutting with shavings or dry needles. Then water the plant.
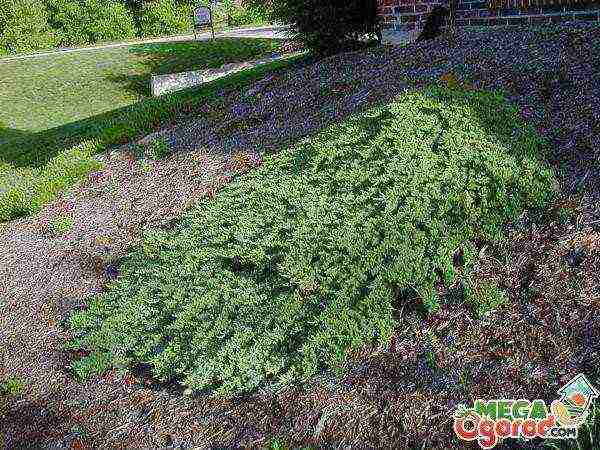
In general, mulching is a mandatory process for all creeping junipers. It protects plant roots that are not deep underground from damage. Young plants are mulched with pine or spruce sawdust, and mature plants with gravel. Below in the picture you can see how experienced gardeners mulch horizontal junipers.

After you have planted this plant, you will need to care for it. It does not need to be watered often, but if the plant is young, then this should be done more often than in the case of an adult plant. In the heat, it is recommended to shelter the plant from the sun; you can make a portable canopy. Water it either early in the morning or in the evening when the sun has already set. The first years, while the plant is young and immature, especially if it is a cutting, it needs to be covered for the winter. Later, at the age of 3-5 years, the plant will not be afraid of frost. As for the snow, you need to make a protective frame from it.
Caring for an adult plant is also very important, it needs to be fertilized, watered, and most importantly, cut off dry and old branches. If you wish, you can also shape the bushes with garden shears so that the bushes have an aesthetic appearance.
Despite the fact that the plant secretes an enzyme that protects it from fungus, parasites and other diseases, there are still some types of diseases that affect the juniper. For example, mushroom rust and gray mold. To get rid of these parasites, make a solution of arceride, 25 grams is enough, this drug must be diluted in 5 liters of water. Then spray the bushes, you need to do this once every 10 days. Repeat the procedure at least 4 times, even if the disease is gone, it is better to spray for prevention.
A plant such as juniper (Juniperus) is also called juniper or heather. It relates to the genus of evergreen coniferous shrubs or trees of the cypress family.In nature, they can be found in the Northern Hemisphere from the Arctic to the subtropical mountain regions. In the classification, the old Latin name of this plant "juniper" was retained by Karl Linnaeus, it was mentioned in the writings of the poet Virgil, who lived in Ancient Rome. This genus currently unites about 70 species of various plants. Most creeping species prefer to grow only in mountainous areas, but a tree belonging to this genus has a height of about 15 meters and is found in the forests of Central Asia and America, as well as in the Mediterranean. Outwardly, this plant is similar to a cypress, and it can live 600-3 thousand years. In places where juniper grows, the air is incredibly clean. In antiquity, it was believed that juniper is the number one remedy for a snakebite; in Russia it was used to make dishes, in which milk did not turn sour even in the heat. Various remedies for diseases have long been made from the root, cones and essential oils of the plant. Ground juniper fruits are widely used in cooking, as a seasoning for meat dishes, as well as in the preparation of sauces, marinades, soups, pates and liqueurs. The wood of certain species of this plant is used in the manufacture of pencils, canes and various crafts.
Features of a juniper (shrub)
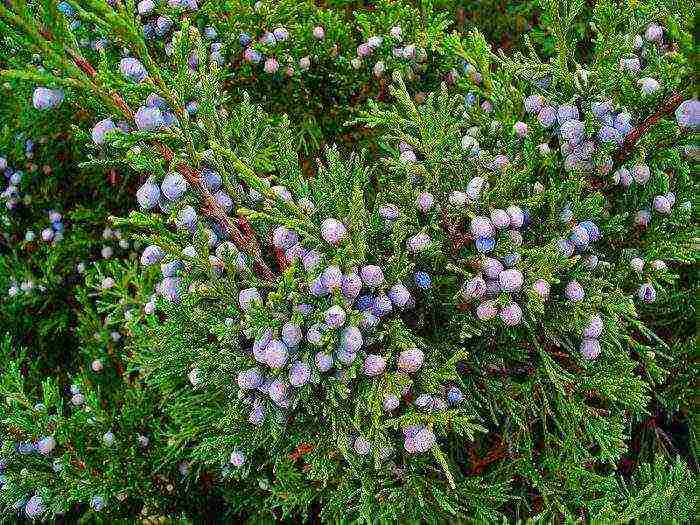

Juniper shrub is more popular among gardeners, its height can reach 1-3 meters. But sometimes tree-like forms are found in gardens, the height of such a plant is 4-8 meters, but in some cases it is about 12 meters. The erect stem is branched. In young specimens, the bark is brownish-red, while in the old plant it is brown. Needle-shaped or scaly leaves are collected in several pieces in whorls. Such a shrub is dioecious. Fragrant with a pleasant spicy taste, female oval cones reach 0.5-0.9 centimeters in diameter, they are colored green. Male cones are similar to elongated oval spikelets, which have a rich yellow color and are located in the leaf sinuses. Ripening of these cones takes place in the second year. Inside they have a dozen seeds, while on the surface there are tightly closed fleshy scales.
Many different types of such a plant are cultivated, while it is grown both outdoors and in the house. For example, juniper bonsai are very popular.
Juniper planting
What time to plant
It is recommended to plant a seedling in the garden in spring (April or May). And such a shrub can be planted in the autumn (October). This plant is very fond of light, but the common juniper can grow in a slightly shaded place. There are no special requirements for the soil. However, it is recommended for him to choose loose, wet, limestone or sandy soil. The acidity of the soil should be within the pH range of 4.5–7 (depending on the type and variety of juniper).
Juniper seedlings
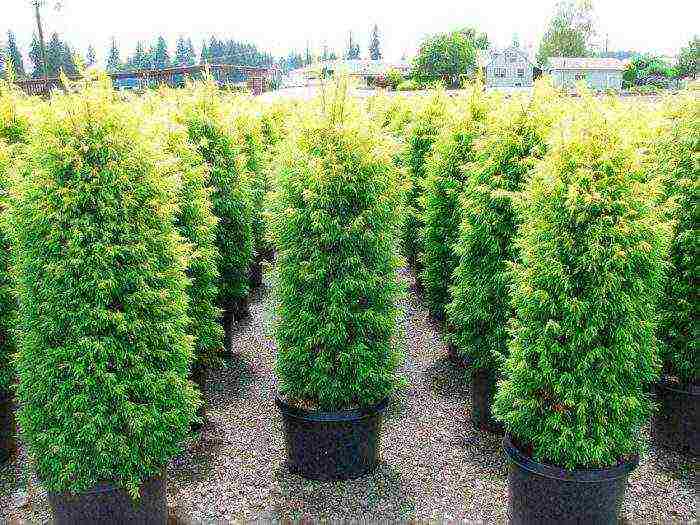

For planting in the garden, seedlings that are 3-4 years old are suitable. It is recommended to buy them in garden centers or nurseries, which have proven themselves well. In the case when the seedling is in a container, the volume of which is from 3 to 5 liters, then it takes root well and begins to grow quickly. If you use fairly large seedlings, then some experience will be needed to plant them, and they will take root much more slowly. Inspect the seedling carefully before purchasing. If there are any signs of illness, then it is better not to acquire such a copy. When planting a plant, try to keep the clod of earth on its roots intact. The fact is that if the soil crumbles, it will lead to injury to the tips of the roots, as a result, the seedling will hurt for a long time and ultimately be able to die.If the seedling is planted in a container, then it can be planted in the garden at any time during the season, but it is better to exclude hot days. Before planting a plant, its root system must be immersed in water for a couple of hours. Young seedlings with open roots are recommended to be planted in spring or in the last summer days in wet weather. If desired, the roots of the shrub can be treated with a root growth stimulating agent (Kornevin) just before planting.
How to plant

If the plant grows large enough, then 150-200 centimeters should be left between the bushes. If the bushes are compact, then the distance between them should be about 50 centimeters. The depth of the hole directly depends on the size of the seedling's clod of earth, while its size should exceed the root system by 2 or 3 times. If the seedling is not very large, then a hole of 50x50x50 centimeters is enough for it. Half a month before landing, a layer of broken brick and sand should be laid out at the bottom of the landing hole for drainage, while its height should be from 15 to 20 centimeters. After that, 2/3 the hole is filled with a mixture of nutrients, consisting of sand, soddy clay soil and peat (1: 1: 2), into which 200 to 300 grams of nitroammophos should be poured and everything is mixed well. If you are planting Verginsky juniper, then add ½ part of a compost bucket to the soil. Moreover, if it is planted in poor sandy soil, then you also need to pour in half a bucket of clay. When planting Cossack juniper in the ground, you need to pour from 200 to 300 grams of dolomite flour. After half a month, the soil will settle and a seedling must be planted. A seedling should be placed in the hole and filled with a soil mixture of a similar composition, but without fertilization. After planting a large seedling, its root collar should rise 5-10 centimeters above the ground level. In the case when the plant is not very large, after planting its root collar should be flush with the soil surface. The planted juniper must be watered, and when the liquid is absorbed, you need to cover the surface of the trunk circle with a layer of mulch (sawdust, peat or chips), its thickness should be from 5 to 8 centimeters.
How to care for the garden
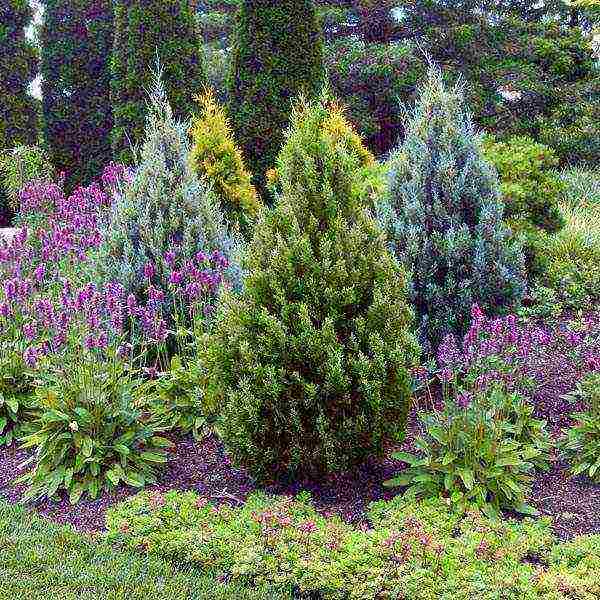

Growing
Growing a juniper is easy enough. During the season, watering should be done only in prolonged heat, while 1–2 buckets of water are taken for 1 adult specimen. Juniper reacts favorably to foliage moisturizing, which is recommended to be done once a week, especially this procedure is required for Chinese and common junipers. Periodically, the surface of the soil of the trunk circle should be loosened and at the same time it is necessary to pull out the weeds. It is recommended to feed the juniper in spring, for this, 30 to 40 grams of nitroammofoska must be distributed over the surface of the trunk circle. Fertilizer is embedded in the soil, and then watered without fail. In the event that the plant is planted in very poor soil, then it should be fertilized in this way throughout the growing season, but the break in feeding should be at least 4 weeks.
Pruning

Juniper pruning is usually done when they want to make a hedge from this shrub. Otherwise, trimming should not be performed. However, in the event that you want to form a bush, then you need to be extremely careful. The fact is that if you cut off something extra, then it will take a very long time to recover, since this is a slow-growing plant. Experienced experts recommend sanitary and thinning pruning, and you can also trim those branches that are too long or look sloppy.
Transplant features

It happens that an already mature plant needs to be transplanted to another place. It should be remembered that for an adult plant, a transplant is a great stress, and even more so for a juniper.Is it possible to transplant a shrub so as to harm it as little as possible? How exactly to prepare a planting hole for a given plant, and what size it should be, is discussed above. The bush itself must also be prepared for transplantation. In springtime, you need to retreat from the trunk or bush from 30 to 40 centimeters, then take a sharp shovel and use it to cut the soil to the depth of the bayonet. This way you can separate the peripheral young roots from the juniper root system. Then you need to wait until the onset of the autumn or next spring period. During this time, young roots will have time to grow inside the clod of earth, which has been cut off. As a result, the plant can be transplanted almost painlessly.
Harmful insects and diseases

Often this shrub is affected by a fungal disease such as rust. In an infected bush, spindle-shaped thickenings appear on the shoots, cones, needles and skeletal branches. At the root collar, swellings and sagging appear, while on their surface the bark dries, crumbles, as a result, not very deep wounds are exposed. Infected branches dry up and die, while the needles turn brown and fall off. If the plant is not treated, it will die. In order to prevent this, as soon as the disease is noticed, it is necessary to cut off the infected branches, while the wounds and sections are disinfected with a solution of copper sulfate (1%), and after that they must be smeared with garden varnish or Ranet paste. Those branches that have been cut must be destroyed. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to spray the juniper in spring and autumn with a Bordeaux mixture (1%) or with a similar action. Also, the shrub can suffer from alternaria, shute, nectriosis of the bark of branches, biotorella cancer and drying out of branches. All of these diseases can be cured in the same way as rust. It must be remembered that if you take good care of the shrub, then it will not become infected with any diseases and pests.

Such harmful insects can settle on a juniper, such as:
- Miner moth. You can get rid of it with Decis solution (2.5 grams of substance per bucket of water). Processing should be carried out 2 times with a break of half a month.
- Aphid. In this case, the treatment should be carried out the same way 2 times with a break of 2 weeks with Fitoverm solution (for 1 bucket of water, 2 grams of substance).
- Spider mite. The infected plant must be treated with a Karate solution (50 grams of substance for 1 bucket of water).
- Shields. For destruction, you should use a solution of Karbofos (for 1 bucket of water 70 grams).
Features of growing in Moscow
Growing juniper in Moscow and the Moscow region, where the climate is cool enough, is no different. This plant tolerates wintering well, however, it is still recommended to cover young plants for the winter with spruce branches.
Reproduction of juniper
How can you multiply
Seedlings of this plant can be purchased quite easily, and therefore there is no particular need to use various methods of reproduction of a juniper. But if you still want to grow a juniper with your own hands, then you need to remember that creeping forms can be propagated by layering, and tree and bush forms can be propagated by green cuttings and seeds.
Reproduction of juniper by seeds

Before sowing the seeds of a given plant, they need to be prepared. To do this, they must be stratified, and this requires cold. In a box filled with earth mixture, you need to sow seeds, then this container is taken out into the street and placed under a snowdrift. The seeds should stay there for 4–5 months. The prepared seeds are sown in open ground in May. If desired, in May, you can sow unprepared seeds, but in this case you need to know that the first shoots will appear only next year.In some species of such a plant, the seeds have a rather dense shell in this regard, before they are planted, they must be scarified. So, to accelerate germination, the seeds are exposed to acid or the shell is mechanically damaged. So, the most often used method is when the seeds are placed between two boards, upholstered with sandpaper from the inside. Then they must be rubbed. After the seeds are stratified, they are sown into the ground, while the planting depth should be from 2 to 3 centimeters. It is quite easy to care for the sown seeds. It is necessary to sprinkle the surface of the bed with a layer of mulch, water if necessary, during the first 14 days you need to protect the bed from direct sunlight. You should also systematically loosen the surface of the beds and pull out weeds. At the age of three, it will be possible to transplant a seedling to a permanent place, transferring it along with an earthen lump.
Reproduction of juniper cuttings
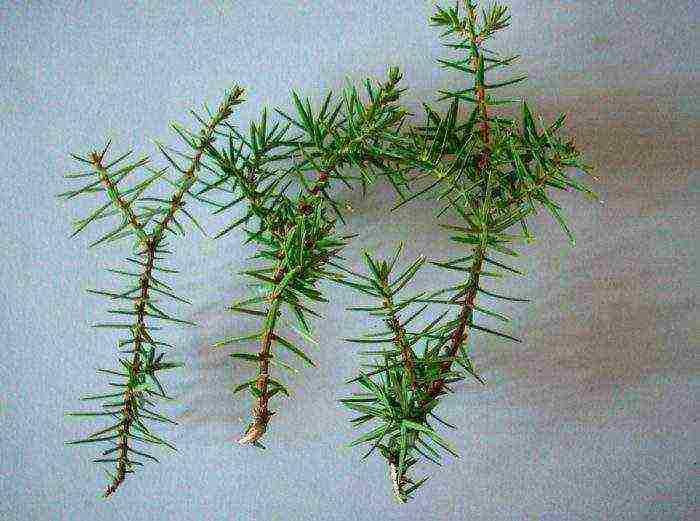

Decorative forms do not propagate by seeds; cuttings are used for this. They should be prepared in the spring, while cuttings are cut from young shoots that have become lignified. The length of the cutting should be from 5 to 7 centimeters, while it must have 1 or 2 internodes, as well as a heel. To do this, the stalk should not be cut, but it is torn off by hand in such a way that a piece of bark from the parent plant remains at its end. Immediately, the cutting should be treated with a root growth stimulating agent. Then the prepared material for planting is planted according to the 7x7 scheme in an earth mixture consisting of sand and peat (humus), taken in a ratio of 1: 1, while the surface must be sprinkled with coarse sand (layer thickness from 3 to 4 centimeters). After planting, each cutting separately must be covered with a glass jar. It is necessary to deepen the cutting by 15–20 mm, in this regard, rooting will take place in the sandy layer. By the onset of the autumn period, the cuttings will take root, however, transplantation to a permanent place can only be carried out after 2 years.
Reproduction by layering
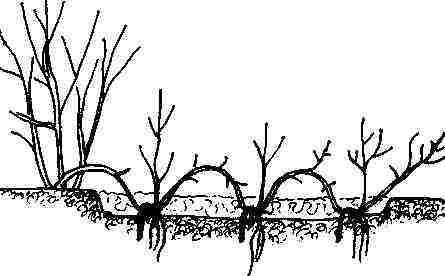
If the juniper is creeping, then layering can be used for its reproduction. At the same time, the plant can be propagated in this way during the entire period of active growth. For layering, you need to choose young, barely ripe branches, since they very quickly give roots. First you need to loosen the surface of the soil around the plant, mix it with loose peat and river sand, and then moisten it. To a height of 20 centimeters from the base, the layers must be freed from the needles, then this part should be bent to the soil surface and fixed with pins. After 6–12 months, the cuttings will give roots, but during this time it should be watered systematically, as well as spud. After young shoots grow on the layer, they will need to be disconnected from the parent plant and planted in a permanent place.
Wintering juniper in the country
Autumn

In autumn, this plant should be prepared for wintering. For this, the juniper is pruned for sanitary purposes, while the injured, dried out and growing branches and shoots are cut off. Then the plant and the surface of the trunk circle are treated with a solution of Bordeaux liquid (1%) in order to prevent various diseases and harmful insects.
Winter
Juniper is frost resistant. In areas with mild winters, you do not need to cover it for the winter, but you should pull off the branches with twine. It is recommended to cover young plants for the winter with spruce branches.
The main types and varieties of junipers with a photo
In landscape design, juniper is very popular, so experts are trying to bring out new, more interesting varieties and forms. Many natural species are also grown quite successfully by gardeners in their garden plots.Below will be presented the most popular species, varieties and forms of this plant, as well as their brief description.
Common juniper (Juniperus communis)
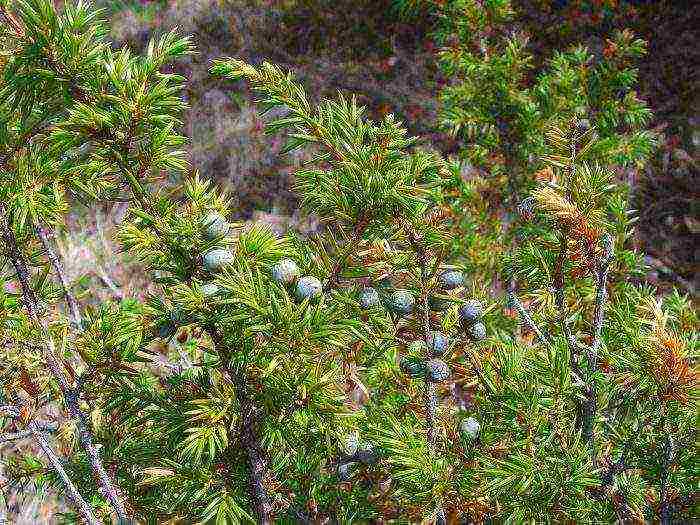

This is a shrub or tree, the height of which can vary from 5 to 10 meters. The trunk reaches 20 centimeters in diameter. The tree has a dense cone-shaped crown, and the shrub is ovoid. The fibrous bark is colored brownish-gray, while the shoots are brownish-red. The green, pointed, needle-like needles are triangular. The length of the needles can reach 15 mm, and they stay on the branches for 4 years. Blooming is observed in May. The female flowers are green and the male flowers are yellow. The life span of this plant is about 200 years. Cones are round in shape in diameter up to 10 mm, while immature they have a green color, and mature ones - bluish-black, there is a coating of wax on their surface. Varieties of this plant:
- Depressive (pinned down) - this creeping wide-flat shape can reach a height of 100 centimeters. Her needles are not as long and thin as in the main species.
- Montana - such a creeping form reaches a height of 20 centimeters. The triangular branches are thick and short.
- Green Carpet - This dwarf creeping shrub has a flat crown. Its soft needles are pale green. For 10 years, the plant can grow only 10 centimeters in height. In this case, the crown in diameter can reach 150 centimeters.
- Columnaris Is a columnar shape. The plant has a blunt top, reaches 150 centimeters in height and 30 centimeters in width. On the ascending shoots there is a short needles, at the bottom it is greenish-blue, and at the top it has a whitish-blue strip.
There are also a very large number of varieties and forms of this species, for example: Horstmann, Erekta, Nana Aurea, Meyer, Pyramidalis, Repanda, Sentinel, etc.
Juniper virginiana (Juniperus virginiana), or "pencil tree"

Such an evergreen tree can reach a height of about 30 meters. In young specimens, the crown has a narrow ovoid shape, then gradually it becomes prostrate due to widely spaced branches. The trunk can be up to 1.5 meters in diameter. The peeling bark is colored brown-red or dark brown, and in young shoots - green. Small, scaly or needle-shaped needles have a dark green color. In diameter, the spherical berries can reach 0.6 centimeters, they have a dark blue color and a bluish bloom. Cultivated since 1664.
The most popular with this species is such a cultivar as Blue Arrow. It has several forms: pin-shaped, columnar and shrub. Among them are Gray Oul, Glauka and Boskop Purple, which have blue needles, Robusta Green and Festigiata - greenish-blue needles, Canaertia - dark green needles, Silver Sprider - greenish-silver needles.
Juniper horizontal or prostrate (Juniperus horizontalis)

Under natural conditions, this plant can be found in Canada and the United States. It prefers to grow in the mountains, on the sandy coasts of rivers and lakes, as well as on the hillsides. This creeping form can reach a height of about 100 centimeters. It has long branches with densely spaced tetrahedral shoots, painted in a greenish-blue color. The needles can be green or blue, but in winter they have a brownish tint. In diameter, the fruits can reach 0.9 centimeters, they have a black-blue color and a bloom of light blue. This species has been cultivated since 1840.The most popular forms:
- Andorra Compact - this cultivar in height can reach from 30 to 40 centimeters. The crown is about 100 centimeters in diameter and has a pillow-like shape. The branches go up obliquely. Small, scaly needles are colored greenish-gray, but in winter they turn purple.
- Plumosa (Andorra Jupiter) - in height such a creeping shrub can reach up to half a meter, and in width - about 2.5 meters. The branches lie on the surface of the ground. On the feathery branches there are subulate needles. The needles are light greenish-gray in color, but in winter they take on a purple hue.
- Prince of Wales - the height of this creeping shrub can reach 30 centimeters, while the crown has a diameter of up to 250 centimeters. The bark is brown in color. Dense blue needles in winter acquire a light red hue.
Juniper Cossack (Juniperus sabina)
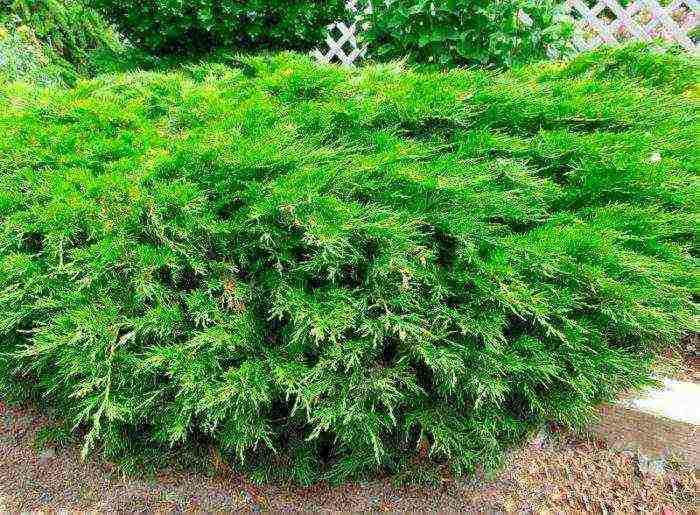

In height, this creeping shrub can reach 150 centimeters. It grows rather quickly in width, as a result of which dense thickets are formed. Less often, you can meet tree-like forms, their curved trunks can reach a height of 4 meters. This species has 2 types of greenish-blue needles, namely: in young specimens - acicular, in adults - scaly. Such a shrub has a characteristic feature, if you grind its needles or a shoot, then you can feel a pungent smell. This is due to the fact that the plant contains sabinol (poisonous essential oil). Cultivated since 1584 The most popular forms:
- Capressifolia - in height, this undersized shrub can reach half a meter. It has a wide crown. The shoots are open, move away from the base of the plant and rise up. Scaly needles are bluish-green in color. At the bottom of the crown, needle-like needles sometimes come across.
- Femina - this shrub reaches a height of 150 centimeters, and its crown has a diameter of about 500 centimeters. The color of the bark is brown-red, while on the shoots it is dark green. Scaly needles smell unpleasant and are poisonous, painted in a dark green color.
- Mac - a bush in height can reach from 150 to 200 centimeters, while the crown has a diameter of about 8 meters. The color of the bark is grayish red. In the lower part of the crown, needle-like pointed needles are green, and in the upper part, they are gray.
Chinese Juniper (Juniperus chinensis)
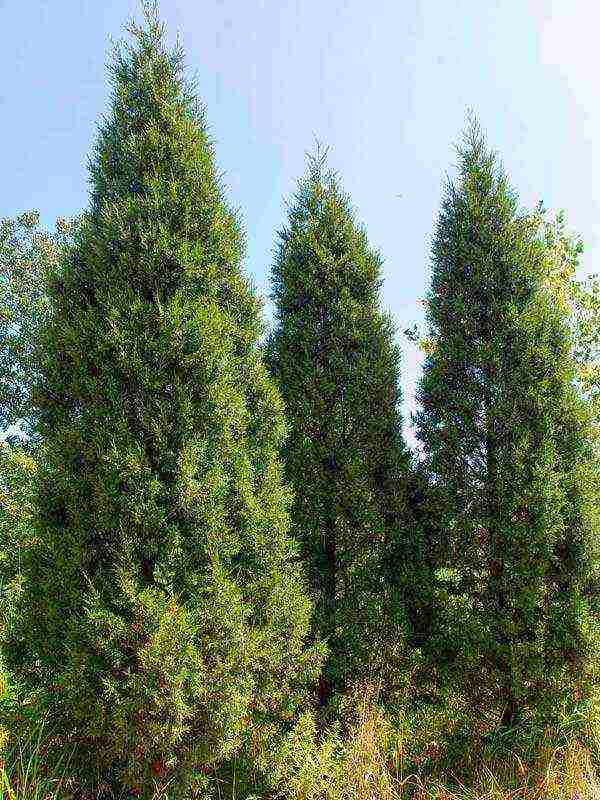

This is a tree with a pyramidal crown, which reaches a height of 8 to 10 meters. However, sometimes there is a bush pressed to the ground or spread out. The peeling bark is grayish red and the shoots are dark green. The foliage is scaly, but at the bottom of the crown or in young specimens there are thorny needle needles. Popular varieties:
- Strickta - a narrow-headed plant branches strongly. The branches are evenly spaced and raised. Straight shoots are short enough. The needles are needle-like, in the upper part they have a bluish-green color, and in the lower part - as if covered with frost. In winter, the needles turn yellow-gray.
- Olympia Is a narrow-columnar form. The branches are raised, the branches are short. There are 2 types of needles: scaly light blue and needle-like bluish green.
- Japonica - dwarf form, it is found creeping, as well as pin-shaped, reaching a height of 200 centimeters. The short branches are quite dense. The spiny, scaly, sharp foliage is pale green in color.
- Gold Coast - in height such a shrub can reach 100 centimeters, while the diameter of the crown is 300 centimeters. The needles are yellowish-golden, they become darker after autumn.
Rocky juniper (Juniperus scopulorum)
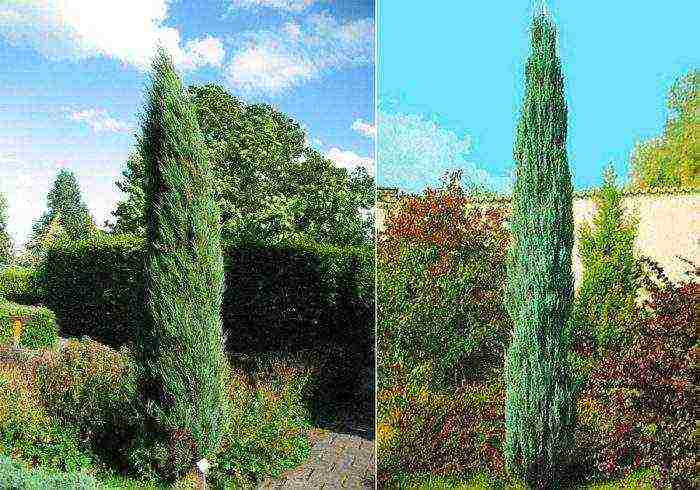

The homeland of such a plant is North America. The species is represented by a shrub or tree, which reaches a height of 18 meters. The crown begins almost from the base and has a spherical shape. Young shoots are 15 mm thick, they are colored pale green or bluish green. In most cases, scaly needles are found, but there are also needle-shaped leaves. On the surface of the dark blue fruit, there is a bluish bloom. Popular varieties:
- Repens Is a creeping shrub.On low-lying branches there are feather-like branches that rush upward. The length of the needle-like leaves is about 0.5 centimeters, they are blue at the top, and bluish-green at the bottom.
- Springbank - the height of such a narrow-gleaming juniper is about 200 centimeters. Its upper branches are flexible and spaced apart, and the tips of the shoots are almost threadlike. Scaly needles are bluish-silvery in color.
- Skyrocket - Dutch tall cultivar with a narrow habit. When the plant reaches 3 years old, its height will be 10 meters. There are straight shoots and greenish-gray needles.
Scaly juniper (Juniperus squamata)
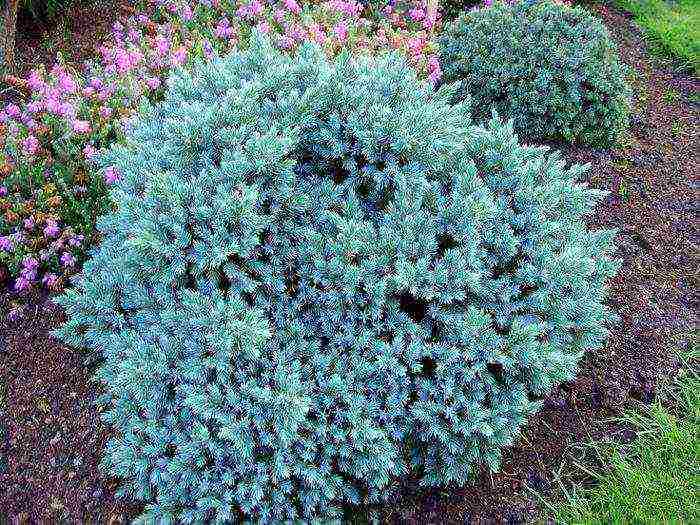

This species is quite variable, and it is represented by an evergreen shrub that can reach a height of 150 centimeters. The color of the bark is dark brown. Tough, sharp, lanceolate needles are colored dark green below, and on top they have a whitish tint due to stomatal stripes. Fruit color is black. Cultivated since 1824 Popular varieties:
- Blue Star - the dwarf Dutch cultivar reaches a height of 100 centimeters. The diameter of the dense semicircular crown is about 200 centimeters. The needles are whitish-blue, they look most beautiful at the end of spring and early summer.
- Meyeri - a decorative form of a shrub. While the plant is young, it branches strongly, and the height of an adult specimen varies from 2 to 5 meters. The needles are very beautiful bluish-white.
- Rodery - an erect shrub has a kegle-like dense shape. Its height is about 150 centimeters. Needle short leaves are quite sharp, they are blue above, and green below.
Juniper medium (Juniperus x media)
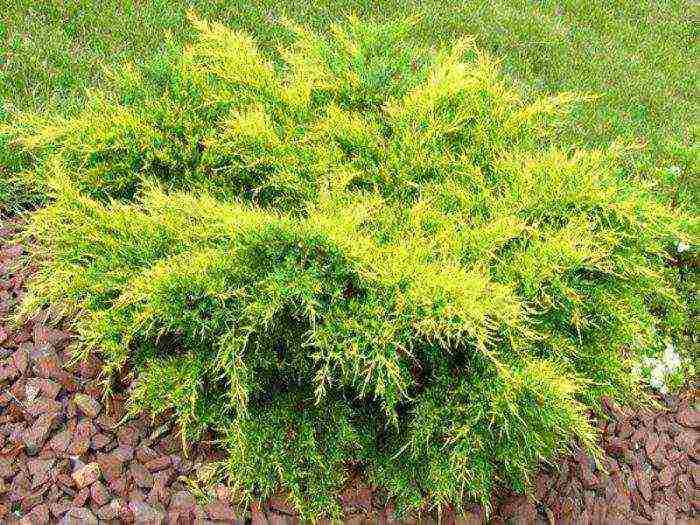

This hybrid is the result of crossing Chinese and Cossack junipers. This shrub has arched shoots with drooping ends. There are two types of needles: inside the crown it is needle-like, and the rest is scale-like. During growth, it has a pale green color, but darkens over time. The height of adult plants is 300 centimeters, while the width is 500 centimeters.
The most popular variety is Mint Julep. It is a sprawling shrub that grows quickly. The shape of the crown is wavy. At the age of ten, the plant is 150 centimeters tall and 300 centimeters wide. Since the size of the shrub is large enough, it is often planted in large gardens and parks.
Also cultivated are such species as: Daurian, recumbent or inclined, false Cossack, oblong, Sargent, Siberian, hard, Turkestan. And also other types of varieties and shapes.
Juniper properties
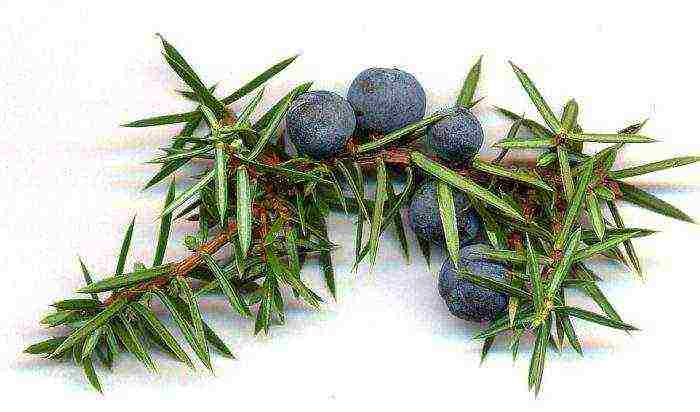

Healing properties
For a long time, such a plant has been considered a cure for any disease. Young shoots and roots are considered medicinal, but cones are often used for treatment. The roots will help heal tuberculosis, bronchitis, skin diseases, stomach ulcers. The plant relieves toothache, swelling, normalizes heart function, removes inflammation in the lung and bronchial tissue, normalizes blood pressure and blood circulation, eliminates constipation. Diathesis is treated with a decoction of the branches. The needles have a powerful antibacterial effect, which is stronger than that of other plants. The composition of the fruits includes carbohydrates, wax, sugars, coloring and tannins, organic acids, vitamins, iron, manganese, copper, aluminum and essential oil, which has a choleretic, antimicrobial, diuretic and expectorant effect. From the decoction of the fruit, compresses are made on sore joints, and it is added to the bath for rheumatism and gout. A decoction taken orally helps to improve appetite and digestive processes, enhance the secretion of bile and improve intestinal motility.
Fruit decoction recipe: crush 1 large spoonful of fruits and add them to 200 grams of freshly boiled water. Let it simmer for 10 minutes.The broth should be infused for 30 minutes, strain.
Contraindications
Juniper products should not be taken during pregnancy, severe hypertension, acute inflammation of the kidneys and individual intolerance.
Every person who sees a juniper will call this plant amazing. It is beautiful, graceful, looks great in landscape design. Due to these properties, juniper has gained extraordinary popularity among designers of various varieties of juniper.
Planting and caring for this plant does not require special knowledge, so it has spread not only in park city landscapes, but also in private gardens and adjoining parks.
Beneficial features
Juniper foliage outwardly resembles needles, has a resinous smell and releases phytoncides that cleanse the air around the plant from pathogenic microbes.
The uniqueness of the plant is also given by the fact that it has the properties to heal those who are nearby: people find peace of mind, experience peace and tranquility. Also, the plant relieves headaches and normalizes sleep. Here is such a useful juniper.
Planting and care, varieties and types of plants, how to propagate and grow it - read on about this.
Description
Juniper is a long-lived evergreen coniferous plant that is represented as shrubs and trees belonging to the Cypress family.
The tree-like representatives of the juniper are capable of reaching 30 m in height, have a pyramidal or cone-shaped crown, consisting of scaly or needle-like needles.
Shrubby plants, as a rule, grow up to half a meter in height. They have spreading and flexible branches, which, thanks to this, form a dense and lush coniferous covering.
Juniper, a description of which can be found in many specialized sources, originally comes from northern forests, but now gardeners are given the opportunity to grow it anywhere.
From the fruits of this plant, medicines are made for the treatment of diseases of the kidneys and urinary system. Decoctions of juniper needles with fruits bring relief from skin diseases such as eczema, dermatitis and others. In addition, the plant is excellent as a spice to some dishes.
Juniper (plant species are numerous - there are about 70 of them) spread throughout the northern hemisphere of the planet.
Peculiarities
Juniper flowers are also quite unusual: female ones are round light green cones, and male ones look like catkins with several stamens. In June, the plant blooms, and in August-September, the fruiting period begins.
If you break a juniper cone, you can see that it is filled with a soft brown substance used for medicinal purposes.
In April-May, male types of juniper produce yellow spikelets, while female types produce green cones. The fruits of the plant are round-shaped cones, up to one centimeter in diameter with three seeds inside. At first they are green, and when ripe, they become black-purple and have a waxy gray bloom. The berries to taste are slightly bitter, with a pleasant spicy aroma.
Varieties and types of tree juniper
Juniper, the species of which is very numerous, is often found in urban areas and in private front gardens. This is explained by climatic conditions: gardeners prefer to grow unpretentious frost-resistant varieties.
The first group includes tall tree-like varieties. The vertical crowns of evergreen trees are suitable for decorating urban landscapes.
The most popular among gardeners and designers are the following varieties from the first group:
- Common juniper. This is a species with fragrant wood up to ten meters high with a dense crown, shaped like a cone or an egg.The growth of its trunk is very slow, so the tree lives up to 200 years. This species will withstand light shading, it is frost-resistant, relatively unpretentious.
- Juniper Chinese Strickta. It is also a long-growing tall tree with a conical crown with green-blue needles. Loves sunny open spaces.
- Red cedar. This is a fast-growing tall tree that can reach thirty meters in height. The juniper has a narrow ovate trunk with a wide crown and green needle-shaped needles. Easy to care for, resistant to pests and diseases.
- Juniper forest. Common northern cypress, forest juniper, planting and caring for it is extremely simple, since the tree is very unpretentious, but loves sunlight and does not tolerate shade. It prefers to grow in a mixture of sand and peat.
The tree group also includes low, rather beautiful species of junipers, reaching from two to three meters in height. These include: pyramidal juniper, Hibernik juniper, Horstmann juniper, rocky juniper.
Shrub juniper
The second group consists of shrubs of the following popular species:
- Juniper scaly Meyeri. Evergreen shrub with elegant crown and originality of the color of the needles, which have silver-blue tips. Loves the sun, therefore fades in the shade.
- Horizontal creeping juniper. Has a second name - prostrate. This is a dioecious creeping shrub, has elongated branches with a gray-silvery shade of needles of a scaly or acicular shape. With the onset of frost, the crown becomes almost purple in color.
- Juniper Cossack. A dwarf species up to 1 m in height, having obliquely spread branches with dark green scaly needles with a pungent aroma. Very poisonous!
- Juniper Repanda. A dwarf shrub of forty centimeters in height, reaching two meters in diameter. It has a symmetrical cushion-shaped creeping crown. The shrub is light-requiring, undemanding to the soil, frost-hardy.
It is important to remember: each of the species is poisonous in different ways, so it is better to work with them with gloves.
Juniper: planting and care
The best option for planting is young seedlings, which are grown in special containers. This is done so that the plants grow faster. At a young age, they are easier to tolerate a transplant.
Transplanting an adult juniper, for example, as tall as a Chinese juniper, requires certain experience and skills. As a rule, the plants are grown outdoors, and before being sold, they are dug up and sold to customers along with an earthen lump. He wraps himself in sacking soaked in water. The second option for sale is together with a container in which the plant has already taken root and has taken root.
The best time to plant junipers is in spring (April-May) or autumn (October). Seedlings sold in containers can be planted at any time, as their root system is protected.
For disembarkation, an open, sunny place is chosen, which is a condition for the decorativeness of the juniper. In conditions of strong shade (under the wall), the plant will fade and may begin to wilt.
Around the trunk of the plant, mulching with a mixture of peat and coniferous wood chips is necessary.
After planting is complete, the seedling is watered abundantly under the root with water.
Juniper: reproduction
Junipers can be propagated in three common ways: cuttings, seeds, and layering.
The best temperature conditions for rooting are:
- 16-19 ºC - before budding, and 23-26 ºC - after that;
- wet soil and systematic spraying;
- moderately diffused light.
Cuttings such as creeping juniper should be rooted obliquely, and columnar varieties should be rooted vertically.
Only creeping juniper varieties can be propagated by layering during the growing season.
To grow non-decorative species from seeds, the seed material is first stratified: in the fall they are sown in boxes, then taken out under the snow until May, and then sown in open ground.
To collect the seed, the pineal fruits are opened, the seeds are cleaned and dipped in sulfuric acid for thirty minutes, then washed thoroughly.
Plant propagation
You can get cuttings of the plant all year round, but it is better to choose spring for this. To begin with, they are planted for rooting in a greenhouse, and in May or June they are transplanted into open ground under a film. If the transplant occurs in February-March, then they are transplanted into a greenhouse.
In order to propagate a juniper, propagation should be carried out in the following sequence:
- In mid-spring, one-year-old cuttings 10 cm long with a piece of old wood are cut from a ten-year-old plant, and 4 cm of needles are removed from the bottom.
- The bark is carefully trimmed with sharp scissors, the cuttings are placed in a growth stimulator, for example, "Heteroauxin", for a day.
- In a peat-sand mixture prepared in equal parts, cuttings are planted under a film and shaded.
- Within 40 days, the root system develops, it is better to spray the cuttings with water than to water.
- In the middle of summer, the planting material is planted in the ground, for the winter it must be covered with spruce branches.
- Re-rooting will last 2.5-3 years, after which matured seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place.
It is almost impossible to grow ornamental species from seeds; it is better to propagate such a juniper by cuttings.
Care
Rooted plants do not require special care, but some rules should be followed:
- In the spring, the plant needs to be fed with nitroammophos at the rate of 35 g per 1 m2.
- The trunk circle should be regularly weeded or mulched. The mulch should be laid on a black geotextile.
- For wintering, the juniper is tied with twine to protect the crown and trunk: from the weight of the snow, the crown can disintegrate and decorativeness will be lost.
- Species with a crown of blue, yellow and variegated should be covered from the spring sun. To do this, they must be tied with spunbond or covered with a green net.
- Juniper requires timely, careful pruning, during which damaged and dry branches are removed.
- Only young seedlings in the first year need shelter for wintering.
If you do not follow these rules, then the gardener will have to watch how the diseases of the juniper develop.
Landing rules
The distance between plants depends on the size and type of juniper, but should not be less than half a meter for medium-sized plants and at least a meter for tall ones.
The depth of the pit depends on the size of the root system and the earthy coma. It should be 2.5 times the size of the coma and have a depth of 70 cm.
At the bottom, a drainage from a battle of bricks and sand with a layer of 20 cm is necessarily arranged. The roots are covered with a soil mixture of sod, peat and sand in a ratio of 2: 1: 1.
Young seedlings require regular, moderate watering, and mature plants have sufficient drought tolerance. Therefore, they need to be watered up to three times a month, depending on the weather. Also, in the heat, juniper is sprayed in the morning and evening twice a decade.
The watering rate is calculated based on the age and size of the plant, but on average it is 10-30 liters for an adult juniper.
Diseases and pests
Juniper diseases are as follows:
- mushroom rust;
- gray mold;
- schütte disease.
Among the dangerous pests are the following:
- juniper miner moth;
- spider mite;
- juniper scale;
- aphid.
If the fight is started on time, then the plant can be saved even before complete defeat.
Against rust, in which the juniper turns yellow, a solution of arceride works well in a proportion of 50 g per 10 liters of water, you need to spray it four times with a break of ten days.
When attacked by aphids, the plant should be sprayed with "Fitoverm" at the rate of 2 g per 1 liter of water twice with an interval of two weeks.
Against moths use "Decis" in a proportion of 2.5 g per 10 liters, the spraying scheme is similar to the previous one.
The spider mite is treated with "Karate" in the amount of 50 g per 10 liters, and the scabbard is treated with karbofos at the rate of 70 g per 10 liters of water.


