Content
- 1 Description of the plant and species
- 2 Planting spirea
- 3 Care rules
- 4 Reproduction
- 5 Description of Japanese spirea
- 6 How to care for spirea
- 7 How to propagate spirea in summer
- 8 Growing spirea from seeds
- 9 Pests and diseases
- 10 Varieties of Japanese spirea with photos and descriptions
- 11 Spirea: types and varieties
- 12 Spirea: features of cultivation
- 13 Shrub propagation
- 14 Landing in open ground
- 15 Outdoor care for spirea
- 16 Plant diseases and pests
- 17 The nuances of growing in Siberia, the Urals, in the Moscow region
- 18 How and when does the spirea plant
- 19 Spirea care
- 20 Reproduction of the spirea bush
- 21 Varieties of spirea and their varieties
- 22 Shrub in landscape design
Spirea, numbering more than 100 varieties, is known as a versatile shrub for landscape design. Among them there are giants over 2 meters high and dwarf species less than 20 cm high. It is successfully grown as a hedge in gardens and parks, serves as an element of rockeries and flower beds.
Lush color, a variety of colors, a long flowering period and unpretentious care are good reasons to settle this beauty in the garden.
You will learn how to grow spirea, how to create ideal conditions for it and all the nuances of care by reading this article.
Description of the plant and species

Spirea, or, as it is often called, meadowsweet, is an ornamental shrub of the Rosaceae family. The natural conditions for its growth are steppe, forest-steppe, semi-desert areas of most of the northern hemisphere.
Her flowers are small, but due to their large number and large inflorescences in which they are collected, the blooming spirea looks luxurious. Flowers of various colors can be collected in inflorescences in the form of a panicle, an ear. Leaves, depending on the variety, are of various shapes: round, lanceolate, colors vary from yellowish green to bright green, small-leaved and large-leaved varieties are found. Therefore, it is not surprising that different varieties of spirea differ significantly from each other.
The meadowsweet varieties are conventionally divided into two main groups: spring-flowering and summer-flowering.
Spring blooming
Plants of this group are characterized by flowering in late spring and early summer. At the same time, the buds are formed in the fall, so in the spring it is absolutely impossible to cut the bushes. From this group, the following varieties are especially attractive, shown in the photo:
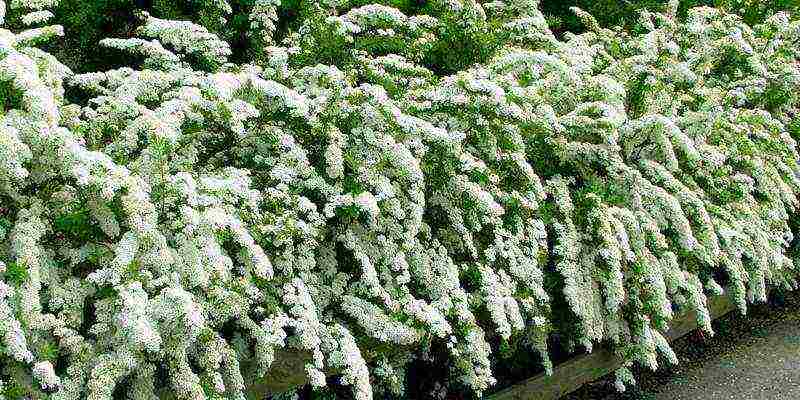
Spirea is gray.A characteristic difference of this variety is gray foliage. Snow-white flowers form a shield-like inflorescence. A bush growing up to 2 meters in height with soft branches looks great both growing alone and in group plantings.

Thunberg.The height of the bush is up to 2 meters, in natural conditions it grows in the mountainous regions of China, Japan, Korea. Long bloom - from May to late June.White flowers on drooping branches are collected in umbellate inflorescences.
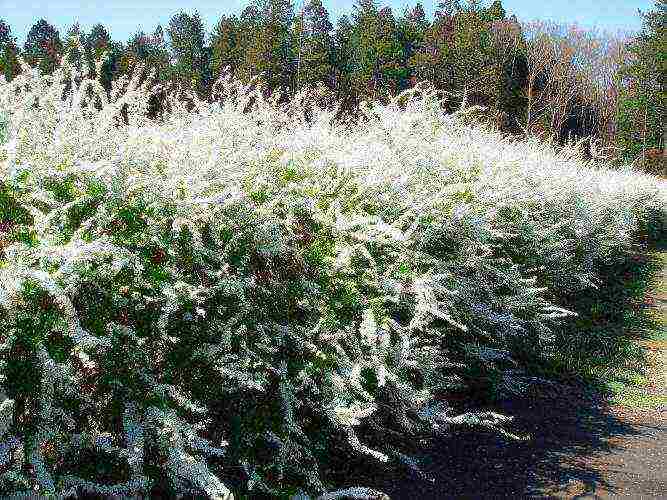

Arguta.This variety is so lush that the foliage is not visible due to the white lace of the flowers. Due to the spreading structure of the plant, shoots do not need pruning, they grow up to 2m in an arched shape. A short flowering period from the end of April, lasts about 20 days.

Summer blooming
Varieties of this group form buds in the spring only on young shoots, which is why the plant needs pruning of last year's already faded branches. Flowering begins later in the summer.
This group includes:
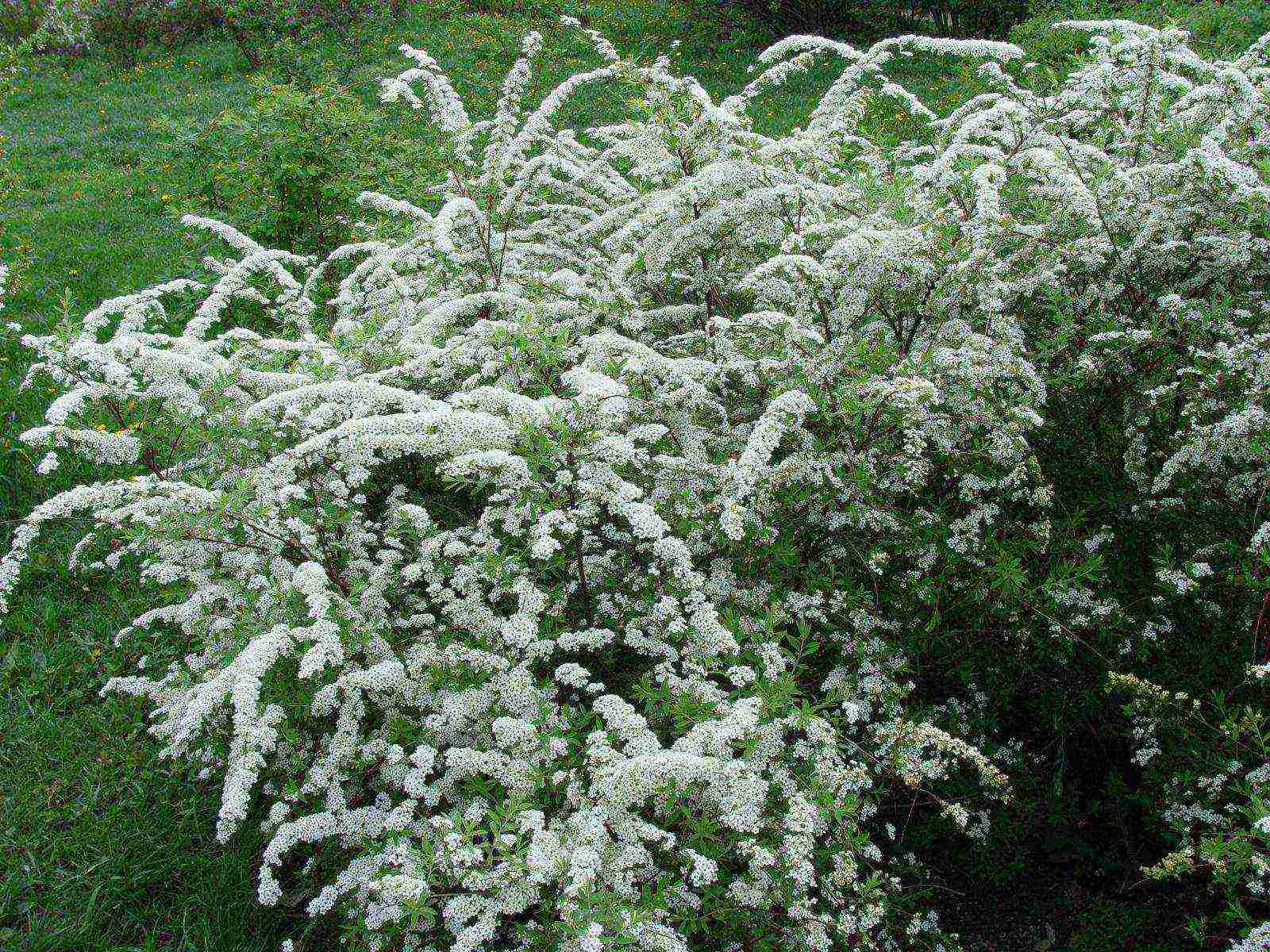
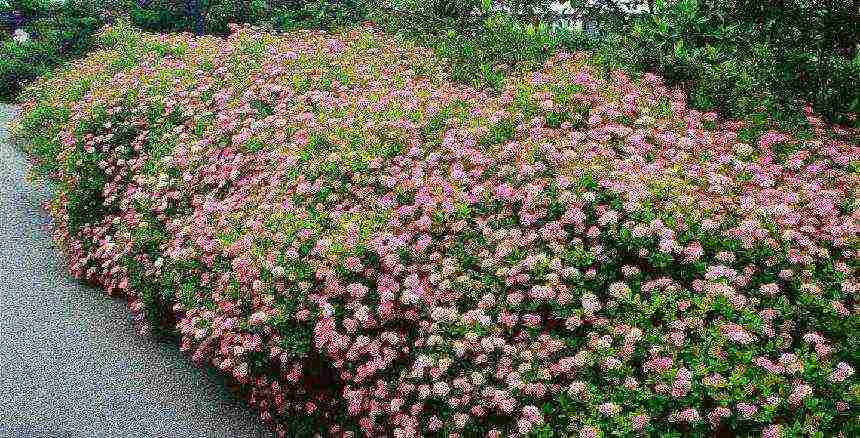
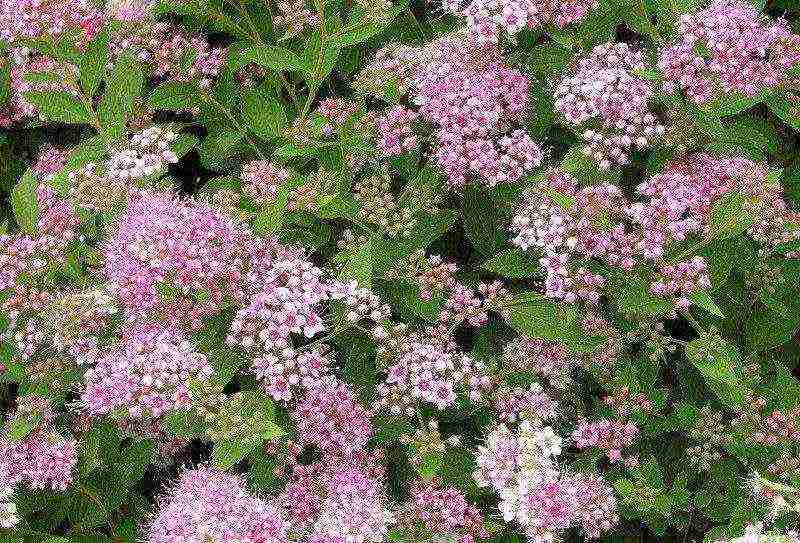
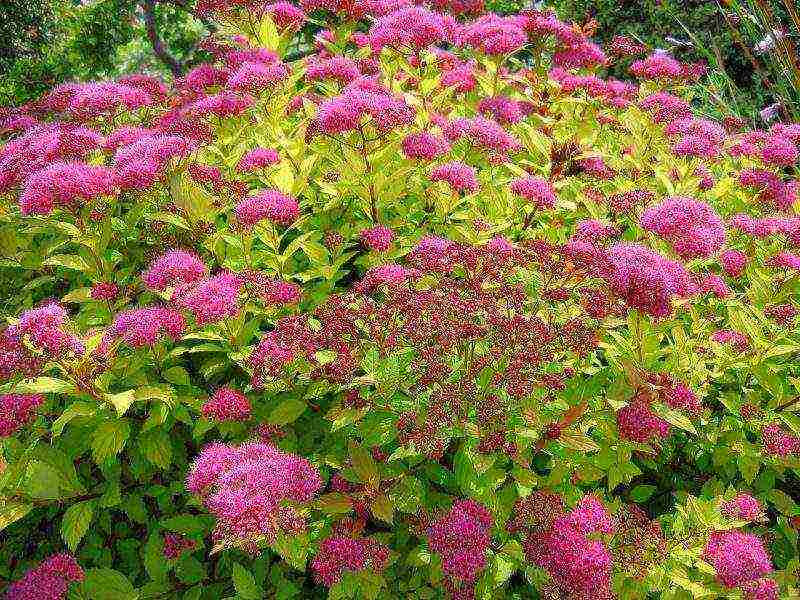
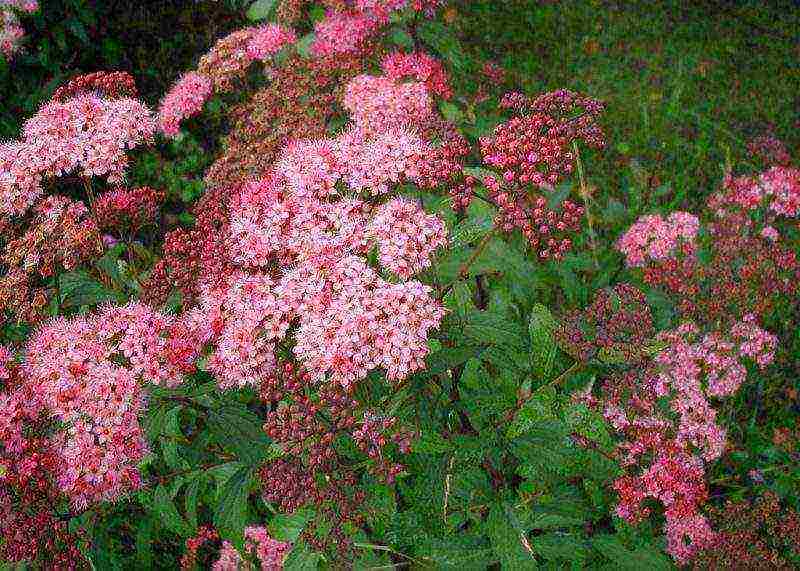
Japanese spirea.The height of the shrub is no more than 1.5 meters. The peculiarity of Japanese spirea is in oblong bright green leaves, on the underside of a bluish tint, which later become reddish. Long flowering period (all summer), pink flowers are collected in shield-like inflorescences.

White spirea. Sprawling shrub about 1.5 m high with long pointed leaves. Flowering begins in July.

Billard. With pink flowers and wide leaves, it blooms from mid-summer until frost. It grows in height up to 2 meters. Due to its cold resistance, it is successfully grown in the northern regions.

Planting spirea
The condition for obtaining a beautifully blooming spirea is compliance with the basic rules of cultivation, including planting.
The optimal planting time is September.
In spring, only summer-flowering species are planted, it is recommended to plant before bud break. Before buying a seedling, you need to make sure that the planting material is suitable: the root system should not be overdried, and the shoots should be flexible, have formed buds.
It is necessary to prepare the seedling. Overgrown roots should be shortened, and, conversely, with dried roots or if they have damage, the shoots are shortened. It is useful to soak overdried roots in water for a while before planting.
For spirea, leaf or sod soil is optimal. To prepare the soil, sand and peat are added to the sod land in a ratio of 2: 1: 1. The planting hole must be provided with good drainage, since the spirea does not tolerate stagnant water well.
It is advisable to plant in rainy or cloudy weather. Planting depth - 0.5 meters, not less. The planting hole is filled with soil, and the seedling is planted in such a way that its root collar is at surface level. After planting, water should be abundantly at the rate of 15-20 liters per bush.
Care rules
Like all other plants, the relatively unpretentious spirea needs certain growing conditions.
Watering
Watering required abundant and frequent, especially for young plantings and flowering in summer. Well protects against moisture evaporation and the formation of a crust on the surface of mulching. Watering rate: 25-30 liters of water per plant up to 3 times a month.
Top dressing
Top dressing with fertilizers stimulates the growth of spirea and the formation of new shoots. Mineral complexes are introduced into the root circle immediately after pruning. In the middle of summer, organic mullein feeding is beneficial.
To provide the root system with oxygen, it is important to loosen the soil.
Pest control
The most common pests are aphids and spider mites. The fight against them should be started immediately after detection, since due to the spreading of the spirea, delayed processing can be difficult. Treatment with complex insecticides is recommended.
Diseases
One of the advantages of spirea is resistance to many diseases. However, if the rules of care are violated, it can be struck by root rot, the main reasons for which are waterlogging of the soil, lack of drainage and the formation of stagnant moisture, heavy soil. For prevention, such phenomena should be avoided; in the event of a fungal infection, treatment with fungicides can save the plantings.
Pruning shoots

Pruning is done to prevent overgrowth and shape the plant.
Depending on the type of flowering, it is carried out in different ways.
In spring-flowering varieties of spirea, only the frozen tips are cut off. To update the spirea after 7-14 years, you can remove all old branches, leaving the stumps. A new bush is formed from the young growth. In the first year, 5-6 shoots are left on it, which grow rapidly. After a year, weak and old branches are cut again.
Summer flowering species need annual pruning in the spring. In this case, the branch is cut to large buds, and it is advisable to remove the weakened branches completely. After 4 years of growing season, it is recommended to prune the branches annually, leaving them up to 30 cm from the ground surface.
Reproduction
Layers
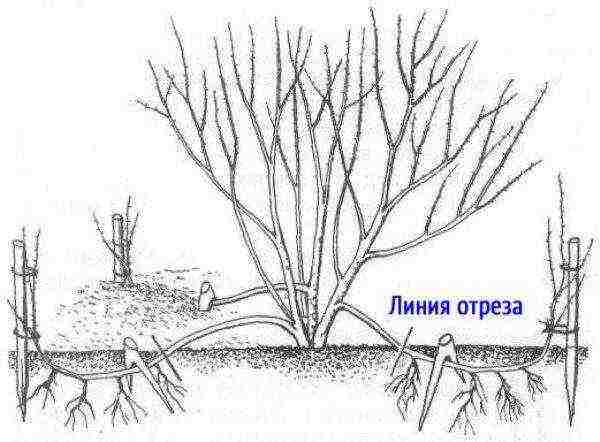
The most effective way is propagation by layering, which is also the simplest. During the blooming of the leaves, the shoot is bent to the ground and sprinkled. With regular watering in the fall, a young seedling with a sufficiently strong root system will form from it to separate from the main bush and plant in another place.
If you want to get more than one layer from one branch, you should pinch its top, bend the entire shoot to the ground and sprinkle it. With this method, by the spring of next year, several young plants suitable for transplantation will be formed from the grown lateral shoots.
Cuttings

Cutting is a rather laborious process. Cuttings are cut out at the end of flowering and planted in a peat-sand mixture and placed in a greenhouse. For planting in open ground, the cuttings will be ready for the next one only in a year.
Seeds

Seed propagation is rarely used. Sowing is carried out in the spring under the film. After their germination, the film is removed, and then grown as a normal seedling until the end of summer. Then the seedlings are transplanted into open ground. In the winter cold, young seedlings must be covered with foliage, spruce branches.
Seed propagation is rarely used due to low seed germination and a long waiting period for flowers (after 3-4 years).
Spirea is a deciduous shrub with a height of 0.15 - 2 m. There are more than 90 species of spirea in the world with different directions of the branch arrangement - they can be erect, spreading, recumbent. A variety of colors of inflorescences, foliage, crowns, ease in the formation of bushes, quick recovery after exposure to adverse conditions are important qualities that distinguish spirea from many other ornamental shrubs used in floriculture.
Japanese spirea is used for landscaping everywhere, even in the most northern regions. It has all the characteristics of an ideal garden plant. Each annual shoot ends in a large panicle with many pink buds. It is covered with flowers from the beginning of summer until the onset of cold weather. It is unpretentious, easily multiplies, and can decorate any, even the most sophisticated landscape with luxurious flowering.
Description of Japanese spirea
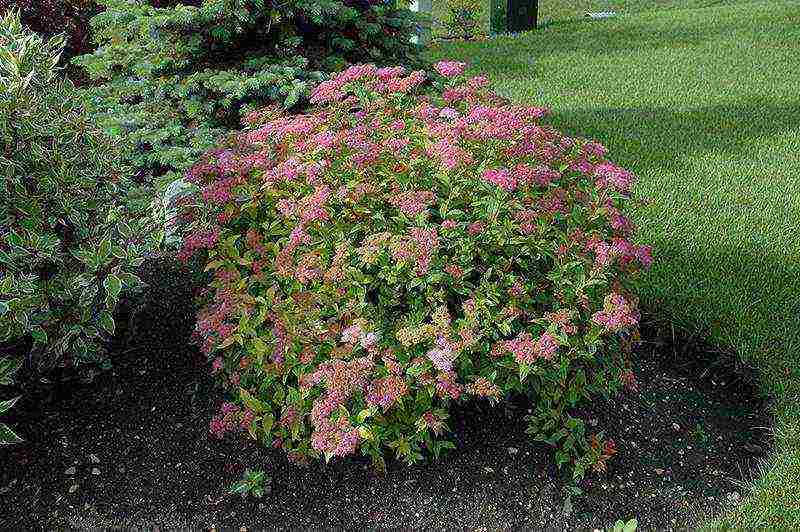

Japanese spirea in landscape design photo
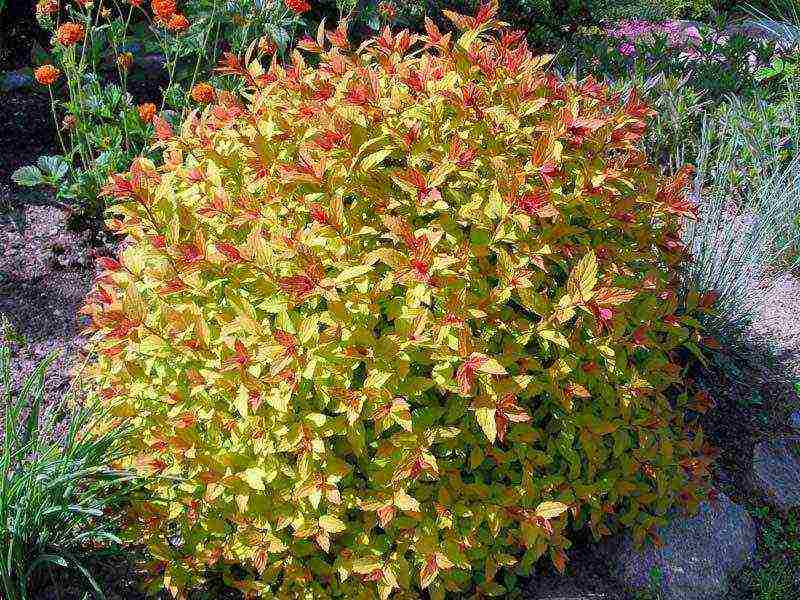
Japanese spirea Spiraea japonica - a representative of the Rosaceae family - migrated to us from Japan and China. A feature of elliptical or ovoid leaves is that when they bloom, they turn reddish-brown shades, turn green in summer, and by autumn they change color again to brown-purple. Breeders, using this effect, have developed many varieties with unusual foliage tones that change throughout the season.
The Japanese spirea is the record holder for the duration of flowering. Its pink-red buds are collected in lush corymbose inflorescences. From mid-June, it is covered with fragrant flower caps. This magnificent sight can continue until the onset of cold weather. Japanese spirea has many garden forms, differing in the color of the flowers, the height of the bush and the size of the leaf blades.
How to care for spirea
Despite their unpretentiousness, Japanese spirea bushes love well-lit areas with fertile soil. She may feel great in shady areas, but the flowering will be less impressive, and the foliage is not so brightly colored.
Planting is best done early in the season. When buying seedlings, they choose specimens that have not yet moved into growth with living buds on branches. Check the roots and shoots carefully - they should not break when bent.
How to plant a spirea the video will tell:
If the seedlings are with a closed root system, then the plant may be with blossoming leaves. In this case, carefully inspect all the branches and leaves - they should not be lethargic and dry, and the soil in the container should not be dry or very wet. In case of overflow or overdrying while in a container, such a plant may die.
The planting hole is prepared with a volume significantly exceeding the volume of the roots - taking into account further growth. Drainage from crushed old brick or expanded clay is laid at the bottom. To do this, you can use the remnants of the foam, after crushing it to the size of a walnut. Thoroughly fill with organic matter and mix.
Planting is best done in cloudy, rainy weather. Having placed the roots in the hole, they are carefully covered with earth and well watered. The root collar should be at ground level. The soil around the bush is carefully mulched - this will prevent moisture evaporation and the formation of a soil crust.
After a day or two, plants with blossoming leaves can be shed with ammonia water. It acts as an anti-stress drug - it provides nutrition for the plant at a time when the roots are not yet able to fulfill their direct responsibility.
Watering
Water the plant sparingly if there has been no rain for a long time. If it rains sometimes, the spirea need not be watered. The mulch will help retain moisture.
Another useful top dressing: a tablespoon of pharmacy ammonia is dissolved in 10 liters of water. Plants can simply be watered with such a solution from a watering can so as to moisten all the leaves and twigs. The rest of the solution can be watered on other plants. Ammonia quickly evaporates, so the solution is used as soon as possible and is not stored.
Ammonia solution is a good product with easily assimilated nitrogen, it can be fed with Spirea in a stressed state to quickly improve green mass growth and recovery.
The soil under the bushes is constantly kept in a loose state - this is achieved by mulching with bark, peat or compost.
Top dressing
To enhance the quality of flowering, the plant is fed after spring pruning with liquid complex fertilizer, and in the middle of summer, you can use a solution of organic fertilizer with the addition of superphosphate. Do this after abundant watering or during rains.
Spirea is quite loyal to the winter cold, but in order to avoid freezing in snowless winters, it is worth covering the roots and the lower part of the plant with dry peat, moss, sawdust or foliage. This is especially true for very young or recently transplanted bushes.
Trim spirea in spring video cropping
Spirea can and should be severely pruned. She quickly recovers and gains strength. Pruning is done in early spring. Dry, old, damaged shoots are removed at ground level. They give shape to the crown, shortening the twigs that have been knocked out of the total mass. Spring haircut is only for the benefit of the plant - the more often the spirea is cut, the more powerful and lush the bush grows. This procedure is carried out taking into account the nature of the formation of flower buds.
The shoot is shortened to developed buds. And small shoots are removed completely. After three years of life, the tops of the old twigs are cut off to avoid deflecting their tops towards the ground. Thoughtful and timely pruning of spirea is aimed at achieving maximum decorative effect and achieving a beautiful appearance.Sometimes cardinal pruning is used - the entire bush is cut off a little above the ground.
How to cut a spirea in the fall, look at the video:
Pruning spirea after flowering is a mandatory procedure not only to maintain the decorative effect of the bush, it is an excellent stimulation of flowering in the next season.
Decorative haircut for spirea in summer on video:
How to propagate spirea in summer
By dividing the bush
By dividing the bush, adult plants are propagated.
- Do this in the fall or early spring before bud break, watering the plantings abundantly.
- An adult plant is dug up, cut with a sharp tool into pieces with several growth points.
- Slices are slightly dried and sprinkled with crushed activated carbon to prevent rotting.
- New bushes are planted at intervals of 0.6-0.8 m.
How to propagate spirea by cuttings

Reproduction of spirea by cuttings in summer
- For cuttings at the end of June, they take a ripe branch and cut it into several 10-12 cm pieces, which are planted in a shady place in the garden and maintain sufficient moisture there.
- You can also use this year's green cuttings.
- Cuttings take root well both in the garden and in pots on the windowsill, you just need to keep the ground moist.
- For the winter, the planted bushes are covered with a layer of fallen leaves or peat, and in the spring they are placed at the intended place of growth.
We look at the video about the grafting of spirea:
Reproduction by layering
For reproduction by layering in early spring, the lower branches are bent to the ground and pinned with a V-shaped wire, falling asleep from above with soil. Already in the fall, roots are formed in these places and young plants can be transplanted to their new place.
Growing spirea from seeds

How to grow spirea from seeds
All types of spirea reproduce without problems by seeds, with the exception of hybrids. They may not set seeds at all, or seeds from such plants do not replicate maternal qualities.
Sowing seedlings
- Seeds are best sown in spring in planting boxes with a light soil substrate.
- Planting depth 1 cm, distance between seeds at least 2-3 cm in a row, between rows 6-8 cm.
- Water in moderation, there must be drainage holes in the bottom of the container so that moisture does not stagnate.
- Usually the germination rate is at least 50%. The first shoots appear within two weeks and in the first year of life they give one winding shoot.
- When 2-4 true leaves appear, they dive into separate cups.
2 months after germination, seedlings can be planted in the ground. At the same time, the roots are slightly shortened to stimulate their branching. In the second year, the bushes begin to branch. It is necessary to monitor the moisture content of the soil and prevent it from drying out. At 3-4 years old, the first flowering begins.
Sowing in the ground

Spirea Japanese photo of seedlings in the open field
Spiraea can be sown directly into the ground as soon as the ground is ripe, in early spring, or in late autumn, before winter. Densely emerged seedlings are thinned out, and when they rise a little, after 2-3 months, they are planted with an interval of 30-40 cm. For the winter, the seedlings are covered, and in the spring they are planted in a permanent place.
If you do not cut off the spirea in the fall, in the spring you can find dense self-seeding shoots. These small seedlings can be left to grow and later transplanted as described above.
Pests and diseases
Usually spiraea is affected by a standard set of pests (aphids, rosaceous miner, rose leafworm, spider mite) to combat which various measures are used - agrotechnical, chemical, biological. Particular attention should be paid to prevention. Healthy and well-groomed plants are less susceptible to attacks from various insects.
Three times treatment with ammonia water with an interval of two weeks, starting from the moment the leaves bloom, will help scare away unexpected guests and increase the spirea's resistance to disease. Such processing will give an additional impetus to the growth of vegetative mass, serving as a kind of foliar feeding. Timely weeding and watering play an important role.Spirea is quite resistant to diseases.
In the design of gardens and parks, spirea is simply irreplaceable. It is distinguished by a wide variety of varieties, does not oppress other plants, and tolerates pruning excellently. Looks great in any garden. Perfectly complements the composition of low trees and shrubs. Serves as an excellent screen for larger brethren with bare trunks.
A spirea bush sprinkled with flowers on a green lawn looks spectacular. She is unusually attractive in a rocky garden in the company of short conifers. It is indispensable for creating a hedge, as it is an inexpensive planting material and is easy to form. It is very decorative in the period of autumn leaf coloring, enlivening the wilting nature.
Varieties of Japanese spirea with photos and descriptions

Spirea Japanese variety Little Princess spiraea japonica little princess photo
Little Princess is a short shrub with a crown diameter of up to 60 cm. It is characterized by slow growth and pink-red flowers in a corymbose inflorescence, appearing at the end of June. This plant makes an excellent hedge.
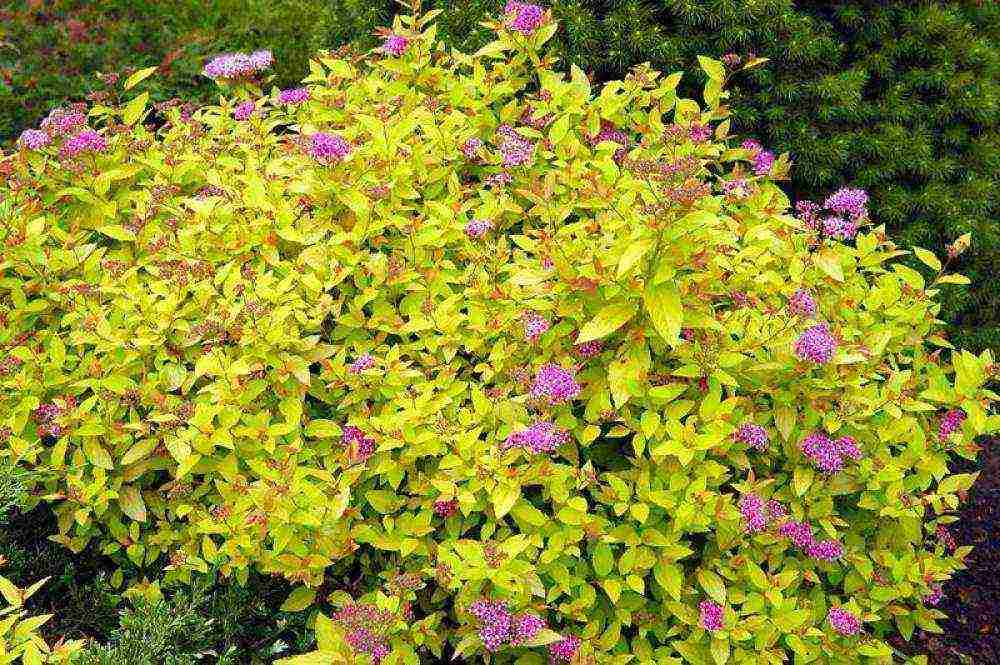

Spirea Japanese Spiraea japonica Golden Princess ‘Golden Princess’ photo in the garden
Golden Pincess - As short, but with bright yellow leaves and pink flowers. Blooms in July. In autumn, the leaves take on a golden orange color.
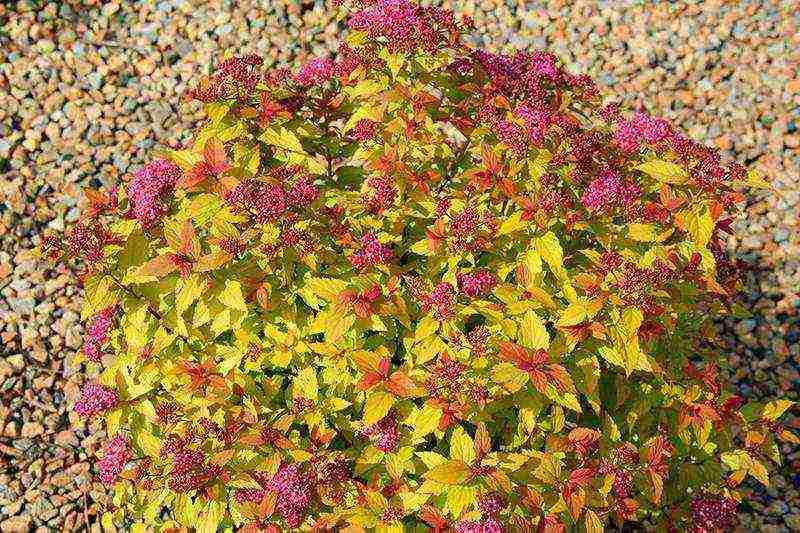

Spirea Japanese Goldflame Spiraea japonica Goldflame photo in the garden
Goldflame - orange-yellow leaves adorn this shrub less than a meter high. Over time, the color of the leaves changes to yellow, and then to green. In autumn, the leaves take on a copper tint. Feels great in urban environments. A powerful and fast growing variety.

Spirea Japanese cultivar Spiraea japonica 'Shirobana' photo in the garden
Shirobana is a short shrub whose flowers change color from white to pink and red. A real chameleon. The round bush reaches a diameter of 0.8 cm.

Japanese spirea Macrophylla Macrophylla photo in the garden
Macrophylla - The large, wrinkled leaves of this variety turn bright red over time. A very decorative variety that produces pale pink inflorescences.

Spiraea japonica cultivar Japanese Dwarf photo in the garden
Japaness Dwarf is a slow-growing dwarf bush up to 30 cm tall. Blooms profusely in mid-summer with pink inflorescences. Ideal on rocky hills, lawns, flower beds.

Spirea Japanese variety Spiraea japonica ‘Crispa’ photo in the garden
Crispa - lilac-pink flowers and wavy-toothed leaves on a spherical bush will decorate any garden.

Spirea planting and care in the open field photo
Among the ornamental shrubs, spirea occupies a special place. She is surprisingly unpretentious and easily forgives the gardener even the most unobtrusive care. A wide variety of shapes and types allows you to choose the plant to decorate the site that will best fit into the surrounding landscape. Planting and caring for a spirea is not difficult, even a novice gardener can handle it.
Spirea: types and varieties
The genus spirea belongs to the pink family and is quite numerous, it includes more than 70 species. The distribution area of this deciduous shrub is wide. It can be found in the northern hemisphere in most climatic zones. Spirea rarely has single flowers, most often they are collected in a corymbose inflorescence, sometimes in a panicle. The color of flowers depends on the flowering time of the species. Plants blooming in spring have white flowers that bloom on last year's shoots, in species blooming in summer pink-crimson gamut prevails, flowers are located on annual growths.

The most common types.
- Medium spirea - an inhabitant of Siberian and Far Eastern forests, a tall shrub - above 2 m with white corymbose flowers that open in May and do not fall for 3 weeks, frost-resistant and drought-resistant, used in landscaping, suitable for northern regions.
- Spiraea birch-leaved - grows in Siberia, from 1 to 2 m in height, white flowers are collected in huge shields - up to 10 cm in diameter, blooms at the end of May and blooms throughout June.
- Spirea crenate - has been used in landscaping for 200 years, there are cultural hybrid varieties. In nature, it is a low shrub, only up to 1 m, blooming at the end of May.Quite large flowers are collected in corymbose inflorescences, due to the large number of long yellow stamens, it seems that they have a golden hue. This type of spirea is drought-resistant and frost-hardy, can be used to strengthen floating soils.
- Spirea St. John's wort is a shrub up to 1 m high, flowering - May-June, white flowers, is used to obtain new forms of the plant.
- Gray spirea - the result of crossing the previous species and whitish-gray spirea, has highly decorative varieties that bloom in spring. The most beloved variety of this species by flower growers is Spirea Grefsheim. The shoots of the tall bush bend towards the ground under the weight of flowers that completely cover the bush. The flowering is so abundant that the leaves are almost invisible.
- Spiraea is oak-leaved - blooms with umbrella-shaped inflorescences of white flowers with a large number of protruding stamens for 25 days, flowering occurs in May-June. The species is used in culture, it tolerates a haircut well.
- Spirea Nipponskaya came to us from Japan - this highly ornamental shrub 1-2 m high is decorated with yellowish-white inflorescence shields that appear in June. It does not differ in frost resistance; in severe winters, the tops of the shoots freeze slightly, but quickly recover. The most famous variety is Snowmound. A huge number of flowers on a bush up to 1.5 m high makes it very decorative at the time of flowering. The width of the bush is 2 times the height.
- No less decorative and spirea Wangutta is a hybrid species that blooms very profusely in June-July with white flowers collected in shields. The bush has an average height and can freeze slightly in frosty winters.
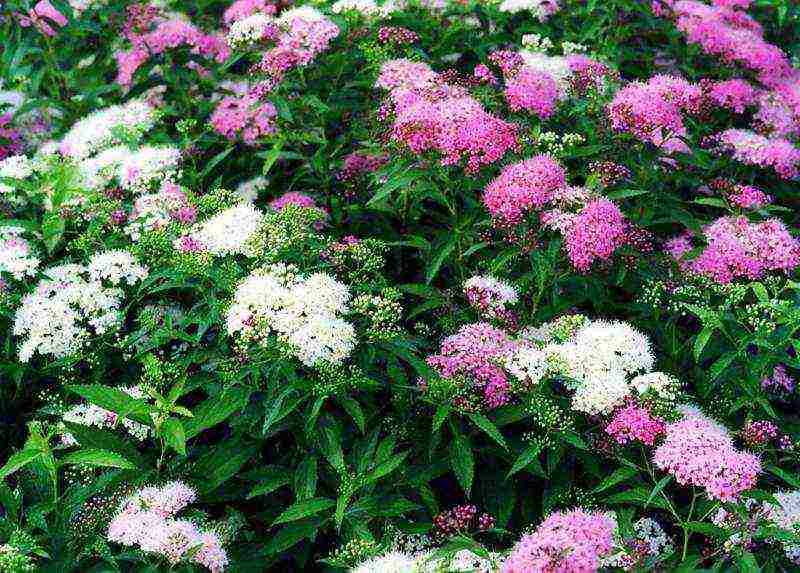
- Japanese spirea is quite thermophilic, but due to the low height of the bush - up to 1 m it winters without loss, covered with snow. The most interesting varieties are Little Princesses and Shirobana. Little princesses - a bush up to 80 cm high and up to 1.2 m wide blooms very profusely in June-July with pink flowers collected in medium-sized shields, grows slowly. Shirobana is a bush up to 0.8 m high and up to 0.6 m wide, blooms in mid-summer. Flowers in corymbose inflorescences have three colors - white, pink and crimson, if you cut off faded inflorescences, new ones will decorate the bush for another month.
- The adorable spirea stands out among other species by double flowering: in June on last year's shoots and in July and August on newly regrown ones. Flowers are collected in complex shields, can be white or pale pink. The species does not differ in frost resistance - up to -18 degrees, so in the middle lane it hibernates under cover.
- Spirea Bumald is a decorative hybrid species, it also has a yellow-leaved form. The bush is low - up to 0.8 m in width and height. It blooms for more than 3 months with bright pink flowers in large shields. The most famous variety is Antoni Vaterer.
- Willow spirea grows wild in Siberia. The tall bush blooms in July and August with bright pink flowers collected in pyramidal panicles.
- Spirea Douglas grows above 2 m. In the second half of summer, it is decorated with pink flowers, collected in a paniculate inflorescence.
- When crossing the previous species and spirea willow leaf we got Billard's spirea. A tall, frost-resistant shrub blooms in the second half of summer and is decorated with large pink paniculate inflorescences until the very frosts.
- The hybrid lilac spirea also blooms for a long time, only paniculate inflorescences, in accordance with the name, have a lilac-pink color. The bush can grow up to 2 m.
Spirea: features of cultivation
Spireas are unpretentious, but with proper careful care they give abundant flowering. Different flowering times dictate different pruning times. Some species and varieties have special soil and maintenance preferences. Most spirits prefer humus-rich, but not heavy soil without stagnant water, but they will feel good even on not very fertile soil. To keep the roots from getting wet, they need drainage. But before you plant a plant, you need to propagate it.
Shrub propagation

Spirea is very easy to propagate. Some species produce root shoots that can be transplanted. Parts of a divided bush take root well. Flexible shoots allow cuttings to be rooted. For propagation of all species, cuttings can be used, and for non-hybrid forms and varieties, seeds can also be sown.
Cuttings
When rooting the cuttings, you will get an exact copy of the parent plant. Green cuttings in early flowering varieties are cut in early June, and in late flowering varieties at the end of the month. For already lignified cuttings, the best rooting time is autumn, September or October.
- The annual green shoot is cut and cut into pieces with 5-6 leaves.
- Remove the bottom pair of leaves, cut the rest by half.
- The lower cut is placed in a vessel with an epin solution for 12 hours.
- It is treated with a powdery root stimulant.
- They are planted in a container with loose soil, sprinkled with a layer of sand at an angle of about 40 degrees to stimulate root formation.
- Cover with foil or glass jar and put in lacy shade under the trees.
- They moisten the soil in the cuttings, preventing it from drying out, and the cuttings themselves are sprayed several times a day.
- In autumn, the container is dropped into the soil, mulched with fallen leaves and covered with a wooden box.
- In the spring, the shelter is removed. After the appearance of young shoots, the plants are planted in the garden in a permanent place.
Seed propagation

In non-hybrid varieties and species, seed germination reaches 80%. Collect them when the boxes turn brown, but have not yet opened. Dose in the room for 2 weeks. You can sow both before winter and in spring. Seeds do not require stratification. Seedlings dive when 2 true leaves are formed. Further care: watering as needed, 2 dressings with full mineral fertilizer. In the fall, seedlings are planted in a seedling bed, and next year in a permanent place. They begin to bloom for 3 years.
Landing in open ground

Proper planting is the key to abundant flowering and plant health. It is very important to maintain the optimal distance between the plants in order to provide them with the necessary nutritional area. When laying a hedge, it is enough to plant spireas 30 cm apart, for a normal planting the distance should be greater, since the bushes grow strongly in width: for tall varieties - about 1 m, for undersized varieties - 0.8 m.
The choice of planting material

Now on sale there are many varieties and hybrids of spirea. The choice of a plant depends, first of all, on what place the spirea will occupy in the landscape design of a particular site. A hedge will require many plants of the same species, it is better if they are tall. As a tapeworm, you can plant an openwork bush with long flowering. On an alpine slide, undersized compact varieties will be appropriate. But whichever variety you choose, the plant should have a developed and healthy root system, consisting of 3 taproots and a well-developed lobe covered with a clay mash. With spring planting, not swollen buds, and with autumn planting, already flown leaves. It is best to choose a container-grown seedling that can be planted throughout the growing season.
How and when to plant?
Spirea is planted in pre-dug holes. Their size should be slightly larger than the root system of the plant. Usually the depth is about 70 cm, 20 of which falls on the drainage of expanded clay or brick fragments. The diameter of the hole is determined by the size of the roots.
Landing Algorithm:
- a plant is placed on a mound of earth poured in a hole, spreading the roots;
- fill up the earth, taking into account that the root collar is strictly at the level of the soil;
- watered in the planting circle using 2 to 3 buckets of water;
- mulch the soil around the bush with a layer of peat 7 cm thick.
Planting time depends on the selected variety: late flowering plants are planted in spring, early flowering ones in autumn, but no later than 3-4 weeks before the onset of frost.
Soil preparation and site

The planting site should be well lit by the sun, a little shading is allowed during the day. It must be remembered that in the shade of the spirea it blooms badly.
This plant is undemanding to the soil. The preferred soil for spirea is light sod or leafy, with a neutral or slightly acidic soil reaction. Heavy clay soils are improved by adding sand and peat, a little clay should be added to light sandy soils. From fertilizers, you can add Art. tablespoons of long-acting ABA fertilizer for each bush. This amount will be enough for the plant for several years.
The nuances of planting in spring, autumn

If the variety blooms in summer, it is better to plant it in spring, early flowering varieties are planted in autumn, but so that the bushes take root before the onset of frost. In both cases, the plants must be dormant. In the spring, the buds should not swell yet, and in the fall the leaf fall should already end.
Outdoor care for spirea
An unpretentious plant does not require special care measures, but top dressing and watering made on time will provide it with maximum decorative effect.
How to water properly?

Spirea is a drought-resistant plant, but in extreme heat and in the absence of rain for a long time, it must be watered. This is especially true for recently planted bushes. For an adult plant, the watering rate is 1.5 buckets per bush. For undersized species and varieties, one bucket is enough. Watering is sufficient once every 2 weeks, well soaking the root layer.
Fertilization and feeding
In order for the spireas to grow and bloom well, they should be fed regularly.

You can choose the following power plan:
- in spring, nitrogen mineral or organic fertilizer; for early flowering varieties, additional feeding with complete mineral fertilizer with microelements is needed;
- in June, plants are fed with full mineral fertilizer;
- at the end of August, fertilizing with phosphorus and potassium salts is needed so that the spireas are better prepared for winter.
At the end of summer, spireas cannot be fed with any fertilizers containing nitrogen, this can provoke the growth of new shoots that do not have time to ripen and freeze in winter.
All dressings can be applied both dry and liquid, combining them with watering. The next day, the soil around the plant must be loosened.
Spirea pruning
It is held on several dates, depending on the destination.
- Spring pruning is sanitary. Only dry and frost-damaged shoots are removed.
- Formative. Spireas blooming in the summer on the shoots of the current year are pruned in the spring immediately after the snow melts, combining formative pruning with sanitary pruning. Thin branches thickening the bush are removed - they will not give a good flowering. Different types of spirea have their own subtleties in pruning. Pruning of Douglas and Boomald spirits begins only in the fourth year of life. Miniature varieties not exceeding 40 cm in height are cut into 2 buds. Cut out shoots with foliage that does not match the color of the variety. After flowering, the seed pods are removed, if there is no need for seeds - this contributes to the re-blooming of the inflorescences. It is enough to cut off a third of the shoot. The green hedge is trimmed to give the desired shape. Spring-flowering spireas form after flowering, cutting off shoots at the level of a strong young growth. The crown of the bush should be symmetrical.
- Anti-aging pruning. It is carried out in adult bushes, starting from the 7th year of life. All old shoots are removed, leaving no more than 5-7 young ones, while maintaining the symmetry of the bush. This pruning is best done in several stages, so as not to greatly weaken the bush.
Preparing for winter
The first wintering at a recently planted bush is a serious test. But adult plants, despite the frost resistance of most varieties, and species also need preparation for winter.For many of them, it is enough to feed the plants in August with potash and phosphorus fertilizers, to carry out moisture-charging irrigation after leaf fall and to mulch the trunk circle with humus.

For less frost-resistant varieties, you will have to build a shelter:
- tie the branches into a bunch;
- bend the beam to the ground, fixing it with special fasteners;
- fall asleep with dry leaves;
- additionally throw in snow.
Plant diseases and pests
Spiraea rarely suffers from disease, but in a damp summer it can be damaged by powdery mildew and gray mold. To eliminate them, copper-containing fungicides, Fitosporin, colloidal sulfur are used.

Among the most common pests are aphids, blue meadow sawfly, whitefly and spider mites. Insecticides are effective against the first three: Fitoverm, Actellik. Insectoacaricides are suitable against the tick: Metaphos.
The nuances of growing in Siberia, the Urals, in the Moscow region
Almost all varieties and types of spirea are suitable for growing in central Russia. Shrubs such as Japanese Spirea and Nippon Spirea need additional winter shelter.

In the Urals, the climate is more severe. In its southern part, almost all types of spirits will grow well. In the middle lane and, especially in the north, frost-resistant shrubs should be preferred. The same can be said for spirea in Siberia. Only undersized varieties are able to overwinter under the snow without much loss. If medium and tall plants are not covered, then constant frosting in winter is guaranteed to them, decorativeness and abundant flowering cannot be achieved in such conditions.
Correctly selected varieties of spirea are able to create a flowering conveyor throughout the growing season and will be a real decoration of any garden.
Spirea, otherwise mistakenly called meadowsweet, is a perennial shrub. Currently, breeders have bred about a hundred species of spirea.
The plant is distinguished by its hardiness and the ability to adapt to any conditions in the open field. For Japanese spirea, it is enough to be in the open sun for only four hours to feel good in the ground. In appearance, it is a bush with a hemispherical crown. Some of its varieties have a lush crown, others - disheveled.

How and when does the spirea plant
Planting a bush in open ground is carried out either in early autumn, or at the very beginning of spring. Planting time usually depends on the selected bush variety. If the variety begins to bloom in the spring, then it is advisable to move it into open ground in the fall. If in the summer, then it is better if the spirea is planted in the spring. It is important to consider that flowering after planting in the soil occurs only after three years. Japanese spirea begins to bloom in July.
Usually, seedlings are purchased to decorate the site. Before planting in open ground, they must be carefully prepared.
First, you should check the root system of the future bush. Long roots are slightly pruned, damaged ones are removed. Secondly, you need to cut the stem by a third.
If you purchased a seedling for planting, the root system of which is closed, it is taken out of the container and watered well with water. If the clod of earth around the roots is very dense, then it is also soaked in water for about two hours. Only then can the seedling be moved into open ground.
Although spiraea is considered an unpretentious plant, you still need to choose the right place for planting.
Only then will she delight you with lush and bright flowering. The shrub loves the sun and loose fertile soil. With a clay composition of the soil, it is best to create a brick-sand drainage, the height of which will be 15 cm.
To create a beautiful landscape design, the spirea can be planted along the entire perimeter as a hedge. In this case, the distance from bush to bush must be at least 50 cm.
After you dug a hole, it needs to stand for a day before planting.Then a mixture of peat, turf and sand is introduced into it. The plant is planted in open ground, spreading the roots, and sprinkled with earth along the root collar. After that it is watered and mulched with peat.

Spirea care
When the planting of Japanese spirea in open ground is over, you just have to take care of the development of the bush in time. Care consists in watering.
This plant, being blooming in summer, needs more abundant watering than the spirea species that bloom early.
Care also includes fertilization. The shrub is fed no more than three times a season, although it is usually fertilized only twice. For feeding, it is best to use mineral complexes. You can also resort to the following fertilizer recipe: take 10 liters of liquid manure, 60 liters of water and just 10 grams of superphosphate.
Spirea care includes pruning. If the plant blooms in summer, then you need to cut it off in early spring.
If your shrub blooms in the spring, then prune it immediately after flowering.
Some gardeners say that Japanese spirea does not require pruning. On the one hand, this is true: even without cutting, it will bloom beautifully. On the other hand, the lack of such care can lead to her sloppy appearance.

To cut the plant correctly, you need to take into account the timing of the inception of its buds. There are two groups of shrubs. In the first, they are laid directly in the year of flowering, and in the second, in the previous year.
Japanese spirea varieties belong to the first group. It should be cut after a few years, thus rejuvenating the bush. Without this care, the old stems will tilt the entire bush down after a while, and the top of the Japanese spirea will dry out. It is a practice to completely cut off the top of the bush after four years of flowering.

If you nevertheless acquired the types of spiraea of the second group, and these include wangutta spirea, long-bud and nippon, old shoots should be removed after seven years. Frozen branches are cut annually. Plants of this group have many shoots.
Japanese spirea tolerates frost well, so it does not need additional shelter for the winter in a temperate climate. And yet, in severe frosts, it can lose two-year-old shoots. Therefore, for the winter in northern latitudes, it is bent to the ground and covered with a layer of dry leaves. It is also better to protect species that were planted in the fall from winter cold. Some varieties can easily tolerate frosts of -50 degrees. But if your garden is located in an area where winters are very harsh, varieties such as jagged or white, it is better to still cover. They are less cold-resistant. There are types of spirea that can not only freeze branches, but also die in frosts of about -45 degrees. These include spiraea wangutta or Douglas. Therefore, it is better not to acquire these varieties at all for cultivation in northern latitudes.

Reproduction of the spirea bush
The plant can be propagated using seeds, cuttings or cuttings. The seed method is only suitable for non-hybrid varieties.
If you try to plant a seed of a hybrid in open ground, then the appearance of the plant will resemble the mother's very distantly.
Seeds are planted in the spring. It is important to prepare a place for the seed before planting. To do this, take a mixture of leafy earth and peat, moisten it, put a seed and mulch the soil. You will notice shoots within 10 days. So that they are not struck by the fungus, they use foundation treatment.
When propagated by seeds in the first year after germination, the plant will form only one shoot. Two months after planting, the spirea needs to be dived: removed from the soil, shortened the root system and planted again in open ground.
In one year, the shrub grows up to ten centimeters, but it will begin to bloom only after at least three years.
For propagation by cuttings, you need to take green cuttings or shoots in which lignification has occurred halfway. If you have chosen an early variety of spirea, it should be grafted in early summer. Reproduction of Japanese spirea using cuttings is best done in July.
After you have received the cutting, you should plant it in a mixture of river sand and peat. It should be watered five times a day. And in the room in which the planting material is located, you need to create high humidity. The stalk dives in the spring.
Before flowering, the plant is propagated by layering. To do this, the branches, concentrated along the perimeter, are bent to the bottom and sprinkled with soil. With regular watering, more plant bushes will appear in the fall. For a successful overwintering, the layers are sprinkled with leaves. And in the spring they can already be planted separately.

Varieties of spirea and their varieties
Despite the popularity of Japanese spirea, you can pay attention to its other types.
Early bushes include spiraea wangutta, gray, arguta, nipponskaya.
Gray spirea is actually white, but so named because of the grayish tint of the leaves. It is a hybrid of two varieties. The height of the bush usually reaches 180 cm. Flowering begins in mid-May and ends in mid-June. It is very popular among gardeners. Especially her variety "Grefsheim", the crown diameter of which reaches two meters. White flowers are collected in umbrellas and reach a centimeter in diameter.
Spirea wangutta grows up to two meters. This is also the diameter of the crown. The dark green leaves are bluish on the underside, and by autumn they acquire a beautiful orange tint. White flowers cover the entire branch. The variety begins to bloom in June, and may recur in August.
Spiraea wangutta of the Pink Ice variety looks great on the garden plot.
Usually this variety is used as a hedge.
Spirea nipponskaya is also considered a tall shrub, reaching a height of two meters.
It is noteworthy that even in autumn its leaves retain their green color.
Its flowers also differ in shade: they are not white, but yellow-green. They are purple inside the bud.
A variety of argut gained popularity due to its beautifully shaped two-meter bush. Its branches spread out so that from the side it looks like a waterfall. A lot of white flowers are formed on the branches, exuding a pleasant aroma.
Summer-flowering varieties include Japanese spirea, Douglas, Bouvald, willow, Bullard. Usually the flowers of these shrubs have a pink tint. Among the summer-flowering varieties, it is the varieties of Japanese spirea that are especially popular.
Japanese spirea reaches one and a half meters in height, although it can grow up to a meter.
Its leaves are also gray-gray underneath. In autumn, they change color, becoming red-yellow. It is noteworthy that Japanese spirea blooms for about 45 days.
Among its varieties, five can be distinguished, which are especially loved by landscape designers and gardeners.
"Little princesses" is a Japanese spirea that grows a little more than half a meter. Small and diameter of its crown with reddish pink flowers. But their diameter is more than three centimeters. The variety grows slowly.
"Golden princesses" - a variety of Japanese spirea differs from the previous one only in the yellow color of the flowers and the height of the bush in a meter.
Among the low varieties of Japanese spirea, "Shirobana" is noted, which grows up to 60 cm. It has small pink flowers, the diameter of which is two centimeters.
"Goldflame" is a kind of Japanese spirea, the height of which is 80 cm. The flowers are red with a shade of pink. By autumn, the leaves change color to crimson.
"Crispa" is a Japanese spirea, reaching 50 cm. It has a spherical crown. Its inflorescences do not hang down, but are directed upwards. The diameter of pink flowers with a lilac shade is about six centimeters. This variety can bloom for two months.
Another type of shrub that blooms in summer is Boomald's spirea.
This hybrid is based on Japanese and white-flowered spirea. In height, it can be either 50 cm or 80 cm. The shade of flowers is light pink or dark red. By autumn, the leaves change color from green to picturesque orange, yellow and purple.
One of the most famous of its varieties is "Goldflame". It differs in that its leaves have an orange tint, which turns red in autumn. However, if the location of the bush is in the shade, then the leaves will be green.
The willow spirea is also distinguished by shoots that grow upward. Long inflorescences have a pink tint.
The Douglas variety has small green leaves and dark pink flowers. The inflorescences are shaped like a pyramid. The plant pleases with flowering for about one and a half months.
Spirea Billard is a hybrid of the latter two varieties. Grows up to two meters. The leaves are small, and the bright pink flowers gather in long pyramidal inflorescences.

Shrub in landscape design
The advantages of spirea are that different varieties of it bloom at different times. So, if you wish, you can ensure that its bushes will bloom from spring to autumn. Moreover, the shade of flowers will beautifully shimmer from white to pink.
Plant species have their own special functionality, well known to designers. For single landings, the Wangutta, Douglas or sharp-toothed spirea is best suited. Their arched shoots are able to create a beautiful bush shape.
Its low types are suitable for registration of the edging planting. Such spireas will look great in green-leaved compositions, especially if their shoots have a reddish tint, and the flowers are red in color. They are also perfect for decorating rock gardens and rockeries. It is interesting to note that it is the undersized varieties that are the owners of a wide root system, which seems to be drawing on the ground. It is worth noting that in addition to its decorative properties, spirea can be called a healing plant: it cleans the air well.



