Content
- 1 How is it correct: mock orange or garden jasmine?
- 2 Chubushnik: planting in open ground
- 3 Chubushnik transplant
- 4 Chubushnik: outdoor care in spring, summer and autumn
- 5 Bloom
- 6 Correct pruning of chubushnik: in spring, after flowering, in autumn
- 7 Preparing for the winter chubushnik
- 8 Pests and diseases
- 9 How to plant a chubushnik
- 10 How to care for a chubushnik in the garden
- 11 What, how and when to feed the chubushnik
- 12 How to water a chubushnik
- 13 How to prune a mock orange after flowering
- 14 How to propagate a chubushnik
- 15 How to transplant garden jasmine mock-orange
- 16 Why the mock-orange does not bloom Pests and diseases
- 17 How to care for jasmine in autumn and winter
- 18 Chubushnik in landscape design
- 19 Types of chubushnik with description and photo
- 20 In what conditions can different varieties of mock-orange grow?
- 21 Landing rules in a suburban area
- 22 Reproduction of mock-orange by seeds and cuttings
- 23 How to provide proper care?
- 24 Pruning as an important part of caring for a chubushnik
- 25 1 Chubushnik: botanical description
- 26 2 Varieties and types
- 27 3 Outdoor cultivation
- 28 4 Landing rules
- 29 5 Plant care
- 30 6 Reproduction
We will tell you the rules for planting and caring for a mock-orange in the open field. We describe in detail when and how best to plant garden jasmine.
We consider caring for a plant in the garden: watering, feeding, pruning, flowering, preparing for winter, as well as diseases and pests.
How is it correct: mock orange or garden jasmine?
Chubushnik belongs to the Hortensia family, and jasmine belongs to the Olive family. At the same time, the shrubs are quite similar to each other, especially with a sweet and strong aroma, which is why confusion arises.
In Russia and the CIS countries, chubushnik is often called garden jasmine, but real jasmine is a thermophilic plant (subtropical zone) and freezes in harsh climates. Some of its species are successfully grown here at home or in greenhouses (Indian, sambac, etc.).
Our planting guidelines and outdoor care tips are designed for the chubushnik or the popular “garden jasmine”.
- These names are used in the article as synonyms, since under these names one and the same plant is hidden.
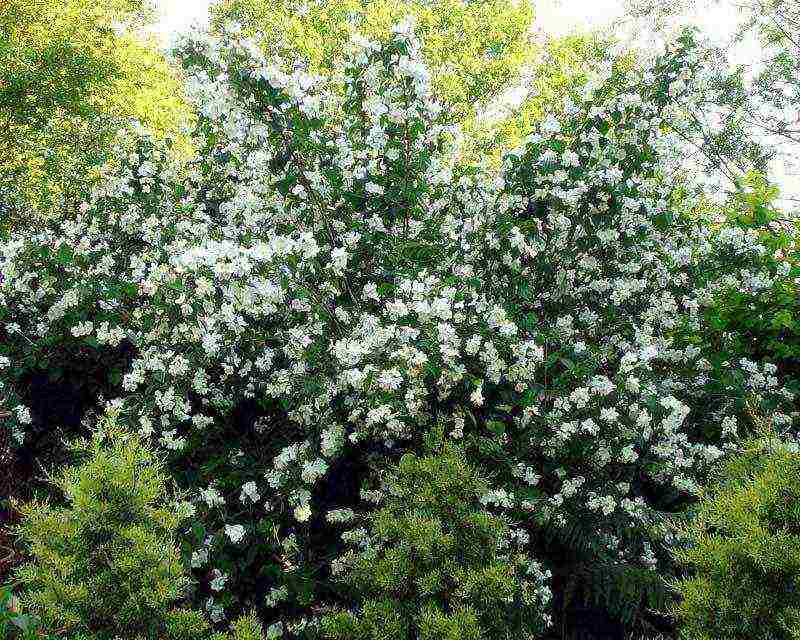
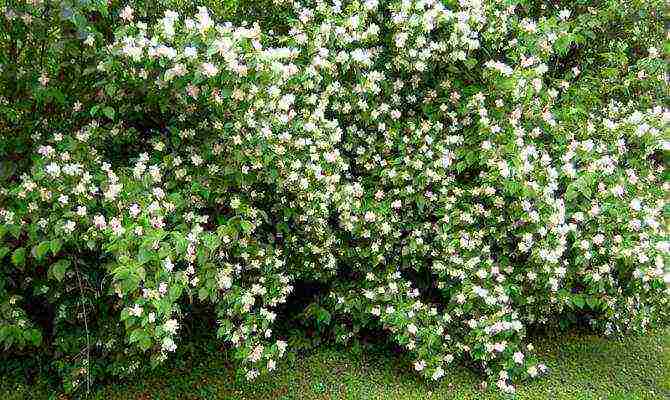
In Russian gardens, the most often cultivated mock-orange (ordinary), virginal, hybrid winter-hardy varieties of Lemoine mock-orange and Nikolai Kuzmich's Vekhov selection.
 Chubushnik "Snow storm"
Chubushnik "Snow storm"
Chubushnik: planting in open ground
For the excellent development and flowering of a plant, the planting site, soil and soil mixture, planting distance and planting depth play an important role.
This is a kind of foundation that provides comfortable conditions for growing chubushnik in the open field for the next 25-35 years.
Pick-up location
The plant is best suited to a quiet place that should be well lit, especially in the first half of the day, but light partial shade at noon is also allowed. It is best to plant chubushnik on the south, south-east and south-west side.
Garden jasmine is able to grow in the shade, but in this case flowering will be much weaker, it will stretch out and acquire a less beautiful appearance.
Do not plant shrubs in places where rain or melt water accumulates, as well as where groundwater is closer than 150 cm from the surface of the earth.
Soil and acidity
Chubushnik loves fertile land with high air and moisture permeability. It is well suited to light and medium loamy soils rich in humus. At the same time, garden jasmine is able to grow in poor soil, but then the development and flowering of the bush will be weaker.
Heavy clayey soils are poorly suited; in this case, more powerful drainage and a lighter soil mixture are needed. On sandy loam soils, on the contrary, you can do without drainage, and it is better to replace part of the sand with garden soil.
The optimum level of soil acidity for mock-orange is pH 6.5-7.5 (close to neutral).
Soil mix
Substrate options for garden jasmine.
- Leafy land, humus, sod (garden) land, peat in equal parts is a universal option.
- Sod (garden) soil, humus (compost) and sand - 3: 2: 1. Well suited for clay soils and chernozem.
- Humus, chernozem - 1: 1. Preferred for sandy soils.
- It is advisable to add one glass of wood ash or two tablespoons of superphosphate to any soil substrate.
Landing distance
Large shrubs and trees - 2.5-3 m
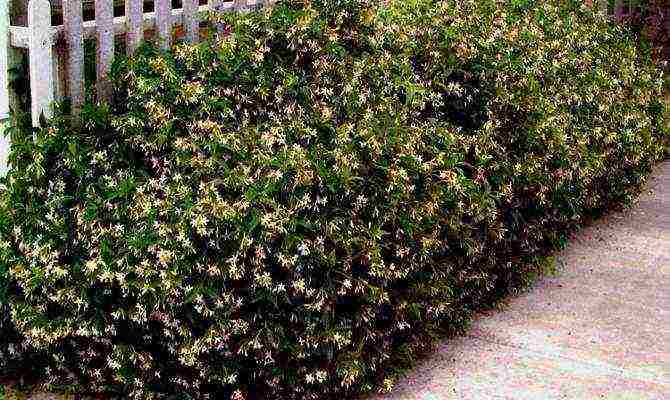
 Chubushnik hedge
Chubushnik hedge
Planting depth
When planting, the root collar of the seedling should be approximately at ground level. The maximum depth is 2-3 cm, otherwise there is a high risk of developing rot.
How to plant garden jasmine correctly? Instructions
- Dig a planting hole: depth and width - 50-60 cm. At the bottom of the hole, make a 10-15 cm drainage layer of rubble, gravel or sand.
- Sprinkle in some potting mix. Place the seedling in the center of the hole so that the base of the bush is about level with the ground.
- Gradually fill the planting hole with soil mixture and compact it so that there are no voids.
- Trim all shoots about 30% of their length (a couple of buds to a strong bud). Pour 10-15 liters of water into the tree trunk circle. Pour a 3-4 cm layer of peat, bark or sawdust on top to keep the root ball moist longer.
Rules and Tips
- Plant a chubushnik in cloudy weather or in the evening so that it takes root better.
- It is advisable to dig the planting hole and fill it with soil mixture 3-4 weeks before planting.
- If the seedling has damaged roots, remove them and treat the cut with charcoal powder.
When is it better to plant a mock-orange in spring or autumn?
Garden jasmine is best planted in spring (April) or autumn (September - October).
A seedling with an open root system can be planted only in the spring before the leaves bloom, otherwise it will die, and in the fall from September 10 to October 15. Seedlings in containers can be planted throughout the growing season.
These dates for planting a mock-orange are also suitable for gardeners of the Moscow region, the Leningrad region, the Urals and Siberia.
 Chubushnik sapling in a container for planting in open ground
Chubushnik sapling in a container for planting in open ground
Chubushnik transplant
The garden jasmine shrub is relatively easy to transplant at any age. The optimal time for transplanting adult bushes is from late August to mid-October, but it is also possible in spring in April.
- Water the chubushnik abundantly the day before digging to make it easier to move with a clod of earth, and it will stock up on nutrients.
- Cut off young shoots of the current year (autumn) or last year by 30-40% (spring).
- Carefully dig out the bush, plant it together with a lump of earth in a new place and pour 10-15 liters of water.
Chubushnik: outdoor care in spring, summer and autumn
The shrub is quite unpretentious to care for, drought-resistant and hardy to unfavorable external factors.
However, to get the maximum decorative effect, garden jasmine must be properly cared for.
Watering
Moisture is of great importance for a chubushnik. With its lack, the bush may not bloom. Water your garden jasmine regularly, especially in hot and dry weather, to prevent the leaves from drooping (loss of turgor).
The maximum demand for moisture is from April to July, when the bush is actively growing, preparing for flowering and blooming. During this time, water approximately every 7-12 days with 15-30 liters of water.
We recommend reading: «WHAT WATER IS BETTER TO WATER PLANTS?»
In the spring, before flowering, it is advisable to spray the shrub with warm and soft water. For young plants, it is useful to add growth stimulants to the water ("Zircon", "Epin Extra" and others).
After the first watering in the spring, mulch the near-stem circle with a 3-4 cm layer of peat to retain moisture in the soil.
Loosening the soil
During the spring - summer, it is necessary to loosen the ground 2-4 times by 4-6 cm in depth. Also, remove weeds in a timely manner - they take away macro- and microelements from the chubushnik.
Top dressing and fertilizers
For the first two years after planting, there is no need to feed the chubushnik with mineral fertilizers. Garden jasmine needs additional nutrients for abundant and lush flowering.
- In early April (before the leaves bloom), dissolve 15 grams of carbamide (urea), 15 grams of potassium sulfate and 30 grams of superphosphate in 10 liters of water and pour over the bush. Or pour the plant with mullein infusion - 1:10.
- After 3-4 weeks (beginning - mid-May), repeat the feeding.
- Immediately after flowering, scatter 20-25 g of superphosphate (1 tbsp. Spoon) and 10-15 g of potassium sulfate per 1 m2 over the surface of the earth.
2nd option
- Before flowering (late April - early May), scatter two tablespoons of nitrophoska and a glass of wood ash over the surface.
- During flowering and immediately after it, pour the solution: for 10 liters of water, 20-25 grams of superphosphate (1 tbsp. Spoon) and 10-15 grams of potassium.
Tips
Instead of mineral fertilizers during and after flowering, wood ash can be used. To do this, pour a glass of ash with 10 liters of water and leave for two days, and then pour the shrub into the trunk circle.
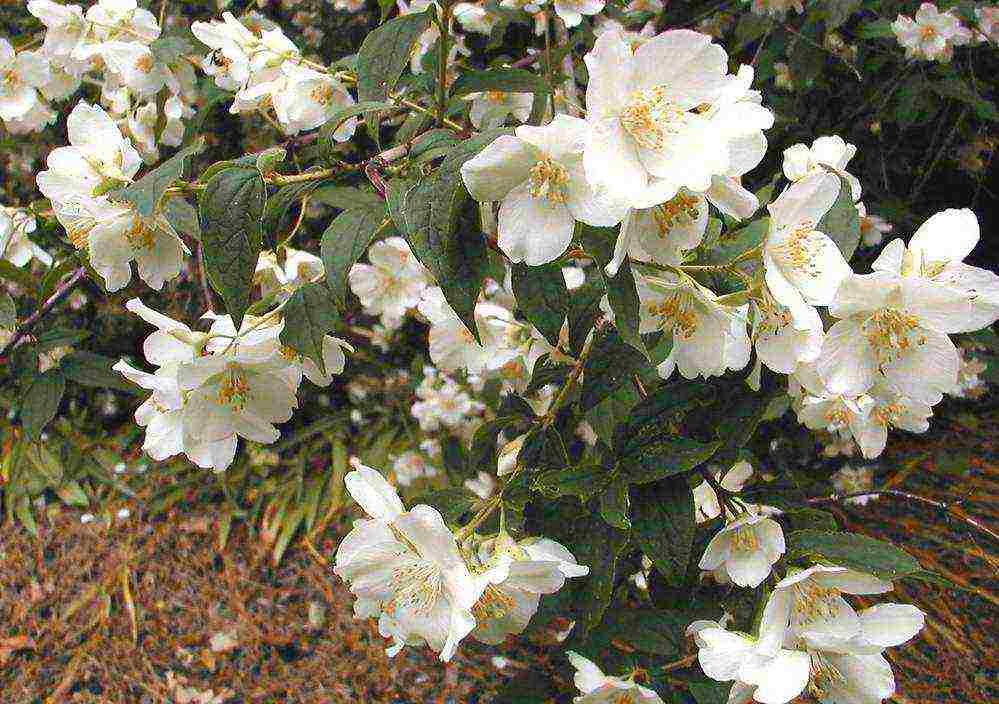
Bloom
Garden jasmine is most attractive when fragrant flowers open up. It is for its pleasant, sweetish and powerful aroma that most flower growers love it.
The smell of chubushnik has a beneficial effect on the human psyche and raises the mood. The plant usually blooms in the 3rd year after planting.
Blossom time
The flowering period of garden jasmine depends on its type and variety. In the conditions of the Moscow region, the crown mock-orange and garden forms based on it are the first to bloom: golden (aureus), dwarf and variegated. They bloom almost immediately after common lilac (the beginning of June).
In the first two weeks of June, the small-leaved, thin-leaved mock-orange, Shrenka, blooms. In early - mid-July, odorless, grayish, broad-leaved and fluffy mock-orange begins to bloom (it blooms later than everyone else).
The duration of flowering is on average 20-25 days, in a shady place a little longer. Schrenk's mock-orange blooms the longest, and, for example, Gordon's mock-orange is able to bloom a second time in the fall.
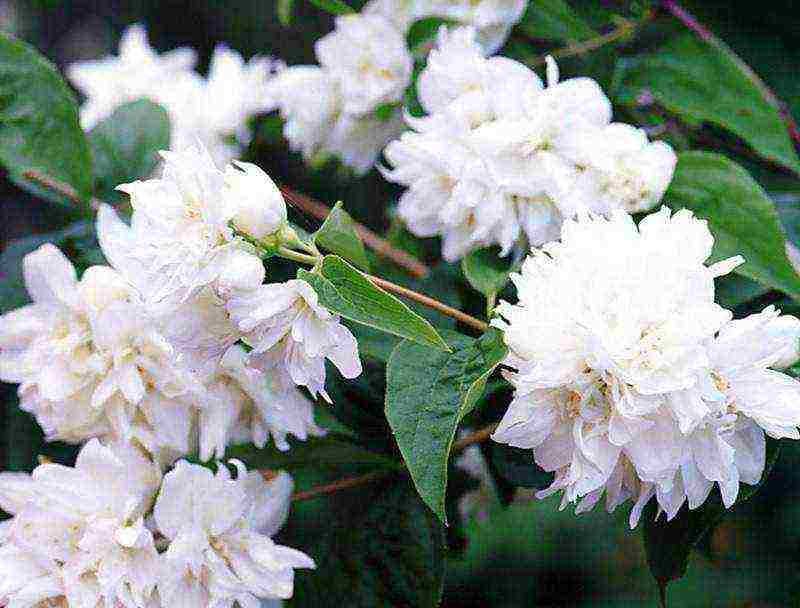
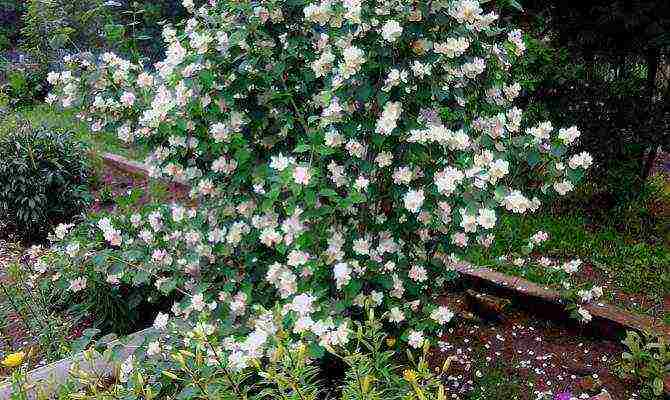
 Chubushnik "Zoya Kosmodemyanskaya"
Chubushnik "Zoya Kosmodemyanskaya"
Why is the mock-orange not blooming? What to do?
Garden jasmine may not bloom in some situations. The most common reasons: lack of light (grows in the shade), lack of moisture or nutrients (watering, feeding), unsuccessful wintering (freezing of annual shoots), excessive pruning in the spring or too deep planting.
Perhaps the mock orange does not bloom due to its age, especially if you grew it from seeds (7-8th year) or from cuttings (4-5th year).
Correct pruning of chubushnik: in spring, after flowering, in autumn
Garden jasmine needs annual pruning to form a decorative crown shape, especially vigorous species and varieties. Otherwise, it will thicken with young shoots and grow ugly.
Sanitary pruning in spring
Before the buds awaken (late March - early April), remove weak and damaged shoots growing inside the bush. If you wish, you can shorten some of the strongest branches, but proceed with caution as over-pruning can result in no flowering this year.
Sanitary pruning can be done at any time of the year. The full formation of the crown of the bush will be performed after the mock-orange has faded.
Anti-aging pruning
About once every 2-4 years, it is necessary to rejuvenate the plant. In the early vein at the garden jasmine, cut off all shoots older than 10-12 years old at the very base of the bush ("on a stump").
Due to such pruning, the crown of the garden jasmine will rejuvenate and stimulate powerful flowering and growth. New strong shoots will bloom next summer.
"Refreshing" an old bush
A very old or neglected bush is easier to rejuvenate by cardinal pruning.
- At the end of April, cut down all the trunks at ground level, and cut 3-4 of the healthiest ones at a height of 35-40 cm. Treat the cuts with garden pitch, and spread a 4-5 cm layer of humus around the bush and dig a little soil (6-8 cm) ...
- Water the chubushnik regularly and abundantly in the summer. It is also advisable to feed the mullein infusion 1-2 times.
- In the fall, new shoots from dormant buds will appear, but in the spring, 3-4 of the strongest ones will need to be left, and the rest will be completely removed. These most developed shoots are the basis of a young shrub.
Formative pruning of chubushnik after flowering
Formative pruning of garden jasmine is best done immediately after flowering (mid-June) so as not to disturb flowering, as it blooms on last year's shoots.
- First, remove any faded buds. If pruning was not done in the spring or there is a need, then completely remove all weak and damaged branches.
- Then cut the shoots of the current year to the last year's growth (green section of the branch to the lignified part).
By October, a new growth with lateral shoots will have time to appear on these branches, on which flowers will appear next spring.
If you want to reduce the height of the bush, then cut off all or the longest shoots below the growth zone. - Also prune 4-5 year old shoots growing inward and bare, weakly flowering, to thin it out. And if the bush is very thick, then cut off 20-25% of the old trunks at the base.
Pruning chubushnik in autumn
You cannot prune young shoots of garden jasmine in the fall if you want it to bloom next year. In autumn, if necessary, you can carry out sanitary pruning and thinning of the bush (growing inward and weak shoots).
Preparing for the winter chubushnik
Most varieties of the plant are distinguished by good winter hardiness, especially of domestic selection. Adult chubushnik bushes do not need winter shelter, and it is advisable to mulch specimens up to 2 years old with a 4-5 cm layer of peat or pine needles.
If the tops of annual shoots freeze in an adult garden jasmine in winter, it will still bloom, and by pruning in the spring it is easy to restore the crown of the bush.
In the conditions of the Moscow region, the Leningrad region, Siberia and the Urals, it is better to plant winter-hardy varieties.
Pests and diseases
Chubushnik is rarely affected by pests or diseases, but it is important to regularly inspect the shrub for their presence.
The most common pests: weevil, mealybug, spider mite, aphid, scale insect and false scale insect... Aphids are especially common on young overgrowth leaves.
Interesting to know
You can make honey from the nectar of the chubushnik. This honey improves sleep, helps relieve fatigue and headaches.
The plant got its name due to the peculiarity of the structure of the stems from which the mouthpieces and shafts for a smoking pipe were made.
ADDITIONS TO THE ARTICLE:
one.HOW BETTER TO REPRODUCT THE CHUBUSHNIK? + VIDEO
2. POPULAR VARIETIES OF CHUBUSHNIK WITH PHOTOS - REVIEW!
3. HOW TO CARE FOR JASMINE IN HOME CONDITIONS?
We wish you a successful planting, easy care of the chubushnik in the garden, and enjoy its wonderful flowering!
Chubushnik Philadelphus from the Hortensiev family can be found almost throughout the entire territory of the Earth in the northern hemisphere, although Greece is considered to be its homeland. The origin of the name of the shrub is even more interesting and it is associated with the Greek province.
Local residents have mastered the craft of making smoking pipes, and by the name of the province - chubuk. And although with such a shrub as jasmine, the chubushnik has a similarity only in visual indicators, gardeners do not want to give up their erroneous opinion, continuing to call the chubushnik jasmine.
How to plant a chubushnik

How to plant a chubushnik photo
So that the shrub can show all its beauty, first of all, they determine a suitable place for it.
If the selected area is swampy and shady, he is unlikely to like it.
In such conditions, the shrub will stretch strongly in search of sunlight, postpone the flowering period.
And in the worst case, it will disappear from excess moisture. Therefore, it is so important to select a place on the sunny side of the site, with soil without signs of waterlogging.
Recommendations for planting garden jasmine:
- You need to start by preparing a pit for a garden jasmine. Its size depends entirely on the volume of the root of the bush. Usually small shrubs are planted, for which a 60 x 60 x 60 pit is considered the most suitable.
- If you are thinking of planting a chubushnik as an element of a hedge or in a composition with other ornamental shrubs, you cannot ignore such an indicator as the maximum size of a jasmine crown. When planting a plant to create a hedge, the distance between the bushes is maintained at a size of 0.7 m.When a composite planting, this figure doubles and is 1.5 meters.
- Before you start planting a plant, you need to start preparing the soil. It should contain 1 share of sand, 2 shares of humus and 3 shares of leafy soil. Before planting the plant, you should dig it in with prepared earth so that the roots do not wind up. It is also important to take care of the drainage, the height of which from the bottom of the pit must be at least 15 cm.
- When planting a chubushnik, they carefully monitor the root collar. It shouldn't be too deep. The depth limit of the root collar is 2 cm from the surface. If you ignore this condition, jasmine can die from its decay.
How to care for a chubushnik in the garden
Garden jasmine does not require a scrupulous attitude towards itself. One has only to give him the very minimum of time, as he will thank him with even more lush flowering. We will explain in more detail below.
What, how and when to feed the chubushnik
Only once a year, in late spring, one bucket of diluted slurry infusion is introduced under the jasmine bush. To do this, take 1 part of the slurry and 10 parts of water. Starting from the second year, in addition to manure, fertilizing with mineral fertilizers is connected.
It includes:
- urea, in the amount of 15 g,
- potassium sulfate - 15 gr
- and superphosphate in the amount of 20 grams.
All these components are bred in a bucket of water, which is enough to feed 2 adult plants. This procedure is recommended to be carried out annually with the beginning of the growing season, in the spring. After flowering jasmine, urea is excluded from the top dressing, while wood ash is added.
In a bucket of water they dilute:
- 15 grams of potassium sulfate,
- 30 gr superphosphate, wood ash 100 gr.
- This solution is enough for 1 m² of land.
How to water a chubushnik
During planting, 10 to 20 liters of water is poured under the bush, depending on the size of the bush. Then another 30 liters of water is distributed to water the plant in the first 2 summer months.
Garden jasmine has enough moisture that gets into the ground with precipitation and morning dew. Only in dry periods is it sometimes worth watering the shrub abundantly, but without stagnant water.
How to prune a mock orange after flowering
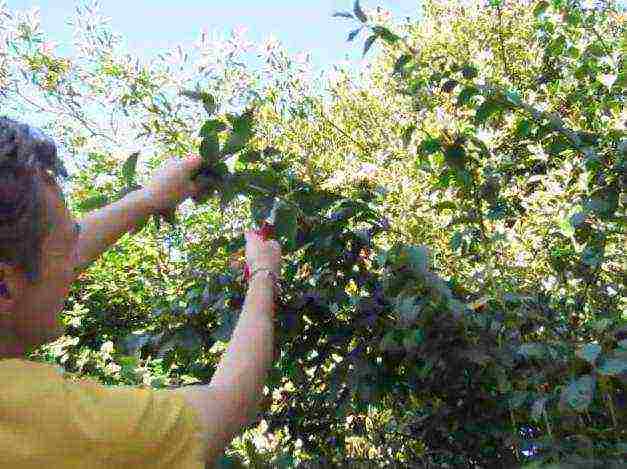

How to cut a mock orange after flowering photo
Even at the very beginning, before planting, it is necessary to inspect the bush, remove all branches that interfere with
the formation of a beautiful crown. Leave branches with two to three healthy buds at the base of the bush. The rest must be removed.
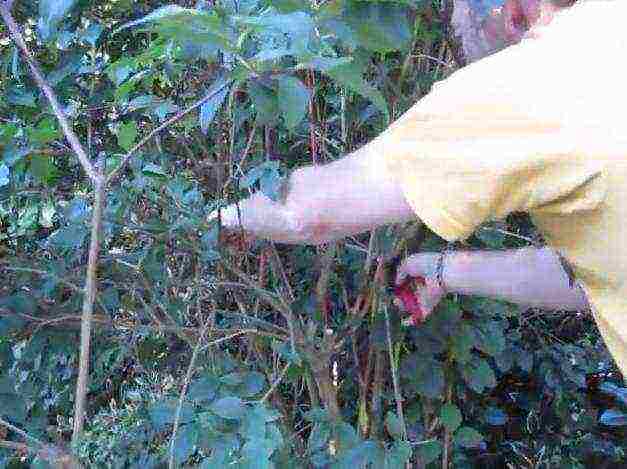

Pruning mock orange after flowering photo
A year later, after the chubushnik has faded, the bush is examined. This is done in order to eliminate weak branches and those that have undergone a degenerative process. They are removed until the start of growth. In the third year and subsequent (after flowering) branches are cut off to part of the growth, on which flowering was observed. If the rules for pruning are violated during sanitary cutting of the bush, up to 25% of dead and old branches are removed. Each subsequent year, it will be easier to prune and form the crown of the jasmine bush.
Jasmine crop video:
How to propagate a chubushnik
For reproduction, plants use one of the 4 proposed methods:
- dividing the bush
- layering
- cuttings
- seeds
The plant tolerates any kind of reproduction well and gardeners do not have difficulties with this. When choosing this or that method, you need to know that using the seed of a bush for breeding, the flowering of jasmine can be observed only 3 years after planting.
Reproduction of mock-orange by cuttings

Chubushnik cuttings photo
There are several ways to propagate chubushnik by cuttings:
- using annual cuttings cut in early spring, before the beginning of the growing season;
- using cuttings cut in the fall.
- green cuttings.
Further actions will depend on which cuttings are used for transplanting.
How to root cuttings cut in the fall
- Cut cuttings are stored until spring. To do this, use the basement, where
zero temperature is maintained. - With the onset of spring, prepared cuttings are placed in pits with sandy soil. In this case, a pair of upper buds should remain above the ground.
- A full-fledged root will be formed by autumn.
- The next spring, when the stalk is out of dormancy, it is pruned. They do this in order to give a course to the development of young growth.
- In the fall, an already fully formed young bush is transplanted to a permanent place specially designated for it.
How to root cuttings of garden jasmine cut in spring video
- Cuttings are cut only from the healthiest and strongest branches. As for their length, approximately 6 - 8 centimeters is quite enough. Each cut should have a pair of leaves and an internode.
- To form a root in such a cutting, it is placed in greenhouse conditions, planted in prepared soil rich in humus, turf and sand.
- Deepening of the cutting - 1 cm.
- After planting, the cutting is sprayed several times a day. They do this so that it takes root faster. Approximately, the rooting period of the cuttings is 2 - 2.5 months.
- Hardening of a young plant is one of the important stages after the rooting of the cuttings. To do this, they begin to open the doors of the greenhouse in the evening. For the winter, hardened, with a formed root system, cuttings are dropped in the open field from the leeward side.
The cuttings are transplanted to a temporary place by May, and the plant can count on a permanent place of growth only after three years.
Reproduction of chubushnik by layering
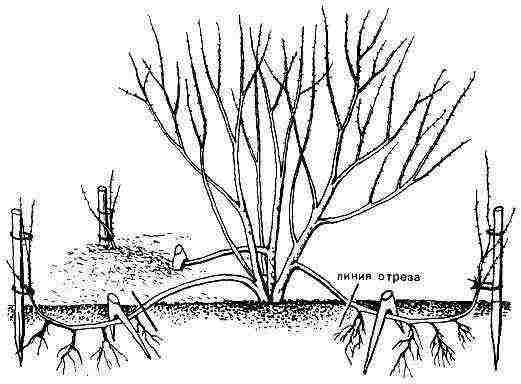
How to propagate a chubushnik by layering
In order for the process of reproduction of the mock-mushroom to be successful by the layering method, the most beautiful and healthy bushes are selected in advance, cutting them to the ground in the spring. Instead of old branches during the growing season, young flexible and pliable shoots will begin to emerge.
The next spring, before the first leaves appear, a bundle of wire is applied to the flexible stem at a distance of 1 cm to the lower bud. After thickening, the stem takes root. They become part of a single root system of a new bush. As soon as the first signs of stem rooting appear, it is tilted and sprinkled with nutritious soil.
During the season, they spud a couple of times and do not forget about watering. You should start separating this stem of the mock-orange only with the onset of the calendar autumn. Make sure that it is well rooted and has new shoots. It is better not to transplant it immediately to a new place, but to arrange it on a temporary bed so that it becomes strong and hardy. In a couple of years, the chubushnik will be ready for transplantation to a new (permanent) place.
How to propagate garden jasmine by dividing a bush

Reproduction of chubushnik by dividing the bush photo
Large jasmine bushes cannot be handled with this type of propagation. A young shrub will work very well. It is not difficult to remove it from the ground and do all the operations for dividing the bush.
At the first stage, the bush is dug up and carefully freed from clods of earth so that it is clearly visible where it is preferable to divide it. It is important to carry out this procedure correctly, even if the bush is not divided in half. Look more at how the root system develops. When dividing, they try not to harm the plant.
It is better to deal with dividing the bush in the autumn (for the middle lane, this is October). Some experimental gardeners are not averse to dividing the bush in the summer. This is also possible. Just make sure that these manipulations do not coincide with the flowering period of the plant. Despite the fact that the transplantation takes place in the hot summer season, new jasmine bushes are still planted in sunny places in accordance with the requirements of the plant itself.
Growing a mock-orange from seeds

Chubushnik seeds of garden jasmine photo Chubushnik from seeds
And this breeding method requires special knowledge, the right approach, which boils down to the following:
- Purchased or those seeds that were collected on the site after ripening are sown in early spring in late February - early March;
- Before sowing, a soil is prepared, which should contain 3 components: peat chips, sand and humus;
- Seeds for planting are placed in an elastic stocking, lowering it for 3 (or more) hours in a special solution consisting of water and a growth stimulator;
- Then the seeds are placed in sawdust right in this stocking for a couple of days;
- After 2 days, the seeds are removed from the stocking and dried.
- Since the soil in the containers has already been prepared in advance, it remains only to make grooves, slightly moisten the soil and plant the seeds at a distance of 5 cm from each other. Sprinkling peat on top, moisten it again and wait for the first shoots to appear;
- When the first two or three true leaves appear, the plants dive into separate cups and grow on a windowsill or balcony to a height of 20-30 cm.
- Watering should be done in moderation, keeping an eye on the humidity and not allowing the earthen coma to dry out.
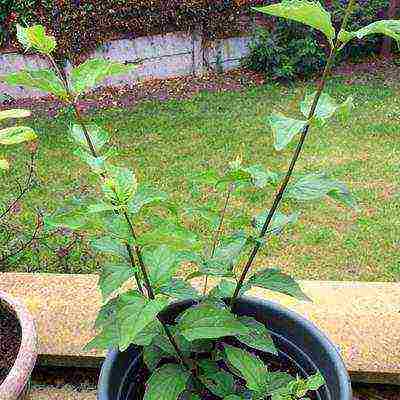

Growing garden jasmine from seeds photo
Before planting in the ground, the seedlings are hardened by taking them out into the fresh air. Gradually, the plants get used to their natural environment and can remain outside painlessly for 24 hours. So you can leave young bushes in a shady place in the garden until autumn. In the absence of the threat of frost, the seedlings are planted in the garden in warm autumn, for the winter they are covered with spruce branches or a thick layer of leaves.
How to transplant garden jasmine mock-orange
Not only for its powerful snow-white flowering, but also for its good adaptability after transplantation, garden jasmine is appreciated by numerous admirers. For transplanting, plants are used at any time except for the flowering period. If the transplant is carried out in the spring, then this year the jasmine will not delight anyone with its flowering.
When transplanting, the following actions are carried out:
- the jasmine bush is filled with water, in excess, so that it is easier to dig it out of the ground;
- while the ground is soaked in water, pruning is carried out: old branches, including last year's branches, are cut off completely, while young ones are slightly shortened;
- then the bush is dug up and transplanted to a new place.
At least 2 buckets of settled water will be needed to water the transplanted bush. Then the ground around the plant is sprinkled with a layer of humus as mulch.
Why the mock-orange does not bloom Pests and diseases
Among the pests that can spoil the appearance of jasmine, the most common are spider mites, aphids, and leafy green weevils. You can get rid of them with insecticides. During the spring and autumn processing of the bush, it is best to use karbofos in accordance with the instructions.
Chubushnik may not bloom for the following reasons:

Why garden jasmine mock-orange does not bloom what to do
- The wrong place for the growth of the shrub was chosen. Shady places negatively affect the plant and should be transplanted.
- The soil does not meet the requirements, the land is severely depleted. Dig up and transplant the jasmine bush into the soil necessary for its normal growth and flowering. Only fertile air-permeable soil, with timely feeding with mineral components, organic matter will be suitable.
- Jasmine does not like strong waterlogging. In areas where it is too damp, it is not recommended to plant a chubushnik. Installing a good drainage system to drain water from the ground will be the ideal way out of this situation. Sometimes a thick drainage layer of 15-20 cm, in a pit for planting a crop, helps to cope with this problem.
- Top dressing of the bush is not carried out according to the rules, an excess of nitrogen is introduced. If you follow all the requirements, the problem will disappear by itself.
- Both over-watering and lack of moisture greatly affect the condition of the plant. During the period of drought, additional watering of the crop is organized, otherwise the plant will not only not bloom, but may also die.
- When planting or replanting a shrub to another place, make sure that the root collar is not buried more than 2 cm.Otherwise, it will underpin, which will lead to its decay and, as a result, the plant growth will be inhibited.
How to care for jasmine in autumn and winter
Jasmine needs care with the onset of the calendar autumn, so it is important:
- feed the shrub with mineral fertilizers;
- water if necessary;
- pruning spoiled, old and dry branches.
How to prepare your jasmine bush for winter dormant time
- in the fall, it is necessary to pay attention to the mock-orange, whose age does not exceed 1 year. He needs increased protection from the winter cold. With the help of dense warm batting, young bushes are covered, tied with twine;
- deciduous humus is scattered on the soil surface in the area of the root system.
- in winter, especially after heavy snowfalls, the shrubs are freed from the snow cap.
- with the onset of the end of winter and early spring, it is also recommended to throw snow from the crown of the bush.
Chubushnik in landscape design

Chubushnik in garden design photo
Designers have found many ways to use snow-white jasmine bushes for renewal
the territory adjacent to the house.
You can often see:
- jasmine bushes as a hedge;
- as an element in the decoration of alleys;
- will attract attention and like a lonely flowering bush;
- in a single composition with other plants, for example, with roses, hydrangeas;
- as a symmetrical geometric pattern in the landscape area of a summer cottage;
- in the design of a thematic garden.
What can be said in conclusion
Be sure to plant a chubushnik on your site. Let it be not one species, but several, and then the whole summer you will enjoy the flowering of this unpretentious shrub.The unique combination of the color of green foliage and the color of the snow-white jasmine flowers contributes to the harmonization of space and peace of mind.
Types of chubushnik with description and photo
Gardeners fell in love with the following types of this culture, which have become very popular when decorating summer cottages:
- Jasmine virgin;
- Crown chubushnik,
- Chubushnik Lemoine.
Any kind of snow-white mock-orange can decorate a garden plot, create a festive atmosphere. As for planting and caring for a plant, it will not be difficult because of its absolute unpretentiousness.
Philadelphus coronarius

Philadelphus coronarius photo
The crown mock-orange is also called the common mock-orange. The maximum height that a plant can achieve is 3.5 m, while it grows up to 2 meters in diameter. On the reddish shade of the shoots, light green leaves of a pointed shape are located.
Somewhere at the end of May, the mock-orange dissolves its flowers and pleases the eye for 1 month. The five-petalled flowers have a creamy shade, a very pleasant aroma. Not pretentious, grows on any soil, is resistant to gusty winds, does not freeze in severe frosts. Very often, an ordinary chubushnik is used by designers when decorating a landscape.
Chubushnik virginsky or maiden Philadelphus x virginalis

Chubushnik virginsky philadelphus x virginalis ‘minnesota snowflake’ photo
Virginia jasmine is obtained by crossing the small-leaved and evergreen mock-orange species. In garden plots, it grows up to 3 meters high. Oval leaves, 7-8 cm long, together with brown shoots form the crown of a shrub. From the middle of summer, it begins to bloom, releasing snow-white inflorescences, consisting of flowers with a double petal type. Flowers reach 5 cm in diameter. Under favorable circumstances, at the beginning of September, the second flowering of Virginia jasmine for the season is observed.
Philadelphus × lemoinei
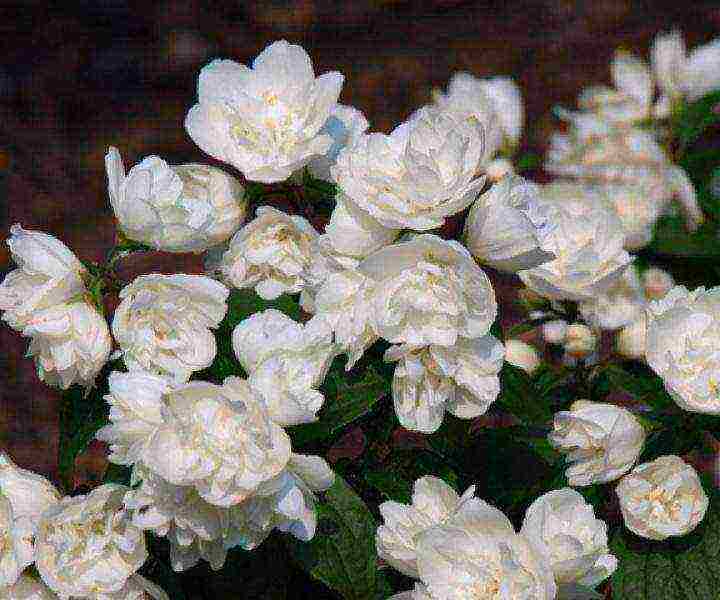

Philadelphus lemoine mock cloak × lemoinei photo
Chubushnik lemoine differs from its counterparts in that it has small ovoid leaves. The crown of the bush is dense, spreading. Reaches up to 2.5 meters (diameter). The flower petals are terry at the end. One gets the impression that with the onset of the flowering time of the chebushnik lemoine, which falls on the month of June, its leaves begin to hide behind the snow-white flowers. A huge white ball is formed, which some time ago was completely green. For jasmine of this type, it is characteristic that it can also be two-colored. A purple-pink core with golden stamens peeps through its snow-white petals.
Foreword
In parks, flowers of a plant often bloom, which can be confused with jasmine, but this is a mock orange, the planting of which is attractive because it is also beautiful, and at the same time it almost does not need care.
In what conditions can different varieties of mock-orange grow?
Most gardeners are not so interested in the full list of garden forms of the mock-orange and their characteristics, as in the description of the growing conditions for certain varieties. There are many regions in which not only weather conditions differ, but also soil and air pollution. Therefore, it is very important to correctly choose the cultural forms of the chubushnik, focusing on the climate, soil composition, and humidity required by the plant.
By itself, this plant is unpretentious, can live up to 30 years, feels great in cities, while clearing the air of dust. Remarkably, jasmine from the olive genus is very similar to it, both ornamental bushes have similar flowers and aroma. Take, for example, such a widespread species in central Russia as the crown mock-orange. Its flowering is accompanied by very strong and pleasant aromas, which is not typical for all cultivated forms of this plant.

Blooming "Crown Chubushnik"
Moreover, the shades of smell can differ in different varieties of this species, of which Aurea of golden color and undersized Nana stand out especially clearly. Withstands, without freezing, rather strong and prolonged cold up to -25 degrees, at a lower temperature the shoots can freeze up to half their length. This is a sun-loving drought-resistant shrub, which, however, needs a lot of moisture. Grows on any soil, including heavy clay.
The Far Eastern chubushnik of Schrenk is completely unpretentious. True, this is just a cultivated species growing on the Amur, and it does not yet have individual varieties, but in nurseries, the decorative form of the plant is already bred in the form of hybrids, crossing with other species. It takes root well in cities, due to the fact that it is practically not picky about the soil, but grows best on light and medium sandy loam and loamy soils with an admixture of organic matter. In cold winters, it may freeze slightly at the ends of the shoots if the temperature drops below -25 degrees, but even if the bush completely dies, the roots will remain viable under the snow cover. In this case, in spring, the plant will again throw out shoots and in summer it will bloom.
Numerous varieties and hybrids of small-leaved mock-orange are very beautiful, in which flowers with a noticeable aroma of garden strawberries or pineapple cover the entire upper part of the bush, almost completely hiding the green mass. It grows well in any conditions, without requiring special care, however, its winter hardiness is average, and in extreme cold, the aerial part of the plant freezes completely, therefore it needs pruning and covering. If the shoots die, then in the spring new ones may appear from the trunk. Shoots grow only 5-6 centimeters per year, so it is better to form a low-growing form from this mock-orange. It is best to plant ready-made seedlings, you can try to propagate by cuttings.
Landing rules in a suburban area
Since most varieties are photophilous and only to a small extent shade-tolerant (a light shadow is allowed, cast on the bush for a small part of daylight hours), you need to choose an open area for planting. If the plant is constantly closed from the sun by the crowns of the surrounding trees, its flowers will be small, and the stems will be strongly elongated to the sides, which will give it a sloppy look. It should be remembered that clay holds water well, and the mock-orange does not tolerate moisture stagnant at the roots. Therefore, it is allowed to plant the bushes of this plant over high-lying groundwater, and planting in waterproof heavy clay soil without preliminary drainage is unacceptable.
We dig holes about 60 centimeters deep and with sides of at least 0.5 meters. If the groundwater is high or there is clay around it, it is imperative to lay drainage from broken bricks or coarse rubble on the bottom, and fill it with coarse sand by 15 centimeters on top. We leave the distance between plantings based on the spreading of the variety, but better with a margin of about 1.5 meters. For a hedge, the gaps between the pits can be reduced to 0.5–0.6 meters, in this case a fairly dense wall should be obtained and the plants will not interfere with each other. The shrub must be easily accessible to provide proper maintenance, so in a group planting, try not to isolate one plant by surrounding it with others.

Growing hedges
It is necessary to root the chubushnik, both seedlings and cuttings, in the spring, the best time for this is April, when the soil is already sufficiently warmed up and late frosts can not be expected. Winter-hardy varieties are best planted in the fall, starting from September 10, when leaf fall ends, the deadline is October 10 or the onset of the first light frosts. We place the root ball of the plant in the hole so that the stem is above the ground.Further, regardless of the soil, we throw the hole with a fertile layer of soil mixed with peat or humus, since the mock-orange is very positive about organic matter. Top can be covered with soil from the bottom layer.
When planting in the spring, if the nights are already warm, you do not need to cover the plant, but in the fall, insulation is necessary, preferably with the help of a greenhouse.
Reproduction of mock-orange by seeds and cuttings
Any cultivated species can be sown by collecting the seeds of the plant after flowering and the appearance of the capsule fruits. Actually, in nature, the mock-orange perfectly reproduces by self-seeding, so you will only imitate the natural process, helping by loosening the soil and watering. In order to get a positive result, sowing must be carried out in December, before heavy snowfall (follow the weather forecasts), having formed high ridges in the fall, before the first frost, and making a groove along the ridge of each.
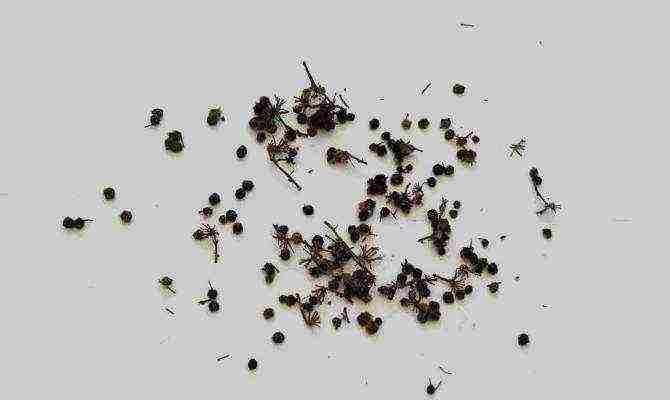

Chubushnik seeds
If the snow has already fallen, it is raked to the side, and small seeds are thrown into the groove. Their dimensions are very small, 8000 weigh only 1 gram. Then the beds are covered with spruce branches and covered with snow. Young green shoots up to 10 centimeters long should be taken as cuttings, and they are not cut off, but broken off with a pull, so that a piece of bark from the branch remains at the base.
A greenhouse is installed over the garden bed prepared at the beginning of spring, under which the shoots of the chubushnik are planted for rooting. During the year, future seedlings require regular watering (preferably drip), and in winter - insulation. It is possible to transplant a mock-orange grown in this way only after a year, when the root system is sufficiently developed.
How to provide proper care?
For each plant, you need to create all the conditions necessary for its growth, therefore, proper care should be provided from the very first days after planting, both in spring and in autumn. In order for the seedling to develop quickly, it is necessary to pour 2 buckets of water into the hole remaining around the root collar immediately after throwing the hole into the hole around the root collar, trying not to erode the soil. Cover the top of the soil with peat, which will serve as mulch in the first year of development of the mock-orange.

Chubushnik care
Further, during the summer, we regularly moisten the ground around the plantings, while watering should be moderate so that the water has time to soak deep into the soil. Within a month after planting, the chubushnik will have a fairly strong root system. Further care will consist in feeding, and the first will need to be done next spring, mixing 15 grams of urea and potassium sulfide, and 30 grams of superphosphate in 10 liters of water. All this is poured out under 1 large bush or divided into 2 small ones.
It is very good to fertilize the ground at the beginning of flowering with slurry, making an aqueous solution in a ratio of 1:10, and 1 bucket is poured under each bush instead of the next watering. Flowering and subsequent fruiting with seed pods can deplete the bush somewhat. Therefore, in the fall, after the ovaries have crumbled, the mock-orange should be poured with a solution of 30 grams of superphosphate and 15 grams of potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water.
Pruning as an important part of caring for a chubushnik
It should be remembered that green shoots, as a rule, do not tolerate winter very well, unlike those that have already become stiff, and if weak young shoots have not matured by the first frost, they should be carefully cut off. You also need to competently shape the bush so that it grows the way you need it, that is, in width or height, for this, all lateral shoots that break the symmetry of the crown are removed.
Before the cold weather, it is better to shorten the main branches to 2 or 3 strong buds, which will give a flowering shoot in the spring, and then tie them together, placing them vertically. Tying the crown is necessary so that, under the weight of wet snow, the branches do not tilt down and do not freeze into the crust under the bush. In the spring, you need to carefully examine the crown of each bush, because in addition to strong shoots, many short ones may appear that will not bloom.In some cases, too many shoots cause the flowers to shred, so the short shoots must be cut off.
In the third year, it is imperative to cut off the faded large branches, which will be replaced by the already significantly regrown stems of the second year. They need to be cut to 2-3 strong buds, repeating the cycle. Such care will allow you to unload the bush, getting beautiful large flowers that will appear on the branches left.
Rate the article:
(2 votes, average: 2 out of 5)
Chubushnik or garden jasmine is a perennial deciduous shrub from the Hortensia family. It has no relationship with real jasmine, but it looks like fragrant white flowers. Natural growing environment: North America, Europe and East Asia. There are about 50–70 species. Many varieties have been obtained as a result of selection. Depending on the species, chubushniki bloom from May to July.
1 Chubushnik: botanical description
Most representatives of the chubushnik genus are plants with small leaves and narrow numerous trunks covered with gray-brown bark. They tend to grow in breadth, form compact and dense bushes. Dwarf species do not grow higher than 70 cm, tall - up to 5-6 m. They are characterized by abundant flowering, white or cream flowers with a diameter of 3-5 cm. Opening in early spring, they exude a sweetish aroma. There are terry, semi-double and simple forms, collected in corollas at the very top.

Leaves are small, 2–7 cm long. Their appearance is different: ovoid, oval, elongated, with a rounded and sharp tip, widened and narrowed, with a smooth or serrated border. Distributed oppositely along the stem, on short petioles. The leaf plate is smooth above and slightly pubescent below. In autumn, the foliage turns yellow. There are evergreen varieties.
Fruit in the form of a three and pentahedral capsule, with seed filling. Semi-inferior pistil, nesting, with accrete columns. In the center there are multiple stamens, on average 50–60 pcs.
The plant is winter hardy, does not need additional protection. Possesses increased endurance to any climatic conditions. Even after freezing, it is able to regain strength and start new shoots.
Planting and caring for David buddleya outdoors
2 Varieties and types
In the natural environment, about 70 species of mock-orange grow, the most common are: ordinary, Minnesota Snowflake, Snowbelle, Lemoine, coronal, small-leaved, Shrenk, Gordon, odorless, fluffy and others. A quick overview of the species:
- Ordinary or pale - shrub about 3 m high, with rough leaves, dark green above, lighter below. Prefers nutritious and loose soil. It blooms with lush cream flowers.
- Virginia Minnesota Snowflake is a shrub with strong erect stems, up to 2 m high and 1.2-1.5 m wide. It blooms in white double clusters of small buds, 2.5 cm in diameter. Blossoms at the end of May, flowering duration 22-24 days ... The leaves are wide, oval, dark green in color, with a rough surface. Loves the warmth of the sun, light shading is possible. With a lack of lighting, the inflorescences lose their splendor. Prefers loose and nutritious soil. Frost-resistant, unpretentious in care. Shoots are able to recover from frostbite.
- Snowbelle is a lush-flowering bush with a voluminous crown of up to 1.5 m. It blooms in May-June with numerous snowy inflorescences exuding a stable pleasant smell. It grows best on fertile, drained loams, with a slightly acidic alkaline environment. It is resistant to frost and drought.
- Lemoine is an ornamental deciduous shrub that grows up to 2 m in height. Forms a spreading crown of leaves, lanceolate-oval.Flowers are large, 5-6 cm in diameter, non-double.
- Coronal - a plant with lignified strong shoots, 2.5–3 m high. Leaves are wide, 7–8 cm long. Inflorescences are cream or white, 3–3.5 cm in diameter, group, double. The flowering period is mid-June. It features yellow foliage in the summer season.

In gardening, hybrid varieties of chubushnik are especially popular. In Siberia and regions of central Russia, including the Moscow region, the Leningrad region and the Urals, cold-resistant varieties take root better. These include the Lemoine breeding hybrids, presented in the table:
| Name | Description | Flowering type | Flowering duration, days |
| Alabaster | The trunks are stable, straight, 1.8-1.9 m high. Group inflorescences are formed on lateral shoots, 10-11 cm long. The flowers are large, snow-white, fragrant | Semi-double, terry, simple | 25–35 |
| Avalanche | Shrub 1.5 m tall with numerous narrow shoots. Foliage - abundant, elongated. The flowers are medium in size, 3.5 cm in diameter. Exudes a strawberry aroma. Poorly tolerates lower temperatures | Simple | 27–35 |
| White bouquet | Low-growing culture, sometimes freezing. Because of this, flowering is observed on the lower branches. Inflorescences are formed by 6-7 buds, including oval petals | Thick double | 22–30 |
| Charm | About 1–1.2 m in height. Inflorescences are dense, include up to 9 white flowers. The length of each individually is 6–7 cm; along the length of the shoot - 40-50 cm. Petals of different sizes, curved at the edges, arranged in circular rows. Emits a light, unobtrusive smell | Thick double | 20–25 |
| Erectus | The flowers are medium in size, 3 cm in diameter. The height of the shrub is 1.5–2 m. The leaves are green in spring and summer, yellow in autumn | Simple | 25–30 |
| Glacier | It has powerful straight stems, up to 2 m high. The foliage is dense, green, oval in shape. Numerous bundle-shaped inflorescences, 6-7 cm long, white, are formed on short annual shoots. Petals - wide, elliptical, cruciform, with gaps | Thick double | 25–35 |
| Ermine mantle | Compact shrub, consisting of many thin stems, no more than 80 cm high. Lateral hanging shoots with narrow leaves. Inflorescences are few in number, small, white in color. Petals in both inner and outer layers - narrowed | Semidouble | 30–49 |
| Pyramidal | The variety is late flowering, no more than 2 m high. The crown is narrowed, dense. In inflorescences up to 9-10 flowers, white and fluffy, rather large. The outer petal row is wide, the inner one is of various sizes | Terry, semi-double | 20–22 |
| Virginal | A bush with a rich crown, 2-3.5 m high. The shape of the leaf plate is oval-wide, with a pointed end. Differs in late flowering period, at the end of July. The inflorescences are large, loose, snow-white. Retains decorative appearance for up to 20 years | Terry | 25–30 |
| Winter avalanche | Frost-resistant variety, preferred for cultivation in Siberia and the Urals. It has long leaves, 4–5 cm. It blooms profusely in late July. The flowers are large, white | Terry | 26–35 |
All varietal varieties of chubushnik are divided into categories: terry, semi-double and simple, as well as with a purple core.

Representatives with simple inflorescences have standard oval petals. Differences only in buds, size and flowering abundance. In double and semi-double, additional rows of small petals are present in the corolla. Densely doubles are often presented in the form of roses or like bells. In non-double varieties of chubushnik, red markings are visible on a white background of buds. The central part contrasts with a white, bright scarlet or purple hue. Most smell like strawberries.
Action: planting outdoors and caring for shrubs
3 Outdoor cultivation
For a chubushnik, you need to choose well-lit areas. In the constant shade, the splendor and abundance of flowering is lost. Ideal soil composition: sheet compost, humus and fine sand.The recommended proportions are 3: 1: 2. In the absence of sufficient water permeability, a drainage layer is laid on the bottom.
It is better to plant a chubushnik in open ground in the fall, but it can also be done at other times of the year. True, this is associated with some difficulties. So, in the spring you need to have time to do this before the buds bloom on the trees.
Planting and caring for a weigela outdoors
4 Landing rules
It is not difficult to grow a chubushnik if you approach the planting and further care correctly. Tips for beginners:
- When planting several shrubs at the same time, an interval of 50–140 cm must be observed. When forming a hedge, the seedlings are placed at a distance of no closer than 50–70 cm to each other.
- The planting hole is dug 60 cm deep and the same height.
- A drainage of brick chips and sand, 15–20 cm thick, is poured to the bottom. The next is a layer of soil mixture. Such manipulations are carried out 7-9 days before the rooting of seedlings.
- After that, a bush is vertically installed in the pit, the root collar is flush with the upper line of the ground and is filled up.
- 2-3 buckets of water are poured under each landing.
- After 3-4 days, the root zone is mulched. Peat or sawdust will do.
It is not critical if the root collar deepens 3-4 cm under the soil. It is no longer possible, otherwise the root system will start to rot.
Full rooting will occur only after a month, subject to abundant moisture.

The yield will be 5 times more if you add ordinary ...
5 Plant care
The plant will only be healthy when there is sufficient moisture. When dry, foliage quickly loses its elasticity and sags. Optimal watering is once a week, 2-3 buckets per bush. When flowering, you will need to do this daily. After the root zone is loosened and hilled. If you plant in the spring and mulch the bushes, then the care is much easier: the frequency of watering and loosening is reduced, and the growth of weeds is minimized.
As a top dressing, liquid mullein is used in the amount of one bucket per plant. Introduced in the spring. At the end of flowering, each bush is sprinkled with wood ash. Starting from the fourth year of life, it is permissible to feed with complex mineral fertilizers, which include superphosphate, urea and potassium sulfate. Nitrogen supplements can only be used in the spring.
For abundant flowering, formation is carried out annually. Since flowers bloom only on strong shoots of last year, old and wilted ones must be removed in time. This stimulates the emergence of young shoots, which will bloom in the next season. The faded branches are cut to the height of the young growth in the lower part of the shrub. Preparation for winter includes sanitary pruning of plantings. The overgrown crown is thinned out by removing dead and affected parts. Shoots over 12 years old must also be cut. The rejuvenating procedure is carried out in early spring: several strong vines are formed up to a height of 30 cm, the rest are cut to the base. The cuts are processed with crushed coal. By the fall, new shoots will develop from the buds.
Chubushnik tolerates a transplant without problems, however, the year of flowering and a dense crown are lost. Planting holes are dug 10-14 days before planting. To make the bush easier to extract from the ground, it should be shed abundantly. Carefully, without disturbing the roots, it is transferred to a new place. Then it is well watered. A good period for transplanting is mid-September to October.
Due to the fact that most species are frost-resistant, the growing area is quite extensive. This is especially true for gardeners in Siberia and central Russia. Chubushnik is unpretentious in care, so there are no special differences in cultivation conditions in the south and north. For regions with frosty and snowy winters, winter-hardy varieties are recommended. They are able to withstand temperatures as low as -35 degrees without protection.
The horticultural crop has an increased resistance to diseases and pests. Occasionally attacks of bean aphids, spider mites and leaf weevils occur. In such cases, treatment with "Karbofos" or "Rogor" helps. Weevil larvae disappear after spraying with Chlorophos.

6 Reproduction
Garden jasmine propagates in several ways: by seeds, dividing the bush, layering and cuttings. Despite the simplicity of seed reproduction, varietal representatives are bred by vegetative methods. In this case, the original characteristics are inherited.
To plant seeds outdoors in spring, stratification is required in January. Mixed with raw sand and peat, placed in an airtight container and placed in the cold. The duration of the procedure is 2 months. In March, the seed is planted in a mixed soil of peat, leaf compost and mullein with a small dilution of sand. Cover with foil or glass. Moisten from a sprayer several times a day, thereby keeping the soil moist. The sprouts will sprout in 2-3 weeks. As soon as the first 2 leaves are formed, you can transplant to a permanent place.
Until the seedlings fully take root, they will need protection from direct sunlight.
The propagation method by green cuttings is more reliable. All plantings will take root with a 100% guarantee. For harvesting cuttings, it is better to choose annual branches with part of last year's, called the heel. Growing ones are also not suitable, since their stems are hollow inside. This increases the risk of developing putrefaction there. At least two developed buds should be present on the surface of the cutting. The sections are treated with a growth activator, the cuttings are planted in a separate container with enriched soil. They are pressed in no more than 0.5–0.7 cm, at a distance of 10 cm. For better rooting, greenhouse conditions are created: a glass shelter, diffused light and frequent spraying.
The method of propagation by layering is no less promising and easy. It is safer to do this after anti-aging pruning. A shoot with developed buds is selected from below. It bends down to the ground and fits to a depth of 1–1.5 cm, sprinkles on top and fixes it. So, several branches can be taken from one bush. As a result, all of them will have time to develop before the onset of winter. In spring, they are separated from the mother bush and planted separately. They grow back for another two years.

Reproduction by dividing the bush is carried out in the spring before the onset of sap flow or in the fall after the leaves are shed. A densely overgrown shrub is dug up, separated and quickly planted. The slightest delay can lead to drying out of the plots.
Chubushnik or garden jasmine is unpretentious to care for, easily adapts to the surrounding climate, and tolerates low temperatures. This allows him to land in the northern regions. With proper care, long-term flowering can be achieved. One has only to pick up varieties with different budding periods. More often the mock-orange is planted along hedges and summer cottages.


