Content
- 1 Wisteria tree
- 2 Wisteria seedlings
- 3 Wisteria planting, care, cultivation
- 4 Wisteria Blue Moon
- 5 Chinese wisteria
- 6 Wisteria photo
- 7 Wisteria buy a sapling
- 8 Plant species
- 9 Planting creepers
- 10 How to care for
- 11 Pruning
- 12 How best to feed
- 13 Seed propagation
- 14 Reproduction by layering
- 15 Let me introduce myself
- 16 Wisteria: care and cultivation in the middle lane
- 17 Leningrad and Rostov region
- 18 Ural and Moscow region
- 19 Siberia
- 20 Belarus and Ukraine
- 21 Reproduction of wisteria
Content:
- Wisteria tree
- Shlitsinia saplings
- Planting, care and cultivation of wisteria
- Wisteria Blue Moon
- Chinese wisteria
- Wisteria photos
Wisteria tree
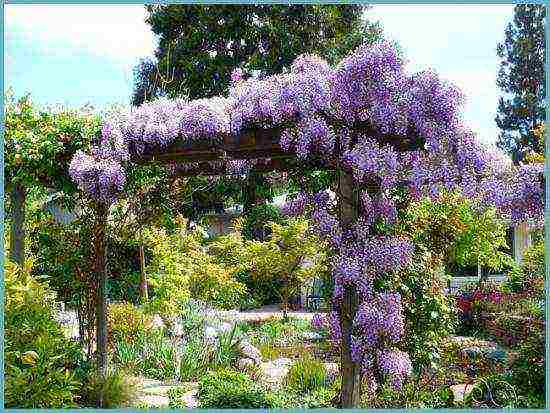
This is a plant of fabulous beauty. Whoever has seen wisteria at least once in their life during flowering, its enchanting flowers and unique aroma will remain in the memory for many years. Her long racemose inflorescences, grow up to half a meter in length, and everyone who passes by stops to admire them.
Wisteria Is a perennial decorative deciduous liana, with beautiful openwork leaves and divine flowers of blue, lilac or white color. Long lasting and bright bloom made wisteria a very popular plant.
Wisteria decorate gazebos, retaining walls, terraces, balconies. With its help, you can safely hide from prying eyes. With the help of pruning, you can control its growth and maintain the desired shape of the liana bush. A stronger pruning of the bushes should be done annually, in the fall.
Wisteria blooms from May to June. But with careful, reliable care, it can bloom re, at the end of summer. Some clusters of inflorescences remain on the bush throughout the summer.... Flowers wisterias appear first, the leaves bloom already during flowering.
Dlingering plant, in one place can grow over the years. An adult plant forms a powerful root system. Therefore, a wisteria transplantpainful... If you are going to purchase or have already purchased wisteria, take care of choosing the right place for planting, so that you do not have to replant it later.
Wisteria seedlings
The best way to grow wisteria is by purchasing seedlings. Choose a one year old or two year old plant. Most varieties are planted in late August or autumn, only very sensitive varieties are planted in spring.
Wisteria planting, care, cultivation
How to choose a place for planting wisteria? We recommend planting wisteria only in spring, as the plant is thermophilic. A place choose sunny, warm, sheltered from wind and drafts. The soil should be neutral to slightly alkaline, although wisteria can adapt to any type of soil.
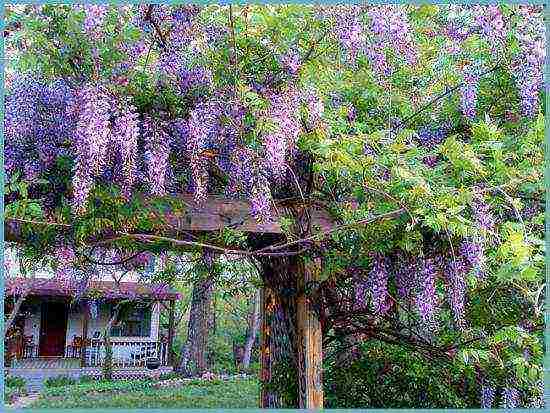
In the early years after planting, wisteria, like most vines, grows a root system and main shoots, which over time lignify and form a powerful trunk. An adult wisteria vine can reach in height up to 20-25 m. Considerthat the shoots of wisteria grow very strong and heavy (especially during flowering), so immediately take care of strong supports.
Concerning winter hardiness, then wisteria cannot be called a frost-resistant plant. Some varieties of wisteria are damaged even at minus 20 ° C. There are more frost-resistant varieties. Therefore, to grow wisteria in the open field possible only in regions with mild winters. In colder areas, wisteria will make an excellent tub plant.
Can wisteria be grown in a tub? Yes, you can. Even necessary if your winters are frosty. Kadki should be large and placed on the sunny side. An important condition for growing wisteria in a tub should be regular watering and feeding. If the plant does not receive the required amount of nutrients, there will be no flowering.
From wisteria, using pruning, you can form a wonderful standard tree.
In autumn, after frost, bring tub plants into the room, where throughout the winter the temperature will be in the range of 5-10 ° C. Lighting during the rest period, it should be bright, ideally south windows or a glazed balcony. If there is no bright balcony, use artificial lighting with fluorescent lamps. Feed wisteria in winter is not necessary, water only so that the lump of earth does not dry out. With the onset spring, carry out shoot pruning or molding crown pruning.
Features of care for wisteria. Choosing the right one seats for landing, the key to good growth and abundant flowering. If you plant the wisteria in a suitable place for it, the care for it will be minimal.
As mentioned above, wisteria loves sun, warmth, moisture, but does not tolerate waterlogging. When planting a plant, the use of drainage is mandatory. In the summer wisteria needs watering. Into drought water plant once a week, but abundantly, while adding fertilizer (use complex mineral fertilizers and organic matter).
If your regions rarely experience frosty winters, wisteria can successfully overwinter in a sheltered garden. How to cover wisteria? Just like climbing roses. Wisteria growing in a windy area also need shelter.
Should wisteria be pruned? Yes need. Pruning stimulates profuse flowering. If this is not done, there will be no flowering.
First cut spend the summer, immediately after flowering. At this time, shorten all side shoots by a third. The second, carry out a stronger pruning at the end of autumn, after the vine has shed its leaves. Shorten all side shoots that were cut in the summer and all those that grew over the summer, leaving up to 5 buds on each shoot. From these buds, flowers are formed in the spring.
Wisteria Blue Moon
Wisteria loves warm climate and sun. But there is also a frost-resistant variety of wisteria - this is wisteria Blue Moon, translated - blue moon. This variety is very fond of many growers, because it can be grown not only in hot areas.
Wisteria Blue Moon can be found in Western Ukraine, as well as in other regions of our country. Features of the variety - these are large inflorescences of a very rich color with a blue tint, very abundant flowering twice a year, as well as excellent winter hardiness. The first time it blooms in May-June, and the second time it can bloom in the fall!
No need to cover for the winter, it tolerates well low temperatures... Some branches may freeze slightly, but the tree will recover quickly.
Wisteria Blue Moon:
Chinese wisteria
Chinese wisteria Is a beautiful variety of wisteria. Latin name - Wisteria chinensis. In nature, it can be found in China, as well as in Japan. Grows high above sea level, most often in mountain forests. In 1816, this beautiful vine brought to Europe, today, even in Ukraine, beautiful Chinese wisteria grow, first grown in Odessa.
Average height trees - twenty meters, in Ukraine - about 10 meters. In April, beautiful inflorescences appear, blooms throughout April and May. Color of flowers - white, light purple, blue. Dimensions (edit) - up to five centimeters, flowers in inflorescences.
Chinese wisteria:
Wisteria photo
Wisteria buy a sapling
Wisteria seedlings can be bought in the Florium online store.
Published: 26.10.2016
Related articles:
- David Austin roses close up
- How to choose climbing roses?
- November.Gardening works
- Clematis
- Lesson 16 - Vines in the garden
With the onset of spring, white and light lilac clusters of beautiful buds begin to bloom in the gardens. It pleases the eye with its blooming wisteria. Planting and caring for a weaving plant is up to every summer resident. It can be planted near a gazebo, or decorated with a vine at the entrance gate and walls of the house. The abundant and long-lasting bloom of wisteria creates an atmosphere of a fabulous country on the garden plot.

Plant species
The second name of the plant is wisteria. It belongs to a rare genus of deciduous vines that are part of the legume family. It grows in natural conditions in the Caucasus, East Asia, Crimea and America. The cultivation of wisteria in the open field is successfully proceeding in the south of Ukraine and Russia, since in these regions there are rather warm winters and hot summers.
Until recently, residents of a more severe climate had to carefully cover the vine with the onset of cold weather, but, despite such care, it often froze and died. This problem has now been resolved. Breeders bred a frost-resistant wisteria variety, which received the poetic name "Blue Moon". It can withstand air temperatures up to -40C, and now the tree-like liana can be safely planted in central Russia, in the Urals and in southern Siberia.
Wisteria has 9 varieties. The most popular among summer residents, in addition to the frost-resistant variety, are the following.
- Chinese wisteria. Liana grows up to 20 meters, blooms almost all summer with pale lilac flowers, the brushes of which reach 30 cm;
- Japanese wisteria. This is a short vine. It grows to a length of about 9 meters, but compares favorably with other varieties with larger leaves and flowers;
- Wonderful wisteria. It weaves up to 10 meters. In June, it blooms with white or bluish flowers.
The rest of the wisteria varieties are less common, and they are rarely used for landscaping in our country.

Planting creepers
Before planting, it must be borne in mind that wisteria is a perennial plant, so the place for it should be carefully chosen. Growing wisteria will be more successful if it is rooted in a sunny area protected from the wind with nutritious weakly alkaline soil. The plant is planted in open ground in spring, when the last frosts end and the ground warms up well. If you do this earlier, tender seedlings may not take root.
- The plot of land where the cultivation of wisteria is planned must be dug up onto a shovel bayonet, after having saturated the soil with mineral fertilizer. The recommended dose is 20-30 g per sq. m area.
- Then dig a hole 50 cm deep and wide, pour a thick layer of broken brick or expanded clay inside and sprinkle it lightly with earth.
- Then pour a bucket of water into the recess. Wait until it is absorbed and place the seedling there.
- Sprinkle it with earth from the garden, gently pressing down with your hands, and moisten the ground again.
Get ready for the fact that at first the wisteria will not actively grow. Do not stop regular grooming, and gradually she will start to release thin shoots. The first abundant flowering can be seen not earlier than in 4-5 years.

How to care for
Competent care consists in the garter of young shoots. Growing vines should take place next to a durable and powerful support that can withstand gusts of wind and the weight of an adult plant.
Advice
It is advisable to tie the wisteria to the support yourself. If it starts to weave itself, then it will be difficult to untangle it and lay it on the ground before frost.
Wisteria care is impossible without regular watering. Make sure that the ground is always moist, but without stagnant water under the bush. From the beginning of flowering until autumn, watering should be slightly reduced. Waterlogged soil can lead to the fact that the wisteria's blooming brushes fall off.The next day after moistening, do not forget to carefully loosen the ground under the vine so that a crust does not form in the hole, which prevents the plant from developing normally. In extreme heat, it is useful to spray the shoots with water from a hose. This treatment removes dust from the leaves and refreshes well.
When the last leaves fall off the wisteria, you need to start preparing for the winter.
- Since most varieties of wisteria do not tolerate severe frosts, they need to be insulated.
- To do this, huddle the root part high, untie the shoots from the support and carefully spread them on the ground.
- Sprinkle the plant on top with a thick layer of dry grass and spruce branches.
Young shoots are vulnerable to low temperatures, so be sure to cover wisteria in central Russia and in the Ural region.
Pruning
In order for the care to be complete, the plant needs pruning. Without it, wisteria will not bloom well and for a long time. Most wisteria flowers bloom on last year and the year before last, so it is important that the flower buds form on them correctly. To do this, all branches of the creeper are shortened by 2 cm in May.
Fall grooming also includes pruning. In September, you need to cut off the tops from young shoots, counting 4 buds from the top. By following these recommendations, you will achieve the maximum splendor of the flowering plant.
After flowering, remember to remove dry buds, and regularly dispose of diseased old branches.

How best to feed
Growing wisteria is impossible without systematic feeding. During active growth and flowering, they must be produced once a week. Experienced gardeners recommend alternating mineral and organic fertilizers.
Kemira Lux has proven itself well. It provides the plant with useful elements for a long time. The fertilizer is sold in liquid form and in granules. To feed wisteria, it must be diluted and used strictly according to the instructions.
From organic dressings for wisteria, a mullein solution is ideal.
- You will need a large barrel to make it. Place a bucket of cow dung there, which you managed to overheat, and pour 5 buckets of water.
- Stir and let sit for 2 weeks to infuse.
- After half a month, the top dressing is ready, and you can use it.
- Before use, dilute the organic solution with water in a ratio of 1:10 and pour the wisteria into the root.
In the middle of summer, you can feed the plant with chalk once. To do this, grind 100 g of chalk into powder, dissolve in 10 liters of water and moisten the soil under the growing vine.
Advice
If you want to see a wild bloom, use nitrogen fertilizers with care. Their excess in the soil will lead to the fact that wisteria will build up green mass and grow rapidly upward, but will stop blooming altogether.

Seed propagation
Growing vines from seeds is rarely practiced, since the method is rather complicated and not always successful.
- You will need to prepare potting soil for planting. Take one piece each of sand and turf, add four pieces of leafy soil to them and mix well.
- Place the soil in a special box with holes in the bottom, sow the seeds and sprinkle the soil with water from a spray bottle.
- Cover the top with plastic or glass. Place a kind of greenhouse in a warm, dark place for 4 weeks.
During this period, do not forget to raise the glass for ventilation and watering. During this time, the first shoots will hatch in the box. After a month, they can be placed on a lighted window sill and provided with normal care. When the plants have 2 leaves, they need to be transplanted into large containers along with a lump of earth on the roots. Continue growing seedlings on the windowsill throughout the winter. In the spring they are rooted in the street. They take root well outdoors, but often do not bloom for a long time.

Reproduction by layering
The easiest way to get a new plant is by layering. In May, pick up a healthy young shoot about 15 cm long. Make an oblique cut in the middle with a sharp knife.Place a wide container with fertile soil next to the vine. Tilt the prepared branch and dig in the pot. The tip of the shoot must necessarily remain free. If the layering is provided with full-fledged care, which includes potassium-phosphorus fertilizing and watering, it will gradually take root and grow.
By the fall, the cuttings grow well, and several branches appear. Excess shoots must be ruthlessly cut off, carefully separated from the adult wisteria, and the plant in a pot must be brought into the cellar for the winter. In the spring he is transplanted to a new place.
In addition to these two methods, some craftsmen manage to propagate wisteria by grafting on the roots or cuttings. The methods are ineffective and rarely give a positive result.
In Siberia, wisteria is often grown in large pots in the summer, which are placed in the garden. When late autumn comes, the plant is brought into the cellar, where it stands until spring. The next year, the vine is transplanted into a wider pot and again taken out into the street.
Wisteria looks great in landscaping. She perfectly disguises unsightly walls, decorates fences or gazebos. Be sure to plant this unpretentious plant, and in a few years your home will be completely transformed.
 Light purple and white brushes of blooming wisteria leave no one indifferent. Since spring, this tree-like liana delights the eye with its flowering, which lasts all summer. In the open field, wisteria is widely distributed as an ornamental plant. This article will discuss the features of planting and caring for this beautiful vine.
Light purple and white brushes of blooming wisteria leave no one indifferent. Since spring, this tree-like liana delights the eye with its flowering, which lasts all summer. In the open field, wisteria is widely distributed as an ornamental plant. This article will discuss the features of planting and caring for this beautiful vine.
Varieties and varieties
The wisteria tree liana also has a second name, "wisteria". The subtropics are considered a natural habitat, however, cultivated species are able to grow in almost any climate, and some varieties bred by American biologists can withstand severe winter frosts without shelter and retain the ability to bloom.

Wisteria is an incredibly beautiful liana that can be easily grown even in the north of Russia.
There are 9 types of wisteria in total, but most often you can find several of them:
- Chinese wisteria represents a liana up to 20 m high with brushes of a light lilac shade up to 30 cm long. Some varieties can have flowers of double appearance and white color.

Chinese wisteria
- Japanese wisteria it is half the length of the Chinese one, and rarely reaches more than 8-9 m, but at the same time it has larger leaves and clusters of inflorescences. However, the flowers themselves are smaller. Very often, Japanese wisteria is called multi-flowered or profusely flowering. This is due to the fact that the number of leaves and flower brushes in her is much greater than in the Chinese one. Depending on the shape of the garden, the shades of flowers can be white, pink or light purple.

Japanese wisteria
- Recently, wisteria is gaining great popularity. Blue moon... This is a frost-resistant wisteria, its perennial vines are able to withstand frosts down to -37 C without damage. This species was bred not so long ago. Blooms in large inflorescences of a blue hue in early summer. Flowering lasts up to two weeks.

Wisteria Blue Moon
Planting wisteria
When planting wisteria, it must be borne in mind that the plant is perennial, and a place for it must be chosen for many years. If you want to achieve maximum flowering, then it is worth choosing an area where the vine will be in the sun for at least half a day. In addition to the sun, care must be taken to ensure that the place is sufficiently protected from the wind, and the soil is nutritious and well-drained. Wisteria gives preference to slightly alkaline soils.
Planting wisteria is best done in the spring, after the last frost has passed. Despite the fact that most of the wisteria varieties are frost-resistant, it is not worth putting young plants at risk once again.

For wisteria, it is imperative to determine a sunny place on the site
Most often, wisteria is grown from seedlings. Before planting, the soil is dug up with mineral fertilizer, after which holes 50 cm deep are dug into which young plants are placed.
If you plant wisteria from seeds, then the vine will not bloom soon. In the best case, after 5 years, but very often only by 10 years.
Wisteria care
Wisteria care begins with a garter of young shoots. Since the vine grows for a long time and has a high windage, the support must be durable and capable of withstanding wind loads.
Advice. It is best to tie the wisteria to the support, because independent weaving around the support can lead to the fact that it will be very difficult to remove the vine to prepare for winter in the fall.
The soil should not be calcareous, otherwise the wisteria leaves will brighten and lose their decorative effect.
Watering. Too wet soil can cause the plant to shed leaves and buds. Therefore, you should observe moderation in watering from the beginning of flowering until the end of summer. In summer, additional spraying can be carried out so as not to overwhelm the roots with water. In September, watering should be minimized and the plant should be prepared for winter.

The soil around the wisteria should not be too waterlogged.
Pruning. A very important condition for the flowering of wisteria is timely and correctly carried out pruning. Wisteria flowers develop on vines of last year and even earlier. Sometimes on young shoots of this year. Therefore, for the correct formation of flower buds at the beginning of summer or at the end of May (depending on the wisteria flowering season), the shoots of the last year are shortened, leaving no more than 30 cm.
In the fall, the shoots of the new season are cut off by cutting off 4 buds. After that, in early spring, during the garter of the vines to the support, last year's shoots are reduced by another 2 buds. By following these simple pruning rules, you will achieve the most decorative and lush flowering, which is so prized in wisteria.

Pruning wisteria
Preparing for winter. Many varieties of wisteria are preferable to cover for the winter, especially in the northern regions. Young shoots are considered the most vulnerable. In autumn, it is recommended to untie them from the support and lay them on the ground. The root part is buried in a thick layer of earth, and the shoots are covered with spruce branches, a layer of leaves or a special covering material. The older the plant becomes, the higher its frost resistance, respectively, the less it needs winter shelter.
Scheme: pruning and shaping vines
Advice. In severe frosts, some of the young shoots still die, but you should not be upset because of this, because this is exactly the material that needs to be pruned.
Fertilizing and feeding wisteria
It is impossible to take your eyes off the photo with blooming wisteria. To achieve the same flowering on your vine, you should pay a little attention to feeding. During active life, it is recommended to fertilize wisteria at least once a week, while it is best to alternate liquid mineral fertilizers with organic ones (for example, with mullein infusion diluted with water in a ratio of 1:20). A one-time top dressing in the summer, you can add a chalk solution. To do this, you need to dilute 100 g of chalk in a bucket of warm water and water the plant at the root.

No need to feed wisteria too often
Advice. Experienced gardeners remind that wisteria refers to legumes, therefore, you need to be careful with nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
Reproduction of wisteria
There are many ways to reproduce this beautiful vine.
The easiest way to propagate wisteria is grafting... In late autumn, the vine is cut off from the bush, cut into cuttings, tied and removed to a cool place, after burying it in a damp base. In early spring, the vine is taken out of the basement and planted under plastic bottles. It can be planted both in a cold greenhouse and immediately at a permanent location.About half of the cuttings planted will take root.
In December, you can try to multiply wisteria inoculation... It must be done exclusively on the roots, because the wood of the vine is too soft, and it will not be possible to vaccinate.

Wisteria propagates well by cuttings
A fairly effective breeding method is rooting of cuttings... In the fall, when all the leaves fall off, the lowest shoots scar slightly, tilt to the ground and sprinkle with soil so that only the tops remain on the surface. Shoots ring from the side of the mother bush in the spring, when buds begin to appear. And in the fall, it is necessary to check whether the root system of the layers has developed enough. If the roots have not yet grown enough, then the layers are left in this form for another year. If the root system has developed enough, then the layers are dug up and planted in a new place.
The breeding method is also widespread. winter cuttings... The best time for this is February. The shoot prepared in advance must be split lengthwise into two parts and cut the resulting halves into cuttings. The length of the cutting is about 5 cm, and there must be a kidney in the center of each. Cuttings are planted in boxes, maintaining a small distance between them, and the soil is sprinkled with sand on top. The boxes are stored in the greenhouse until rooting.

Young liana
Another way that brings almost 100% of the result is reproduction shoots of this year... In order for the root system to form faster, the lower edges of the cuttings must be treated with synthetic phytohormones in accordance with the instructions. After the cuttings have stood in the solution for 12 hours, they are washed with running water and planted in a greenhouse with a friable substrate prepared from equal parts of sand, earth and peat. You can plant the petioles in boxes, which must be covered with glass and removed in a light shade and watered once a day, maintaining sufficient soil moisture. When the first shoots appear, they switch to moderate watering (once every three days). In the fall, they are transferred to a sunny place or shading is removed.

Wisteria seeds
Reproduction of wisteria seeds many gardeners consider it ineffective, because the flowering of such vines may not start, or begin only after a few years. And the decorative properties are very rarely preserved. However, some seedlings from seeds give unexpected results and young vines overshadow the maternal ones in their decorative qualities. Such findings are subsequently used for selection.
The seeds are sown in a greenhouse in the middle of winter. When sowing directly into open ground, it is best to do this in early spring. Seeds germinate late. However, this method of reproduction also has its advantages - plants grown from seeds from the first days are adapted to natural surprises and are much more resistant and hardy.
Pests and diseases of wisteria
Wisteria is quite resistant to diseases, but from time to time it is occupied by aphids, which can be easily corrected with an insecticide. Some gardeners also noticed the raids of the clover mite, which are successfully destroyed by acaricidal preparations. Of the diseases, wisteria can be overcome by chlorosis, if you place your vine on alkaline soil. You can identify this disease by yellowing and falling leaves. As a treatment, it is necessary to make top dressing with iron salts.
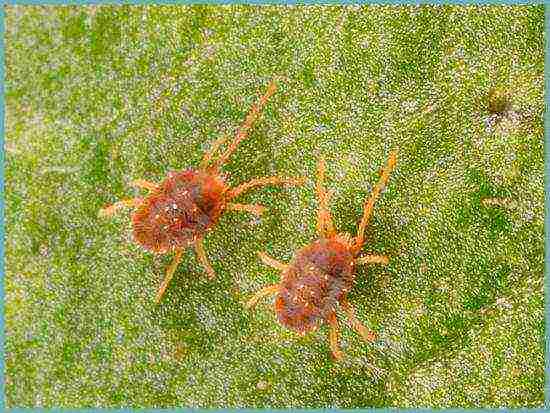

Clover mite
Wisteria in the garden
The bloom of wisteria is an unforgettable maelstrom of colors, in which long brushes of many shades - blue, red, white - rush downward like an unrestrained waterfall, exuding a sweet aroma. In Japan, a walk in a garden with blooming wisteria is equated with a walk in paradise.

Perennial flowers can be planted under wisteria
Very often in landscape design, wisteria is used as vertical gardening of the site.Despite the fact that the liana occupies a minimum of area, its decorative effect is exceptional. It is used to decorate unsightly walls, fences and any other buildings and technical structures that can spoil the overall appearance. This vine will help zone areas, acting as a screen and creating natural shelters from the sun and wind. To create an original ensemble, try planting hyacinths and daffodils at the base of the wisteria. The hazel grouse, white tulips or wolfberry will look good against the background of wisteria. Numerous photos will tell you how best to decorate your garden with this beautiful vine.
Unpretentious in care, wisteria can please the eye of any picky gardener.
How to properly crop wisteria: video
Wisteria: photo








 Wisteria, the care and cultivation of which in the subtropical zone is problem-free, in other climatic zones requires special attention. The second name is wisteria and it is one of the most beautifully flowering plants. Seeing once, one cannot help falling in love with a gorgeous liana with a waterfall of flowering inflorescences and a pleasant sweetish aroma. To have such an asset in your garden is the dream of every gardener.
Wisteria, the care and cultivation of which in the subtropical zone is problem-free, in other climatic zones requires special attention. The second name is wisteria and it is one of the most beautifully flowering plants. Seeing once, one cannot help falling in love with a gorgeous liana with a waterfall of flowering inflorescences and a pleasant sweetish aroma. To have such an asset in your garden is the dream of every gardener.
Let me introduce myself
 Wisteria is a plant that looks like a huge decorative liana, belonging to the legume family. It is mainly tree-like and deciduous, but sometimes semi-leafy, woody at the base specimens are found. The plant got its name in honor of the American professor of anatomy Caspar Wistar and translated from Greek means "sweet". For decorative purposes, the plant is grown all over the world. But the main distribution area is East Asia and North America, mainly in subtropical zones. Also found in the forests of China, in the Kuban, in the Crimea, in the North Caucasus. In general, there are 9-10 varieties, but only two are grown in the garden - lush and Chinese.
Wisteria is a plant that looks like a huge decorative liana, belonging to the legume family. It is mainly tree-like and deciduous, but sometimes semi-leafy, woody at the base specimens are found. The plant got its name in honor of the American professor of anatomy Caspar Wistar and translated from Greek means "sweet". For decorative purposes, the plant is grown all over the world. But the main distribution area is East Asia and North America, mainly in subtropical zones. Also found in the forests of China, in the Kuban, in the Crimea, in the North Caucasus. In general, there are 9-10 varieties, but only two are grown in the garden - lush and Chinese.
It is a fast-growing perennial (trees live for 150 years), growing up to 18 m in height. The branches are represented by climbing vines. They are naked (sometimes there are specimens with pubescence) and drooping. The size of the plant is impressive - the liana can reach 0.4 m in girth. The shoots of wisteria are thin, painted green, and the bark is gray.
The foliage of wisteria is pinnate, colored in a dark or light green shade, is arranged alternately and consists of 7-13 fragments, each of which has an oblong-ovoid or narrow-elliptical shape. In general, the length of the leaf reaches 30 cm in length.
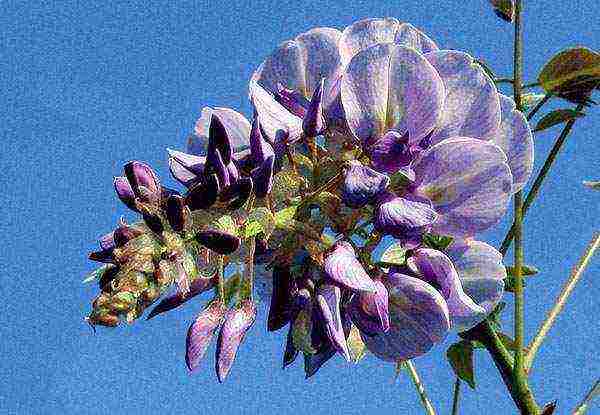 Wisteria blooms twice a year. The first time - in March-May, the second - in the middle or late summer. Some species may have different budding times. Outwardly, the flower is a drooping bunch, consisting of many densely planted buds. On average, the length of the bunch is 10-80 or 100-120 cm. The flowers bloom from the base to the top of the bunch, emitting a delicate aroma. There is a snow-white corolla and a zygomorphic perianth.
Wisteria blooms twice a year. The first time - in March-May, the second - in the middle or late summer. Some species may have different budding times. Outwardly, the flower is a drooping bunch, consisting of many densely planted buds. On average, the length of the bunch is 10-80 or 100-120 cm. The flowers bloom from the base to the top of the bunch, emitting a delicate aroma. There is a snow-white corolla and a zygomorphic perianth.
 The color of the buds is varied. Mostly pink, white, various shades of purple and lilac.
The color of the buds is varied. Mostly pink, white, various shades of purple and lilac.
At the end of flowering, fruits are formed - pods measuring 15 cm, containing seeds of a flat-round shape, painted in brown-black color.
When cultivating and caring for wisteria (photos of the most luxurious specimens are presented), you need to remember that some plants are poisonous, so you should be extremely careful and wash your hands thoroughly after contact.
Wisteria: care and cultivation in the middle lane
Unlike the usual wisteria zone, growth in the middle lane is problematic. Long and very cold winters can save only young shoots and rhizomes. Flowering also expects much to be desired - adult plants bloom only at 6-8 years of age. And where the summer is cold and rainy, you need to try hard to see the buds.
The ideal environment is a constant temperature without sudden changes, both during the day and at night, as well as a lot of sunlight.
For good development in the middle lane, you need to create growing conditions and care for wisteria close to ideal.
Choosing a landing site and soil
Wisteria is a very thermophilic plant, therefore it prefers sunny areas and walls of buildings facing south. Open areas are not recommended; it is better to plant a vine along a high fence or under the wall of a house.
Achieve full and abundant flowering is possible only in bright light for at least 6 hours a day. In this case, winds and drafts should be avoided.
Wisteria is not particularly demanding on the soil. As a rule, it grows well on any soil, but black soil or rich loams are especially favorite. But a limestone substrate or a swampy one is completely unacceptable.
Planting and care features
 The vine is planted in the ground at the beginning of June, having prepared a hole 60 * 60 cm and pre-digging mineral fertilizers at the rate of 25-30 g per m2.
The vine is planted in the ground at the beginning of June, having prepared a hole 60 * 60 cm and pre-digging mineral fertilizers at the rate of 25-30 g per m2.
To prevent the vine from rotting and getting wet, a good drainage layer must be laid on the bottom of the hole. This will further protect the root.
Like planting wisteria, care has its own subtleties:
- After planting, the plant must be well watered.
- You should wait for the adaptation, which lasts about a month. After that, the vine will grow and she will need to install a support.
- In hot weather or during a drought, watering should be periodic and sufficient.
- Spraying vines in summer is permissible.
- When the summer period approaches the end, watering is reduced.
- Rotten manure with water (20: 1) or mineral fertilizers (dissolve 20 g in a bucket of water) are used as top dressing.
- When the foliage falls off, pruning should be done. It is also carried out in the spring during active growth.
- Before the first frost, the liana is removed from the supports, laid on boards located on the ground and carefully covered with moss, and then with lutrasil. Root areas should be "covered" with earth. This procedure is especially important for young plants.
Leningrad and Rostov region
 Many gardeners choose a Chinese or multi-flowered variety for growing wisteria in the Leningrad Region and caring for it. Alas, this is completely unacceptable for this area. As a rule, the plant dies. If it is possible to grow a liana, then its flowering will be very meager - just a couple of frail inflorescences.
Many gardeners choose a Chinese or multi-flowered variety for growing wisteria in the Leningrad Region and caring for it. Alas, this is completely unacceptable for this area. As a rule, the plant dies. If it is possible to grow a liana, then its flowering will be very meager - just a couple of frail inflorescences.
It is best to give preference to a hybrid variety with high frost resistance - "Blue Moon". It is a large-leaved variety that will not only develop well, but will also give excellent flowering. Planting is carried out with seedlings, planting in the ground with the onset of June. To prevent the plant from dying in winter, before freezing, the liana should be carefully removed from the supports and carefully insulated with lutrasil. They do the same when planting and caring for wisteria in the Rostov region.
Ural and Moscow region
 Wisteria does not tolerate a temperature drop of more than 20 degrees. Therefore, growing and caring for wisteria in the Moscow region is extremely difficult. There are special requirements for the safety of vines in the winter. The plant overwinters best when growing a crop in a container way.
Wisteria does not tolerate a temperature drop of more than 20 degrees. Therefore, growing and caring for wisteria in the Moscow region is extremely difficult. There are special requirements for the safety of vines in the winter. The plant overwinters best when growing a crop in a container way.
It should be borne in mind that the "house" for the creeper does not require a small one - at least 40 liters. Plastic fonts, tubs, garden barrels are used.
The cultivation of wisteria in the Urals is similar. Yes, you have to work hard, but the result will surprise you.
With the arrival of autumn, before the first snow falls, the liana is sent in containers to winter in a warm room, where a minimum six-hour lighting can be provided. In this case, the plant should be watered once a week. Top dressing is excluded.
With the onset of March, the vine is moved to a bright room and watered well 2-3 times / week. Spraying with growth stimulants is allowed.
The practice of gardeners shows that even with seed growing of frost-resistant wisteria in the Moscow region and in the Urals, the liana will be able to give abundant two-time flowering (in summer and autumn). True, for a start, you will have to wait a long time for the sprout to turn into an adult tree.
Siberia
 Wisteria is incredibly beautiful. It is not surprising that absolutely everyone wants to see her. But growing wisteria in Siberia is almost impossible. Even a variety like Blue Moon, which can withstand 40 degrees of frost, bows to its environment. In addition to a mild and warm climate, wisteria needs a long growing season. It is he who is responsible for the abundant and long flowering. The climate of Siberia cannot provide the necessary conditions. Even if you contrive and grow a vine, covering and protecting it at the same time from frost (providing a good shelter for the winter), and carefully watching that the plant does not get wet, flowering most likely will not come. If a miracle happens, the inflorescences will be weak and single.
Wisteria is incredibly beautiful. It is not surprising that absolutely everyone wants to see her. But growing wisteria in Siberia is almost impossible. Even a variety like Blue Moon, which can withstand 40 degrees of frost, bows to its environment. In addition to a mild and warm climate, wisteria needs a long growing season. It is he who is responsible for the abundant and long flowering. The climate of Siberia cannot provide the necessary conditions. Even if you contrive and grow a vine, covering and protecting it at the same time from frost (providing a good shelter for the winter), and carefully watching that the plant does not get wet, flowering most likely will not come. If a miracle happens, the inflorescences will be weak and single.
Belarus and Ukraine
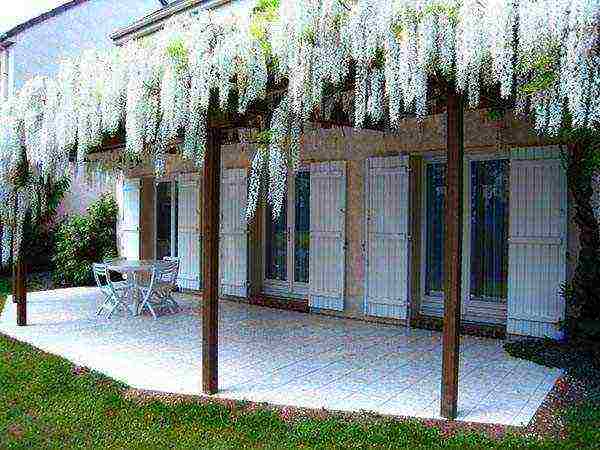 These countries are in a much warmer climate than in central Russia. So summer residents can rejoice - they will be able to grow wisteria.
These countries are in a much warmer climate than in central Russia. So summer residents can rejoice - they will be able to grow wisteria.  Moreover, they can grow thermophilic varieties, for example, "Chinese".
Moreover, they can grow thermophilic varieties, for example, "Chinese".

Growing wisteria in Belarus, they give preference to seedlings. At one year of age, they are planted in a sunny area when the soil and the environment are well warmed up.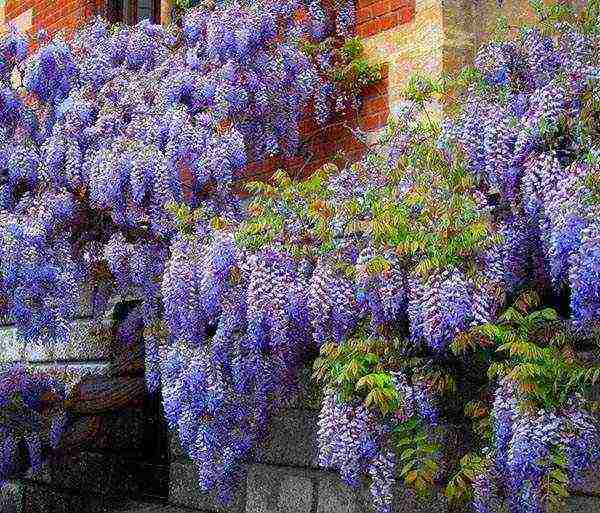  This time comes in April-May. Adult vines will bloom during the summer months beginning in late June. With the arrival of autumn, the plant should be well insulated.
This time comes in April-May. Adult vines will bloom during the summer months beginning in late June. With the arrival of autumn, the plant should be well insulated.
Reproduction of wisteria
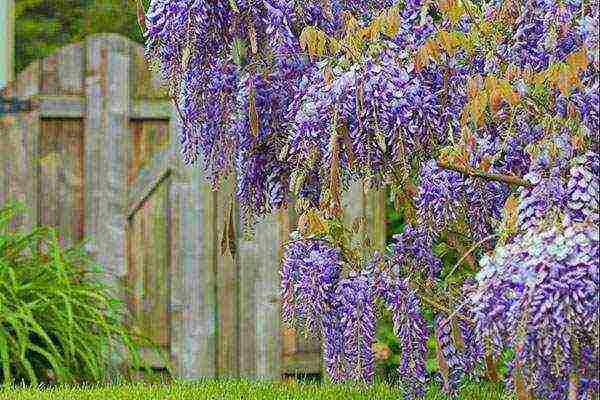 There are several breeding options for wisteria, each of which is good in its own way.
There are several breeding options for wisteria, each of which is good in its own way.
Layers
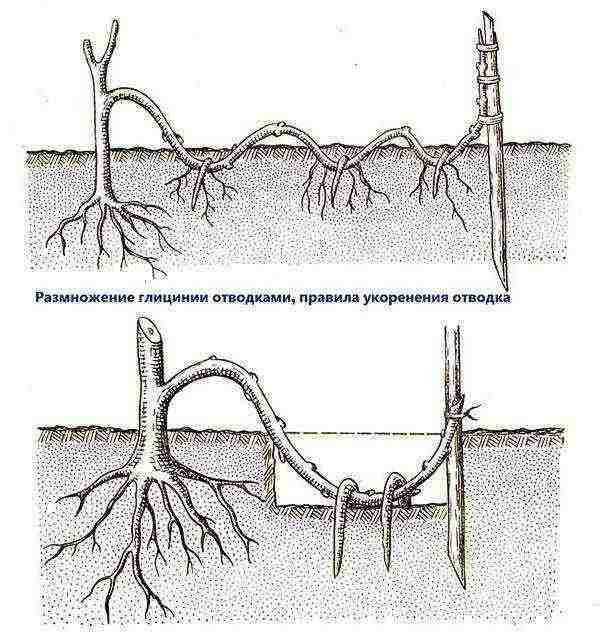 In addition to reliability and simplicity, the method is good in that it conveys all the signs of the mother plant to the children. They take part of the shoots of the last year and, with the arrival of spring or autumn, dig a row of 20 cm deep near them, add nutrient-rich soil into it, and spill it well with water. On the shoot, just above the buds, small cuts are made and the shoot is placed in a hole, remembering to pin it so that it does not come out, and sprinkle it with earth.
In addition to reliability and simplicity, the method is good in that it conveys all the signs of the mother plant to the children. They take part of the shoots of the last year and, with the arrival of spring or autumn, dig a row of 20 cm deep near them, add nutrient-rich soil into it, and spill it well with water. On the shoot, just above the buds, small cuts are made and the shoot is placed in a hole, remembering to pin it so that it does not come out, and sprinkle it with earth.
It is impossible to sprinkle the top of the shoot with earth, the plant will "breathe" through it. You just need to tie it to the peg in an upright position.
The shoot rooted in the leaf nodes is separated from the "mother" only after 1-1.5 years. If its root has developed strongly, it is immediately transplanted permanently into the ground, weakly into pots and sent to grow further.
Lignified cuttings
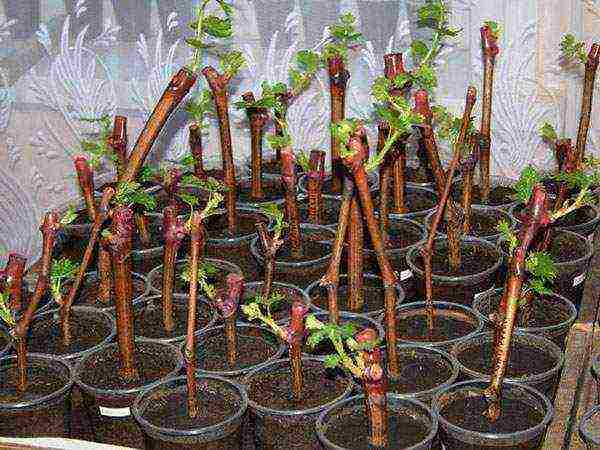 Cut them in the fall from the middle zone of ripe shoots. Each branch should have two buds and a length of 5-8 cm. After they are planted and kept until spring at 3 ° C. With the onset of April-May, cuttings are transplanted into containers with wet sand on the soil surface. Planting is carried out vertically to a depth of 4 cm, observing the distance between the cuttings of 10 cm. In the spring, they are transplanted into pots and sent for growing. After a year, the vines can be planted permanently in the ground.
Cut them in the fall from the middle zone of ripe shoots. Each branch should have two buds and a length of 5-8 cm. After they are planted and kept until spring at 3 ° C. With the onset of April-May, cuttings are transplanted into containers with wet sand on the soil surface. Planting is carried out vertically to a depth of 4 cm, observing the distance between the cuttings of 10 cm. In the spring, they are transplanted into pots and sent for growing. After a year, the vines can be planted permanently in the ground.
Winter root grafting
 The method is very complex, but it conveys all the varietal characteristics. In the fall, seedlings with off-grade wisteria are dug up, the root is separated (the thickness of the roots should be at least 6 cm), they are transplanted into containers with sand and sent to a cool place devoid of light. In December-January, they bring it into the warmth. Two weeks later, cuttings of varietal wisteria are inoculated with a length of 6 cm, having 2 buds and a sharp cut of 2-3 cm under the lowest. A similar cut is made on the root-rootstock for tighter contact. The vaccination site is well fixed with a plaster.
The method is very complex, but it conveys all the varietal characteristics. In the fall, seedlings with off-grade wisteria are dug up, the root is separated (the thickness of the roots should be at least 6 cm), they are transplanted into containers with sand and sent to a cool place devoid of light. In December-January, they bring it into the warmth. Two weeks later, cuttings of varietal wisteria are inoculated with a length of 6 cm, having 2 buds and a sharp cut of 2-3 cm under the lowest. A similar cut is made on the root-rootstock for tighter contact. The vaccination site is well fixed with a plaster.
Next, the cuttings are planted in a container with a nutrient substrate, without deepening the grafting site, and covered with glass. Further conditions of detention: at least 15 ° C and humidity 80%. If everything is done correctly, shoots from the axillary buds should appear in two weeks. Well-rooted vines can be transplanted into the ground.
Wisteria from seed
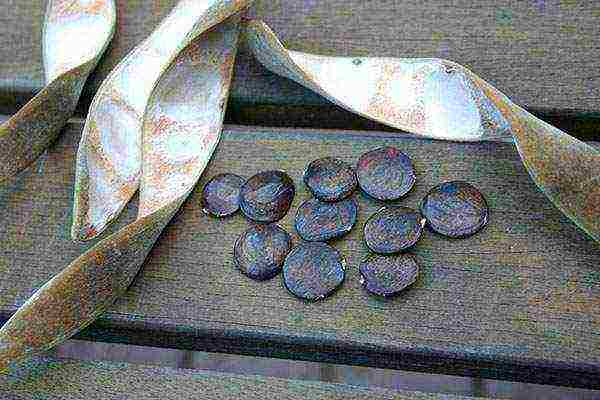 You can sow seeds in March in open ground or in December in small greenhouses. In the second case, a mixture of leaf and sod land with sand (4: 1: 1) is used as a substrate. The seeds are simply laid out on the soil and lightly sprinkled with sand, covered with glass and sent to a warm (at least 20 ° C) and dark place. At the same time, they control that the soil is constantly moist.
You can sow seeds in March in open ground or in December in small greenhouses. In the second case, a mixture of leaf and sod land with sand (4: 1: 1) is used as a substrate. The seeds are simply laid out on the soil and lightly sprinkled with sand, covered with glass and sent to a warm (at least 20 ° C) and dark place. At the same time, they control that the soil is constantly moist.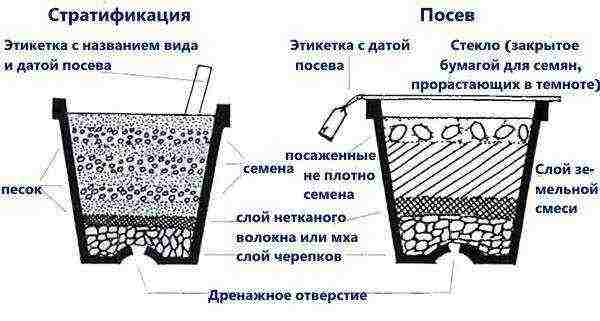
After a month, the seeds will hatch, after another 1.5 weeks they are brought out into the light, shading at first from the sun. When 2 pinnate leaves appear, a pick is made, trying not to damage the roots. In the future, such sprouts can be used for grafting. Please note that homemade wisteria from seeds does not convey varietal characteristics. Therefore, its flowering may not come or be very poor, even after 8 years.
As you can see, growing wisteria and caring for it in the middle climatic zone has significant difficulties. But it's never too late to experiment. Subject to all the nuances, you can grow a real beauty. Of course, not the same as in China, but its bloom will delight you.


