Content
- 1 1 Landing
- 2 2 Care
- 3 Description
- 4 The necessary conditions
- 5 Growing from seeds
- 6 Care
- 7 Pruning and shaping the bush
- 8 Shelter for the winter
- 9 And a little about secrets ...
- 10 Plant species
- 11 Planting creepers
- 12 How to care for
- 13 Pruning
- 14 How best to feed
- 15 Seed propagation
- 16 Reproduction by layering
- 17 Description of wisteria
- 18 Types of wisteria
- 19 Planting wisteria outdoors
- 20 Outdoor care for wisteria
- 21 Reproduction of wisteria
- 22 Diseases and pests of wisteria
Wisteria has a beautiful flowering. Fragrant lilac, purple or white inflorescences are collected in hanging clusters up to 40 cm long, and some up to 70 cm. The first flowers appear at the end of March, and the flowering period can last until the end of summer. Amateur gardeners and landscape designers use the flowering liana extensively in their projects. Branches can be wrapped around a gazebo, garden arch or porch of a house.
The plant grows on the southern coast of Crimea and in the subtropics of the Caucasus, in Stavropol and Astrakhan. Cultivated species of thermophilic wisteria are also grown in other latitudes, but they do not give such a beautiful and abundant flowering without special care. It is possible to cultivate wisteria at home in the form of a bonsai tree. Breeders have grown frost-resistant varieties that are suitable for temperate climates. Although the southern culture is a subtropical liana, cultivation in the middle lane is also permissible.
1 Landing
It is necessary to take into account the factor that the plant is perennial, and the place must be chosen for it for many years. If it is sunny, and the land is nutritious and sufficiently sheltered from the wind, then abundant and bright flowering is guaranteed. Despite the resistance to light frosts, it is preferable to plant wisteria in open ground in the spring, when the threat of cold weather has already passed. In order for the vine to bloom faster, it is grown from seedlings.
Before planting, the soil is dug up with the addition of mineral fertilizers. The holes are made square 50 x 50 cm, in which the plant is planted vertically. It is not recommended to grow wisteria with seeds, as it will bloom in the best case in 5 years (or even 10).
The most common types of wisteria for planting are:
| View | Peculiarities | Photo |
| Chinese | For the middle lane and the Moscow region, this is one of the most popular types of flowering vines. And in the northern regions and Siberia, it is advisable to land in containers. The species is distinguished by a wide variety of shades of inflorescences; with adequate care, vines can grow up to 20 m in length. The racemose inflorescences have a very pleasant smell, which is vaguely similar to the smell of acacia. At the end of the flowering period, beans up to 12 cm long with seeds inside are formed on the brushes |  |
| Abundantly flowering (multi-flowered) | Grows well in colder regions of Russia. Vines reach a length of 8-10 m. The stems twist strictly clockwise, and at the base the diameter is 20-30 cm. When they age over the years, light green shoots are covered with dark gray bark. Wisteria blooms a little later than Chinese wisteria, and flowers bloom in stages, starting from the base. The cultivation of a variety of flower growers was engaged in the 19th century. |  |
| Shrub | This liana reaches a height of 12 m. The drooping branches with a large number of leaves form a dense crown. The flowers of the plant are very beautiful, with a violet-blue tint. For flower growers living in cool regions, the flower can be grown in tubs and containers |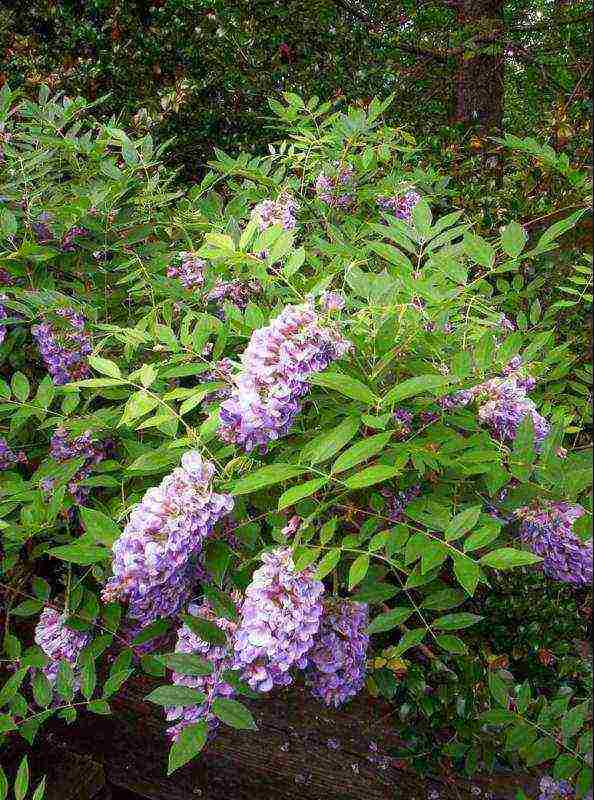  |
2 Care
When growing wisteria at home, you need to follow some rules:
- 1. Soil. The plant loves fertile black soil or loamy soils.An important condition is the absence of stagnant water on the site. Many growers for growing a plant completely replace the planting site with fertile soil and drain the soil.
- 2nd place. Since the plant is quite thermophilic, the location should be open and sunny. Sunlight should fall on the flower at least 5-6 hours a day. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a site for planting taking into account this condition. Better if it is on the south or southeast side of the building. It is also necessary to take care of a reliable support for the climbing vines of the plant.
- 3. Time. If these are seeds, then they feel more comfortable in the greenhouse. Planted in November-December. And it is better to plant cuttings in the ground in the spring, they take root easier this way.
After planting, young cuttings must be mulch 10 cm above the neck. For this, peat or dry compost is used. The mulch lays down in an even layer and remains there until next year. In the summer, it will protect from the sultry sun, and in the winter it will help protect the fragile root system from frost. One of the main tasks after planting is proper watering: regular, but without excessive stagnation of moisture. The first time after moistening, it is necessary to regularly loosen the soil and fertilize with organic fertilizers. If the recommendations were followed in a timely manner, then the next year the seedling will delight you with bright and strong shoots.
Wisteria, like many related plants, is susceptible to fungal diseases. Powdery mildew is one of the most common. Modern fungicides such as Fundazol, Vitaros and others will help to solve the problem. Chlorosis is not uncommon, which occurs due to a lack of iron in the soil. In this case, experts recommend replanting the plant to another place or trying to enrich the soil with iron using the preparations "Ferovit" or "Antichlorosis".
Another important condition is pruning. After all, the number of flowers in the current year depends on its implementation. So, it should be trimmed regularly twice a year. Wisteria will bloom well if all annual growths are shortened in August so that the length remains up to 30 cm.And in the spring of next year, after flowering, the shoots are shortened more, leaving up to 10 cm of the length of the shoots. This process is not difficult, but it must be carried out without fail, otherwise there will be no abundant flowering.
In different regions of the country, wisteria cultivation has different characteristics. In the Moscow region and the middle lane, care is not difficult, the main thing is to cover the plant well for the winter. In the Urals and Siberia, it must be borne in mind that delicate wisteria may not withstand severe frosts, so planting a plant in tubs would be a good option. For the winter, it is recommended to bring them indoors, on terraces, balconies. And with the first heat, take it outside again.
Subtropical plants in their decorative qualities are much higher than the northern ones. Thanks to the efforts of breeders, new frost-resistant species and varieties of them appear. Wisteria is one such exotic plant. It is successfully grown in the southern subtropical regions. There she creates wild thickets.
Now wisteria is grown not only in the Central lane, but even in Siberia. True, there she gets into fresh air only in summer. But it can bloom, subject to the conditions of detention.
Subtropical plants in their decorative qualities are much higher than the northern ones. Thanks to the efforts of breeders, new frost-resistant species and varieties of them appear. Wisteria is one such exotic plant. It is successfully grown in the southern subtropical regions. There she creates wild thickets.
Now wisteria is grown not only in the Central lane, but even in Siberia. True, there she gets into fresh air only in summer. But it can bloom, subject to the conditions of detention.
Description
Wisteria is rare in Russian yards.This unusual flowering vine belongs to legumes. Another name is wisteria. At home, in China, it is widely used to decorate arches, gazebos, pergolas, tall buildings. With age, the branches of the plant thicken, and the vine itself becomes like a tree. It can reach a height of up to 15 m, but there are lower species, up to 9 m. Low species and varieties of wisteria are grown as indoor.
 ErnstErnst: “I threw Malakhov to hell after the broadcast about“ sore joints ”! He dared ...
ErnstErnst: “I threw Malakhov to hell after the broadcast about“ sore joints ”! He dared ...
>>
The leaves are complex, their plates have serrated edges. The root is powerful, occupies a large area in an adult plant. This must be considered when choosing a growing location, including a pot or container.
Flowers are the main decoration of the plant. They look like acacia flowers, but they are striking in the variety of colors and sizes of inflorescences hanging from the branches. Its length in different species reaches from 15 to 30 cm. The color is white, various shades of pink and purple, blue and red.
They bloom early, even before the leaves bloom. The second time flowering can occur in early August, subject to the growing conditions.
Views
The most common types of wisteria are:
- Chinese grows up to 20 m, blooms with blue and purple flowers. Poorly tolerates frost.
- Japanese (abundantly flowering) - relatively low, up to 10 m, with large leaves and small flowers. The number of inflorescences and their size are larger than that of the Chinese. Frost resistant.
- Beautiful with inflorescences up to 15 cm in length, covered with white flowers. Blooms from May to October.
- Shrub with small flowers grows up to 12 m.
- Large-scaled tolerates cold well, but young shoots often freeze slightly. The flowers are white and purple, rarely red. An example is Blue Moon, a cold hardy variety that can survive temperatures below 40 degrees below zero.

Chinese wisteria

Beautiful wisteria
The necessary conditions
Wisteria is a thermophilic plant, most species of which do not tolerate frost well. She prefers nutritious and light soil. To successfully grow wisteria, you need a lot of sunshine, from 12 hours a day. If the daylight hours are shorter, the flowers will be smaller and paler. Water sparingly, keeping the soil slightly moist.
Propagate wisteria by seeds, branches or cuttings. Wisteria grown from seeds will bloom no earlier than 3 years (Chinese). Some species will please with flowering after 10 years (profuse flowering).
Experts say that not all plants grown from seeds will bloom. In addition, with this method of propagation, hybrid varieties do not retain the properties of the parent plant. Therefore, you need to take only seeds purchased in specialized stores. Better if they were collected from plants that grow in the same climate.
Better to use cuttings or layering. But it is not always possible to purchase them. Therefore, if there is a free area, several plants grown from seeds are planted. They wait for them to bloom, and then remove the extra ones.
Growing from seeds
Sow at home immediately after collecting the seeds. If you do this in November or December, then in May it will be possible to plant in open ground. You can plant in early February, but then the plant will be ready for planting next spring.
A mixture is prepared, the main part of which is leafy earth (4 parts), in terms of turf and sand. It is not advised to introduce peat. It makes the soil loose, but oxidizes it. The seeds are disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate and germinated in a damp cloth. The soil and dishes are treated against the fungus. Lay a drainage layer of about 3 cm.
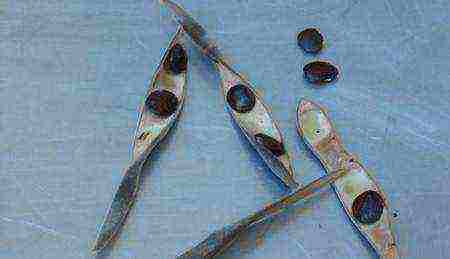
Wisteria seeds
The seeds are placed in the grooves in a horizontal position to a depth of 2 cm, watered and covered with foil or glass to maintain constant humidity. The room temperature should be around 30 degrees.
When the shoots sprout, the dishes are placed in a well-lit place, but the sun's rays should not fall on the delicate leaves. In the phase of four true leaves, plants dive into a separate bowl with a volume of at least half a liter. Watered with a pink solution of potassium permanganate to protect against fungal diseases.

Wisteria seedling
If the seeds are purchased in winter, you can sow them in open ground after the threat of frost blows, and the ground warms up to 10 degrees. They are looking for a bright area, protected from northern winds and drafts, with slightly alkaline soil.
Mineral fertilizers are applied, mixed with the soil taken out of the prepared pit. Its depth is 60 cm, diameter is 50 cm. They put the earth in a pit, slightly compacting it. Several seeds are sown, covered with soil, watered. It is advisable to cover with black polyethylene before germination. Then it is removed, mulched with cut grass with a layer of at least 7 cm. The sprouts are sheltered from direct sunlight.
Seedlings are planted in a permanent place in holes prepared in the same way. Landing is carried out by transshipment. You need to plant together with a clod of earth. Sprinkle with humus on top.
Care
The tree grows very slowly for the first 5 years. Outdoor care includes watering, fertilizing, loosening the soil around the trunk. During flowering, wisteria needs to be fed with potash and phosphorus fertilizers every 10 days. In the spring, compost is applied, but so that the amount of nitrogen in the soil is not large. Otherwise, the wisteria will grow and be covered with leaves, but will not bloom. On a plot with acidic soil, once a summer, 100 g of crushed chalk is dissolved in a bucket of water and watered over the liana.
Sometimes the young parts of the plant are affected by aphids or clover mites (briobia). Aphids feed on the juice of young shoots. You can fight it by treating it with a solution of laundry soap or insecticides.
Briobia are 0.6 mm insects with a brown or green body. They run quickly through the leaves, laying round red eggs on the outside of the leaf. As a result of their activity, the leaves curl. You can fight them by spraying with acaricides, drugs that destroy ticks ("Apollo", "Masai").
Wisteria can be affected by chlorosis and renal blast. Chlorosis is susceptible to crops growing on heavy clayey limestone soil. You can get rid of light spots on the leaves by adding iron salts.
Renal blast is manifested by the fact that the kidneys darken and become moldy. At the first sign of illness, the affected areas are cut and burned.
Pruning and shaping the bush
In order for wisteria to please with a large number of flowers, it needs to be cut 2 times per season. It is taken into account that flower buds are formed on last year's shoots in the leaf axils. Therefore, they are not cut off completely, but only shortened to 40 cm. Flower buds will form in September and bloom next year.
In the summer, at the beginning of August, the main pruning is carried out, which is aimed at thinning the bush and reducing the number of young shoots. Open the stems growing from the bottom. To do this, remove the shoots that go up or into the bush, cut off the stems growing from the base. Branches growing in several pieces from one place are cut off or cut off with a sharp secateurs.
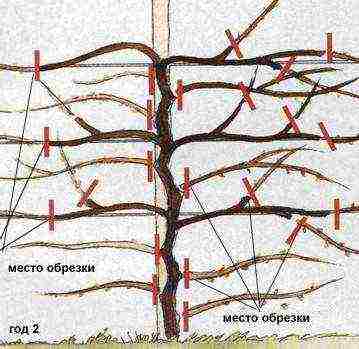
Pruning wisteria
Branches that have faded are removed. They can be identified by the tendrils that remain after the flowers have fallen off. With good care, flowering can be repeated a second time at the end of summer. There will be fewer flowers than in spring. Sanitary pruning is carried out in the spring. First of all, dry and damaged shoots are cut.
Some gardeners perform the main pruning in the spring, when the formed flower buds are clearly visible, and the leaves do not interfere with the assessment of the shoot ratio. 5 axillary buds are left on the shoots. After cutting off thick branches, the cut sites are treated with garden pitch.
Shelter for the winter
Without shelter, you can grow wisteria in the south, for example, in Astrakhan.Most wisteria species do not tolerate frost well, so they need shelter for the winter. If the temperature drops below 20 degrees below zero, even old branches die. In the spring, young shoots can grow, but they will be able to bloom in a few years if they do not freeze again.
To grow wisteria in the Moscow region or the Middle lane, you need to choose frost-resistant varieties, for example, Blue moon. Liana is removed from the shelter, laid on spruce branches or other protective material. The root system is covered with earth or compost. The trunk is laid on the ground, covered with spruce branches or dry leaves on top. It is impossible to cover with wet ones, so as not to bring in fungal diseases. The thickness of the protective layer must be at least 15 cm.
In Siberia, wisteria can be grown in containers and moved indoors in the fall. The volume of the barrel or container must be at least 40 liters. They are brought into the warmth in autumn, before the onset of frost. They light up a little, sometimes watered, maintaining a minimum soil moisture.
And a little about secrets ...
The story of one of our readers Irina Volodina:
I was especially depressed by the eyes, surrounded by large wrinkles plus dark circles and swelling. How to remove wrinkles and bags under the eyes completely? How to deal with swelling and redness? But nothing makes a person look older or younger than his eyes.
But how to rejuvenate them? Plastic surgery? Recognized - not less than 5 thousand dollars. Hardware procedures - photorejuvenation, gas-liquid pilling, radiolifting, laser facelift? Slightly more affordable - the course costs 1.5-2 thousand dollars. And when to find all this time? And it's still expensive. Especially now. Therefore, for myself, I chose a different way ...
Read the article >>
With the onset of spring, white and light lilac clusters of beautiful buds begin to bloom in the gardens. It pleases the eye with its blooming wisteria. Planting and caring for a weaving plant is up to every summer resident. It can be planted near a gazebo, or decorated with a vine at the entrance gate and walls of the house. The abundant and long-lasting bloom of wisteria creates an atmosphere of a fabulous country on the garden plot.

Plant species
The second name of the plant is wisteria. It belongs to a rare genus of deciduous vines that are part of the legume family. It grows in natural conditions in the Caucasus, East Asia, Crimea and America. The cultivation of wisteria in the open field is successfully proceeding in the south of Ukraine and Russia, since in these regions there are rather warm winters and hot summers.
Until recently, residents of a more severe climate had to carefully cover the vine with the onset of cold weather, but, despite such care, it often froze and died. This problem has now been resolved. Breeders bred a frost-resistant wisteria variety, which received the poetic name "Blue Moon". It can withstand air temperatures up to -40C, and now the tree-like liana can be safely planted in central Russia, in the Urals and in southern Siberia.
Wisteria has 9 varieties. The most popular among summer residents, in addition to the frost-resistant variety, are the following.
- Chinese wisteria. Liana grows up to 20 meters, blooms almost all summer with pale lilac flowers, the brushes of which reach 30 cm;
- Japanese wisteria. This is a short vine. It grows to a length of about 9 meters, but compares favorably with other varieties with larger leaves and flowers;
- Wonderful wisteria. It weaves up to 10 meters. In June, it blooms with white or bluish flowers.
The rest of the wisteria varieties are less common, and they are rarely used for landscaping in our country.

Planting creepers
Before planting, it must be borne in mind that wisteria is a perennial plant, so the place for it should be carefully chosen. Growing wisteria will be more successful if it is rooted in a sunny area protected from the wind with nutritious weakly alkaline soil. The plant is planted in open ground in spring, when the last frosts end and the ground warms up well.If you do this earlier, tender seedlings may not take root.
- The plot of land where the cultivation of wisteria is planned must be dug up onto a shovel bayonet, after having saturated the soil with mineral fertilizer. The recommended dose is 20-30 g per sq. m area.
- Then dig a hole 50 cm deep and wide, pour a thick layer of broken brick or expanded clay inside and sprinkle it lightly with earth.
- Then pour a bucket of water into the recess. Wait until it is absorbed and place the seedling there.
- Sprinkle it with earth from the garden, gently pressing down with your hands, and moisten the ground again.
Get ready for the fact that at first the wisteria will not actively grow. Do not stop regular grooming, and gradually she will start to release thin shoots. The first abundant flowering can be seen not earlier than in 4-5 years.

How to care for
Competent care consists in the garter of young shoots. Growing vines should take place next to a durable and powerful support that can withstand gusts of wind and the weight of an adult plant.
Advice
It is advisable to tie the wisteria to the support yourself. If it starts to weave itself, then it will be difficult to untangle it and lay it on the ground before frost.
Wisteria care is impossible without regular watering. Make sure that the ground is always moist, but without stagnant water under the bush. From the beginning of flowering until autumn, watering should be slightly reduced. Waterlogged soil can lead to the fact that the wisteria's blooming brushes fall off. The next day after moistening, do not forget to carefully loosen the ground under the vine so that a crust does not form in the hole, which prevents the plant from developing normally. In extreme heat, it is useful to spray the shoots with water from a hose. This treatment removes dust from the leaves and refreshes well.
When the last leaves fall off the wisteria, you need to start preparing for the winter.
- Since most varieties of wisteria do not tolerate severe frosts, they need to be insulated.
- To do this, huddle the root part high, untie the shoots from the support and carefully spread them on the ground.
- Sprinkle the plant on top with a thick layer of dry grass and spruce branches.
Young shoots are vulnerable to low temperatures, so be sure to cover wisteria in central Russia and in the Ural region.
Pruning
In order for the care to be complete, the plant needs pruning. Without it, wisteria will not bloom well and for a long time. Most wisteria flowers bloom on last year and the year before last, so it is important that the flower buds form on them correctly. To do this, all branches of the creeper are shortened by 2 cm in May.
Fall grooming also includes pruning. In September, you need to cut off the tops from young shoots, counting 4 buds from the top. By following these recommendations, you will achieve the maximum splendor of the flowering plant.
After flowering, remember to remove dry buds, and regularly dispose of diseased old branches.

How best to feed
Growing wisteria is impossible without systematic feeding. During active growth and flowering, they must be produced once a week. Experienced gardeners recommend alternating mineral and organic fertilizers.
Kemira Lux has proven itself well. It provides the plant with useful elements for a long time. The fertilizer is sold in liquid form and in granules. To feed wisteria, it must be diluted and used strictly according to the instructions.
From organic dressings for wisteria, a mullein solution is ideal.
- You will need a large barrel to make it. Place a bucket of cow dung there, which you managed to overheat, and pour 5 buckets of water.
- Stir and let sit for 2 weeks to infuse.
- After half a month, the top dressing is ready, and you can use it.
- Before use, dilute the organic solution with water in a ratio of 1:10 and pour the wisteria into the root.
In the middle of summer, you can feed the plant with chalk once.To do this, grind 100 g of chalk into powder, dissolve in 10 liters of water and moisten the soil under the growing vine.
Advice
If you want to see a wild bloom, use nitrogen fertilizers with care. Their excess in the soil will lead to the fact that wisteria will build up green mass and grow rapidly upward, but will stop blooming altogether.

Seed propagation
Growing vines from seeds is rarely practiced, since the method is rather complicated and not always successful.
- You will need to prepare potting soil for planting. Take one piece each of sand and turf, add four pieces of leafy soil to them and mix well.
- Place the soil in a special box with holes in the bottom, sow the seeds and sprinkle the soil with water from a spray bottle.
- Cover the top with plastic or glass. Place a kind of greenhouse in a warm, dark place for 4 weeks.
During this period, do not forget to raise the glass for ventilation and watering. During this time, the first shoots will hatch in the box. After a month, they can be placed on a lighted window sill and provided with normal care. When the plants have 2 leaves, they need to be transplanted into large containers along with a lump of earth on the roots. Continue growing seedlings on the windowsill throughout the winter. In the spring they are rooted in the street. They take root well outdoors, but often do not bloom for a long time.

Reproduction by layering
The easiest way to get a new plant is by layering. In May, pick up a healthy young shoot about 15 cm long. Make an oblique cut in the middle with a sharp knife. Place a wide container with fertile soil next to the vine. Tilt the prepared branch and dig in the pot. The tip of the shoot must necessarily remain free. If the layering is provided with full-fledged care, which includes potassium-phosphorus fertilizing and watering, it will gradually take root and grow.
By the fall, the cuttings grow well, and several branches appear. Excess shoots must be ruthlessly cut off, carefully separated from the adult wisteria, and the plant in a pot must be brought into the cellar for the winter. In the spring he is transplanted to a new place.
In addition to these two methods, some craftsmen manage to propagate wisteria by grafting on the roots or cuttings. The methods are ineffective and rarely give a positive result.
In Siberia, wisteria is often grown in large pots in the summer, which are placed in the garden. When late autumn comes, the plant is brought into the cellar, where it stands until spring. The next year, the vine is transplanted into a wider pot and again taken out into the street.
Wisteria looks great in landscaping. She perfectly disguises unsightly walls, decorates fences or gazebos. Be sure to plant this unpretentious plant, and in a few years your home will be completely transformed.
Anyone who has ever seen a wisteria bloom will never forget the impression she left. This plant can be used to decorate a gazebo, a wall, an entrance to a house or a garden arch. But only it grows mainly in warm regions - in the Crimea or the Caucasus, for example. In other latitudes, thermophilic wisteria will not produce such abundant and beautiful flowering without proper care.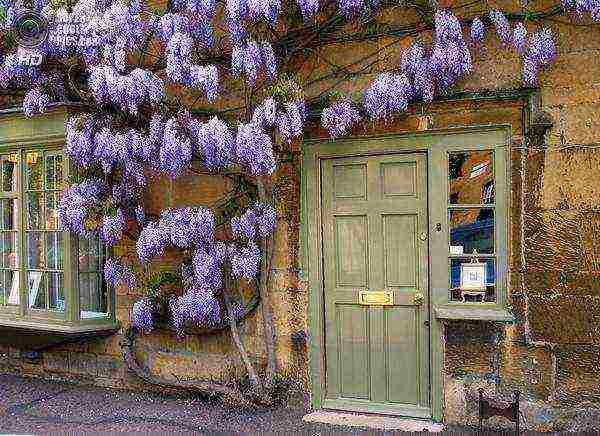
Description of wisteria
Wisteria is Greek for "sweet" due to the wonderful aroma of its flowers. There was a lot of controversy as to whether it was a flower or a liana. However, as a result, the general concept was formed that wisteria is a tree-like climbing and flowering plant. In appearance, it is a woody liana with drooping branches.
Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
An adult wisteria liana in height can reach 15-18 m, and in diameter the crown sometimes grows up to 8 m in diameter. It differs not in very fast growth - during the season it can grow by only 20 cm. The leaves of wisteria are large, odd-pinnate, which consist of 7-13 small leaves. Young leaves are slightly pubescent, later glabrous.Wisteria blooms with pink, lavender, purple, blue and white flowers, which are collected in loose inflorescences up to 30 cm in length. Flowering of this amazing liana begins in spring in late March or early April and lasts almost until the end of summer. Wisteria flowers have a delicious aroma. Wisteria is the queen of garden vines and is widely used to decorate the site and buildings. In total, there are 9 species of this plant in nature, of which only a few have become widespread in the territory of a temperate climate.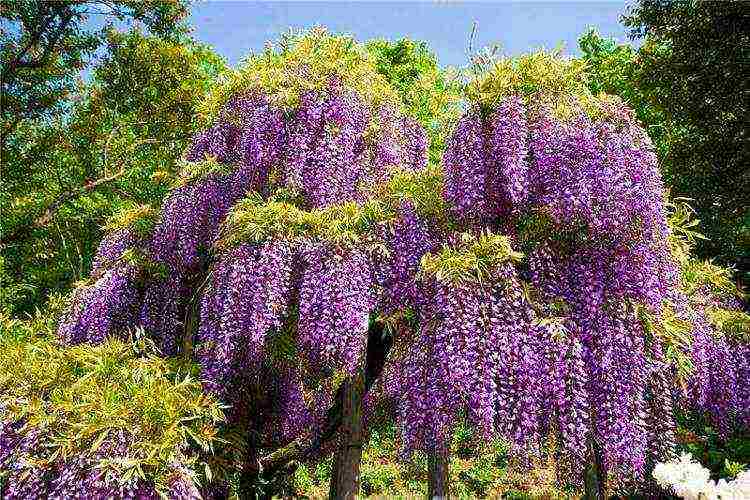
Types of wisteria
There are several varieties of the plant:
- Chinese wisteria with light purple flowers. It can grow up to 15-20 meters in height, blooms all summer, at the end forms 15-centimeter legumes. Can be grown as a standard tree.
- Multi-flowered wisteria with bluish-purple flowers. Grows up to 8-10 meters. Has elongated brushes - up to half a meter long. More frost-resistant than the previous variety.
- Wisteria is beautiful with white and purple double flowers. It grows up to 10 meters, has an inflorescence length of about 20 cm. It blooms all summer with the formation of leguminous fruits.
- Japanese wisteria with white flowers. Not as impressive as other varieties, and besides, it does not tolerate frost. It grows mainly on the Black Sea coast.
- Shrub wisteria with bluish-purple inflorescences of small size. Grows up to 12 meters in height. It takes root well in the Crimea. It can be grown in a container if desired.
 Planting wisteria outdoors
Planting wisteria outdoors
Traditionally, flowering liana is planted near the south or southeast wall or next to a solid support in a well-sunlit area. In addition to the light, it should be very warm here during the day and especially at night. Wisteria will not be against a light breeze, but stagnant air and excess moisture will destroy it.
Planting vines is best done with seedlings at the age of 1-2 years in well-fertilized, oily and slightly moist soil. If there is a lot of lime in the soil and it is too damp, the plants will not take root or will suffer from chlorosis.
For a seedling, lianas dig a deep hole, fill it with river sand, humus, leaf and clay-sod soil, mixed in equal parts. Additionally, a complex mineral fertilizer is applied. The prepared soil is allowed to compact slightly for 5-7 days, and then the plant is dug into it and watered abundantly with warm water. This should be done in the spring, when the air and earth are already warming up well, and return frosts have passed.
Outdoor care for wisteria
Wisteria care begins with a garter of young shoots. Since the vine grows for a long time and has a high windage, the support must be durable and capable of withstanding wind loads. It is best to tie the wisteria to the support, because independent weaving around the support can lead to the fact that it will be very difficult to remove the vine to prepare for winter in the fall. The soil should not be calcareous, otherwise the wisteria leaves will brighten and lose their decorative effect.
Too wet soil can cause the plant to shed leaves and buds. Therefore, you should observe moderation in watering from the beginning of flowering until the end of summer. In the summer, additional spraying can be carried out so as not to overwhelm the roots with water. In September, watering should be minimized and the plant should be prepared for winter.
A very important condition for the flowering of wisteria is timely and correctly carried out pruning. Wisteria flowers develop on vines of last year and even earlier. Sometimes on young shoots of this year. Therefore, for the correct formation of flower buds in early summer or at the end of May (depending on the wisteria flowering season), last year's shoots are shortened, leaving no more than 30 cm.
In the fall, the shoots of the new season are cut by cutting off 4 buds.After that, in early spring, during the garter of the vines to the support, last year's shoots are reduced by another 2 buds.
Many varieties of wisteria are preferable to cover for the winter, especially in the northern regions. Young shoots are considered the most vulnerable. In autumn, it is recommended to untie them from the support and lay them on the ground. The root part is buried in a thick layer of earth, and the shoots are covered with spruce branches, a layer of leaves or a special covering material. The older the plant becomes, the higher its frost resistance, respectively, the less it needs winter shelter.
It is impossible to take your eyes off the photo with blooming wisteria. To achieve the same flowering on your vine, you should pay a little attention to feeding. During active life, it is recommended to fertilize wisteria at least once a week, while it is best to alternate liquid mineral fertilizers with organic ones (for example, with mullein infusion diluted with water in a ratio of 1:20). A one-time top dressing in the summer, you can add a chalk solution. To do this, you need to dilute 100 g of chalk in a bucket of warm water and water the plant at the root.
Reproduction of wisteria
Seed propagation of wisteria is troublesome, especially since some plants may not bloom at all. To obtain planting material, it is best to propagate wisteria by layering.
Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
An annual shoot is incised and instilled, leaving the top for free growth. The procedure is carried out in the spring. After a year, a young seedling can be planted in a permanent place, providing it with proper care.
Some gardeners resort to grafting wisteria, but few succeed in this method. The cuttings do not take root well, so there is no point in wasting time and effort.
Diseases and pests of wisteria
Wisteria is resistant to disease, and because of its poisonous properties, it is extremely rarely attacked by pests. It can be:
- Caterpillars that make holes in the leaves. They are rendered harmless by spraying with a biological preparation.
- Green aphid. It affects leaves and flowers, is destroyed by insecticides.
- Clover mite. It is determined by the unnatural bronze color of the leaves, in which case the vine is treated with acaricides.


