Storage rules and periods
The storage conditions of the safety harnesses must ensure, first of all, that there is no likelihood of any kind of damage (mechanical, chemical or damage associated with the effects of atmospheric phenomena). Therefore, equipment kits are stored in dry rooms, thoroughly cleaned of any contamination and protected from sunlight.
Do not store products near heating devices, as well as in close proximity to flammable substances (gasoline, kerosene), acids or other chemical compounds that can cause the destruction of the material from which the safety harnesses are made. It is possible to store the product after cleaning it from dirt only if the material is completely dried in a natural way.
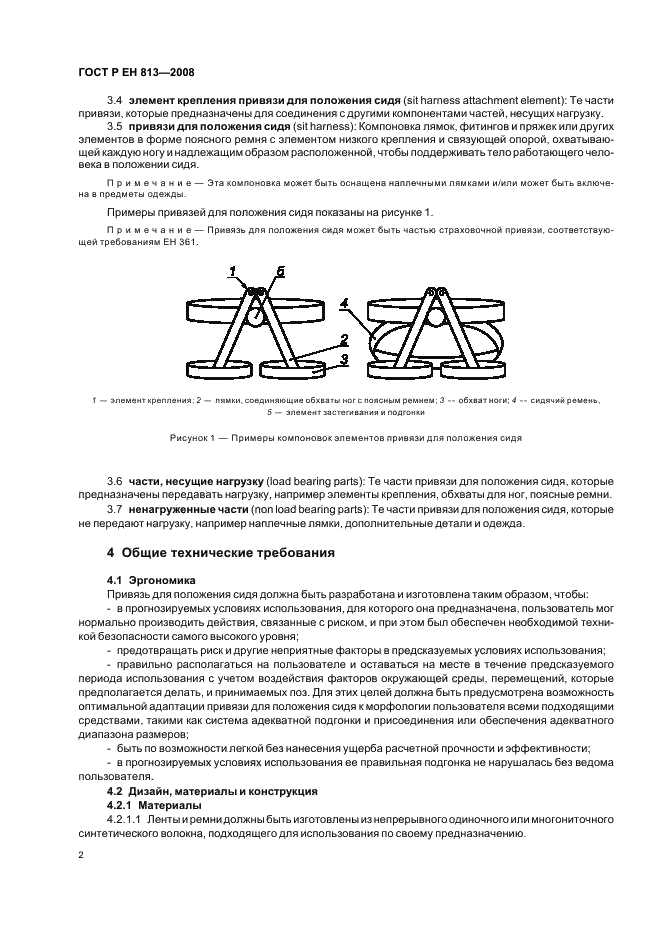
Do not dry with any heat sources or near open flames. It is also unacceptable to clean systems using chemicals.
The guaranteed service life and storage of the harness with shoulder and leg straps is one year. The manufacturer's expiration dates are usually three to five years.
It is strictly forbidden to use the product after the expiration date. In this case, as in the case of damage detection, or the implementation of a fall arrest, the harness is discarded and destroyed in order to avoid accidental or deliberate use by incompetent persons.
In conclusion, we suggest that you watch an interesting video on how to properly dress and use a safety harness with shoulder and leg straps while performing high-altitude work.
Views
The table below shows the types of safety systems for work at height in accordance with the requirements of the Ministry of Labor of Russia.
Types of safety systems for work at height
| № | Diagram-drawing | Title and explanation |
| 1 | Restraint system:
1 - restraining harness (safety belt without straps), covering the body and consisting of separate parts, which, together with the slings, are fixed at a certain height during operation; 2 - opening device for connecting components, which allows a worker to attach a lanyard in order to connect himself directly or indirectly to a support (connector, carabiner); 3 - anchorage point to which PPE can be attached after the installation of the anchor device or structural anchor, fixed for a long time to the structure (building); 4 - tensioned sling of adjustable length to hold the worker; 5 - the difference in height is more than 1.8 m. Requirement: the components and elements of the restraint systems must withstand a static load of at least 15 kN, and slings made of synthetic materials - at least 22 kN. |
|
| 2 | Positioning that allows you to work with support, in which a fall is prevented:
1 - waist belt for body support, which covers the body around the waist; 2 - tensioned adjustable lanyard for work positioning, used to connect the waist belt to an anchor point or structure, encompassing it as a means of support; 3 - a sling with a shock absorber; 4 - safety harness. Requirement: When using the positioning system, the worker must always be attached to the harness. The connection must be free of any slack in the anchor ropes or connecting straps. |
|
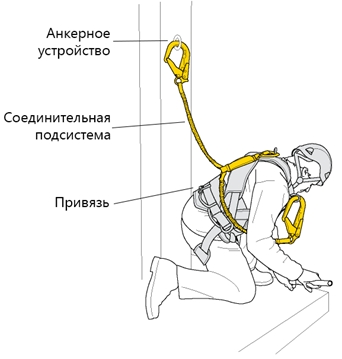
| 3 | Full body harness and subsystem attached for belaying:
1 — structural anchor at each end of the anchor line; 2 - anchor line of flexible rope or cable between structural anchors to which PPE can be attached; 3 - sling; 4 - shock absorber; 5 - full body harness (safety harness) as a component of a harness system for covering the body in order to prevent falling, which may include connecting lines, buckles and elements, secured appropriately, to support the whole body and hold the body during and after a fall. Requirement: the connection of the connecting-shock-absorbing subsystem to the worker is made for the harness element marked A. Recommendation: connection to a point on the back (in the figure the letter "A") is more desirable, since it excludes the possibility of accidental detachment (unfastening) by the worker himself and does not interfere with the performance of work. |
|
| 4 | Rescue and evacuation system - retractable protective equipment with built-in winch:
1 - anchor rigid line, allowing the simultaneous fastening of rescue and evacuation systems of the victim and the safety system of the worker conducting rescue work; 2 - retraction-type protective equipment with a built-in winch; 3 - a rescue harness, including straps, fittings, buckles or other elements suitably positioned and mounted to support the body in a comfortable position for rescue; 4 - sling; 5 - shock absorber; 6 - safety harness. |
|
| 5 | Rescue and Evacuation System - Portable Temporary Anchor Device:
1 - tripod; 2 - winch; 3 - rescue leash; 4 - a belay device with an automatic self-locking function for pulling out the sling and automatically pulling out and returning an already stretched sling; 5 - shock absorber in a retractable sling (energy dissipation can be performed by the belay device 4 itself); 6 - safety harness. |
|
| 6 | Rescue and evacuation system - an individual rescue device (ISU) for saving itself.
1 - a device that excludes rotation and the possibility of free fall during descent, as well as a sudden stop of descent and automatically provides a descent speed of up to 2 m / s; 2 - class B rescue loop (class A acceptable). |
Also see Working at Height: Safety Precautions.
5.2 Test methods for static strength
5.2.1 Hip belt
5.2.1.1 Fit the belt
the belt and test cylinder into the test equipment (see Figure 1).
Apply the specified test force between the test cylinder and
fastening element for the waist belt. Maintain the force for 3 minutes and
observe whether the waist belt releases the cylinder.
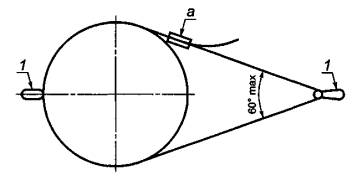
1 - fastening element;
a - buckle, which should not be in contact with the cylinder
Figure 1 - Static strength test of the hip belt
5.2.1.2
If the fastening elements of the lap belt differ in design or method
attachment to the belt, the test is repeated for each type of attachment. For
a new lap belt is used for each test.
5.2.2 Hip belt with integrated lanyard for
work positioning
Fit the waist belt with
integrated work positioning lanyard and test cylinder in
test equipment (see figure 2). Make sure that the regulator
length is not less than 300 mm from the free end of the sling. Celebrate this
position. Apply a force of 5 kN for 3 min between the test cylinder
and a connecting element at the free end of the sling for the worker
positioning. Any movement (slippage) of the material is recorded
sling through the length adjuster. Any movement (slippage) through
the length adjuster should be no more than 50 mm. Relieve stress and immediately
move the line length adjuster for work positioning to the end
lanyard stop.Apply the specified test force (15 kN) between
test cylinder and connecting piece at the free end of the sling
for work positioning. Maintain the force for 3 minutes and observe
Whether the cylinder releases the hip belt or work positioning lanyard.
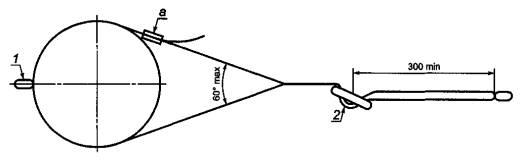
1 —
connecting element; 2 - length adjuster A - buckle that should not
be in contact with the cylinder
Figure 2 - Test for the static strength of the belt
belt with integrated work positioning lanyard
5.2.3 Removable work positioning lanyard with
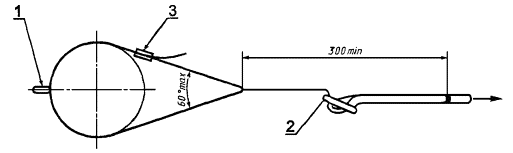
length adjuster
Install a sling for work positioning
(see figure 3). Make sure the length adjuster is at least
300 mm from the free end of the sling. Celebrate its position. Make an effort
5 kN for 3 minutes between the connecting piece at the anchor point and the regulator
length. Record the movement (slippage) of the sling material through
length adjuster. Moving (slipping) material through the length adjuster
should be no more than 50 mm. Relieve the load and immediately reposition the regulator
lanyard length for work positioning to the lanyard end stop.
Apply the specified force (15 kN) between the connecting element in the anchor
point and length adjuster. Maintain the force for 3 min and observe that the
Whether the work positioning lanyard collapses.
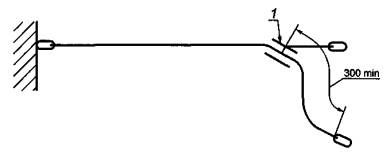
1 - element
length regulation
Figure 3 - Test of the static strength of a removable lanyard for a worker
positioning
Application of the safety trail
When working with travel at height, belay should always be used. It can include both a sling and a rope, which are equipped with a shock absorber.
Important! If you fall, the extra jerk of the body can cause serious injury. The double lanyard slightly facilitates freedom of movement as the ends can be secured at different points
When roofing or when on an inclined surface, use a slide-type belay.
The double sling makes freedom of movement slightly easier as the ends can be fastened at different points. When roofing or when on an inclined surface, a slide-type belay is used.
With its help, a person can move freely, but in the event of a fall, the system will stop and fix the body at one point
It is important to take into account that there is a lifespan of the safety harness and when it expires, the equipment cannot be used.
Storage and operation
To prevent the harness from being damaged during storage, the following conditions must be observed:
- the leash is stored flat on shelves or special hangers;
- the room must be at room temperature and be dry, ventilated;
- it is forbidden to store equipment near heating devices, sources of open fire, poisonous and hazardous substances;
- it is forbidden to use aggressive chemicals for cleaning equipment;
- transport and transport equipment according to the rules specified by the manufacturer;
- if the equipment is exposed to temperatures above the level for which it is intended (typically from -40 to +50 degrees), its service life and reliability are reduced, therefore it is better to prevent it from overheating, hypothermia (for example, when transporting in an airplane), keep it away from sun rays;
- when washing and cleaning the leash, you must follow all the manufacturer's recommendations;
- wet or contaminated equipment must first be dried and cleaned, and only then put into a protective case or cabinet;
- only natural drying is permissible in a well-ventilated place with a suitable temperature (indoors or outdoors).
Compliance with all the rules is a guarantee of safety.In case of any damage, deformation of all protective equipment or any elements, its use is prohibited.
The harness must not be used beyond the manufacturer's specified service life. In case of violation of this provision, the employer is subject to liability.
You can learn how to properly put on a harness in the following video.
Appointment
The main purpose of safety belts is to fix the position of a person, and as part of a safety harness - to protect in case of a fall.
The use of such personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when more than 1.8 m above the supporting surface or when working in hazardous conditions.
Therefore, a safety harness is used:
for professional high-rise work - on communication lines, power transmission lines, on trees, on high-rise industrial structures (pipes, towers), various buildings, when descending into wells, trenches, cisterns;
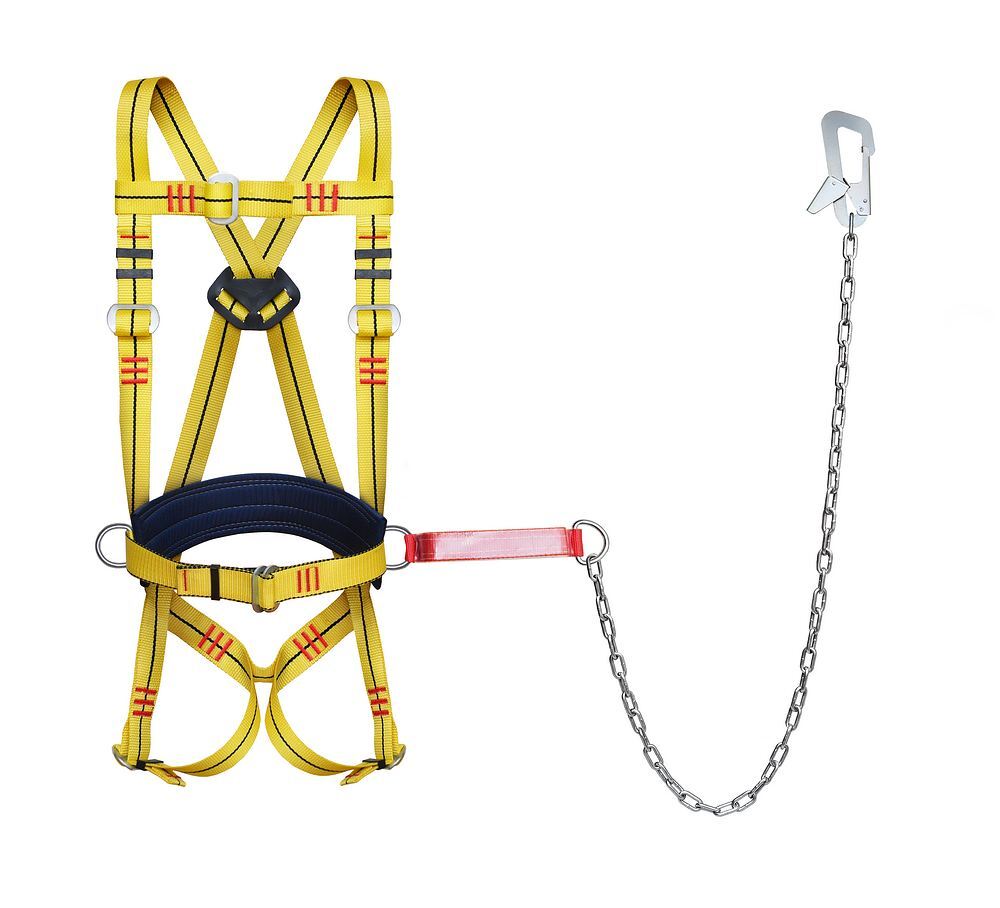
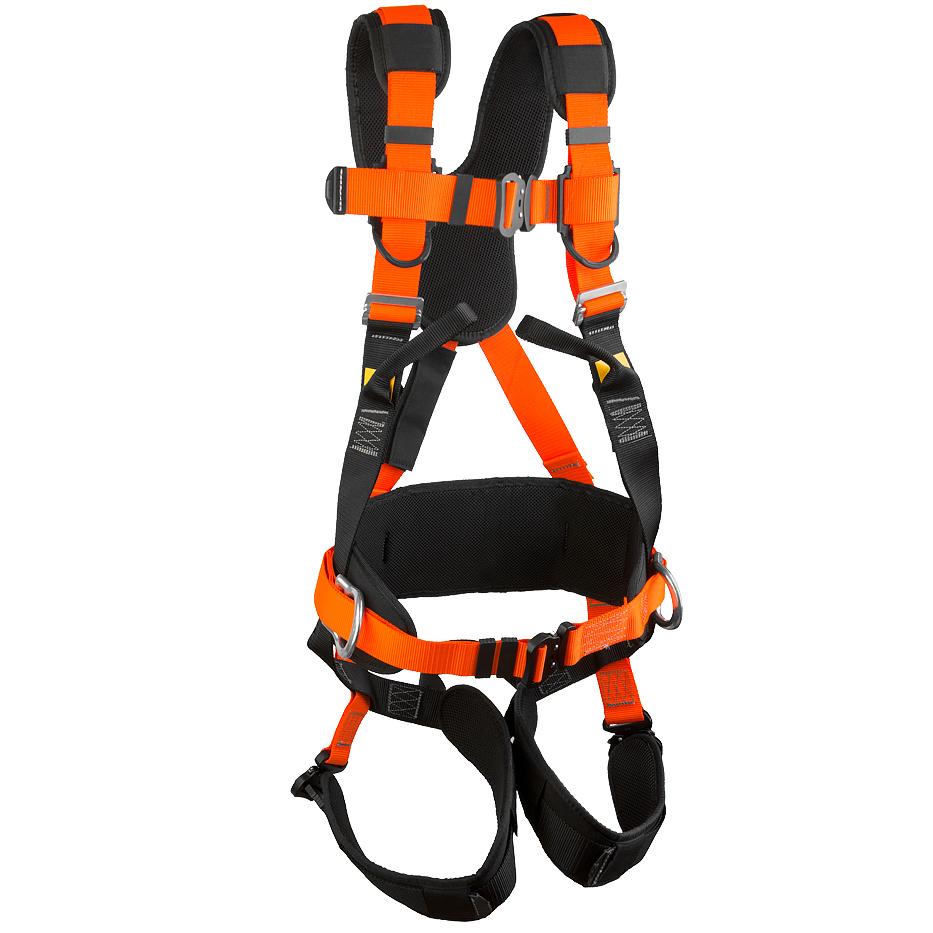
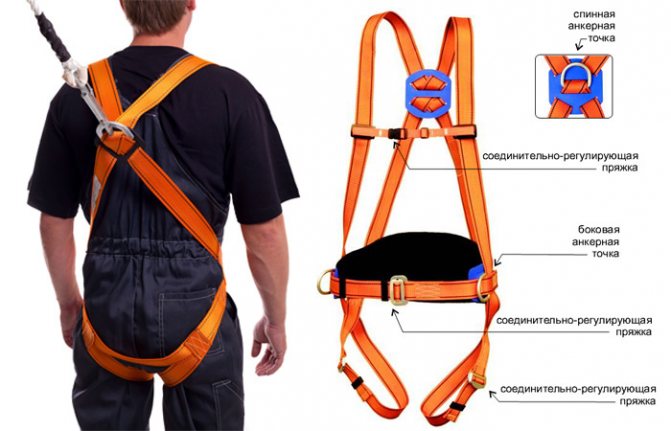
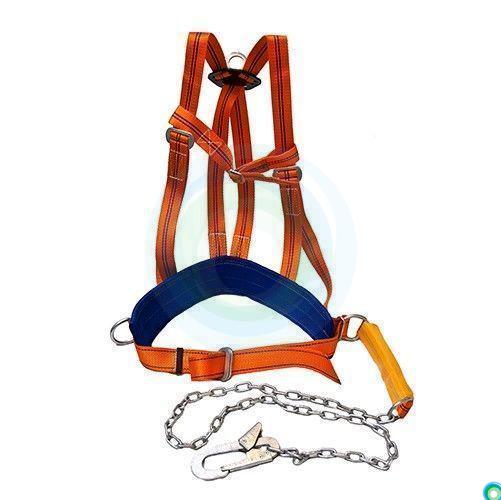
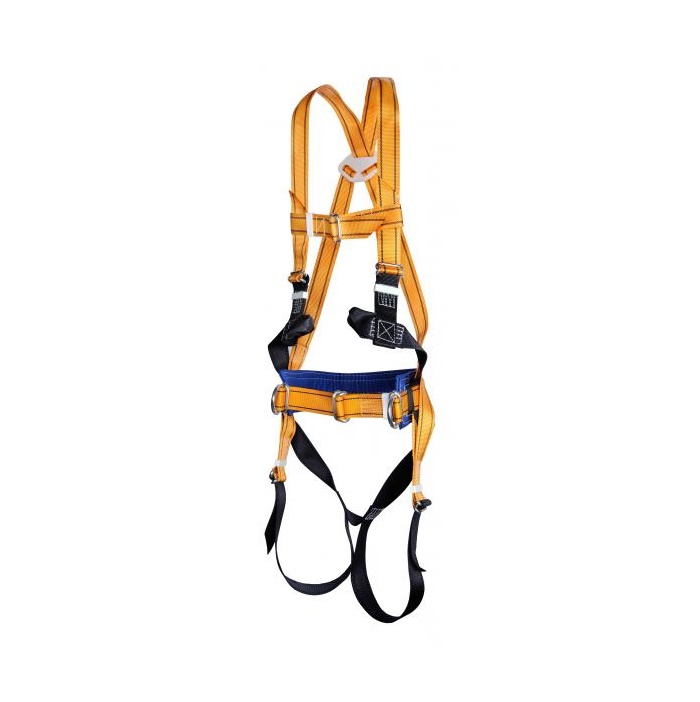
For high-altitude and hazardous work, the harness always includes a mounting belt, unlike sports equipment. For professional work, the most common option is with shoulder and hip straps - this is the most versatile type, safe, suitable for most jobs, and for quickly rescuing an employee from a dangerous area in the event of a fall, structure collapse, explosion, and the like. Such belts are supplied with a shock absorber, and the material of the belt, straps, halyard is selected based on the conditions. For example, if contact with fire, sparks is possible (for example, equipment for firefighting, work in a steel workshop), the belt and straps are made of refractory materials, the halyard is made of steel chain or rope. To work on power transmission line poles, a fitter's belt made of synthetic materials with a special "catcher" is used to fix it on the pole.
If the employee must be suspended at a height for a long time (during the whole working day), a 5-point safety harness is used, which has a belt with a comfortable back support and a saddle strap. For example, such equipment is used by industrial climbers when working on the facade of a building - washing windows, restoration work.
A harness without a shock absorber is mainly used when working in wells, tanks, trenches. The strapless belt is used only on a safe surface where there is no risk of falling, and the worker has a reliable support under his feet that can support his weight.
How to choose the right one
In order for the safety system to fulfill its purpose as a belaying and restraining device and to ensure correct positioning in the working position, it is necessary to pay attention to a number of criteria. The structure should work in such a way that the performer does not experience any discomfort if it is necessary to perform long-term work
Therefore, strict requirements are imposed on harnesses.
The structure should work in such a way that the performer does not experience any discomfort if it is necessary to perform long-term work. Therefore, strict requirements are imposed on the harness.
The model meets the requirements if:
- The material from which the harness is made can withstand a weight significantly exceeding the weight of a person (polyamide systems have proven themselves well);
- The harness is lightweight;
- The system is simple and easy to use;
- The size corresponds to the individual characteristics of the employee;
- The sash supports the back, while reducing the degree of fatigue;
- The shoulder straps are spaced a sufficient distance from each other to prevent any neck injuries;
- Self-locking buckles, which do not allow arbitrary unfastening of belts or shoulder straps during operation;
- All characteristics of the harness are in full compliance with the requirements of GOST.
The frequency of inspection of harnesses should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST. A properly sized harness made of high quality materials must be checked regularly before each use.
First of all, the equipment is inspected for the presence of damaged areas, the correct compatibility of components, the absence of mechanical or chemical damage, as well as the possible likelihood of spontaneous opening of the buckles.
If at least one of these problems is present, it is strictly forbidden to use a safety harness.
Safety harness requirements
Recall that high-altitude work includes any kind of work performed at a height of over two meters - construction and steeplejack without support (at a height of over five meters), installation and roofing work, descent and ascent, etc. The mandatory requirements for an individual safety harness include:
- Technical requirements regulated by the standards GOST R EN 361-2008: composition of single- or multifilament synthetic materials, their tensile strength, compatibility of woven tape and sewing threads with the fabric of slings and belts.
- To visually check the integrity, the woven tapes and sewing threads are made in contrast to the base color of the straps.
- A safety harness is a design with the obligatory presence of straps in the hip and shoulder areas (should not be confused with a mounting belt, which does not have such structural elements).
- The harness must be able to adjust the straps according to the volume of the body - only correct and tight fixation of the system on the body will prevent serious injury in the event of an emergency.
- The fixation of the straps must be absolutely reliable with the exclusion of the possibility of arbitrary loosening.
- The width of the base straps should be at least 4 cm, and the auxiliary ones - at least 2 cm: this will prevent the straps from cutting into the muscle tissue in the event of an abrupt stop during a high-altitude fall.
- The harness should be made of a material that can withstand a weight much greater than the weight of a person, while the structure itself should not be heavy - often polyamide is used as such a material.
- Convenience and ease of use of a leash, a properly fitted size will allow a person to easily prepare for work and navigate, if necessary, in a difficult situation.
Only the exact fulfillment of these requirements will be able to ensure high-quality, optimal in terms of time and labor costs, and, possibly, save human life.