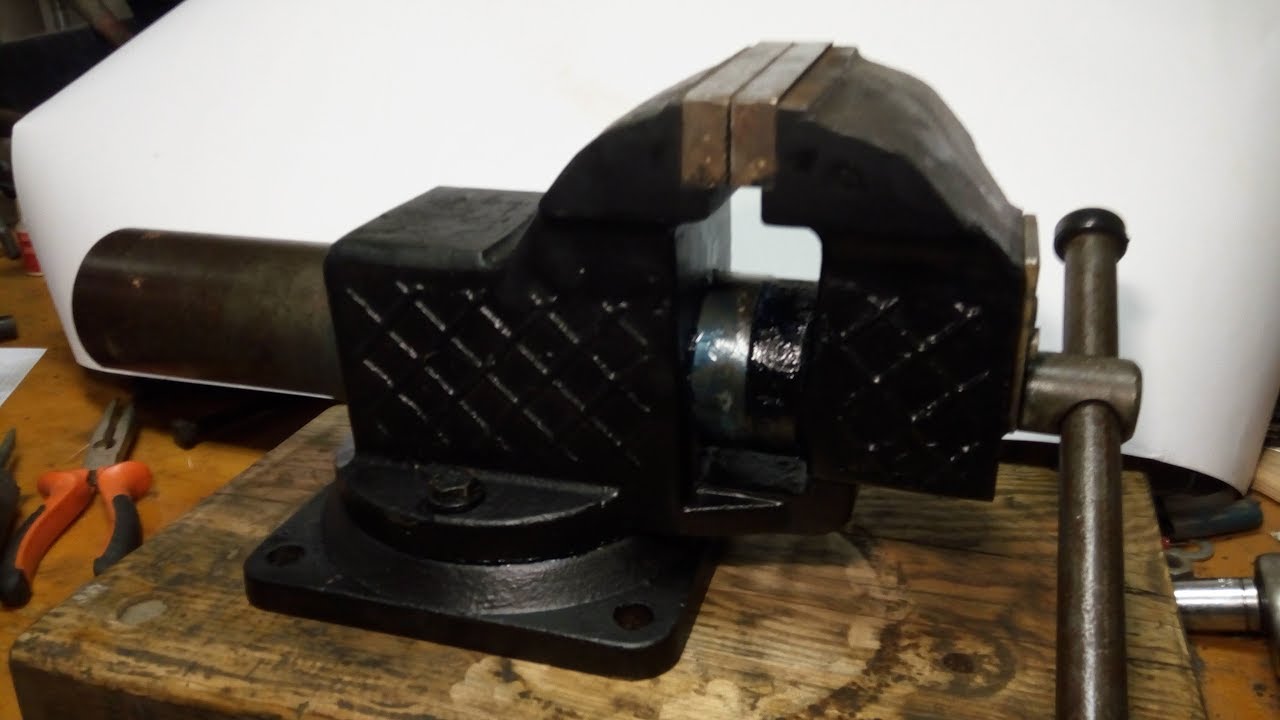
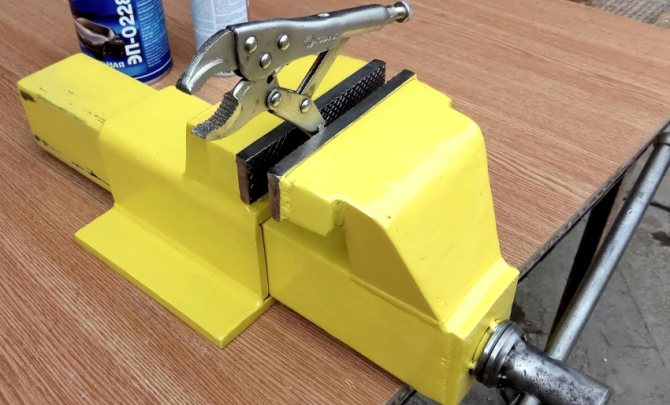
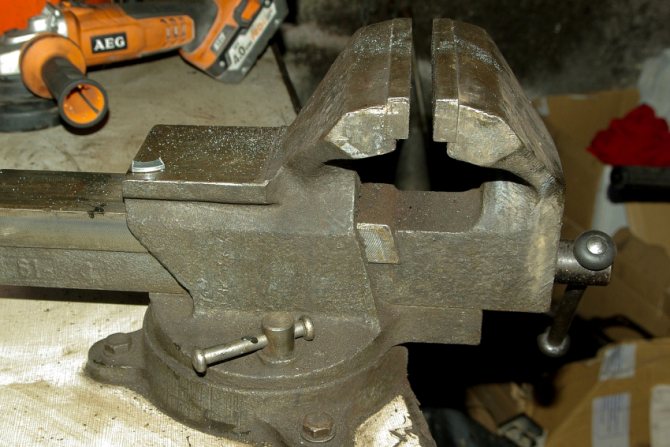
Do-it-yourself locksmith vice
It will not be difficult for a skilled craftsman to make the necessary tool on his own. A solid homemade locksmith vice will effectively fulfill its function, saving a considerable budget. What you need to assemble the device:
- corner of steel;
- channel cut;
- metal rod (d = 20 mm);
- guide rods;
- bolts, washers and nuts;
- electric drill;
- welding machine;
- Bulgarian.
Before starting work, you should make a screw from a metal rod yourself or in a workshop using special equipment. Then you can follow the instructions:
- A plate with holes is welded across the two parallel-spaced pieces of the corner from below to secure future vices to the surface.
- On top of these cuts, across their upper edges, a piece of the corner is welded, which will serve as a fixed sponge.
- Opposite it, from the other edge, a corner with a hole and a nut welded to it is also fixed.
- After that, the movable part of the vice is made: a hole for the lead screw is punched in the channel, a nut is welded to it, all this is attached to the shelf of the piece of the corner and put on the screw.
- The seams are cleaned, all elements are covered with paint and assembled into a ready-made low-cost locksmith vice.
Tool vise
Tool steel fasteners are a special type of vice used for fixing on a magnetic table when carrying out operations for grinding parts. They are made of parts made with high precision, have a high parallelism of all planes. The part is fastened once in a vice, and to change the part to be machined, only the fastening device is turned over. Vices are made in various sizes and are used depending on the volume of the workpiece. Changing the position of the jaws is carried out using a special bolt without the use of an adjustment mechanism.

High precision tool vise
Views
There are several types of locksmith vices.
Parallel
This type belongs to the machine vice. This is the most popular and demanded type of vise, since it allows you to process wood, metal, plastic products, as well as workpieces from other materials and long parts. The vise can be manually operated, which causes the lead screw to move.
There are also improved models with a modernized design, which allows them to be installed not only on the workbench, but also on the floor. In these models, the fastening mechanism has a simple device, and their installation is quick and easy.
Parallel models, in turn, are subdivided into several more types.
Swivel vise
They are designed so that the device can rotate. The base of the case is securely and rigidly fixed to the desktop. The fixed jaw is equipped with a rotary part and is connected to the base by means of a guide screw with a handle, which allows the vice to rotate around an axis (vertical or horizontal) at an angle of 60-360 degrees. Thus, the vise can be rotated to every corner of the worktable.
Fixed or stationary
This type has a fixed base, which is fixed to the workbench with bolts. This vise can only be used in one position. To change the position of the workpiece, first unclench the jaws, manually change the position of the workpiece, and then fix it again.
They are used for processing small workpieces when the part cannot be held by hand, or for performing work and simultaneously holding a vice with one hand.If it is necessary to process the product with 2 hands, the manual vice is additionally fixed with parallel models.
Chair models
Such a vice is used to perform laborious work with the use of impact force (for example, riveting). They are mounted on the edge of the desktop and are named after the chair-like retention element.
Their design feature is the double fixation of the fixed jaw. The sponge is fixed to the horizontal surface by means of a foot (special plate). Its lower part is attached to the leg of the workbench. This mounting method is highly resistant to powerful side impacts.
Another feature is a different direction of movement of the movable jaw: it occurs along an arc, and not along a straight path. The design makes it possible to work with products of complex configuration.
Pipe vise
Round parts cannot be machined in a conventional locksmith's vice. For this, there are pipe models. This vise has a concave jaw to securely hold tubes or round workpieces.
Depending on the type of attachment, in addition to stationary ones, there are also portable models that are fixed to the surface with suction cups or using clamps. The advantage of these types of fixation lies in the possibility of using it without a permanent workplace.
There are also quick-clamping types of tools. Their feature is the presence of a quick-clamping mechanism, which shortens the installation time and provides convenience during operation. To set the jaws in the desired position or, conversely, to open them, you do not need to manually rotate the clamping device, but you just need to pull the trigger.
Professional models of locksmith vices can differ in larger dimensions, the presence of a large anvil, a thrust bearing on the screw, which simplifies the clamping of the part, and adjusting screws to eliminate the gap.
Types of locksmith vices
As a type, locksmith fixing vices are also divided into several groups. Let's consider the main ones:
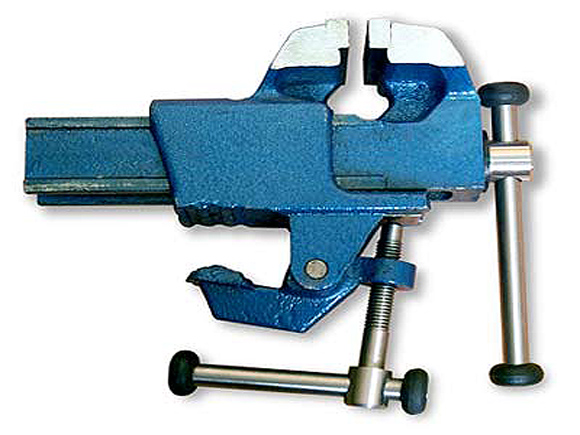
- Manual... The smallest subspecies of vice, the task of which is to fix small workpieces in the process of working with them. They are not fixed to surfaces, but clamped with one hand, while the other hand is busy processing the part.
- Chairs... The complete opposite of manual vices: massive, heavy vices that provide the ability to rivet, bend and chop metal in the forge. They are made of high-strength carbon steel, mounted on a stable wooden base - "chair", which determined their name.
- Parallel... The most popular tool for household use. Parallel locksmith vices are called so because of the strictly parallel movement of the moving jaw relative to the stationary one. The dynamics are provided by a screw that is screwed along the guides and regulates the compression force of the workpiece. Such vices are rotary and non-rotary.
Swivel locksmith vice
The blank material requires processing from all sides, in order to gain access to which it is necessary to bypass the fixed part, bend and twist, sacrificing its convenience. If you clamp the workpiece in a bench vise, you will have to make several dozen circles around the table in the process. The ability to rotate the locking device solves this problem. The Swivel Locksmith Vise is a standard tool that is equipped with a swivel mechanism that makes work much easier.
Fixed locksmith vice
With the domestic use of a vice, the swivel mechanism is rarely used, and there is no need for it. A fixed workpiece clamping tool with a one-piece body and static setting is often the best option for the home workshop.Additional turning parts increase the cost as well as the risk of breakage, so it is worth assessing your actual needs before making a choice.
Types of vices - the main types of locksmith, machine and other vices
A vise is a mechanical fixing device used in manual and machine processing of workpieces. They are used when it is necessary to rigidly fix the workpiece, to place it at a safe distance from it, or to free hands for other work.
Design and application
Vices are used in the processing of metals, wood, plastic and other materials in single and small-scale production, as well as during repair and other operations. Due to the simplicity of design and versatility, most types of vise can be used in everyday life, and in small repair shops, and in the workshops of large enterprises.
The main working element of the vise is two jaws, between which the workpiece is clamped. The required clamping force is provided by a manually adjustable locking mechanism. One jaw is stationary and securely attached to the body. The second moves under the action of the locking mechanism providing clamping of the part.
The locking mechanism includes a trapezoidal lead screw. It is connected to the moving part of the body and ensures its linear movement by rotating clockwise through the nut located in the body. The rotation of the screw is provided by the handle. The vise body is located on a base plate or bed with holes for attachment to a workbench or machine bed. Fastening is carried out using screws or clamp.
The main types of vice
Depending on the purpose and design features, the vice is subdivided into:
- Locksmiths - designed for fastening workpieces during processing with hand tools.
- Pipe. They are used for cutting and processing pipes and round parts. They are distinguished by a special, semicircular shape of the jaws to increase the contact area with the part.
- Machine tools. Devices of increased accuracy designed for fixing workpieces when machining on metal-cutting machines.
- Joiners. Designed to work with wood and plastic blanks.
- Manual. A compact tool that does not require fixing to the workbench. Designed for fastening small workpieces.
Consider machine and basic types of locksmith vices as the most commonly used in modern metalworking.
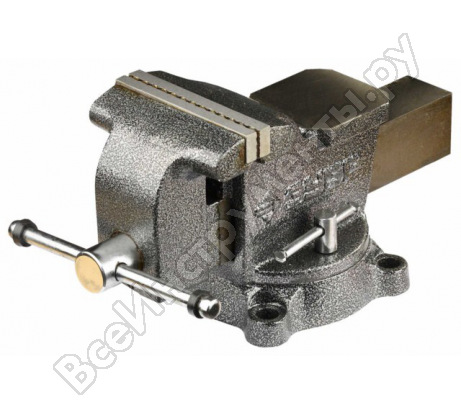
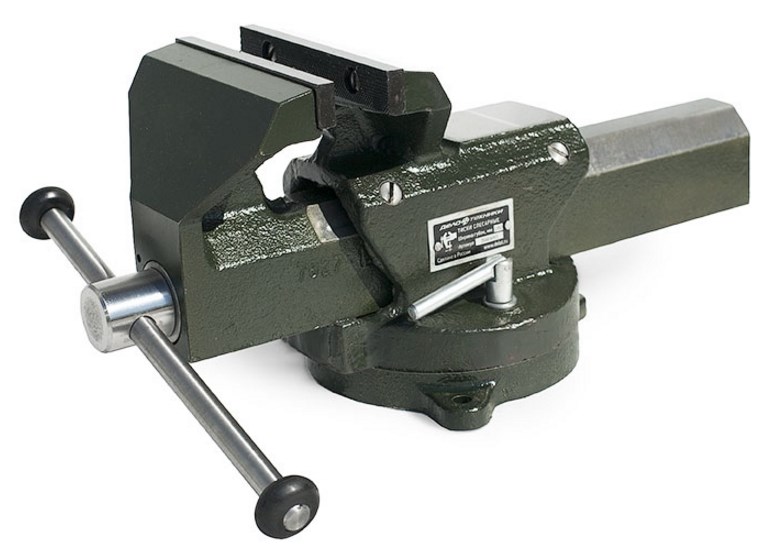
Locksmith vice
A device for fixing parts and workpieces before processing with a hand or power tool. Mounts on a table or workbench and bolts to the base. By design, they can be chair or parallel, stationary or swivel, with a jaw width from 45 to 200 mm. On average, the width of the part to be fixed, which is determined by the stroke of the movable jaw, is 140 mm.
Parallel vise can have a stationary or rotary structure with the ability to rotate around the axis by 60 ° or more. Stationary vise models are cheaper and are used for work in one position. They got their name due to the parallel movement of the movable jaw relative to the fixed part. The vise is equipped with applied tool steel jaws, the base is made of cast iron or steel, the movable elements are made of carbon steel.
The chair vice is an obsolete type of design, but continues to be used in everyday life and repair shops. They got their name due to the fact that they were fixed on a chair-shaped base. They are a structure consisting of a base and a rotary disc, which are connected in the center with screws. The body usually has an anvil. The width of the jaws ranges from 90 to 180 mm.The advantages of this design are simplicity and strength, quick release of the jaws and the ability to fix long parts.
Machine vice
These are devices for high-precision fixation of workpieces before processing on drilling, milling and other types of machines. They differ from the plumbing variety by a small take-off run or a complete absence of backlash. Designed for fixing on the beds of metalworking equipment or production workbenches. For the convenience of work, as a rule, they are equipped with a swivel mechanism.
Depending on the possibility of positioning the workpiece, there are the following types of machine vice:
- Stationary. The part is fixed at right angles to the vise.
- Sinus. It is possible to fix the workpiece at any angle required for processing.
- Multi-axis. The vice has the ability to rotate along different coordinate axes.
The main advantages of this type of tooling are high clamping force, rigid attachment of parts and the ability to carry out high-precision operations.
Views
But they have a higher cost, so they are not always suitable for a home workshop.
The rotary vise makes it possible to work along the entire coordinate plane without removing the workpiece from the clamp and without changing the position of the tool itself. The difference from previous models is that there is a special turntable up to 360 degrees in a circle, so the part can be turned literally at any angle for further processing.
There are also composite self-centering models that make it possible to work just as efficiently in the horizontal plane. Due to this, work can be significantly accelerated up to the serial production of workpieces of a certain type.
Globe-type vise makes it possible to work in three planes at once due to a special platform, so that even inclined holes can be reproduced
The most important thing in the process of work is to choose the right angle. Working with a part with this tool will be painstaking and time consuming.
Sinus quick-clamping vise is an auxiliary tool for various types of machine tools, with which you can perform a number of operations, from milling to planing or grinding. As a rule, they are actively used in plumbing work when processing a workpiece at an angle to the vertical. The angle for processing is usually sharp, it all depends on its size and the complexity of the task assigned to the master.
Three-axis machine vice is installed on milling and drilling machines as an additional piece of equipment. The material of manufacture is foundry cast iron; the design provides for a turntable and a number of additional small parts, which significantly increase the accuracy of working with any materials. The total weight of the tool is from 4 kg, the pressure zone is quite wide so that the master has the opportunity to work with large-sized workpieces.
There are more complex models with pneumatic clamping. This hydraulic heavy duty vise is installed on milling machines as the main tool for processing. The material for the manufacture is cast iron or any other metal similar in technical characteristics and level of resistance to mechanical damage, corrosion and other breakdowns during operation. When the workpiece is clamped, a certain amount of pressure is exerted on it.
Pneumatic vices are often additionally equipped with hydraulic boosters. With their help, you can work with heavy metal workpieces without the risk of damaging the product. The body and fasteners are made of steel and cast iron, the jaws have a wide movable stroke - up to 250 mm inclusive. The vice can be installed on any horizontal surface using special fasteners.There are several springs in the clamping mechanism, which additionally enhances the indicator of its reliability and safety under air pressure during operation.
Making a frog
Jewelry vise in amateur work, as mentioned above, in most cases is replaceable with frog vise; they can also be clamped in an ordinary vice. Its best homemade option is if the handle of your pliers or other pliers has broken, at the top in fig. To drill the jaws of the pliers, you need to purchase a carbide twist drill - the usual for metal will not take them.
Homemade frog vice (locksmith clamps with fixation)
A simple replacement, if the pliers still do not break, a frog vise made of oak or beech bars, a steel bracket, overhead jaws from a steel corner and fasteners, at the bottom left in Fig. A stronger option is a frog from a door or small barn hinge, bottom right. But you will have to pant over it, using the usual vice. You may have to release the workpiece by heating it red hot and then slowly cooling it down.
What is a mechanical locksmith vise made of?
Vise design elements.
Details of which the vise consists:
- movable and fixed jaws;
- screw terminal;
- attachment mechanism to the workbench;
- spring;
- sleeve;
- handle for rotating the screw clamp;
- replaceable pads.
A locksmith vise is an all-metal device that is installed on the working surface of a workbench using bolts that are attached to the base of a fixed jaw. There are also varieties that have a special screw that allows them to be fixed like a clamp. Rotation of the screw mechanism changes the position of the movable jaw relative to the entire structure, forcing it to move inward or outward. This creates a gap between replaceable pads, into which the workpiece is fixed for subsequent processing. The clamping tool is often supplemented with an anvil, which is located on the back of the fixed jaw.
Types of locksmith vices.
Locksmith's vice is divided into swivel and non-swivel. Fixed ones are rigidly fixed on the workbench and allow you to work with parts in only one position. Swivel locksmith vise can rotate parallel to the workbench by 60 ° or more around its axis. Some of them, in addition to horizontal rotation, can also rotate vertically, thereby providing work with the workpiece in a wider range of positions than their "stationary" counterparts. However, the weak point of such models is precisely the rotary mechanism. This should be taken into account by applying excessive force to them.
Replacement pads are most often made of a softer metal than sponges. The linings are smooth, this allows you not to leave marks on the workpiece being processed and very accurately fix it in a vice. Also, the overlays are covered with a notch for a more solid and reliable fixing of the workpiece. In addition, there are special elastic pads that allow you to fix the workpiece as tightly as possible, completely distributing the force of the pressure of the jaws over the entire surface of the part.
How to choose a vise
When choosing a vice, the scope of their application and the dimensions of the blanks that are planned to be installed in them are taken into account.
Locksmiths - require an increased clamping force when processing parts, therefore, rigid models made of steel are preferred, rather than powder metal.
- The lead screw with a triangular metric thread wears out quickly and the clamping force is not sufficient to machine large workpieces.
- The weight of a structure indirectly characterizes its strength.
- For the processing of parts in a vertical position, an upgraded locksmith vice is selected. Their base rotates 360 °. More often equipped with an enlarged anvil.
- For round workpieces, models with a body equipped with prisms are preferred. This vise is more commonly used with a slider.
Joinery - Pay attention to the diameter of the auger and the evenness of the alignment of the rods. Assumes parallel movement when screwing in
If the tool runs unevenly, the risk of damage to the workpieces increases.
Additionally, the clamps are inspected; when choosing, they are checked on a piece of plastic
It is important that there are no marks or dents on the surface.
In models with a workbench or bed, the flatness of the plane is visually checked. To do this, you need to stand in such a way that the nearest corner of the bed is at eye level - flaws become noticeable when the plane looks like a string.
Front vise only available with screw mechanism and guide bar
It is worth considering whether it is convenient for the current operational needs.
Machine tools - are selected for processing materials of increased rigidity, therefore, functionality is a priority.
- Jaws for fixing the workpiece with a lower height than other types.
- Compared to a bench vice, the design is more rigid.
- The tool secures the part at a specific angle and supports rotation around the vertical axis.
When choosing, the material from which the tool is made is taken into account. Hardened steel models are preferred.
If this option doesn't fit your budget, try to choose a device with steel moving parts, as these are subject to the most wear and tear.
The anti-corrosion treatment of the tool is important - the coating is most often applied to the threaded parts, but there is also a solid one.
Double machine tools - support the simultaneous processing of several parts, but are inconvenient for constant household use.
Sinus - used for complex machining of parts. They support the slope of the fastening of the part in several mutually perpendicular planes.
Manual - when choosing, it is worth checking the parallelism of the jaws, the quality of convergence and the size of the gap.
- Handle play is a sign of a tool that will be difficult to handle.
- The width of the working gap in the open state is a parameter that determines whether the workpiece will enter the tool. The gap in hand-held models is usually small, so it is worth carefully trying on the dimensions.
- Check for dents on soft metal. In such a case, a tool with a smaller clamping thread height is preferred.
The swivel base for fixing the tool is easy to use, but reduces the rigidity of the structure. The swing mechanism is the weakest link of the tool, so this functionality is chosen only in cases where work is impossible without it.
When choosing, it is worth determining the value of the angle, which is often required during work. Variations are available with a minimum angle of rotation and models that rotate 180 or 360 degrees.
Static models are more reliable, but the selection of the attachment point is made difficult by the parameters of the workbench. With non-standard workpieces, additional fixation devices are more often used: baiting with bolts or gripping with a clamp.
Bed: metal or wood?
A stationary wooden workbench has advantages over that on a steel bed, not only in lower cost and labor intensity. First of all, wood is not plastic. A workbench on a wooden base can be broken, but if the wood is seasoned and impregnated, it will never bend. Secondly, the tree perfectly dampens vibrations. The foundations of your buildings are not reinforced, vibration-absorbing, like the shops at a factory? And the general strength and stability of the bed of a home workbench will be fully provided by coniferous commercial wood of ordinary quality.
Wooden benches of workbenches
The construction of the wooden frame of the workbench made of 120x40 boards is shown on the left in Fig. Permissible static load - 150 kgf; dynamic vertical downward for 1 s - 600 kgf. Corner posts (legs) are assembled on self-tapping screws 6x70 in a zigzag (snake) with an indent from the edge of 30 mm and a pitch of 100-120 mm.Fastening two-sided; snakes on both sides of the package are mirrored. Intermediate support beams are fastened with steel corners on self-tapping screws; edge - in pairs of self-tapping screws at the studs of the racks and, outside, with corners.
If there is a 150x50 or (180 ... 200) x60 timber available, the structure can be simplified, as shown in the center in fig. The bearing capacity will increase to 200/750 kgf. And from a bar of 150x150, 150x75 and (180 ... 200) x60, you can build a bed that can carry 450 kgf in static and 1200 in dynamics, on the right in Fig.
If there is no welding
A solid wood workbench, without the need for welding work for its manufacture, can be made according to the scheme on the trail. rice. The "trick" is here in the countertop, assembled with glue from a 75x50 bar and fastened with ties. If the timber is oak, then the permissible load is 400/1300 kgf. Corner posts - timber 150x150; the rest is a bar 150x75.
Solid wood workbench construction
Metal
It happens the other way around: metal is more accessible than wood, and there is welding. Then a workbench table for a load of 100/300 kgf can be assembled according to the drawing on the left in Fig. Materials - corner 35x35x3 and 20x20x2. The boxes are galvanized. The disadvantage is that it is impossible to make an opening at the bottom for the legs, the structure will lose its ability to carry a dynamic load.
Metal workbenches
A more convenient metal workbench is suitable for a load of 200/600 according to the scheme at the top right from a 50x50 professional pipe (corner posts), 30x30 (other vertical parts) and a 30x30x3 corner. The board cushion of both workbenches is laid only across (bottom right) of grooved boards (120 ... 150) x40.
Shelf - steel 2 mm. The shelf is attached to the pillow with 4x self-tapping screws (30 ... 35), a pair from each edge of each board, and along the outer boards - with a step of (60 ... 70) mm. Only in this version will the workbench show the given bearing capacity.
These workbenches are already universal: under the carpentry, the lid is turned over with the wooden side up or adjusted, as described below. The locksmith vise is installed on a wooden cushion, but is not fastened with a clamp. A collet anchor is driven into the vise cushion from below under the M10-M14 bolt, and a through hole is drilled under it in the cover. A washer from 60x2 is placed under the bolt head. Such a solution is convenient in that it is possible to use inexpensive non-rotating vices.
Pipe yews
Design features
Some models are equipped with handles for increased ease of use. Small holes are made at the bottom of the case, which allow the tool to be securely attached to the workbench with bolts. Such a vice can also be installed on a tripod, which allows processing parts far from the workplace.
The advantages of such yews:
- high quality, durable and reliable materials are used in the manufacture;
- vices have a wide scope of use, they are able to withstand increased mechanical loads;
- are distinguished by a long-term service life;
- provide free access to any part of the part and high comfort in work;
- allow high-quality drilling and grinding of rods, pipes of different diameters, quickly strengthen and position the workpiece.
- minimize the risk of injury to the operator.
Important! In order for pipe yews to last as long as possible, all contacting surfaces must be regularly lubricated with machine oil.
The tool making process is as follows.
- Initially, you need to prepare all the necessary details. For a medium-sized vise, you will need a threaded bolt with a diameter of about 22 millimeters and a length of no more than 15 centimeters. You can buy it or find it in the vertical pipe of the sports corner - the structure is pressed against the arch with a bolt. Studs will be needed, they can be replaced with fasteners from the mirrors of the moped (irregularities are easily corrected). For manufacturing, you will also need shock absorbers, a steel corner, for the handle - a rod from a gas shock absorber and a 6-sided nut M-18.
Advice! We recommend choosing long threaded screws as they allow you to increase the distance between the clamping plates.
- A shallow groove is made in the screw head - it is needed to strengthen the handle. When the diameter of the hole is small, it is widened with a round file.
- A bolt with a ring is used for screwing and unscrewing the clamp.
- A pine board attached to the worktop becomes an immovable vise sponge. The movable part is made of a board 52 centimeters long, 19 millimeters wide, and about 22 mm thick.
- In the boards, a d-21 mm drill makes a through hole for the screw. Stud nests are made with a d-11 mm drill. To prevent the displacement of parts in several places around the perimeter, the boards are fastened with nails. After drilling the holes, they are removed with a nail puller. Studs, bolts, nuts, washers are placed in the holes.

- When yews are used for processing steel pipes and other parts, it should be possible to reinstall the studs - additional holes are made in the board, located near the clamping bolt.
- The sponges are covered with rubber, wooden or PVC pads - the type is determined by the purpose of processing, shape, material of the workpiece.
- The fixation of the structure to the table is carried out in this way: through holes are made in the corners between the shock absorbers, in which screws with a recessed head are placed. To facilitate the movement, the corners are welded in advance, the shock absorbers are burned.
Photo of locksmith vice
We also recommend viewing:
- Retaining belt with ratchet mechanism
- How to choose a building rule
- Overview of top vibrating rails
- Construction brackets for fixing timber
- How to choose a plastering bucket
- How to use a sealant gun
- The best guns for polyurethane foam
- Nice hand winch
- How to choose crosses for tiles
- What are metal scissors
- How to choose a manual riveter
- Good mounting belt for tools
- Trowel for plaster
- Crowbar nail
- Types of scaffolding
- How to choose a paint roller
- How to choose a glass cutter
- Concrete trowel
- What are the construction plumb lines
- How to choose a construction mixer
- Rating of the best concrete mixers 2018
- How to choose the right ladder
- How to make a tool shelf with your own hands
- How to choose a good spatula
- How to choose a tile cutter
- Best tool boxes
- Choosing good paint brushes
Help the site, share on social networks 
Common types
The most common types of structures that are produced in accordance with GOST should be considered. These include parallel, chair, chain vices, as well as the machine type of the apparatus (machine vise):
- Chain vise. They are designed to make quick clamping of structures, even suitable for pipe welding. This type does not occupy high positions in the rating for the reason that it is quite expensive. The manufacturers of such structures are most often the countries of Europe and the United States.
- Parallel fixtures. They can be either swivel or non-swivel. They are made mainly of cast iron, and their parts are made of steel. They can be used for different types of work.
- Machine tools. Designed for high precision work. They can fix even large metal parts, their body is able to withstand high mechanical loads. Often these machines are made of a material that is resistant to corrosion, so they can last a long time.
- Chair vice. They are considered obsolete today. They are made of steel. In the process, dents may remain on their surface.
- Manual. They have already been mentioned earlier, but they also belong to the rating of the most popular. The hand vise does not need to be fixed to any surface. They can be either with sponges or with levers. Depending on the type of fixation, the functioning of the device also varies.
- Joiners.Suitable exclusively for working with wood or plastic parts, and therefore cannot be universal. However, they have special overlays, thanks to which no marks remain on the structure.
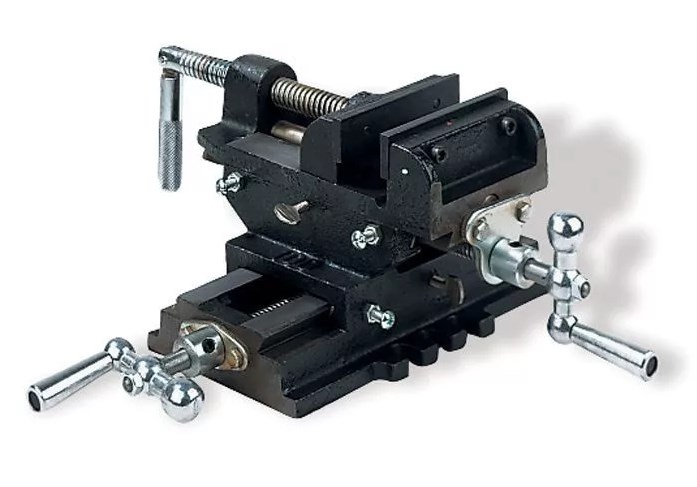
In addition to these varieties of vise, there are other types, the use of which is not so widespread. In small production, for example, a cross vise is used. However, this type of apparatus is not necessary to clamp any parts, but mostly as a base instead of a coordinate table. With the help of such a device, you can make a box for non-ferrous metal and small parts, the width of which does not exceed 20 mm.
For drilling machine
The vice can be used not only in general production, but also directly in combination with a drilling machine. In this case, they are necessary in order to make more accurate holes. The device is often used to ensure maximum operational safety.
However, not all drilling machines have built-in vices, since their presence in the device, albeit to an insignificant extent, still increases its cost. If the master plans to work exclusively with soft materials, then he will not need a vice in the drilling machine, so you can safely save on them.
Engraving devices
Today it is difficult to find engraving devices in the vastness of the post-Soviet space. They are usually sold only second-hand, but can be ordered in other countries.
It is important to understand that the cost of such a product will not be low, because accuracy of work is important here.
Their use is limited, they are usually used in the arms industry. Such a vice is necessary in order to engrave a particular part. Thanks to their versatile design, they can grip any size and engrave at any angle.
Shrabkogels design
Shrabkugels are widely used in the jewelry industry and are small in size. They allow you to turn the object to the desired position and fix it in this way. Sometimes the device has holes at the top, which allows you to fix objects of irregular shape.
Pipe vise
Pipe vices have a narrow scope of use and cannot be included in the rating of the most popular. They differ in that their the maximum diameter is equal to the maximum diameter pipes. Due to the specifics of the work, the structure is attached to the workbench exclusively with bolts, because operations with pipes often imply that considerable efforts will be exerted on the material.
Outwardly, they resemble a steel frame along which a vertical sponge moves. Such a vice is used in plumbing or in larger areas related to the use of pipes. Such a device is not suitable for other tasks.