Where do shiitake grow and what do they look like?
In the wild, Shiitake grows in the countries of East and Southeast Asia: in the mountainous regions of China, Japan and Korea. In Europe, America, Africa and Australia, this mushroom does not occur in its natural wild form. In Russia, shiitake lives only in the south of the Far East; in Siberia and in the European part of the country, no foci of natural habitat of the fungus have been identified.
By the nature of their diet, shiitake mushrooms are saprophytic fungi that feed on organic matter from decaying wood, therefore they are found mainly on old stumps, wood cuts, and drying trees.
In Asian countries, this mushroom is considered curative and has been cultivated on tree stumps for more than a thousand years.
Outwardly, a shiitake looks like a hat mushroom on a short thick stem. The diameter of the cap can reach 20 cm, but on average it is 5-10 cm, in contrast to many xylotroph fungi. Shiitake grows alone without forming clusters of articulated fruit chalk. The cap of the fungus in the first phase of the growth of the fruiting body has a dark brown color and a pronounced spherical shape; as the fungus grows and develops, the cap flattens and becomes lighter.
The pulp of the mushrooms is light, delicate in taste, slightly reminiscent of the taste of porcini mushrooms; if the cap or leg of the mushroom plate is damaged, it darkens.
Stroke or other illness?
Circulatory disorders of the brain are diverse, and nausea and vomiting accompany many diseases, ranging from food poisoning to osteochondrosis. Therefore, before self-diagnosis, go to the local doctor, tell about your symptoms, and he will refer you to the appropriate department. In addition to a stroke, the following ailments can occur with nausea and vomiting:
- poisoning or exacerbation of gastritis;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure or hypotension;
- concussion;
- overheat;
- intoxication.
These methods of examining the brain will help detect any abnormalities in its structure. Also, with their help, you can find places where blood flow is impaired. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then you should immediately go to the hospital to get help.
Remember that nausea or vomiting are very common symptoms that indicate a wide variety of diseases (most often gastroenterological). Do not rush to diagnose yourself with a stroke and call an ambulance, it is better to just go to a general practitioner and tell him about your symptoms. And he will write you a referral to the appropriate specialist.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must conduct a differential diagnosis
Some non-serious diseases that are not strokes but cause nausea and vomiting:
- poisoning and other gastroenterological diseases;
- intoxication with various chemicals;
- sunstroke;
- concussion of varying severity.
Hello! My mother had a massive hemorrhagic stroke six months ago, as a result, the right side is motionless, she cannot speak, but understands everything that we tell her. Once a month, she has an attack: blood pressure rises or falls, vomiting begins, after which profuse sweat appears. What is a recurrent stroke?
How long ago did your mother have a stroke, to what numbers does blood pressure rise / fall? Please write to us by mail:
- Tatyana on Prognosis after a stroke: how long will life be?
- Musaev on Duration of treatment for meningitis
- Yakov Solomonovich on Consequences of CVA for life and health
Copying of site materials is prohibited! Reprinting of the information is only allowed if an active indexed link to our website is indicated.
ABOUT SHIITAKE MUSHROOMS
Shiitake are native to China and other parts of Asia; they do not grow in the wild in the United States, where they grow naturally, spores are released from the caps of fruiting mushrooms in the spring, flow through the air and settle on the branches of trees, both living and dead. The spores eat up the wood pulp and grow, emerging the next year, ready to be harvested.
GROWING SHIITAKE MUSHROOMS
In commercial cultivation, Shiitaki are usually grown on sterilized sawdust blocks. Some say this faster method produces shiitake that are not as meaty or tasty as those grown on logs. Most home shiitake growers grow their mushrooms on logs using any of a variety of methods.
You can purchase to start growing shiitake mushrooms outside or even indoors, or you can grow your mushrooms from scratch using a method similar to the one described below. In most parts of the country, vaccinations are best done in the spring.
- To get started, you will need freshly cut hardwood logs, preferably oak, poplar, or alder. The logs should be about forty inches long and four to six inches in diameter. The logs must rest for about three weeks after they are cut to allow the natural fungicides to die out, but must be used before they dry, usually within six months after being cut.
- Purchase mushroom caviar (mushroom tissue used for breeding) in the form of corks, thimbles, or sawdust. A number of internet sites sell mushroom caviar, offering different strains of shiitake caviar with different characteristics. You need about 25 shiitake plugs per log.
- Drill quarter-inch holes around the circumference of your logs, starting at two inches at each end and drilling every six to eight inches. Drill holes about one inch deep.
- Plug the holes with caviar.
- Melt the beeswax or use food grade paraffin wax (called cheese wax) and, using a brush or turkey, cover the holes with wax to protect the caviar from contamination.
- Stack your logs like teepees against a fence or lay them on the ground on a bed of straw. They should be in a shady, humid place with good air circulation. If there is not a lot of rain, you can dip the logs in water or give them heavy watering (four to six hours a week). Keeping the logs moist but not damp is the only tricky part of the operation, and it can take trial and error to get right.
- Six to twelve months later, after a rainy day, the shiitake will come out of the logs and continue to produce in the spring (and maybe fall) for three to four years, until all the pulp in the log is used up. Average yield reports range from one pound of shiitake for each linear foot of the log to eight pounds over the life of the log. If you grow more than you need, you can sell them, give them away, dry or freeze them.
You can order the Shiitake Plug Spawn Starter Kit on Amazon, such as this one: Shiitake Plug Spawn Starter Kit - for growing your own mushrooms.
 starter kit for growing mushrooms
starter kit for growing mushrooms
Growing at home for beginners
First, it is advisable to prepare a room where mushrooms will be grown:
- It is necessary to make good ventilation, install standard room lighting in such a way as to be able to control the air temperature.
- Shiitake loves coolness, so the optimal temperature for them should be + 15-18 ºC during the day and +10 ºC at night.
- After preparing the premises, place the racks on the shelves.
- Further work should take place with gloves so that the fungi do not absorb germs and bacteria.
- You must purchase shiitake mycelium in advance (seeds cost from 100 rubles per 10 pcs.) And substrates (sawdust, dry leaves, hay, sunflower husks).
- It is recommended to boil the substrate for about one and a half to two hours, cool and squeeze. The mycelium bag must be prepared by rinsing it with a chlorine solution.
- When everything is ready, dry substrates are alternated with mycelium (each block should account for no more than 8% of mycelium). Tie the edge of the bag.
- "Pouches" must be spread out at a small distance from each other. With a sterilized knife, small cuts are made on the bag to allow air and humidity to get inside (up to 20 holes).
- A drip irrigation system is recommended for irrigation.
Next, you need to be very careful with regard to mushrooms. As soon as you see that the first crop begins to erupt, the temperature should be lowered to + 18ºC during the day and lowered at night. Shiitake need lighting for 5-6 hours a day.
Growing shiitaki in a greenhouse
In addition to home conditions, the mushroom can be planted in greenhouses, in garden plots. A kit for growing shiitake mushrooms costs from 2400 rubles. Ready-made packages are placed on the ground or on shelves. The temperature is maintained at + 18ºC, and irrigation increases in summer drought. Lighting should be present for 8-10 hours a day, the light should not be bright.
For edible lentinula, it is not necessary to build a separate greenhouse in the country. Shiitake plants bear fruit well in a greenhouse surrounded by other plants. A special structure can be built in the shade or protected from direct sunlight by fencing with an opaque roof on the south side of the house.
Straw cultivation technology: pros and cons
Straw mixes are very nutritious for more than just shiitake. Straw cultivation is an intensive method. Most often, barley or oat base is used as a substrate. Consider the pros and cons of this method:
Pros:
- mushrooms grow faster and more abundantly;
- it is an excellent nutrient material;
- budget technology for one-time fruiting.
Minuses:
you have to change the substrate more often;
other microorganisms can compete with fungi;
very careful attention to the conditions of the room;
requires sufficiently spacious and specially equipped isolated rooms.
But each technology has its drawbacks, so refer to the extensive method for comparison.
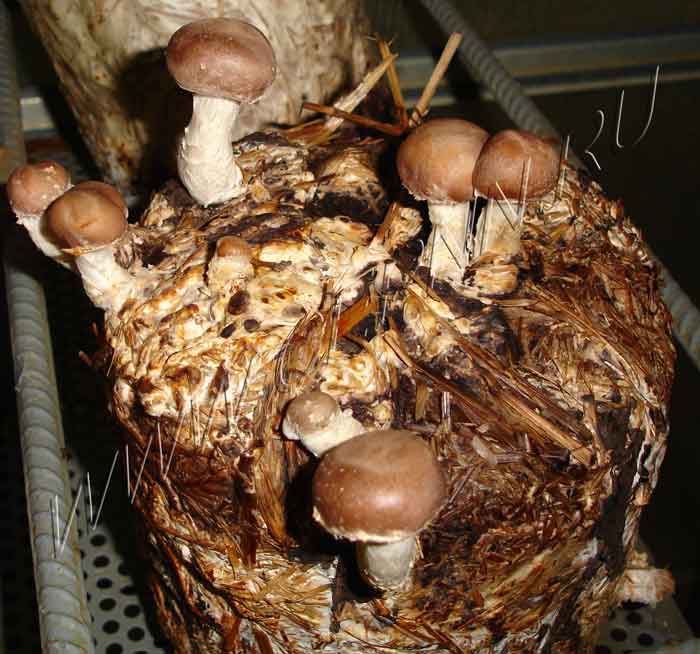
Features of growing mushrooms on stumps and logs
On tree stumps, lentinula grow slower and more capricious. Let's consider the basic requirements for this method.
Any low-grade wood is suitable for cultivation, but it is better to harvest those varieties on which shiitake spores grow naturally. Look for options with little signs of decay because fungi will wear down the tree and the growth medium will quickly deplete resources. This method is used to bring the fetus closer to its natural habitat.
When growing shiitake, the crop can be harvested from stumps or logs only after a year, and profit can be obtained in the second year of mushroom cultivation on the site, so mushroom pickers use artificial methods more often.
The valuable properties of the mushroom
This woody mushroom has excellent taste, as well as an indescribable aroma, which resemble porcini mushroom and champignons at the same time.
There are many areas of application for shiitake. They are actively used in the following areas:
- in culinary recipes,
- for medical purposes.
- for cosmetic purposes.
Its main value for cooking is its special property, which allows, in combination with other products, not to interrupt their taste, but to saturate it, giving special notes to the dish.
Shiitake is used in alternative medicine to treat a variety of diseases: cardiovascular, diabetes mellitus. It destroys many different types of viruses and strengthens the immune system
But it is necessary to treat it with caution, because this mushroom can cause a serious allergic reaction.
It is also irreplaceable for cosmetic procedures, because it is saturated with lipids, proteins, vitamins and microelements that saturate the skin, making it healthy and radiant.
Now it is clear why the black mushroom is so valued not only in the countries where it grows, but also in most others, where it is exported in large volumes.
Back to content
Extensive growing method
The principle of extensive technology for growing shiitake at home is to create an environment for mushroom growth that is as close to natural as possible.
The introduction of the mycelium is done using freshly cut fragments of tree trunks. For this, oak, beech, chestnut, hornbeam, birch are usually selected. Harvests are made during the period of the highest concentration of sugars in the tree sap: after dropping the foliage and before the start of sap flow
Pay attention to the absence of signs of damage by xylotrophs and pests. The trunks are sawn into blocks of 1 to 1.5 m in length and 10–20 cm in diameter, kept in an open space for 1 to 3 months, then inoculation is carried out

Taking into account the climatic conditions of the area where shiitake is grown, it is advisable to inoculate with the corresponding strains.
- Heat-loving (summer) fruits bear well in humid, warm climates from May to September at temperatures from 14 to 27 ° C.
- For cold-loving (autumn-spring), the optimum temperature will be from 7 to 16 ° C. The strain bears fruit from March to May and from September to November. The mushrooms are of good quality, although they develop rather slowly.
- The mycelium of all-season strains grows rapidly in wood, fruiting occurs in a wide temperature range from 10 to 25 ° C from May to November. In closed rooms with the ability to control the microclimate, the use of this strain allows you to get a year-round harvest.
The process of inoculation itself is carried out as follows. In aged chocks, holes are made to the floor with a diameter of 2 cm to a depth of 1.5 cm, placing them in a checkerboard pattern. Shiitake grain mycelium is placed in them and covered with wax. The logs sown in this way are stacked in shaded areas on the cleared areas.
The incubation period (the time of mycelium growth in wood) depends on the volume of sown material, the quality of the mycelium, temperature indicators, air humidity and lasts from 6 to 18 months. The optimum air temperature for germination is 24-28 ° C with a humidity of 70-90%. In the middle lane and southern regions, the mycelium tolerates wintering well: it is enough to cover the logs with straw or transfer them to the basement.

After complete germination of the mycelium, fruit formation is stimulated. To do this, the logs are soaked in water for 24-72 hours, then they are placed vertically or at an angle in a shaded area, but not in complete darkness. The first rudiments of fruiting bodies appear in 7-10 days.
Shiitake fruiting period occurs usually twice a year. At the end of each fruiting wave (in the dormant period), to maintain stable environmental parameters, the chocks are covered with breathable material. Depending on the size of the chocks, the yield lasts from two to five years. The average amount of mushrooms harvested with this method of growing from 1 m² of wood for the total time is from 200 to 250 kg.
This is how shiitake is grown, an imperial mushroom, long known, but still not fully studied, modest in appearance, but possessing an exquisite taste and, in the aggregate of its qualities, deserves the close interest of a keen person.
Preparing the substrate for sowing mycelium
 For the cultivation of shiitake, it is better not to use whole pieces of wood like hemp or wood blocks, but finely chopped wood substrate. In this way, the mushroom mycelium will receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and develop faster.
For the cultivation of shiitake, it is better not to use whole pieces of wood like hemp or wood blocks, but finely chopped wood substrate. In this way, the mushroom mycelium will receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and develop faster.
The nutrient medium is prepared from chips cut with a garden grinder or freshly prepared twigs with a diameter of no more than four centimeters. For this, wood of the following species is suitable: willow, oak, alder, apple, birch, aspen, yellow acacia, pear and many other deciduous trees. However, the ideal option is still oak sawdust or shavings. In this case, the size of individual grains should be from two millimeters to two centimeters.
It is better to put the prepared substrate into action right away, but you can also dry it in a Russian oven or in the oven and send it for storage.
For every 1.5 kilograms of dry wood and 2.2 kilograms of freshly cut branches, it is useful to add 100 grams of barley grain and 10 grams of chalk. Barley can also be replaced with wheat grain or barley.
Wood waste is placed in a three-liter jar, slightly compacting each layer. As soon as two to four centimeters remain to the neck of the jar, boiling water is poured into it (for the purpose of disinfection). After a couple of hours, the water is drained, and the cans with wood are kept at room temperature for another 24 hours.
 During this period, fresh spores of bacteria and molds appear in the wood pulp, the destruction of which should be perfectly handled by the last heat treatment. To do this, the remnants of the liquid accumulated in it during the day are drained from the jar, cover its neck with several layers of gauze and put it in an oven heated to 80-110 degrees for 2.5-3 hours.
During this period, fresh spores of bacteria and molds appear in the wood pulp, the destruction of which should be perfectly handled by the last heat treatment. To do this, the remnants of the liquid accumulated in it during the day are drained from the jar, cover its neck with several layers of gauze and put it in an oven heated to 80-110 degrees for 2.5-3 hours.
As soon as the jar has cooled, the upper chips are slightly moistened with boiled water at normal temperature (from 1 to 1.5 teaspoons). Then on the surface of the wood with a spoon disinfected with boiling water spread 20-25 grams of grain or 40-50 grams of shiitake substrate mycelium. The mycelium is slightly pressed into the substrate with the same spoon.
A lid with a hole 1 cm in diameter is placed on the jar (the hole is closed with a piece of sterile medical plaster). After 7 days, the plaster is torn off, and a piece of sterile cotton wool rolled into a roll is inserted into the hole. If you do not perform the last action, then mushroom mosquitoes can climb into the jar and spoil its contents.
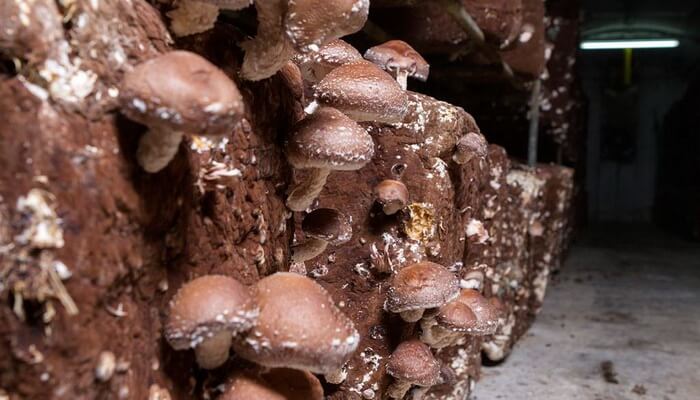
Shiitake - photo and description
Shiitake mushroom (more correct transcription - shiitake) is also known as Japanese forest mushroom and edible lentinula.
Shiitake is medium in size: a hat is from five to twenty centimeters in diameter, has a brown or coffee color. The shape of the cap is convex or slightly flattened. The outer skin is dotted with small light scales. In old mushrooms, the edges of the cap are uneven and bent.
On the underside, the cap is covered with white plates, which, if damaged, darken, taking on a brown tint. The stem is also brown, but always noticeably lighter than the cap. Its length ranges from three to nineteen centimeters with an average diameter of about one centimeter.
The pulp has a light creamy or yellow-whitish hue, as well as pleasant taste (even raw) and smell. In the cap, the flesh is fleshy, in the leg it is much more rigid and fibrous.
In their natural environment, Japanese shiitake are found in deciduous and mixed forests in Japan, Korea, northern China and Russian Primorye. These are typical saprotrophs living on dead tree trunks, especially preferring castanopsis pointed, Mongolian oak and Amur linden. Small groups of Shiitake appear after rains throughout the warm season.
Where and how best to grow shiitake
 For the best fruiting of shiitake, it is necessary to ensure the following conditions: ambient temperature - + 15 ... 18 degrees, relative humidity - from 80 to 90%, the duration of daylight hours - at least 10 hours. It is also desirable that the area designated for growing mushrooms be protected from the winds of all directions and the southern sun.Thus, mushrooms will feel best in the shade of garden buildings or under the canopy of a garden shed.
For the best fruiting of shiitake, it is necessary to ensure the following conditions: ambient temperature - + 15 ... 18 degrees, relative humidity - from 80 to 90%, the duration of daylight hours - at least 10 hours. It is also desirable that the area designated for growing mushrooms be protected from the winds of all directions and the southern sun.Thus, mushrooms will feel best in the shade of garden buildings or under the canopy of a garden shed.
A shade-tolerant spot is also a good place for shiitake.
A more plentiful harvest of mushrooms will provide you with shiitake cultivation under a specially equipped shed. Such a canopy is usually placed under the crown of garden trees. To give the structure stability, install a frame from an old greenhouse in the garden. Make one side from agrofibre or any other non-woven material, and make the other three from usually film. Place pieces of slate, dark film or any other material out of direct sunlight on the cover of the greenhouse.
Before placing the blocks in the prepared place, remove them from the bags and thoroughly pour cool water from a hose day. In the house, not the blocks themselves are sprayed from the greenhouse, but the film walls.
 To stimulate the growth of shiitake in an open area, a large bag-cap can be thrown over each block of mycelium.
To stimulate the growth of shiitake in an open area, a large bag-cap can be thrown over each block of mycelium.
The first harvest of mushrooms ripens in the second or third week after removing the blocks from the bags
In mushrooms, only the caps are cut off, the legs are carefully turned upside down
After that, blocks with intact mycelium crust should be placed in a pool or shallow pond to moisturize. After two to three days, the mushroom blocks are turned over on the other side, and so that they do not unfold in random order, a weight is fixed to their lower part with the help of a clove. In general, it is necessary to saturate the block with moisture so that its final weight is 35-65% more than the initial one (that is, if before the first wave of the harvest the substrate in the bag weighed 1.5 kilograms, then after moistening the weight should already be from 2 to 2, 5 kilograms).
The moistened blocks are returned to their original place and after two to four weeks they begin to bear fruit with renewed vigor. In one mushroom season, you can see from five to six such harvest waves. Mushroom picking ends when the blocks start to fall apart. Such residues can be used to make an excellent fertilizer suitable for all garden plants.
By the way, did you know that shiitake can grow even in water? To do this, the blocks are simply left in a pool, puddle, barrel or in any other body of water on one of the sides down for about a week, until the first rudiments of fruit chalk are formed. Then they are turned over with their wet side up and after a week and a half, the first caps of young mushrooms appear on its surface, and in a couple of days it will be possible to start harvesting.
Read about all the methods of growing mushrooms in the country in the article - "How to grow forest and cultivated mushrooms in the country."
Of course, shiitake can also be grown on stumps (although this method is less productive). But if you choose this particular option, then by all means watch the following video.
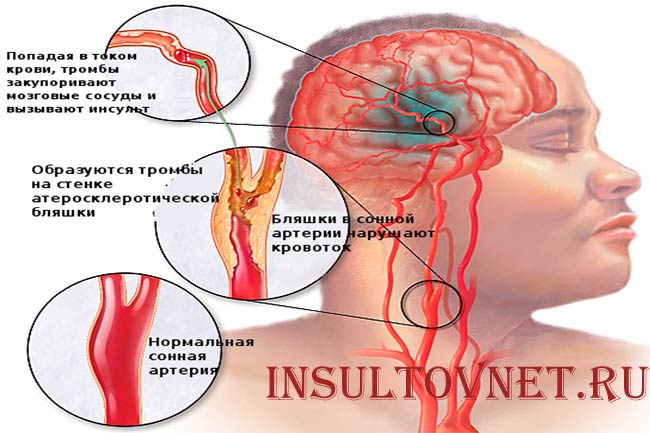
2> Nausea after stroke
It is reliably known that many functions of the gastrointestinal tract, which are regulated at the unconditioned reflex level, directly depend on the work of the brain - not the cerebral cortex, of course, but on the work of other parts of this organ of the central nervous system.
Accordingly, with the necrosis of its neurocells, the regulation of the digestive process is disrupted, and various disorders characteristic of the dyspeptic syndrome arise, which include nausea and vomiting.
Yes, with respect to all the other difficulties that occur with stroke, and regardless of its severity, these symptoms, it would seem, are far from being of paramount importance, but in fact, this is not at all the case. If only because an attack of vomiting can lead to aspiration - the ingestion of food masses into the respiratory tract. In turn, this phenomenon can lead to respiratory arrest, as well as the development of severe aspiration pneumonia.
Constant nausea is far from the best effect on the psychoemotional state of the patient, which, given the presence of neurological insufficiency, is a doubly aggravating factor, since emotional lability will significantly worsen the prognosis of recovery. In fact, a vicious circle will form when one unfavorable factor will enhance the effect of another.
Where to keep the Shiitake substrate?
The bags with the substrate should be kept in a dark place at a temperature of +22 ... + 28 degrees immediately after the mycelium is colonized.
It can be a container, a cabinet, personally, I have an old non-working refrigerator. The mycelium "colonizes" the substrate in 30-40 days. When white bulges appear, I untie the bags and put them in a bright room with a temperature of + 15 ... + 25 degrees, but avoiding direct sunlight. During this period, the first mushrooms begin to grow. As soon as they start to rest against the walls of the bag, I make small cuts in these places so that the mushrooms do not deform.
I constantly monitor each block. If the mushrooms have dried up, to increase the humidity, I put on a clean plastic bag or spray it with water (do not overdo it, otherwise mold will appear!). When the air temperature rises above +30 degrees, I take the blocks to a room with a lower temperature.
Features of the use of the intensive method
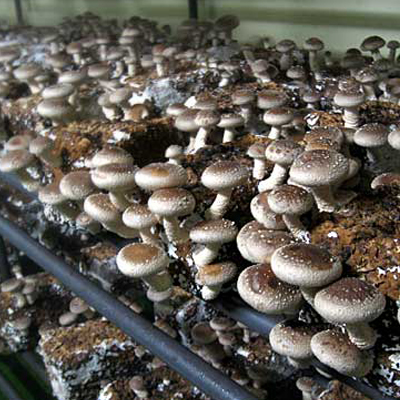
It is possible to achieve the maximum possible results from breeding shiitake by placing mushroom blocks in greenhouse complexes. Despite the laboriousness and high cost of this method, the yield is obtained both qualitative and quantitative.
Substrate preparation
The basis of the mixture for growing shiitake is sawdust with a fraction of 3 mm or more. The added shavings from the same deciduous trees allow increasing the air permeability of the prepared substrate.
The optimal ratio of components for a mushroom block:
- 50% sawdust;
- 25% wood chips (straw);
- 25% of a mixture of grains, tea leaves, bran, flour (ingredients are taken in an arbitrary proportion);
- up to 1% of the total mass of chalk (gypsum).
When choosing plastic bags for creating a block, it is recommended to give preference to options with a volume of 2.5 liters, since in a large container, fungal spores are poorly distributed.

Cooking mushroom blocks
Before planting mushrooms, it is necessary to sterilize or pasteurize the substrate in order to destroy all pathogenic microflora. To carry out heat treatment, a barrel is required, into which the stems from cereal plants are placed and poured with boiling water. Then the container is placed over the fire and heated for 2-3 hours. Alternatively, you can simply wrap the container and hold the raw material for 8-12 hours. Then the straw is transferred to a clean container and allowed to cool.
Inoculation
At this stage, the prepared substrate is sown with grain mycelium. But the nutrient mixture should not be too wet, otherwise there is a high likelihood of mold development. To check the readiness of the base for infecting it with spores, you need to take a small part and squeeze it in a fist - droplets of water should appear between your fingers, but do not flow too much.
Having achieved the required moisture content (60-70%) in the substrate, they proceed to filling the plastic bags. One block should contain 3-7 kg of nutrient mixture.
The process of placing mycelium in prepared bags consists of the following steps:
- Make a kind of channel in the center of the substrate block using a clean wooden stick (3 cm in diameter and 1 m in length).
- Introduce grain mycelium into the hole made at the rate of 4-5% of the total mass of the substrate. This technique makes it possible to speed up the process of mushroom reproduction.
- It is recommended to take mycelium only with clean hands. It is best to use rubber gloves that have been disinfected with 70% alcohol.
- Lay cotton wool on top of the substrate, it will serve as a cork.
- Tie the mushroom block tightly.
- Place in suitable boxes and transfer to a greenhouse, another prepared room.
Care and harvest
The formation of fungi rudiments occurs at a low air temperature - 17 degrees. If the indicators exceed the mark of 30 degrees, then the mycelium will die, it will be covered with mold. At this stage of cultivation, it is not necessary to adjust the moisture parameters, only to regularly ventilate the basement, shed or hangar. There is no need to turn on the lighting. The main thing is to monitor the temperature regime in the room and the ventilation.

The ripening period lasts 20-60 days, in some cases even 120 days. This time is necessary for the spores of the fungus to develop the territory. The shiitake then absorbs the nutrients. After 2 months, the surface of the substrate will turn white, and the block will become a monolithic mass. At this stage, the bags are removed from the containers, the mixture is moistened and stacked on the racks. The humidity level in the room should be 90%, the air temperature is 18 degrees.
If earlier lighting did not affect the development of fungi in any way, now they need a day of light with a duration of more than 12 hours. Fluorescent lamps with an intensity of 120 lux are suitable for these purposes. You should also regularly ventilate the room so that carbon dioxide released by the mycelium does not accumulate. Otherwise, fruiting bodies will not be able to fully grow and develop. When the shiitake buds have formed, the moisture level is reduced to 80%. If this is not done, then the legs of the mushrooms will stretch out, and the caps will be small.
When kept in greenhouses, shiitake yields three times. The first wave is characterized as the most abundant - up to 70% of all mushroom production, the second is already 25%, and the third, which comes in a couple of months - is a unit of fruit chalk.
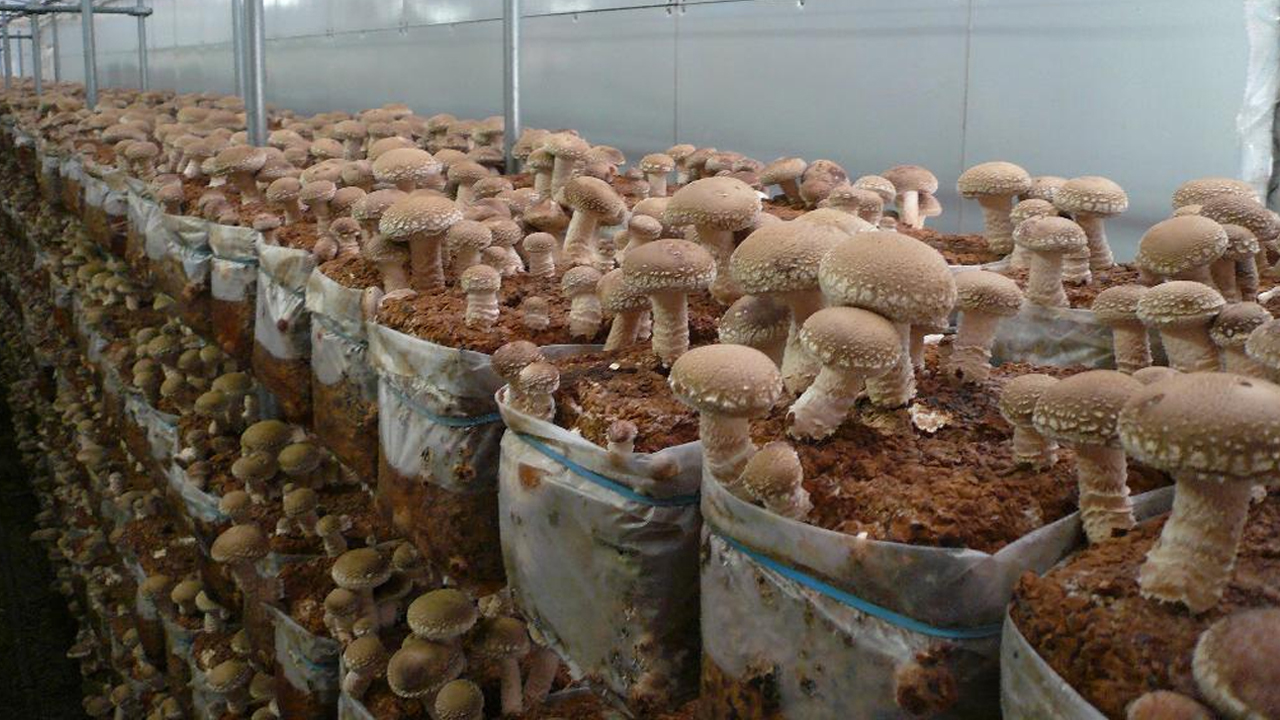
Growing shiitake on sawdust
If you want to get a mushroom harvest faster, choose growing mushrooms on sawdust, shavings, husks, etc. The only thing to get such a crop will take a little more personal time, but the result pays off. This method of growing mushrooms is suitable for basements and greenhouses, the main requirement is to create suitable and comfortable conditions. We described how to prepare the substrate above
The only thing to pay attention to is the addition of cereal crops (for example, wheat, barley, rice) to the soil, as well as dry chalk or gypsum. The total amount of the additive should not exceed 30% of the total volume of harvested soil. Such additives to the substrate will improve the structure and acidity.
 Growing shiitake on sawdust
Growing shiitake on sawdust
We place the mushroom mycelium in pasteurized soil with a temperature of 20-22 degrees, carefully in small pieces of about 1 cm, without damaging the "seeds" and cover with plastic wrap, making small cuts. Thanks to this, we will create a microclimate and allow the soil to breathe. After 1 month, the soil should be covered with mycelium. If the mycelium is overgrown, remove the entire substrate completely and soak it for 2-3 days in water and then cover it with a film.
In about a week and a half, you will receive fruiting bodies, which, with a frequency of 1 time per month, will begin to yield. To make the mushrooms grow faster, periodically spray the fruit bodies with water.
Thanks to the acquired knowledge, the cultivation of the "imperial oriental mushroom" will become not only an exciting but also a useful hobby.
Where Does Shiitake Grow?
In the natural environment
In nature, leitinula lives in China, Japan and Korea. For local residents, this is one of the most important mushrooms in the world. Here it bears fruit actively in the spring and autumn. It also grows in the far eastern corner of Russia - in the Primorsky Territory, part of the Khabarovsk Territory, and the islands of Sakhalin and Kunashir.
In an artificial environment
Although the natural habitat of shiitake is small, this mushroom is quite unpretentious and has long spread from Southeast Asia around the world, where it is grown on special mushroom farms.Recently, in terms of world production per year - about 800 thousand tons, shiitake has bypassed even the main competitor - champignon.

Mushroom farms have also existed in Russia for over 30 years. Little by little, their number is increasing, and the assortment they offer is growing. In recent years, due to restrictions on the import of imported agricultural products into Russia, the development of this industry in our country has been given a powerful impetus.
So far, the bulk of the mushrooms artificially produced in the country are champignons and oyster mushrooms. Shiitake accounts for only 0.30% of the total production volume. The reason, in part, is that this mushroom is not very well known in Russia yet. However, taking into account all its advantages, it must be assumed that the share of shiitake in the Russian mushroom production will grow steadily.
At the moment, professional farms where lentinula are grown are located in the Moscow, Voronezh and Saratov regions.
In addition, every year the number of enthusiasts growing shiitake on their own in their personal plots increases, so that the future of this mushroom in our country will clearly be happy.
Sterilization of the substrate and packaging in bags
Growing shiitake in a substrate is impossible without first sterilizing it. The conditions in which mushrooms grow are favorable for the reproduction of mold, which develops rapidly and drowns out the reproduction of shiitake spores. All fungi and bacteria die in it only during sterilization.
At home, sterilization can be done in two ways:
- steam the substrate with boiling water in a separate container, and then pack it in bags;
- first pack in bags, and then sterilize in boiling water.
Sterilization by the first method, packaging and insertion of mycelium
When using the first method, you will need a large container into which the entire substrate is poured. At home, it is convenient to use an enamel pot with a lid; the dishes must be thoroughly washed beforehand. The mixture is poured to the top with boiling water, wrapped in a blanket and left for 10 hours. After that, the excess water is drained off, slightly squeezing the substrate. It should cool to room temperature under a lid, only after that it is packed in bags. Packages for packing blocks must be clean. Fill them only with sterile gloves.
Shiitake cultivation should be carried out in ventilated bags. You can do it yourself by piercing the holes on the side after forming the block, or buy special bags in which ventilation is provided.
After filling the bag, the center of the mixture is carefully pierced and the mycelium is introduced into it. The amount of mycelium should be 3-5% of the block weight. If the block has a volume of 2.5 liters, then the mycelium needs 100 or 150 grams. You cannot tie the bag tightly. Mushrooms ripen with a special gas exchange, therefore, before tying, a sterile cotton wool plug with a diameter of 2 cm is inserted into the neck. There is no need for this in ready-made bags, gas exchange will be carried out through filters.
Second method sterilization and filling with mycelium
Growing mushrooms in the second way at home is more convenient, but block bags must withstand temperatures up to + 110 °. Before packing, the mixture is moistened, wrung out and filled into bags. Moisture can be checked by squeezing the mixture in a fist:
- if trickles of water flow down, then the spin is insufficient;
- if drops stand out, the mixture is ready.
The bag is tied loosely and placed in a saucepan. Water is poured, a little short of the string. Boil over low heat for 2-3 hours. After that, the bag is removed and cooled to room temperature. Filling with mycelium is carried out in the same way as in the first case. Be sure to use sterile gloves.
The block in the package is formed in the form of a bar, the lower part of which is slightly smaller than the upper one. Mushrooms will grow at the top and sides.























































