TREMELLA MESENTERICA
System:
NormalfalsefalsefalseRUJAX-NONE
Kingdom: Mushrooms (Fungi)
Department: Basidiomycota
Class: Tremellomycetes
Order: Tremellales
Family: Tremellaceae
Genus: Tremella
Species: Tremella mesenterica (Batsch) Šutara (1992)
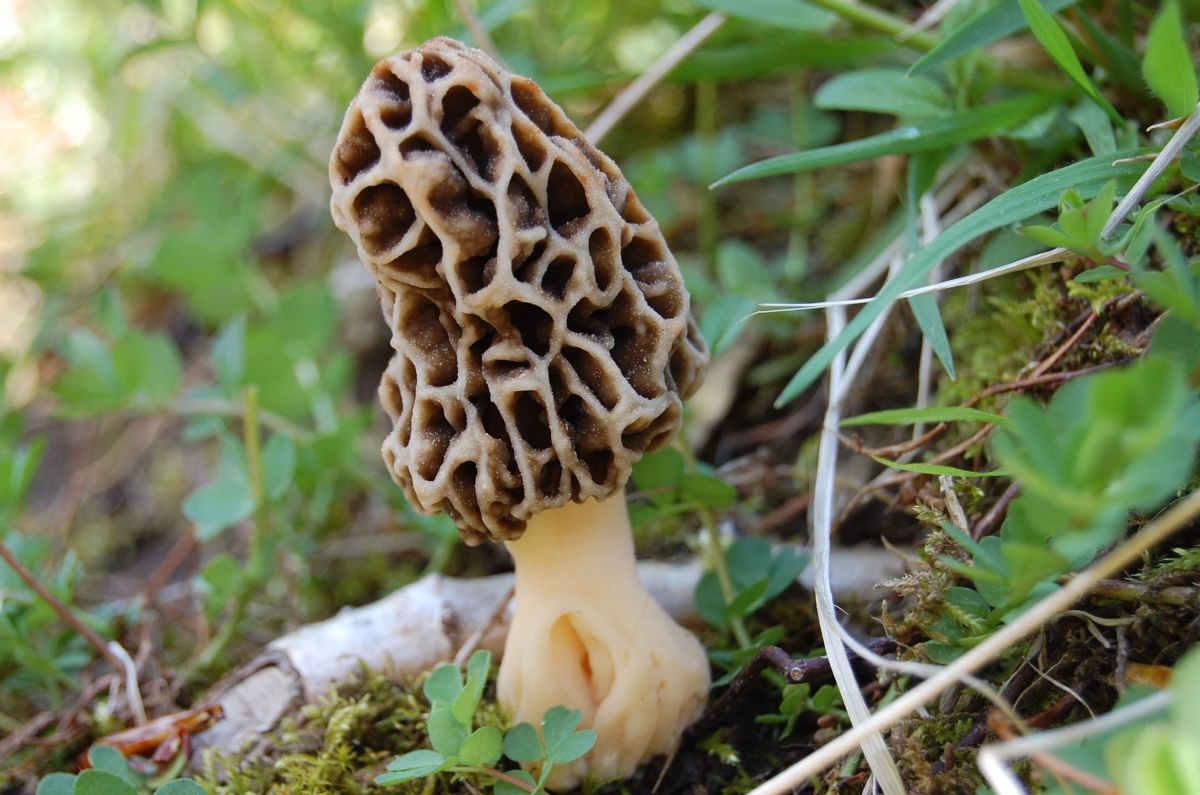
Fruit body: pale yellow, yellow, sometimes to orange, partly transparent, 1-10 cm, at a young age cerebral, later folded, gelatinous, dense gelatinous, often with a sticky surface. In dry weather, the fruiting bodies dry out, taking the form of crusts adhering to the substrate. When the humidity changes, the crusts swell and the mushroom regains its normal shape. With excessive moisture, it fades to white, translucent. Old fruit bodies dry out, darken, become flattened and coarser. Habitat: like the fucus-shaped shiver, this fungus parasitizes on the mycelium of the host fungus (tinder fungus of the genus Peniophora) located in rotting wood. Following the host fungus, it settles on the trunks, branches and stumps of deciduous, much less often conifers. Sometimes there is a simultaneous fruiting of the tremor and the peniophora affected by it.
Fruiting period: from August to May (freezes in winter and continues to develop in a thaw). Distribution in the Russian Federation: throughout the forest zone, often abundantly in places.
Similar species: Fruit bodies, discolored to white in rainy weather, can be confused with trembling fucus. But only in the Primorsky Territory.
Edible: the mushroom is edible, used fresh for salads (with the addition of sweet and sour dressing). From fresh or dried fruit bodies, nutritious broths are cooked.
In China, it is considered a delicacy; among other recipes, it is used to prepare immunomodulatory cold vegetarian soups (with the addition of lotus seeds, lily bulbs, Chinese dates, etc.).
Medicinal properties: the biologically active polysaccharide glucuronoxylomannan was isolated from the orange shiver. Laboratory tests have shown that it has immunostimulating, radioprotective, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergenic activity, and also participates in the protection of the liver (hepatitis B).
Ethanol extract of fresh fruit bodies causes complete death of A549 cancer cells (lung cancer), increases the production of interferon and interleukin-2, kills cervical cancer cells and enhances the effect of chemotherapy.
In China, on the basis of glucuronoxylomannan, several medications are patented (antineoplastic, anti-inflammatory, blood pressure regulating).
The fruit bodies of the tremors contain essential amino acids and B vitamins, which makes these mushrooms valuable not only in medicinal but also nutritionally.
For medicinal products, the mushroom is cultivated by the deep method (China).
In Chinese folk medicine, the orange tremor was used as a general tonic, for the treatment of pulmonary diseases, bronchitis, as well as for paralysis, eye inflammation, and as a sedative. Known use in England (rubbing with a fresh fruiting body) for the healing of skin ulcers.
Cookie Policy Mikhail Vishnevsky, 2012-2019 Log out | EditLAT Tremella mesenterica Edible Synonyms: Filmy Tremella, Dragla, Helvella mesenterica, Hormomyces aurantiacus, Tremella brasiliensis, Tremella lutescens, Tremella lutescens var. brasiliensis
Specifications:
| Group: | Indefinite |
|---|---|
| Plates: | Absent |
| Colour: | White to orange |
| Info: | Jelly-like fruiting body |
Systematics:
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
|---|---|
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Tremellomycetes (Tremellomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Tremellomycetidae (Tremellomycetids) |
| Order: | Tremellales |
| Family: | Tremellaceae (trembling) |
| Genus: | Tremella |
| View: | Tremella mesenterica (Orange trembling) |
The mushroom is edible, but practically never used in Russia. This is due to the difficulty of transporting this mushroom from the place of collection (it dissolves quickly).
Morel traditional medicine recipes
Research results have shown that polysaccharides from morel fruit bodies have many healing properties, including antitumor, immunoregulatory, and antiviral effects. Extracts from them have, among other things, antioxidant properties.
Morels are used in folk medicine to treat indigestion, excessive sweating, and shortness of breath. For this purpose, a decoction or tincture of mushrooms is used for a long time, the beneficial properties of which are obvious.
Morel juice
It is believed that morel juice is able to benefit the body, providing a healing and tonic effect. You can get it by preparing a concentrated mushroom broth. This is done simply. The proportion is calculated as follows: for each glass of water there should be a tablespoon of chopped mushrooms. The mixture is boiled for half an hour, after which it is left for several hours. The finished broth should be filtered and taken in small quantities (no more than 50 ml at a time).
Alcohol tincture on morels
The tincture is used externally for medicinal purposes. To prepare it, you will need the following:
- dried chopped mushrooms;
- absolute alcohol;
- purified water;
- glycerin of vegetable origin.
The dried chopped mushrooms are divided into two equal portions. Then cover half of the mushrooms with a mixture of 70% alcohol, 20% glycerin and 10% water. Insist 4-6 weeks.
Then a decoction is prepared by mixing the second half of the mushrooms with a volume of water twice as large as that used in the previous step. Boil it for at least one, preferably two or more hours, adding water as needed during cooking. After that, you need to continue boiling until the liquid begins to evaporate. It should remain exactly the same as the alcohol solution. After that, the broth is removed from the heat and completely cooled.
It is necessary to mix the liquids from the decoction and the tincture, while the final product should contain about 25% alcohol. A useful traditional medicine is ready!
Growing at home
Morel breeding principle:
Preparing the soil for sowing mycelium. Considering that morels do not tolerate stagnant water, a drainage system should be built on the selected plot of land, and the top layer of soil should be replaced with a specially prepared substrate. The "correct" soil mixture is prepared according to the following scheme: every 6 portions of garden soil are combined with one part of ash and half the volume of wood chips. The finished substrate is mixed, and then spread in a ten-centimeter layer on the equipped beds. The laid soil is watered abundantly with water (10 liters per 1 square meter of land).
Sowing mycelium. To get a good harvest, it is better to purchase spores from trusted suppliers, rather than using overripe morels, independently collected in the forest. The mushroom mycelium is spread over the surface of the prepared substrate, and then crushed with a small layer of earth (5 cm). After that, the soil is watered and covered with natural "insulation" (straw, foliage, small branches, apple pomace).
Cultivation and harvesting
After sowing mycelium, it is important to monitor the moisture level of the substrate. As it dries up, a special nutrient concentrate is introduced into the soil, which promotes intensive germination of spores (for example, "Baikal EM-1")
In addition, to stimulate fruiting, the beds can be sprinkled with a thin layer of ash.
In most cases, after 2-3 weeks, morels begin to bear fruit. Considering that young mushrooms have delicate flesh, it is better to use a sharpened knife and a spacious container to collect them.
Remember, because of the fragility, morels quickly lose their presentation, so they should be transported as carefully and as soon as possible.
Where they grow, in what forests and how to collect
All varieties are represented throughout the Russian Federation. They can be found not only in forests, but also in parks, steppe zones and even in summer cottages.Sometimes mushrooms of this species are found at the site of deforestation.
Curious!
A particularly large number of morels are harvested in the field of forest fires. Moreover, the crazy fruiting activity of such myceliums does not decrease for 3-4 years.
There is an assumption about the possibility of morels forming mycorrhiza with ash. But it has no scientific evidence.

The fruiting period of mycelium falls in the spring months, mainly in May. This is considered one of the advantages of morels, since in spring the rest of the forest species practically do not bear fruit. Moreover, these mushrooms belong to saprophytes, which makes it possible to grow myceliums at home.
Are morels dangerous?
Are Morels Poisonous Mushrooms? The issue is controversial. They contain the toxin gyromitrin. He is also present in the lines, where, by the way, his concentration is greater.
Gyromitrin tends to accumulate in mushrooms. Scientists say that in some areas morels do not contain this toxin.
But it is important to know that gyromitrin is destroyed when mushrooms are heat treated. To avoid poisoning, they must be boiled or scalded with boiling water before use.
You cannot eat raw morel mushrooms! Proper handling and cooking of mushrooms will save you from unwanted consequences.
How dangerous can morels be?
Morels, like stitches, contain a dangerous substance called gyromitrin. But there is much more of this substance in the lines than in morels or morels. Some researchers are confident that morels grow in many areas, which do not contain the toxin.

In any case, it is recommended to pre-scald, but it is better to boil morels, and then drain the water. In this case, the mushroom will delight you with its taste and will not cause any harm.
A dangerous resemblance, or how to distinguish an edible morel from a line?
Some mushroom pickers confuse morels with their poisonous cousins.
Indeed, related species are very similar, but they can be distinguished by their shape, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the cap of the edible morel is round, in addition, its size is larger than that of poisonous species
In the morel, the length of the cap and the legs are almost the same, and in the stitching, the leg is often shortened, sometimes it is not visible at all.

In morels, both the cap and the leg are hollow inside, and the lines are filled with sinuous pulp. There are sinuous cells on the surface of the morel.
Description morel
The real morel belongs to the third category, it is considered a tasty mushroom, but it belongs to conditionally edible. Morel is real very much loved by Americans, and in 1984 it was even officially recognized as a mushroom of Minnesota. Morels are also in demand in Russia and European countries - they have good taste and are easy to recognize in forest glades.
Let's consider what characteristics you can recognize morels and what you should pay attention to
Hat
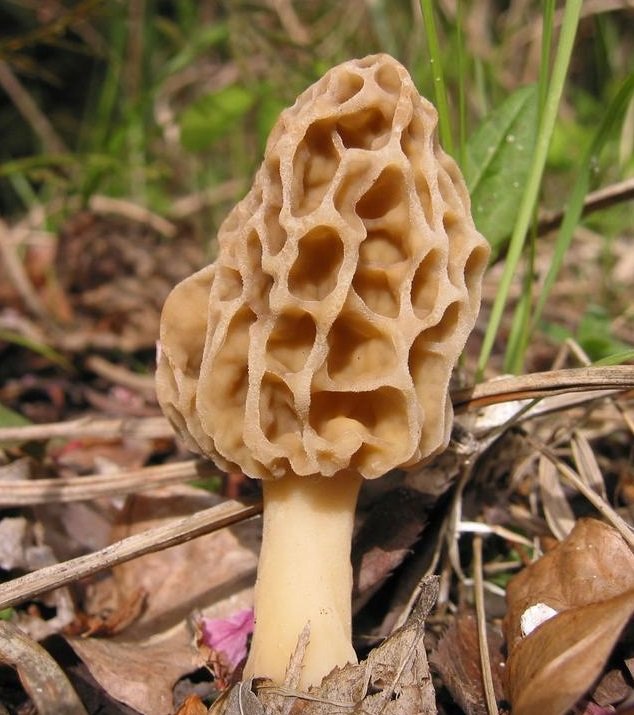
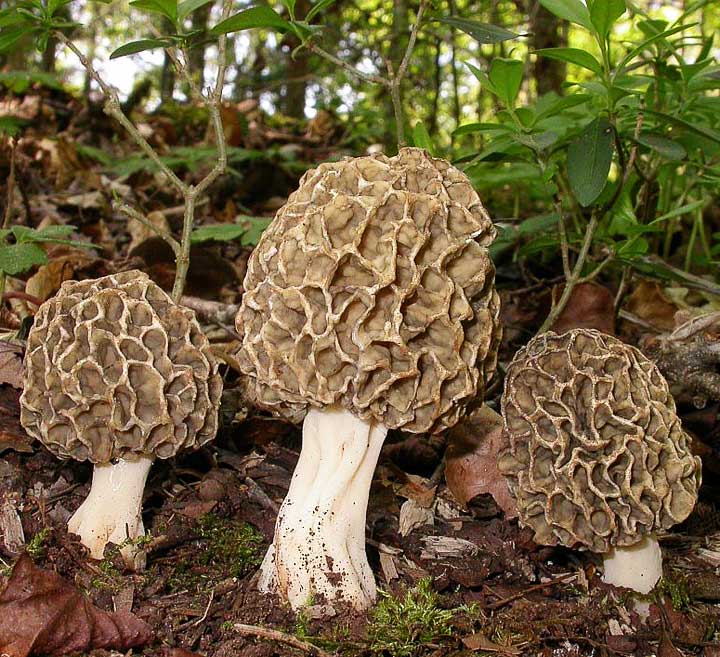
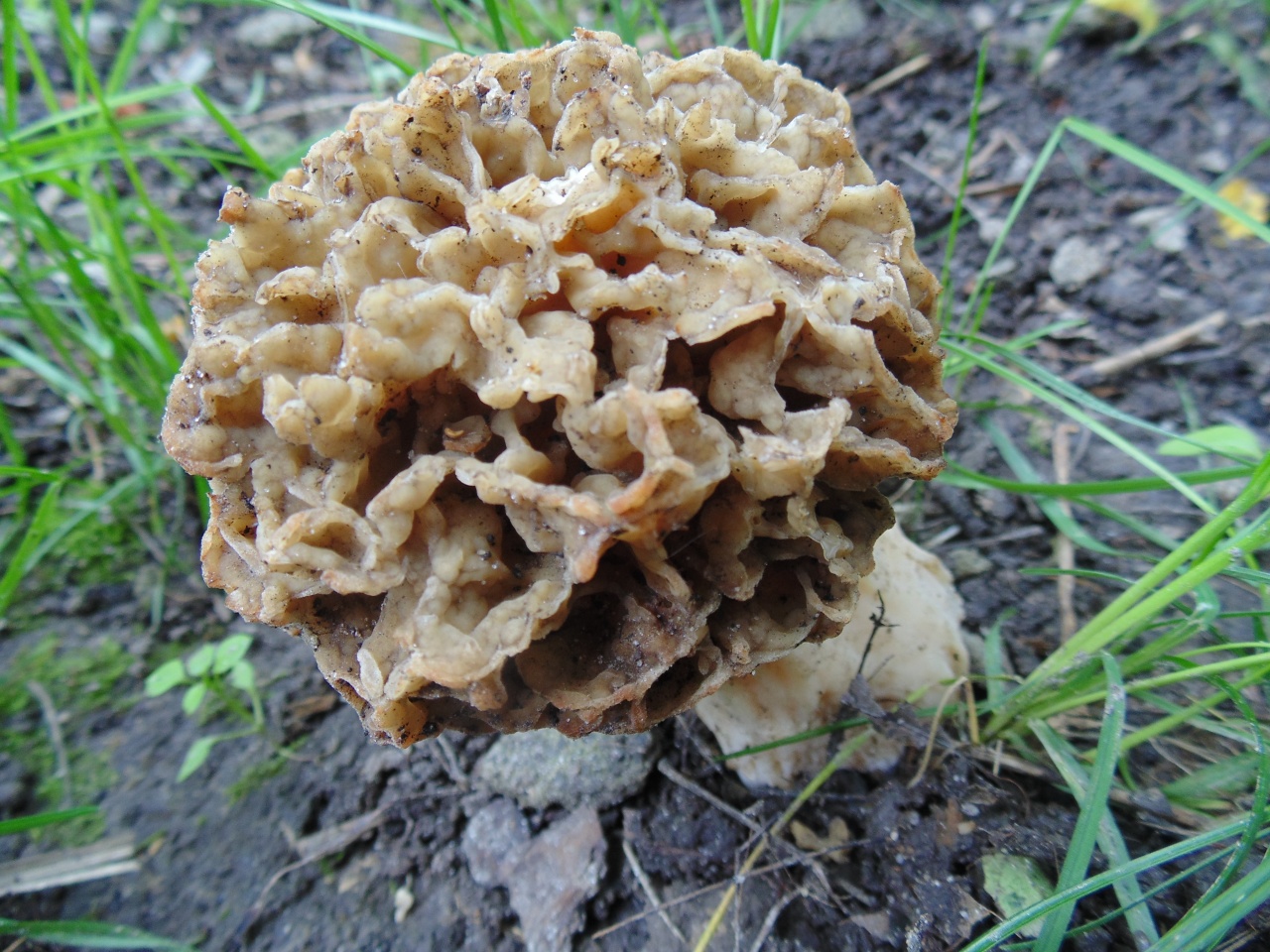
Morels have an unusual cap shape and this makes them stand out from other species. As a rule, morels have a spherical or ovoid cap, medium in size and very light. At the edges, the cap fits snugly against the leg, and its maximum diameter is 8 cm, but such large specimens are rare. As a rule, a morel cap grows up to 7 cm in height, and from 3 cm to 6 cm in width. Difficulties in identification may arise due to the variability of morels - they can be colored in different shades. There are specimens with a yellow-ocher, grayish and even brown cap. Mature mushrooms may become darker.
But, it is important to pay attention to the surface of the cap - in edible morels, it is necessarily wrinkled, with many honeycomb grooves, separated by folds. The surface of the cap is similar to that of a honeycomb. It is noteworthy that the folds separating the grooves may be slightly darker or colored in a more saturated shade than the cells themselves.
Spores are yellowish in color and can be ovoid or granular.
It is noteworthy that the folds separating the grooves may be slightly darker or colored in a more saturated shade than the cells themselves. Spores are yellowish in color and can be ovoid or granular.
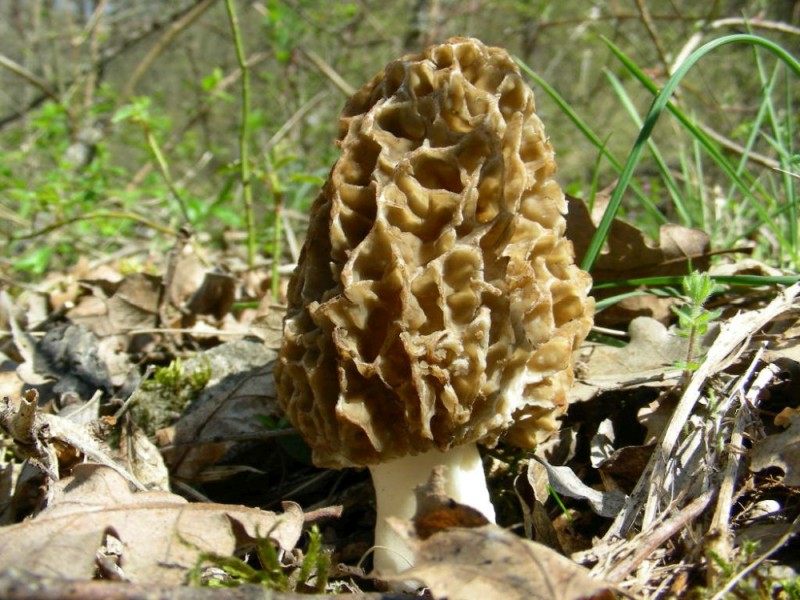
Leg
In morels, the legs have a cylindrical shape, they can slightly expand towards the base. The inside of the cap is hollow, the void inside is connected to the cavity of the cap. Initially, the legs of young mushrooms are white, rarely with a grayish tint. But, as it grows, the leg darkens, acquires a creamy or brownish tint. In old mushrooms, the base of the stem is covered with gray-brown flakes.
 Morel
Morel
Pulp
The pulp of the mushroom is brittle, loose and dry, has a waxy texture, and crumbles easily. As a rule, the flesh is white, but in old mushrooms it can turn yellow, later even acquire an ocher tint. The taste of the pulp is light, mushroom and unobtrusive, the smell is barely noticeable, combines mushroom and sweetish notes.
Such different morels
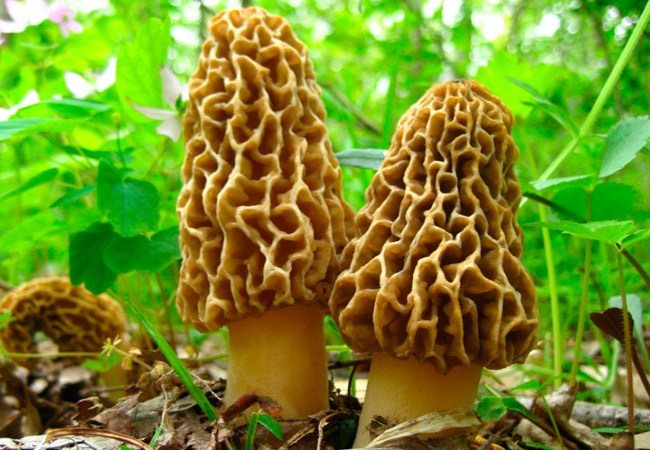
And here is an old friend - morel (Morchella)! That is, as if an old acquaintance, but changed. Here, in the Kuban, I often come across at first morel caps and a little later - conical morels, but in the suburbs, I remember, there were mostly real ones.
In general, morels and morel-like mushrooms are of several types.
Morel cap (Verpa bohemica). blabto Conical cap (Verpa conica). Fred stevens
Morel cap and conical cap
I would call a morel cap (Verpa bohemica) a morel bell - its cap is conical, it grows to the stem at the very top, it seems that it even dangles. Otherwise, it looks like a morel.
The conical cap (Verpa conica) may have a smooth cap. The mushroom itself is rather miniature, like a finger with a thimble on. The legs of the mushrooms are hollow, although the morels at a young age have loose flesh inside. You can confuse hats with morels when viewed from above. Beanies prefer wet places. Mushrooms are quite edible, not the lowest category, but not the highest either.
Steppe Morel (Morchella steppicola). Viktor Sevidov Edible cone (Morchella esculenta). Andreas Kunze Semi-free mucus (Morchella semilibera). H. Krisp
Morels
With morels, things are not so simple. Behind the morels has long and thoroughly been trailing a trail of information about "conditional edibility", although these are delicious edible mushrooms that are not noticed by mycologists in any unhealthy manifestations, and in Europe and America, in general, these mushrooms are considered a delicacy.
Another thing is that inexperienced mushroom pickers often confuse it with a poisonous line, collecting both together - here, of course, you need to carefully study each mushroom and throw out everything suspicious.
The steppe morel (Morchella steppicola) is radically different from all others - a stocky mushroom on a short or very short stem, sometimes reaching a size of 25 cm and a weight of 2 kg. And his hat is wrinkled, grayish-brown. Grows in wormwood steppes or forest-steppe. Listed in the Red Book of Kalmykia, Rostov, Saratov and Volgograd regions.
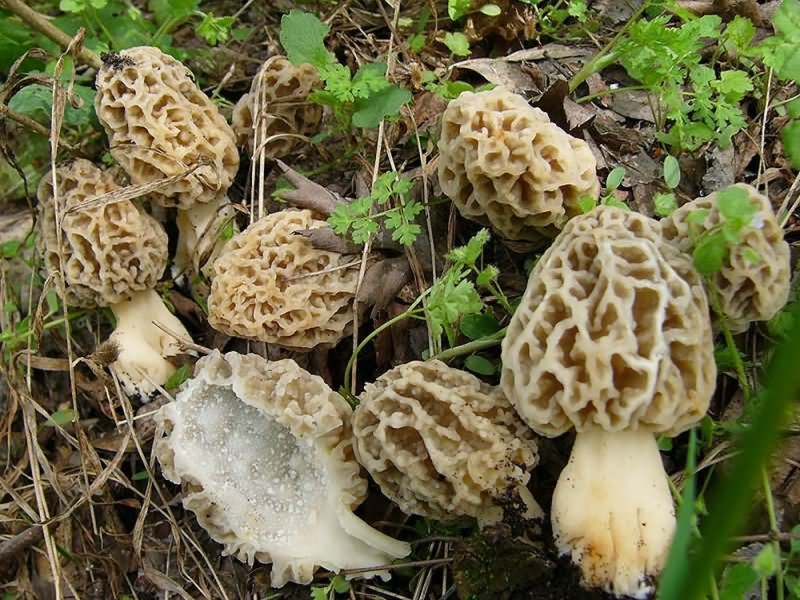
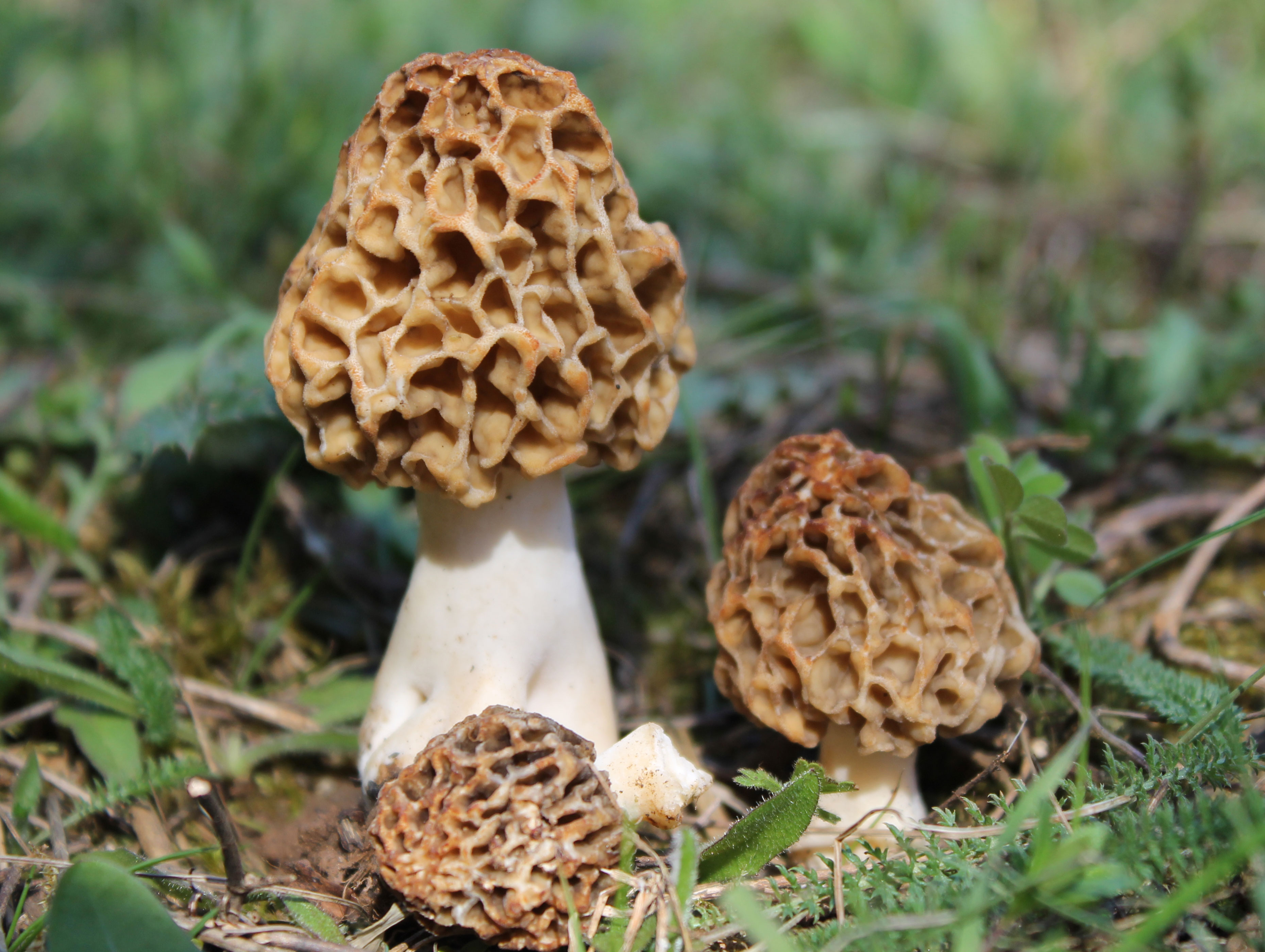
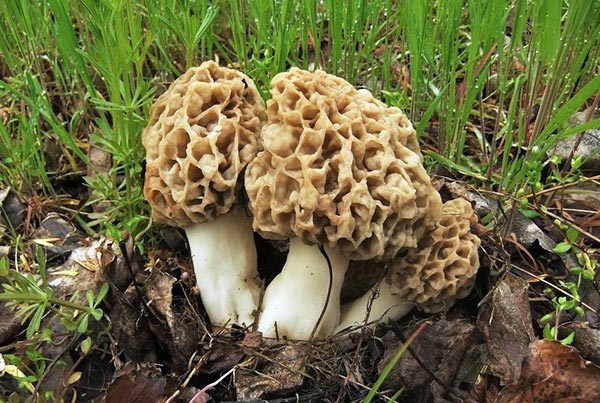
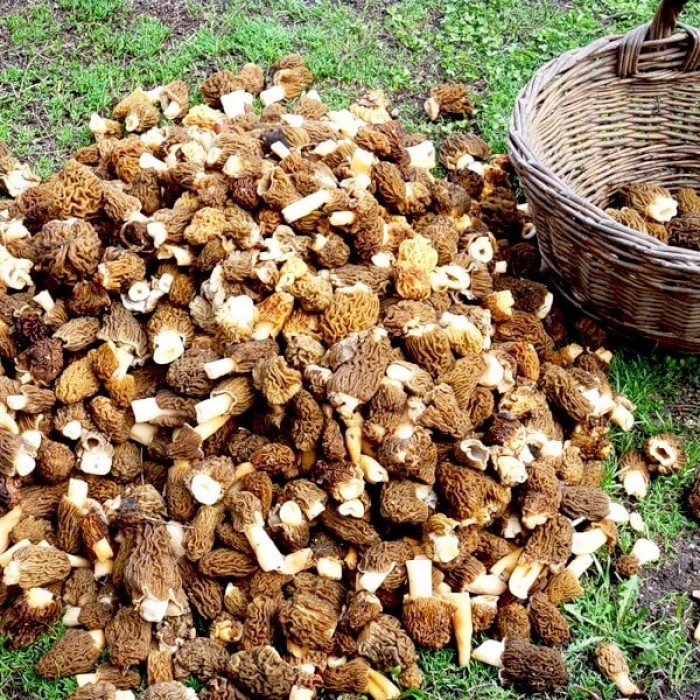
The most common in Russia is the edible morel (Morchella esculenta) - a mushroom on a long stem with an ovoid or rounded cap, firmly adhered to the stem. If cut, it is hollow inside, one skin. Therefore, mushrooms are quite light. You can fill a basket, but it is easy to carry. When you start frying, you immediately feel that 30% of the forest air has been brought home.
An even void inside the morel is a significant difference from a line containing poisonous compounds. The line has a sinuous pulp inside, rather chaotically intertwined. Morel is somehow more harmonious, in my opinion.
Cutting morels is a mandatory operation not only to identify the fungus, but also to drive slugs out of the warm edible place. Or other living creatures that use the morel cavity for their, not always harmless, purposes.
The lines are most often hidden in the litter, and a curly hat sticks out of them, while the morel's leg rises above the litter and the mushroom is visible in its entirety.
It is quite easy to identify the semi-free morel (Morchella semilibera): its cap grows to the stem at half the height, and the bottom is free. It also doesn't smell very good. But it is quite edible, however, it is not often found.
There is also a thick-legged morel (Morchella crassipes) with thick, long and somewhat corrugated legs, a rare mushroom.
The conical morel (Morchella conica), the cap of which may not even be conical at all, but rounded, is similar to the gourmet morel (Morchella deliciosa), but it is more common.
Morels grow almost everywhere. In the forest, where there is a lot of last year's dry grass, you need to get used to looking for them, you cannot immediately see them. But on burned-out areas, not old clearings, in pine forests they can be seen well and they grow there willingly.
Since ancient times in Russia, morel tincture was used for eye diseases: myopia, farsightedness, clouding of the lens and cataracts. Morel preparations also have antitumor, immunomodulatory, antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity.
The line is giant (Gyromitra gigas). Imbi vahuri
Description of steppe morel
Steppe morel is the largest among Russian morels. His hat is spherical or egg-shaped, its diameter is 2-10 centimeters, and sometimes it reaches 15 centimeters, while the height corresponds to the diameter. The edge of the cap is adherent, it is hollow inside, it can be divided into sections.
The leg to which the cap is attached is very dense and short - its length does not exceed 1-2 centimeters, sometimes the leg may be absent altogether. The color of the leg is white with a cream shade. There are rare voids inside the leg. The pulp is quite elastic, whitish in color. Spore powder is white or light gray.
Growing places of steppe morels
Steppe morels grow in the European part of our country and in Central Asia. These mushrooms settle in the wormwood steppes. They bear fruit from April to June. When collecting, it is recommended to cut the morels with a knife so that a whole mycelium remains. To find these mushrooms, you have to visit the harvesting sites every day at the beginning of March, otherwise you can skip the beginning of the harvest, and after 3-4 days the season will end altogether.
Fruit bodies in steppe morels develop very quickly, and their lifespan is only 5-7 days, in comparison with ordinary "long-playing" morels, this is extremely small.
In years with humid winters, steppe morels can form "witch circles", consisting of about 20 fruiting bodies, and the diameters of such circles reach 7-8 meters. In dry springs, mushrooms may not appear for several years in a row.
Edibility of steppe morels
Steppe morels are delicious edible mushrooms. They are mushroom delicacies, from which you can prepare independent dishes, as well as sauces and side dishes.
Drying steppe morels is not difficult at all, since they are the densest among other morels. These fungi have practically no internal cavities. The pulp of the steppe morels is similar in consistency to the pulp of the porcini mushroom. Before drying, these mushrooms must be blown out, since there are too many folds and convolutions in their caps, into which sand and dirt are clogged. The sand from the mushrooms simply cannot be shaken out, they are first dried a little in the sun, then they are blown out, and only then they are dried.
Also, these mushrooms can be dried in a special electric dryer, but in the sun they will have a more pronounced mushroom aroma.
If the dried morel is soaked for 8-10 hours, it will completely restore its structure, volume and shape. Steppe morels do not need preliminary boiling. They go well with meat, poultry and fish. Steppe morel powder makes an excellent seasoning for broths, sauces, vegetable and meat dishes. In addition, very tasty mushroom kebabs are obtained from steppe morels.
Other morels
Morel conical - conditionally edible mushroom. His hat is elongated and conical. Its diameter does not exceed 3 centimeters, and its height reaches 10 centimeters. The color of the cap is reddish-brown with a gray or green tint, sometimes the cap may be black.Its surface is cellular, outwardly it looks like a honeycomb. The leg is straight, hollow, white or yellowish.
Conical morels grow on well-heated soils, in clearings and forest fires. Often these mushrooms settle in aspen forests. They bear fruit from April to May. The flesh of conical morels is tasty and soft, but it requires preliminary boiling for 15 minutes.
Morel cap, or cap, or tender morel is a conditionally edible mushroom. A small cap has the shape of a cap, its diameter is 2-4 centimeters, and its height is 2-5 centimeters. The color of the cap at a young age is chocolate brown, and in mature it becomes ocher yellow. The leg is smooth, most often curved, its length is 6-10 centimeters, and its thickness reaches 2.5 centimeters. The leg is often flattened on the sides. With age, an enlarged cavity forms in the leg. The cap and the leg are not firmly connected. The color of the leg is cream or white.
The morel cap is the smallest species in the morel family. These mushrooms bear fruit in mid-May. They often grow among young aspens and lindens. They give preference to poor soils. Under favorable conditions, morel caps are found in large numbers.
Morel hats are eaten only after preliminary boiling, then they can be fried, boiled and cooked in any way. It takes at least a month to dry a morel cap.
Taxonomy, characteristics and description of the structure
Edible Morel, or Real Morel (Latin Morchella esculenta) is an edible mushroom belonging to the Morel family.
In the scientific community, the morel has several synonyms:
- Phallus esculentus;
- Helvella esculenta;
- Morellus esculentus;
- Morchella rotunda var. esculenta.
The fruiting body is represented by apothecia - a special type of body that differs from other cap mushrooms.
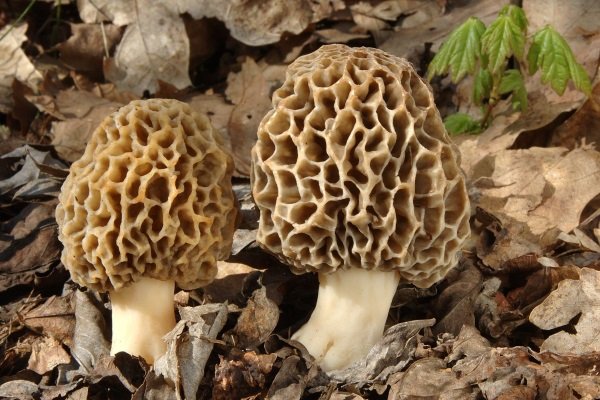
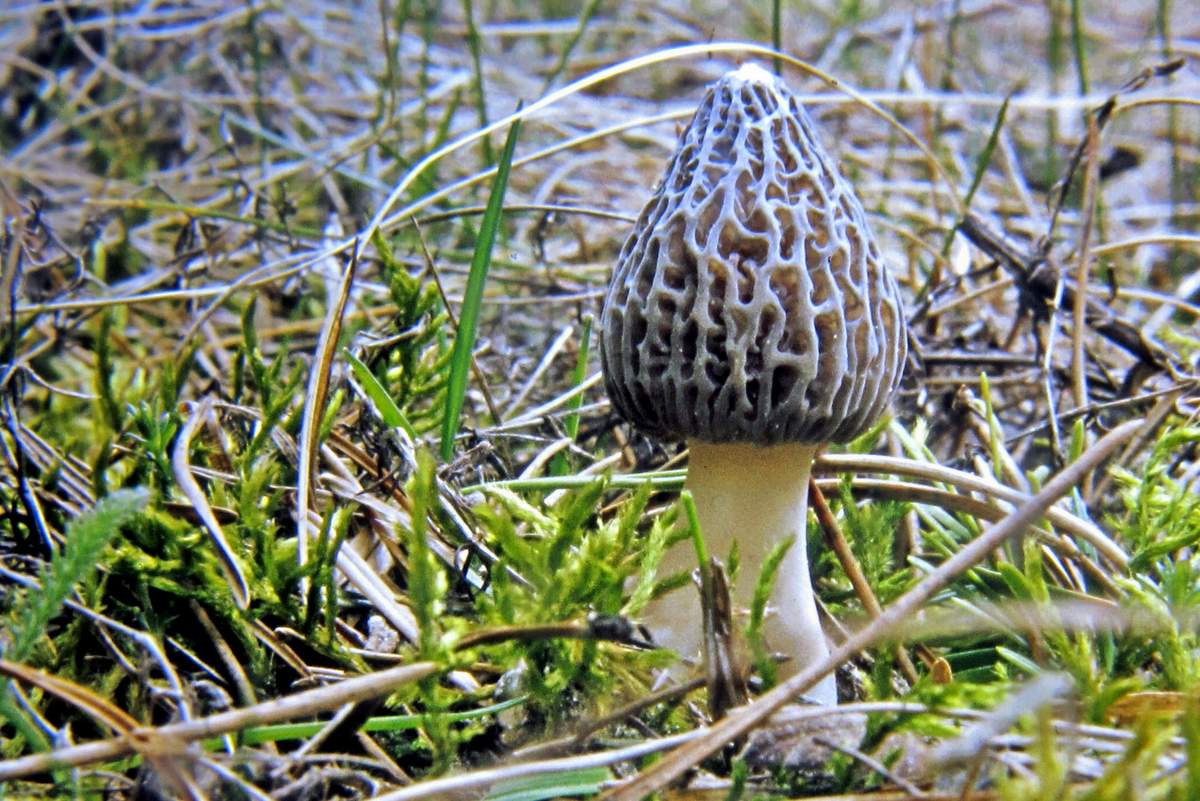
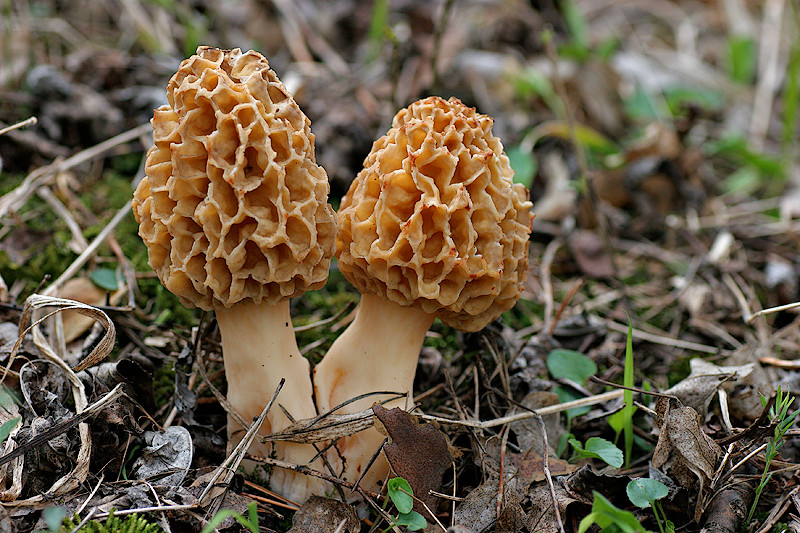
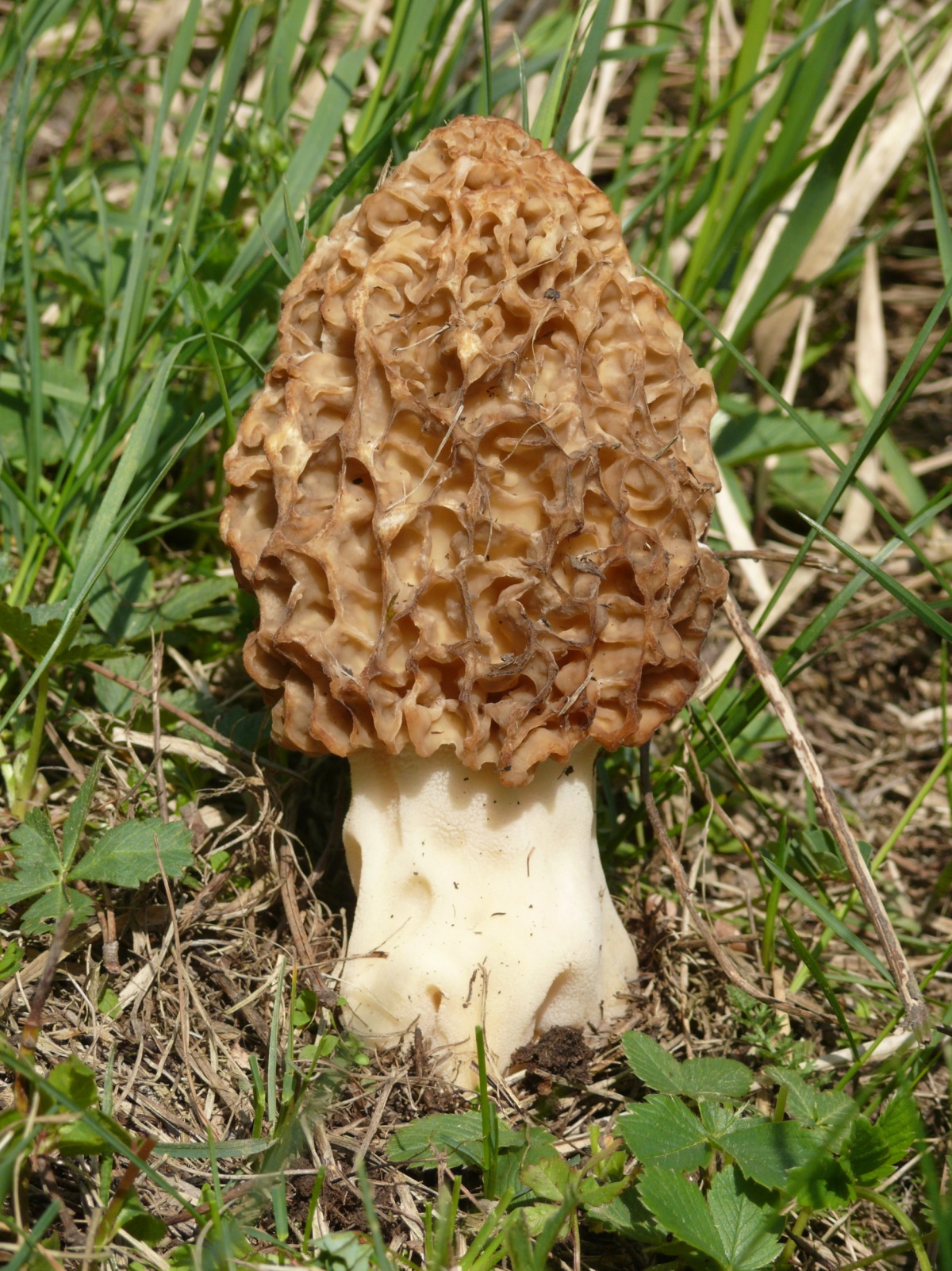
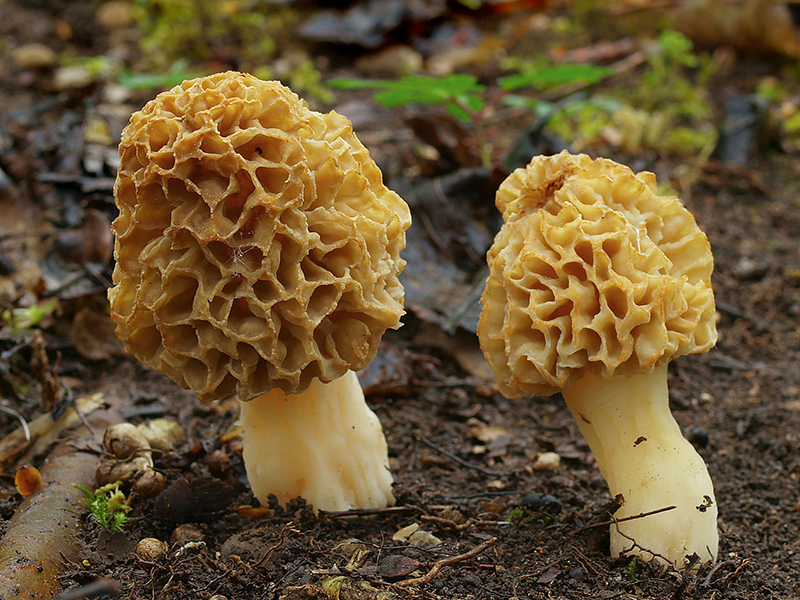
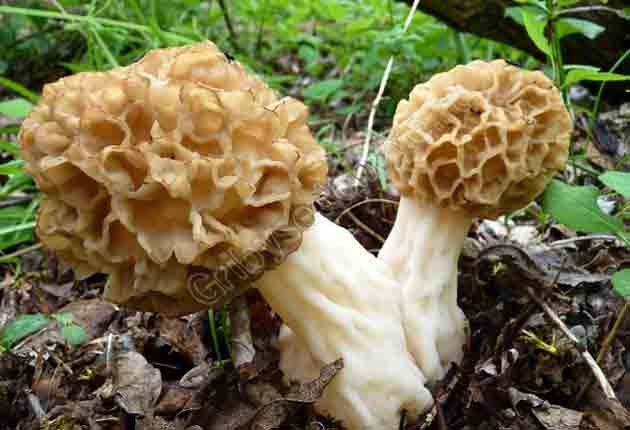
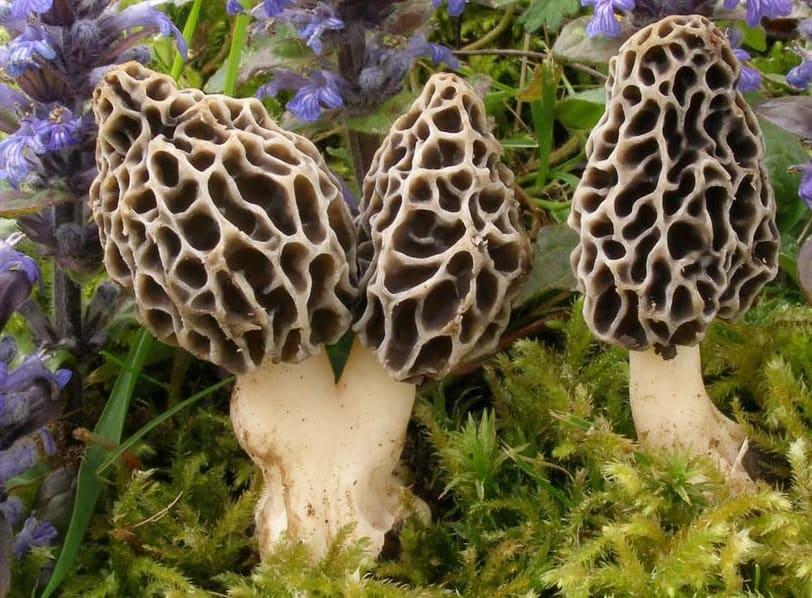
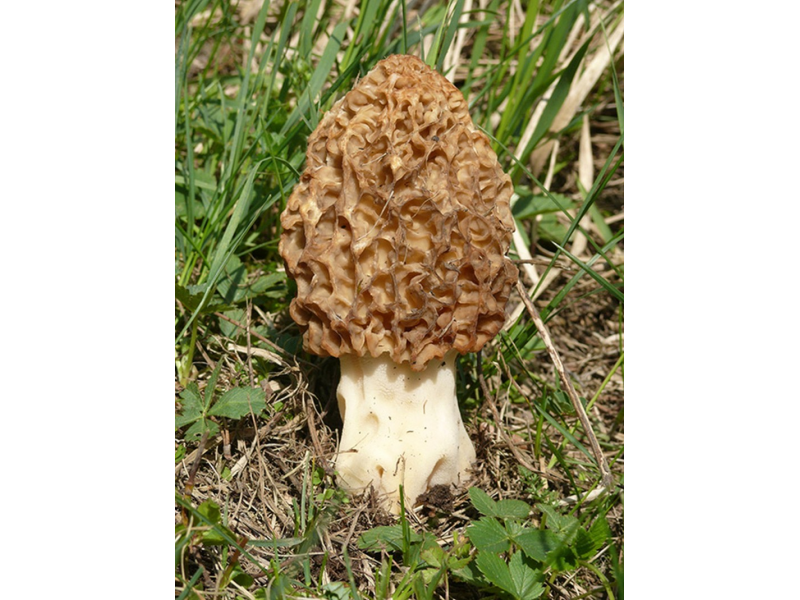
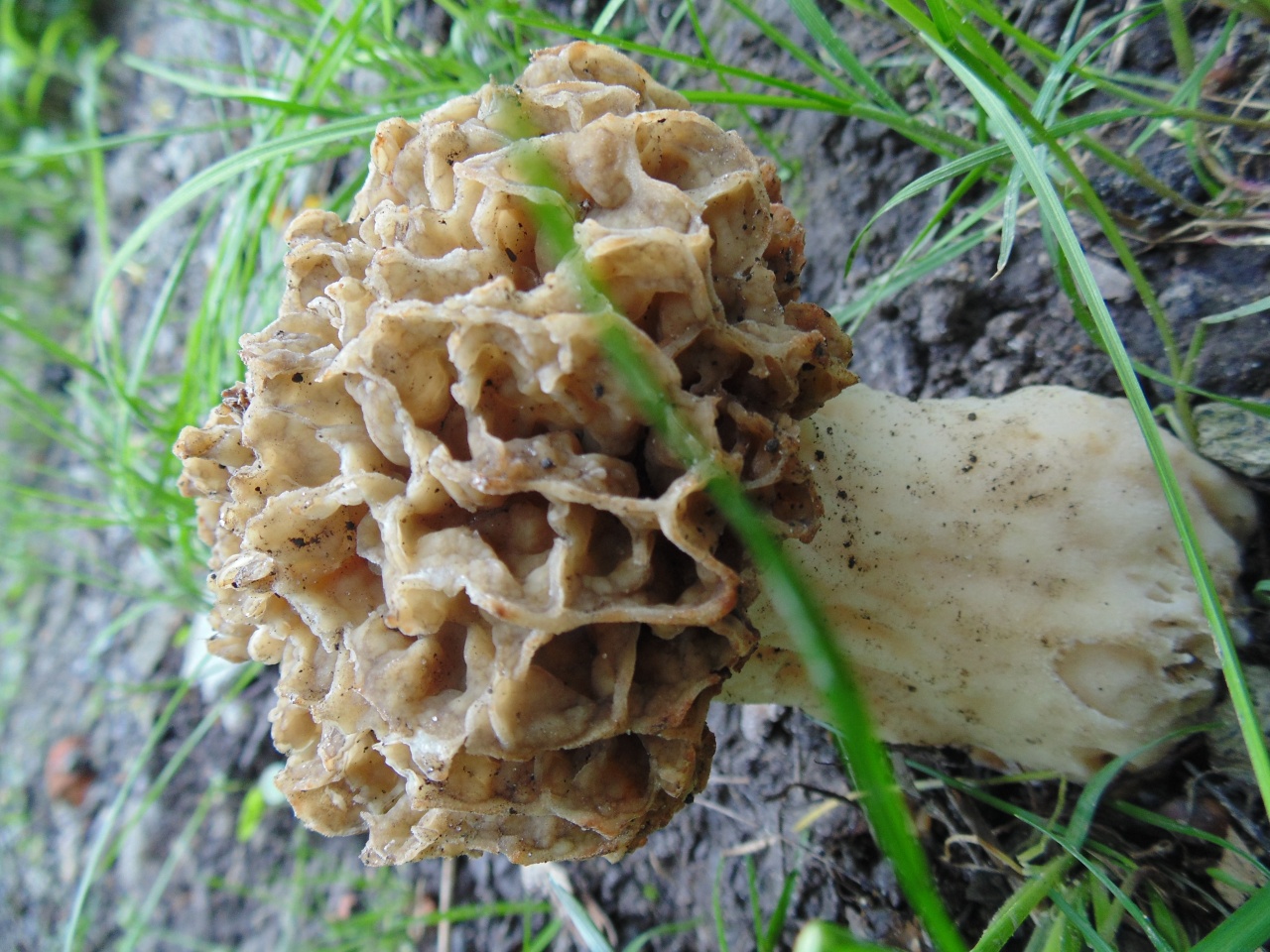
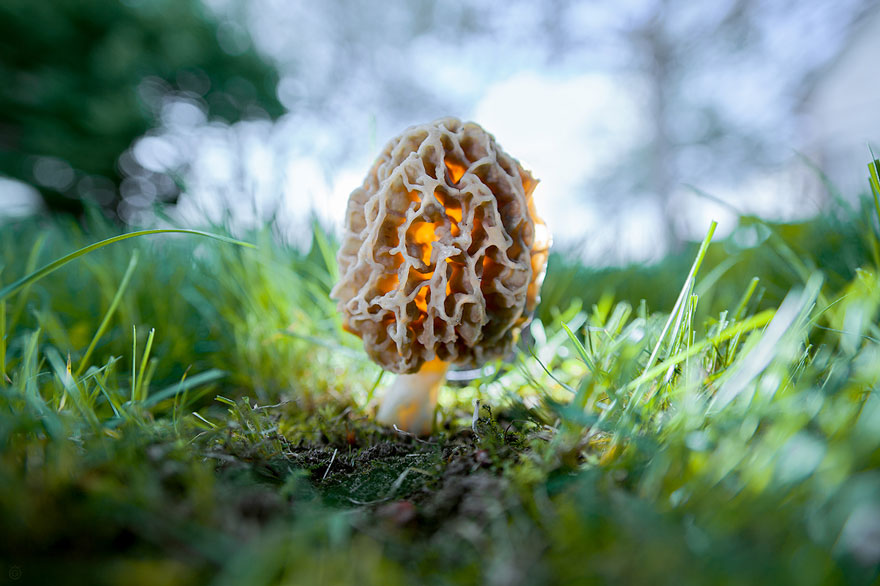
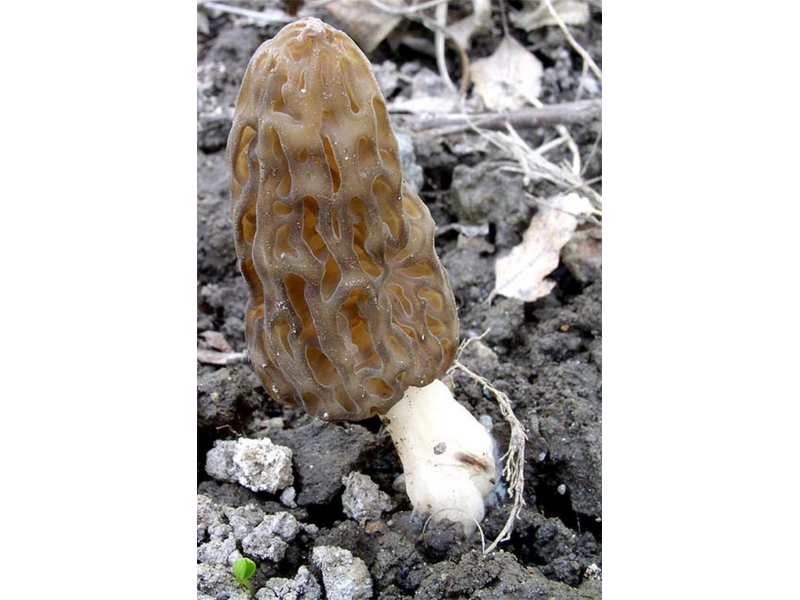
The cap of the morel edible has a characteristic ovoid blunt-pointed shape with a large number of folds; in young mushrooms it can be round or flattened-spherical. The color strongly depends on the growing conditions - from yellow-ocher to dark brown. The older the morel, the darker the hat. Sizes range from 3-7 cm in height and 3-8 cm in diameter. The folds are thin (1–2 mm thick).
The hymenophore - the part of the fungus that carries the tetium - in morels is located not inside the cap, but outside, lining its bottom and pits.
The leg is hollow inside, the thickness of the walls is 3-4 mm, the diameter is on average 1.5-3 cm. The length of the leg ranges from 3-9 cm. In young mushrooms, milky white or creamy white, smooth, darkens as the fungus ages and covered with thin flakes.
The flesh on the cut is the same color as the leg, does not darken. Very fragile, crumbles quickly, especially in old mushrooms. It has no distinct smell after cutting.
A bit of history
The mushroom was discovered and systematized several times by Karl Linnaeus. The first description under the name Phallus esculentus was made in 1753. The name Morchella esculenta was given later - in 1801 by the Dutch mycologist Christian Person.
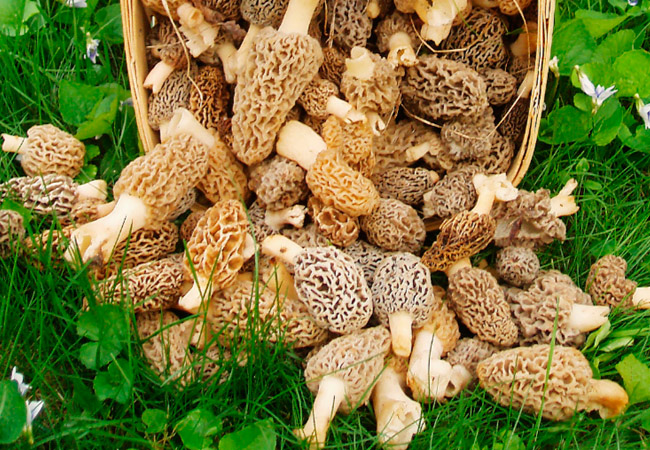
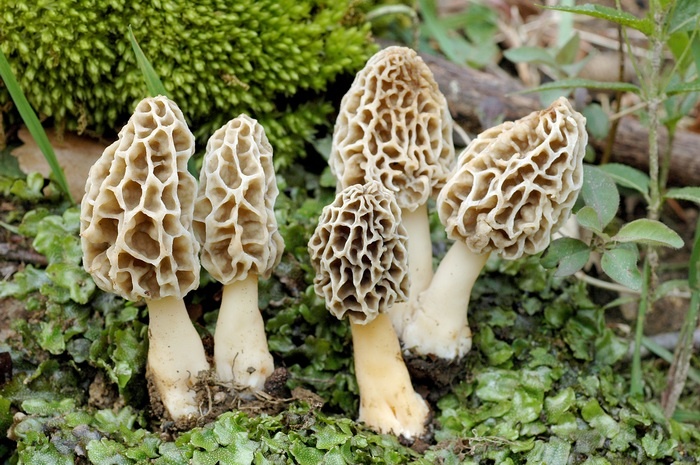
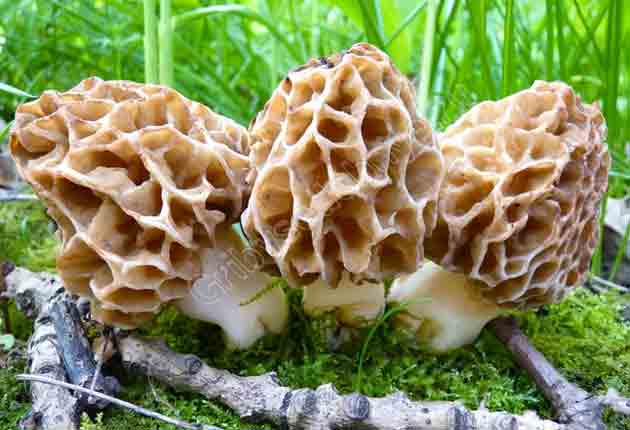
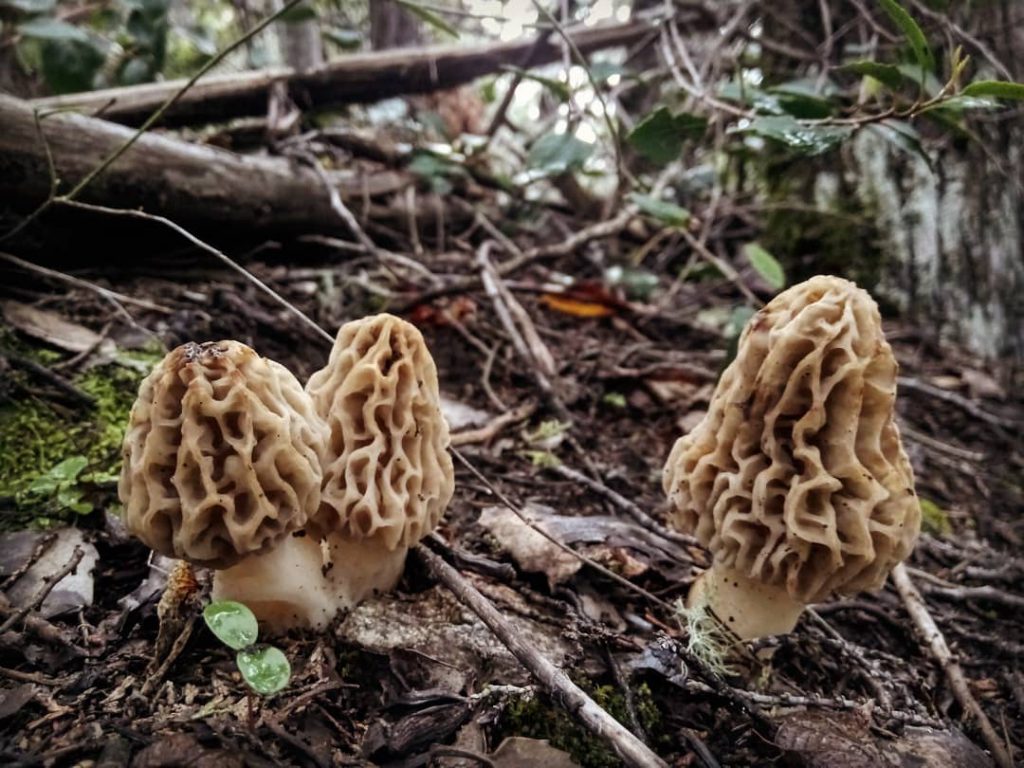
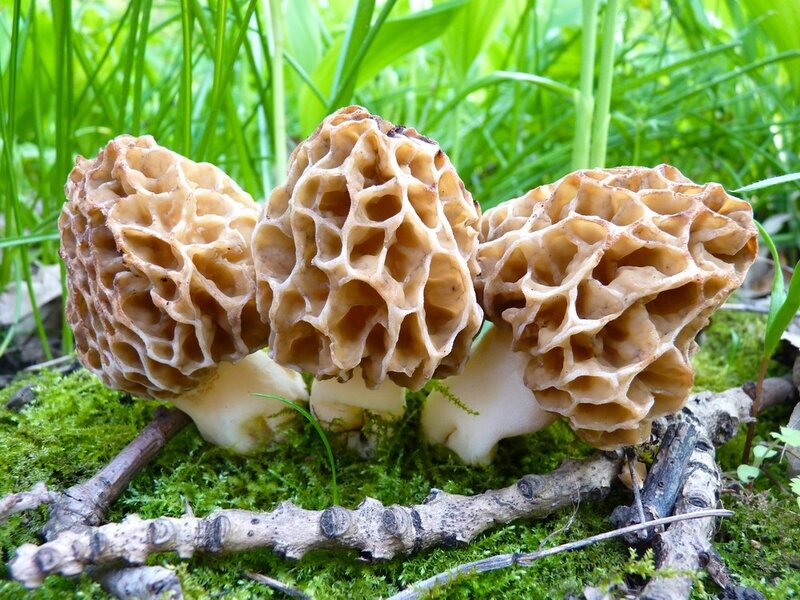
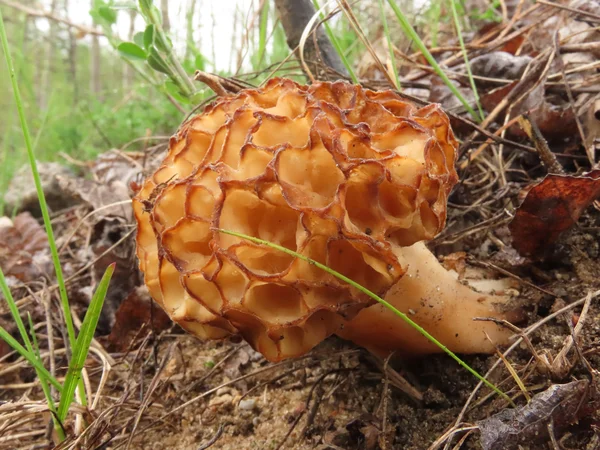
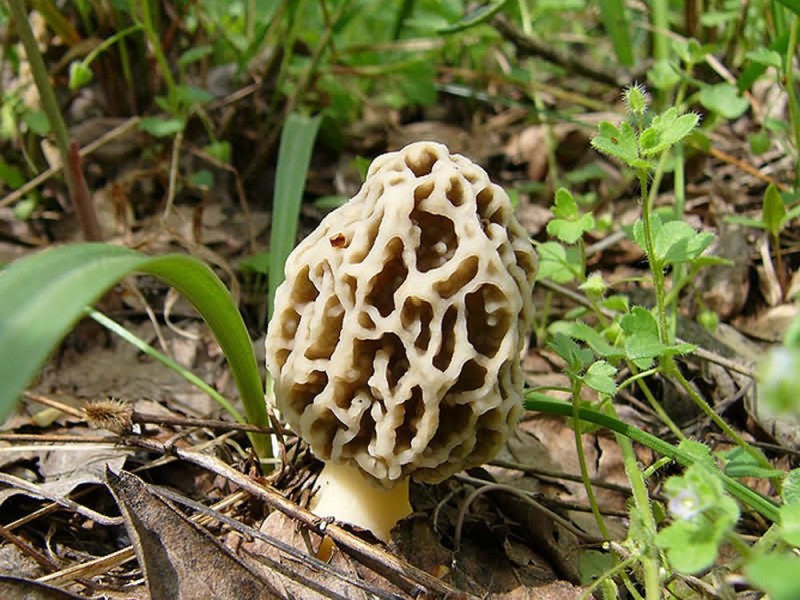
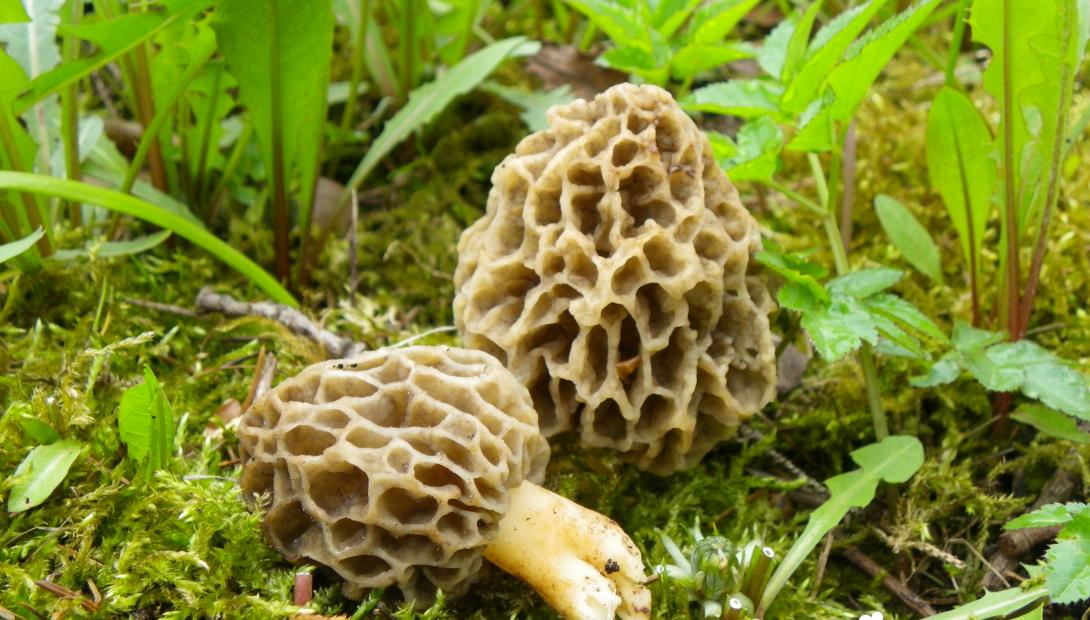
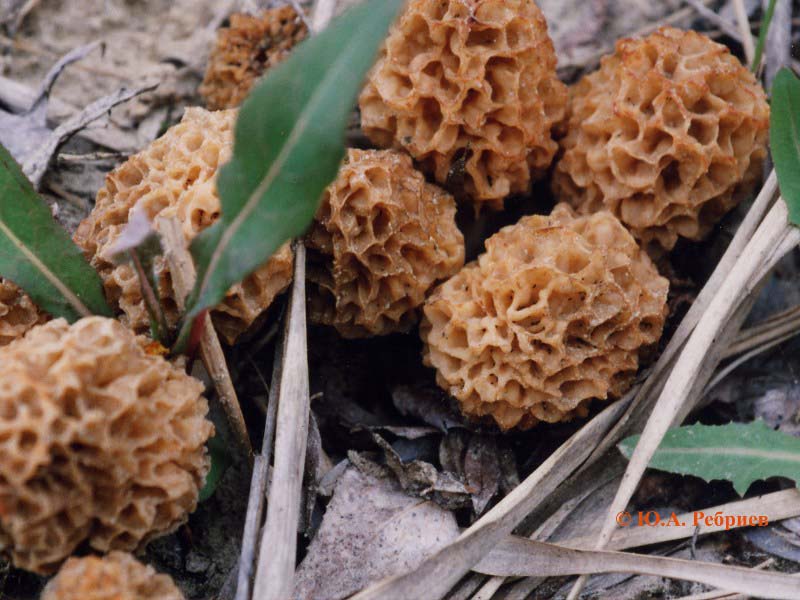
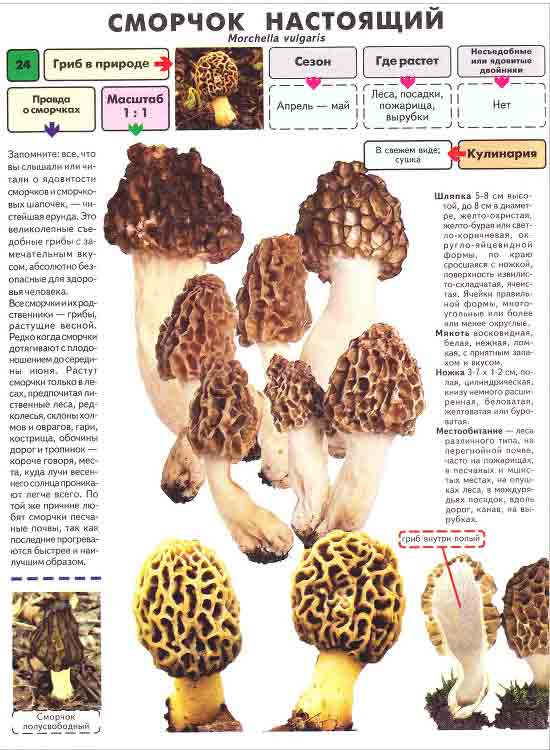
Morels - description and photo. What does a morel mushroom look like?
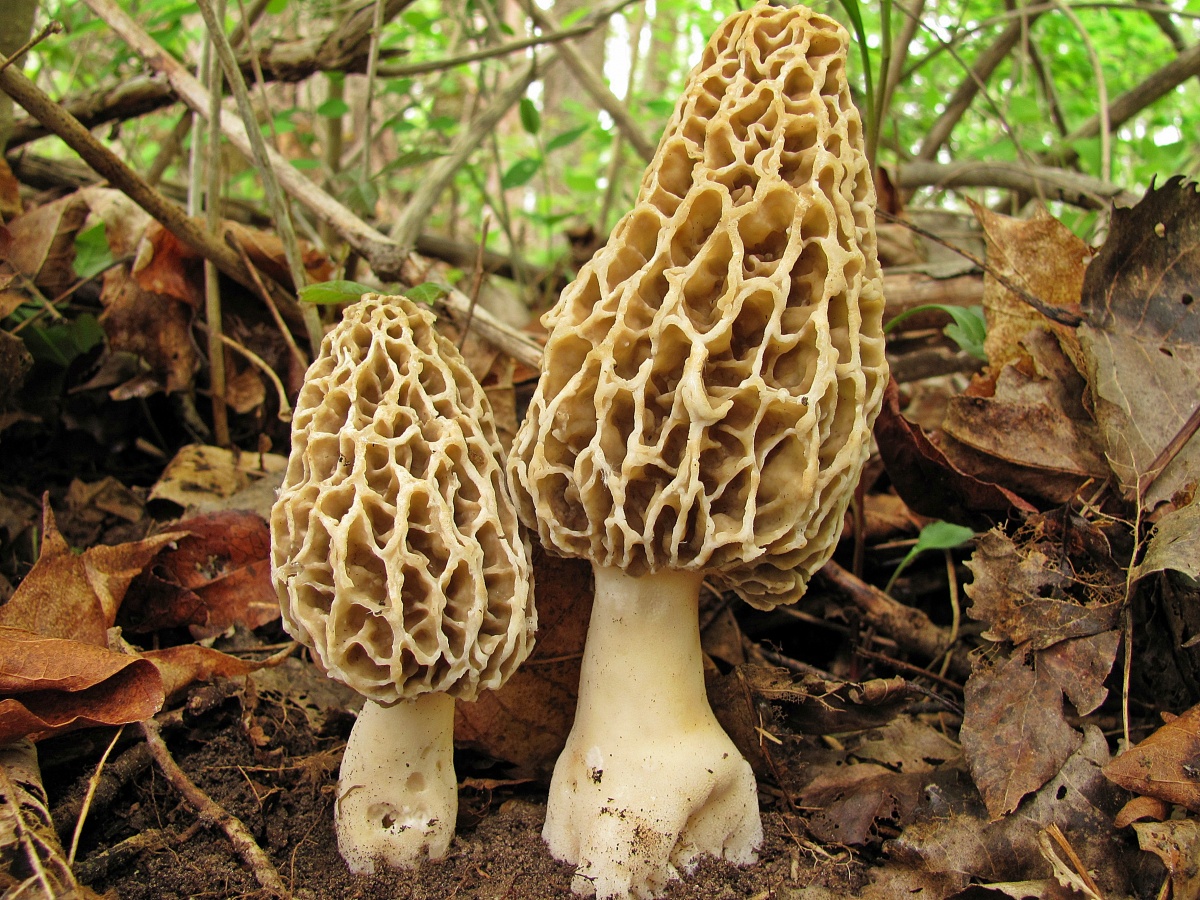
These are the first mushrooms to grow in spring. Their large and fleshy fruiting bodies 2-25 cm high consist of:
- caps (up to 15 cm high, up to 10 cm in diameter),
- legs (up to 10 cm long and up to 5 cm in diameter).
The cap of the morel is ovoid, spherical-bell-shaped, conical or ellipsoidal, with a network of longitudinal and transverse oblique convex ribs, cellular, spongy, more often fused below the leg. Outside, it resembles a honeycomb, but in the section it is clear that there are cells only on its outer side. Its color varies from dirty grayish white to dark brown, depending on the type and age of the fruiting body.
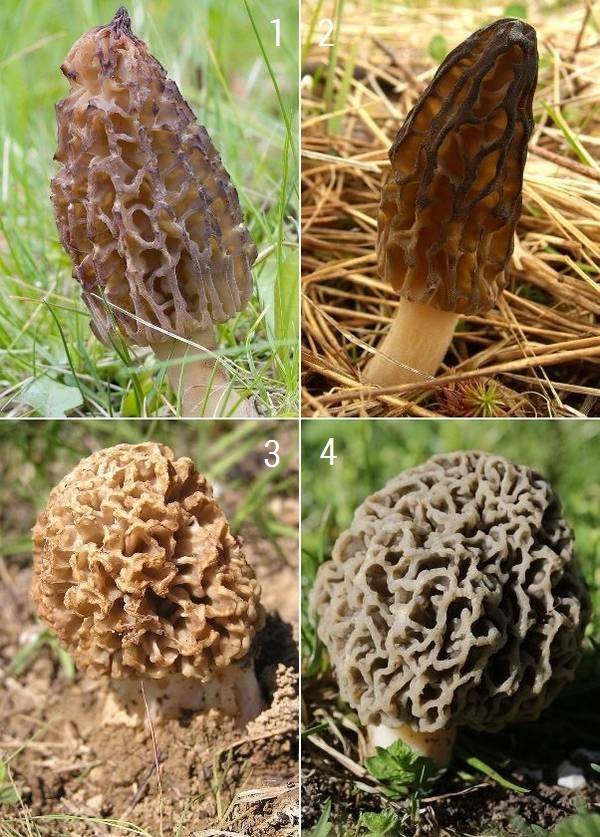

1. Morel conical (lat. Morchella conica), author of the photo: Jörg Hempel, CC BY-SA 2.0 de. 2. Tall morel (lat. Morchella elata), photo by Jason Hollinger, CC BY 2.0. 3. Steppe morel (lat. Morchella steppicola), photo by Andrew Butko, CC BY-SA 3.0. 4. Edible morel (lat. Morchella esculenta), author of the photo: Björn S…, CC BY-SA 2.0.
The stem of the morel is glossy, white or yellow-brown, cylindrical, slightly widening or very thick upward or downward, sometimes furrowed or longitudinally folded, scaly or smooth, fragile.
The entire fruiting body of the pioneer is usually hollow inside, consists of colored, highly branched hyphae with a diameter of 5–10 µm.The hyphae are separated by evenly spaced partitions (septa), in the center of which there is a pore, through which the migration of nutrients and cell organelles occurs.
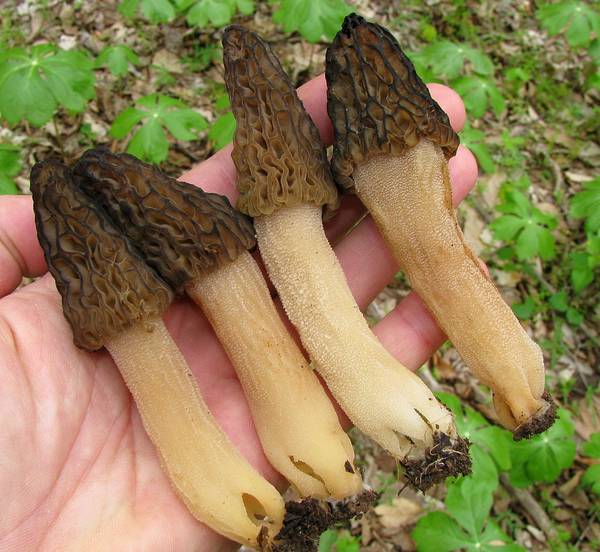

Photo Credit: Dan Molter (shroomydan), CC BY-SA 3.0
The pulp of the mushroom is waxy-white, often brittle and thin, with a pleasant smell.
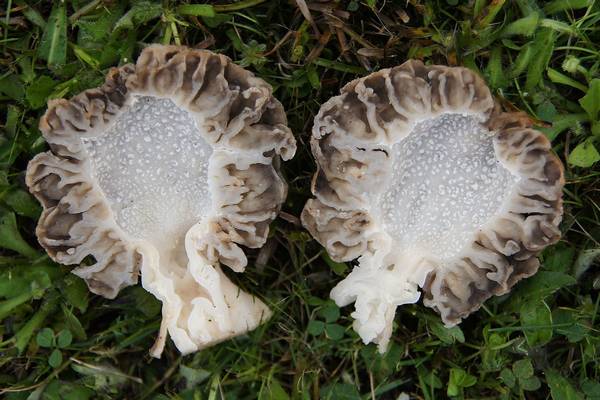

Photo by: TOMMES-WIKI, CC BY-SA 3.0
Can morels be grown at home?
Morels are delicious mushrooms that are considered a delicacy in European countries. Therefore, more than once attempts have been made to breed mushrooms at home.
German mushroom pickers suggested simply sowing pieces of morels into the ground and covering them with ashes. In the fall, the place is covered from above with straw or leaves, and in the spring, mushrooms are already found. And it was also noticed that morels grow well in those places where fallen decaying apples remain. Therefore, the French make beds on which they scatter pieces of mushrooms. In autumn, the ground is watered with apple pomace. Harvest in the spring.
Morel mycelium can be purchased at a specialist store and planted in your garden. Morels are planted in spring. To do this, a "mushroom" place is selected on it near deciduous trees. It should be darkened. On the selected area, remove 15 cm of the top layer.

Prepare soil mixture:
- 3 parts of sawdust;
- 1 part of the leaves;
- 1 part wood ash;
- 6 pieces of garden land.
All components are mixed and poured into the prepared well, watered. The mycelium is laid out on top of the soil and covered with removed earth. Water again, cover the garden with leaves. In the summer they take care of it, do not allow the earth to dry out and fertilize it with wood ash. In autumn, they cover with natural material - straw, branches, leaves. In the spring, after the snow melts, the shelter is removed. The first mushrooms will appear in 2 weeks. The mycelium bears fruit for 3-5 years.
Stitching
A few words about the lines (Gyromitra). From time immemorial in Russia, they ate lines with preliminary boiling and draining of water. And our family as well. But the Europeans manage to poison themselves with them, and a fatal outcome has also been recorded. Mycologists associate poisoning with gyrometrins toxins, which accumulate in the lines in different ways: somewhere more, somewhere less.
If you have no experience of using lines, it is better not to risk it. If there is any doubt about the definition of the mushroom, it is better to leave it in the forest - the forest dwellers will figure it out. And the most important thing is not to be greedy: you do not need to eat a frying pan of fried mushrooms at a time. You can try a little and postpone the rest until tomorrow. A pan with mushrooms will not run away. Checked!
How to cook morels
Morels are boiled, fried and dried. Before using them, boil them, drain the broth, and rinse the mushrooms in cold water. After that, they can be fry, stewed and boiled fearlessly. Harmful substances are completely neutralized during drying. Morels are stewed in sour cream, milk and butter. Before that, they are boiled, and the water is drained.
Morels in oil. To do this, fresh morels are boiled for 10 - 15 minutes, thrown back in a colander and rinsed with cold water or wrung out. The drained water must not be eaten. Cut the mushrooms into slices, season with salt, pepper and sprinkle with lemon juice. Fry under the lid for another 15 - 20 minutes.
Pancakes with morels. In America, this dish is served at gala dinners of the Morel Society. To do this, fried morels are wrapped in pancakes, which are then fried on all sides.
Podmoskovye website, 2012-2019. Copying texts and photos from the site pоdmoskоvje.cоm is prohibited. All rights reserved.
Giant stitching (Gyromitra gigas)

Conditionally edible mushroom. The fruit body looks like a brain or a walnut. The cap is covered with convolutions, hollow, irregularly rounded, folded, with a velvety surface, yellowish or yellowish-ocher color. Diameter 8-30 cm, the edge is connected to the leg. The leg is irregular in shape, short and wide, the surface is furrowed-folded, hollow inside, whitish in color. The pulp is thin, brittle, waxy, has a pleasant mushroom aroma.

The fruiting season coincides with the morels. This is a spring mushroom. Grows in groups in deciduous and mixed forests, often near birches, in Europe and North America.
Ordinary line (Gyromitra esculenta)

Conditionally edible mushroom. A cap of irregular shape, like a brain, up to 10 cm high, about 15 cm in diameter. In young mushrooms, it becomes smooth, wrinkled as the mushroom matures. The color of the cap is brown, occasionally red, orange or purple. Leg length 2-3 cm, 2-6 cm in diameter, even, hollow inside, tapers towards the base. Light, with a pink tint. The pulp is waxy, brittle, the taste is pleasant, the smell is fruity.
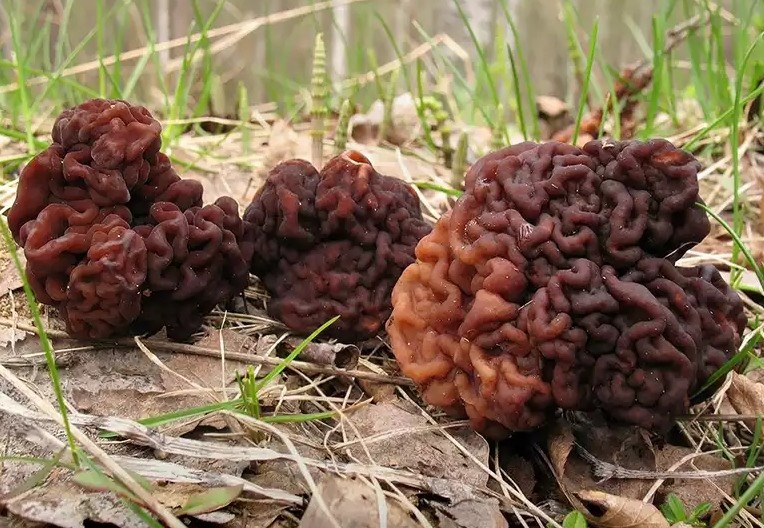

It grows on sandy soils, in places of deforestation, under conifers and poplars. Found in Europe, Asia and North America.
Autumn stitching (Gyromitra infula)
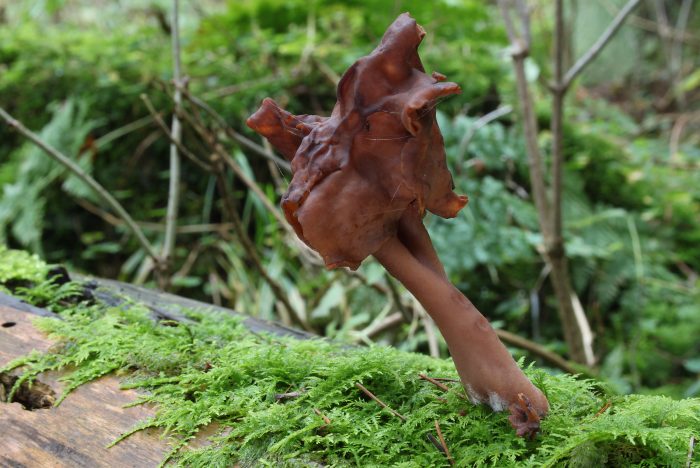

Poisonous mushroom. The cap is 2.5-10 cm in diameter, the shape is saddle-shaped or irregular, 2-4-lobed, the edge is tucked up, adheres to the stem. The surface is red-brown or dark brown, wrinkled, pale underneath, velvety to the touch. The flesh is grayish, thin. Leg 2-6 cm long and 2-3 cm in diameter, hollow, fine-grained, whitish with a pink tint.

Grows on soil and decaying wood of deciduous and coniferous species, bears fruit in autumn. Found in Eurasia and North America.
Growing morels and stitches at home
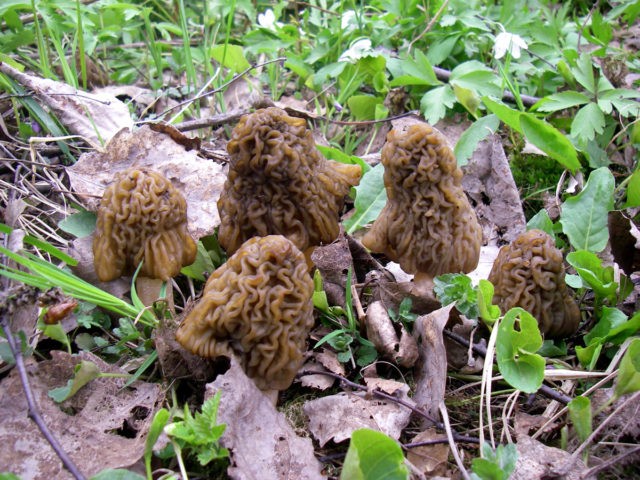

Fruit bodies of mushrooms collected in the forest are used as planting material. The hats are separated from the legs, crushed into slices of 0.5-1 cm in size.

Next, a site is selected in a warm place, on light sandy loam or loamy soil. The site is fluffed and paper, cardboard, straw are burned on its surface, abundantly moistened and slices of mushroom caps are sown. From above, the planting is covered with a forest floor or spruce or pine spruce branches, with a layer thickness of 1-7.5 cm. The site is regularly moistened. In early spring of next year, the top layer is removed.

The first crop usually appears the next spring after planting the mushrooms. After collecting morels and lines, the area is covered with spruce branches for the summer and moistened, fertilized with ash, ash or apple waste. Fruiting continues for several years in a row.
Calorie content of morels and lines

The calorie content of 100 g of morels is 24 kcal. Energy value of morels: Proteins: ………………… .2.9 g (12 kcal); Fats: …………………… 0.4 g (4 kcal); Carbohydrates: ………………… 2 g (8 kcal); 100 g of fresh stitches contains about 20 kcal.
Interesting Facts

Both morels and lines contain a dangerous poisonous substance - gyromitrin. Most of it is in the lines, in morels and morels, the concentration of this substance is very low. But nevertheless, it is recommended to use morels after preliminary boiling or scalding with boiling water, so that these delicious mushrooms do not harm and bring only pleasure.

The stitching tincture is used in folk medicine as a pain reliever that is rubbed into the skin.

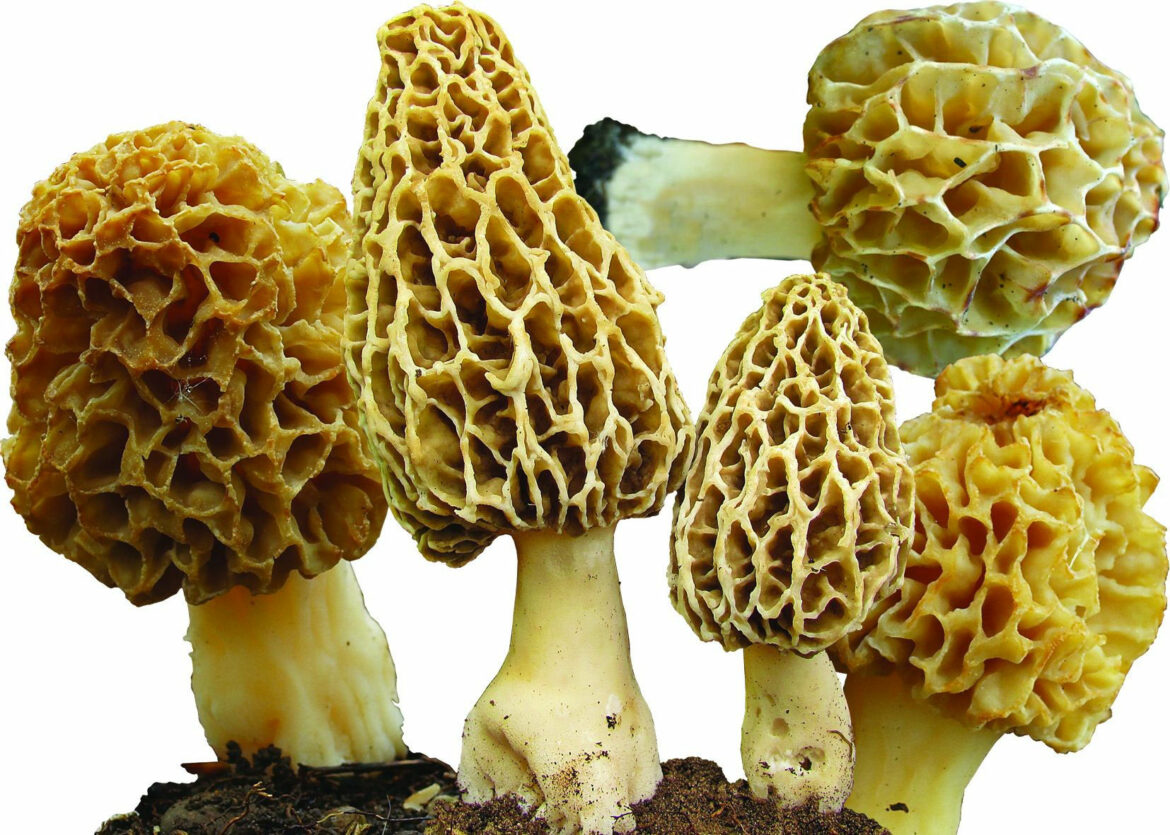
All species of the genus Morel:
| Morel conical (Morchella conica) | High morel (Morchella elata) | Morel (Morchella esculenta) |
| Morel semi-free (Morchella semilibera) | Steppe Morel (Morchella steppicola) |
If you are in doubt about the edibility of the mushrooms you find, do not take them. The site administration does not bear any responsibility for the actions of people taken on the basis of the information received on the site. Some types of poisonous mushrooms cannot be identified without special equipment and can be confused with edible ones.
Similar species
Morels themselves look quite original so as not to be confused with other mushrooms.
So the steppe morel can only be mistaken for a mushroom belonging to the same genus:
First of all, it has a much more modest size, and in addition it differs in its characteristic shape. If the steppe morel has an almost spherical cap, then the conical morel fully justifies its specific name. Its height is much greater than its width.
Outwardly, it is similar to the steppe morel, but rarely grows larger than 6-7 cm, and in addition, it has a pronounced leg.
 1-Morel conical 2-Morel cap
1-Morel conical 2-Morel cap
It has a much darker colored cap, less tortuosity and a pronounced stem.
It also has a fairly pronounced leg, reaching a diameter of 3-4 centimeters and a cap that is much less sinuous.
 1-Morel is common 2-Morel is thick-legged
1-Morel is common 2-Morel is thick-legged
Can morels be eaten and how to cook them properly?
In practice, morels belong to the group of conditionally edible mushrooms of the 3rd quality category. This means that you can eat them, but not raw, but after proper pre-processing. The fact is that morels contain harmful Helwellic acid, which has a hepatotropic and hemolytic effect. Therefore, these mushrooms cannot be eaten raw. Before cooking, they need to be rinsed well and scalded with boiling water. Then the mushrooms are boiled in salted water for 10 minutes. The poison does not break down from the high temperature, but turns into a decoction: it must be drained, and the mushrooms must be squeezed out and rinsed several times in hot water. Only then can you start cooking morels. They can be boiled, stewed or fried, but in any case, it is advisable not to consume more than 200 grams of morels per day.
Mushrooms can be dried in the sun: direct sunlight destroys toxins. Dried morels are stored in a dry container. And when frozen, they can be kept in the freezer for up to a year.
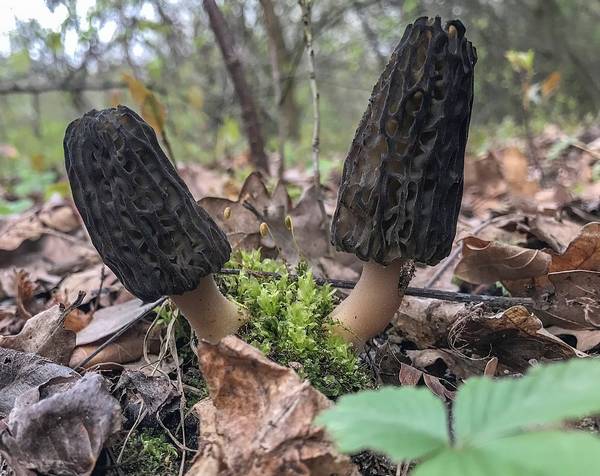

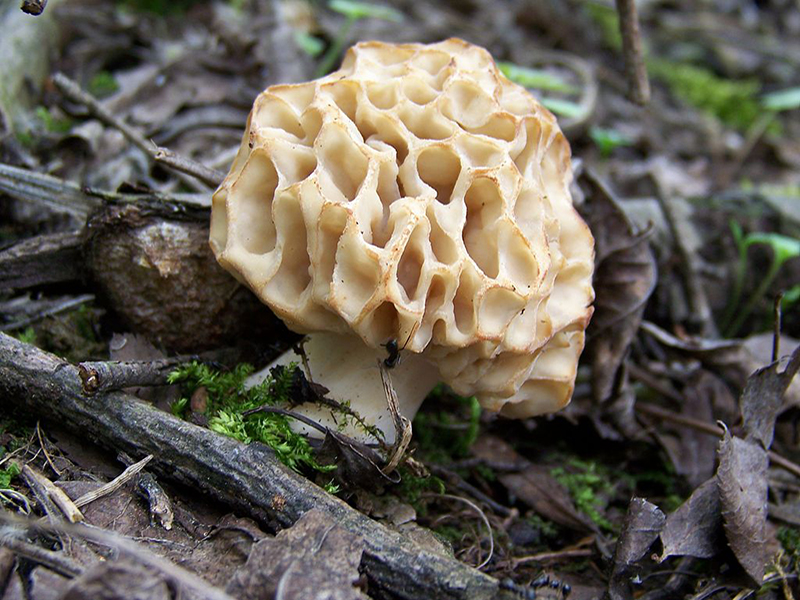
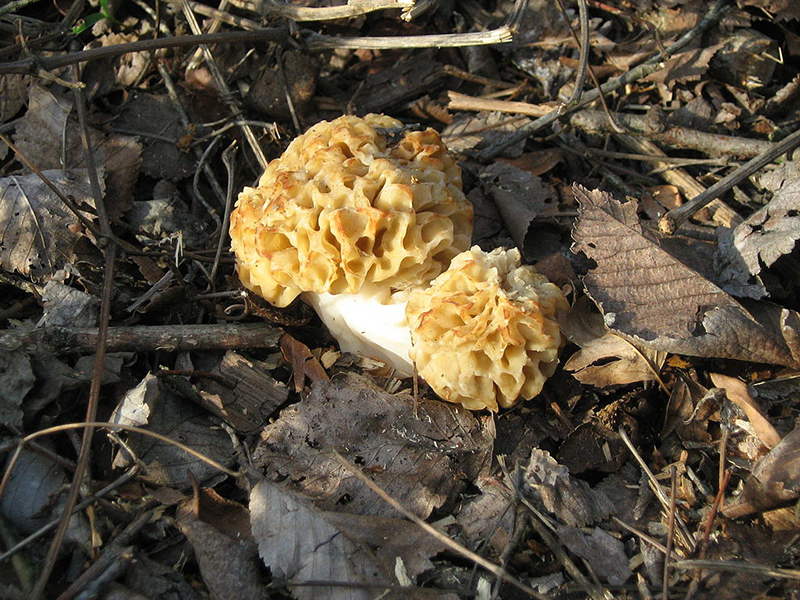
Only young morels can be collected and eaten. Old inedible mushrooms can be easily identified by discoloration: with age, the morel cap becomes almost black (see photo). Photo Credit: Jerzy Strzelecki, CC BY-SA 3.0