Canine mutinus
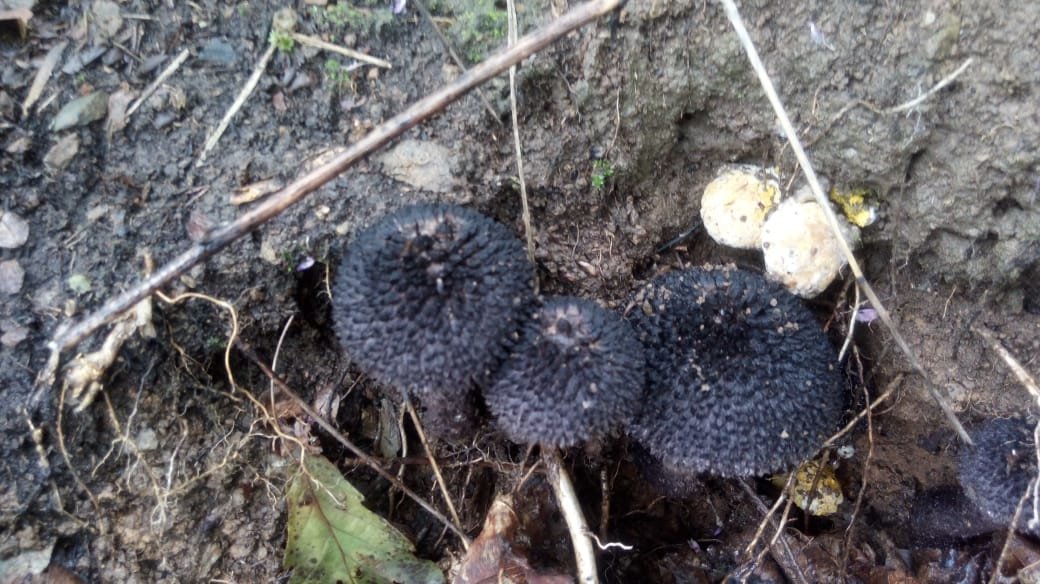
The shape of this mushroom is elongated, and the cap is weakly expressed. The length of the canine mutinus reaches 18 centimeters, while the diameter of the leg is small, about one and a half centimeters. As a result of full maturation, its crown opens up, while the tip of a pale color becomes visible. Canine mutinus is a very rare fungus, found mainly in Europe. There are also cases of its appearance in North America. He loves coniferous forests, often grows alone. You can see the mutinus on rotten snags or stumps.
The mushroom is considered edible, but only if it is not yet ripe, that is, when it is in the egg shell. The dog mutinus itself has a specific smell, which, in turn, attracts various insects. They flock to the smell and begin to gnaw the mushroom. After that, he begins to decompose quickly.

Canine mutinus
Evaluation of taste, initial processing and recipes
The taste qualities of this representative of the Boletov family are low. The stem is stiff and fibrous, and has an unattractive black and purple color. Caps of young specimens that have undergone careful culinary processing are suitable for eating. Before cooking, conditionally edible mushrooms must be boiled for 15–20 minutes.
Salting
Boiled mushrooms can be salted. Ingredients required for salting 10 kg of fresh fruits (after cooking, their amount will decrease by 3 times):
- rock salt - 400 g;
- young leaves of cherry or black currant;
- Bay leaf;
- whole cloves of garlic - 5 pcs.
Preparation:
- Throw the mushrooms in a colander to drain excess liquid.
- Cover with salt and mix thoroughly in a large saucepan.
- Arrange in sterile jars.
- Place garlic cloves on top and cover with spices and leaves.
Roll up the cans tightly and store in a cool place. Salting time is 1-1.5 months.
Pickling
Put the boiled and squeezed from liquid caps of young mushrooms (raw 1.5 kg) in sterile jars, pour hot brine and roll up.
Marinade is prepared from the following ingredients:
- water - 1 l;
- salt - 20 g;
- sugar - 10 g;
- laurel - 2-3 pcs.;
- allspice - 10-12 pcs .;
- cloves - 2 pcs.;
- garlic - 5 cloves;
- vinegar 9% - 30 ml;
- currant leaves, dill umbrellas.
Preparation:
- Mix all the ingredients (put vinegar and garlic before clogging).
- Cook for 5 minutes.
- Pour the prepared brine into jars of mushrooms.
- Roll up with iron lids.
Pickled or salted flaked pine mushroom is a good cold snack that is kept cool throughout the winter.
Red Book
Why is it said everywhere that you are the cotton-footed cone mushroom widespread in Russia? However, few of the mushroom pickers can say that they really once came across it. Rarely does anyone have a photograph of this mushroom in its natural environment.
Indeed, you need to look for it carefully enough and there are a number of reasons for this.
You can see for yourself that the appearance of this forest dweller is unusual and attracts attention. People who see such a strange mushroom in front of them, even having no idea whether it can be eaten or not, tend to pluck it, if only for the sake of entertainment.
Due to its appearance, the cotton leg mushroom has earned many different nicknames. They call him an old man, a devil and a keeper. As a result, due to excessive curiosity, people destroyed a huge number of such mushrooms, simultaneously damaging the mycelium.

Now the forests are somewhat deserted, and the mushroom itself was listed in the Red Book.
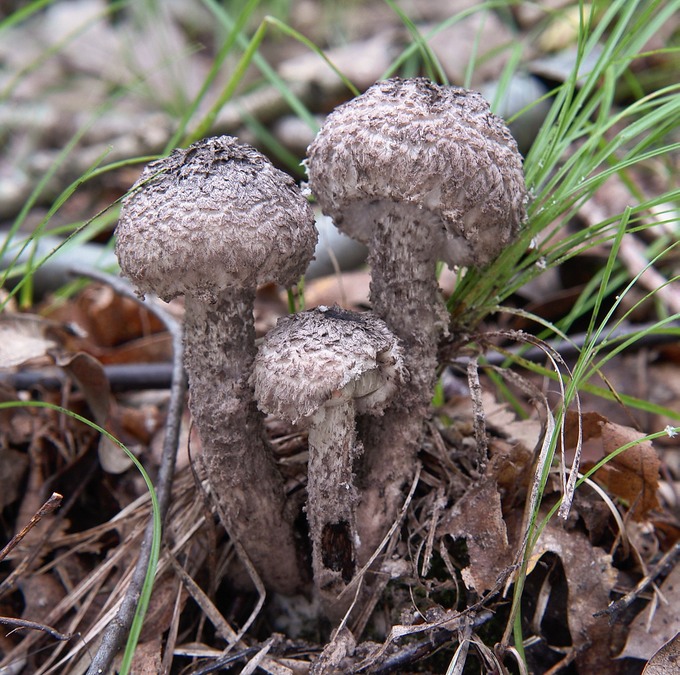
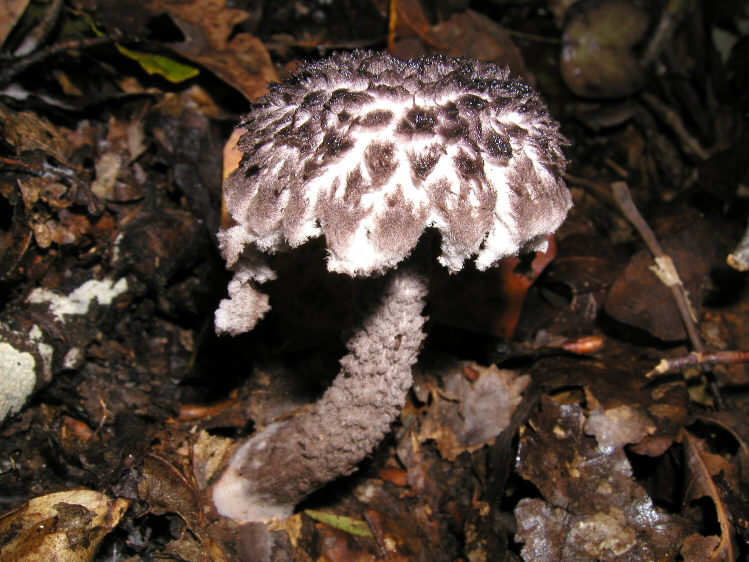
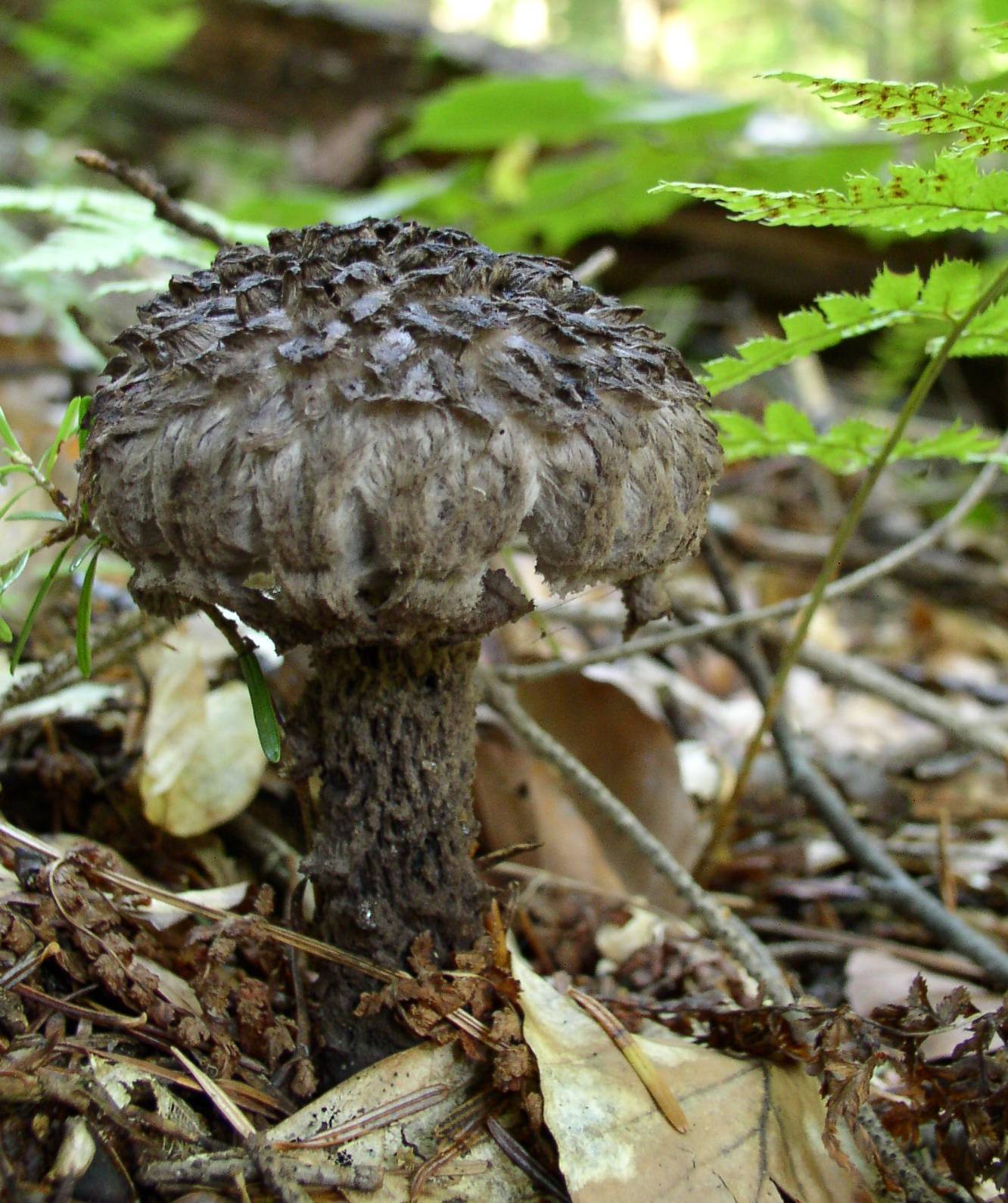
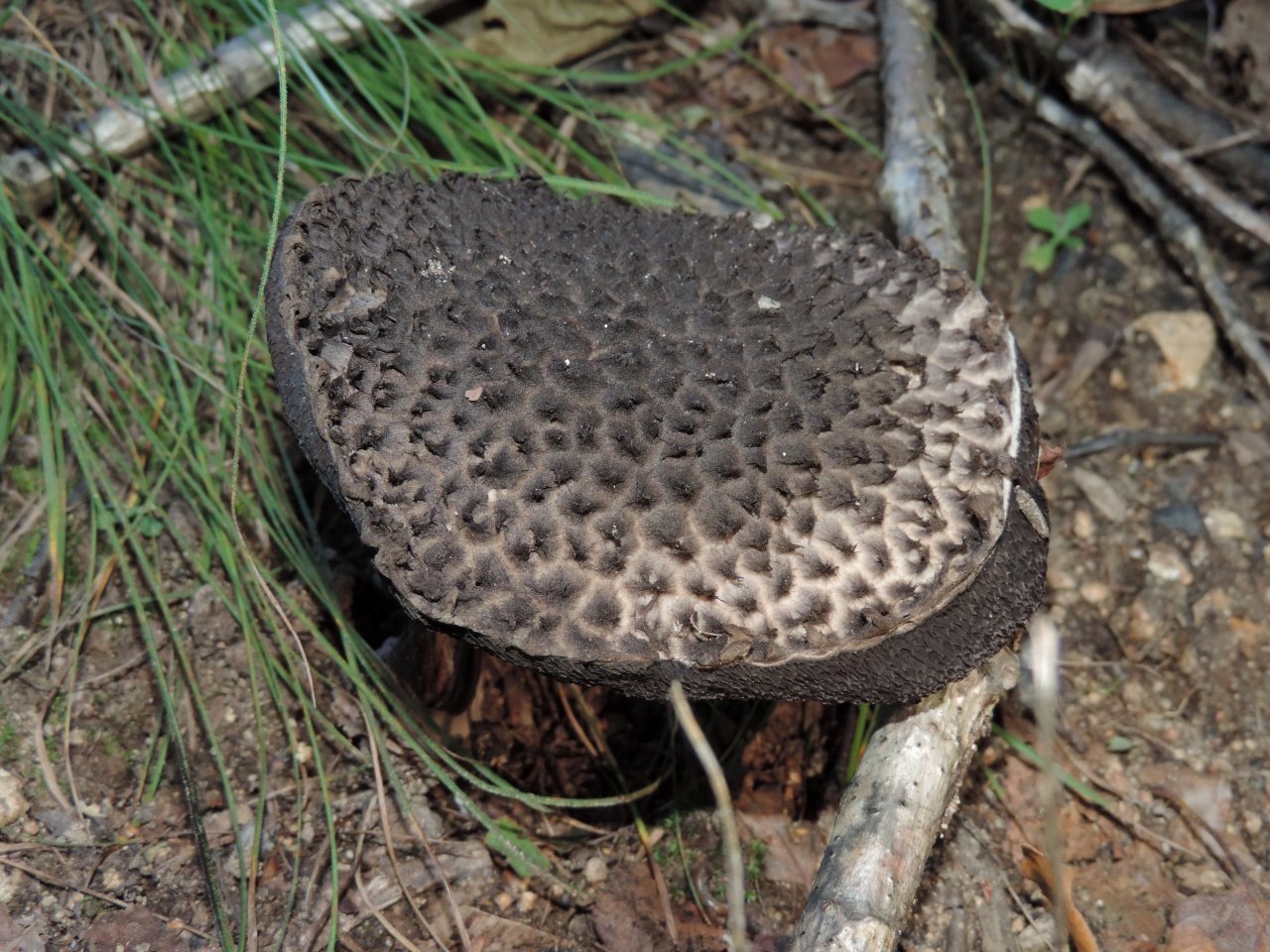
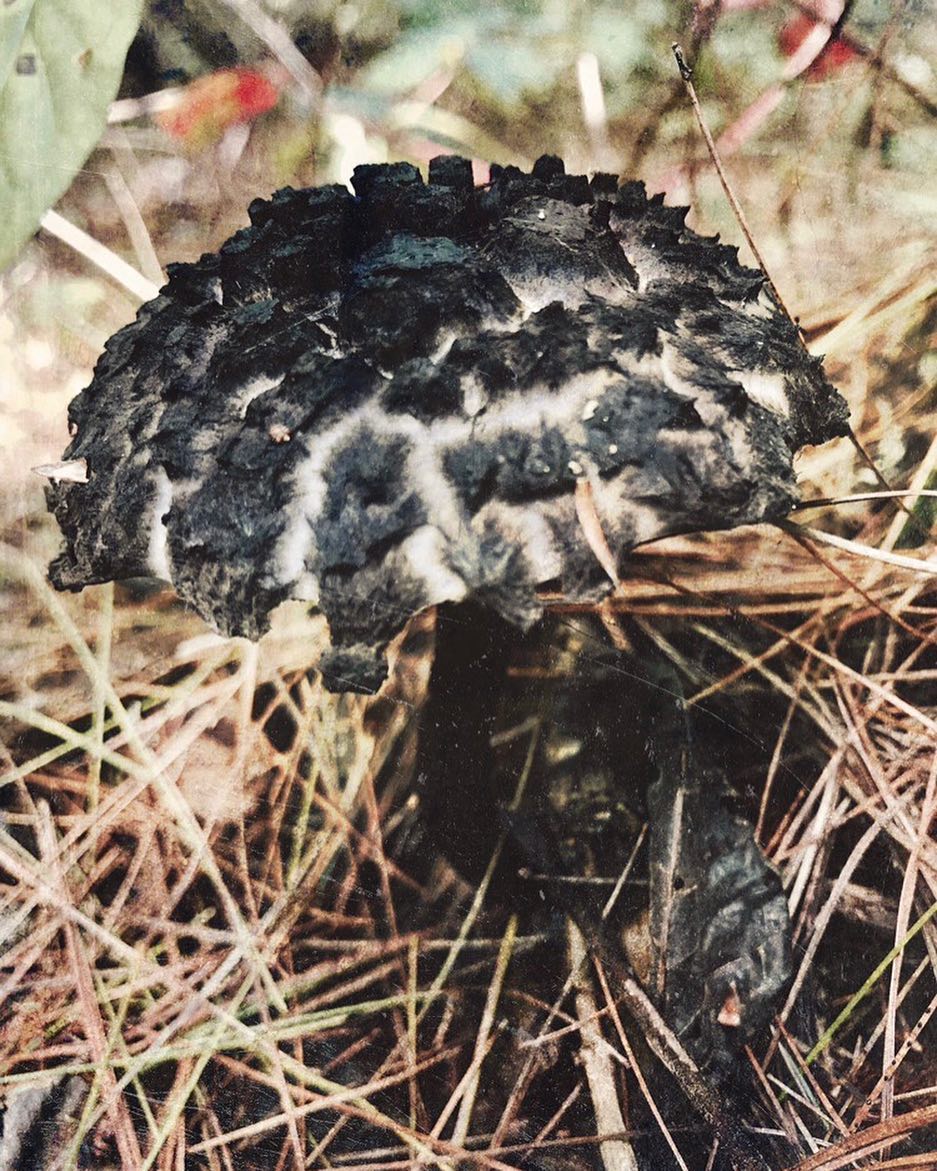
The mushroom is unusual in that its cap has a large surface. In young mushrooms, this is not so noticeable, but the older the forest dweller, the more it stands out.Not only the cap is covered with scales; in adulthood, the legs acquire the same structure.
From a distance, it seems as if the mushroom is dressed in some kind of mink coat. With age, the “fur” begins to appear more strongly, but at the same time, as if it is thinning, due to the fact that the skin of the cap begins to peel off unevenly. As a result, we begin to see the outlines of the mushroom.
The diameter of the mushroom cap can reach a maximum of 10-13 cm. Most often it has a gray-white tint and hairy scales are located on it, more or less often.
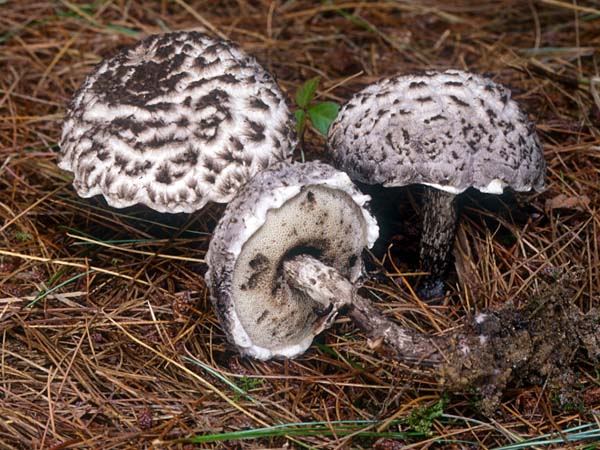
Let's take a look at the layer that is responsible for the spread of spores. It has a gray tint, however, it becomes darker and darker with age. Over time, it completely becomes brown.
By themselves, the tubules and spores are quite small in their location. Young mushrooms have one attractive feature. Their edges seem to be tucked up to the leg, as a result, some spores, when hit, remain in a kind of pocket.
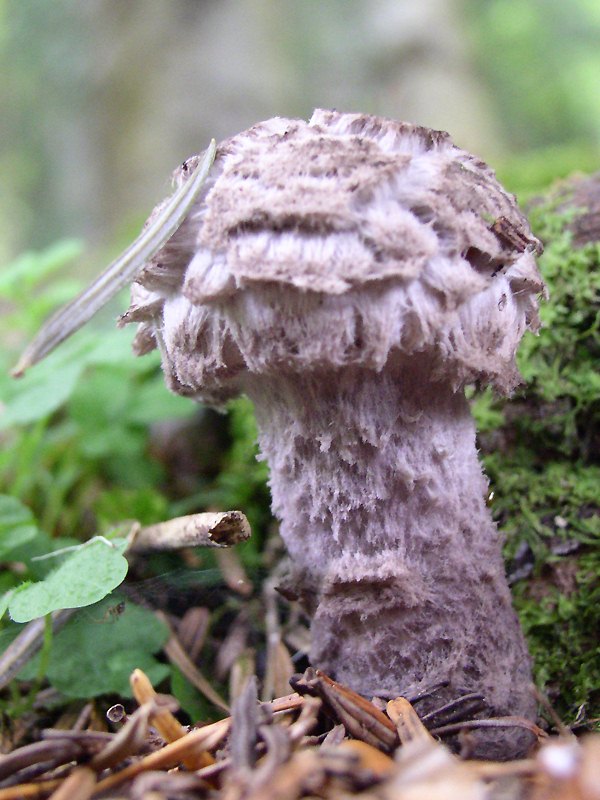
If you look at the leg, you can see that it is quite dense. At a young age, it has a uniform color, but with age it becomes covered with small scales.
The diameter of the leg reaches 3 cm, but this applies only to sufficiently large mushrooms. On average, it is equal to one and a half to 2 cm.
The color of the leg appears under the skin scales. Most often it is white-gray and stands out brightly against the background.
The flesh in the cut has a white tint and slightly secretes milky juice. However, when interacting with oxygen, it begins to darken quickly, acquiring a spicy, slightly weak taste.
Interesting Facts
The popcorn mushroom can not live and develop in every region and climate. For him, the ideal territory is located in the Far East, on the border of Ukraine or Georgia. There is no frost here, the weather is optimal with moderate humidity.
However, the pineapple mushroom continues to boldly spread across the territory of Russia. It was found in the Volga region, even in the Moscow region, which is very surprising, because the mushroom prefers a good ecological situation.
The fungus chooses strictly defined soils for growth. For example, it grows in mixed and deciduous forests mainly; it chooses acidic humus soils for growth.
Have you heard about this mushroom?
Yes
16.67%
No
75%
I saw him, but did not know what it was called
8.33%
Votes: 12
He prefers to grow on a special deadwood, which half sinks into the ground.
The growth time that is typical for this mushroom begins in mid-summer, that is, around July and continues until October. However, if the weather in October is relatively warm, it can grow and bear fruit until mid-November.
With regard to nutritional value, the question is different here. Despite the delicious and pleasant aroma that can be felt from the mushroom during picking, during cooking they are completely lost, just like the spicy taste.
This means that the mushroom cannot give a dish any special pleasant taste characteristics, therefore it is not used in cooking and is not a component of any dishes of various peoples of the world. Even chefs from Europe, who like to use anything that gives at least some taste and is not poisonous, practically do not use the popcorn mushroom in their recipes.
The mushroom is called conditionally edible, and they say about its low taste. And in some countries, it is considered inedible and even forbidden, for example, in Germany.
Edibility
If you come across a pine cone in the forest, do not rush to run away from it at a safe distance. We dare to assure that the mushroom is absolutely not poisonous. However, it has several nuances that people with poor digestion should be aware of.
The mushroom has very stiff legs. If at a young age they can somehow be checked, then at an old age, even after prolonged cooking and heat treatment, they remain tough. They are very poorly digested.
However, not everywhere are loyal to the shishkogrib as in Russia.For example, in Germany, this mushroom was recognized as poisonous and inedible at all.
The mushroom received such a bad reputation as a result of the fact that cases of poisoning were recorded.
In America, the pineapple mushroom has been classified as an edible mushroom. In Europe, pineapple mushroom is also harvested, but left for making tinctures, and not for food. It is believed that it has low taste, which is not able to somehow influence the dish.
Indeed, as a result of heat treatment, the pineapple mushroom somewhat loses its mushroom aroma and spicy taste. It becomes practically insipid, so its use in cooking is questioned.
An excerpt characterizing the Pine-leg mushroom
Who among the Russian people, reading the descriptions of the last period of the 1812 campaign, did not experience a heavy feeling of annoyance, dissatisfaction and ambiguity. Who did not ask themselves questions: how did they not take away, not destroy all the French, when all three armies surrounded them in superior numbers, when the frustrated French, starving and freezing, surrendered in droves and when (as history tells us) the goal of the Russians was precisely to stop, cut off and capture all the French. How could that Russian army, which, weaker in the number of the French, gave the Battle of Borodino, how did this army, which surrounded the French from three sides and had the goal of taking them away, did not achieve its goal? Is it possible that the French have such a huge advantage over us that we, having surrounded them with superior forces, could not beat them? How could this have happened? History (the one that is called by this word), answering these questions, says that this happened because Kutuzov, and Tormasov, and Chichagov, and he did not make such and such maneuvers. But why didn't they do all these maneuvers? Why, if they were to blame for the failure to achieve the intended goal, why were they not tried and executed? But, even if we admit that Kutuzov and Chichagov, etc., were to blame for the failure of the Russians, it is still impossible to understand why and in the conditions in which the Russian troops were located near Krasnoe and Berezina (in both cases the Russians were in excellent forces), why was not the French army taken prisoner with marshals, kings and emperors, when this was the goal of the Russians? The explanation of this strange phenomenon by the fact (as is done by Russian military historians) that Kutuzov prevented the attack is groundless because we know that Kutuzov's will could not keep the troops from attacking at Vyazma and at Tarutin. Why was that Russian army, which with the weakest forces won a victory at Borodino over the enemy in all his strength, at Krasnoye and near Berezina, in excellent forces, was defeated by the upset crowds of the French? If the goal of the Russians was to cut off and take prisoner Napoleon and the marshals, and this goal was not only not achieved, and all attempts to achieve this goal were destroyed every time in the most shameful way, then the last period of the campaign is quite rightly represented by the French alongside victories and is completely unfairly presented by Russian historians as victorious. Russian military historians, insofar as logic is obligatory for them, involuntarily come to this conclusion and, despite lyrical appeals about courage and loyalty, etc., must involuntarily admit that the French retreat from Moscow is a series of Napoleon's victories and Kutuzov's defeats.
Curly griffin
Another name for the mushroom, more popular, is the ram mushroom. The ram mushroom is very large, in mass it can reach 10 kilograms. The diameter of the mushroom is 80 centimeters. The fruiting bodies consist of many small spatulate-shaped caps that are held on to branching stalks. As a result, all these legs merge into a common base, forming a multi-tiered body of curly griffins. Curly griffin can be found in deciduous forests in August and September. Mushrooms grow on the trunks of old oak or maple trees, most often at their base.It is worth noting that they can grow very quickly and form white rot.
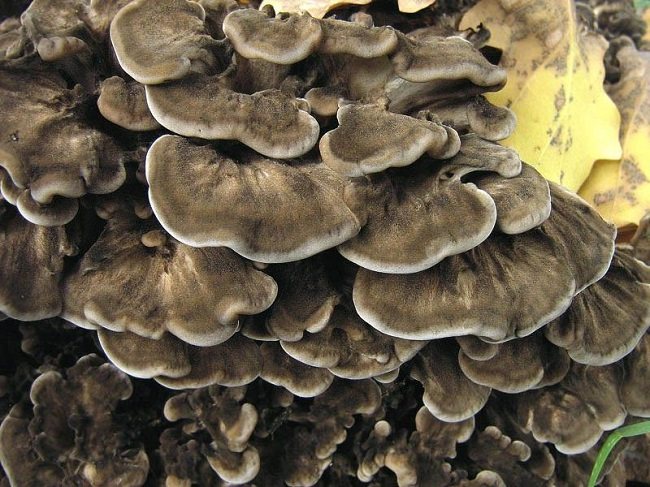

Curly griffin
Red Book
Why is it said everywhere that you are the cotton-footed cone mushroom widespread in Russia? However, few of the mushroom pickers can say that they really once came across it. Rarely does anyone have a photograph of this mushroom in its natural environment.
Indeed, you need to look for it carefully enough and there are a number of reasons for this.
You can see for yourself that the appearance of this forest dweller is unusual and attracts attention. People who see such a strange mushroom in front of them, even having no idea whether it can be eaten or not, tend to pluck it, if only for the sake of entertainment.
Due to its appearance, the cotton leg mushroom has earned many different nicknames. They call him an old man, a devil and a keeper. As a result, due to excessive curiosity, people destroyed a huge number of such mushrooms, simultaneously damaging the mycelium.

Now the forests are somewhat deserted, and the mushroom itself was listed in the Red Book.
The mushroom is unusual in that its cap has a large surface. In young mushrooms, this is not so noticeable, but the older the forest dweller, the more it stands out. Not only the cap is covered with scales; in adulthood, the legs acquire the same structure.
From a distance, it seems as if the mushroom is dressed in some kind of mink coat. With age, the “fur” begins to appear more strongly, but at the same time, as if it is thinning, due to the fact that the skin of the cap begins to peel off unevenly. As a result, we begin to see the outlines of the mushroom.
The diameter of the mushroom cap can reach a maximum of 10-13 cm. Most often it has a gray-white tint and hairy scales are located on it, more or less often.
Let's take a look at the layer that is responsible for the spread of spores. It has a gray tint, however, it becomes darker and darker with age. Over time, it completely becomes brown.
By themselves, the tubules and spores are quite small in their location. Young mushrooms have one attractive feature. Their edges seem to be tucked up to the leg, as a result, some spores, when hit, remain in a kind of pocket.
If you look at the leg, you can see that it is quite dense. At a young age, it has a uniform color, but with age it becomes covered with small scales.
The diameter of the leg reaches 3 cm, but this applies only to sufficiently large mushrooms. On average, it is equal to one and a half to 2 cm.
The color of the leg appears under the skin scales. Most often it is white-gray and stands out brightly against the background.
The flesh in the cut has a white tint and slightly secretes milky juice. However, when interacting with oxygen, it begins to darken quickly, acquiring a spicy, slightly weak taste.
Interesting Facts
The popcorn mushroom can not live and develop in every region and climate. For him, the ideal territory is located in the Far East, on the border of Ukraine or Georgia. There is no frost here, the weather is optimal with moderate humidity.
However, the pineapple mushroom continues to boldly spread across the territory of Russia. It was found in the Volga region, even in the Moscow region, which is very surprising, because the mushroom prefers a good ecological situation.
The fungus chooses strictly defined soils for growth. For example, it grows in mixed and deciduous forests mainly; it chooses acidic humus soils for growth.
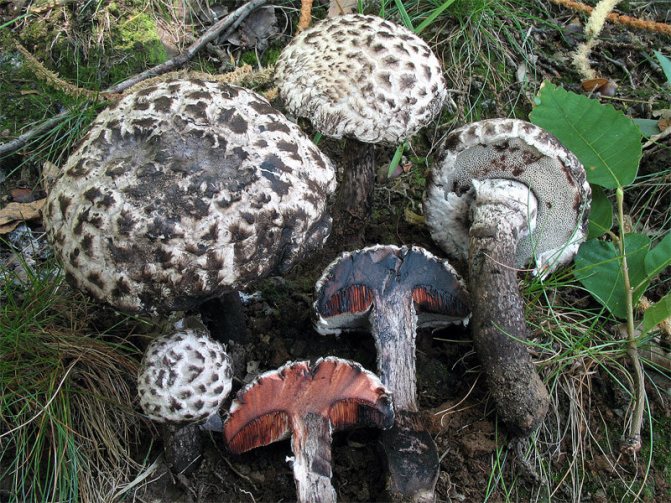

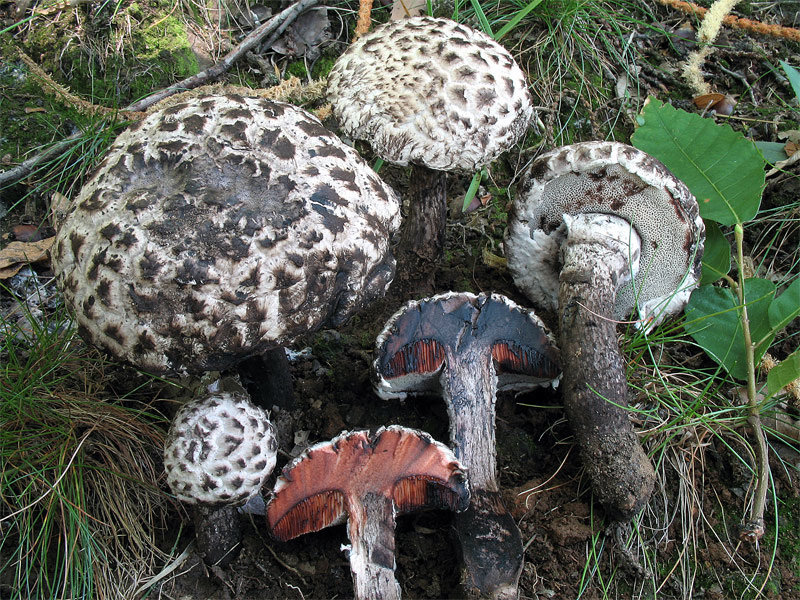
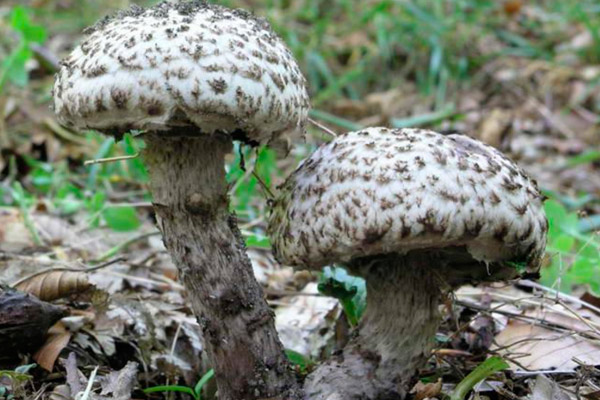
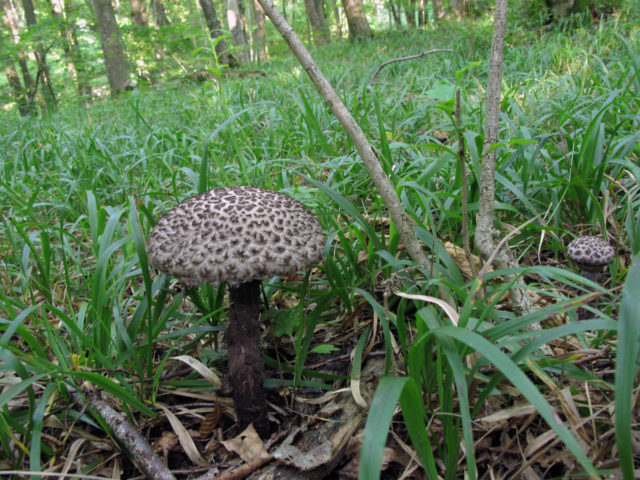
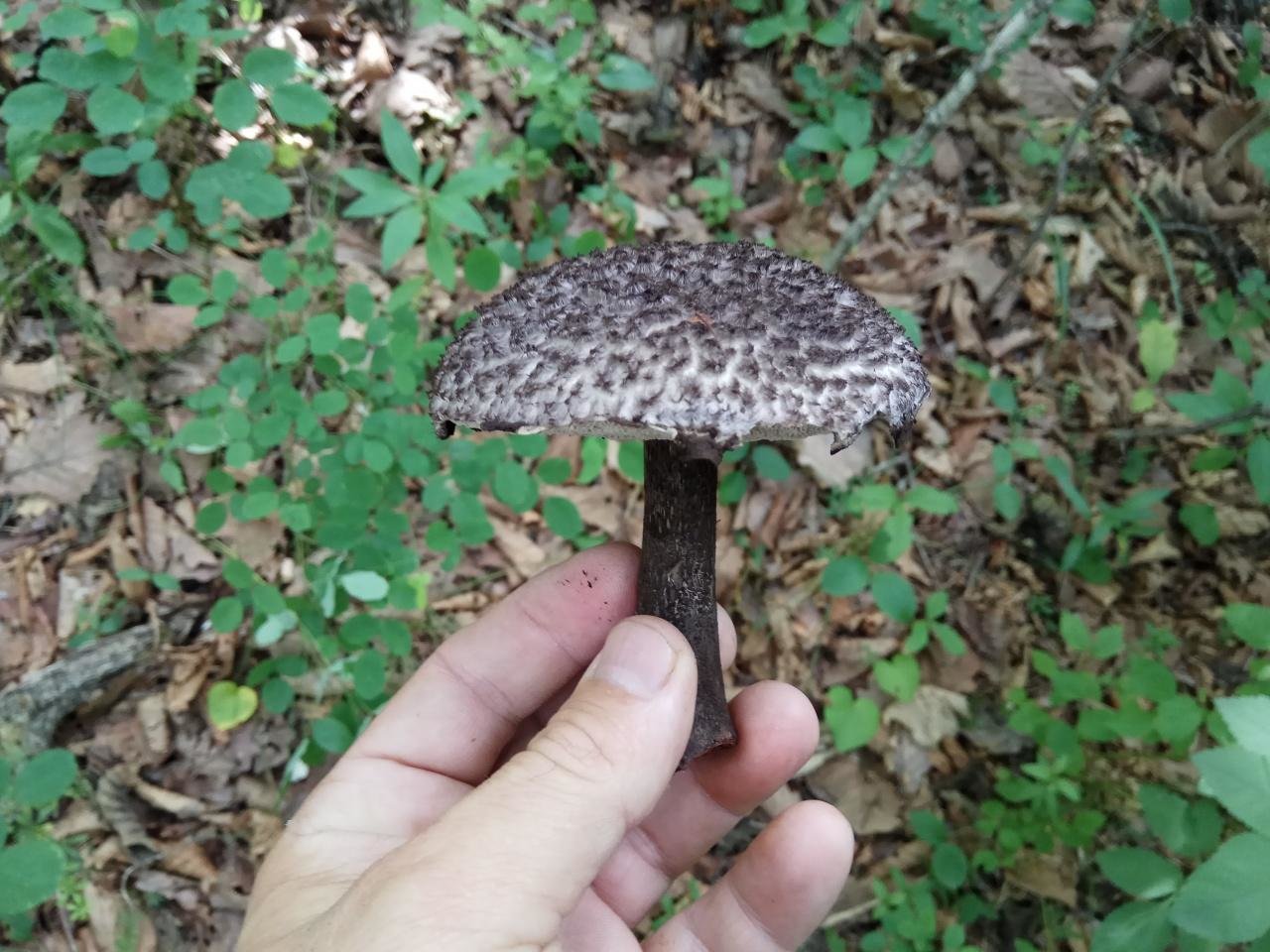
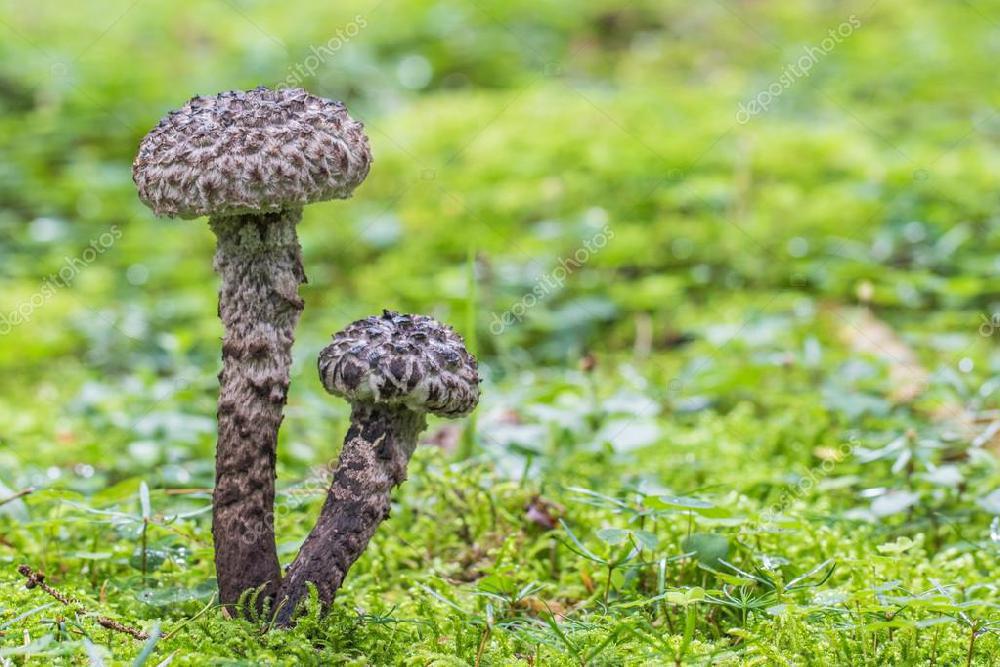
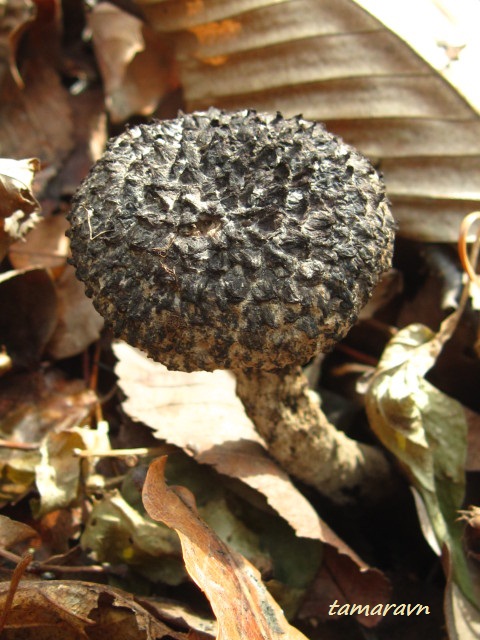
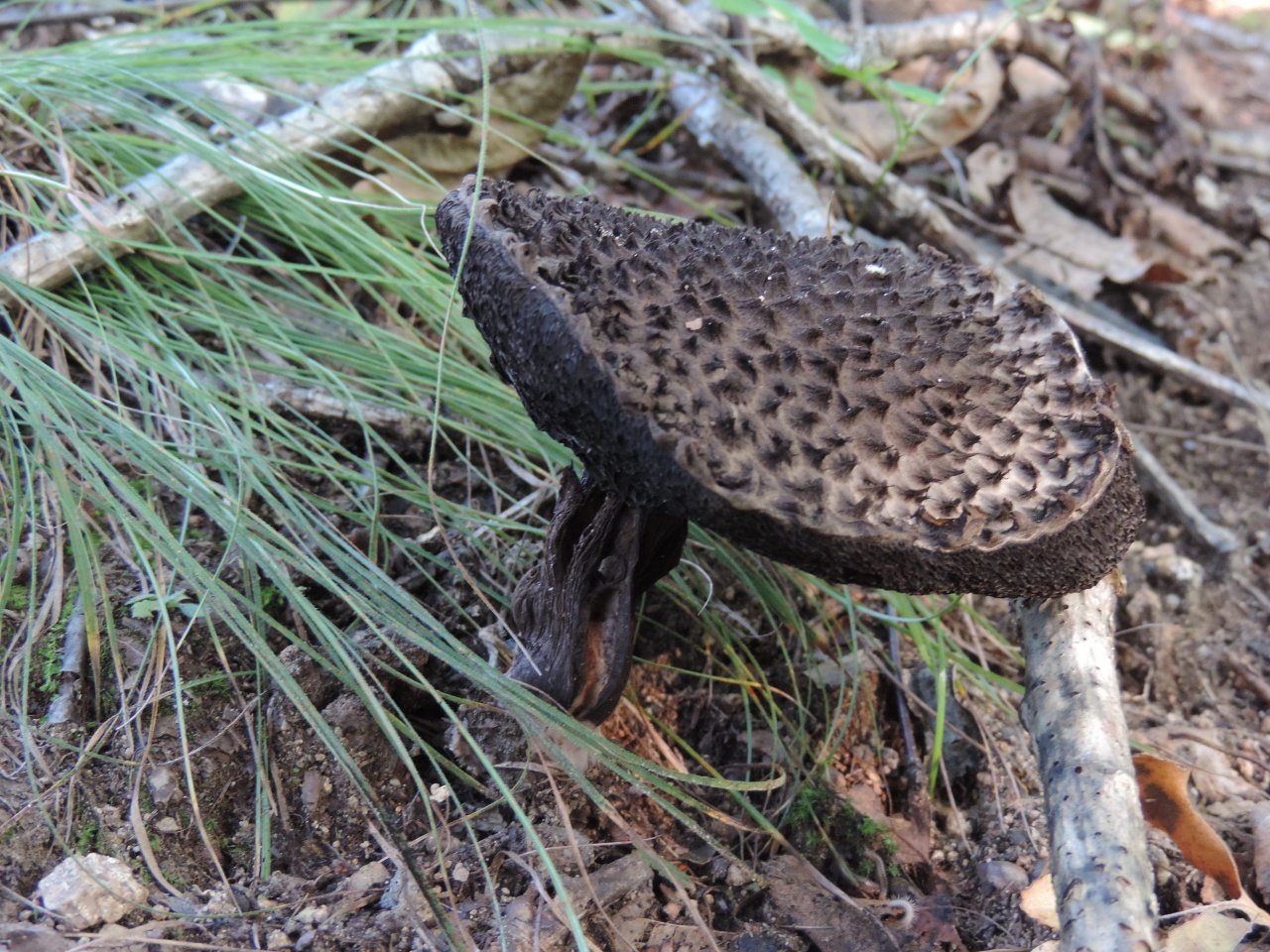
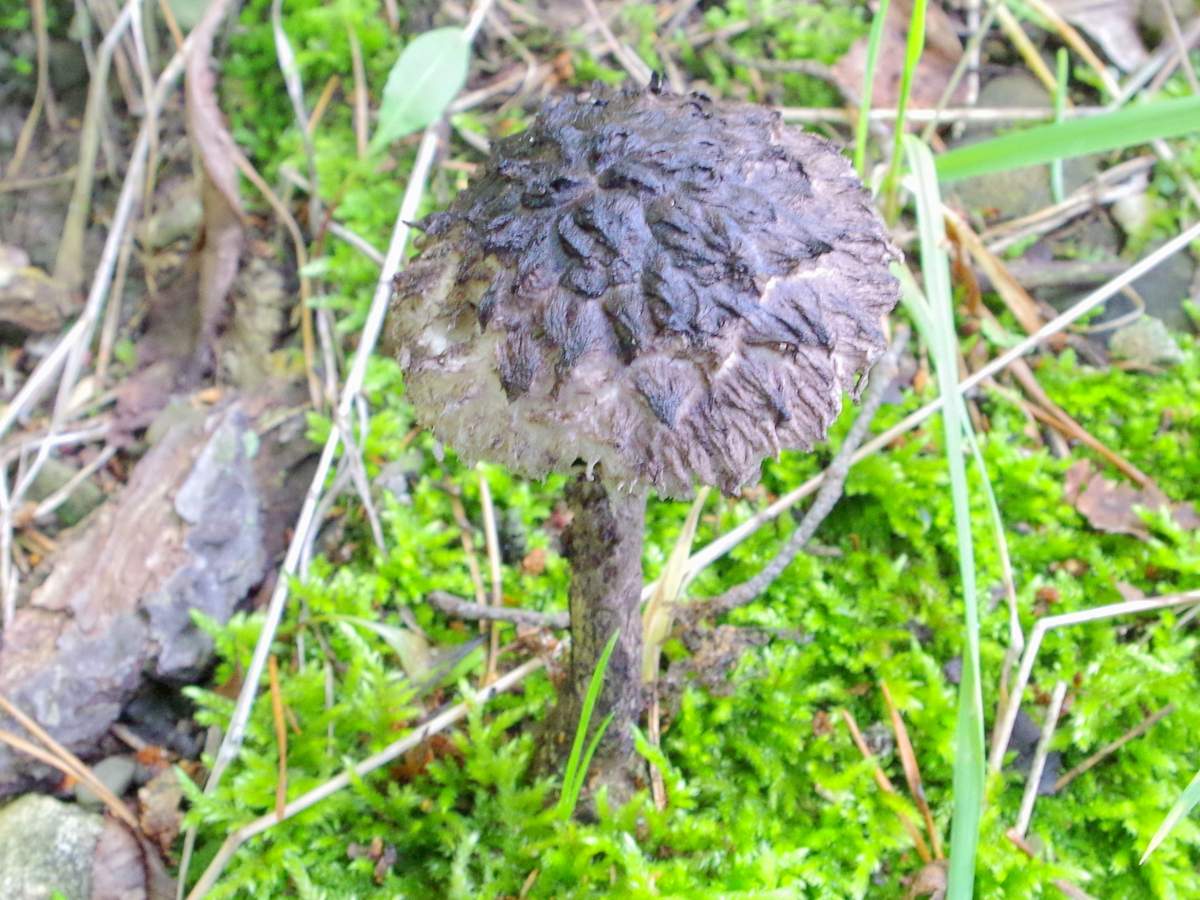
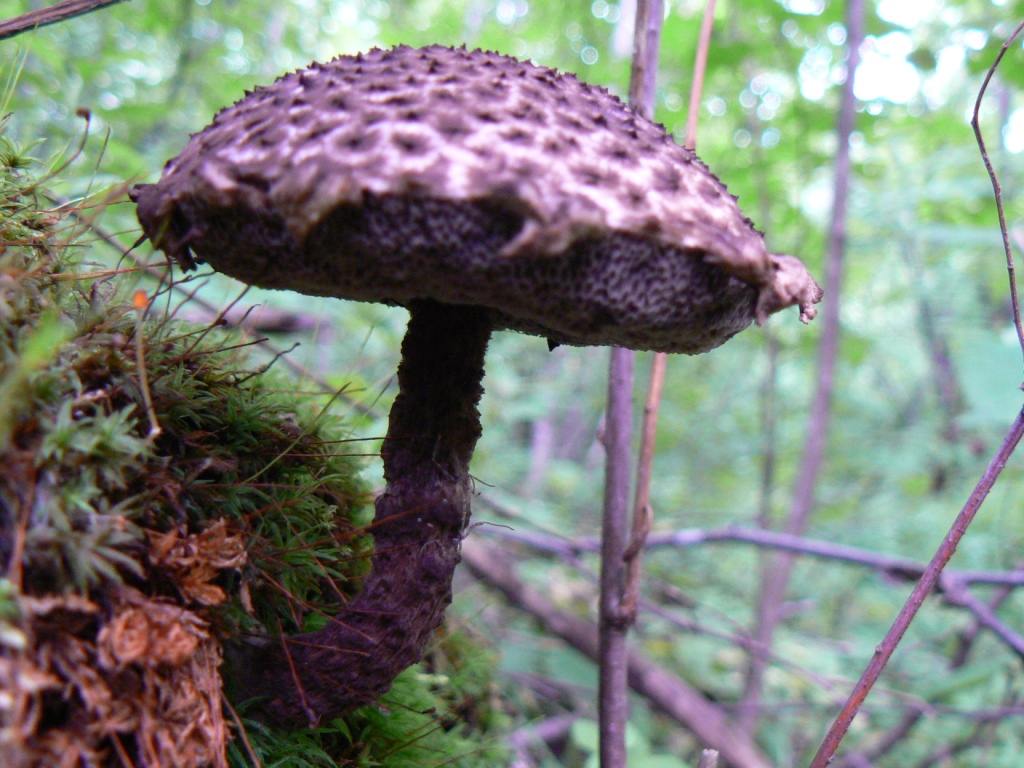
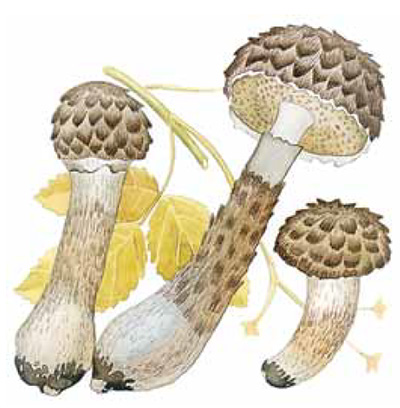
Description and photo of Shishkogriba cotton leg
The cotton-footed cone mushroom belongs to the cone fungus species, the cone fungus genus. The family of bolts. It is widely known for its unique appearance and no less unique structure. It attracts glances to itself, in many respects, thanks to a kind of hat. Let's talk about her.
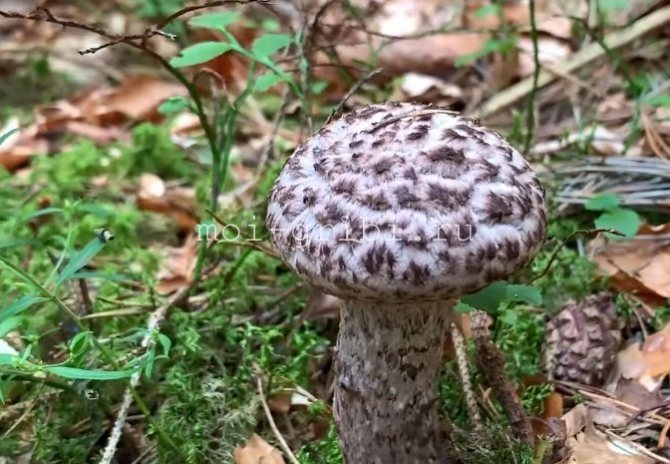

Hat
The first thing we pay attention to when we first encounter a pineapple is its hat. She attracts attention, and some call her "polar owl" because of the specific color
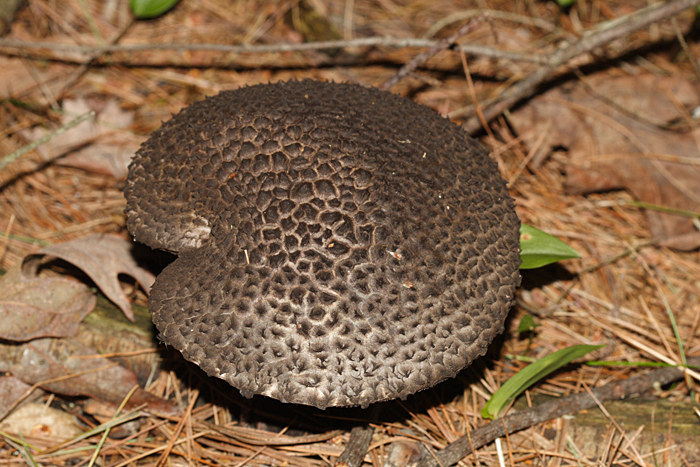
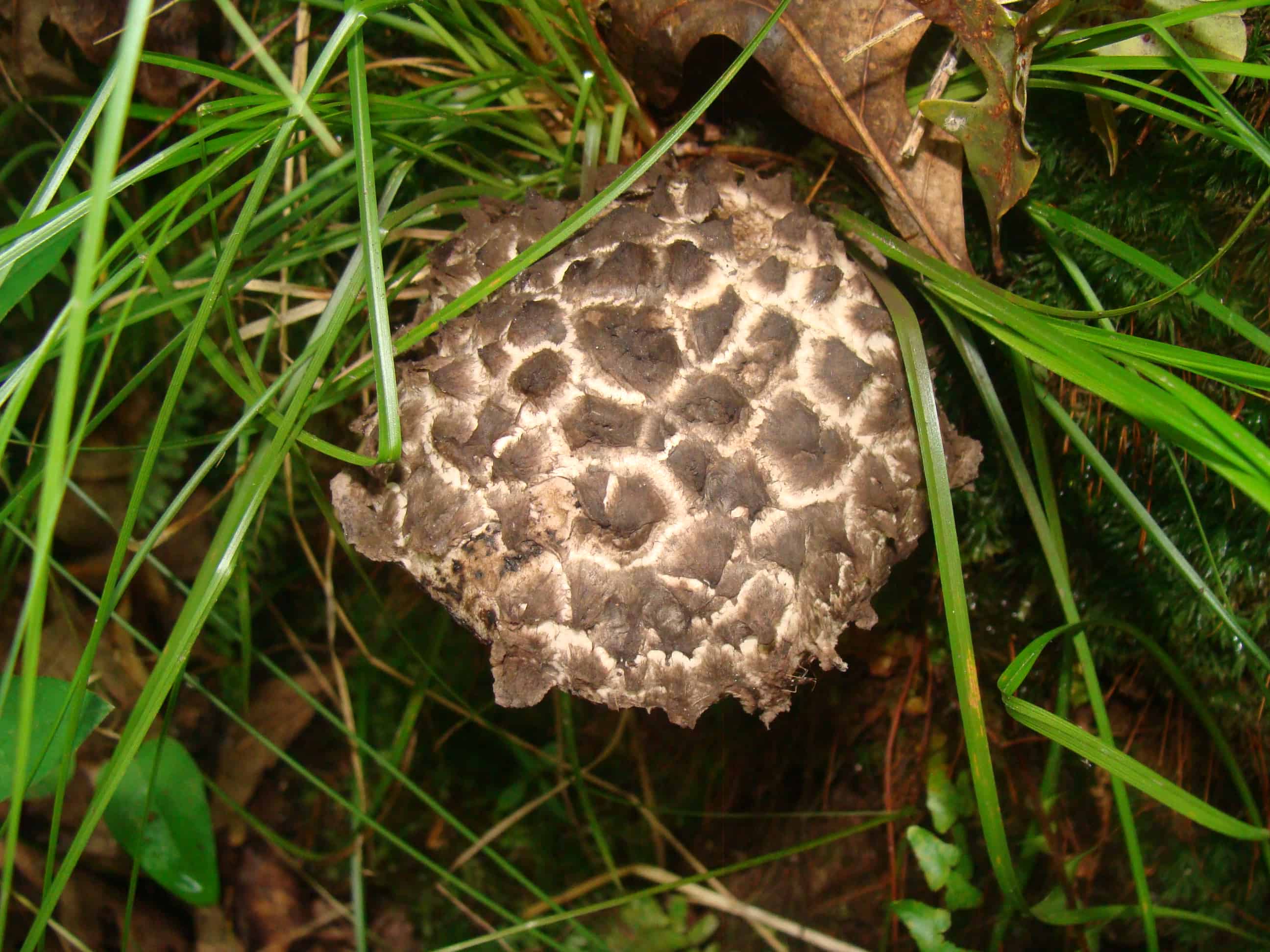
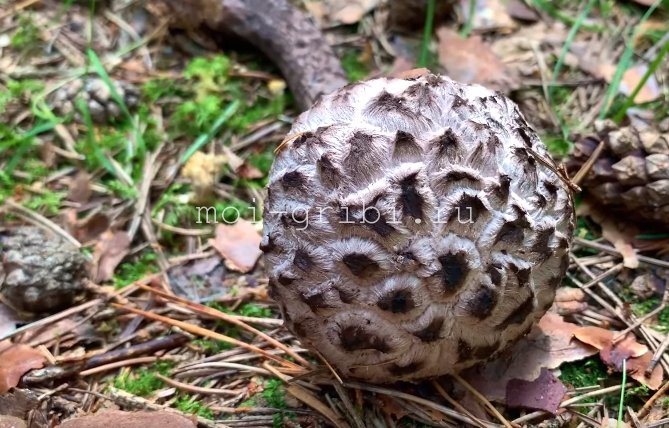
The cap is quite convex to the touch, elastic, it can be removed, however, it quickly takes shape. Very similar to a large pine cone covered with snow.
The maximum diameter of the cap can reach 12 cm, however, mushrooms are less common, the cap of which is 5 cm in diameter. There is a gray-brown shade, less often black-brown. In many ways, the color directly depends on the composition of the soil and weather conditions.
The hat is completely covered with various scales that are neatly positioned all over the hat, from the edges to the very center.
The older the mushroom, the larger in size and quantity the corresponding scales on it.
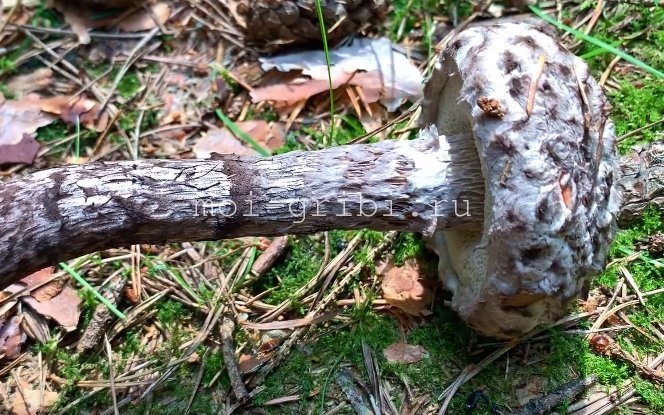

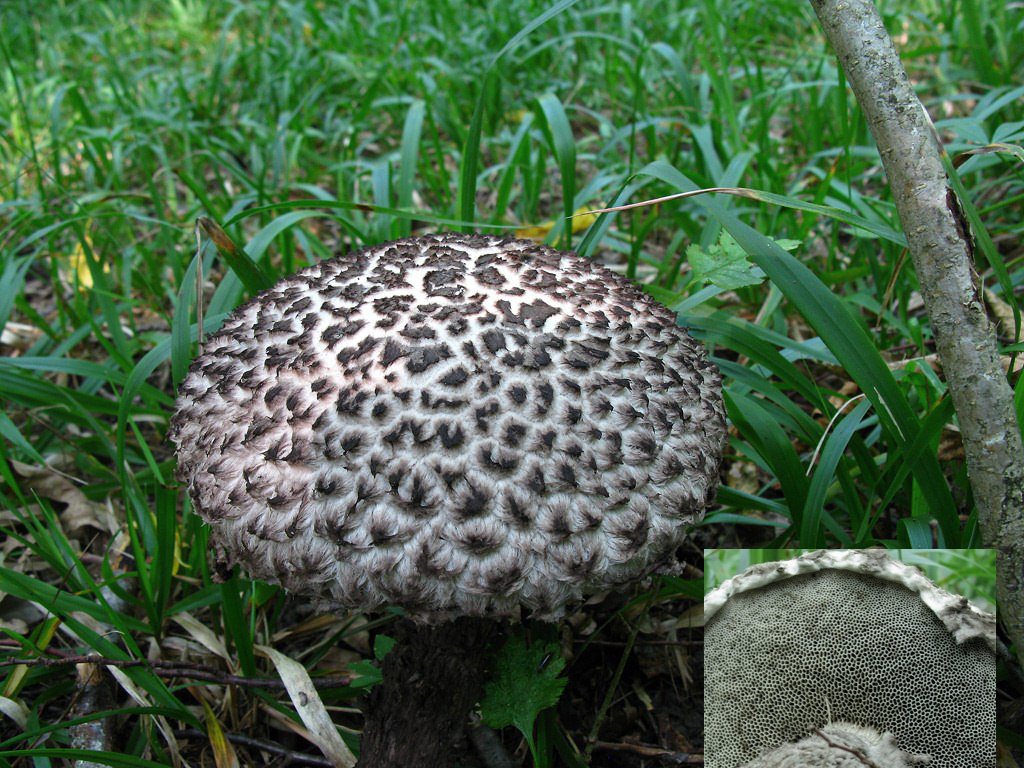
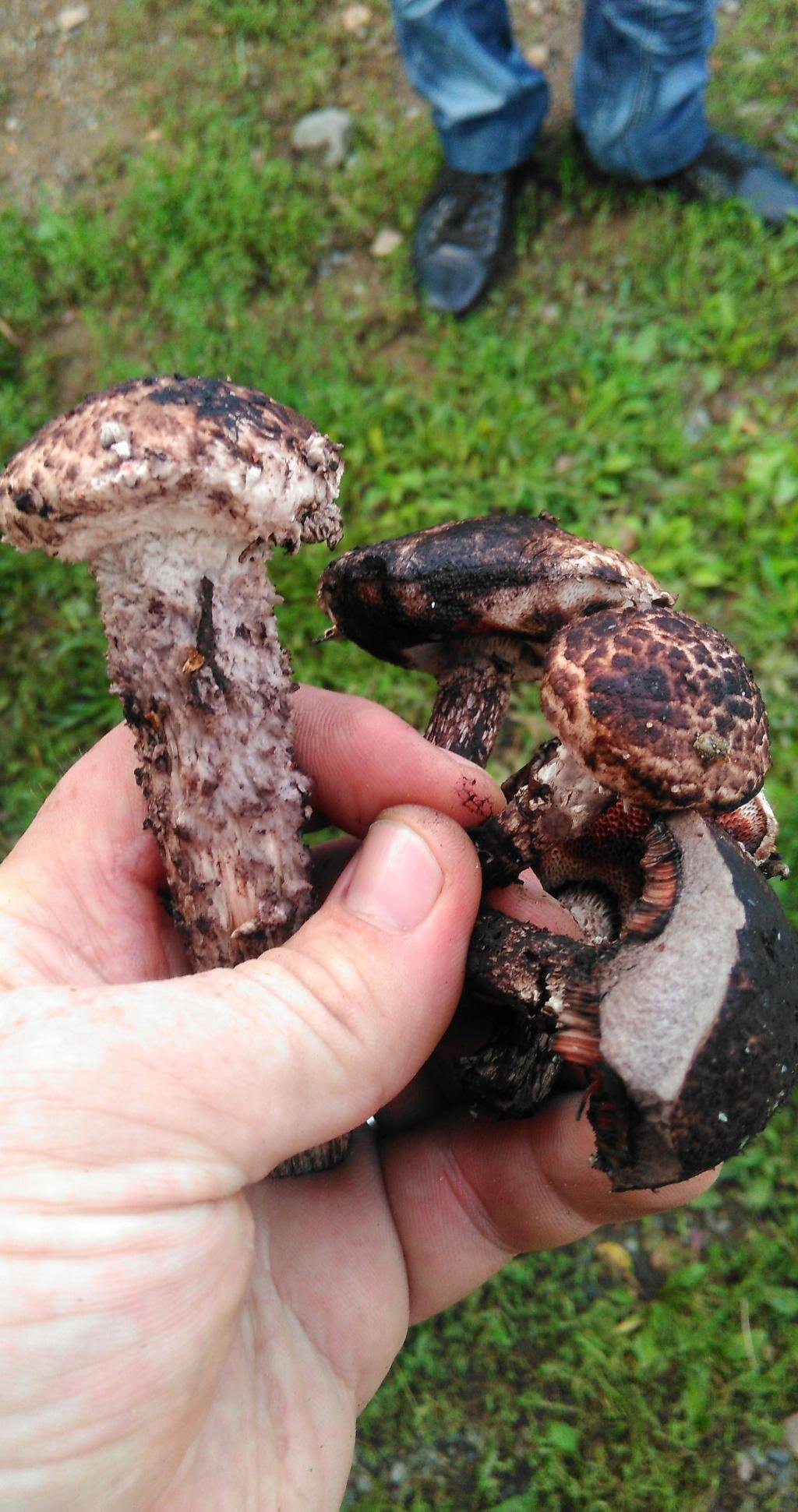
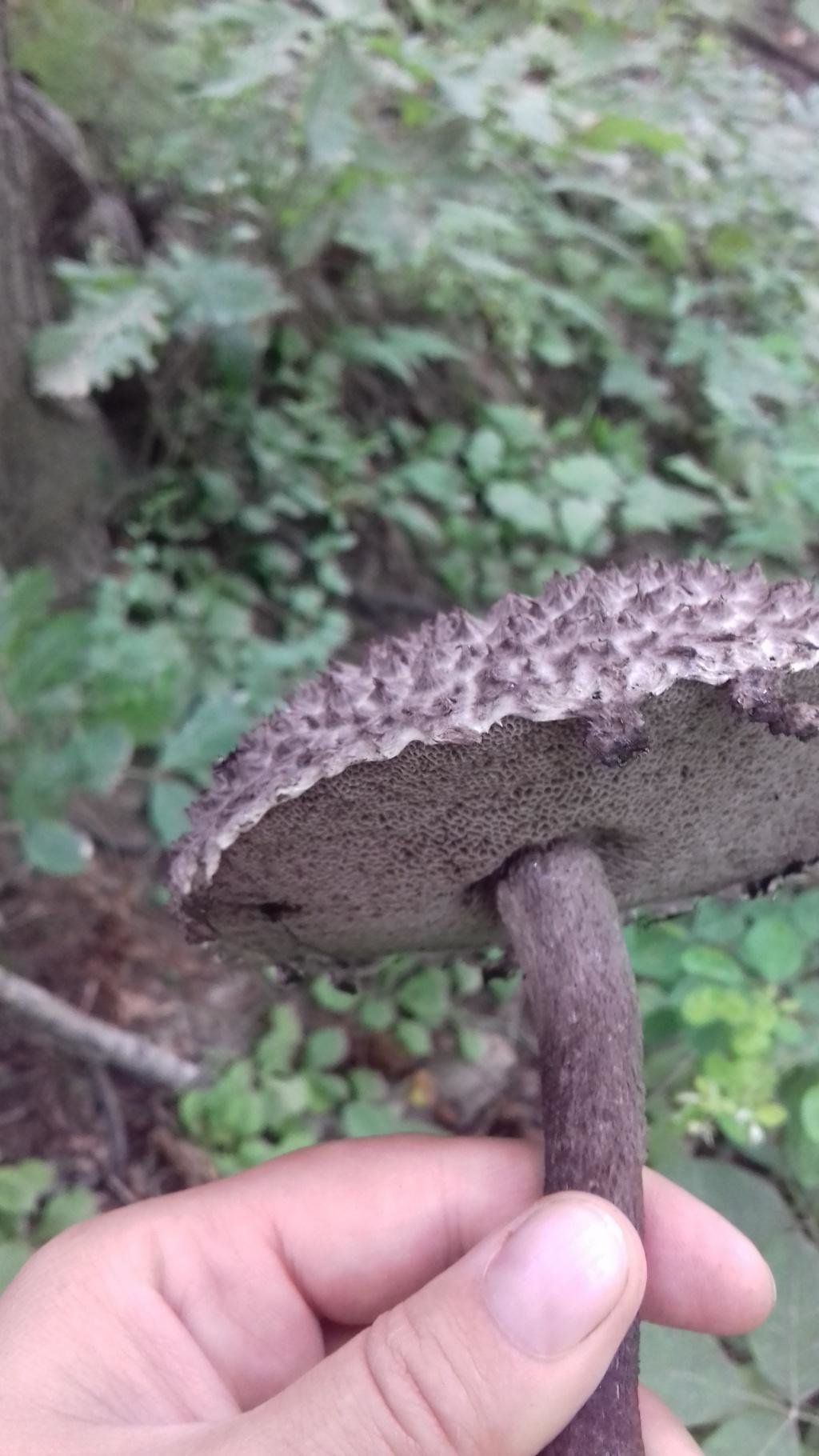
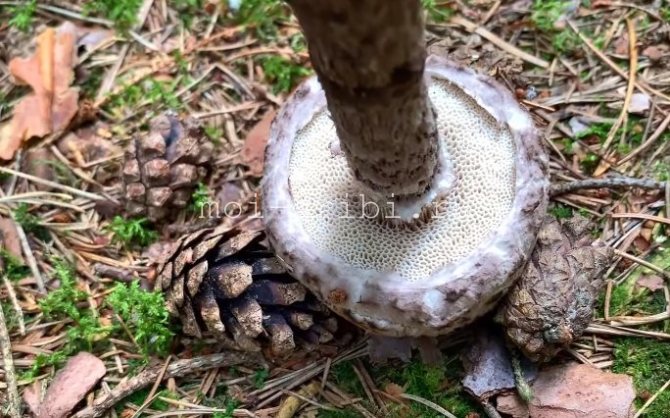
Hymenophore
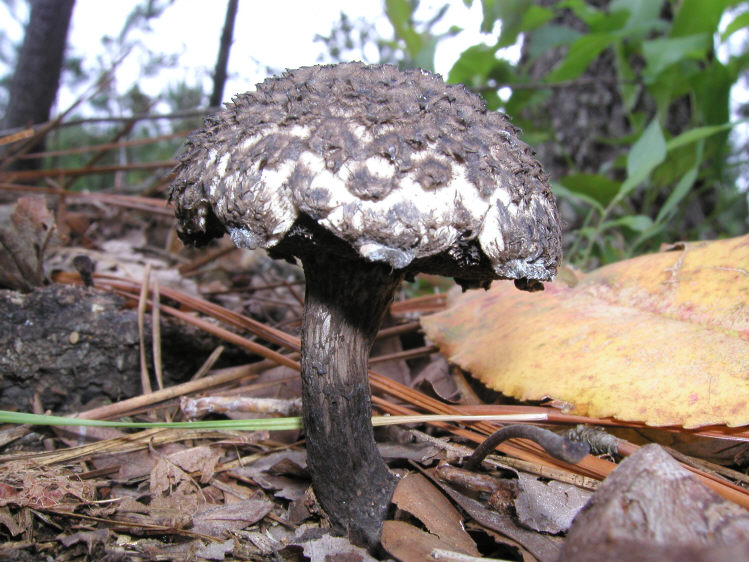
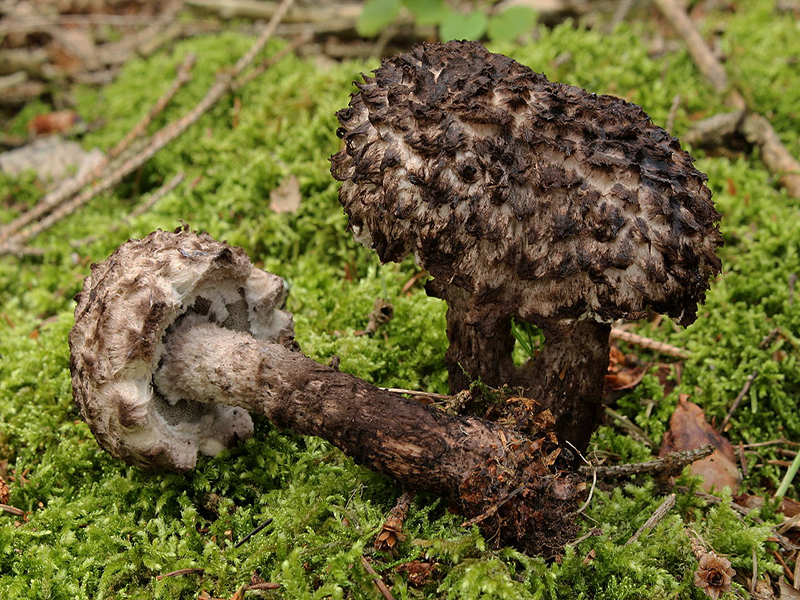
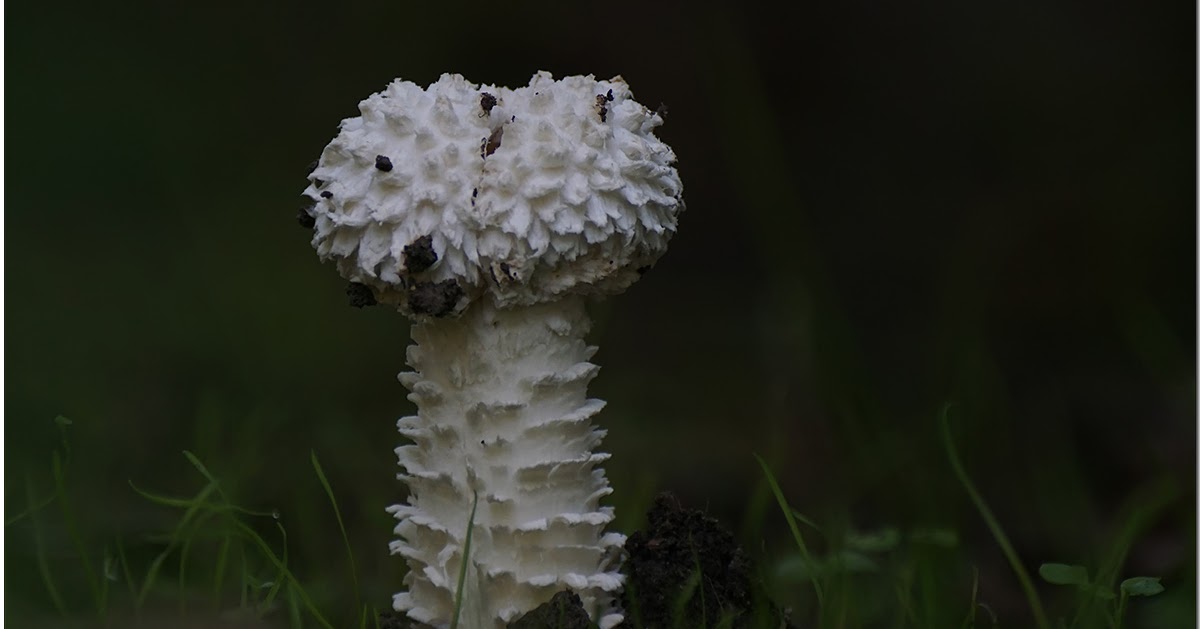
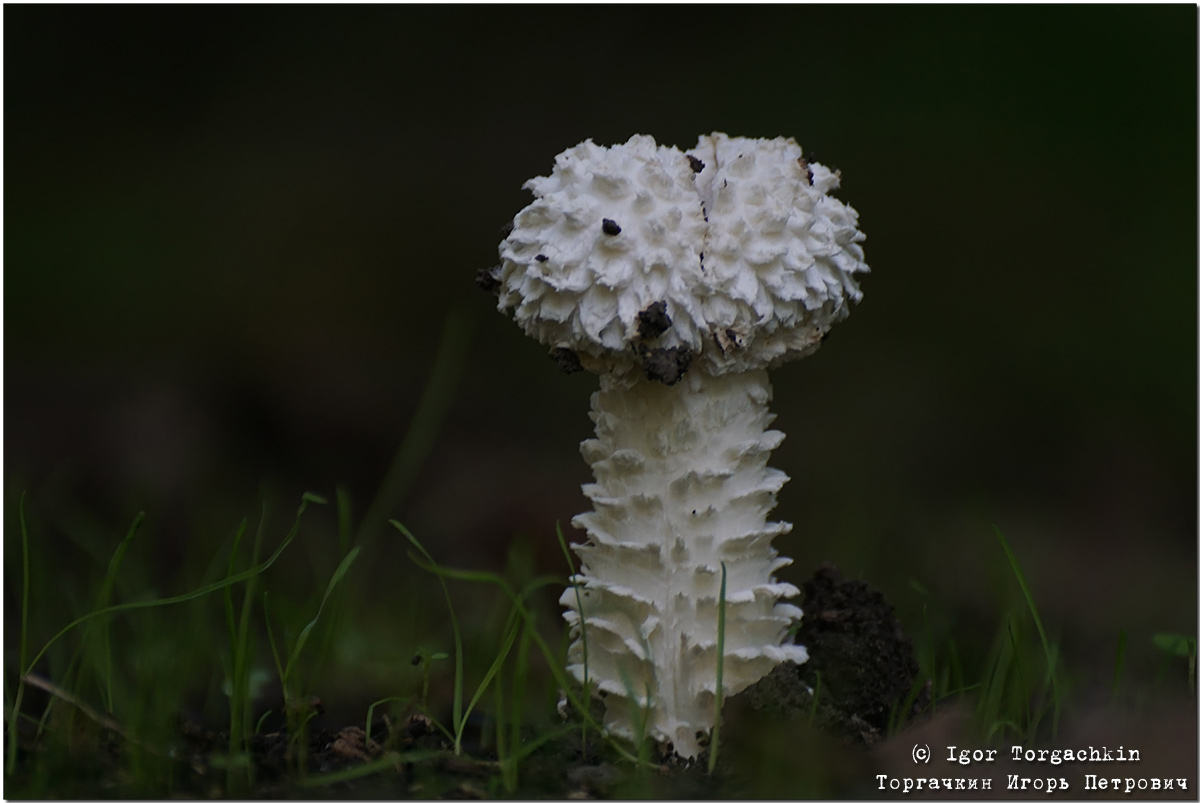
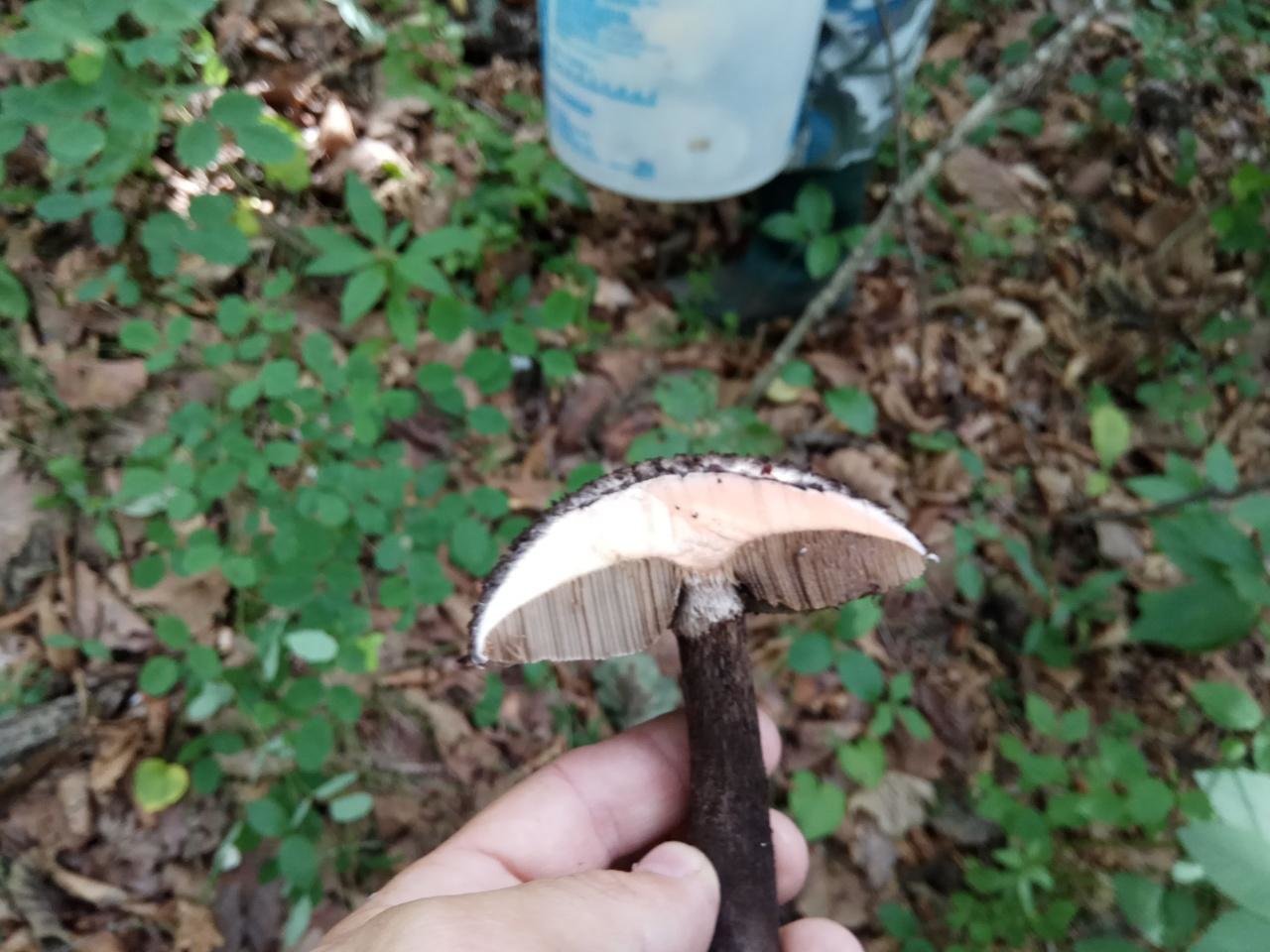
A hymenophore is called tubules that have grown into mushrooms. In the cotton-footed cone, they reach a length of one and a half cm. If you look closely at the tubes, you can see that their edges are initially white, covered with a kind of blanket of gray, less often of a white hue.
Then, they turn olive brown or gray-brown, and when pressed, they begin to blacken.
Leg
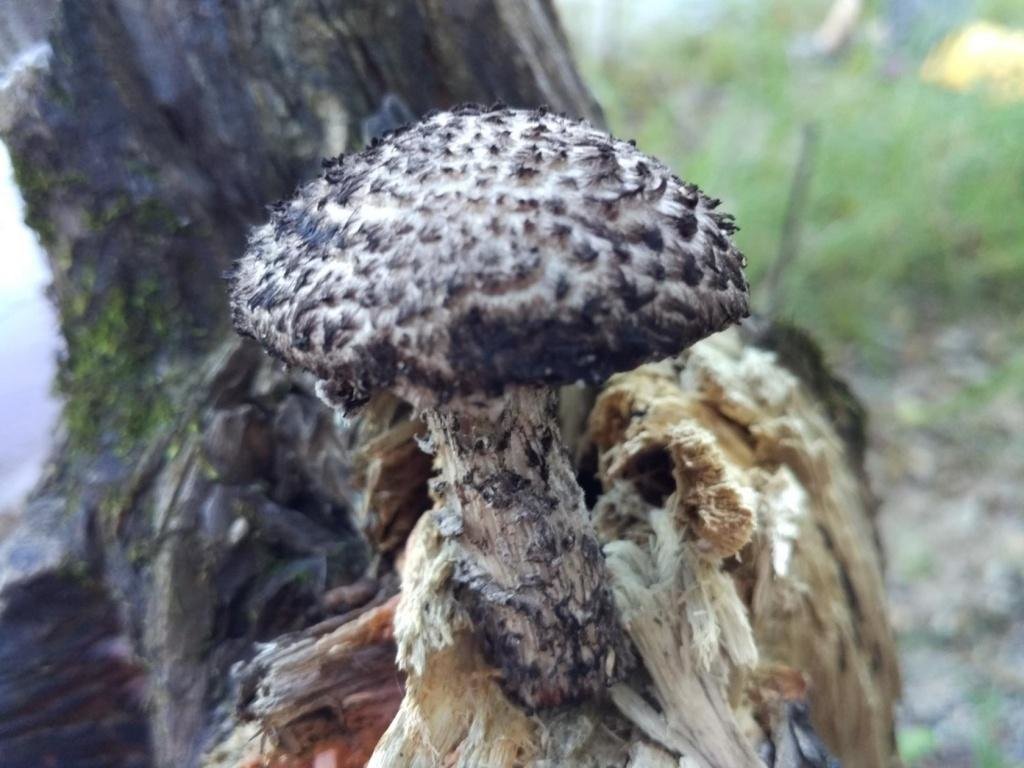
The next thing that falls under the keen eye of a mushroom picker is a leg. It is strong enough and does not become hollow even in old age. In length it can reach a maximum of 15 cm, but more often there are options when the leg is in the range of 7-10 cm. The thickness varies from 1 to 3 cm. It has the same shade as the hat. The leg itself is covered with scales, which are rather rough and at the same time fibrous to the touch. The base of the leg is rooted, the mycelium fits snugly. The mushroom loves to settle in such a way that the leg is almost half buried in the ground. This is because the mushroom desperately needs the warmth that the earth can give it.

Pulp
The flesh of the cotton leg mushroom has a white tint. Elastic, since when squeezed, the mushroom crumples well, but then it recovers.
In the context, when interacting with oxygen, the pulp quickly acquires a red tint, then, it becomes purple, and sometimes even dark, up to black. When interacting with saliva, as well as some alkaline drugs, the fungus acquires a blue undertone.
The pulp exudes a small amount of milky juice of a transparent shade. The mushroom tastes pleasant, a little spicy. Has a pronounced mushroom aroma.
When talking about pulp, one cannot but mention the controversy. If we consider the whole family of boletes, then the pineapple mushroom is exceptional among them. It is significantly different not only due to its interesting appearance, but also due to the special structure of the spores. They are so small, one might say, microscopic, that they are very difficult to see. They have a purple-brown hue, and sometimes overlap and turn black.
The shape is spherical and atypical for mushrooms.
The wall of the spores is significantly thickened and has a peculiar ornament. The spores are very light and easily spread by wind over long distances.

Where does it grow and at what time
Despite such a specific appearance, the pineapple mushroom can still be called a common mushroom. It can be easily found in the temperate zone, which is characteristic of the northern hemisphere. You will meet him in Russia, other CIS countries, in Europe, North America and even in Canada. However, this mushroom is preferred to be avoided due to its slightly specific appearance. Therefore, we know a lot about this forest dweller.
Pineapple rarely chooses the southern hemisphere for its growth and development, however, it is still found in the Krasnodar Territory, and in other countries in which the weather is more loyal.
For growth, it prefers mainly deciduous and mixed forests, less often it can be found in conifers.
Loves acidic soils and high hills at the same time. If the fungus is in the lowlands, it quickly begins to form mycorrhiza with other trees. Among the favorites are beech, maple, ash. If the mushroom has entered the coniferous forest, then it easily enters the mycorrhiza with pines or spruces. Fruiting singly or in very small groups.
Loves places where the sun practically does not penetrate and moderate humidity.But if, unfortunately, he finds himself in direct sunlight, he quickly loses in growth and becomes dry.

How to cook cotton leg mushroom
The cotton-footed pineapple mushroom is versatile in processing. Fruit bodies can be used to prepare meals and preparations for the winter. Mushrooms are fried, stewed, boiled, dried. There is no bitterness in the taste, there are no toxic compounds in the composition, so there is no need for preliminary soaking.
The crop is cleaned of soil residues, grass and leaves, the hard legs are cut off, and washed with hot water. It is dipped in salted water, citric acid is added, and left for 15-20 minutes. If there are insects in the fruiting body, they will leave it. The fruits are cut into arbitrary pieces and processed.
How to salt
Salted mushrooms do not differ in taste from those with high nutritional value: milk mushrooms, saffron milk caps, butter mushrooms. An uncomplicated recipe for salting Shishkogriba cottonleg is designed for 1 kg of fruit bodies; for cooking, you need salt (50 g) and spices to taste. Salting algorithm:
- The washed fruits are dried so that there is no liquid left.
- Prepare containers. If these are glass jars, they are poured over with boiling water, wooden or enameled dishes are cleaned with baking soda, washed well and treated with boiling water.
- Black currant or cherry leaves are placed on the bottom.
- Top with a layer of pine cones, sprinkle with salt.
- Add pepper and dill seeds.
- Sprinkle in layers, cover with leaves on top and add bay leaves.
- Cover with a cotton napkin or gauze, set the load on top.
They put the workpiece in a cool place, after a few days juice will appear, which should completely cover the fruit bodies.
Important! After 2.5 months, the cotton leg mushroom is ready for use.
How to pickle
Only the caps are pickled (regardless of the age of the mushroom). For the recipe take:
- Pineapple - 1 kg;
- bay leaf - 2 pcs.;
- sugar - 1 tbsp. l .;
- vinegar - 2.5 tbsp. l. (better than 6%);
- citric acid - ¼ tsp;
- salt - 0.5 tbsp. l .;
- water - 0.5 l.
Mushrooms, sugar, bay leaves, salt, citric acid are placed in the water, boiled for 20 minutes. During this time, jars are sterilized. Vinegar is added 5 minutes before cooking. The boiling mass is laid out in containers and rolled up with lids.
Useful properties and restrictions to use
It is difficult to talk about the beneficial properties of the pineapple mushroom, since it is rarely used in cooking. Also, due to its narrow prevalence, this fruit is not used either in folk or official medicine.
The restrictions on the use of this mushroom specimen are the same as for other breeds. That is, it is contraindicated:
- pregnant women;
- small children;
- nursing mothers;
- patients with stomach diseases;
- patients with pancreatitis or pancreatic enzyme deficiency;
- persons with impaired liver and gallbladder function.
Important!
It is strictly forbidden to use this mushroom with individual intolerance to any of its components.
It is not recommended to add this fruit to the menu for the elderly. The reason lies in a decrease in the activity of the pancreas with a parallel decrease in the level of enzymes. Also, in old age, the work of the gastrointestinal tract is inhibited, so the mushrooms cannot be fully digested in the intestines. If you do not neglect contraindications, then the mushroom will not be able to harm health.
Cotton-footed pine mushroom Strobilomyces strobilaceus (Scop.) Berk. [S. floccopus (Vahl) P. Karst.]
|
|
Taxonomic affiliation:
Family Boletovye - Boletaceae.
Conservation status of the species:
Vanishing.
Scientific significance:
immoral appearance. The only species of the genus and family in the mycoflora of Ukraine.
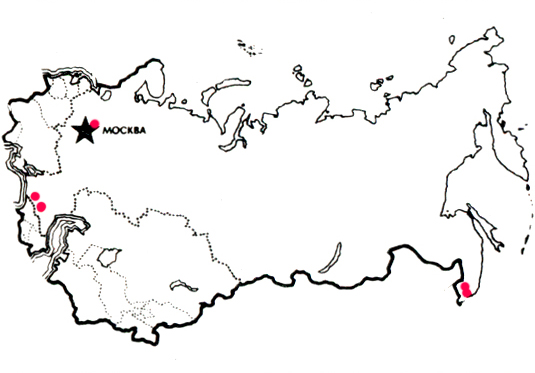
The area of the species and its distribution in Ukraine:
Eurasia, North. Africa, North and Central America. In Ukraine, it is known from the Carpathians, Transcarpathia, Western Ukrainian forests and Roztochya. Adm. regions: Lv, Tr, Zk, Chts.
Number and structure of populations:
It happens mostly singly, sporadically.
Reasons for the change in numbers:
Deforestation, collection by the population.
Growing conditions:
Deciduous, coniferous (predominantly spruce) and mixed forests, on the soil or the remains of rotten wood immersed in the soil.
General biomorphological characteristics
The cap is 4-10 cm in diameter, gray-brown to black-brown, with large skullcaps, often spaced oblique scales, with remnants of a veil along the edge. The tubules are 1-3 cm, whitish, with age they quickly turn gray to dark brown. The pores are large, angular. Spores 9.5-15 × 8-12 μm, rounded-oval, spherical, often reticulate, dark brown. The spore print is almost black. Leg 4-15 × 1 -3 cm, cylindrical, cap-colored, fibrous-scaly, densely fleshy, with a ring that quickly disappears. The flesh is whitish, turns red at the break, later turns black, with an unpleasant earthy odor. Fruiting bodies appear in July-October. Humus saprotroph.
Population conservation regime and protection measures:
It happens on the territory of the Carpathian Biological Zone and the Roztochye Root Zone, where it is protected as a rare representative of biodiversity. It is necessary to create botanical reserves in the locations of the species known outside the reserves, and to monitor the state of its populations.
Reproduction and breeding in specially created conditions:
There is no information.
Economic and commercial value:
Soil-forming. Edible mushroom.
Bazyuk, 2000; Bazyuk, Geluta, 1999a, b; Keys to mushrooms of Ukraine, 1979; Dudka, 2008; Red Data Book of the USSR, 1984; Fungi of Ukraine, 1996.
Areas of growth of the cone of the cotton leg.
The cotton-footed cone mushroom grows throughout the temperate zone of the northern hemisphere. Most likely, this species was introduced to the southern regions. You can find these mushrooms in summer and autumn. Their habitats are deciduous and coniferous forests. Pineapple prefers to settle on acidic soils, in hilly areas.

If the pineapple mushroom settles in a lowland, then it forms mycorrhiza with oaks there, and in higher places it is found under fir and spruce trees. This type of mushroom bears fruit in small groups or single specimens.
Evaluation of the edibility of the cone mushroom.
This mushroom does not contain poison, it can be safely collected, but it should be borne in mind that old specimens are poorly digested. In Germany, these mushrooms are considered inedible. And in America, the pineapple mushroom is valued as a good mushroom. In most European countries the pineapple mushroom is harvested but considered to be of low quality.

Related species of the cone clump.
In Europe, there is only one representative of this genus. In North America, a similar species grows - Strobilomyces confuses, but it is smaller in size, and its spores are not reticulate, but wrinkled.

In Australia, a relative of the cone mushroom grows. This species was first discovered on humus, in the forest, in Malaysia. The shape of its cap is convex, there are dark brown or black scales on its surface. The upper part of the leg is mesh. The pulp is dense, white, at the break it becomes brown-black.
Conclusions about the collection
Despite the fact that the mushroom is trying to multiply and revive at an accelerated pace, nevertheless, this does not save it from the fact that there are not enough such forest inhabitants left on the earth. Therefore, if suddenly you are lucky enough to meet the cotton-footed mushroom in the wild, we ask you, in any case, do not pluck it, do not cut it off and do not try to take it away with you. You will not make delicious dishes from it, because this mushroom will give you absolutely nothing. You will not get pleasant sensations from it by preparing any tinctures from it. Yes, and as a drug, this mushroom has not proven itself in any way.
Therefore, we strongly recommend that you just walk by, enjoying the beauty and uniqueness of this forest dweller. Let's hope that soon the population of these mushrooms will revive, which means that it will leave the pages of the Red Book and continue to grow, delighting us with its appearance.
(2 assessments, the average: 5.00 out of 5)