The flap is lead-gray: what it looks like, where it grows, a photo, is it possible to eat

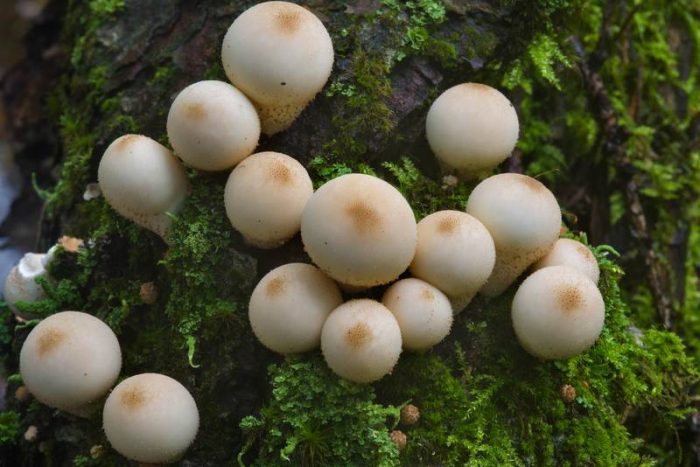
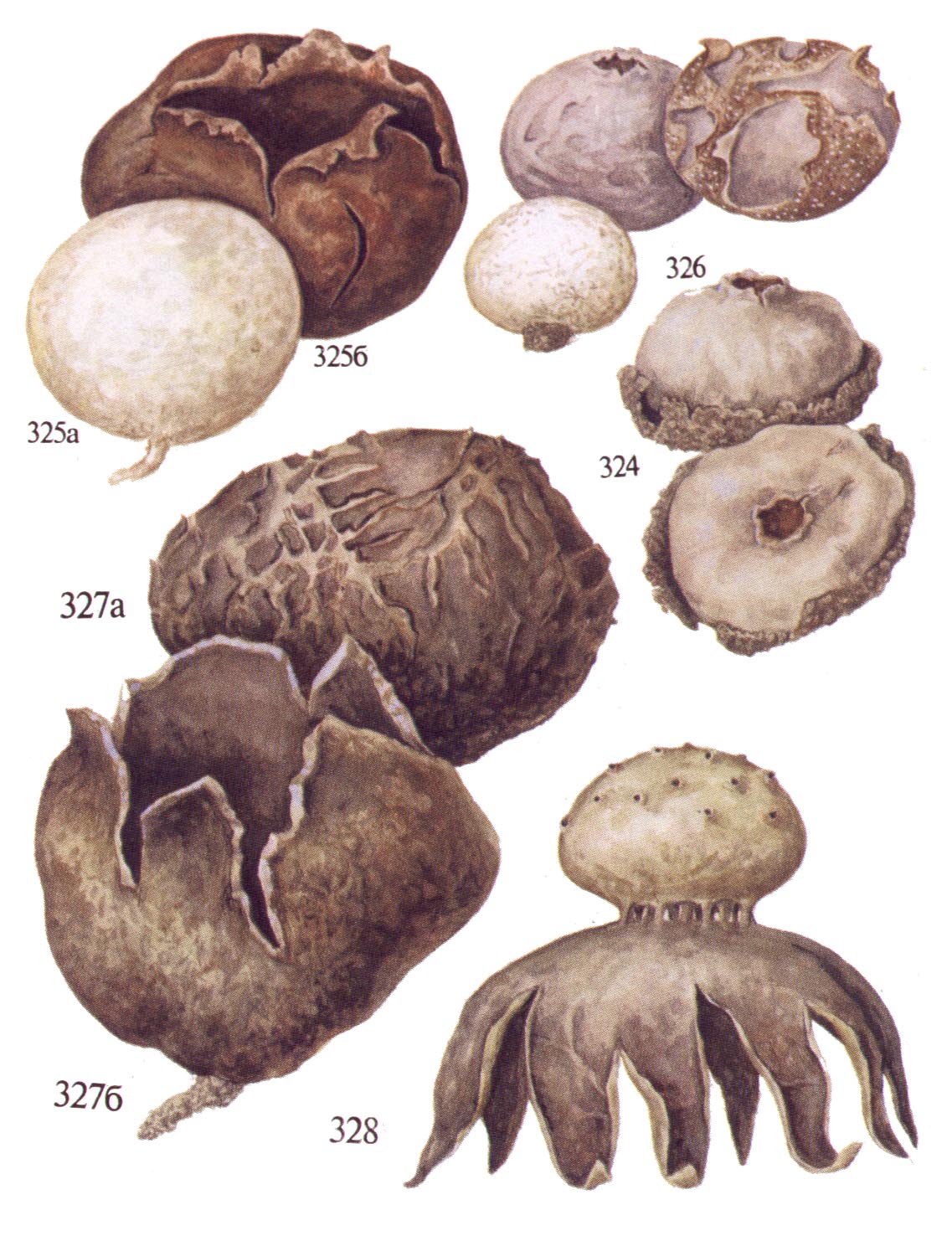
The lead-gray flap has the shape of a ball. White at a young age. When ripe, it becomes gray. The fruit body is small. The mushroom was first identified by the mycologist Christian Heinrich Person. It was he who, in his work in 1795, gave the mushroom the Latin name Bovista plumbea.
In scientific works, there are also designations:
- Bovista ovalispora;
- Calvatia bovista;
- Lycoperdon bovista;
- Lycoperdon plumbeum.
The most common name for this variety in Russian is Porkhovka lead-gray. There are others: Devil's (Grandfather's) tobacco, Lead raincoat.
Where the lead-gray flaps grow
They are thermophilic. They grow from early summer to autumn. They prefer areas with sparse grass. Growing places:
- lawns;
- parks;
- meadows;
- roadsides;
- embankments;
- sandy soil.
How lead-gray flaps look
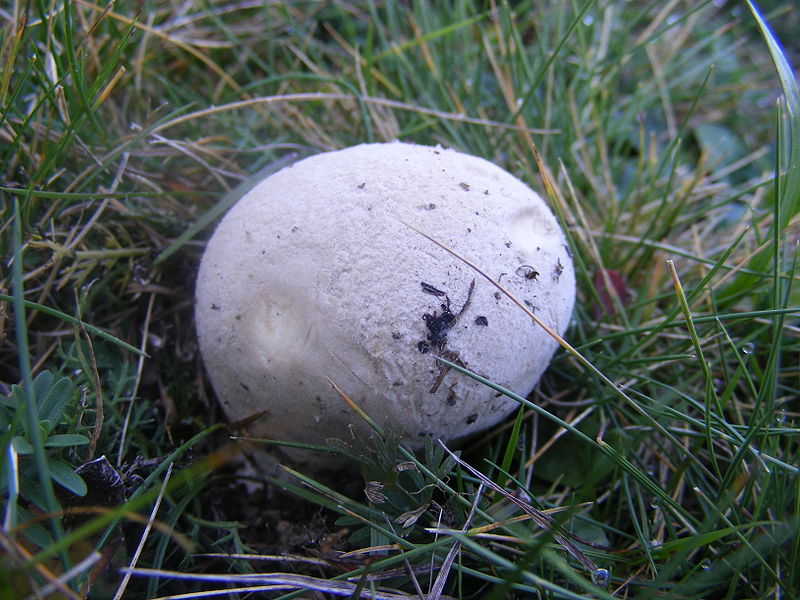
Fruit bodies are rounded. They are small in size (1-3.5 cm in diameter). The leg of the lead-gray flap is absent. The spherical body goes directly to the root system. It consists of a thin mycelium. They grow in groups.
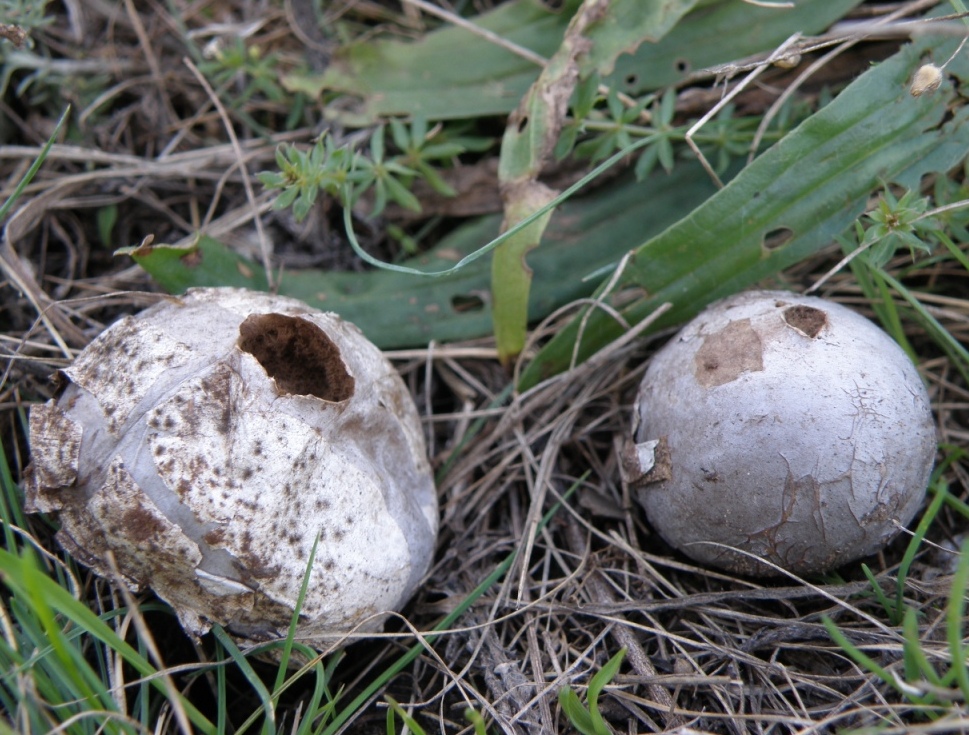
White first (both inside and outside). Over time, the lead-gray flare acquires a yellow tint. At maturity, the color ranges from grayish brown to olive brown. The pulp is snow-white, elastic. Then it turns gray or black-green, as it fills with ripe spores. There may be more than a million of them. Stepping on an adult, darkened raincoat, a cloud of dust appears.
The spore print is brown. The seed powder exits through the apical pore formed at the top of the fungus.
Is it possible to eat lead-gray flares
Lead-gray flap is an edible mushroom. It can only be eaten at a young age when the flesh is completely white.
Mushroom taste
The taste of the lead-gray flutter is rather weak. Some people don't feel it at all. The smell is pleasant, but barely perceptible.
Important! It belongs to the 4th category. This means that the taste is not good enough.
This variety is ranked as type 4 in a larger sense due to its very small size. Such mushrooms are recommended to be eaten as a last resort when there are no alternatives. The 4th category also includes russula, oyster mushrooms, dung beetles.
Benefits and harm to the body
Lead-gray flap is not in demand among mushroom pickers, although it increases immunity quite well, strengthens the cardiovascular system. On its basis, doctors make anticancer drugs.
It contains the following minerals:
- potassium;
- calcium;
- phosphorus;
- sodium;
- iron.
Has the ability to absorb heavy metals and other toxic substances. Once in the body, the fungus absorbs harmful elements, then removes them.
But the ability to absorb substances from the environment can be harmful. The fungus absorbs toxic components from the soil, accumulates them in tissues, and when it enters the human body, releases them. Therefore, the lead-gray flap should not be collected along roadsides and in ecologically unfavorable areas.
False doubles
This mushroom can be confused with other raincoats. For example, with Vascellum field. It differs from the lead-gray flap in the presence of a small stem and a diaphragm that separates the spore-bearing part.
Possible confusion with neighboring species is quite harmless. But there is a mushroom that, being young, looks like a lead-gray flap. This is a pale toadstool. It is very dangerous - 20 g is enough to cause death.
At an early age, the mushroom also has an ovoid, rounded shape, but is wrapped in a film. The pale grebe is distinguished by a sweetish, unpleasant odor, the presence of a leg. Its fruit body is rounded, but not as merged as that of the flap. Spore print white.
Collection rules
Only young mushrooms should be picked.They should not have dark spots. Pigmented areas on the fruiting body indicate the beginning of the formation of spores and the loss of nutritional properties and taste.
Use
Lead-gray flap contains 27 kcal per 100 g. Rich in protein (17.2 g). It is fried, stewed, pickled, salted, added to soups and stews.
Conclusion
Lead-gray flap is an excellent food product, as it is saturated with trace elements. Very beneficial to health due to its absorbent properties. And despite belonging to the 4th category of edibility, it is tasty and nutritious.
It is important not to confuse her with a pale toadstool.
What does it look like, where it grows, photo, is it possible to eat
Lead-gray flap: description and photo, edibility
The lead-gray flap has the shape of a ball. White at a young age. When ripe, it becomes gray. The fruiting body is small. The mushroom was first identified by the mycologist Christian Heinrich Person. In fact, in his own work in 1795, he gave the mushroom the Latin name Bovista plumbea.
In scientific works, there are also definitions:
- Bovista ovalispora;
- Calvatia bovista;
- Lycoperdon bovista;
- Lycoperdon plumbeum.
The most popular name for this variety in Russian is Porkhovka lead-gray. There are others: Devil's (Grandfather's) tobacco, Lead raincoat.
How lead-gray flaps look
Fruit bodies are rounded. Smaller (1-3.5 cm diameter). The leg of the lead-gray flap is absent. The spherical body goes directly to the root system. It consists of a thin mycelium. They grow in groups.
Primarily white (both in the middle and on the outside). With some period of time, the lead-gray flare acquires a shade of yellow. At maturity, the color can vary from grayish brown to olive brown. The pulp is white, plastic. Then it turns gray or black-green, as it fills with ripe spores. There will be much more than a million of them. Stepping on an adult, darkened raincoat, a cloud of dust appears.
The spore print is brown. The seed powder exits through the apical pore appearing at the top of the fungus.
Is it possible to have lead-gray flaps
Lead-gray flap is an edible mushroom. It can only exist at a young age, when the pulp is full of white.
Mushroom flavor qualities
The taste of the lead-gray flutter is rather weak. Some people do not feel it at all. The aroma is pleasant, but barely perceptible.
This variety is ranked as type 4 by and large due to its very small size. Similar mushrooms are advised to be available in the exceptional case when there are no alternatives. The 4th category also includes russula, oyster mushrooms, dung beetles.
Benefits and damage to the body
Lead-gray flap is not in demand among mushroom pickers, although it increases immunity very well, strengthens the cardiovascular system. On its basis, doctors make anti-cancer drugs.
It contains the following minerals:
Has the ability to absorb heavy metals and other toxic substances. Once in the body, the fungus absorbs harmful parts, and then removes them.
But the ability to absorb substances from the external environment can be harmful. The fungus absorbs toxic elements from the soil, accumulates them in the tissues, and when it gets into the human body, it releases them. Therefore, the lead-gray flap should not be collected along roadsides and in environmentally unfavorable areas.
False doubles
This mushroom can be confused with all other raincoats. For example, with Vascellum field. It differs from the lead-gray flutter by the presence of a small stem and a diaphragm that separates the spore-bearing part.
The potential confusion with neighboring species is fairly harmless. However, there is a mushroom that, when young, looks like a lead-gray flap. This is a pale toadstool. It is very dangerous - 20 g is enough to cause death.
At a young age, the mushroom also has an ovoid spherical shape, but is wrapped in a film. Pale toadstool stands out with a sweetish, fetid odor, the presence of a leg.Its fruit body is rounded, but not as merged as that of the flap. Spore print white.
Collection rules
Only young mushrooms should be picked. They should not have dark spots. Pigmented areas on the fruiting body indicate the beginning of the formation of spores and the loss of nutritional parameters, the quality of taste.
Consumption
The lead-gray flap has 27 kcal in 100 g. Rich in protein (17.2 g). It is fried, stewed, pickled, salted, added to soups and stews.
Conclusion
Lead-gray flap is considered an excellent food product, as it is saturated with trace elements. Very beneficial to health due to its absorbent properties. And regardless of belonging to the 4 category of edibility, it is tasty and nutritious
It is important not to confuse it with a pale toadstool.
Why is a mushroom raincoat useful: medicinal and useful properties
In order to understand why the raincoat mushroom is useful, you should know that calvacin is found in the pulp of the fruit bodies, which has antibiotic (bacteria, fungi) and anticancer effects. Pure mycelial cultures exhibit high antitumor activity.
Spore preparations promote the elimination of radionuclides, heavy metals, toxic fluorine and chlorine compounds, toxins after helminthiasis, hepatitis, dysbacteriosis, acute inflammation of the kidneys. The medicinal properties of the raincoat mushroom are widely used in traditional and folk medicine.
Traditional medicines based on Langermannia spores effectively reduce blood viscosity, high blood pressure, help with angina pectoris, gastrointestinal diseases, and strengthen immunity in the treatment of benign and malignant tumors. In Bulgarian medicine, water infusions of spores are used internally for diseases of the bladder, including bladder cancer. The beneficial properties of the raincoat mushroom can effectively increase the level of the body's immune defense.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Ash willow: a bush or a tree?
Spores can be safely applied to the bleeding surface of the wound and used externally as a pain reliever and for the healing of festering wounds and skin malignant ulcers.
Spore preparations are also used for diseases of the lymphatic system and sarcoidosis, endocrine diseases (goiter, diabetes, adrenal dysfunction), pulmonary tuberculosis, tuberculous intoxication, pleurisy, bronchial asthma.
How not to do
However, there are a number of contraindications. First, bypass the adult bighead. A mushroom that has managed to overripe is not suitable for food. He has accumulated in his pulp such a quantity of toxins that in terms of destructive power he can compete with all kinds of fly agarics and toadstools.
Young mushrooms are completely safe. However, even they cannot be included in the menu for children under eight years old. This limitation applies to absolutely all forest mushrooms, since the child simply does not have enough enzymes necessary to digest and assimilate mushrooms.
Otherwise, there are no taboos. Cook bighead mushrooms the way you like, eat it yourself and treat your guests.
Did you know that one of the species of this mushroom got into the Guinness Book of Records because of its enormous size? Such a bighead was found in England, and its growth reached 1.7 m in height. It is often confused with a raincoat, but these are completely different types. How it looks, as it is called by the people, and most importantly where the collection time grows, you will learn from this article.
The first question is: is the mushroom edible or not? Is it worth taking him home or is it better to walk by? Of course, Golovach or in Latin Calvatia from the mushroom family is edible, belongs to the fourth category in terms of taste.
The baggy bighead is considered the best for eating. Only young specimens can be eaten, since in adulthood the mushroom cap breaks to release the spore powder from the pulp or scientifically gleba.
Giant Golovach
The Latin name is Calvatia gigantea. Other names: Langermany.
Peculiarities:
A spherical hat, slightly flattened, can grow up to one meter in diameter and weigh up to 35 kg.At a young age, milky white, turns brown with aging and becomes unsuitable for food. The pulp resembles cottage cheese or marshmallow. It grows rapidly, so small specimens are practically not found. It is unique in its size and weight.
Where it grows:
In forests of any type, prefers acidic and nitrogen-containing soils, likes forest outskirts, meadows and pastures, found in parks. Grows singly or in a small group.
When it grows:
From August to September, after heavy rains, in the south of the country it grows to November.
Baggy golovach
The Latin name is Calvatia utriformis. Other names: round, saccular head.

Type of:
Edible, 4th category. The inside of the hat is suitable for eating. You need to collect only young specimens, while the pulp is white. Be sure to remove the skin before cooking. Suitable for frying, can be eaten raw.
Peculiarities:
The main difference: the surface of the cap has a warty structure, it grows in diameter up to 20 centimeters. Has a false stem. Young specimens are white, turn yellow over time and become brown in old age. The pulp with a pleasant smell, sterile and able to stop bleeding.
Where it grows:
In deciduous forests and mixed types, can be found on forest edges, meadows, glades and gardens. It grows mostly alone.
When it grows:
May to September.
Golovach oblong
The Latin name is Calvatia excipuliformis. Other names: elongated raincoat.
Peculiarities:
Unlike its counterparts, it has a club-shaped cap, and not a spherical one. It grows up to 15 centimeters in length and up to 5 centimeters in diameter. With age, it turns from white to brown. In youth, they have growths on the surface, old ones are smooth. Over time, the cap breaks and falls off completely.
Where it grows:
In deciduous and coniferous forests, young plantings, throughout Russia. Loves bright places, meadows and edges. It grows both singly and in groups.
When it grows:
July to October.
Composition and calorie content of flashing
This mushroom cannot claim to be the most useful of all. It is significantly inferior in its chemical composition to boletus, mushrooms, chanterelles, mushrooms. It is appreciated for its high percentage in the composition of various micro and macro elements. There are not so many vitamins in it to seriously consider this product as their source.
The calorie content of flashing per 100 g is 27 kcal, of which:
- Proteins - 4.3 g;
- Carbohydrates - 1.5 g;
- Fat - 1 g;
- Water - 81.5 g;
- Ash - 1.2 g;
- Dietary fiber - 2.1 g.
Vitamins per 100 g:
- C, ascorbic acid - 6 mg;
- B1, thiamine - 0.09 mg;
- B4, choline - 13.2 mg;
- B6, pyridoxine - 0.07 mg;
- D, calciferol - 0.06 mg;
- PP, niacin - 1.245 mg.
Macronutrients per 100 g:
- Potassium, K - 215 mg;
- Magnesium, Mg - 11 mg;
- Sulfur, S - 23 mg;
- Phosphorus, Ph - 72 mg;
- Calcium, Ca - 95 mg.
Microelements per 100 g:
- Aluminum, Al - 25 μg;
- Iron, Fe - 0.038 mg;
- Iodine, I - 7 mcg;
- Rubidium, Rb - 21 μg;
- Zinc, Zn - 0.42 mg;
- Selenium, Se 2 - 55 mcg.
The composition of the flask also includes digestible carbohydrates, represented by glucose and dextrose. In 100 g, they are contained in a total aggregate of no more than 2.5 g. These substances are important for brain function and satisfying hunger. The mushroom includes a few amino acids, essential, non-essential and fatty. The latter make it extremely beneficial for the health of the heart, blood vessels and mental activity. After heat treatment, the amount of these substances remains practically the same, in contrast to vitamins, micro- and macroelements, of which about 20% is lost.
Due to the presence of protein and calcium in the composition, flashing is a valuable substitute for animal products - milk, meat, fish. This allows adherents of a plant-based nutrition system to successfully take care of teeth, joints, tissues and just general well-being.
Benefits and harm to the body
This specimen is not considered a valuable species, since it is inferior in chemical composition to mushrooms, mushrooms, chanterelles and boletus. But the composition of the fruiting body includes a large number of macro- and microorganisms.Blackening Porkhovka also contains rapidly digestible carbohydrates, which are responsible for brain function and satisfying hunger.
The benefits of flashing blackening:
- increases hemoglobin;
- strengthens bone tissue;
- removes toxins and toxins;
- strengthens the heart muscle;
- slows down cell aging;
- improves digestion.
Important! To improve the functioning of the body, it is necessary to use this type in small quantities and only in boiled form. Porkhovka also has contraindications
Mushroom dishes are not recommended:
Porkhovka also has contraindications. Mushroom dishes are not recommended:
- children under 5 years old;
- people with peptic ulcer disease and severe heart disease.
Since this species has poisonous specimens, only an experienced mushroom picker should be able to collect the flap.
Summer and autumn large mushrooms with round fruit bodies
Field raincoat (Vascellum pratense).

Family: Raincoats (Lycoperdaceae).
Season: summer - autumn.
Growth: in small groups, rarely singly.
Description:

The fruiting body of this large mushroom is round, usually with a flattened apex. A transverse septum separates the spore-bearing spherical part from the leg-shaped part. Young fruiting bodies are white, then gradually turn light brown.

The pulp of the spore-bearing part is at first dense, white, then becomes soft, olive.

The base is slightly narrowed.
Ecology and distribution:
It grows on soil and humus in fields, meadows and glades.
Common pseudo-raincoat (Scleroderma citrinum).

Family: Sclerodermataceae.
Season: July - mid September.
Growth: singly and in groups.
Description:

The shell is hard, warty, ocher tones, reddens in places of contact.

The fruiting body is tuberous or spherical-flattened
Sometimes there is a tapered process.

The flesh is light, very dense, whitish sometimes with a spicy odor; with age, it quickly darkens to purple-black. The flesh of the lower part always remains white.
This autumn mushroom is inedible and in large quantities can cause gastrointestinal upset.
Ecology and distribution:
It grows in light deciduous forests, in young plantings, in sparse grasses, on bare sandy and clay soil, on roadsides, in glades.
Giant raincoat (Calvatia gigantea).

Family: Champignon (Agaricaceae).
Season: May - October.
Growth: singly and in groups.
Description:

The fruit body is spherical, at first white, turns yellow and turns brown as it ripens. The shell of the ripe mushroom is cracked and falls off.

As it ripens, the pulp turns yellow and gradually turns olive brown.

The pulp of a young mushroom is white.
Ecology and distribution:
It grows on the edges of deciduous and mixed forests, in fields, meadows, steppes, in gardens and parks, in pastures. It is rare.
Summer truffle (Tuber aestivum).

Family: Truffle (Tuberaceae).
Season: summer - early autumn.
Growth: fruiting bodies are underground, usually shallow, old mushrooms sometimes appear above the surface
Description:

The fruit body is tuberous or round.

The surface is from brown-black to bluish-black, covered with black pyramidal warts.

The pulp is initially very dense, in older mushrooms it is looser, the color changes from whitish to brownish-yellow with age. The taste of the pulp is nutty, sweetish, a strong pleasant smell is compared to the smell of algae. Light veins in the pulp form a marble pattern.
This edible tuberous or round mushroom is considered a delicacy, but less prized than other true truffles.
Ecology and distribution:
Grows in mixed and deciduous forests in calcareous soils, usually under the roots of oak, beech, hornbeam, birch. Very rare in coniferous forests. Yellowish flies swarm over the areas where truffles grow at sunset. Distributed in Central Europe, in Russia it is found on the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus.
Detection: Trained dogs are used to search for truffles.
Views:

Red truffle (Tuber rufum) is common in Europe and North America; found in Siberia.

Winter truffle (Tuber brumale) is common in France and Switzerland.

Black truffle (Tuber melanosporum) is the most valuable truffle. Most often found in France.

White truffle (Tuber magnatum) is most common in northern Italy and neighboring regions of France.
Share article:
Pepper mushroom
This mushroom has another well-known name - pepper oil can. It belongs to the Boletov family. This mushroom is inedible. But, despite this, it is used in cooking. The question arises, how if it cannot be eaten? Due to its special pungent taste, pepper mushrooms are used to make seasonings. True, such a spice should be added to food in small portions.
The taste of this mushroom is very similar to pepper, from which the name of the variety came from.
Its size is not very large. The hat can be either two centimeters or five, the color of which is orange, red, brown. The stem of a pepper mushroom is 7 cm long, it is somewhat lighter than the cap.
The growth period is in the fall. You can find such a mushroom in a deciduous forest, and sometimes in a coniferous forest.

Blackening flap: what it looks like, edibility
| Name: | Blackening flap |
| Latin name: | Bovista nigrescens |
| Type of: | Conditionally edible |
| Specifications: |
|
| Systematics: |
|
Porkhovka blackening is a conditionally edible species of the Champignon family. This specimen is referred to as rain mushrooms, in appearance it resembles a bird's egg. This mushroom is edible, but only young representatives of the species are used in cooking. Since this family contains poisonous and inedible specimens, in order not to harm your body, you must carefully read the external data, view photos and videos.
Porhovka mushroom (Bovista): where it grows, when to collect, species, photo

| Latin name: | Bovista |
| English name: | To be specified |
| Domain: | Eukaryotes |
| Kingdom: | Mushrooms |
| Department: | Basidiomycetes |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Agaric |
| Family: | To be specified |
| Genus: | Raincoat |
| Edibility | Edible mushroom |
Flap or puffer belongs to the genus Lycoperdon, a little-known edible mushroom.
Hat
The fruit body is spherical, 1.5-3 cm in height, 1.5-3.5 cm in diameter. Outside, the surface of the mushroom is white, from the inside it is lead-gray.
Where flaps grow
Porkhovka grows on fertile soils in deciduous and coniferous forests, it can also grow along forest roads and paths, in meadows and places for grazing livestock. In general, this mushroom is undemanding to habitats and is found everywhere in Eurasia.
Edible flutter
In cooking, porkhovka has not gained much popularity, however, young mushrooms they give a delicate taste and pleasant aroma to any of the dishes in the preparation of which they are used.
For use in food, the flask is dried or boiled, the mushroom is always thoroughly cleaned from the tough skin beforehand. Also, young flies are used fried and baked, pickled and salted.
The fleshy pulp of this mushroom with a pleasant taste is an excellent addition to salads and sauces, first courses and broths, pies and pizzas.
Poisonous and inedible species of mushroom porkhovka
Similar poisonous species of mushrooms for flitting have not been described. It is sometimes confused with the inedible Scleroderma citrinum mushroom, which has a very tough black flesh and a rough, warty skin.
Common pseudo-raincoat (Scleroderma citrinum)
The diameter of the fruit body reaches 6 cm, its shape is tuberous, the surface is smooth or finely scaly, dirty yellow or brownish. Thick warts appear on the upper yellowish part of the fungus during cracking.
The lower part of the fungus is wrinkled, naked, narrowed, on it there is a bundle of tapered mycelium fibers. The shell is 2-4 mm thick. Inside, the flesh of young mushrooms is white.
In mature specimens, it turns black, with white fibers, and gradually turns into an olive-brown spore powder, after which the shell at the top of the fungus breaks. The smell of the pulp of the common pseudo-raincoat is similar to raw potatoes.
Common pseudo-raincoat is found in deciduous and coniferous forests, near roads, on forest edges, prefers clay and loamy soils, grows from August to September.
The mushroom is inedible in large doses. It is harmless when 2-3 pieces of it are mixed with other types of mushrooms. In cooking, it is occasionally used due to the fact that it tastes and smells like truffles.
Calorie content of the mushroom porkhovka
The calorie content per 100 g of fresh porkhovka mushroom is 27 kcal. Energy value:
- Proteins: ……………………. 4.3 g
- Fats: ……………………. 1.0 g
- Carbohydrates: ………………… 1.0 g
Interesting facts about the mushroom
Young specimens of flutter outwardly resemble bird eggs that have fallen out of the nest. Mushroom pickers discover their mistake only when they try to lift such an "egg" and find a small leg in it.
It is not recommended to collect flaps after rain. Like all raincoats, this species absorbs moisture, so instead of a mushroom, you can get a soggy mass.
Porkhovka contains special enzymes, thanks to which the mushroom is used to treat cancer.
This mushroom is advised to be eaten with mental fatigue, severe fatigue, anemia, uremia.
It is good for inclusion in the diet of vegetarians and those who do not eat meat, as it contains the proteins the body needs, as well as fats and carbohydrates, so that flap can be a complete substitute for meat and meat products.