Danger of use
Semi-white pain is not poisonous. Nevertheless, when using it, you should follow some rules:
- Don't eat too many mushrooms.
- It is best to eat sick at lunchtime or in the evening, but no later than a few hours before bedtime.
- Try to combine mushrooms with a variety of side dishes. Eating a lot of "pure" mushrooms can cause severe heartburn.
It is worth excluding the consumption of yellow boletus in such cases:
Age up to 10 years. The digestive system is not yet sufficiently formed in children. Eating yellow boletus, especially in large quantities, can lead to colic, abdominal pain, belching. The mushroom contains a large amount of fiber, which is not very suitable for a child's stomach.
The semi-white pain contains disaccharides
In this regard, people with type 1 or 2 diabetes should eat it with extreme caution. And it is best to exclude the semi-white mushroom from their diet altogether.
Also, you should not eat mushrooms for those people who have serious kidney problems. This is due to the fact that such products may contain an increased concentration of nitrates.
In addition, do not forget that the semi-white one hurts, like other mushrooms, is capable of absorbing various toxins and other harmful substances from the soil and air. So do not collect them in the immediate vicinity of highways and other contaminated places.
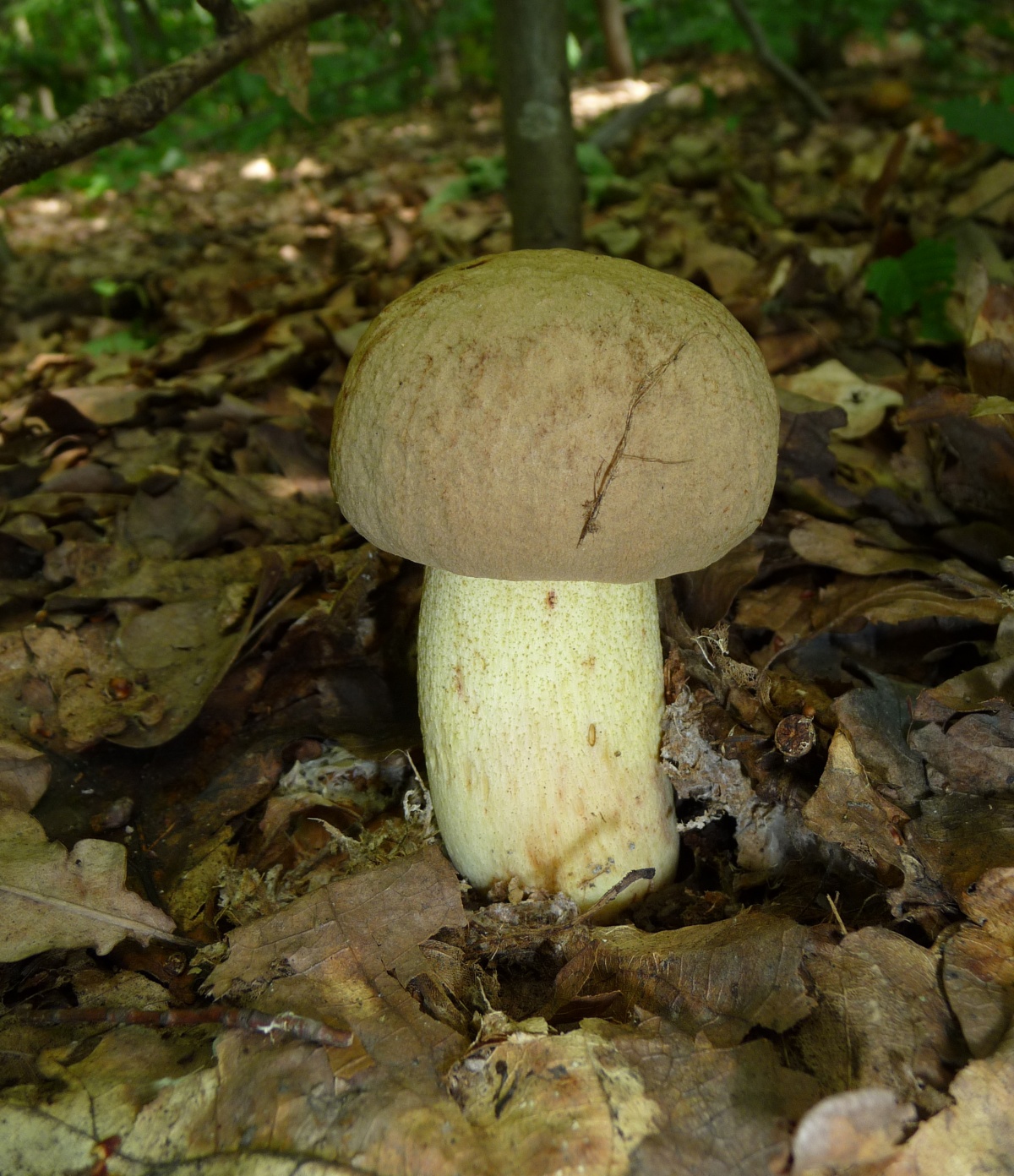
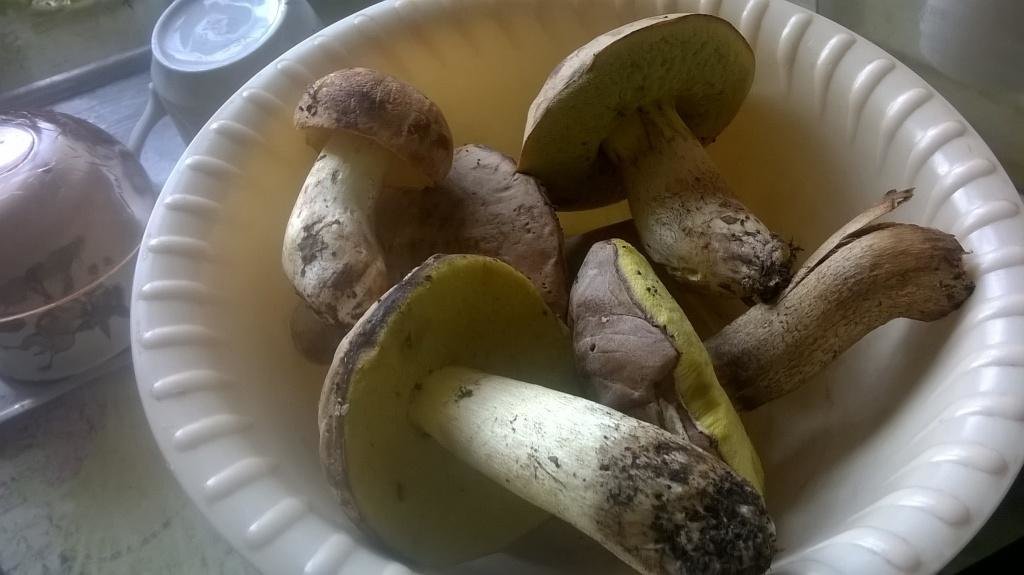
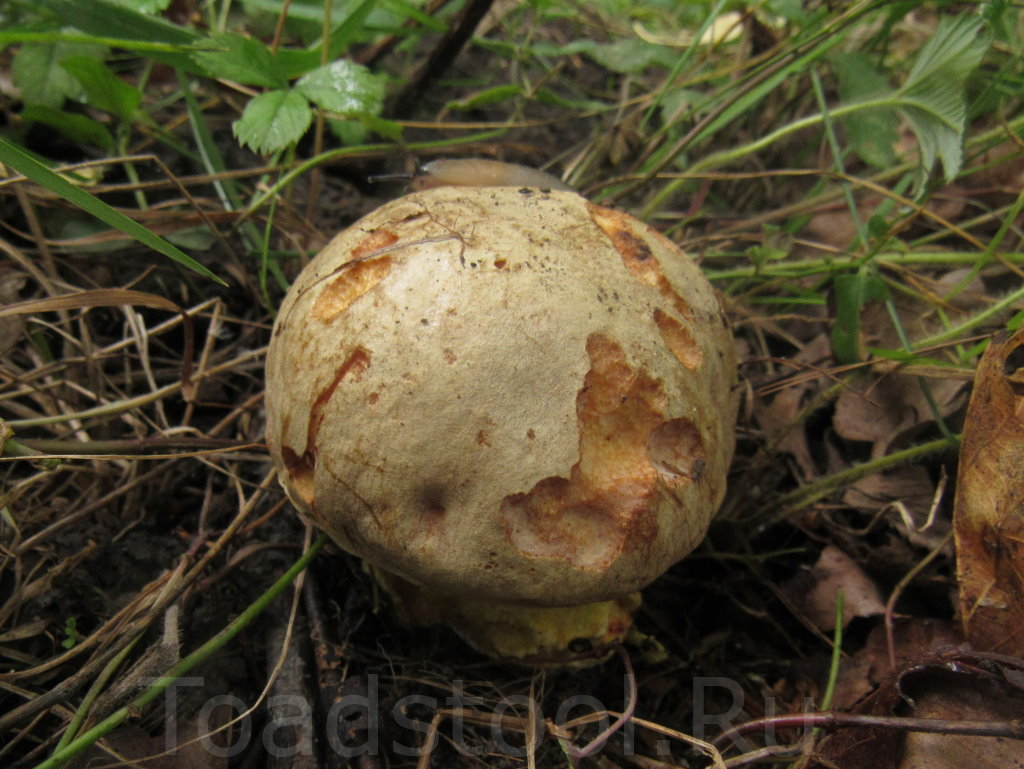
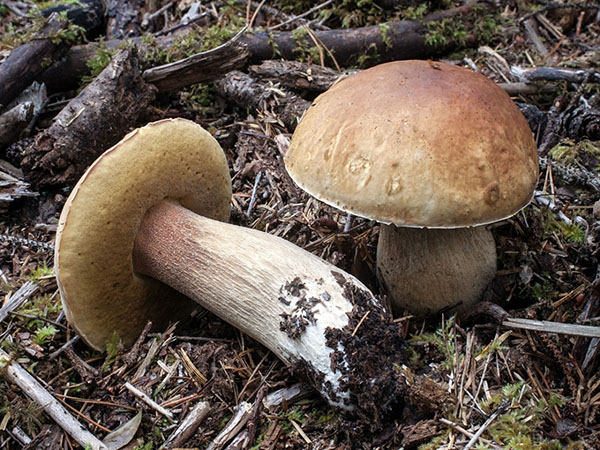
Half white mushroom
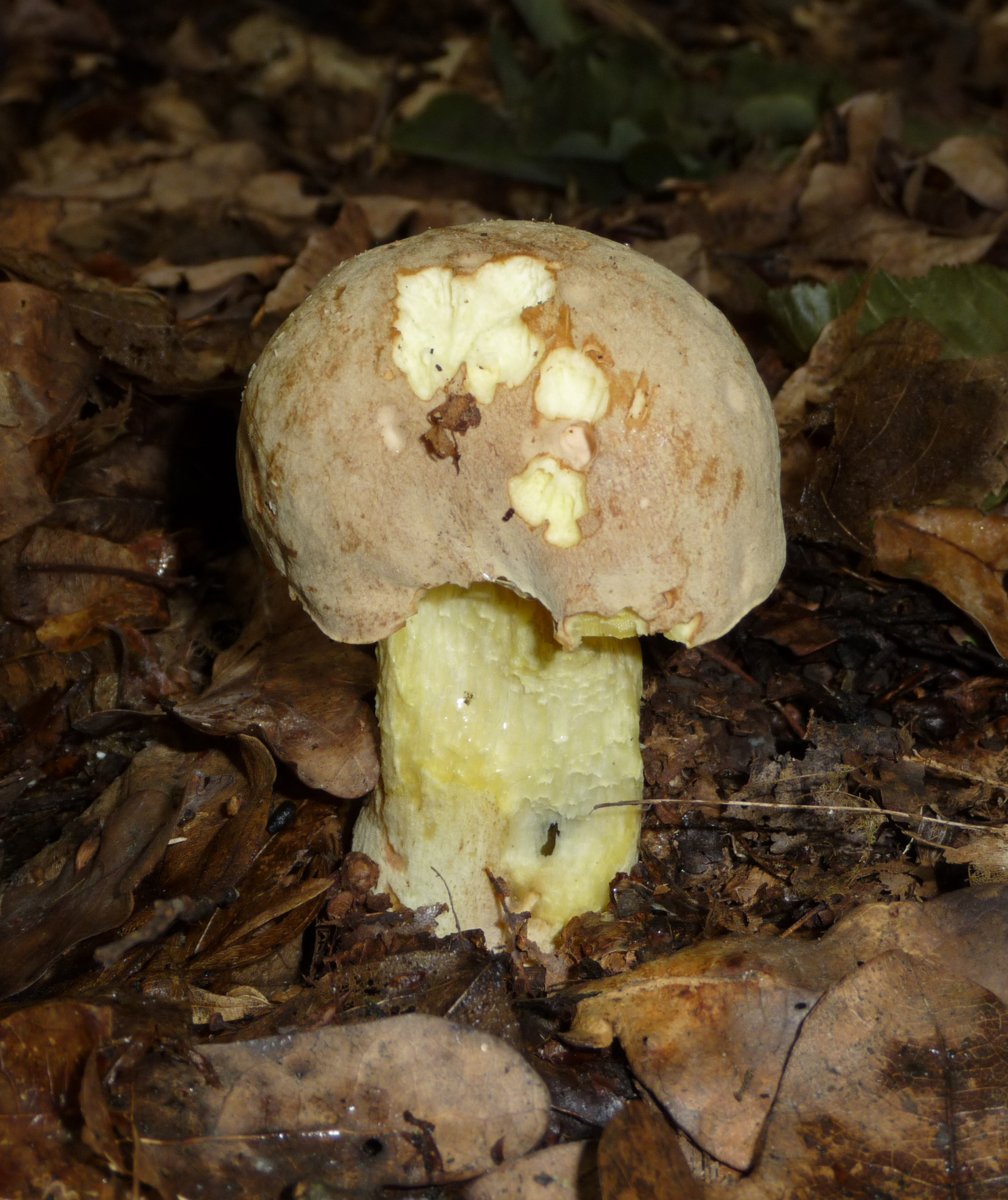
Semi-white mushroom - Boletus impolitus
In another way, he is called yellow Borovik or semi-white Bolet.
A rare mushroom, the distribution sites of which need protection.
External characteristics of the species
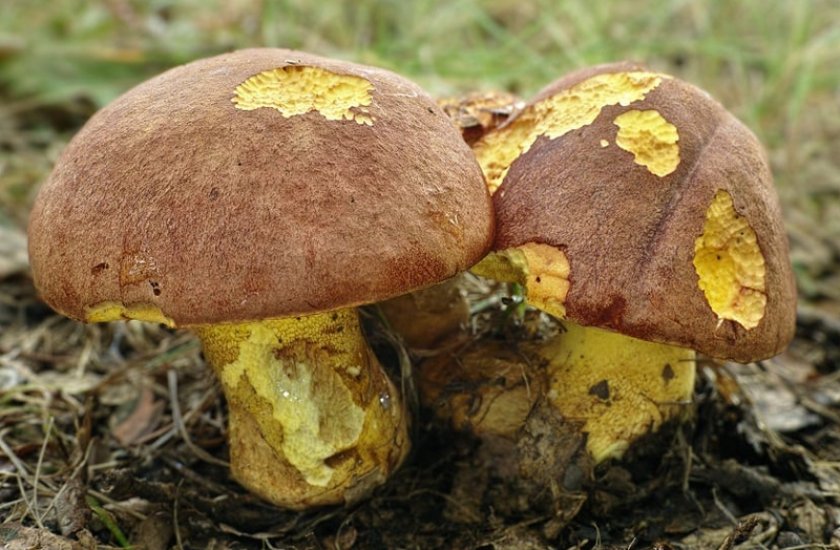
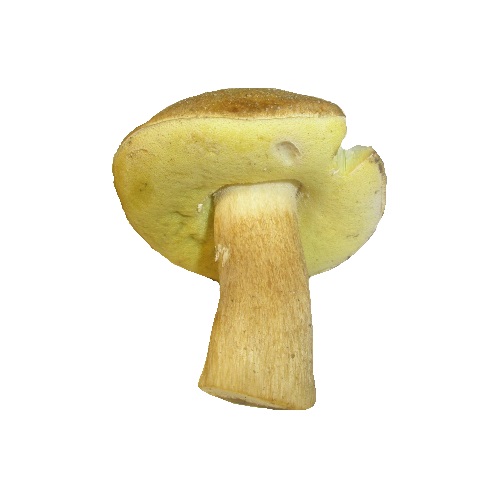
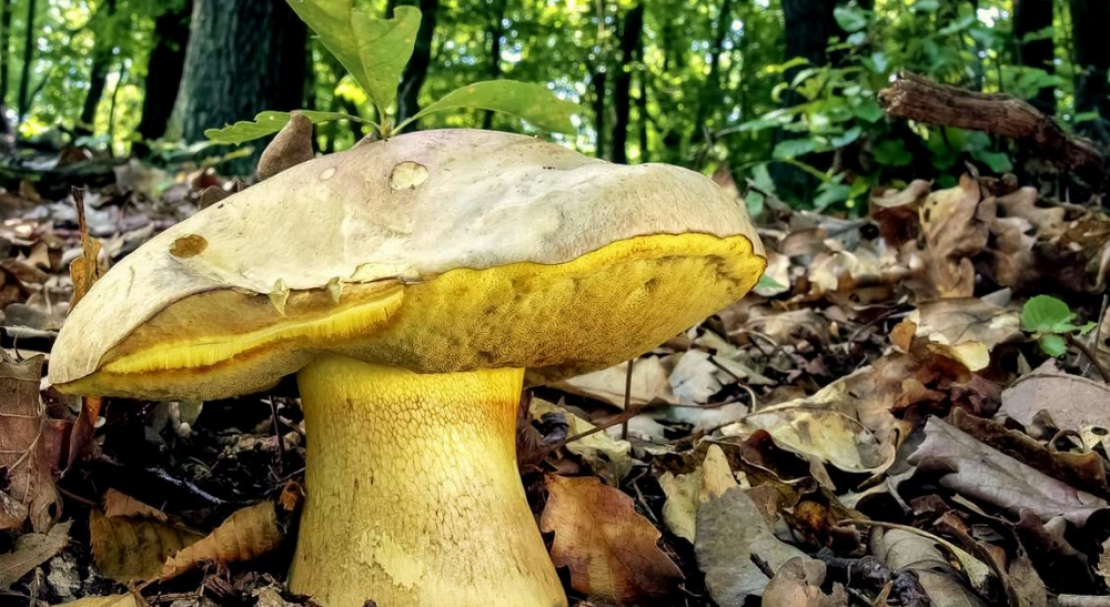
Mushroom cap
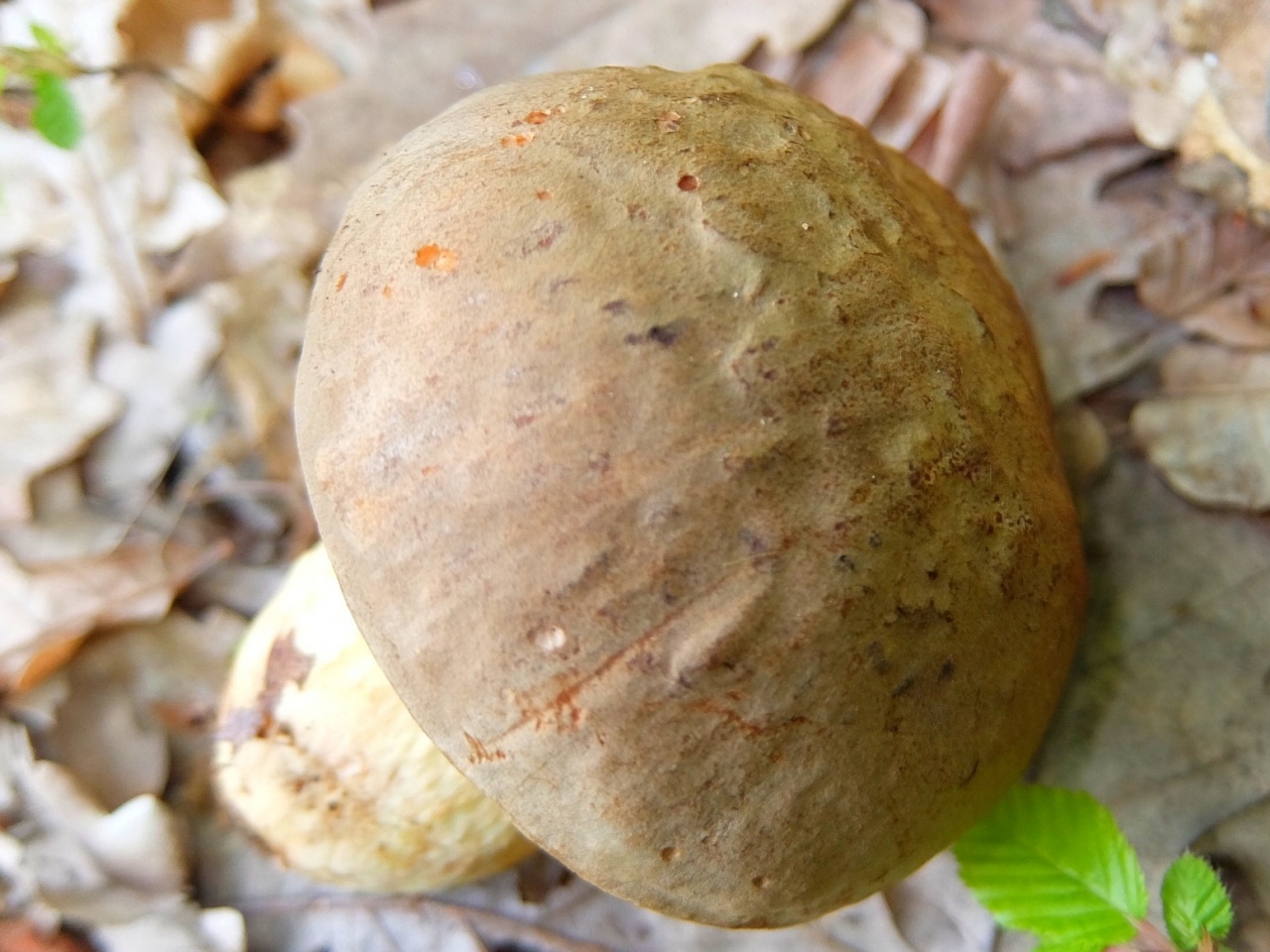
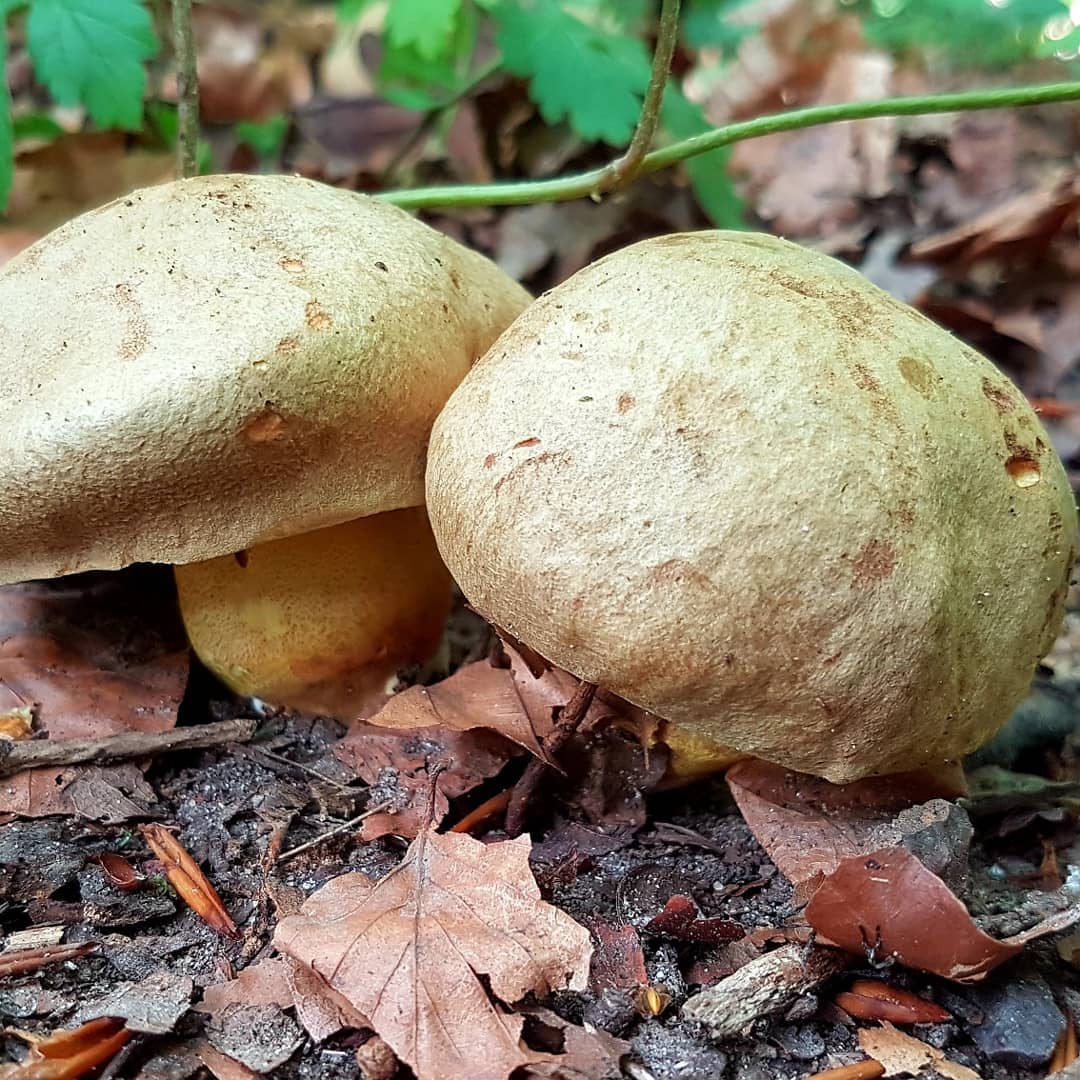
Boletus of this species grows a hat from 5 to 20 cm in diameter, at first it grows convex, later acquires a prostrate or partially prostrate appearance.
Young hats are covered with a velvety skin that becomes smooth over time. They are colored clay with an orange tint or have a pale gray tinged with olive.
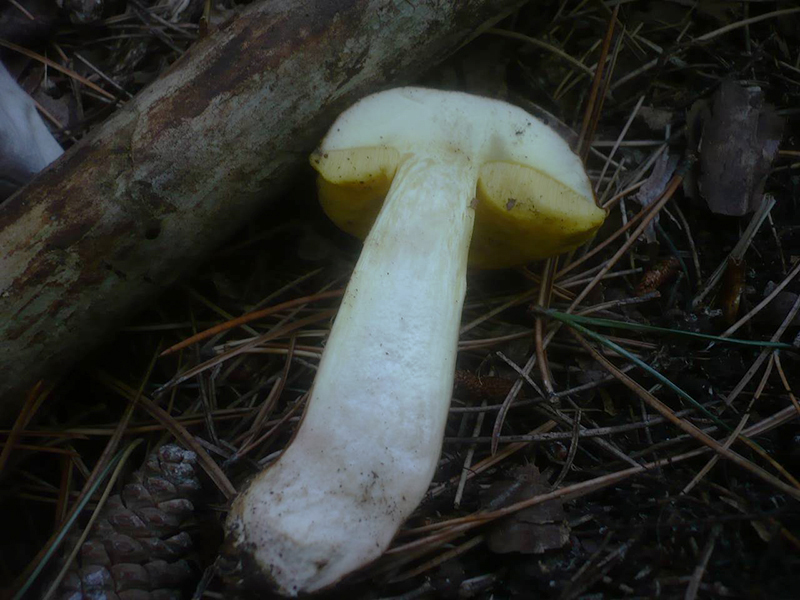
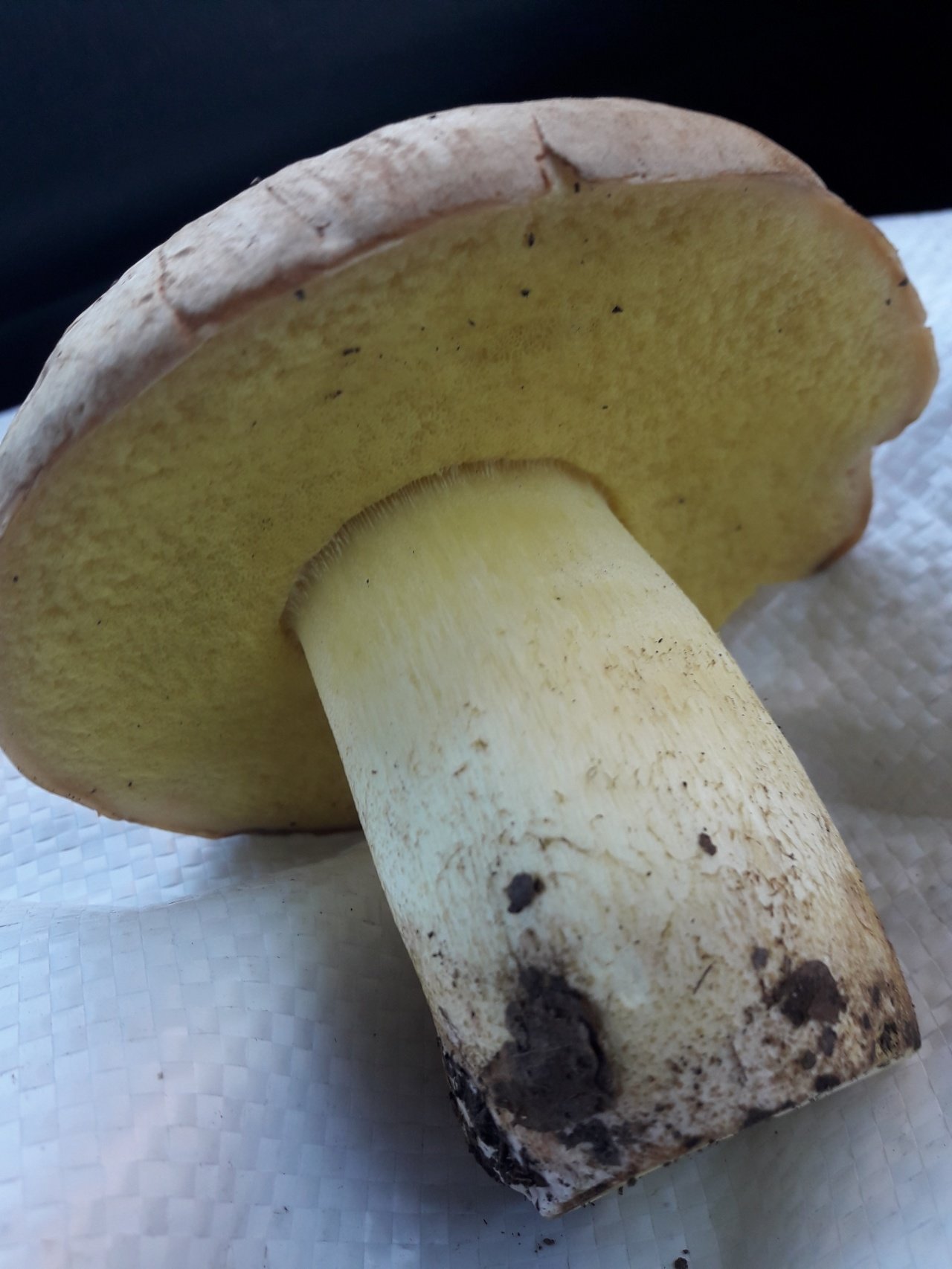
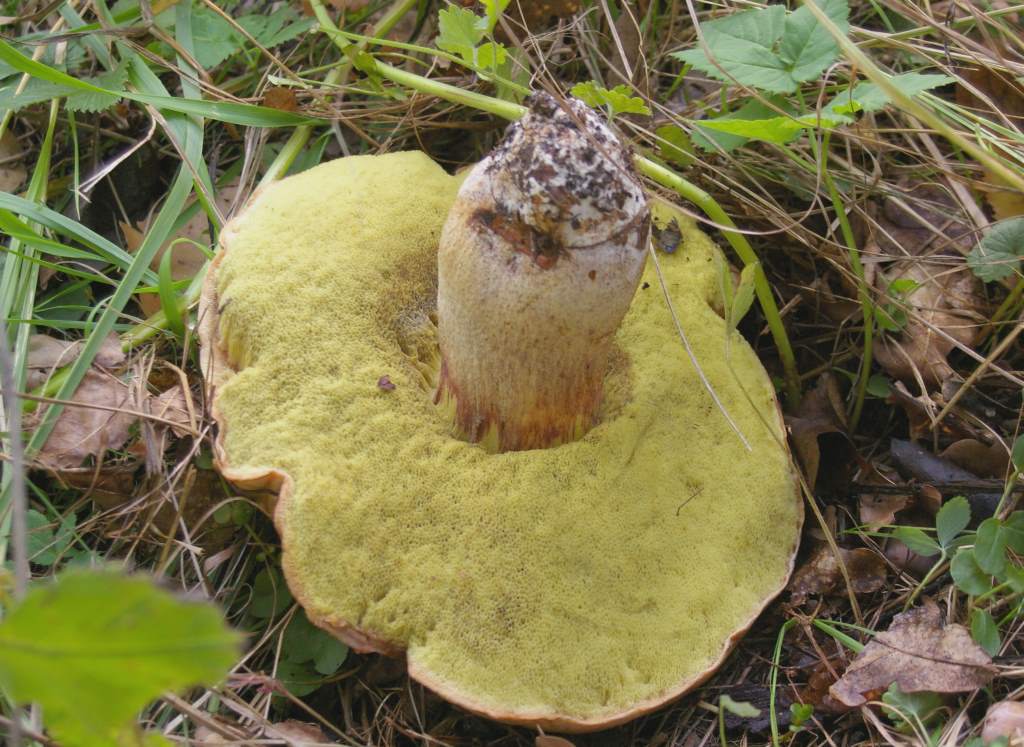
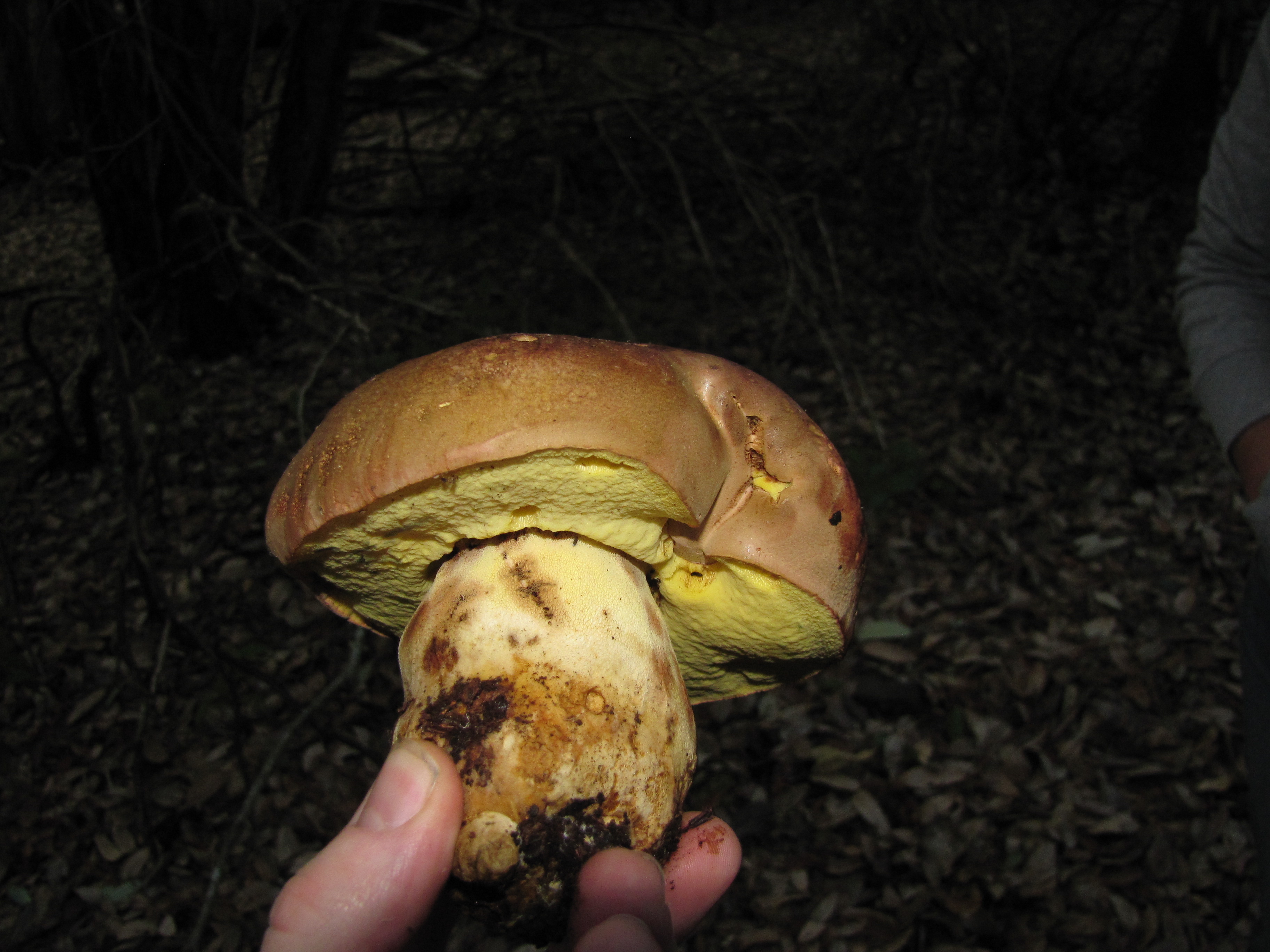
Under the cap there is a free tubular mass of light yellow or golden-yellow hue, which acquires a yellow-green color in adulthood. If you press on it, it does not change color.
When Boletus semi-white ripens, ocher-olive round-angular small spores are formed.
This boletus has thick light yellow flesh and bright yellow near the tubular mass. When cut, it rarely changes color, only occasionally turns slightly pink or blue.
Stipe
The legs of the Semi-white mushroom reach 30-60 mm in diameter and grow up to 6-10 cm in height. In young fungi, they are stocky and rounded - swollen, later become cylindrical, reticulate or dotted, not smooth to the touch and fibrous.
Above they turn yellow, below they acquire a dark brown color. The pulp is colored in a rich yellow tone.

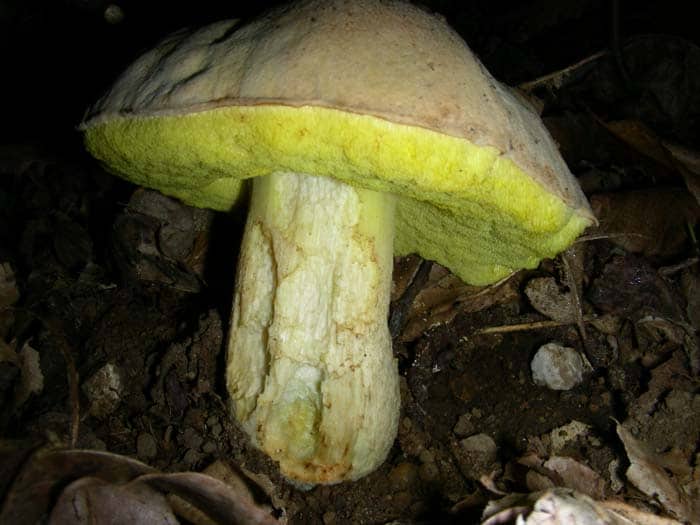
Semi-white mushroom - Boletus impolitus
Where does boletus grow
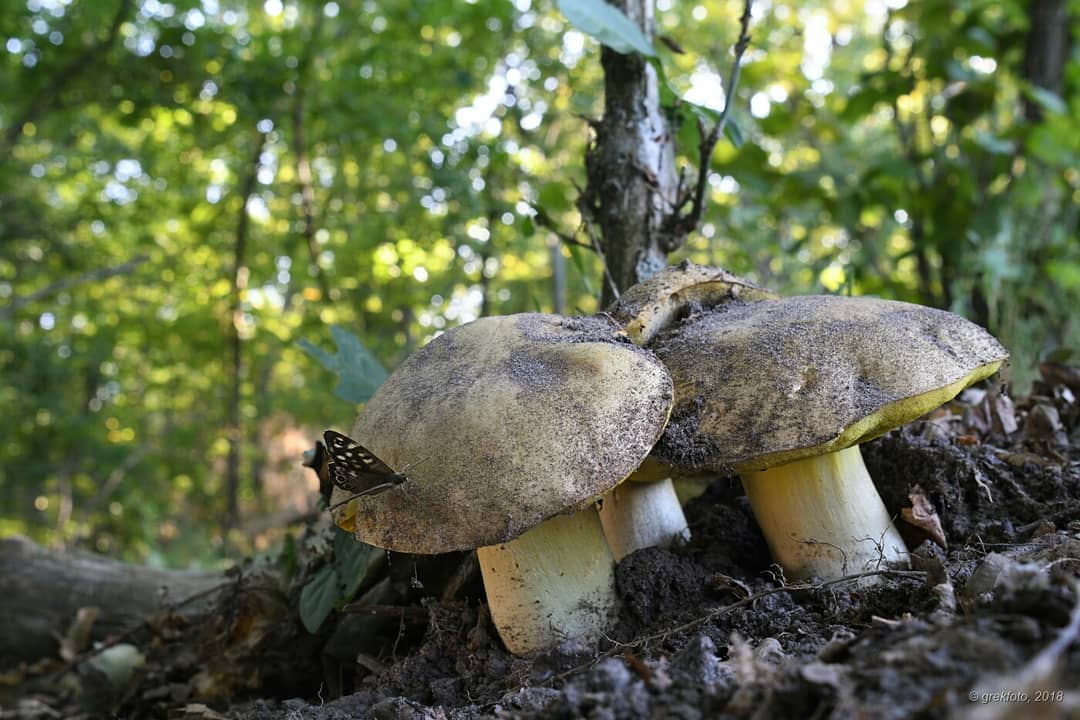
The fungus, which prefers soils rich in limestone and a warm climate, is found in conifers, under beech and oak trees, in a beech-hornbeam forest with dogwood bushes.
Fruiting of this very rare fungus is not observed every year, it is scarce and abundant, and occurs at the end of May - beginning of autumn.
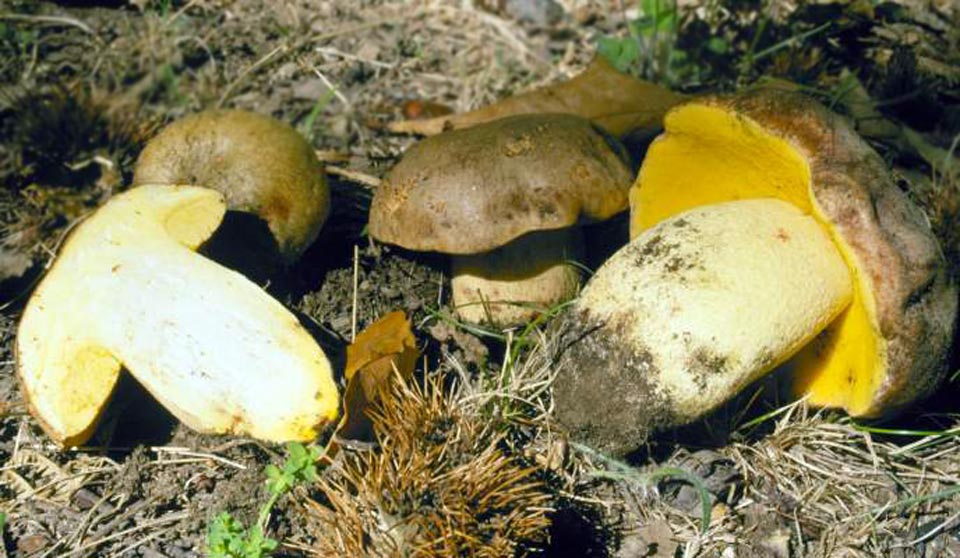
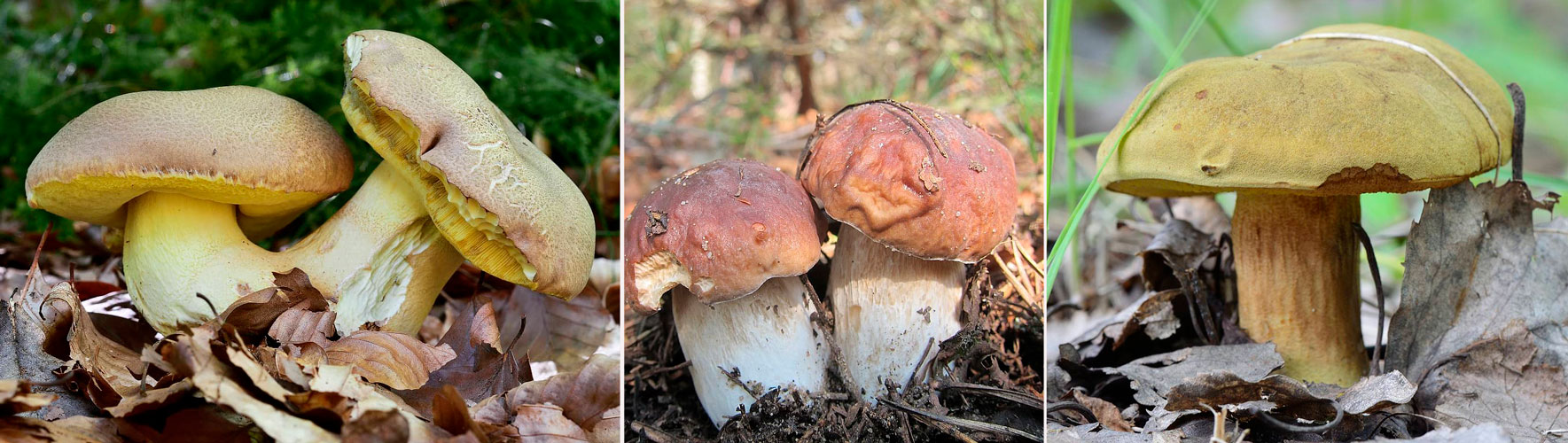
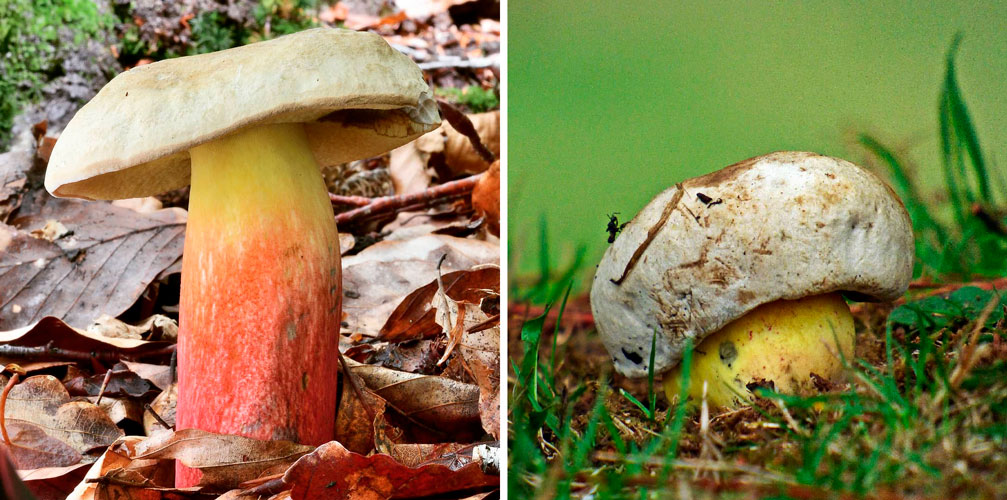
Similar species
Edible
- White mushroom;
- Girl's bolette.
In contrast to them, the semi-white Bolet's pulp is colored in a different color and emits the smell of carbolic acid.
Inedible
Deep-rooted fly. It is distinguished by a lemon-yellow leg and a pale gray hat, and is bitter in taste. And if you press on his pores, they immediately turn blue.
The edibility of the mushroom
The semi-white mushroom has a sweetish aftertaste; after pickling, it acquires no less noble taste than its white counterpart, and a beautiful pale golden color.The smell of carbolic acid, emanating from the raw pulp, disappears after cooking.

Description of the mushroom
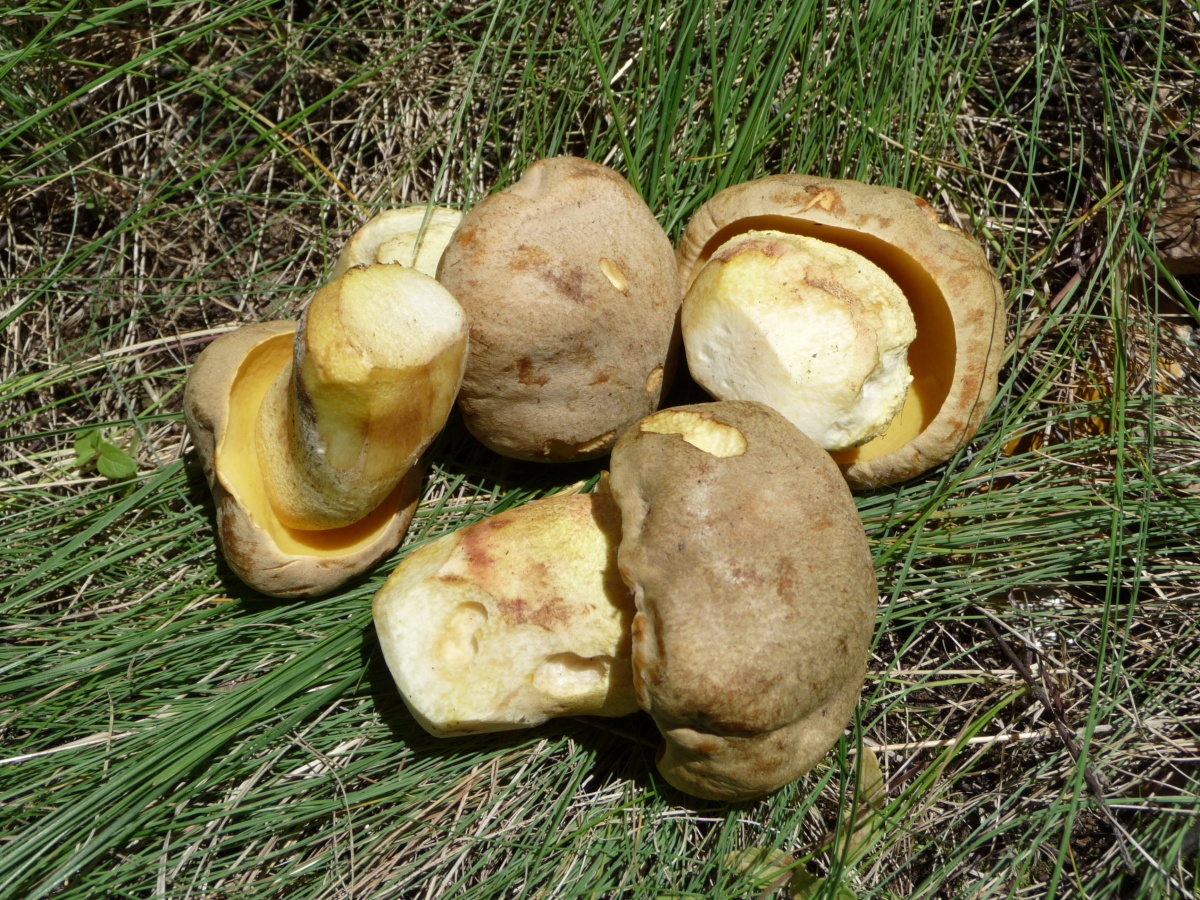
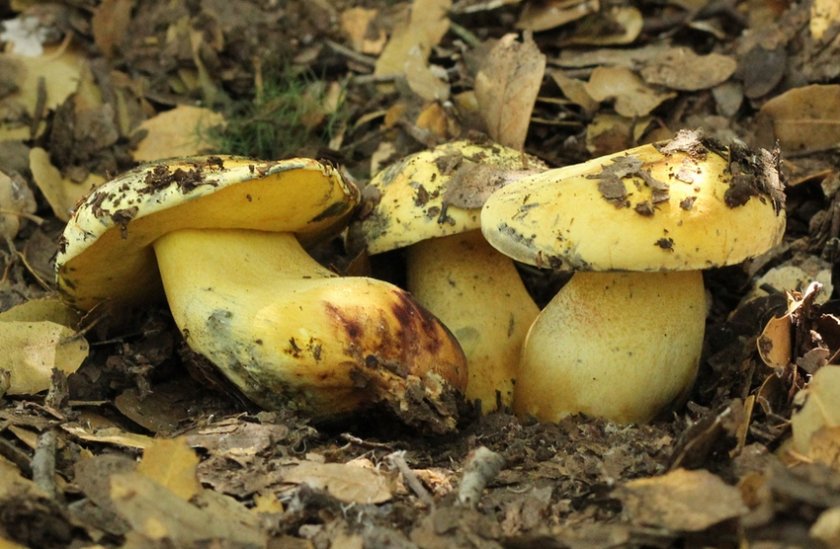
This edible mushroom belongs to the Boletov family. The diameter of its cap can reach 20 cm. In young organisms, it is convex, but later acquires a cushion shape. The cap has a velvety surface; in older mushrooms it becomes smooth, sometimes cracking. The color varies from light yellow with a reddish tint to dark brown.
This mushroom has a soft massive yellowish flesh. The color does not change when damaged, but sometimes turns a little pink when cut. There is a faint smell of carbolic acid, which disappears during cooking. The hymenophore has a tubular porous layer, its thickness is 2-3 cm... The pores are small, rounded. The hymenophore is colored golden yellow or pale yellow in young specimens and greenish yellow in older specimens. When pressed, they do not change color (do not turn blue), they can only darken slightly
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
For boletus yellow, or semi-white mushroom, as well as for a number of other mushrooms, the presence of twins - edible and inedible is characteristic. So, novice mushroom pickers can confuse it with edible species: maiden boletus and green moss. In this case, there will be no problems, because these mushrooms are also edible. But if they take a beautiful boletus or rooted boletus (deep-rooted) for a semi-white mushroom, then problems cannot be avoided.
Boletus often grow under beeches, oaks and in coniferous forests on calcareous soil. They bear fruit abundantly, but not every year. This type of mushroom belongs to the thermophilic and on the territory of Russia it can be found in the central and southern strip of the European part of the country.
 Boletus edulis
Boletus edulis
.
 Boletus luridus
Boletus luridus
 Suillus luteus
Suillus luteus

 imleria badia¸ boletus badius
imleria badia¸ boletus badius
 Macrolepiota procera
Macrolepiota procera


What are the signs of mushroom poisoning
A false white mushroom can be a real challenge for a mushroom picker. Its toxins are able to penetrate the bloodstream upon contact with the skin. As a result, headaches, weakness, and muscle discomfort appear.
Despite the fact that such ailments disappear quickly enough, after a couple of days or even a week, abnormalities in the functioning of the liver may appear.
If such symptoms occur, you need to consult a doctor in a timely manner so that the ailments do not turn into cirrhosis of the liver.
In recent years, there has been a dangerous tendency among mushroom pickers - to eat even inedible mushrooms. They claim that even toadstools can become a delicacy if cooked properly.
However, it is not. Even with long and careful soaking, toxic substances remain in the false porcini mushroom, which slowly but surely poison the human body, causing the main blow to the liver.
There is no need to spend personal time collecting toxic mushrooms, health is always more expensive, even if false mushrooms resemble noble ones, which are difficult to pass by.
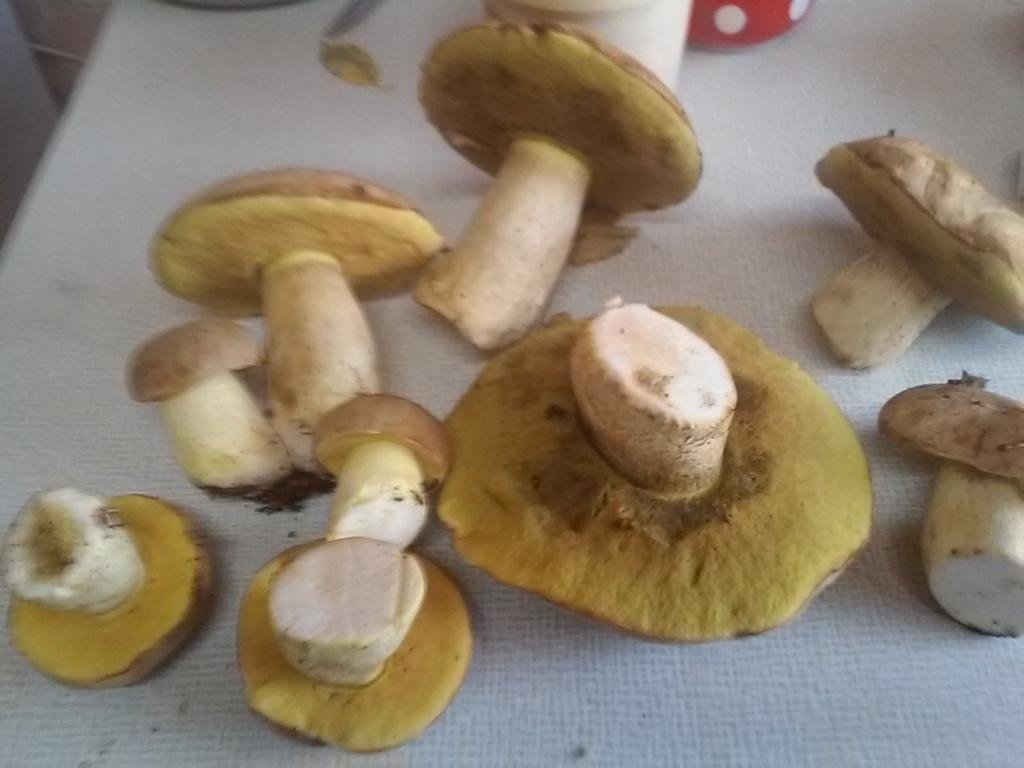
Semi-white mushroom: edible or not, description, photo

There are many types of mushrooms that are used in cooking and medicine. They also include a semi-white mushroom, it is also called yellow boletus. It is often found in coniferous and moist deciduous forests between May and late September.
Description of semi-white mushroom
Description of the mushroom
This edible mushroom belongs to the Boletov family. The diameter of its cap can reach 20 cm. In young organisms, it is convex, but later acquires a cushion shape. The cap has a velvety surface; in older mushrooms it becomes smooth, sometimes cracking. The color varies from light yellow with a reddish tint to dark brown.
The leg width reaches 6 cm, height - up to 11 cm. Its surface is rough to the touch, light yellow in color. The leg is widened at the base.
This mushroom has a soft massive yellowish flesh. The color does not change when damaged, but sometimes turns a little pink when cut. There is a faint smell of carbolic acid, which disappears during cooking.
The hymenophore has a tubular porous layer, its thickness is 2-3 cm.The pores are small, rounded. The hymenophore is colored golden yellow or pale yellow in young specimens and greenish yellow in older specimens.
When pressed, they do not change color (do not turn blue), they can only darken slightly
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
For boletus yellow, or semi-white mushroom, as well as for a number of other mushrooms, the presence of twins - edible and inedible is characteristic.
But if they take a beautiful boletus or rooted boletus (deep-rooted) for a semi-white mushroom, then problems cannot be avoided.
Boletus often grow under beeches, oaks and in coniferous forests on calcareous soil. They bear fruit abundantly, but not every year. This type of mushroom belongs to the thermophilic and on the territory of Russia it can be found in the central and southern strip of the European part of the country.
Beneficial features
The semi-white mushroom has a wide range of beneficial properties. It contains amino acids and vitamins that are essential for the body to function. Boletus nutritional value:
- water - 86.4;
- mono- and disaccharides - 1.11;
- unsaturated fatty acids - 0.41;
- saturated fatty acids - 0.41;
- ash substances - 0.93;
- dietary fiber 3-3.21.
Trace elements contained in these mushrooms help to strengthen hair, restore skin tone and normalize the thyroid gland. Vitamins A, B and zinc help relieve fatigue, cope with stress and nervous tension.
Contraindications
A semi-white mushroom is not dangerous to the body. It is worth being careful when collecting, because it is easy to confuse it with poisonous counterparts.
Like other species, the semi-white mushroom absorbs toxins that are in the soil. You should not collect it near roads, large cities and industrial enterprises (on the territory of their sanitary zone). Before cooking, be sure to soak the mushrooms in salt water for 30 minutes: this will help get rid of harmful elements.
growing methods
Yellow boletus is easy to grow on a personal plot
Only the presence of coniferous and deciduous trees is important.
Overripe fruits are used to obtain spores. They are poured with water for a day, then filtered and the resulting liquid is poured over the soil under the trees. The first crop will appear in 2-3 years.
Another way to grow a semi-white mushroom is to use soil that contains mycelium.
To do this, you need to find it in the forest and carefully dig out soil with a radius of 25-30 cm and a thickness of 15 cm.The selected mycelium is placed in a garden bed to a depth of 7 cm, watered abundantly and covered with leaves
Conclusion
Semi-white mushroom (yellow) is edible. It is a thermophilic species. It is found in coniferous and deciduous forests. It is used in cooking for pickling, drying and first courses.
It contains many beneficial vitamins and amino acids. Also boletus yellow is used in folk medicine to strengthen immunity and treat a number of diseases.
It is grown independently on personal plots.
Description
If you collect boletus for cooking, it is worth finding out how they differ from other similar mushrooms. The accidental inclusion of false boletus or their counterparts in food can make it inedible and sometimes dangerous.
The false white mushroom (Tylopilus felleus) was first described by the French mycologist Pierre Bulliard in 1788. It was first named Boletus felleus. He was assigned to the same genus as the real boletus. But later it was separated into a separate one - Tylopilus. And now it is the only representative of this genus that grows in Europe.
Did you know? Tylopilus felleus was tested for antitumor and antibiotic properties and showed a positive result; therefore, the fungus is used in some medicinal preparations.
Tylopilus felleus grows in deciduous and coniferous forests. It is often found under beech and oak. False white grows in separate groups or alone. It appears in mid-summer and continues to bear fruit until mid-autumn.
The description of the fungus contains the main external signs that can be recognized in the forest.But it's best to focus on taste, as edible whites never taste bitter.
Did you know? The brown mesh leg is the reason why the inedible Tylopilus felleus is mistaken for the edible Boletus edulis. Although the latter is lighter.
The main characteristics of the double:
- Hat. Diameter 5–13 cm, sometimes up to 18 cm. Convex in shape, but becomes broadly convex or nearly flat as it grows old. The edges are smoothed, split and slightly wavy. The surface is dry, smooth, soft leathery, sometimes cracked. The color is brown, but if the mushroom grows in the sun, it burns out and becomes pale: yellow, light brown, gray-brown, greenish. Upon reaching maturity, the cap takes on a darker shade.
- Leg. Long - up to 10 cm, often curved, thick, but not always. Basically, it is noted that its thickness is 1.5–4 cm. The shade from above is whitish or pale brown. Sinking lower, it becomes pale brown or brown. The surface is highly reticulated with a wide brown mesh. Basal mycelium is white.
- Pulp. Thick, not hard, often elastic, white. Does not change color when cut. But some sources note that it is pale red on the cut.
- Tubular layer. White at first, turns pink over time. It looks like a sponge. When pressed, it changes color to pinkish-brown, but it is never red. This shade can be a sign of a birch tree. The tubes are dense, rather small, up to 20 mm long, ending in round pores 1–2 mm in diameter.
- Spore powder. Brownish pink. The spores are small, elliptical.
- Smell and taste. Very bitter taste and neutral odor.
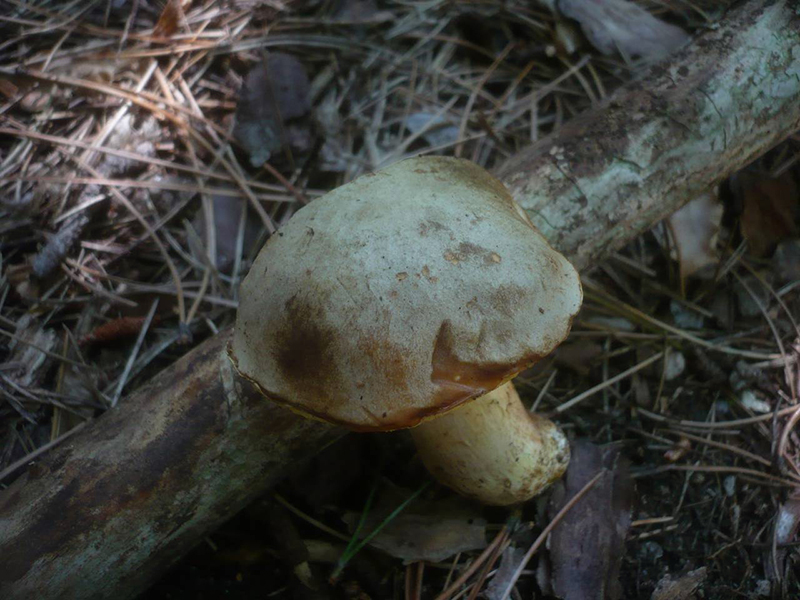
Description and photo of Semi-white mushroom
How to understand that in the forest you found exactly boletus? What are the characteristic differences that will make it stand out from other mushrooms?
Experienced mushroom pickers will surely tell you that you need to pay attention to the appearance of the boletus. It really is
And according to some characteristics, in fact, you can understand that this is exactly the representative of the family in front of you.
Hat
Let's start the description with the hat. It has an impressive diameter of up to 20 cm. Average individuals have a diameter of about 15 cm. The diameter of the cap is about 5 cm, in thickness, but at a more mature age it grows up to 20 centimeters.
The cap is very fleshy and elastic. However, with age, she becomes more malleable.
Over time, the boletus becomes completely flat as it matures.
If you run your hand over the cap, you will realize that it is somewhat wrinkled and smooth. At the same time, the color of the cap itself has a yellow-brown tint.
As soon as dry weather appears and the cap dries, cracks will form on it. However, during wet weather, the cap becomes mucus again.
The hat gives off a pleasant aroma, which is very similar to the smell of champignons.
Leg
As for the leg, it is mostly solid, tuberous and at the same time thick. Its height also varies. At an early age, the boletus leg is about 4 or 5 cm tall. With age, the mushroom rises to a height of 12 cm. It is clearly visible among grass and plants.
As for the girth of the leg, it can reach from 2 to 6 cm in diameter, that is, it is very stable. The leg is yellowish in color, but becomes more brown with age. On the very surface of the leg there are peculiar meshes, which implies small brown scales.
Pulp
As for the fighter's pulp, it is very dense, without a characteristic odor. At the same time, the color of the pulp is bright yellow, while the older the mushroom, the more its color stands out. However, if you cut open the mushroom and leave its softness to interact with oxygen, then it will very soon take on a bluish tint.
As for the spores, they are stored in special tubes, the length of which is about 2 cm. These tubes are very smooth and have a slightly bluish tint.
The spores themselves are also smooth and fusiform.The spore powder itself does not have an olive color, however, acquires it with age.
How to distinguish a real porcini mushroom from a false one
When collecting true boletus, especially if you do not know what their counterparts are, you should not be guided only by their appearance. Often, in order to distinguish the real fruiting body from the false one, it is necessary to carry out certain additional procedures.
Remember!
The main criterion by which bitterness is distinguished from a true white fruit is taste. In the double, it is bitter, which is why it got its name. But since it is strictly forbidden to try unknown mushrooms, this option for recognizing inedible mushrooms disappears immediately.
Do not immediately get lost in guessing whether it is possible to use a mushroom that a novice mushroom picker found in the forest. To understand whether it is gorchak or boletus, you need to carry out the following tests:
Cut off the fruit with a knife and pay attention to the color of the pulp, which is adjacent to the ground. For a true boletus, it will remain unchanged.
At the same time, it will immediately begin to darken in bitter potatoes. The shade will become pinkish-brown, and this should be the reason for refusing to further collect such fruits.
Examine the stem of the plucked fruiting body. A real boletus does not have the characteristic mesh that its counterpart has. But in a birch tree, nevertheless, there may be a dark scale on the leg, similar to the coloring of a birch trunk.
Examine the bottom of the mushroom cap. The bitterness has a tubular layer of a dirty pink color, while in the boletus it is white, grayish or yellow.
Helpful advice!
You can also pay attention to the condition of the pulp and cap of the mushroom. Boletus has a pleasant smell and taste, so forest insects, animals and worms are very fond of them.
For this reason, their flesh often exhibits bite-like strokes or damage. But the bitter taste of bitterness is burning, so almost always such mushrooms remain untouched.
Semi-white mushroom or yellow boletus
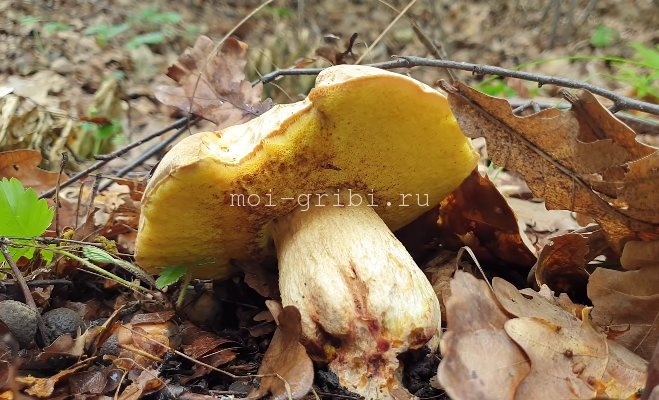
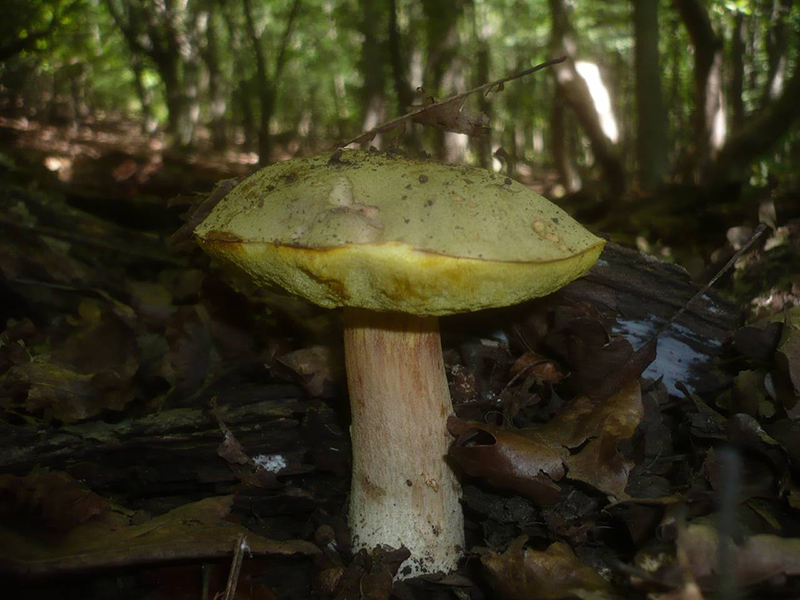
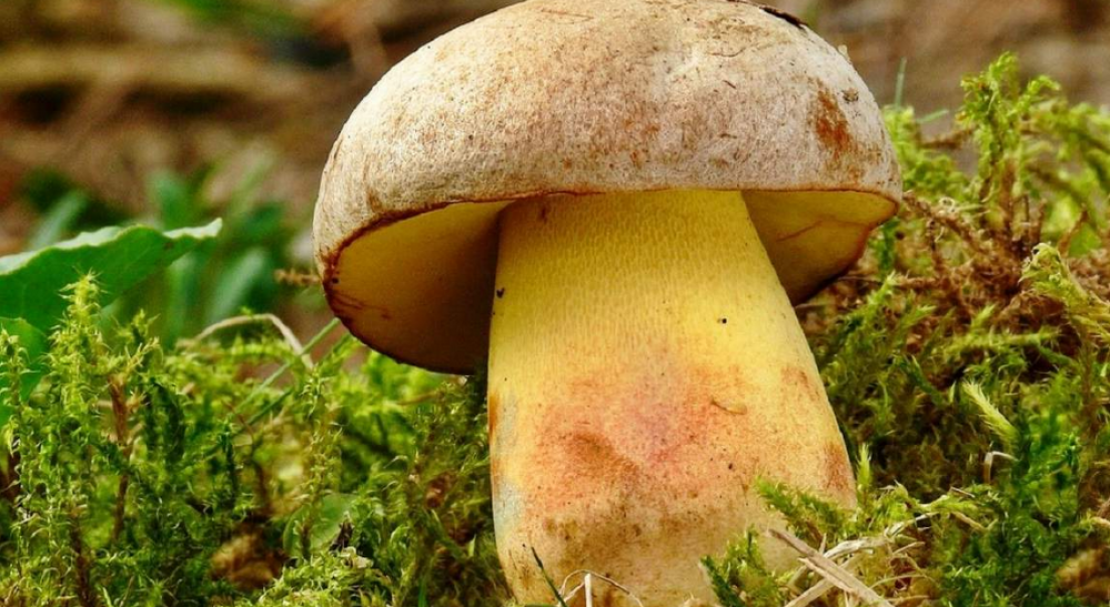
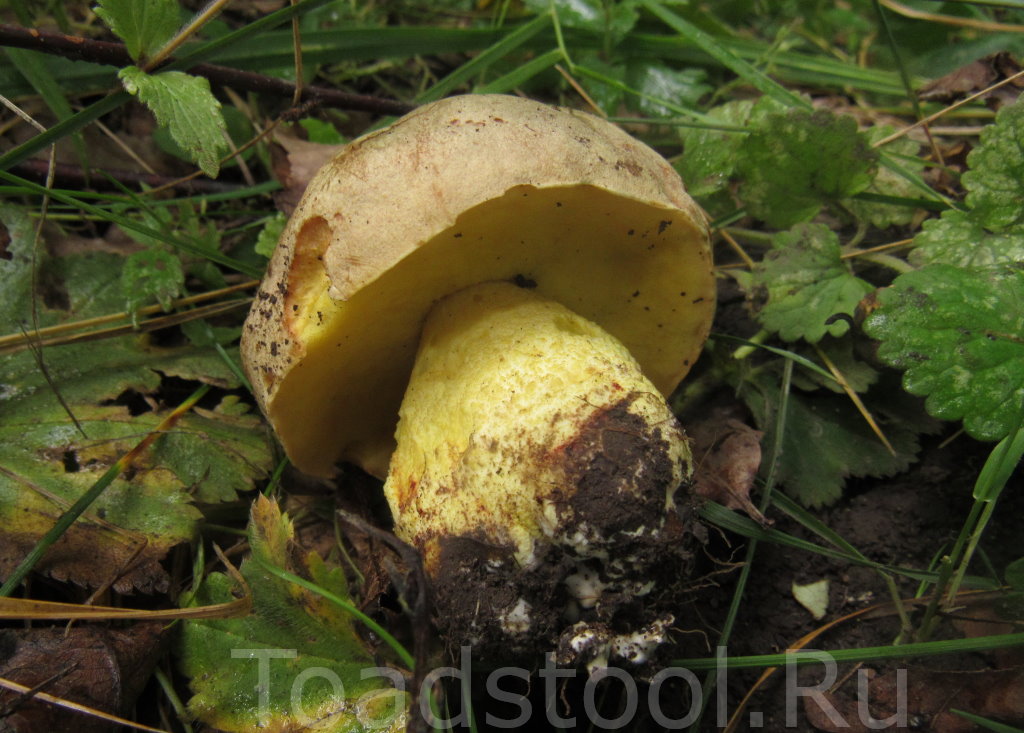
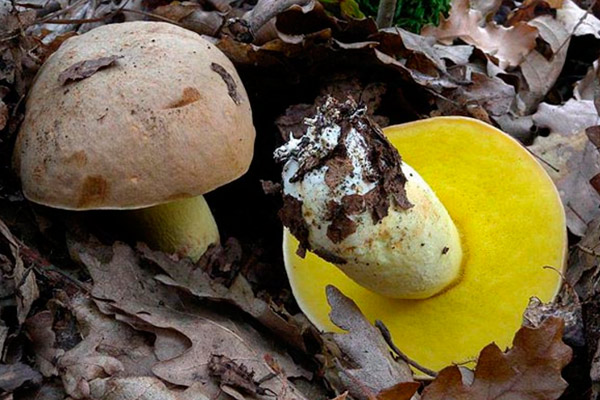
The semi-white mushroom (Boletus impolitus) is edible. The hat is up to 6-20 cm, hemispherical, then convex, fleshy matt, clay-ocher, light gray with a brown tint. The skin is not removable. The tubular layer is lemon yellow, golden yellow, then greenish yellow. The leg is yellow, with a reddish-brown tint below, fibrous. The pulp is yellow, non-bitter, does not change color on the cut, with a weak carbolic or iodine odor.
Grows in deciduous and mixed forests on limestone soils. More often found under an oak tree.
Fruiting from June to September. It is rare.
Detailed description and main distinguishing characteristics
In color, it can be confused with a gall fungus, but the latter has a smaller cap, denser and bitter flesh, a clear mesh on the leg.
The mushroom can be eaten after boiling or other heat treatment. All odors, except for mushroom, disappear after cooking. The taste of a semi-white mushroom is not inferior to a porcini mushroom.
Based on the name, it can be understood that it is a close relative of the famous porcini mushroom. And indeed it is. Therefore, people who are not experienced mushroom pickers can easily confuse the two. Among the people, such a resident of the forest is also called a yellow boletus.
Below we will talk about a semi-white mushroom, its description and show a photo, by looking at which, you will quickly learn to distinguish this subspecies from white.
Characteristic features of a semi-white mushroom
Here are the main characteristic external features of the boletus.
- The upper part of the mushroom reaches a diameter of up to 22 cm. Its shade can range from yellowish to brown. The young boletus has a convex cap. As it grows, it bends, and in the old mushroom it becomes almost flat. If you touch it, then it is smooth, during the rainy season it can be slightly slippery.
- The leg of a semi-white mushroom is thicker at the base. Its shade is light yellow.
- A tubular part is defined under the head. It has pronounced rounded pores. The shade of this part is yellow, which can change to dark beige as it grows.This is a distinctive feature of this species: in the porcini mushroom, the tubular part is of a light shade.
- When broken, a pronounced yellow pulp is observed. It is dense, fleshy. Its shade does not change when interacting with air.
Another difference from its white counterpart is that the pulp has a pronounced aroma of carboxylic acid.
Boletus is a thermophilic type of mushroom, therefore they prefer to grow in the southern parts of the country, where the summer is hot with sufficient rainfall.
Useful properties of yellow boletus
The mushroom boletus yellow, like other edible subspecies, has a number of properties useful to humans.
Eating them in food, you can completely compensate for the lack of some B vitamins, zinc, amino acids, easily digestible proteins. They are capable of:
- normalize the work of the nervous system;
- have a beneficial effect on the skin and hair;
- restore the endocrine system.
In cooking, a semi-white mushroom is used for salting, frying, cooking broths. Marinating makes this species very close in taste to white.
It is also possible to confuse them with the inedible boletus twins: rooted, inedible, girlish
To prevent this from happening, note that the leg of the poisonous species is of a brighter shade, the cap is much darker, and when pressed on the tubular part, it quickly turns blue
Similar species
What forest dwellers can you easily confuse boletus with? There can be many options, however, the answer is obvious. The boletus family includes a huge number of mushrooms and species that thrive in forests, moreover, they grow in abundance on the territory of Russia.
Let's get acquainted with the most common species that you can surely meet on your way.
Borovik girlish
This mushroom has a very interesting intricate name. It is edible, and also belongs to the family of paints.
It is a boletus.
Its appearance distantly resembles a semi-white mushroom. Its cap has a maximum diameter of 20 cm. The shape is predominantly convex, and the edges are bent inward. Itself seems quite thin, the hat has a golden hue, much less often red or brown.
The flesh itself is very dense, it also has a blue tint on the cut.
The leg reaches a maximum of 15 cm in height, very thick, up to 6 cm in diameter in thickness.
This species is widespread in southern Europe, however, such boletus cannot be found in large groups. Likes to grow alone. Mainly bears fruit during the early fall stage.
Root boletus
Another representative of the bolet family, the boletus genus. A mushroom that will surely not go unnoticed.
It is very large, the cap can reach a diameter of up to 30 cm. At the very beginning of growth, it has a conical shape, but then it acquires a flatter shape, the edges are bent inward.
The surface of such a cap is slightly woolly, and can often crack.
The pulp of this mushroom has a lemon-yellow hue, somewhat bluish. It does not have the most pleasant smell, but the taste is rather bitter.
The leg is thick, raises the mushroom to a height of 12 cm. It has a yellow tint.
This mushroom is widespread in Europe, and chooses only deciduous forests for its development. Loves calcareous and other neutral soils. He also prefers dryness. It grows from July to October.
Mosswheel green
A mushroom widespread in Russia.
Very beautiful, attracts attention. Despite the name, it belongs to the genus Boletus
This mushroom is easy to spot in the forest. Its cap is small, reaching a diameter of 10 cm. Individuals of 16 cm are very rare. It is somewhat convex and very velvety. The flesh is white, however, turns blue when cut.
The leg itself has a cylindrical shape, which tapers slightly towards the mycelium itself. It is about 10 cm high and up to 2 centimeters thick.
The spore powder is brown, frequent.
This mushroom chooses a variety of forests for its growth. In addition, he also prefers meadows and roads.
The fungus grows singly, and sometimes even in groups. Can form mycorrhiza with deciduous and coniferous trees. He is a cosmopolitan. It is equally often found both in North America and in Europe and Australia.
Boletus inedible
Inedible boletus can also be found in Russian forests. However, despite the fact that the name contains the word inedible, this mushroom is not poisonous. The fact is that it is unpleasant to cook mainly because of its taste, however, it does not carry any danger to the human body.
In order not to confuse this inedible species with a simple porcini mushroom, you need to carefully study the description.
The hat can be up to 15 cm in diameter. It has a conical shape. Sometimes, slightly convex, the edges curl inward or hang down in waves.
This hat is very smooth to the touch, somewhat matte and wrinkled. The skin has a light brown tint, however, at a young age it already has a brown or gray-brown color.
The flesh itself has a creamy or white tint, however, it can sometimes take on a blue tint at the cut. Bitter enough.
The leg rises 15 cm in height and is about 4 cm thick.
As for the tubular layer of this forest dweller, it has a lemon yellow tint, and a greenish tint predominates. The spore powder itself has a brown and olive color.
This mushroom is widespread in the south of the European part of Russia, most often it chooses the Kaliningrad region for its place of residence. It is also common in Europe, namely in warm countries, such as Italy or Spain. Mainly chooses coniferous forests, as well as oak and broad-leaved forests, prefers sandy and acidic soils, and also settles in places in parks and lawns.
Mushrooms grow from July to October.