Description
The genus russula (russula family) is extremely numerous and varied. Only on the territory of Russia and the CIS countries there are about 60 species. In total, the genus is made up of hundreds of species of lamellar mushrooms that grow in Europe, Asia, America.
Coniferous, deciduous, mixed forest, birch grove, park, even a few growing trees, swamps or roadside - all these are the habitats of representatives of the genus.
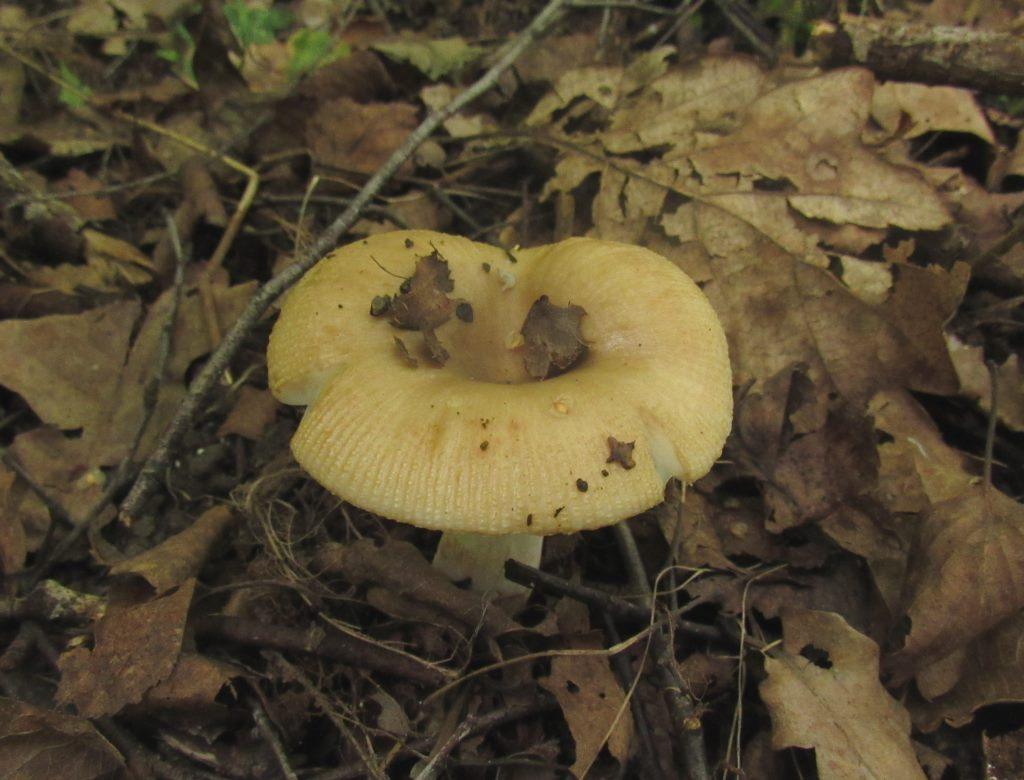
The russula has a short, cylindrical leg. As a rule, it is even, less often slightly thickened or narrowed at the bottom. The diameter of the cap varies from two to two tens of centimeters. During the life of each instance, the hat is transformed. In young fungi, it has a spherical shape. As they grow older, the edges straighten and rise, forming a depression in the center.
A distinctive feature of the genus is its bright skin. It is no exaggeration to say that coloring can be of all colors of the rainbow and all kinds of shades. It is because of her that these mushrooms are called "dapper". It often becomes the main criterion for determining species independence.
The peel is easily removed or breaks off on its own at the edges, exposing the white flesh. The plates are thin, also white or slightly yellowish, fully or partially adhered to the peduncle. The pulp of Russula is characterized by fragility. It happens that mushrooms just crumble in your hands or in a basket.
Russula appear in early summer, and disappear only in late autumn. Contrary to the name, they are not suitable for consumption in their raw form, as well as for drying. But russula can be boiled, fried, salted and pickled. They are not included in the "major league", but refer only to the III and IV categories. Vitamins B2 and PP are worthy of mention among the “useful components”.
Among russules there is not a single one that is definitely poisonous. Even many bitter tasting varieties are used for cooking after pre-soaking or boiling. Nevertheless, it is advisable to bypass some representatives of the genus.
Evaluation of taste, medicinal properties, benefits and possible harm
Despite the fact that the mushroom is a goby, Valui belongs to less valuable species (compared to milk mushrooms, mushrooms, boletus mushrooms), it has a pleasant taste, and is widely used in cooking.
Important! The calorie content of the cams is only 29 kcal per 100 grams. Valuei mushrooms: the benefits and harms of this species are still not fully understood
It is known that ancient Chinese healers used them to relax muscles. Modern traditional healers also use the barn, preparing compresses and tinctures from it, which help relieve pain, lumbago and numbness in the legs.
Valuey mushrooms: the benefits and harms of this species are still not fully understood. It is known that ancient Chinese healers used them to relax muscles. Modern traditional healers also use the barn, preparing compresses and tinctures from it, which help relieve pain, lumbago and numbness in the legs.
There is a lot of protein in the barn, it is actively involved in building cells. Svinur contains small amounts of fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. In addition, the mushroom has beneficial antioxidant properties, has a beneficial effect on the heart rate, blood sugar levels, and normalizes metabolism.
In snivels there are also beta-glucans, which help to strengthen the immune system, as well as chitin, which helps to remove toxins and heavy metals.
The harm from the use of values can also manifest itself; you cannot use them fresh or undercooked. If you develop nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal upset, abdominal pain after consuming culbs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
You cannot pick any mushrooms near highways, highways, major highways, since fruit bodies tend to absorb all harmful substances and toxins.In addition, it is forbidden to eat valuei for children under 12 years old, pregnant and lactating women, people with chronic diseases of the stomach, kidneys or liver.
Value specificity
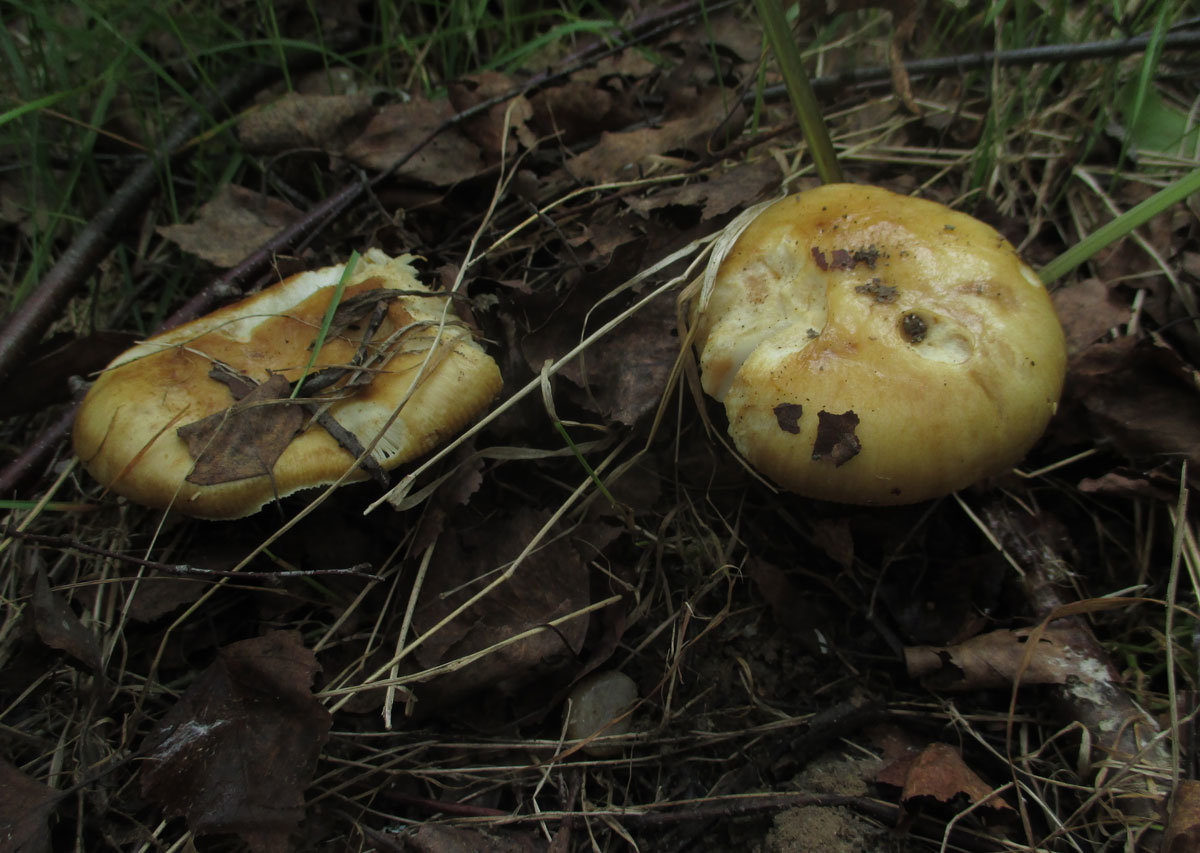
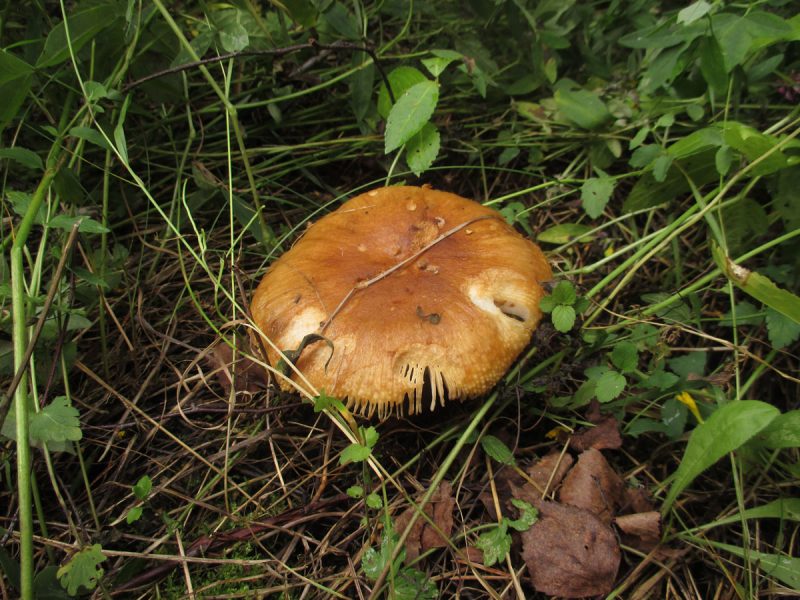
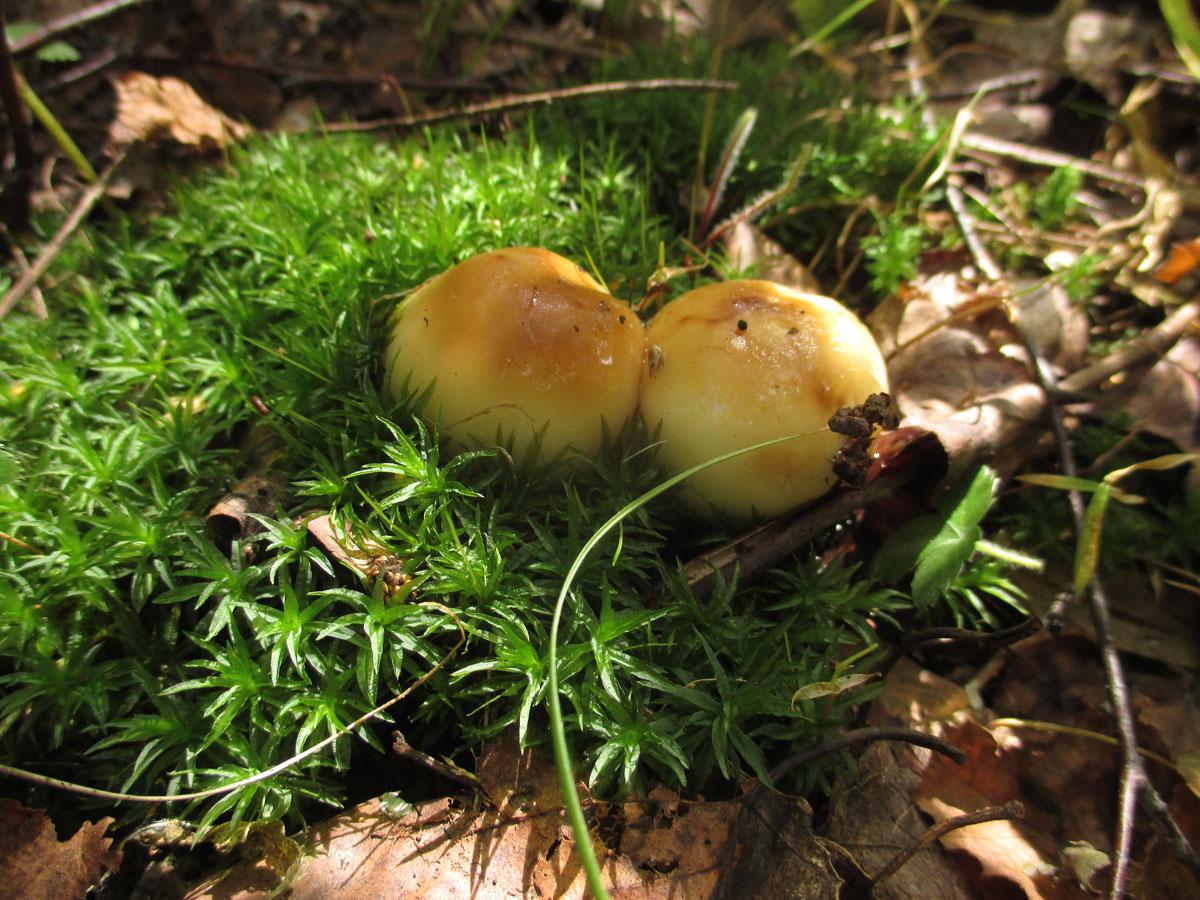
The mushroom grows rather large, has a smooth, slightly slimy cap, similar to a cam in youth. With age, it straightens and takes the form of a concave disc, which often grows to 15 cm in diameter. In addition to the bitter pulp, Valui can "boast" of a specific, not too pleasant smell, similar to the aroma of rancid oil. In addition, often mushrooms turn out to be wormy, and in adults, the leg becomes fragile and crumbles even with a light touch. It would seem that one should not pay attention to value mushrooms: how to cook, it is not clear, to run into a worm is as easy as shelling pears, smell, bitter ... However, they also have pleasant features: the hat is dense, and remains so even after processing. The only condition: to collect only young copies of the so-called cams.
Growing at home and in the country
Cowsheds can be successfully cultivated on a personal plot. This is a rather unpretentious plant that can grow near any trees. To begin with, it is worth purchasing mushroom mycelium in a specialized store (its price is about 180 rubles). Further actions must be carried out in this order:
- Dig up, fluff the ground near the tree. Dig a groove 5-15 cm.
- Spread the mycelium over the entire surface of the soil.
- Mix equal parts of the soil and humus. Powder the planting site.
- Water at the rate of 10 l / 1 m².
- Sprinkle with earth that remains from digging.
- The first mushrooms will appear no earlier than 2.5 months after planting. Crop can be harvested 4 times a year: twice in spring and 2 times in autumn. The mycelium grows as long as the tree exists.
Indoors, you can also grow Valui, but the results can be much worse than in an open area. The likelihood of germination is also reduced.
Processing of harvested fruit bodies
Even edible fruiting bodies need to be prepared for consumption in order to get rid of bitterness and possibly dangerous corrosive juices.
Features of using the fruit bodies of Valuya:
- they are not used for frying and drying;
- hot salting is considered optimal;
- they are pickled and rolled up in jars.
Edible mushrooms also need to be prepared for consumption.
Due to its natural bitterness, Valui needs to be soaked or blanched for a long time before cooking.
Soak them in cold water, changing the liquid regularly. Sometimes in older specimens, the skin is cut from the cap, since it is tough and especially bitter. The soaking time is at least 3 days, and the water must be drained and replaced with a new one several times a day. The soaked mushrooms are boiled for 10-15 minutes, removing the foam.
Cool the product under running water. Now mushrooms are used to prepare a snack or prepare for pickling. Also, delicious mushroom caviar is obtained from this species:
- Fruit bodies boiled for half an hour are crushed with a blender or meat grinder.
- Stew with spices and onions.
- It is immediately eaten or harvested for the winter.
On a note. If, even after boiling, the values are bitter, roll them up in jars and leave for 2 months. During this time, the bitterness should go away. Often I use young fruit bodies for pickling and pickling, because they are small and dense, pickle better and look pleasant on a dish. And caviar is made from old mushrooms.
Pickled mushrooms
This processing method also gives excellent results. Before marinating Valui mushrooms, they are soaked as with cold salting, after which they are boiled for about a third of an hour and washed. A marinade is cooked up: one and a half tablespoons of coarse salt are taken per liter of water, the same amount of sugar - and boiled. Values are boiled in brine for twenty minutes; before turning off, pour in the essence of vinegar (the same one and a half tablespoons per liter of marinade).Peas and allspice, laurel, mustard seeds and cloves are laid out on the jars, then mushrooms with brine. Roll up, turn over and wrap until natural cooling.
Valui mushroom: how to salt with a hot method
Salting is the most popular and correct way to handle the bull. In this form, he may well compete with milk mushrooms and mushrooms, and some like them even more than these. First you need to thoroughly rinse the valuei mushrooms. How to cook them - peeled or not - is controversial, but most chefs are inclined to believe that the skin should be removed from the hats. Moreover, she climbs without any difficulty. Mushrooms are boiled; after boiling, at least a quarter of an hour should pass, during this time the notorious bitterness will go away. When the values are cool, they are put in an opaque container (for example, in an enamel pan) and sprinkled with coarse salt in an approximate amount - one and a half glasses per 10-liter container. A load is placed on top of the rammed flush with the edges of the roll; under its weight, bitter juice will flow through the top. From time to time, to get oxygen inside, you need to pierce the mushrooms to the bottom. When the juice stops flowing out, the oppression is removed, spices are placed on top (for example, black currant foliage, horseradish and dill), the pan is covered with a cloth and left for 40 days. After the Valui are packed together with herbs in sterile jars and hide in the basement.
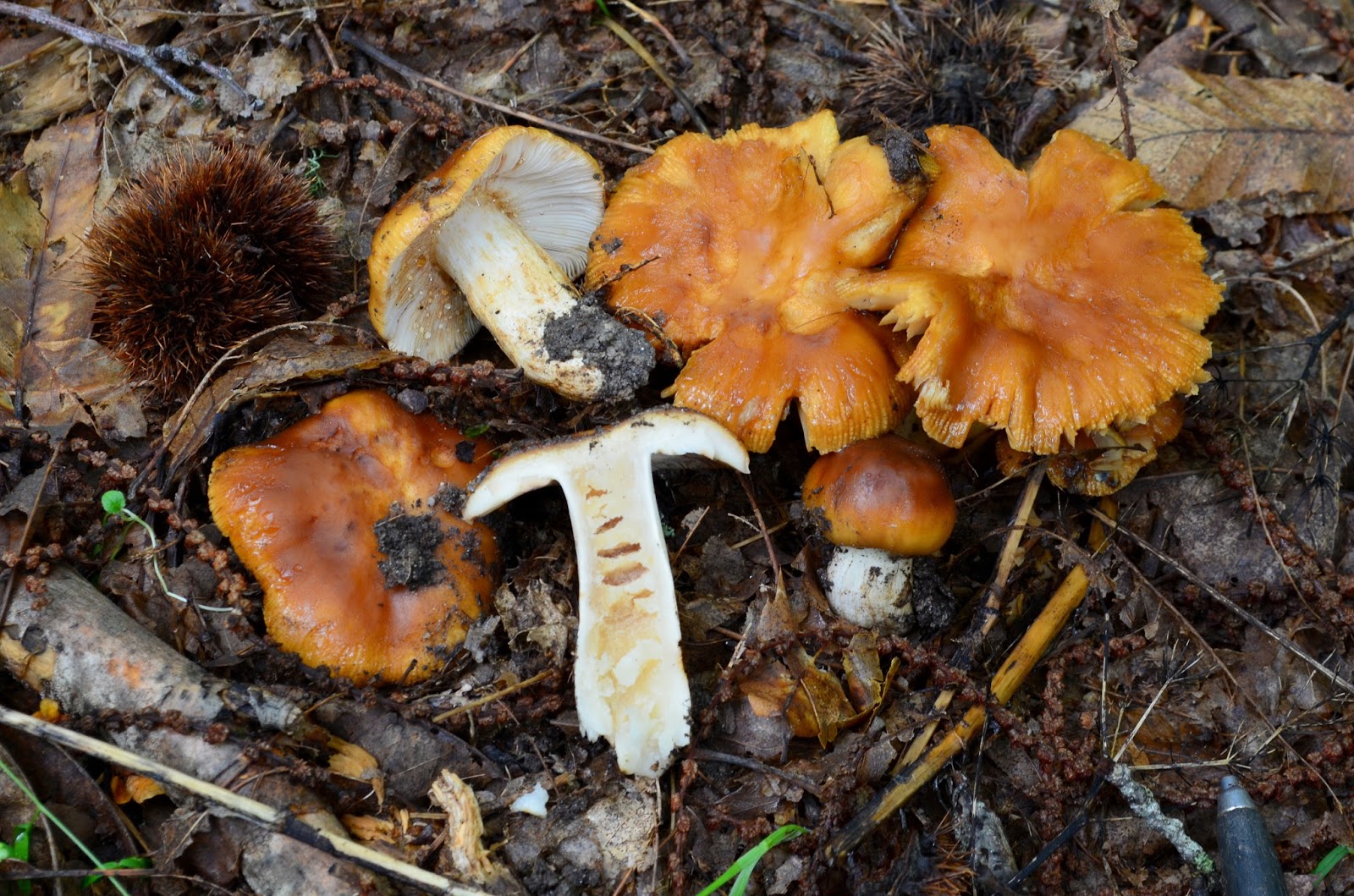
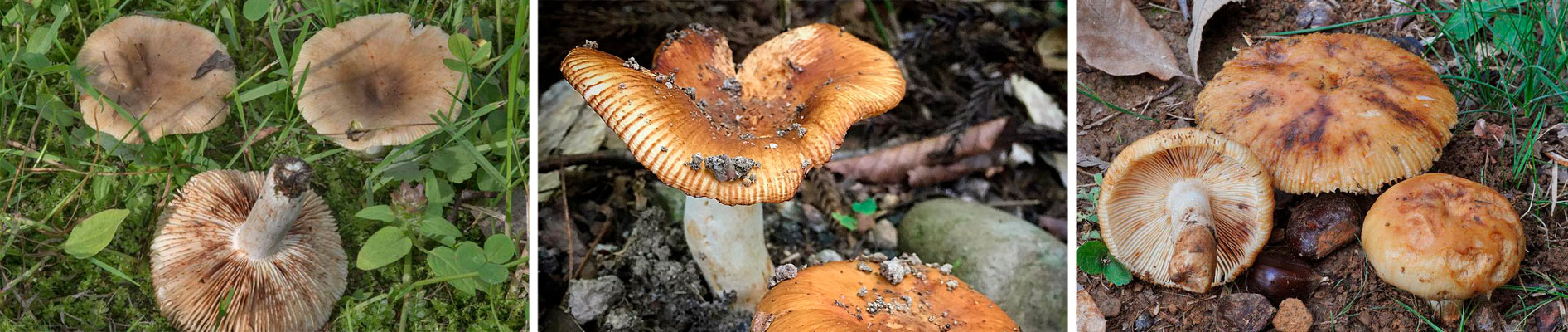
Inedible russules
- a mushroom with a red or pink cap, often covered with white or yellowish spots. When cut, the pulp turns pink. The white leg is slightly wrinkled. It grows mainly in deciduous forests in damp places.
- lives in pine forests and is very similar to the stinging one. It differs only in the more saturated color of the cap and the presence of reddish strokes on the stem. In addition, the flesh remains white when cut.
with a light yellow or beige cap with a grooved edge. After rain, the skin becomes sticky, it comes off with difficulty. The smell resembles that of Geranium. Stem strongly wrinkled, light ocher. The pulp in young mushrooms is white, in adults it is yellowish. It tastes very bitter. More common in beech forests.
Editorial office.Valui (Russula foetens)
Shinoim:
- Fetid russula
- Goby
- Svinur
- Kulbik
- Snotty
- Cam
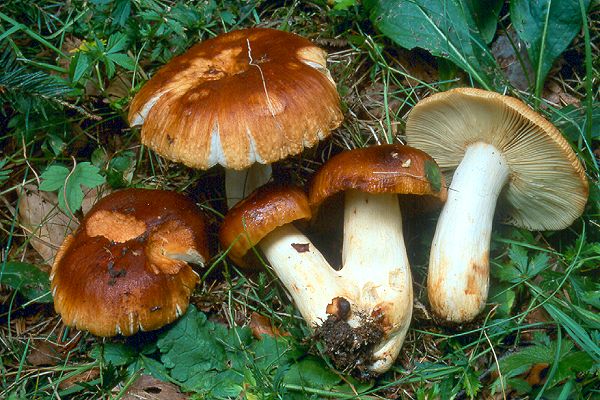
Valuy is a species of mushrooms from the russula genus of the russula family.
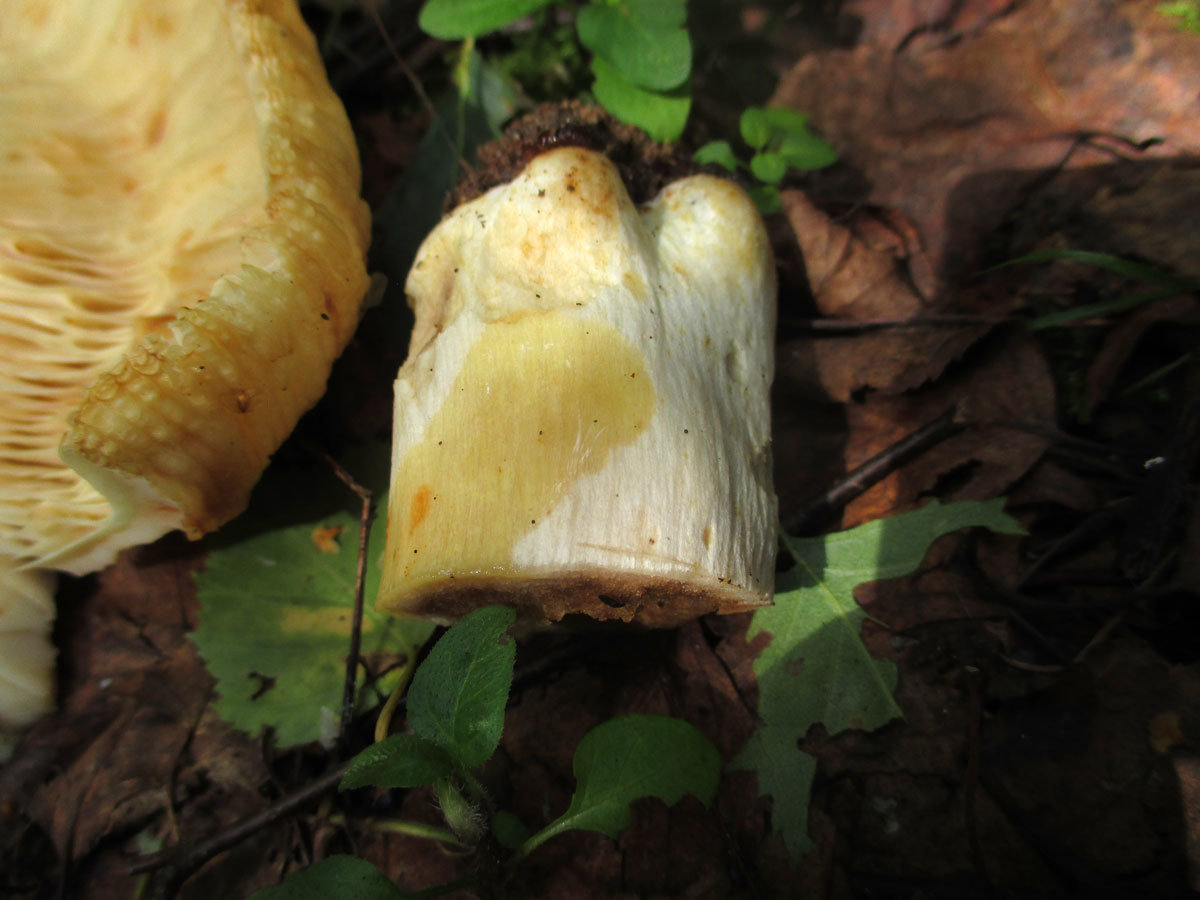
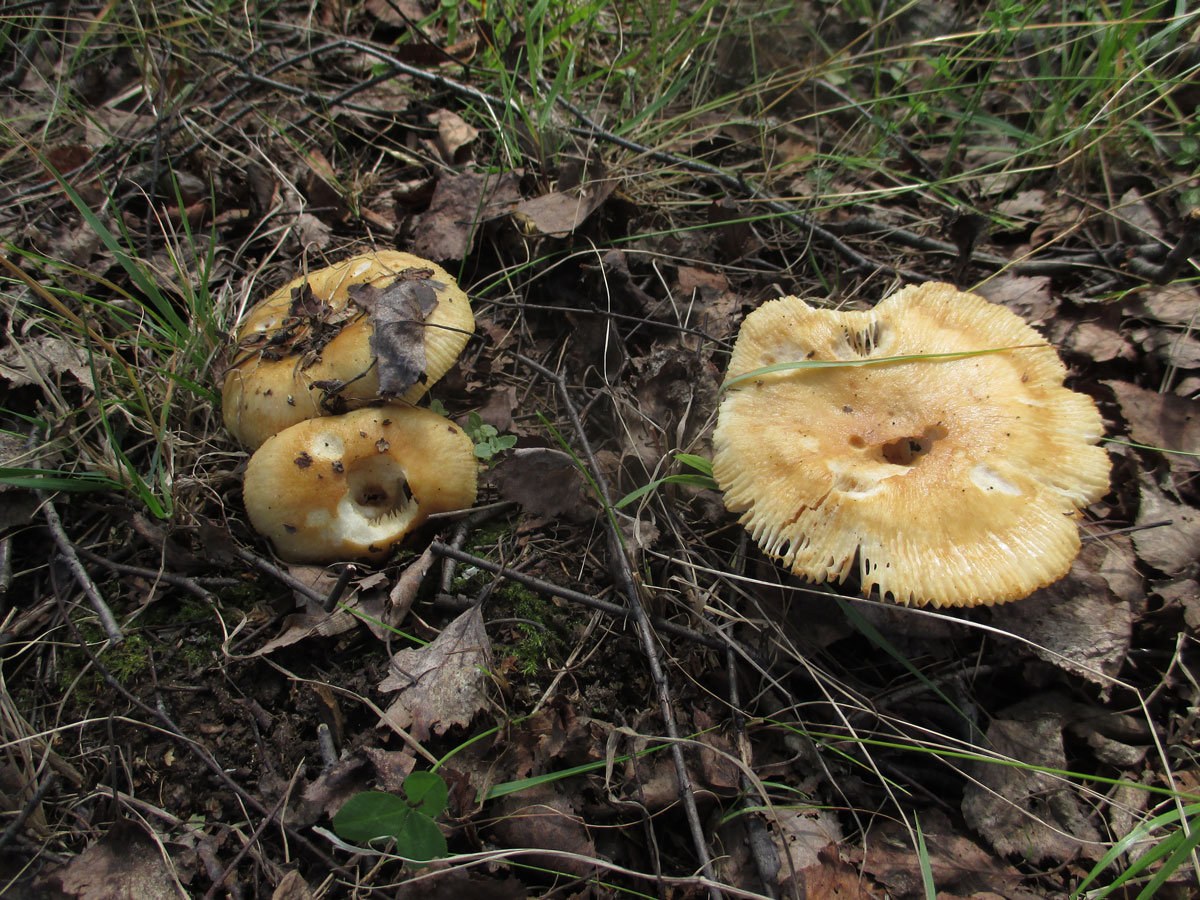
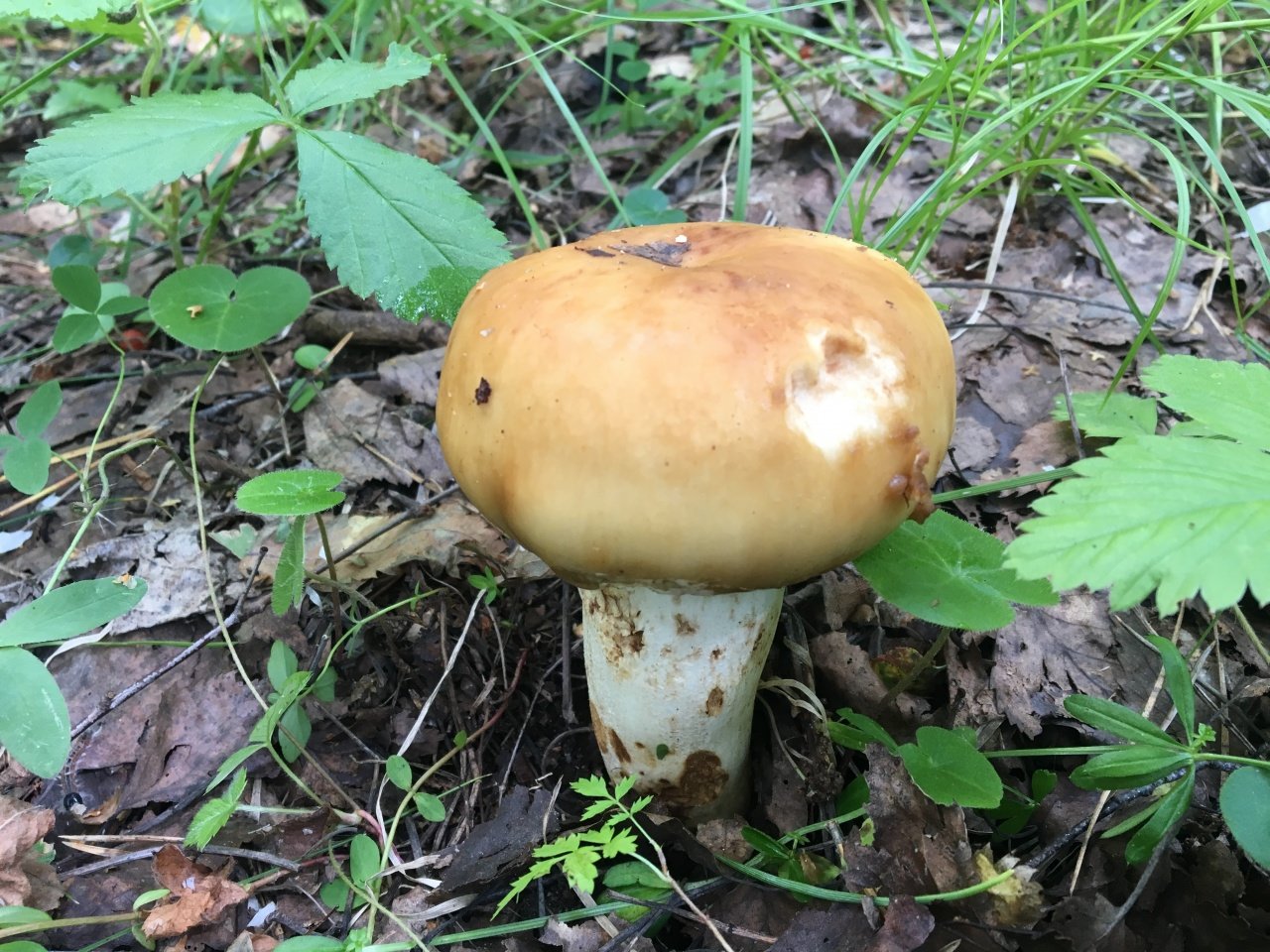
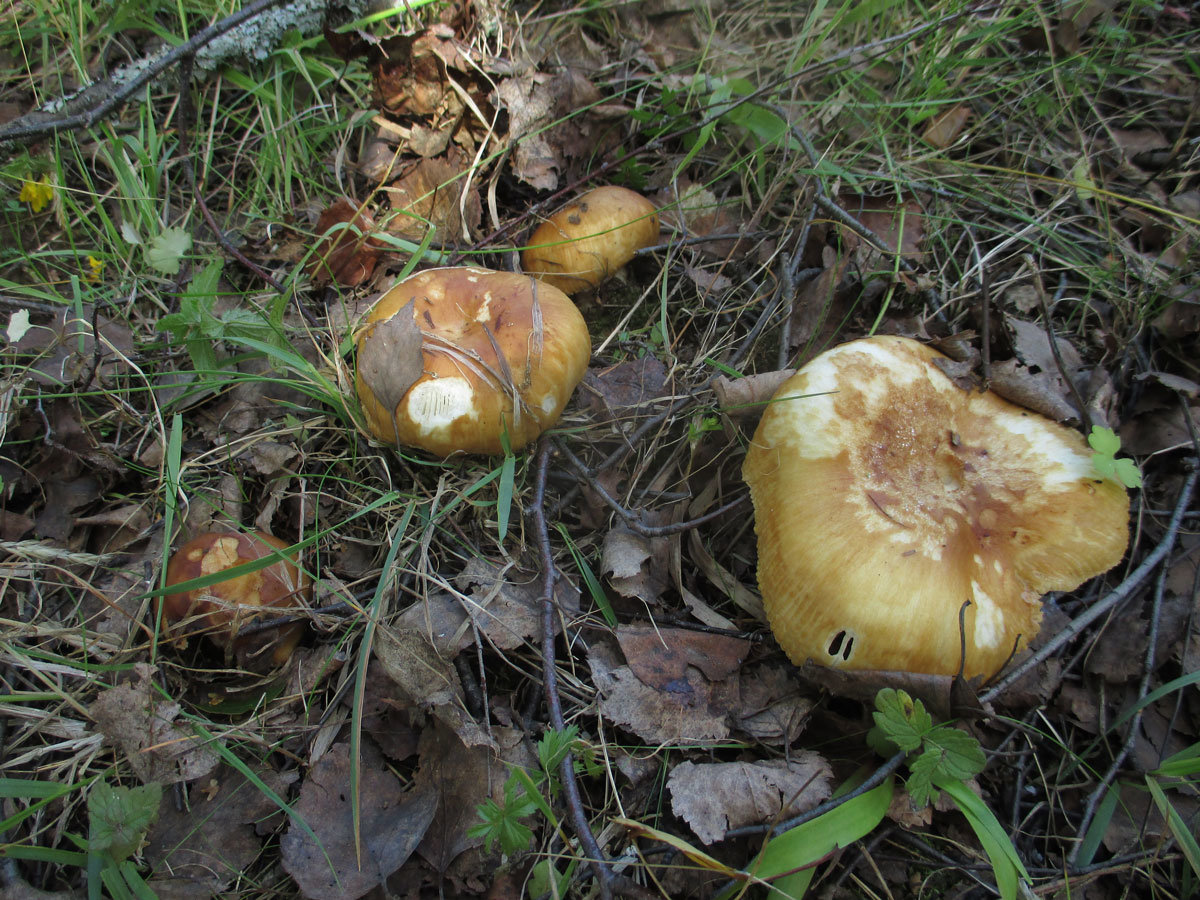
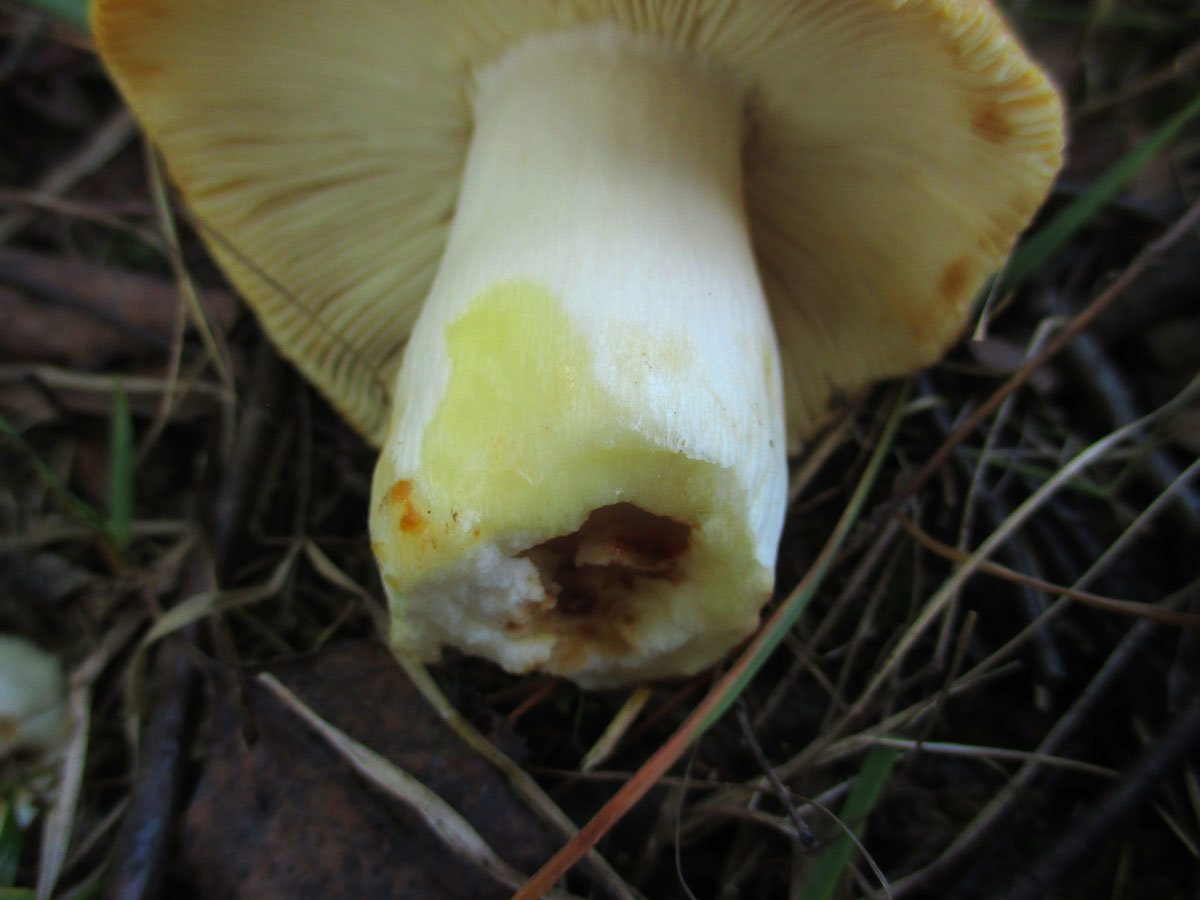
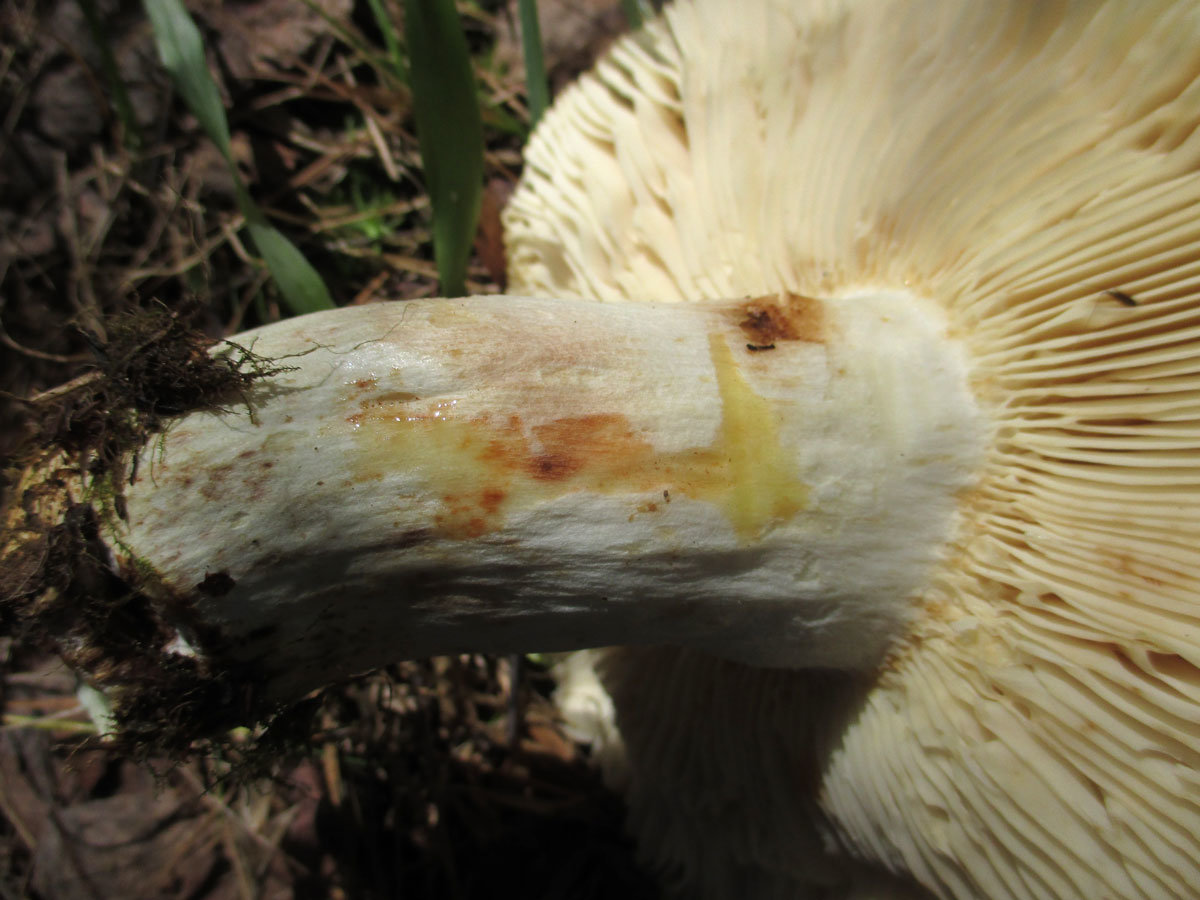
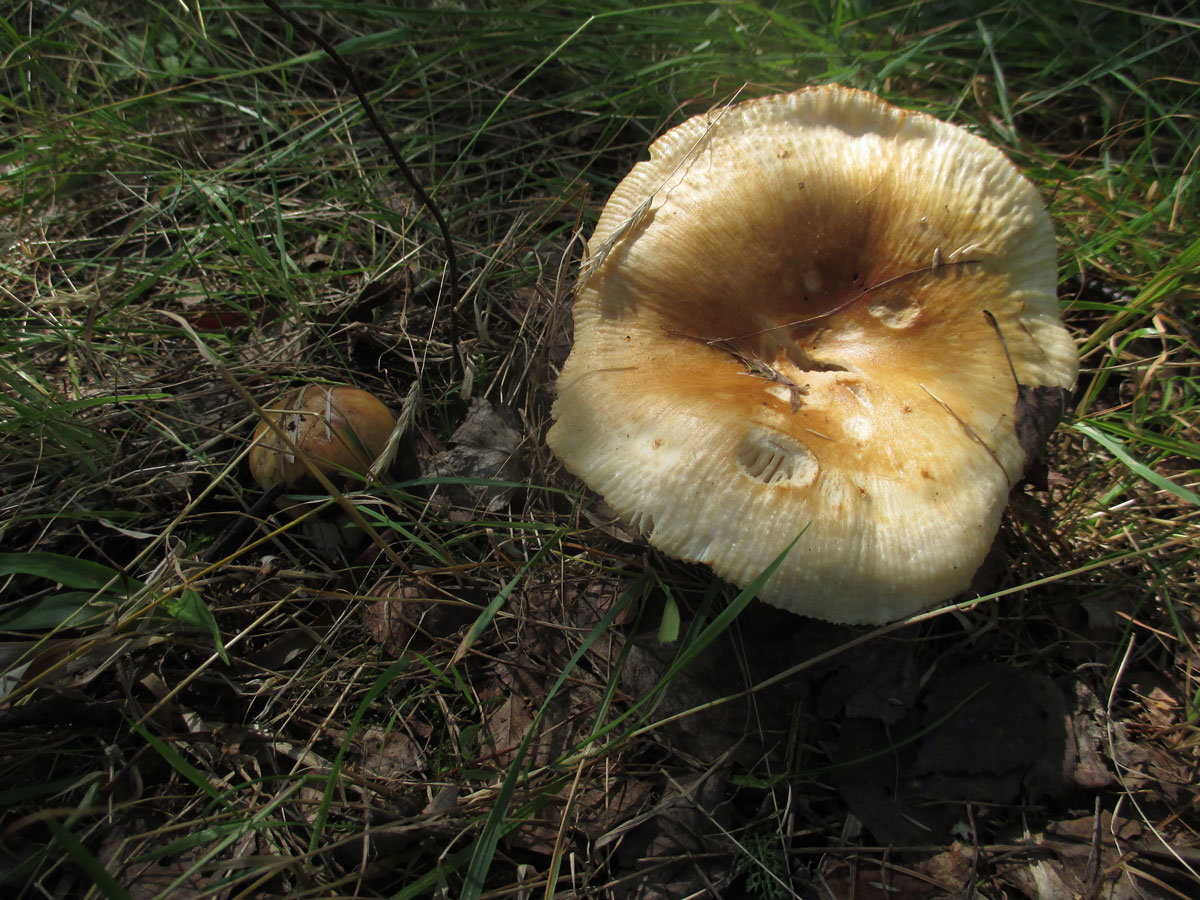
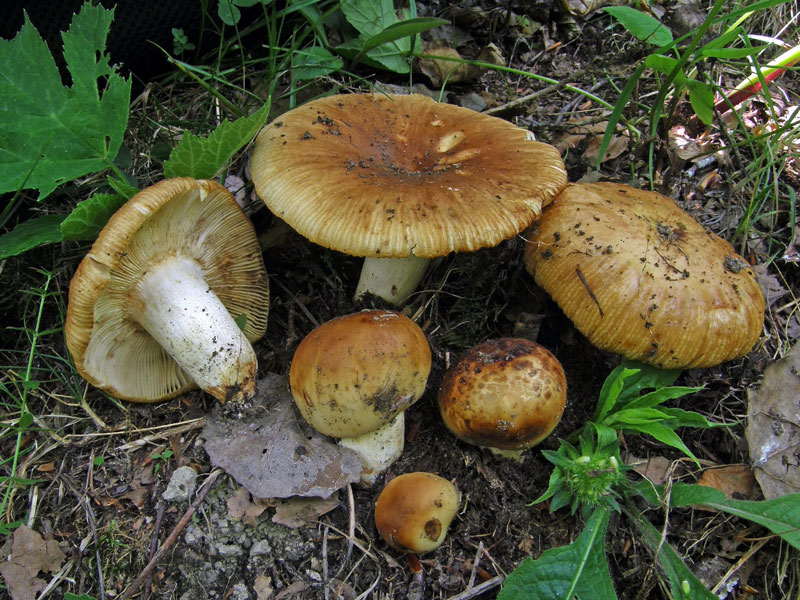
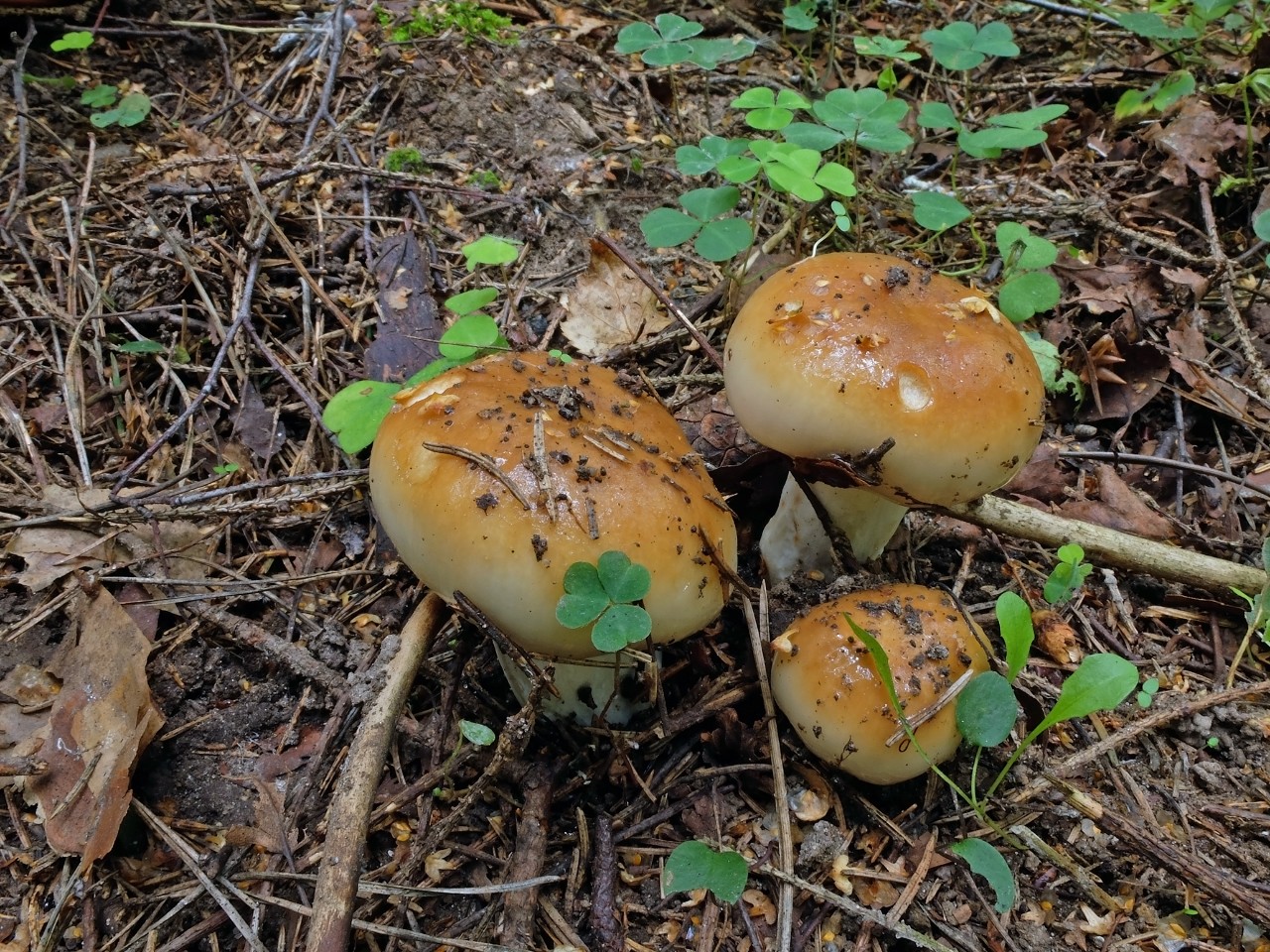
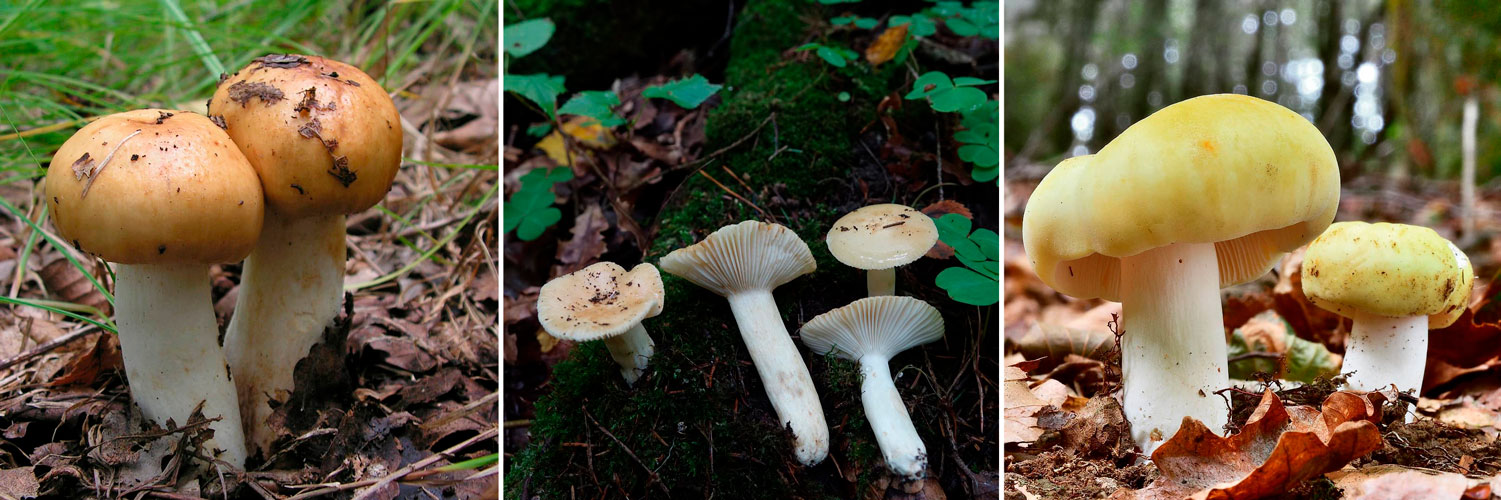
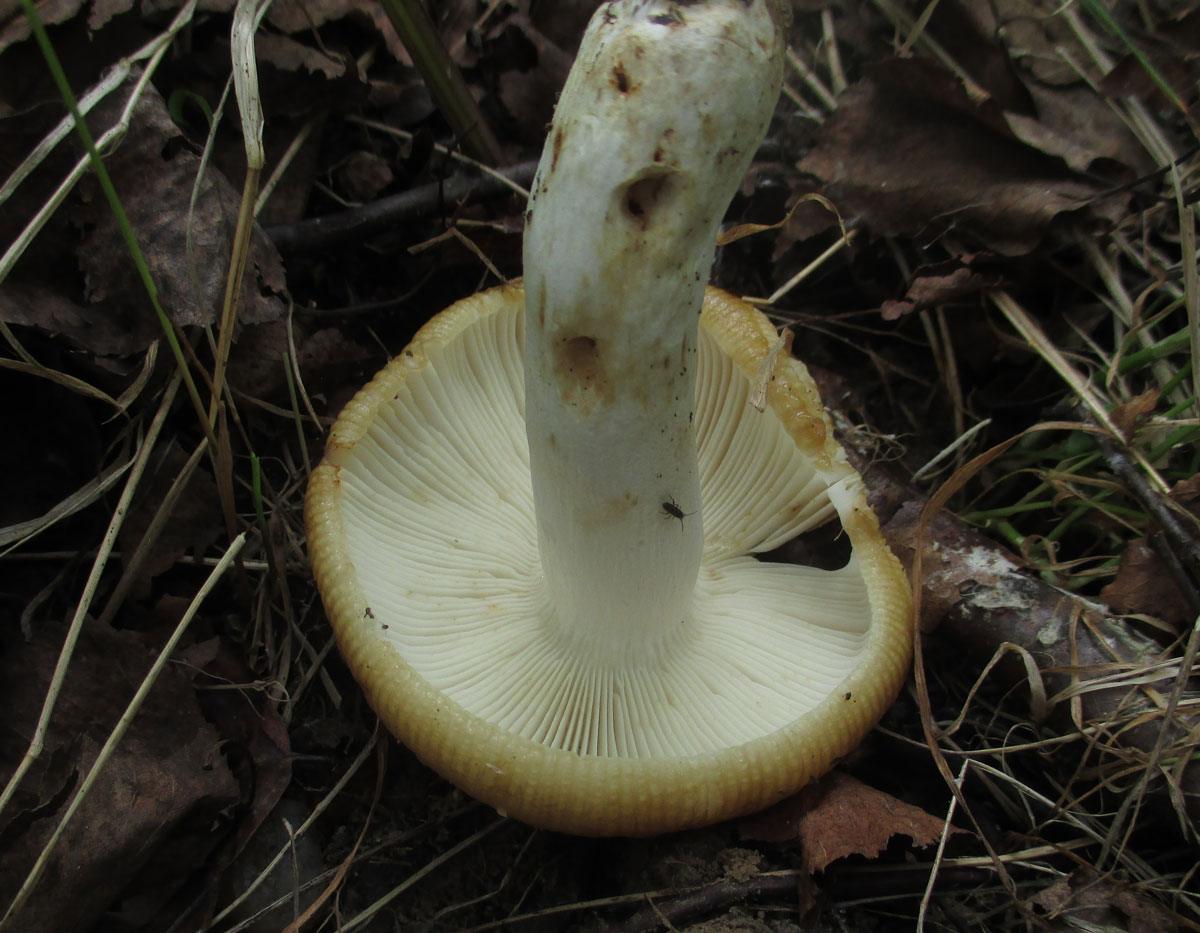
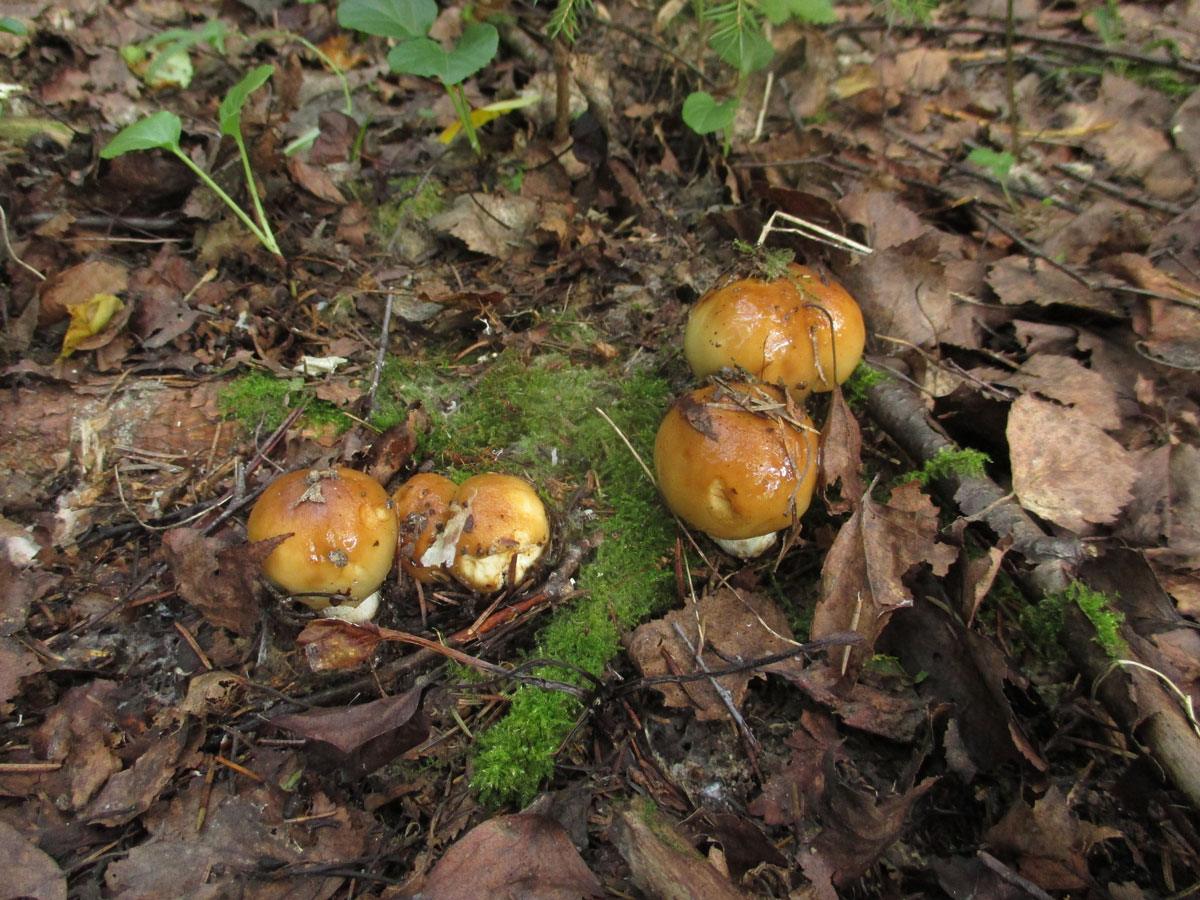
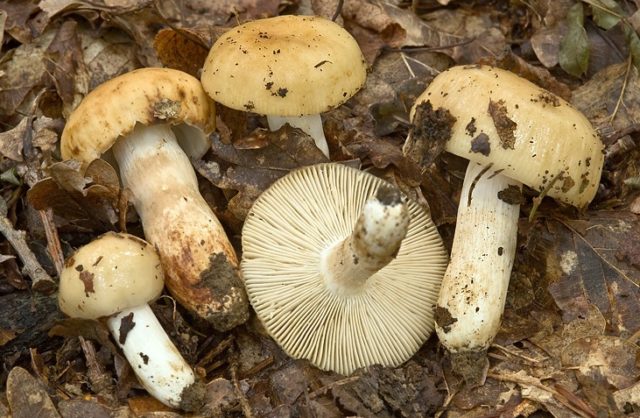
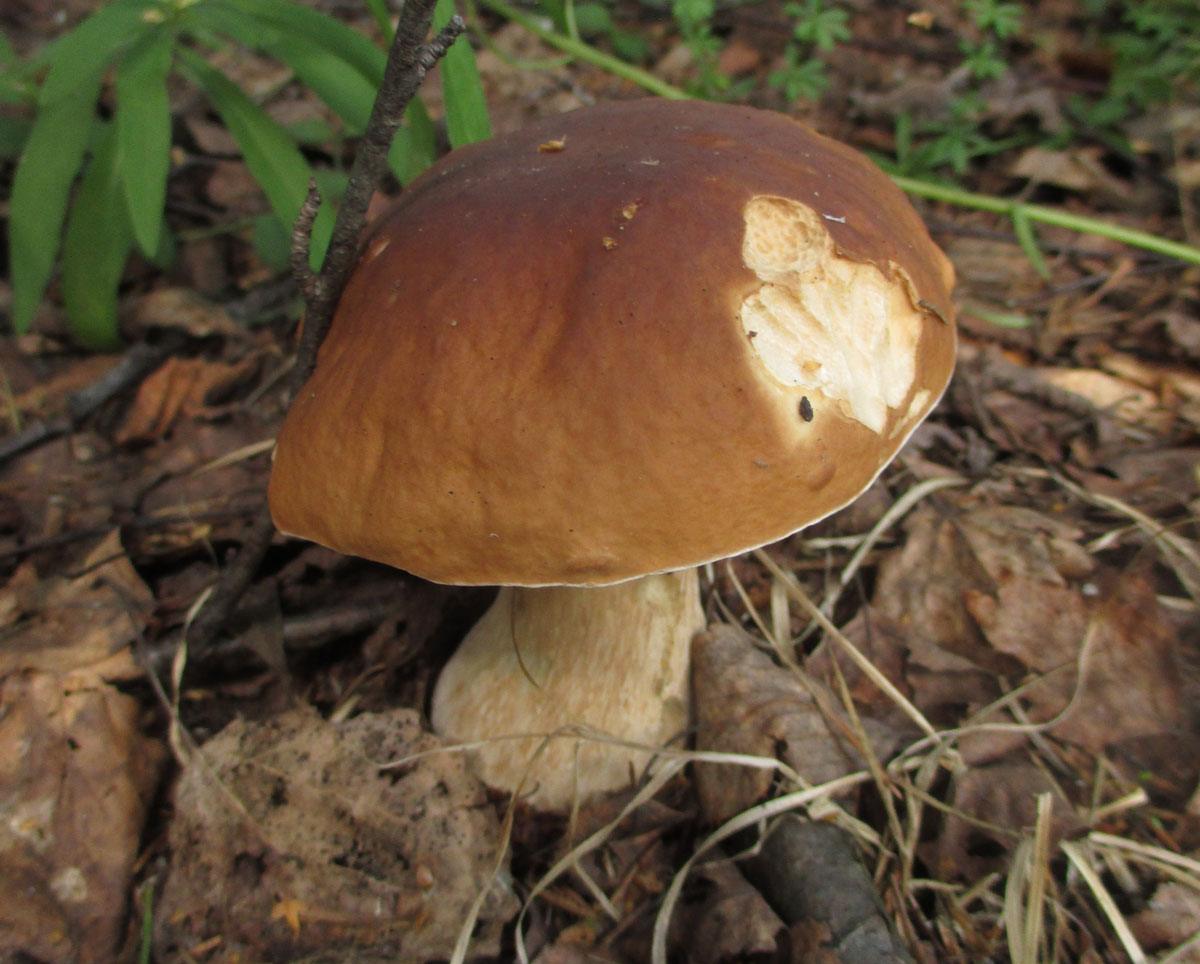
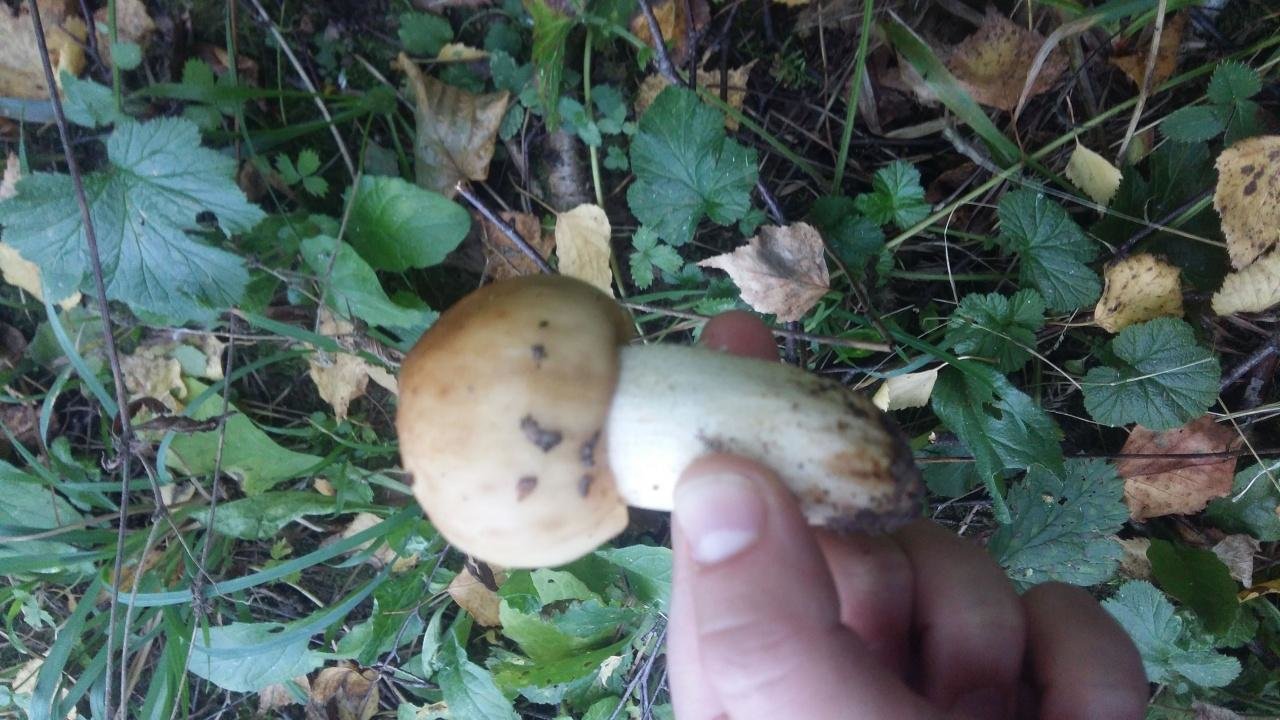
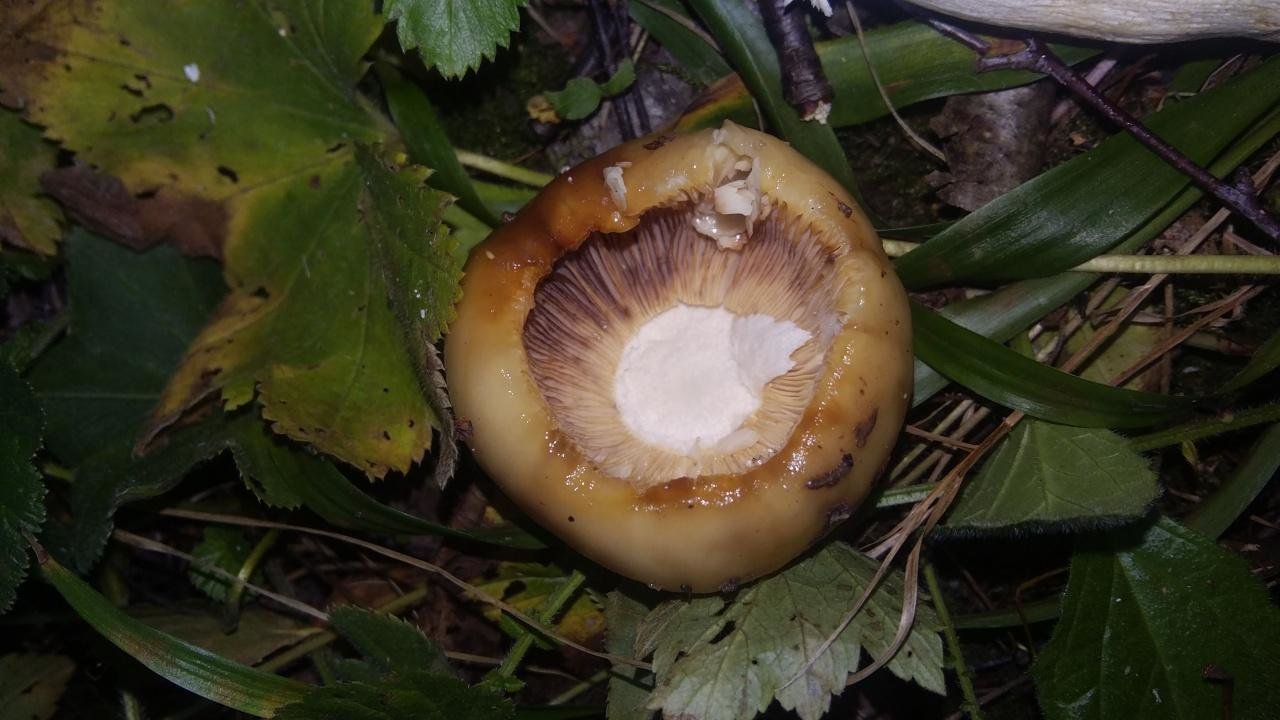
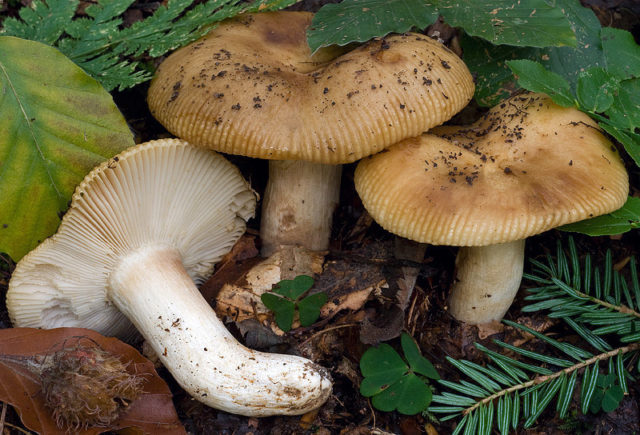
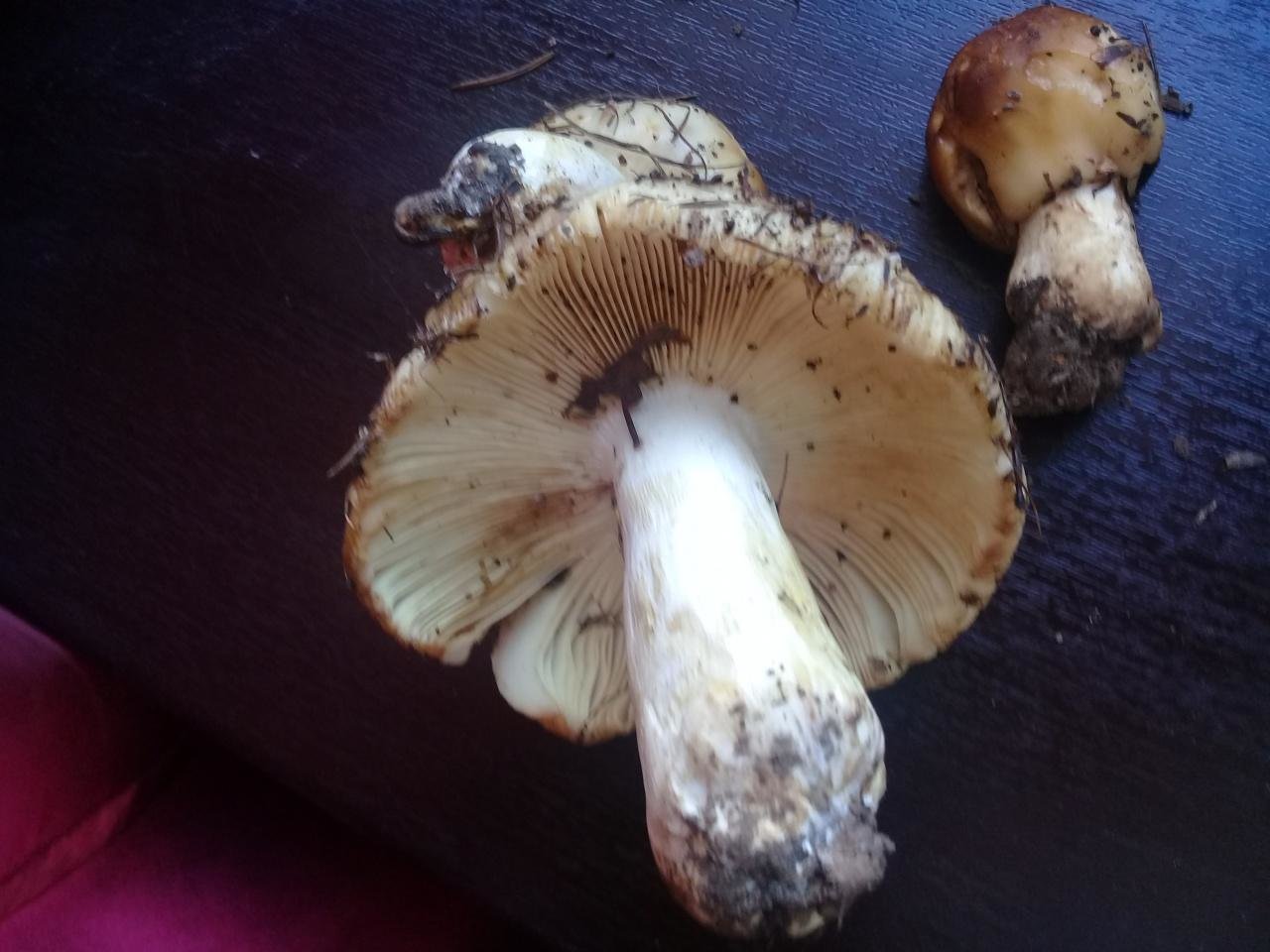
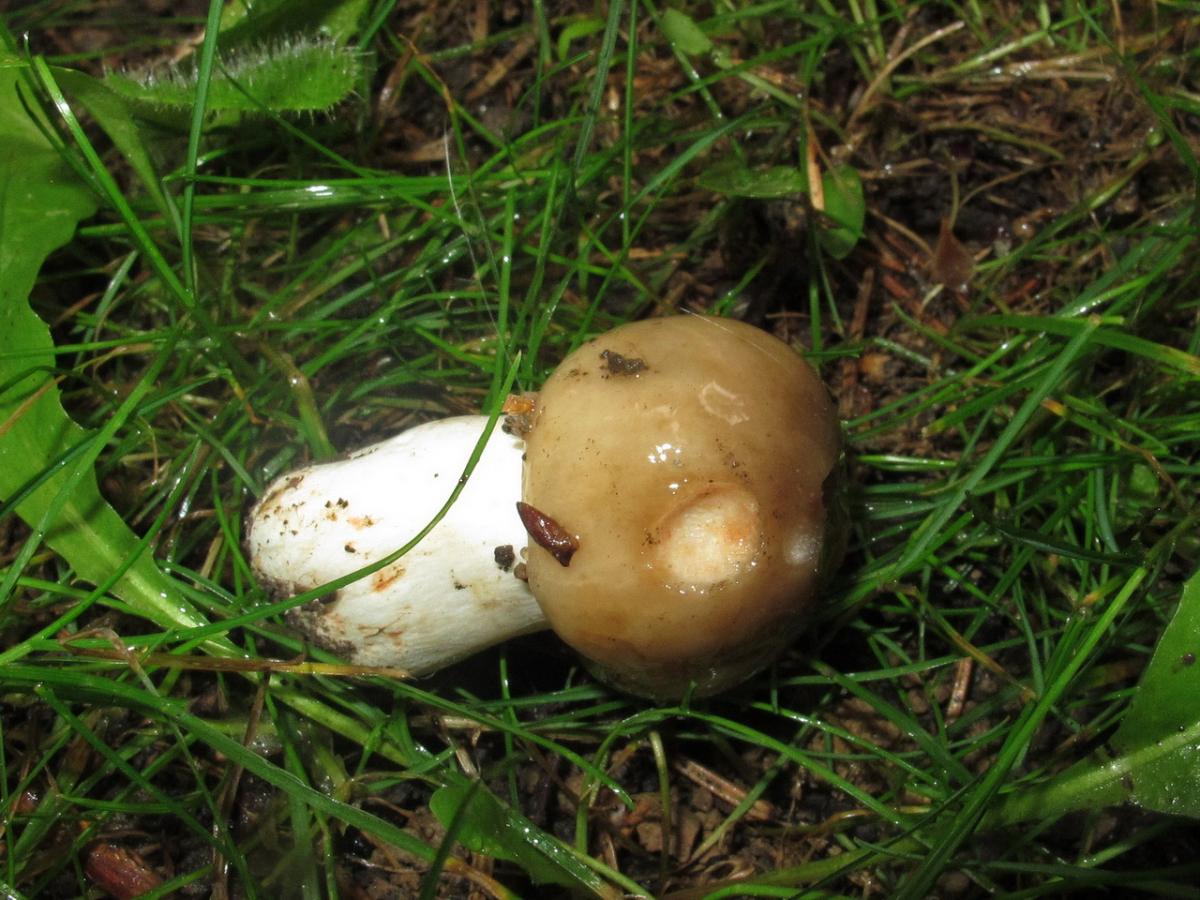
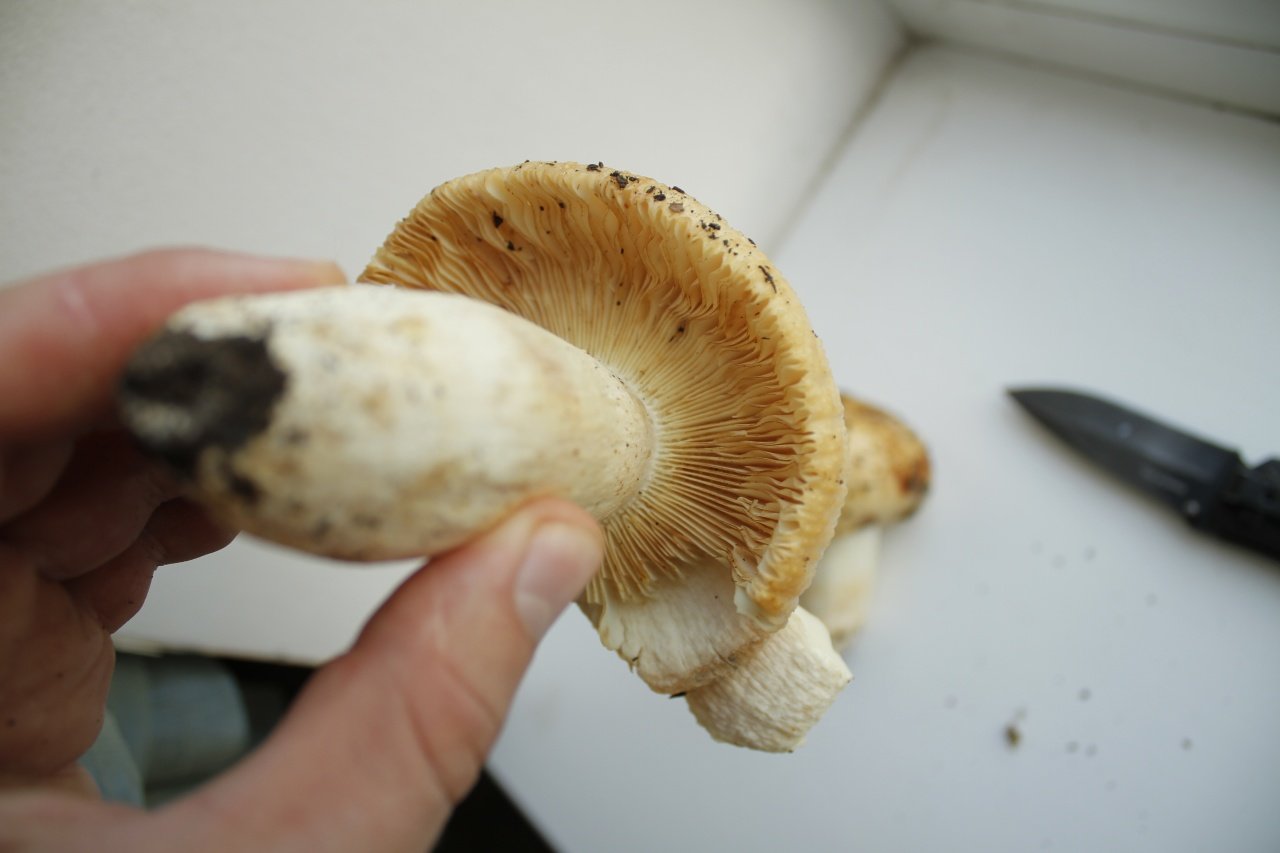
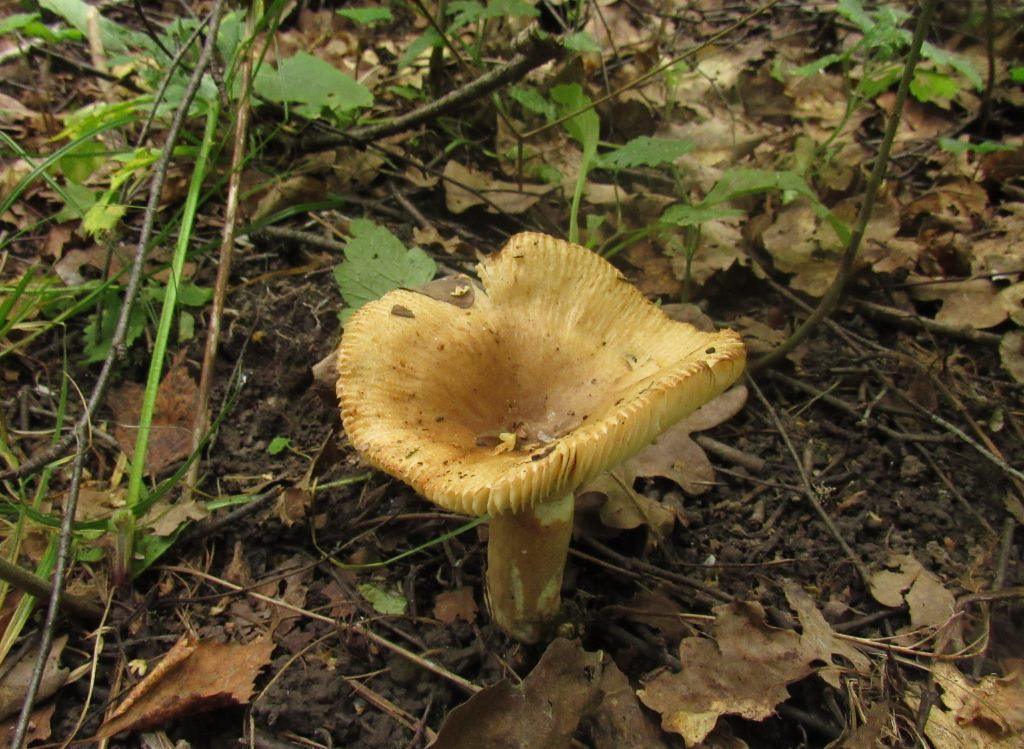
The hat of the Valui is 8-12 (up to 15) cm in diameter, yellow or yellow-brown. In young mushrooms, the cap is spherical; later it opens to almost flat, with a depression in the center and clearly defined radial grooves along the edge. The skin is smooth, shiny, highly slimy, easily removable.
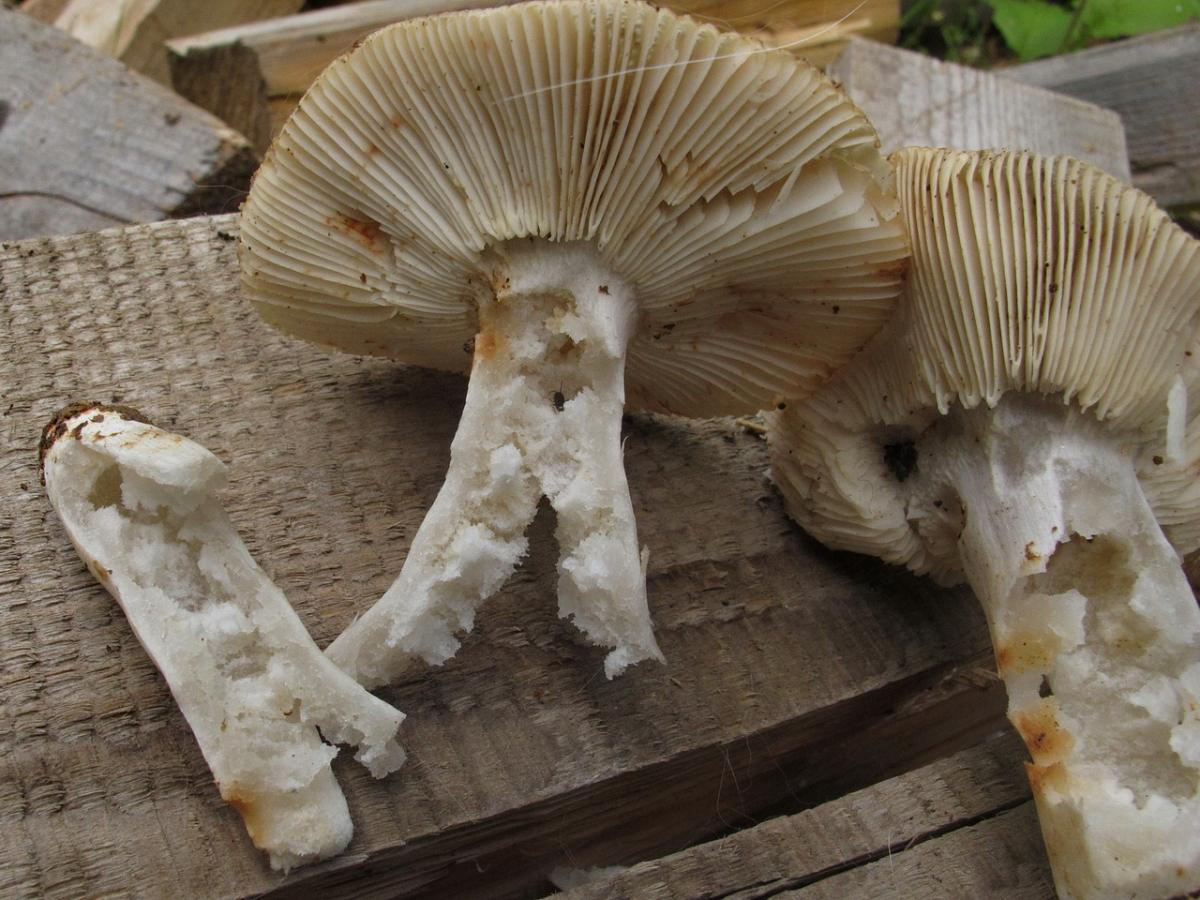
The leg is cylindrical or barrel-shaped, 6-12 cm long and up to 3 cm thick, white, often covered with brown spots, especially near the base. In the middle of the leg, an irregular cavity forms with age, and the leg, at the beginning is relatively strong, becomes very loose.
The pulp is very fragile, white, gradually darkens on the cut and becomes brown. Burning bitter taste, can cause nausea, odor unpleasant, similar to rancid oil.
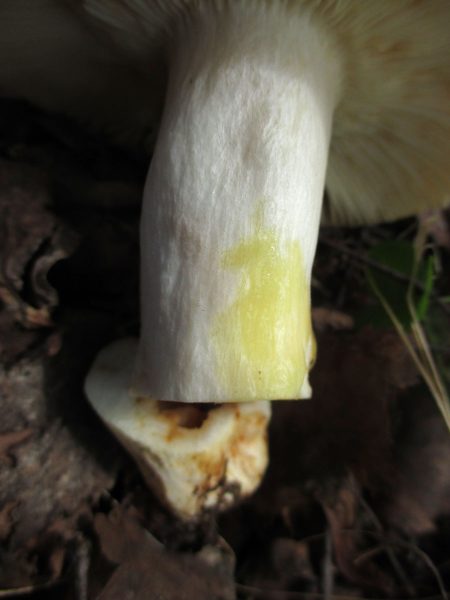
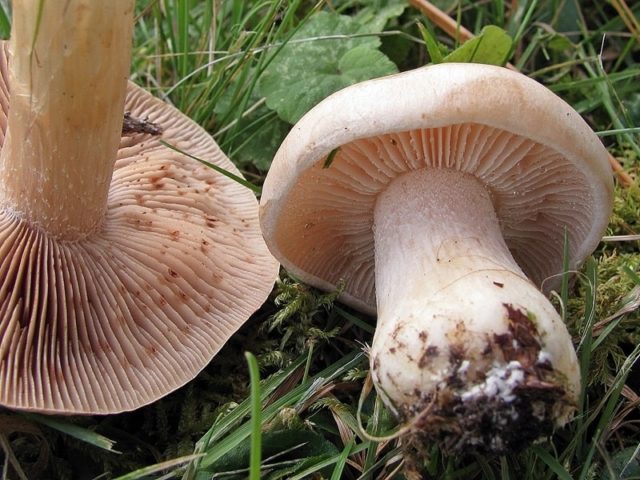
Valuy plates of different lengths, frequent, narrowly accreted, whitish or dirty-cream, emit a yellowish transparent liquid that dries up and leaves brown spots.
Distribution: In some areas, this mushroom is also called a goby. It is found in various forests, but especially where there is a birch, from July to late autumn. Prefers shady, humid places, especially often found in birch forests and forests mixed with birch. Fruiting profusely, singly or in small groups. Season: July to October.
Similarity: From a distance, Valui is very similar to a porcini mushroom. Almond russula (Russula laurocerasii) differs in the smell of bitter almonds. Russula subfoetens gives a yellow coloration of the pulp under the action of alkali solutions, Valui does not give such a reaction. The russula Morse (Russula illota) is distinguished by yellow plates with dark to purple-brown edges; her smell is more like bitter almond.
Note: Despite the pungent pulp with an unpleasant odor, Valui is edible, suitable for pickling.
Mushroom photo Valuy from questions in recognition:
Despite the dissonant name in Latin, which means “stinking russula”, the Valui mushroom is edible. Although, as the name indicates, its use in food is preceded by long-term processing. But pickled, pickled mushrooms will become perhaps one of the most delicious snacks on the table. It is also useful for every mushroom picker to know how not to confuse edible and poisonous mushrooms.
Mushroom Valui
The appearance of fruit bodies and habitat
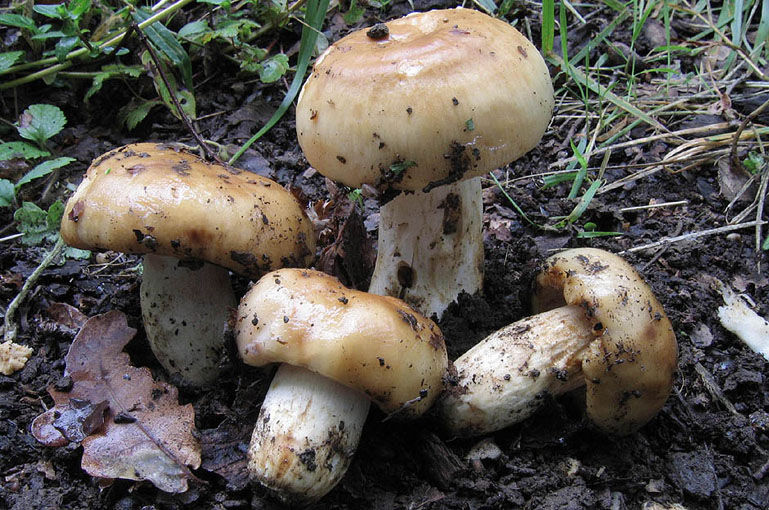
Valui mushrooms are classified as russules. Many people think that they are not suitable for food, and are not harvested in season, but Valui is a conditionally edible mushroom. The people gave him the names "bull", "snotty" and "cam". It looks like a russula.
The appearance of Valui mushrooms:
- A curved or flattened cap up to 15 cm in diameter has a ribbed edge. There is mucus on it, which dries up in the heat. The skin is buffy-yellow or buffy-brown.
- In young individuals, the plates are white-cream, in adults, they are yellow. When damaged, juice is released.
- The pulp darkens with age and in humid weather has an unpleasant odor of dampness and a burning taste. Can cause nausea.
- According to the species description, the young Valui mushroom has a dense, barrel-shaped leg. In adult specimens, it is hollow and filled with soft tissue, growing up to 12 cm in height. Shades range from cream to brownish yellow.
By July, whole placers of Valuev ripen in the forests, and remain there until the end of October. They are not whimsical to the soil and its cover, therefore they grow in any forest, but they prefer moist soil. Often, value mushrooms are scattered in the shade of both deciduous and coniferous trees, although many mushroom pickers believe that one should look for the species only in deciduous forests.
Valui are mycorrhizal organisms that enter into symbiotic relationships with representatives of coniferous and deciduous tree species; it can often be found in birch forests or in forests with an admixture of birches.
You can also meet the Crimean species. According to Western European opinion, this species is inedible, but in the Slavic territories it has long been consumed in salted form and caviar was prepared.
Valui mushrooms are classified as russules
In order not to endanger your life, you need to know how edible fruiting bodies differ from false ones. The most dangerous for humans is considered to be gebele - a poisonous mushroom that disguises itself as russula or white.
Definitioner
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it.However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
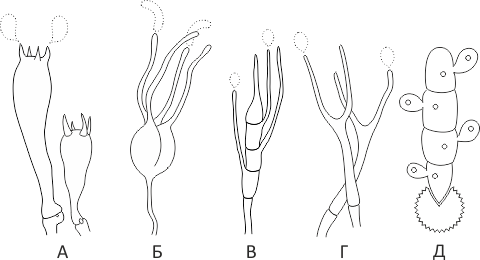
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
- Apical (Apical)
-
Apical.
See Basal.
False doubles
To correctly recognize and identify cowsheds in the forest, you should familiarize yourself with the differences between this mushroom and others. You can see the difference in the photo or carefully study the table:
| Name | Differences | Growing places | Edibility |
Buffy russula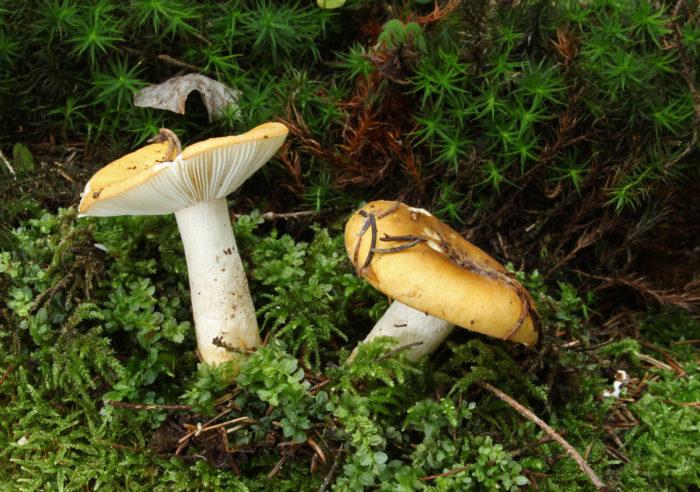 |
A flat or upward-curved hat has a green tint. The stem is smooth, almost white. | The species is widespread in pine, mixed and deciduous forests of Europe, it is very common. | Edible |
Almond russula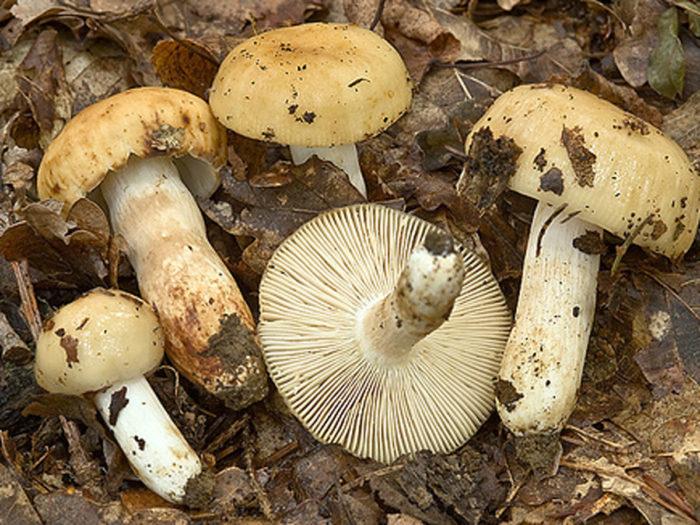 |
The pulp of the mushroom has an almond smell with a slight bitterness | They are found in summer and autumn mainly in mixed and deciduous forests; they are extremely rare in conifers. | Edible |
Russula morse |
It has yellow plates, the edges are purple with brown, the aroma is similar to almond. | They grow in deciduous and pine forests. They live singly or in small groups. | Edible |
False value (false value), gebeloma, shitty mushroom |
There is a small tubercle in the center of the cap, the stem is covered with small scales, thickens at the base. The cap and stem are brown or dark yellow. The pulp of a freshly cut mushroom has a pungent horseradish odor. | Grows from late summer to early September | Poisonous |
Conclusion
This species has a description similar to the porcini mushroom, russula and gebeloma. Edible mushrooms grow in all forests, prefer moist soil and tree shade. Before eating, even edible mushrooms are subjected to long processing to get rid of the pungent bitterness.
For some reason, many mushroom pickers do not know or do not take mushrooms called gobies or valuy. It is also surprising to me that not all even old mushroom pickers know about such a mushroom. So I would like to introduce you to him in this post. It is worth taking this mushroom, since it has no equal in pickled or salted form. Personally, I really love pickled gobies under boiled potatoes with onions and butter. But, to my regret, I’m not particularly lucky with this mushroom. One and only summer 2012 I was lucky to go to the forest for three days in a row and each time I bring 2 ten-liter buckets of these wonderful mushrooms. It was in July, the weather was cloudy, but it was warm and humid, it was raining. Every time, tall to the skin, I brought a full backpack and buckets full of mushrooms. These memories are priceless to me. And here are the gobies, prepared for salting, already now they will be laid out in jars and poured with marinade.
How to identify a Valui mushroom in the forest?
Rolls grow along the edges of deciduous forests, or on well-dug land inside the forest, or inside deciduous forest, where there is low and sparse grass and few trees. Swaths do not grow in dense grass. The rolls are located in heaps, families and circles, where you find one roll, there and others nearby should be looked for. It grows only in deciduous forests and most often along the edges of deciduous forests, more often from the southwestern side. Looks like this in the forest:
How to distinguish Valui from toadstool?
The Valui mushroom has a slippery (snotty) cap, but sometimes in dry weather, the cap may be dry, but nevertheless, when soaked in water, the cap should still become slippery, otherwise it will not be Valui.In water, after half an hour, the cap becomes slimy, covered with mucus.
The second difference is the smell. Valui mushroom has a pronounced raw mushroom smell, a little spicy. It smells good to me.
The third, most important, difference: on the cut of the leg, the leg has an empty channel inside. This feature is inherent in all mushrooms of the russula family. Very often and quickly, these mushrooms become wormy. They quickly outgrow and become wormy and with a developed cap.
Valui belongs to conditionally edible mushrooms, its juice is bitter. This mushroom can only be salted, nothing can be cooked from it raw. In addition, the windrows should be soaked in cold water for no more than two hours before sitting.
How to salt?
The procedure for hot salting of mushrooms with a bitter taste (milk mushrooms, volnushki, valuei) is standard. To do this, already prepared mushrooms (read above how to do this) must be boiled for 20-30 minutes in salted water or blanched (i.e. immersed in boiling water for 15 minutes). Then we put the mushrooms in a colander to dry and drain excess water from them. After that, we take from sterilized suitable containers and fill them with mushrooms, sprinkling them with salt layer by layer (1 tsp per layer) as it is done with the cold method. After that, close the jars with lids or parchment paper tightly and let cool. The jars are now ready for storage - in the cellar or refrigerator. Mushrooms can be eaten after half a month.
3
Valui mushrooms are not very popular among lovers of "quiet hunting". Few know how to cook them, but everyone is aware that they have a pronounced bitterness, which spoils the finished dish with terrible force. However, those who know how to overcome the gustatory peculiarities of valuy collect it willingly and assure that, properly prepared, it is not inferior to other, beloved and revered, brothers.
























































