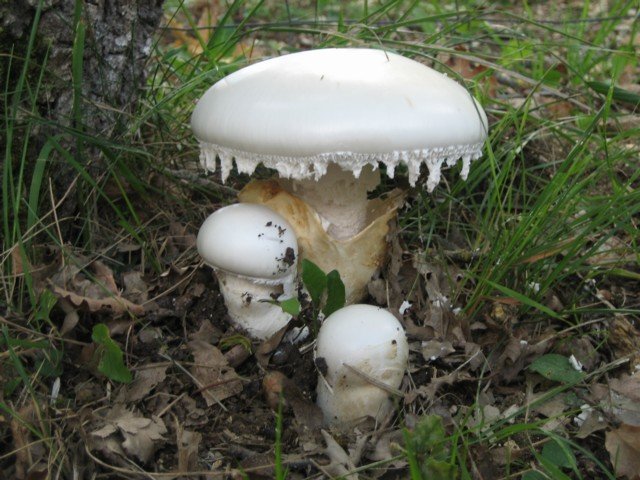
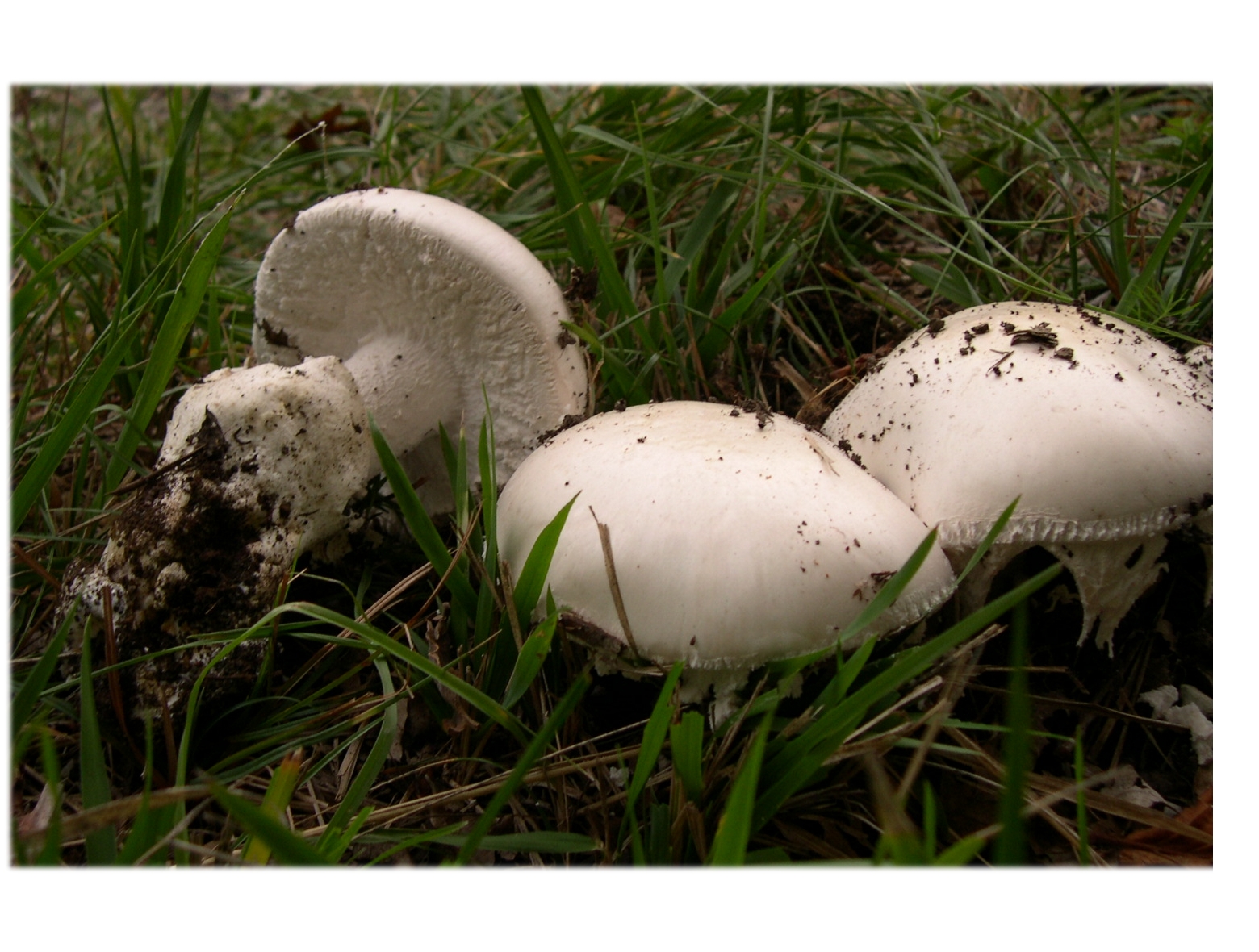
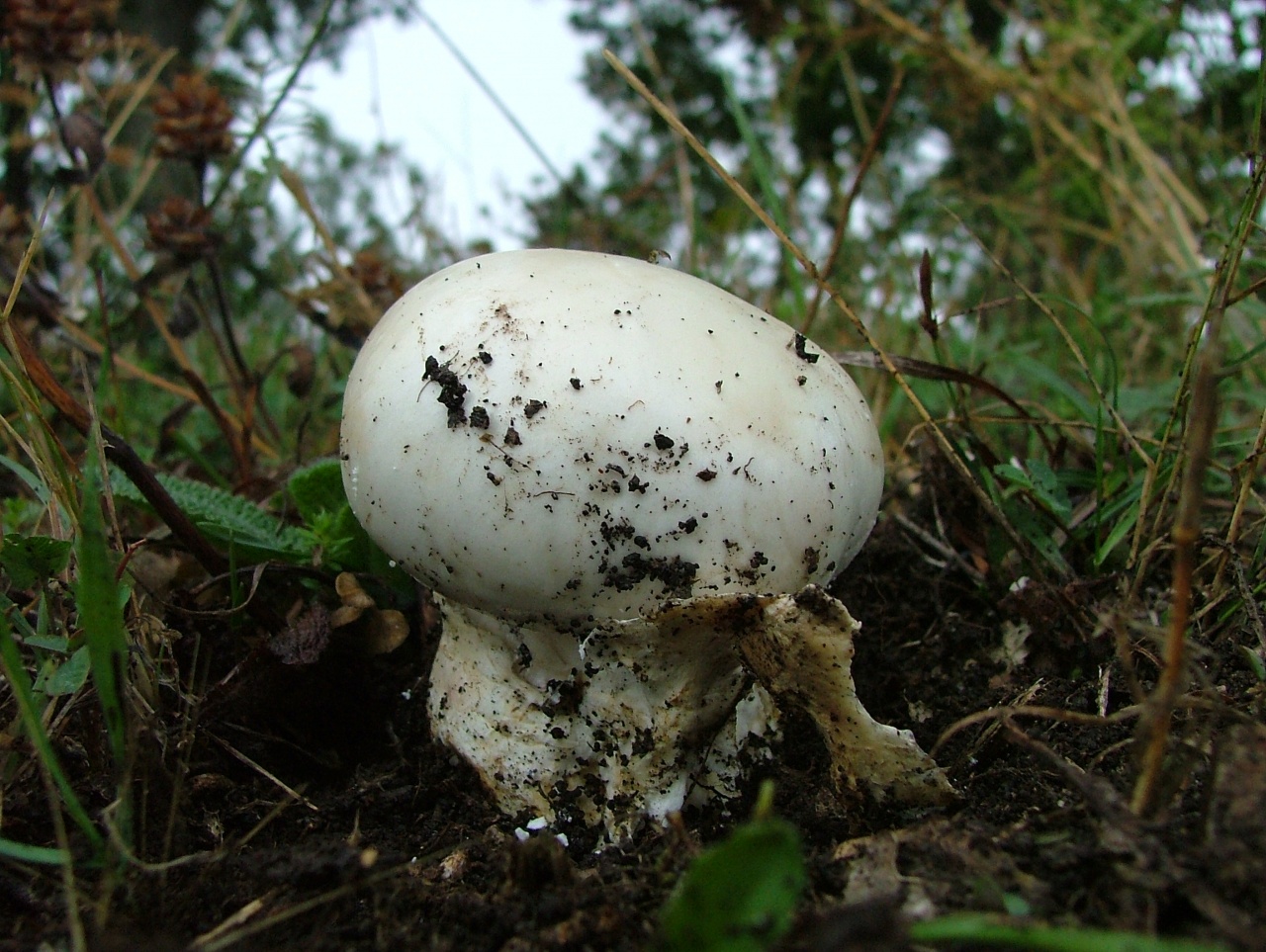
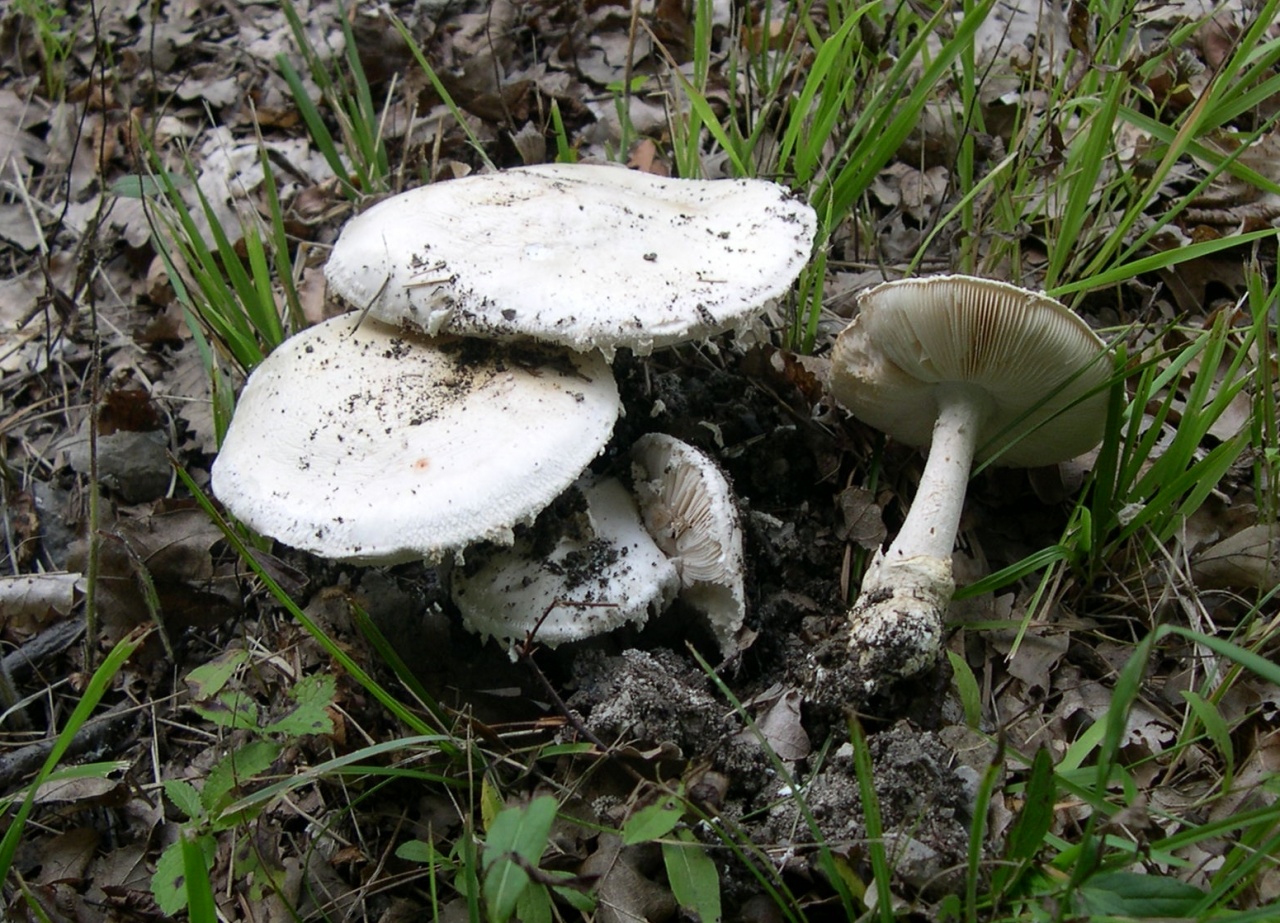
Amanita muscaria (lat.Amanita phalloides)
Name Amanita is green.Latin name: Amanita phalloides.Other names: Death cap.Department: Basidiomycota.Class: Agaricomycetes.Order: Agaric.Family: Amanite.Genus: Amanita.Deadly Poisonous Mushroom!
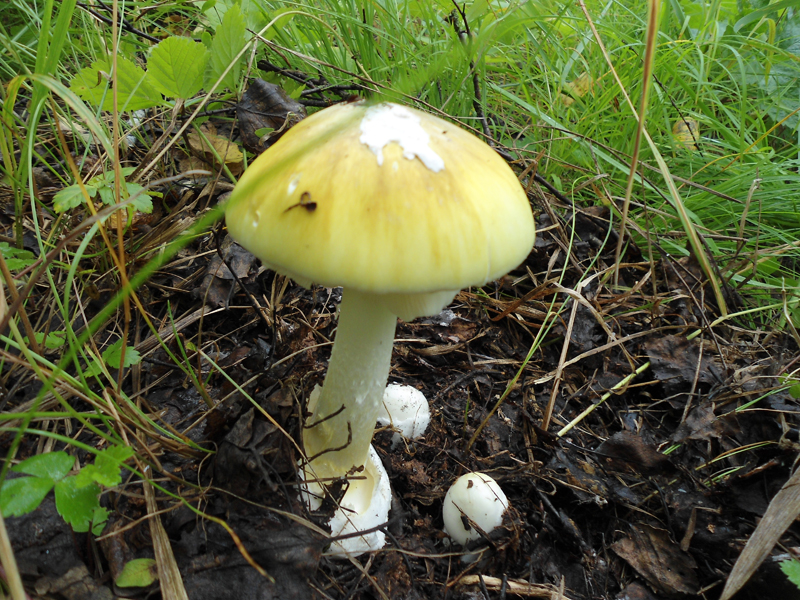 Name Amanita is green.Latin name: Amanita phalloides.Other names: Death cap.Department: Basidiomycota.Class: Agaricomycetes.Order: Agaric.Family: Amanite.Genus: Amanita.Deadly Poisonous Mushroom!
Name Amanita is green.Latin name: Amanita phalloides.Other names: Death cap.Department: Basidiomycota.Class: Agaricomycetes.Order: Agaric.Family: Amanite.Genus: Amanita.Deadly Poisonous Mushroom!
Leg
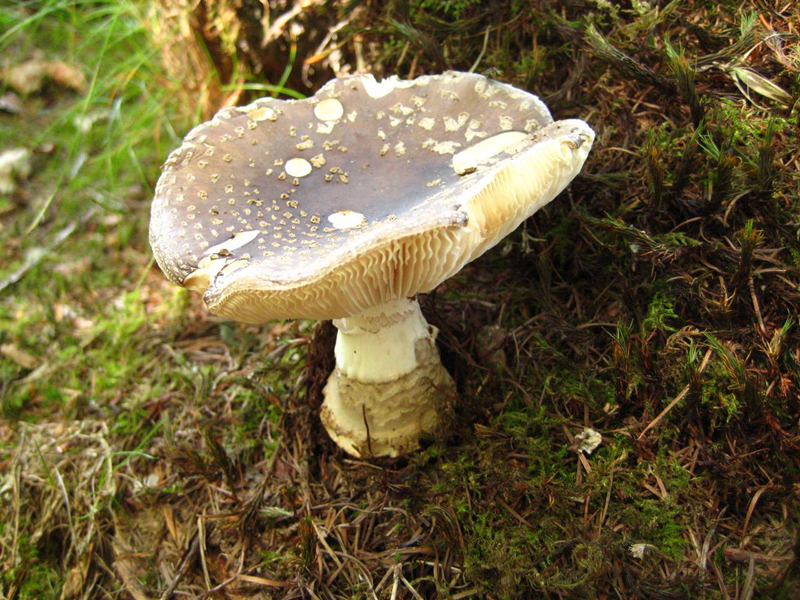
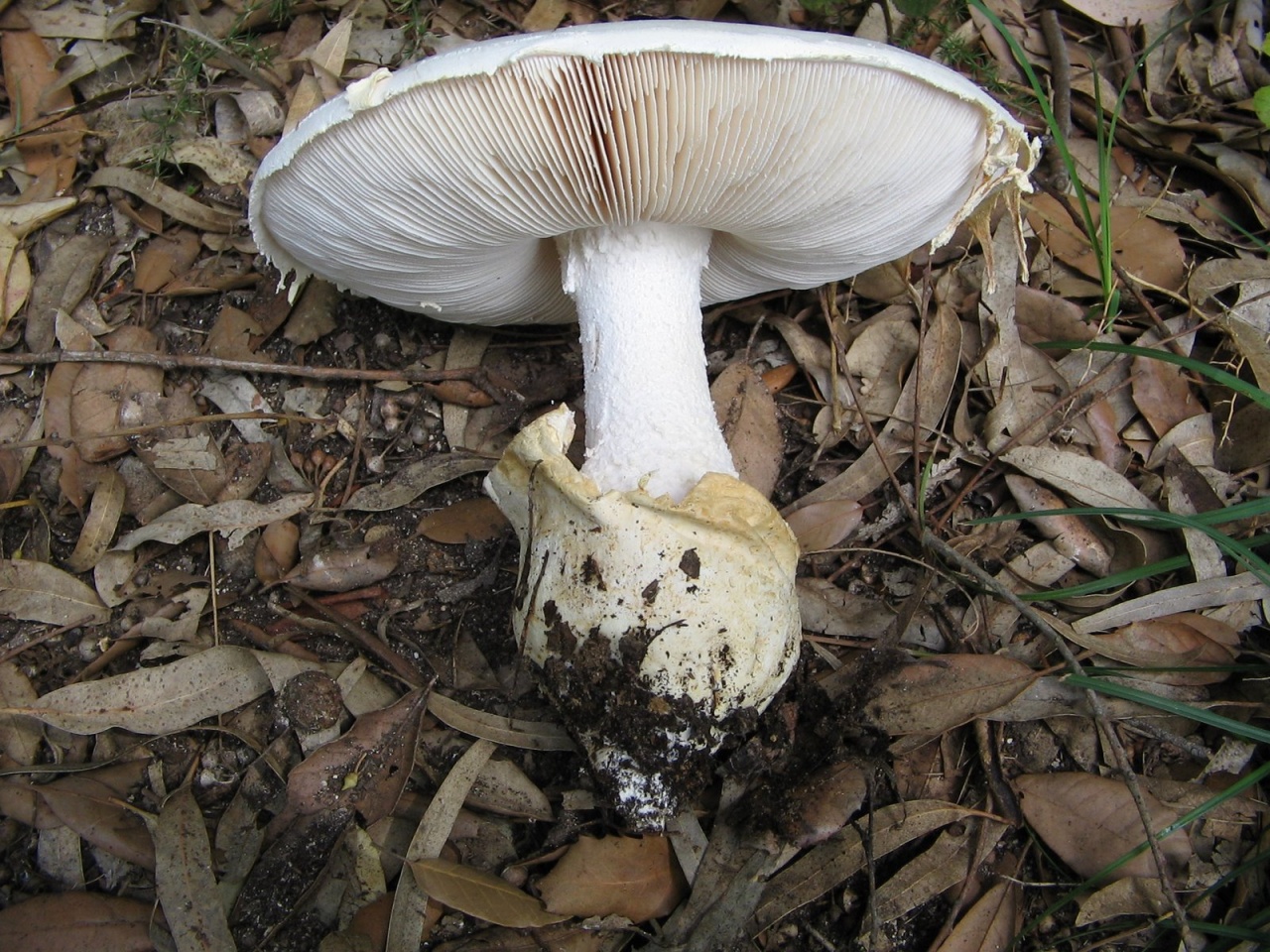
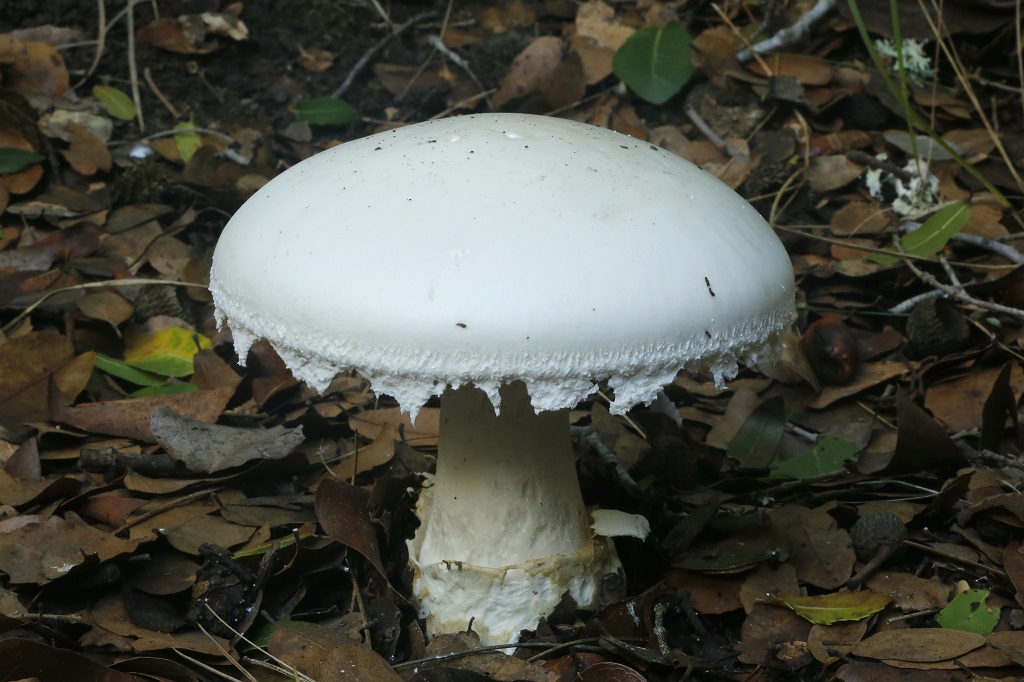
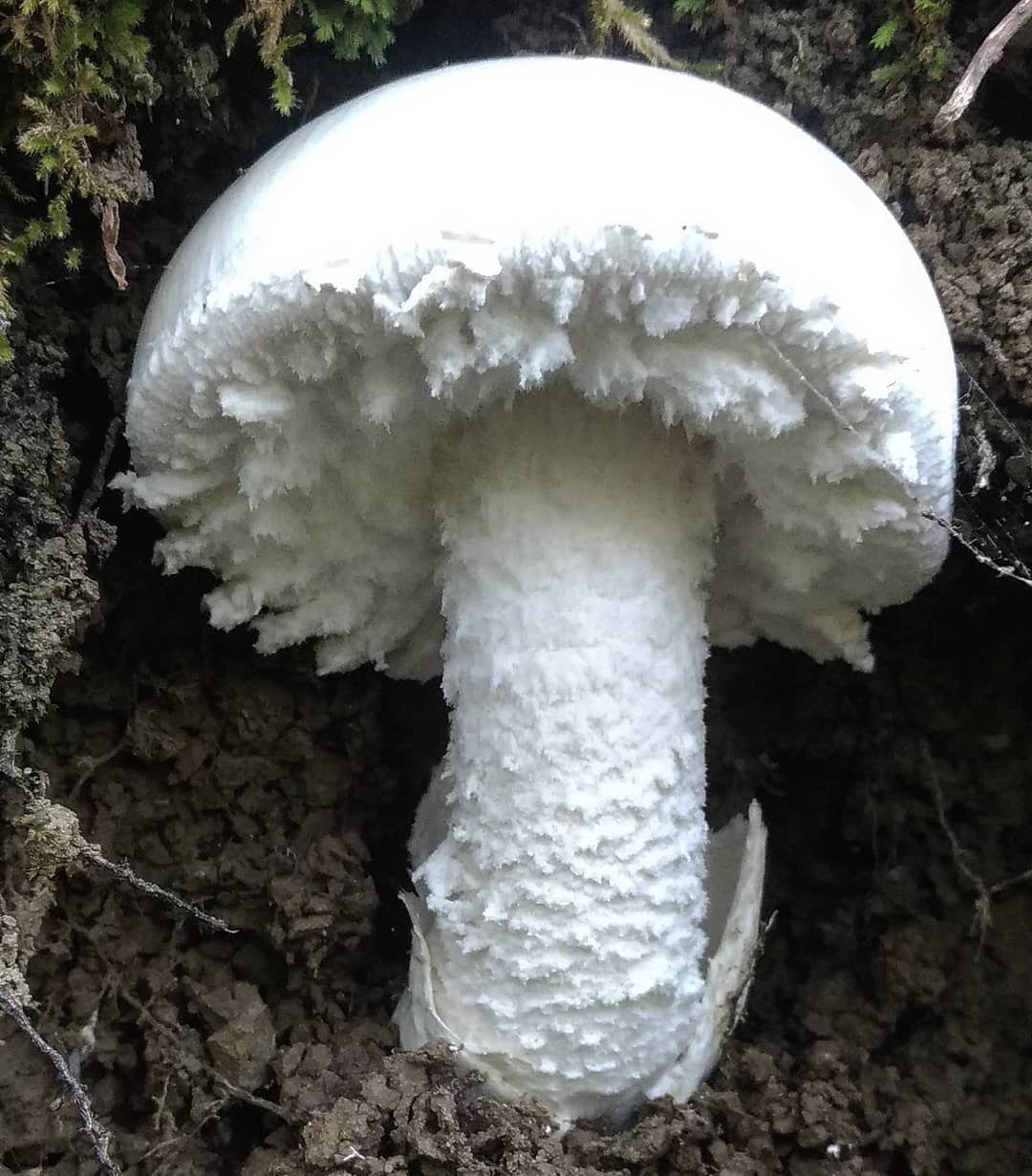
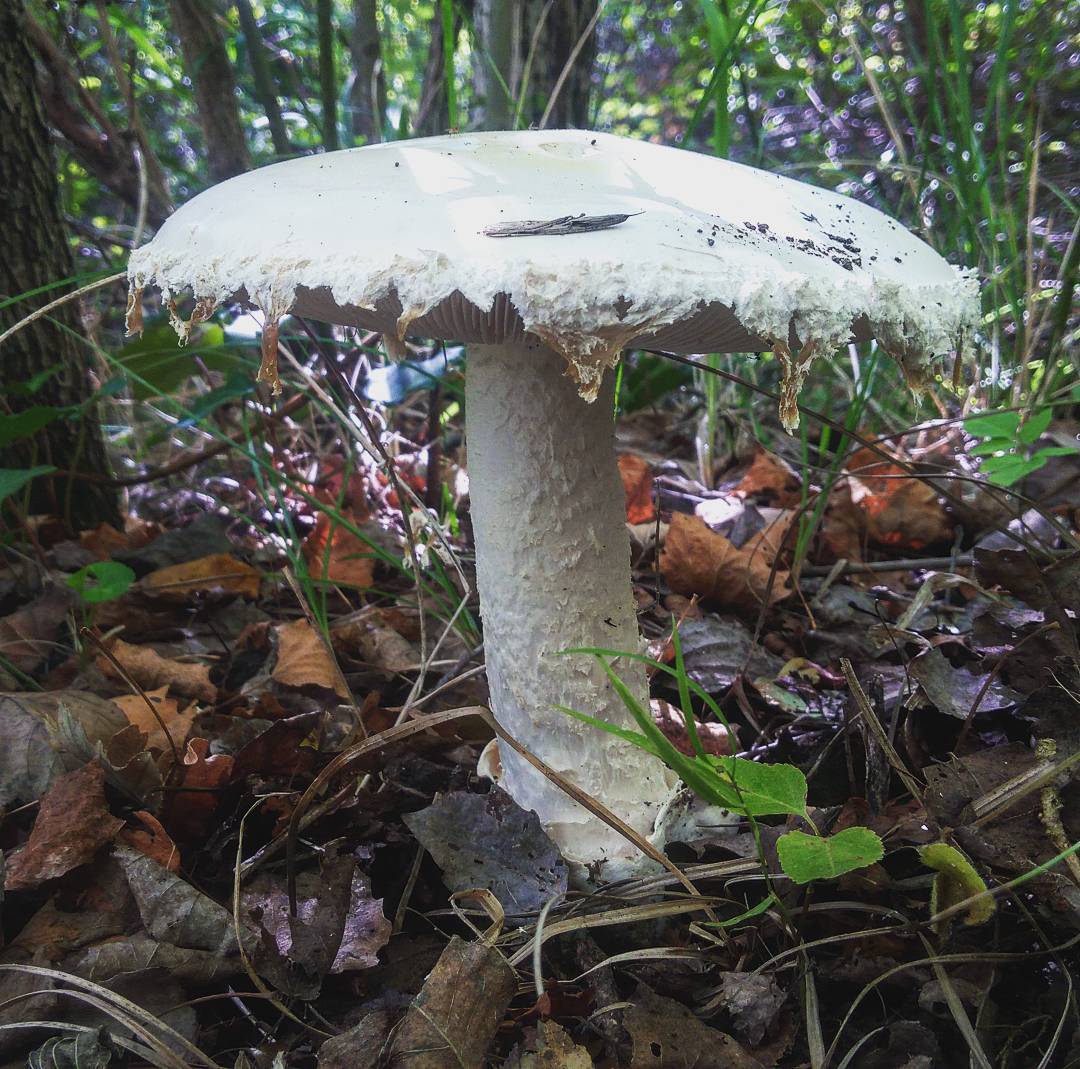
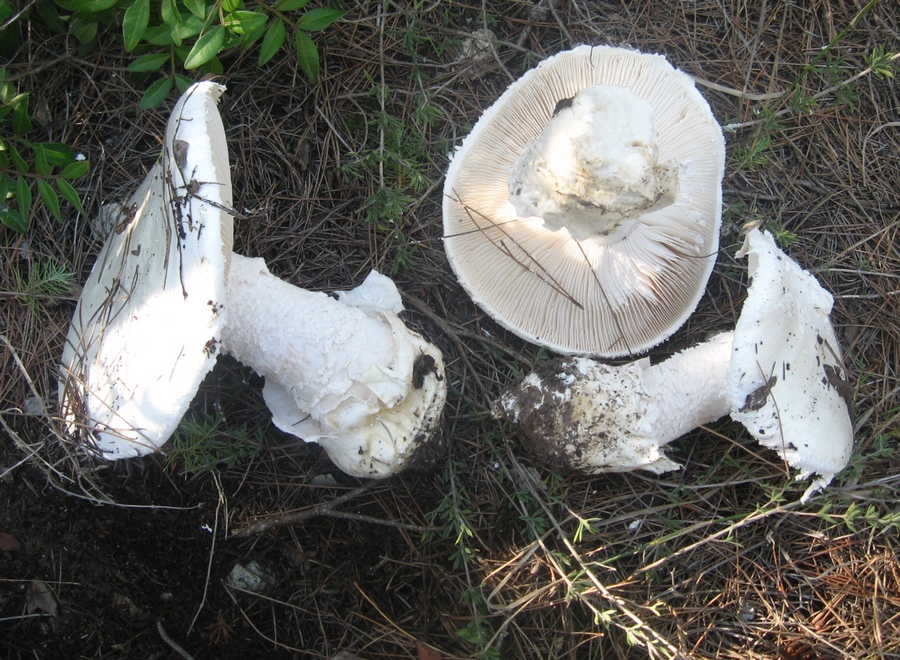
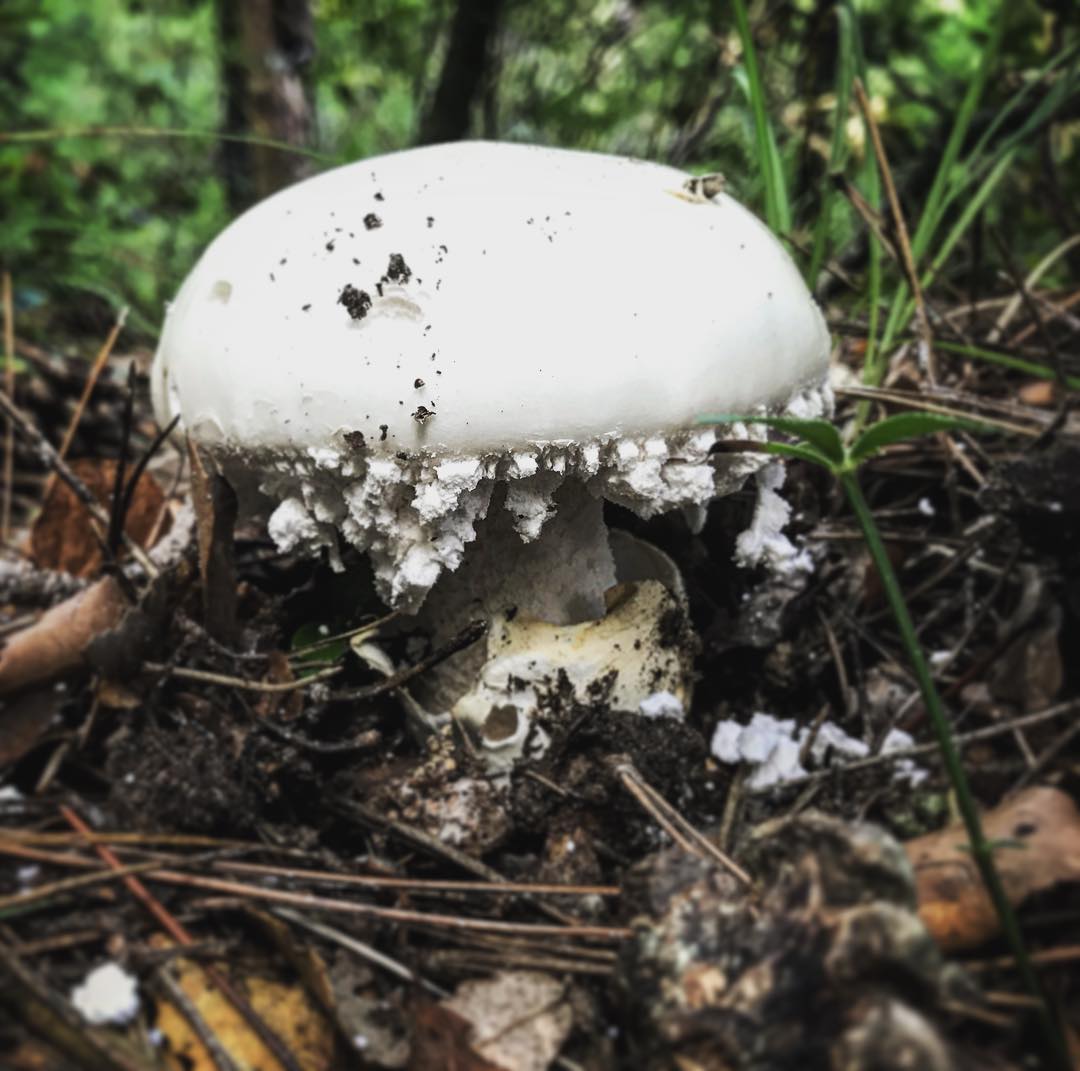
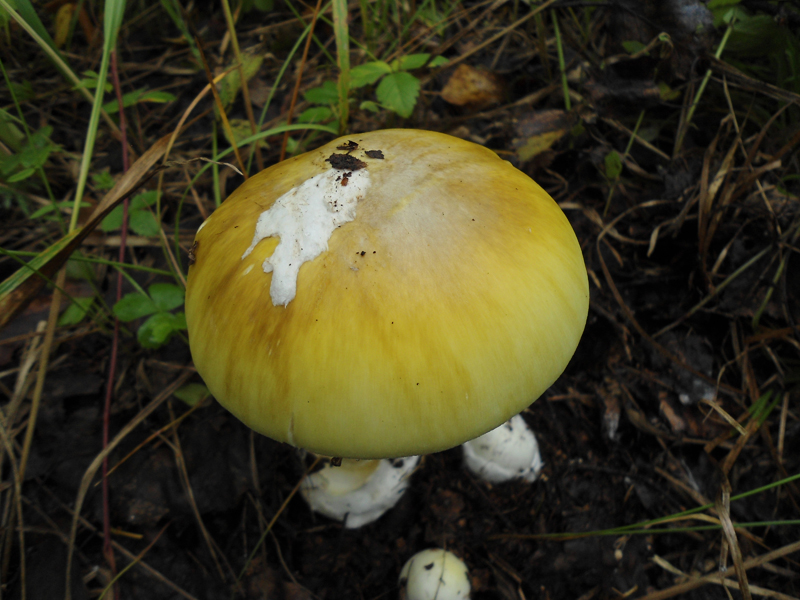
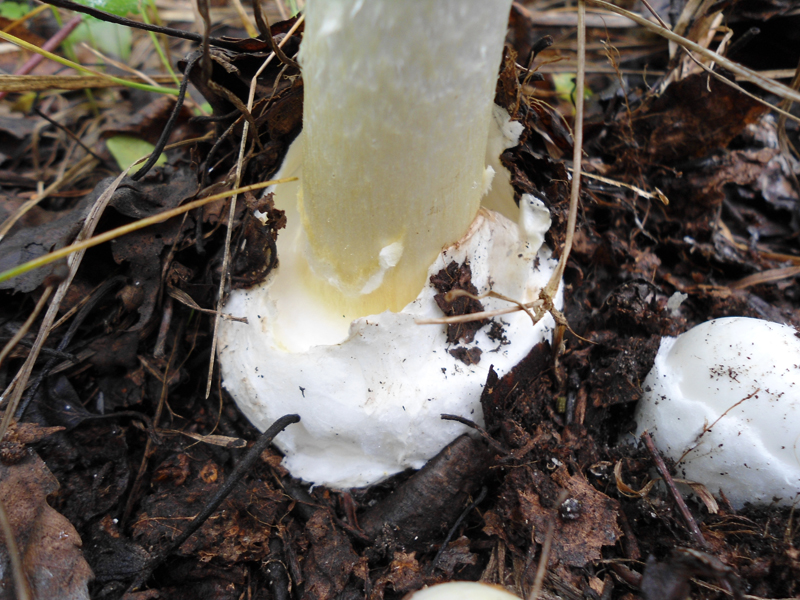
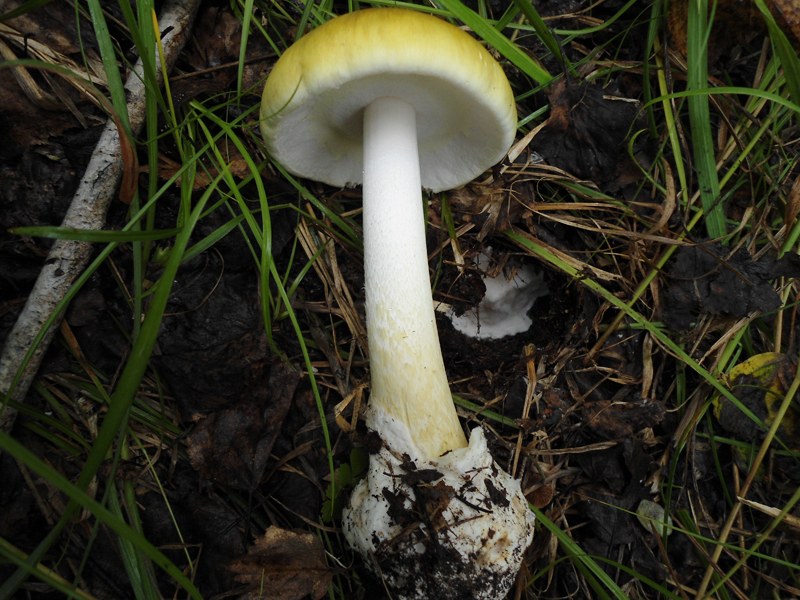
50-150 mm high and 10-25 mm thick, cylindrical, tuberous base and wrapped in white free volva. Inside, it is at first solid, later the pulp becomes cottony and, by maturity, the pipes are chato-hollow. Easily detaches from the cap. Most often it is white, occasionally yellowish-green or grayish with a striped slightly greenish ornament. There is a thin white ring in the upper third.
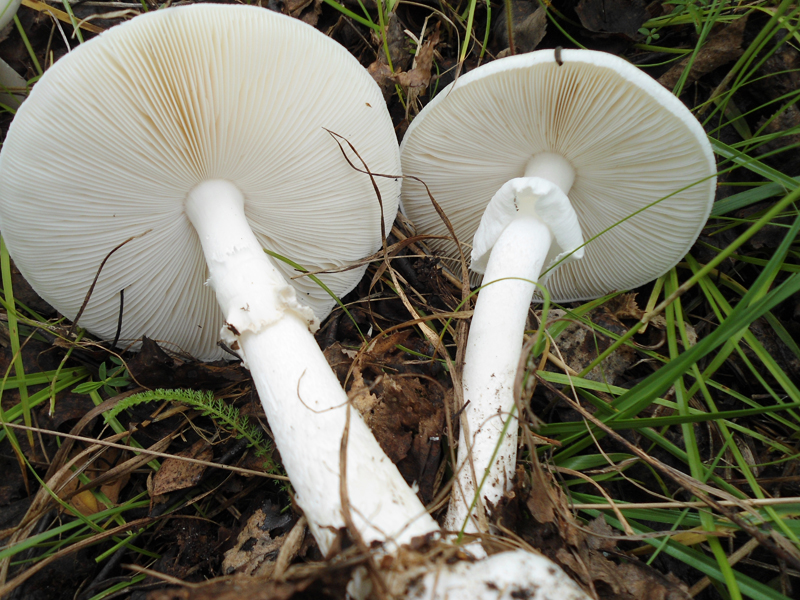

Hat
60–150 mm in diameter, most often yellow-green, brown-green or gray-white, always darker in the middle. Occasionally it is ocher and white. In young fruiting bodies, bell-shaped, convex, flat towards maturity. The surface is silky, delicately fibrous, smooth and bare.
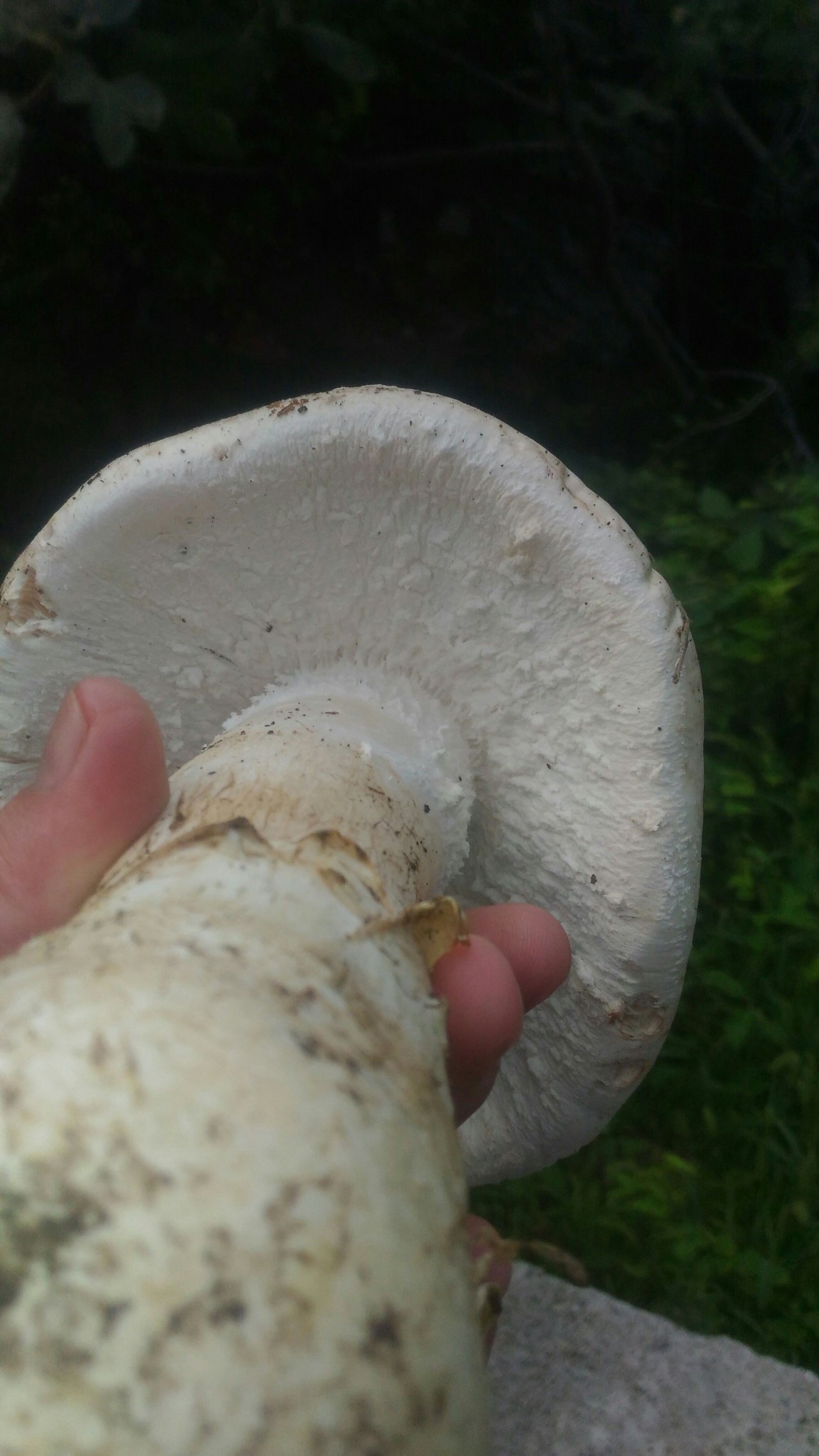
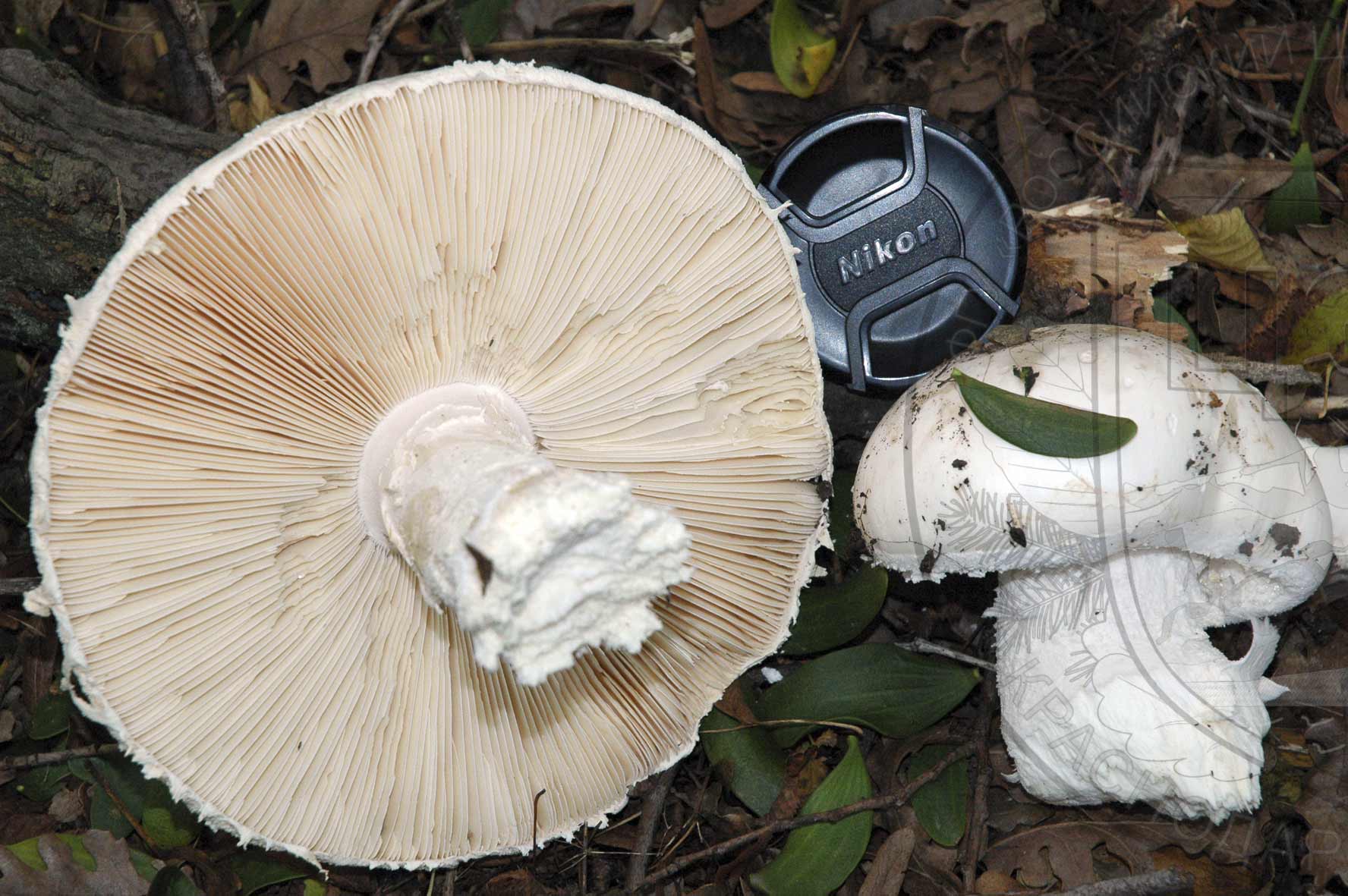
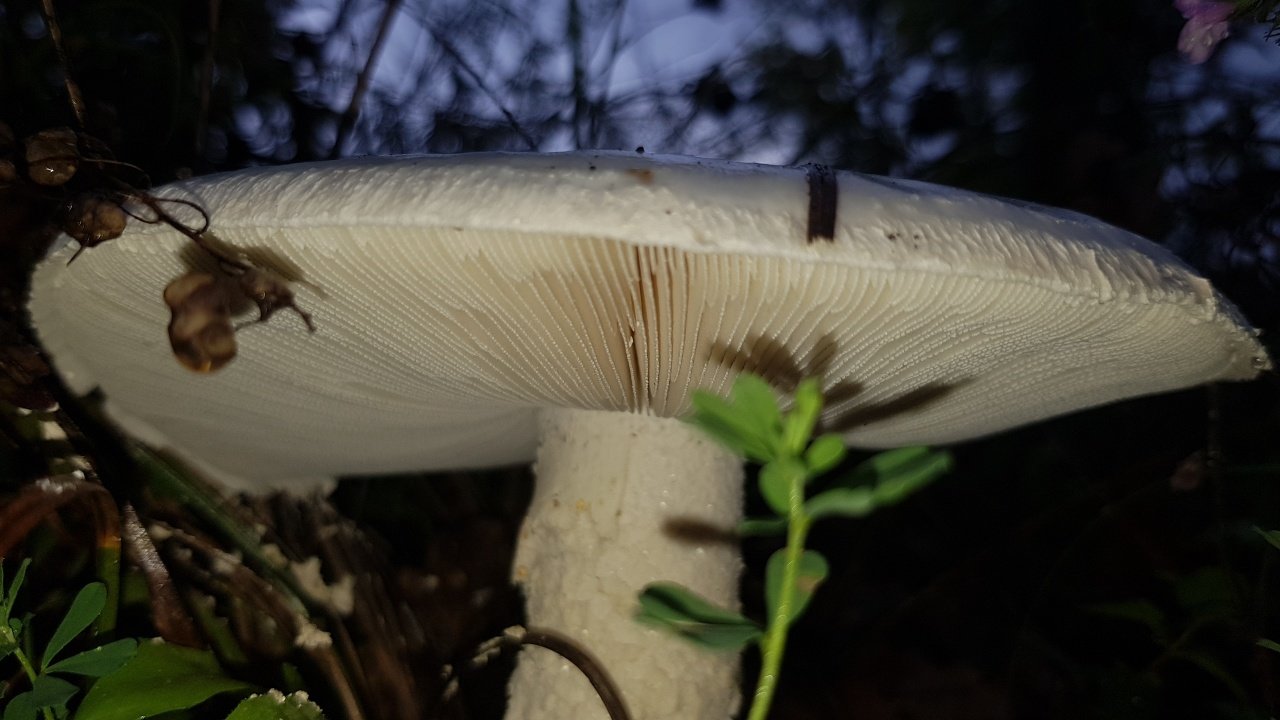
Lamellar, white plates, frequent, 8-12 mm wide, free at the stem, rounded at the edge of the cap.
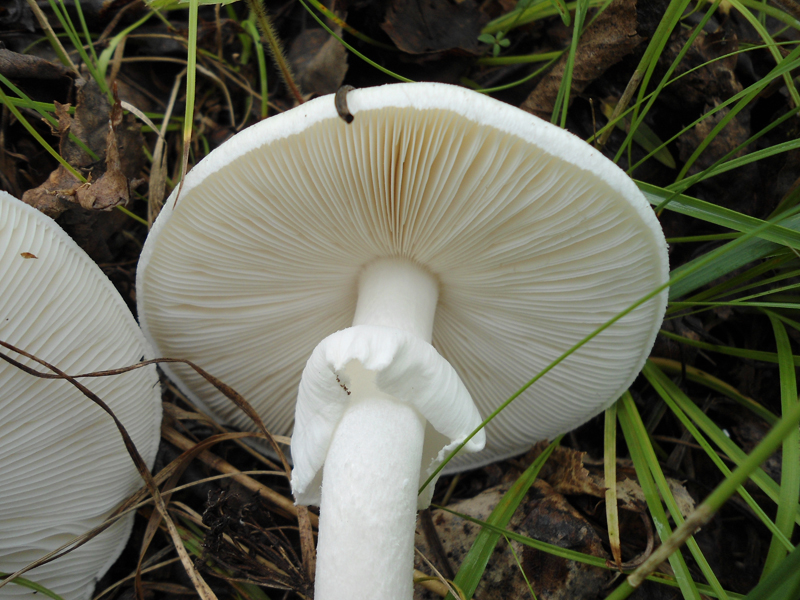

Pulp
Soft, dense, white, slightly yellowish-brownish under the skin of the cap, does not change color when cut. Young mushrooms have an inexpressive smell, while mature ones have an unpleasant smell, like the smell of old raw potatoes.
50–62 x 12–15 µm, clavate, four sterigmata.
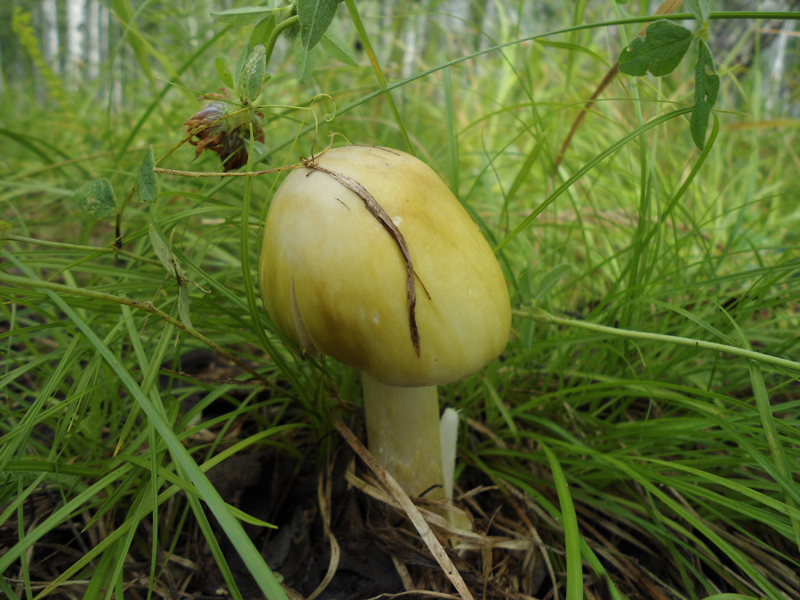





Habitat
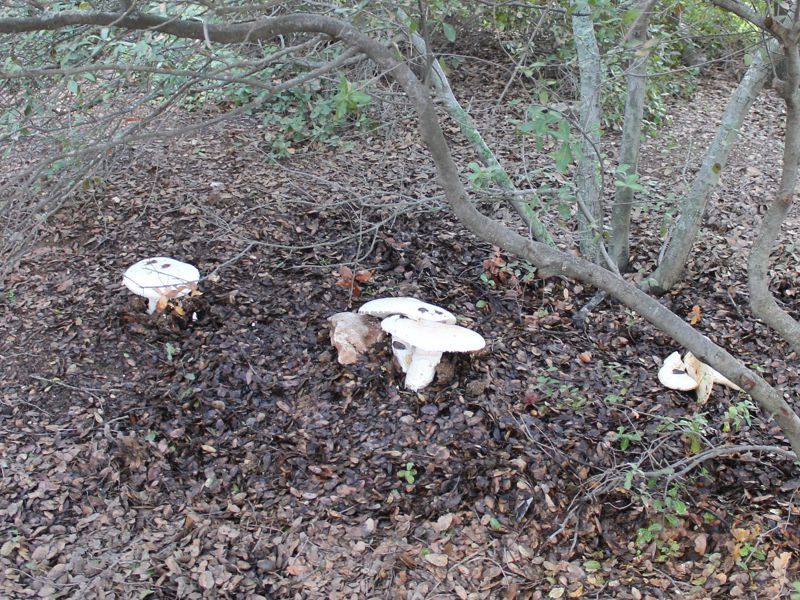
Grows singly or in small groups on soil in broad-leaved and less often coniferous forests. Forms mycorrhiza with various tree species.
Similarity
Green fly agaric (Amanita phalloides) resembles Amanita citrina, Amanita vaginata, Amanita submembranacea, Green-yellowish float (Tricholoma viridilutescens), Green grass (Tricholoma viridilutescens) ...
|
December |
January |
February |
|
March |
April |
May |
|
June |
July |
August |
|
September |
October |
November |
Poisoning symptoms
¼ part of the middle fruiting body (about 30 g) causes severe poisoning. Heat treatment does not eliminate the toxic effect. The main symptoms: after 2 days there is indomitable vomiting, intestinal colic, muscle pain, unquenchable thirst, cholera-like diarrhea (often with blood). Jaundice and liver enlargement are possible. Pulse - weak, threadlike. Blood pressure is lowered, loss of consciousness is observed.
As a result of toxic hepatitis and acute cardiovascular failure, death occurs in most cases. The particular danger of the fungus is that the signs of poisoning do not appear for a long time. Symptoms may not appear for the first 24 hours or more, during which, nevertheless, the body is already being poisoned and damaged. A feature of intoxication is also the "period of false well-being", which occurs on the third day and usually lasts from two to four days. In fact, at this time, the destruction of the liver and kidneys continues. Death usually occurs within 10 days of poisoning.
Links
- Taxonomy at www.mycobank.org
- Dr. Rodham E. Tulloss.Amanita ovoidea (English). Date of treatment September 22, 2009.Archived April 8, 2012.
This page was last edited on 22 October 2018, at 08:24. From Cyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search
Amanita muscaria
Taxonomy
| Domain | Eukaryotes |
| Kingdom | Mushrooms |
| Subkingdom | Higher mushrooms |
| Department | Basidiomycetes |
| Class | Agaricomycetes |
| Order | Champignon |
| Family | Fly agaric |
| Genus | Fly agaric |
| View | Amanita muscaria |
Amanita ovoidea (Bull.) Link 1833
EOL (1029997)
|
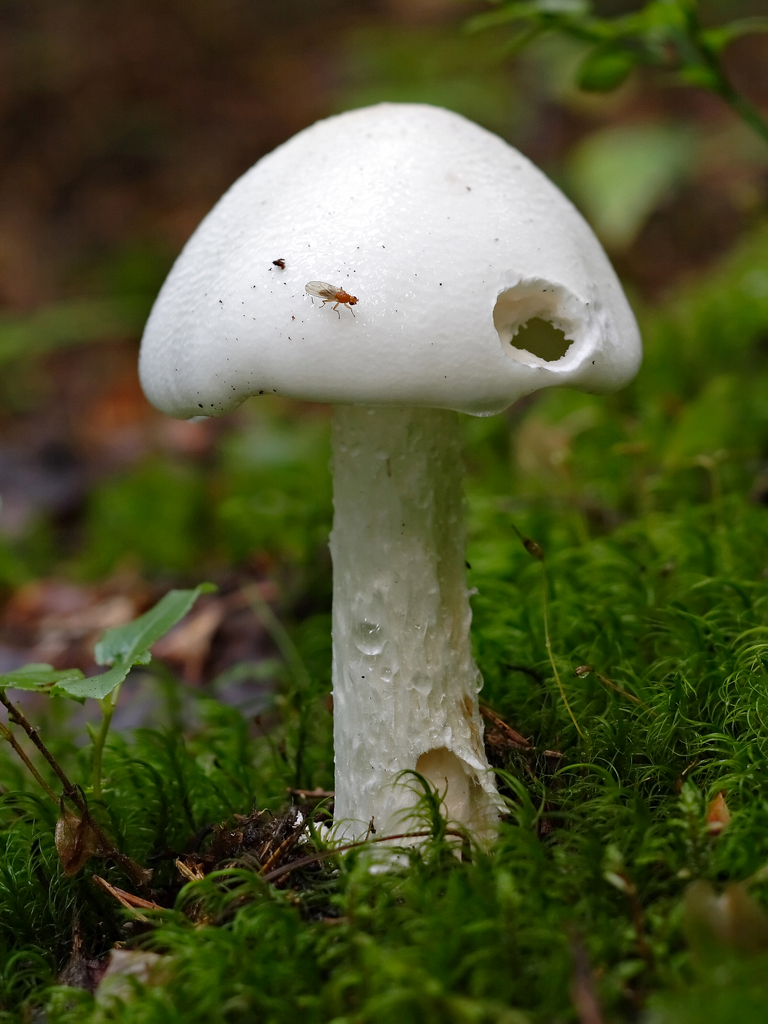
Amanita muscaria (lat.Amanita ovoidea) - an edible mushroom from the genus Amanita (Amanita) of the family Amanita (Amanitaceae).
Spring fly agaric: description, properties
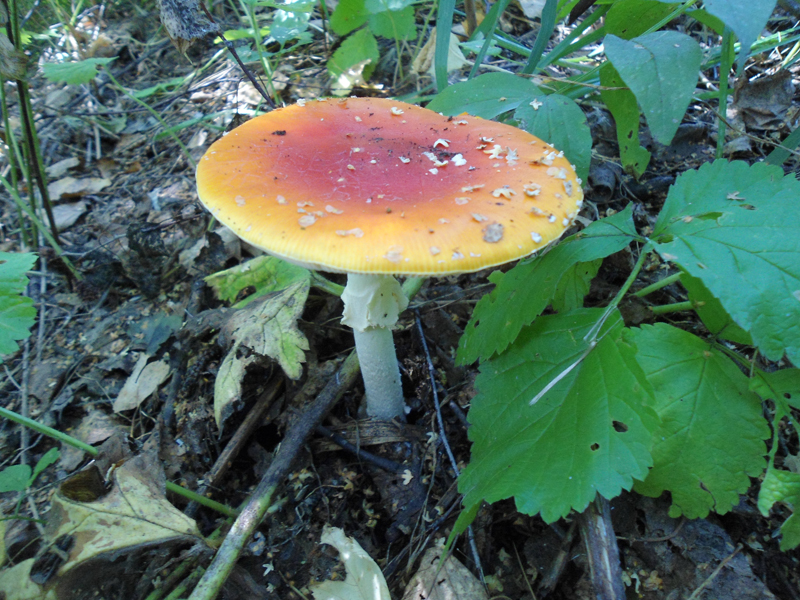
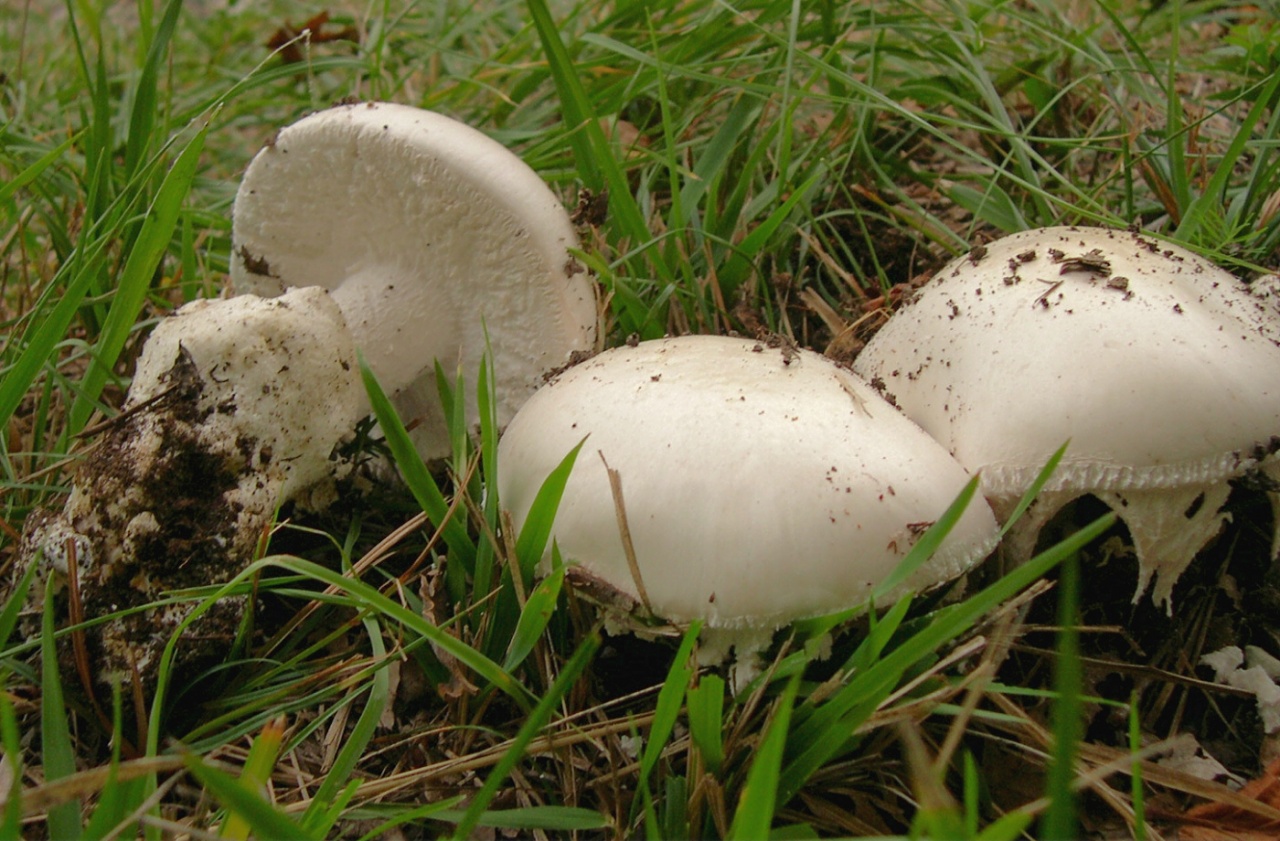
Spring fly agaric (Amanita verna) is another inedible mushroom. It has a white, shiny and smooth cap with a diameter of 4 to 12 cm. Sometimes its color has a grayish tint. The shape of the cap of young mushrooms is in the shape of a hemisphere, in adults it is almost flat.

Spring fly agaric (Amanita verna)
The leg is thickened at the base. The surface is smooth, the height is from 5 to 13 cm. It has the same color as the cap and a light bloom. The plates are white. The flesh of the mushroom is very brittle, white and dense
This mushroom does not have any bright aroma or taste, however, given its toxicity, this does not matter
The counterparts of the spring amanita are various types of mushrooms, the green russula (Russula virescens), the green russula (Russula aeruginea) and various floats. But champignon plates, as a rule, are colored and, moreover, they do not have volva, just as very fragile russules do not have it. And if we talk about a greenish russula, then it also does not have a mushroom ring and it is very small.

Spring fly agaric (Amanita verna)
The spring amanita grows in warm regions, from late April to mid-summer. On the territory of Russia, it is easiest to find it in the south and in the Volga region. Prefers deciduous forests and moist soils. It is not used either in cooking or in folk medicine.
Death cap
Next, we will talk about the most poisonous mushroom in the world, which also belongs to the genus Amanita. Let's find out more about what a pale toadstool is.
Edible or not
It is forbidden to eat pale toadstool in any form. Even after boiling with a change of water, this mushroom retains its toxicity.
To kill an adult, it is enough to give him about 30 g of pulp. Death occurs as a result of a powerful intoxication, which causes the appearance of toxic hepatitis (liver failure), as well as acute heart failure. As a result of the action of toxic substances, the liver begins to deteriorate rapidly. The kidneys do not have time to remove toxins and simply refuse.
Important! The danger lies in the absence of symptoms of poisoning on the first day. Death after use occurs after 1.5 weeks in any case
Other name
Amanita muscaria is also called green fly agaric or white fly agaric. The Latin name of the species is Amanita phalloides.
What does it look like
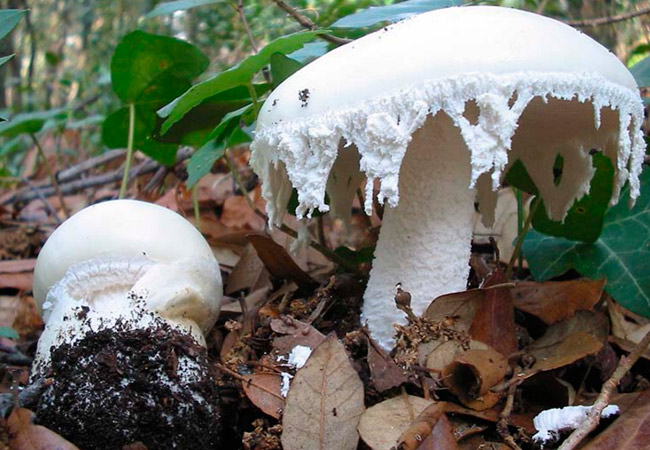
- The mushroom cap has a diameter of up to 10 cm. At the initial stage of development of the fruiting body, it has a domed shape, but over time it becomes flat and then concave. As for the color, there are several variations. In some regions, there is a marsh-green grebe, in others, a yellowish-brown one. Also, the hat can be white.
The pulp is colored white. A distinctive feature is that after damage and prolonged contact with oxygen, the pulp does not change its color. Has a very faint odor.
The length of the leg varies between 8-15 cm in length and 1-2.5 cm in diameter. The color is identical to the hat. Sometimes there are mushrooms with a moiré pattern on the stem.
The plates are white, soft to the touch, located freely.
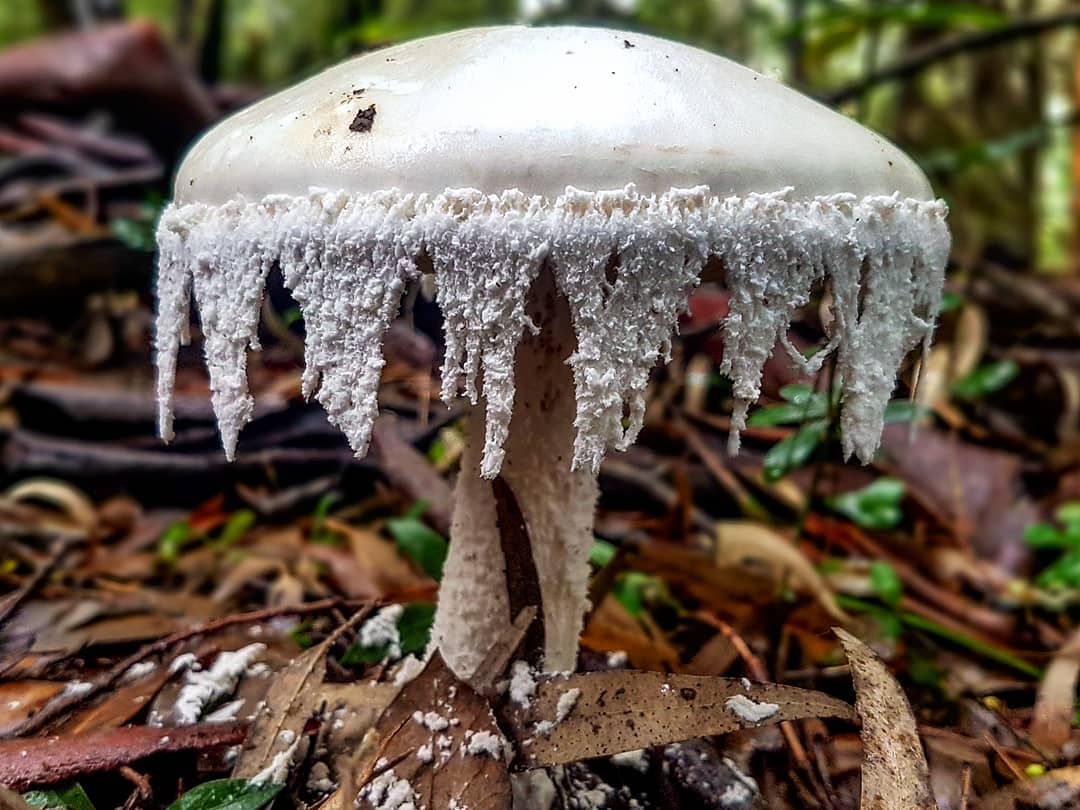
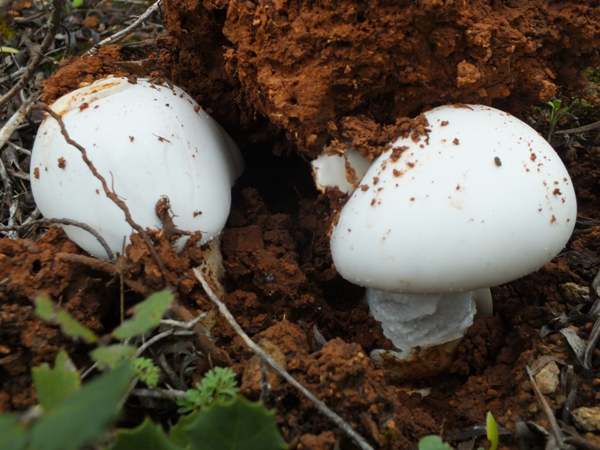
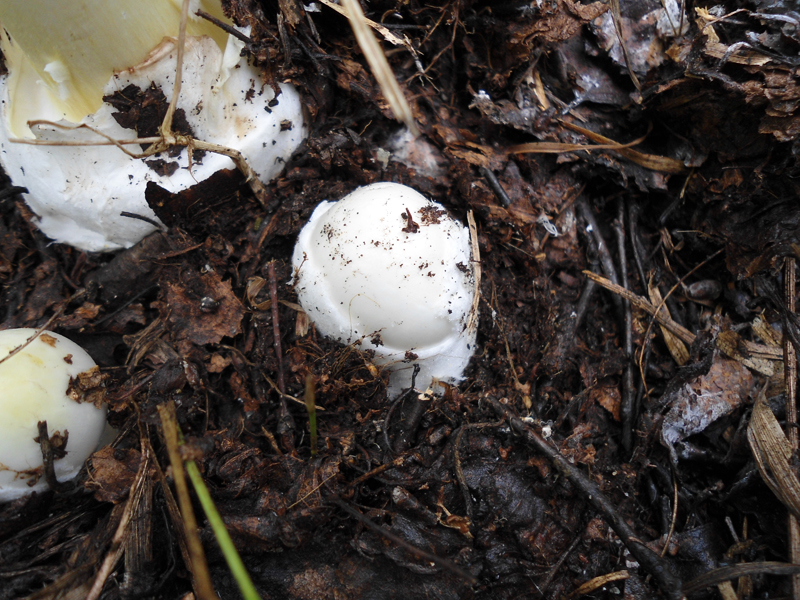
A distinctive feature of the white toadstool is the presence of a Volvo. This is a small part of the mushroom that looks like a burst egg and serves as a defense. Volvo can be noticed only in young mushrooms. In them, it has a width of up to 5 cm, is partly in the soil, the color is white, sometimes slightly yellowish.
When and where it grows, doubles
You can meet the most dangerous mushroom in the world on fertile soils where it feels best. As in the case of the red fly agaric, the toadstool enters into symbiosis with trees, so this mushroom can be found in any deciduous forest where beeches, oaks, and hazel grow. Sometimes found in open areas, where livestock is often grazed.
Distributed in the temperate climate of Eurasia, and also found in North America.
Separately, it should be said about the doubles. The fact is that due to toadstool, a huge number of people die every year only for the reason that it is confused with champignon.
Learn more about champignons: benefits and harms to the body, methods of growing, technology of growing at home, freezing in a home refrigerator.
If the toadstool is painted pure white, then an inexperienced mushroom picker, cutting off only the cap, can easily confuse and eat an incredibly dangerous mushroom. Also, toadstool is confused with green russula, floats and green tea.
In order not to confuse champignon with toadstool, you should first of all look at the color of the plates, which darken with time in champignons. In the green fly agaric, they always remain white. As for russules, they never form a volva, and there is also no ring in the upper part of the leg. The flesh of the russula is brittle, and that of the fly agaric is fleshy, dense.
Video: how to distinguish between pale toadstool and green russula
At the greenfinch, not only the outer part of the cap is painted, but also the plate. They are greenish in color. Also, greenfinch lacks a Volvo.
Evaluation of edibility
Egg-shaped fly agarics belong to the category of conditionally edible, however, it is recommended to cook them for food only after preliminary heat treatment.
For long-term storage, it is recommended to dry, freeze or pickle the mushrooms. Amanita pickled with spices can be harvested for the winter. Canned food can be used to prepare various snacks, caviar, soups and main courses.
The best recipes
Sandwich:
- Lightly dry a few slices of bread in a pan and cool.
- Separately boil the fly agarics, drain the water, throw in a colander so that the excess liquid is glass. Put the prepared mushrooms in a pan, pour in a little vegetable oil and fry well until tender.
- Boil the chicken egg, cool and peel. Cut into small cubes and mix with the sautéed mushrooms.
- Add some chopped nuts and finely chopped fresh parsley, salt to taste.
- Grease the finished croutons with butter, put the filling on top and cover with another slice of bread.
 Mushroom and cheese sandwich in crispy toast
Mushroom and cheese sandwich in crispy toast
Seafood salad:
- Wash the mussels, put on a baking sheet and bake in a preheated oven for 5 minutes. Drizzle lightly with olive oil and place in a salad bowl.
- Boil fly agarics separately, cool and chop into thin strips or cubes.
- Cut celery root and 1 medium sweet potato into thin strips.
- Mix all ingredients well, season with soy sauce or mayonnaise.
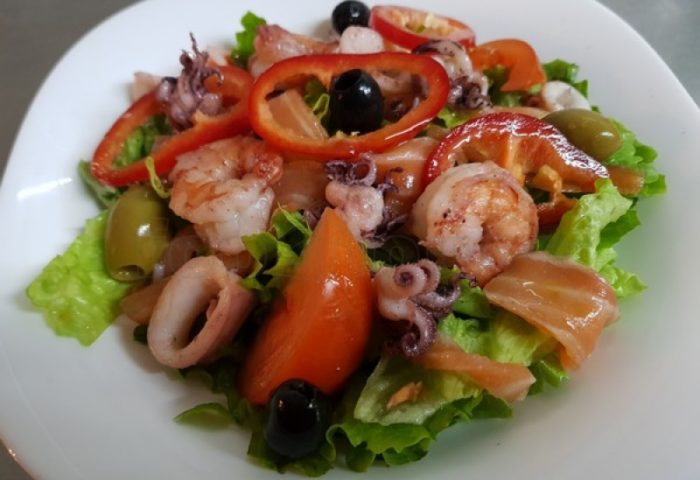 Seafood salad
Seafood salad
Roast:
Required Ingredients:
- Amanita - 10-12 pcs.
- Chicken fillet - 1 breast.
- Potatoes - 5 pcs.
- Carrots - 1 pc.
- Bulb onion - 1 pc.
- Vegetable oil - 5 tbsp. l.
- Sour cream 20% - 50 ml.
- Parsley - 1 bunch.
- Salt and spices to taste.
Cooking method:
- Take all the food you need, a clay pot, a skillet, and a separate pot for boiling fresh mushrooms.
- Sort out the fly agarics, make sure that there are no wormy and spoiled ones, rinse. Cut the prepared mushrooms into 3-4 pieces, add cold water and bring to a boil. When the broth boils strongly, the water will need to be drained. Pour hot water over the mushrooms a second time and boil for 30 minutes (after boiling). When the mushrooms settle to the bottom, remove the pan from the heat, discard the contents in a colander and cool.
- Cut the chicken fillet into thin strips, put in a pan and fry until golden brown on all sides. Transfer to a pot.
- Pour oil into a frying pan, put mushrooms in it, fry to evaporate excess liquid.
- Chop the onion into rings, add to the mushrooms. Continue to fry until the onions are soft. Transfer to a pot for meat.
- Peel potatoes and carrots. Cut the potato tubers into 4-6 parts, chop the carrots into strips or chop them on a grater.
- Place vegetables in a skillet, add a little oil and fry for 3-5 minutes.
- Combine all products, put them in a pot, add salt and spices. For a milder taste, add 3 tbsp. l. sour cream.Simmer in a preheated oven for 40-50 minutes until the potatoes are cooked. To make the dish less greasy, you can replace sour cream with milk.
- Add finely chopped fresh parsley in a pot before serving.
 Roast with mushrooms
Roast with mushrooms
Dried fly agarics can be used to cook roast. To do this, they will need to be pre-soaked in warm water, and then cooked in the same way as fresh.
Taste evaluation, initial processing and cooking recipes
Despite the fact that the mushroom is conditionally edible, you need to be very careful when picking and preparing it. Due to its close resemblance to some very poisonous fruits, it is better to bypass it, especially for novice mushroom pickers

The taste of cooked egg-shaped fly agaric is a bit specific and not everyone likes it. Some people are afraid of just one name, because in Russia, fly agarics, like edible mushrooms, are almost unknown to a wide circle. Before the main preparation, the fruits must be cut from the edge of the leg, make sure that there are no fungal pests - worms. The leg and cap, clean of wormholes, are washed under running water from forest debris and earth. Next, fly agarics are cut and boiled twice for 10 minutes in different water. Then they are thrown into a colander and allowed to drain. After that, proceed to the main stage of preparation.
- Amanita sauce. Flour is fried in a frying pan until browning, water is poured in until a homogeneous paste-like mass is obtained. The resulting mixture is salted, pepper, herbs are added to taste, then equal parts of mustard and sour cream. The mixture is cooked over very low heat to avoid burning the flour. After a light boil of the mass, ready-made boiled mushrooms, finely chopped beforehand, are added to it. The sauce is served hot to potatoes, buckwheat porridge, meat.
- Amanita in oriental style. The boiled mushroom is cut into small pieces (some amateurs do not boil it, but cook it right away), fry it in vegetable oil with salt and pepper. After the liquid has evaporated, chopped tomato and half rings of onion are added to the mushrooms. The dish is stewed for a few minutes. Capers are added at the end if desired.
You can even get poisoned with edible mushrooms, including conditionally edible fly agarics. Some people develop an allergic reaction similar to the symptoms of poisoning. All fly agarics, including edible ones, contain mild toxins that affect the nervous system. With insufficient heat treatment, they can enter the human blood.
In addition, poisoning with the use of an ovoid fly agaric can occur with insufficient washing of the fungus from pathogenic microorganisms on its surface.
What does a panther fly agaric look like?
The panther fly agaric is considered to be a kind of younger brother of the entire variety of these mushrooms. However, it does not have such an attractive characteristic appearance as the other species. In this regard, it is sometimes confused with other types of mushrooms, quite edible. It is especially easy to confuse it with edible mushrooms at the very beginning of growth, therefore, before going to pick mushrooms, it is necessary to study the characteristic features of this fly agaric in order to distinguish it.
The main shade of the cap of this fly agaric is olive, which often leads to the fact that it is confused with edible mushrooms. In general, depending on the age of the mushroom, the color of the cap varies from light green to brown. In addition, completely inexperienced mushroom pickers sometimes confuse young panther fly agarics with boletus and milk mushrooms.
The pulp is white, in the cut it remains white, but at the same time it is not perceptibly watery. The pulp is very fragile and breaks easily, has an unpleasant smell, like most fly agarics, and a sweetish aftertaste. There are many petals, they are white, never grow to the stem and sometimes have brown spots, especially in old mushrooms.
The leg of the fly agaric, depending on its age, is from 4 to 12 cm tall, thin, usually about a centimeter in diameter. The leg tapers slightly upward, at the bottom it forms a characteristic tuber, empty inside.On the surface of the leg, you can see a characteristic white pile, the ring is very low or sometimes absent altogether. This species is often confused with the edible amanita, gray-pink.
Amanita reproduces by spores, feels great next to many trees and is found in almost all forests: deciduous, coniferous and mixed. Most often it is noticed growing under oak and pine trees, for growth the fungus prefers soil in which there is a lot of alkali. This species is most widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, preferring a temperate climate without heat or severe frosts. The growing season is mid-summer and ends around mid-September. In those places where the panther fly agaric grows, there are never any insects, since they all die only from the smell of this mushroom.
Areas of growth of ovate fly agaric.
This type of fly agaric can be found in various mixed forests. Amanita muscariae most often settle in the Mediterranean. Calcareous soil is a favorite growing place. These mushrooms are often found under beech trees. Amanita muscaria is listed in the Red Book of the Krasnodar Territory.
Reproduction of ovoid fly agaric.
Amanita muscaria reproduce by spores. The spores are round, colorless. The color of the spore powder is white, sometimes there may be a pink tint.

Disputes remain viable for a long time - tens of years. With their help, mushrooms are spread over long distances. Spores are spread by wind, water, animals. When the spores of the ovoid fly agaric get into the right conditions, they germinate, mycelium forms, and a new fungus appears.
What is the danger of ovate fly agaric.
As noted, you should be very careful when collecting ovoid fly agaric. The fact is that they are outwardly similar to pale toadstools, which cause severe poisoning. Toadstools are very dangerous poisonous mushrooms, so only experienced mushroom pickers can collect egg-shaped fly agarics.

Related species of fly agaric ovate.
Amanita muscaria is a poisonous representative of the genus. The caps in young specimens are spherical, then they become open, sometimes the edges rise. The color of the cap is yellow-ocher or brownish, the surface is completely covered with yellow or white warts. The leg is tuberous at first, later it becomes slender. The color of the leg is brown-ocher with a whitish felt bloom. Sometimes scales are visible at its base. There is a thin, sagging, smooth ring on the knife. The pulp is brittle, fleshy, odorless, white.
Amanita mushrooms bear fruit from July to November. They grow in forests mixed with spruce, as well as spruce coniferous forests. They settle on the soil. Meet in small groups or singly. They rarely come across. They prefer the northern regions.
Amanita muscaria bright yellow is another poisonous mushroom. His hat is smooth, first convex, and then flat. The surface of the cap is dry, and its color is ocher yellow. The pulp gives off a faint radish smell. The color of the pulp is white or yellow. The leg is long, fragile. Its surface is smooth or pubescent, yellowish. At first there is a ring on the stem, but it quickly disappears, leaving a slightly noticeable color.
Amanitae are bright yellow from spring to autumn. The degree of toxicity of these fungi depends on the place of growth. Basically, these fly agarics grow under coniferous trees. The species is common in the Northern Hemisphere. Not very common.
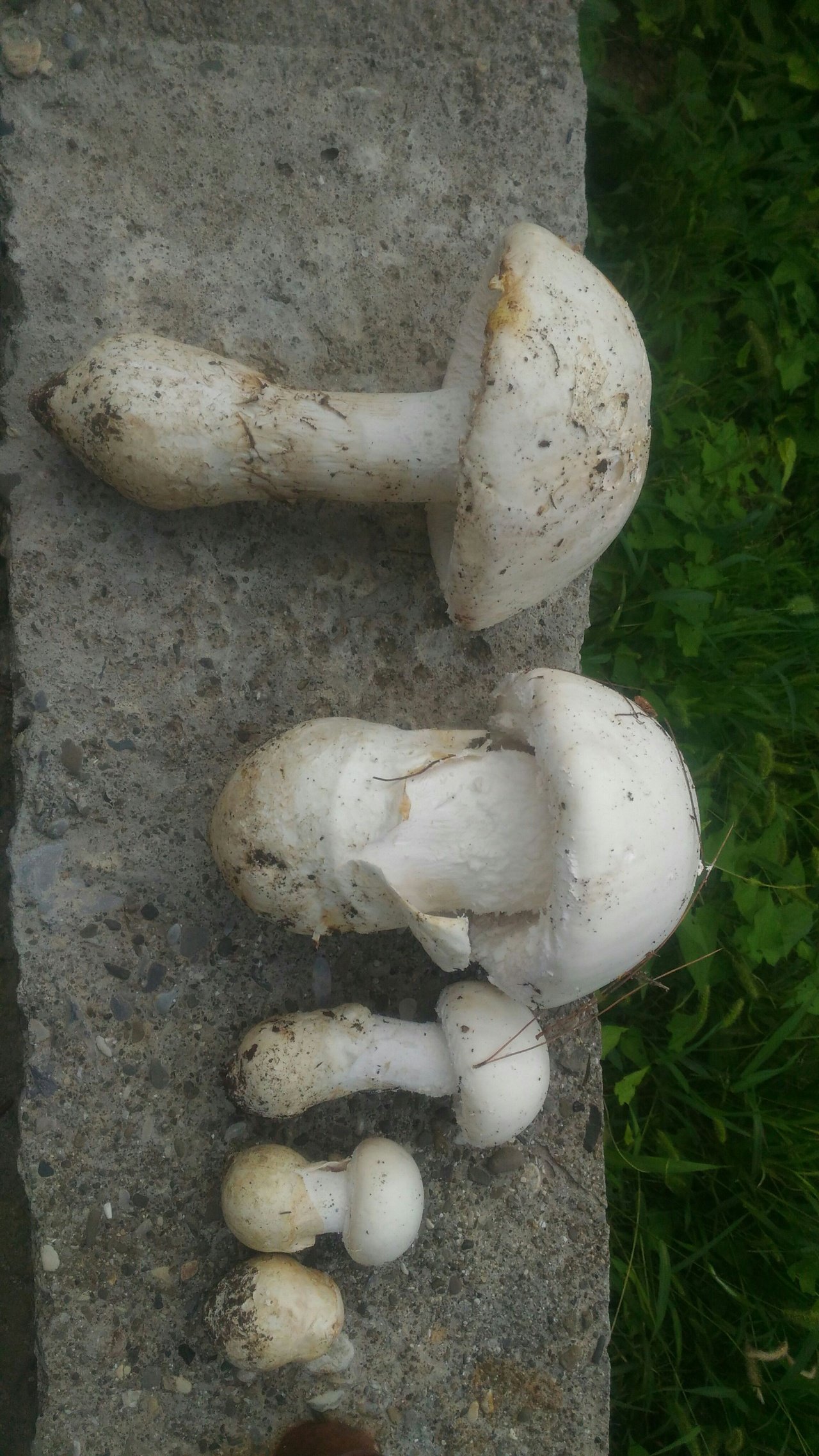
LAT Amanita ovoidea Conditionally Edible Synonyms: Agaricus ovoideus, Amanita alba, Amidella ovoidea
Specifications:
| Group: | Lamellar |
|---|---|
| Plates: | White, cream |
| Colour: | White |
| Info: | Flakes on a hat |
Systematics:
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
|---|---|
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Agaricomycetidae |
| Order: | Agaricales (Agaric or Lamellar) |
| Family: | Amanitaceae |
| Genus: | Amanita (Amanita) |
| View: | Amanita ovoidea (Amanita muscaria) |
Refers to conditionally edible or even edible mushrooms.Some mushroom pickers believe that, unlike most fly agarics, it is ovoid, edible, very tasty and can be used in any form. However, a number of sources have questioned the edibility of the mushroom.
In addition, beginners and inexperienced amateurs should treat it with caution, since there is a very high risk of confusing a mushroom with a poisonous toadstool and getting severe poisoning
Prescription drugs
It is not difficult to prepare a medicine, the main thing is to do it right. The most common medicines are ointments and tinctures for external use. Cooking methods:
- For the preparation of the ointment, only caps are used. They are ground into powder and weighed. Fatty sour cream is added to the powder, in an amount equal to the weight of the caps. The finished ointment is stored in the refrigerator in sealed glass or ceramic containers.
- Tincture for external use is used for compresses and rubbing. For cooking, only hats are also used. They are crushed and placed in glass or ceramic dishes. The hats should be kept cold for 3 days.
Mushroom tincture
Then the container intended for infusion is ¾ filled with chopped caps, and the rest of the space is poured with vodka. Mushrooms are infused in a dark place for 2 weeks. Alcohol tincture should not be taken internally. Alcohol multiplies toxicity several times.
Due to the high risk of poisoning, the dishes and tools used during the preparation of medicines should be washed thoroughly. Funds are stored out of the reach of children and pets. Medication can be taken only on the recommendation of a homeopathic physician.
Types of edible amanita
Amanita pink-gray (Amanita rubescens)
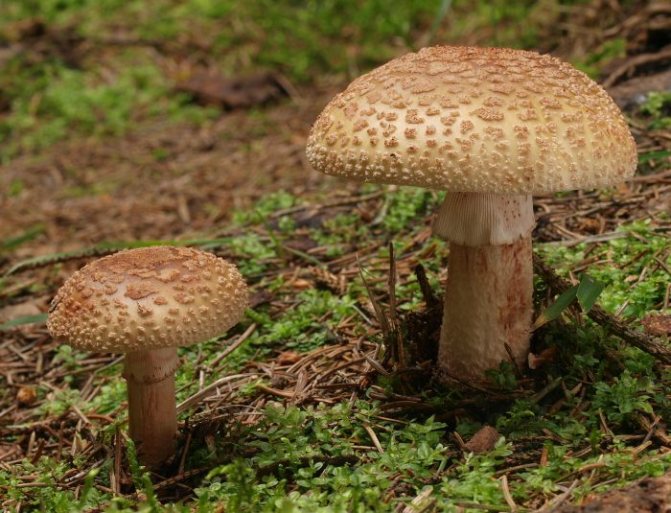

Also known as Amanita muscaria, Amanita muscaria, or Amanita muscaria.
The diameter of the cap is 6-20 cm. In young mushrooms, its shape is hemispherical or ovoid, later convex and flat-spread, without tubercle. The color of the cap is grayish-pink or red-brown, the surface is shiny, slightly sticky. The pulp is white, fleshy, the taste is weak, the smell is not pronounced. On the cut, it immediately becomes light pink, and then gradually - wine-pink. The stem is 3-10 cm in height, 1.5-3 cm in thickness, cylindrical, solid in young mushrooms and hollow in mature ones. Painted white or pinkish, the surface is lumpy. There is a tuberous thickening at the base.
Grows in small groups or singly next to deciduous and coniferous trees, on any soil, in the temperate climate of the Northern Hemisphere. The season lasts from spring to late autumn, bears fruit in large quantities in July-October.
Conditionally edible mushroom. It is not consumed fresh, it is used fried after boiling.
Caesar mushroom (Amanita caesarea)

The cap is 8-20 cm in diameter, ovoid or hemispherical, in mature mushrooms from convex to flat, the edge is furrowed. The color of the cap is golden orange or bright red, the surface is dry. The pulp is fleshy, light yellow in color, white in the stem, the smell and taste are not expressed. Leg 8-12 cm long, 2-3 cm thick, tuberous base, yellow-orange color, smooth surface. There is a ring.
Grows next to beech, oak, chestnut, in deciduous, less often in coniferous forests, on sandy soils. Inhabits warm regions of northern latitudes, sometimes in the subtropics. The fruiting season continues in summer and autumn.
An edible, delicious mushroom that is baked on a wire rack, fried, dried, and used fresh.
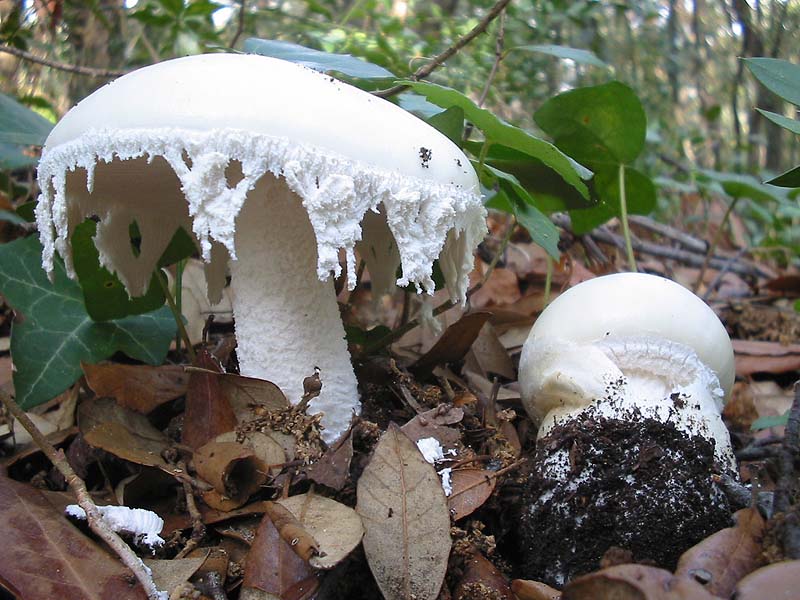
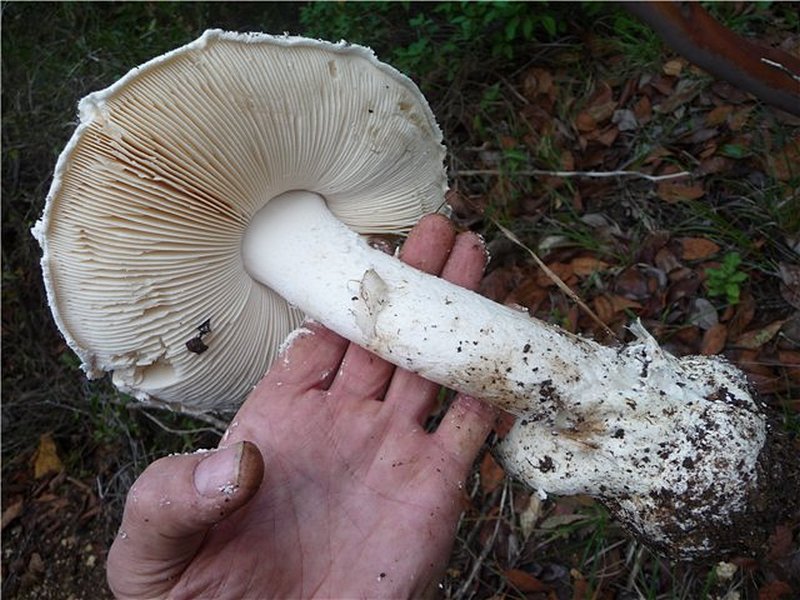
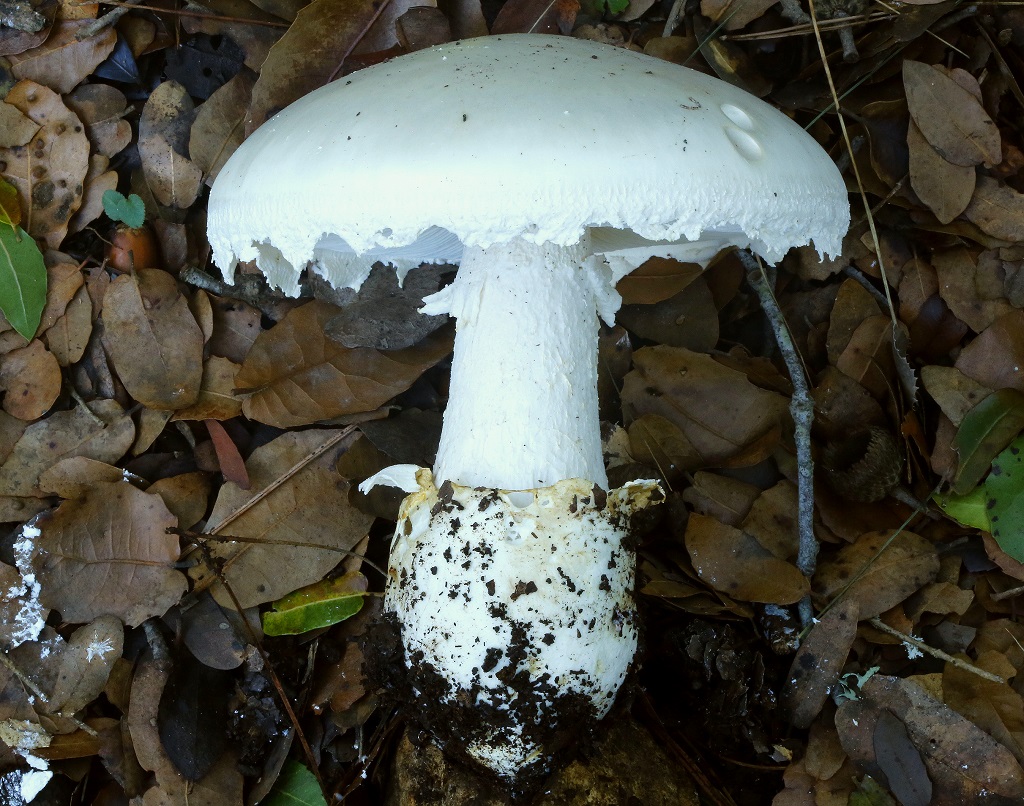
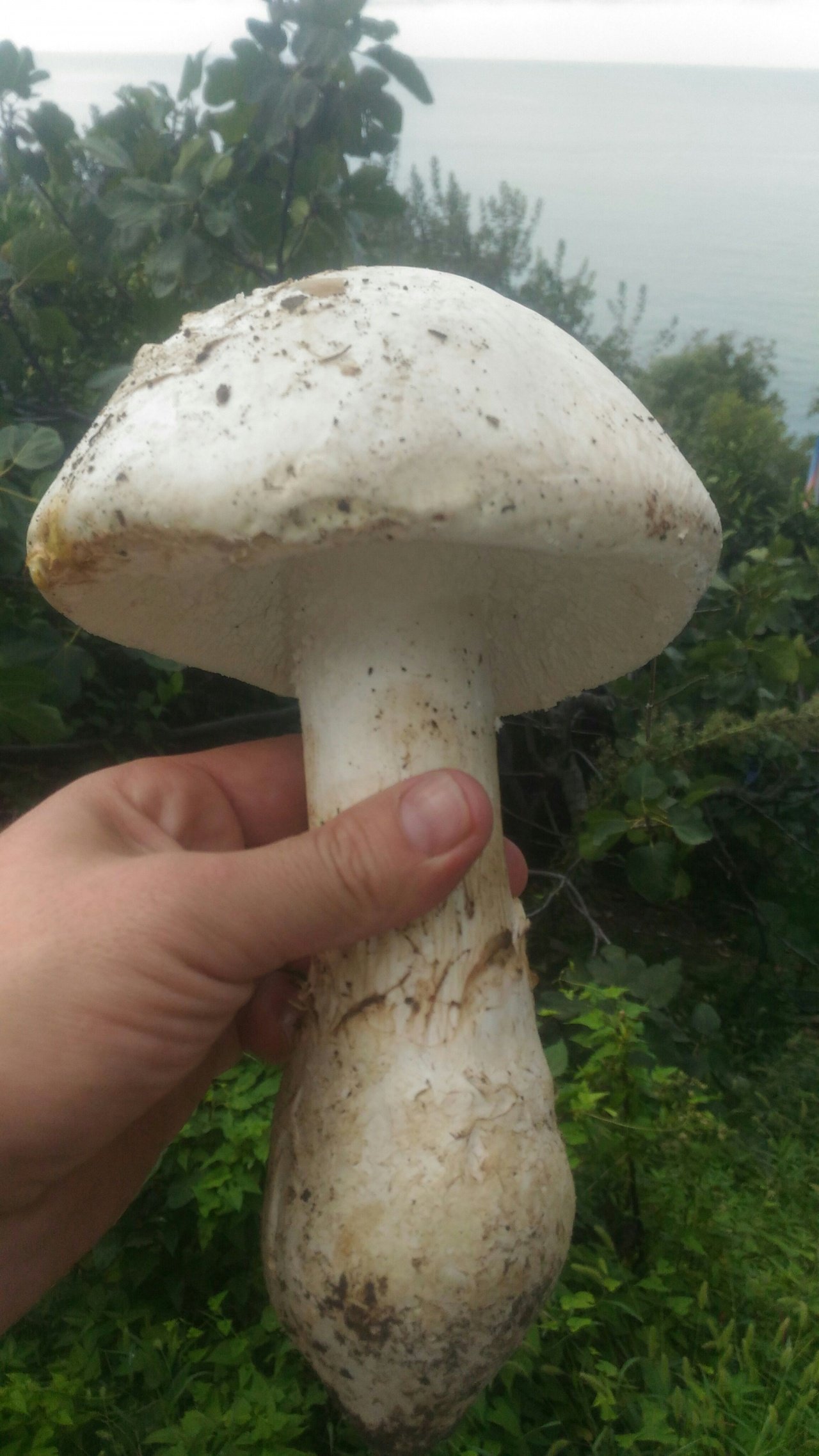
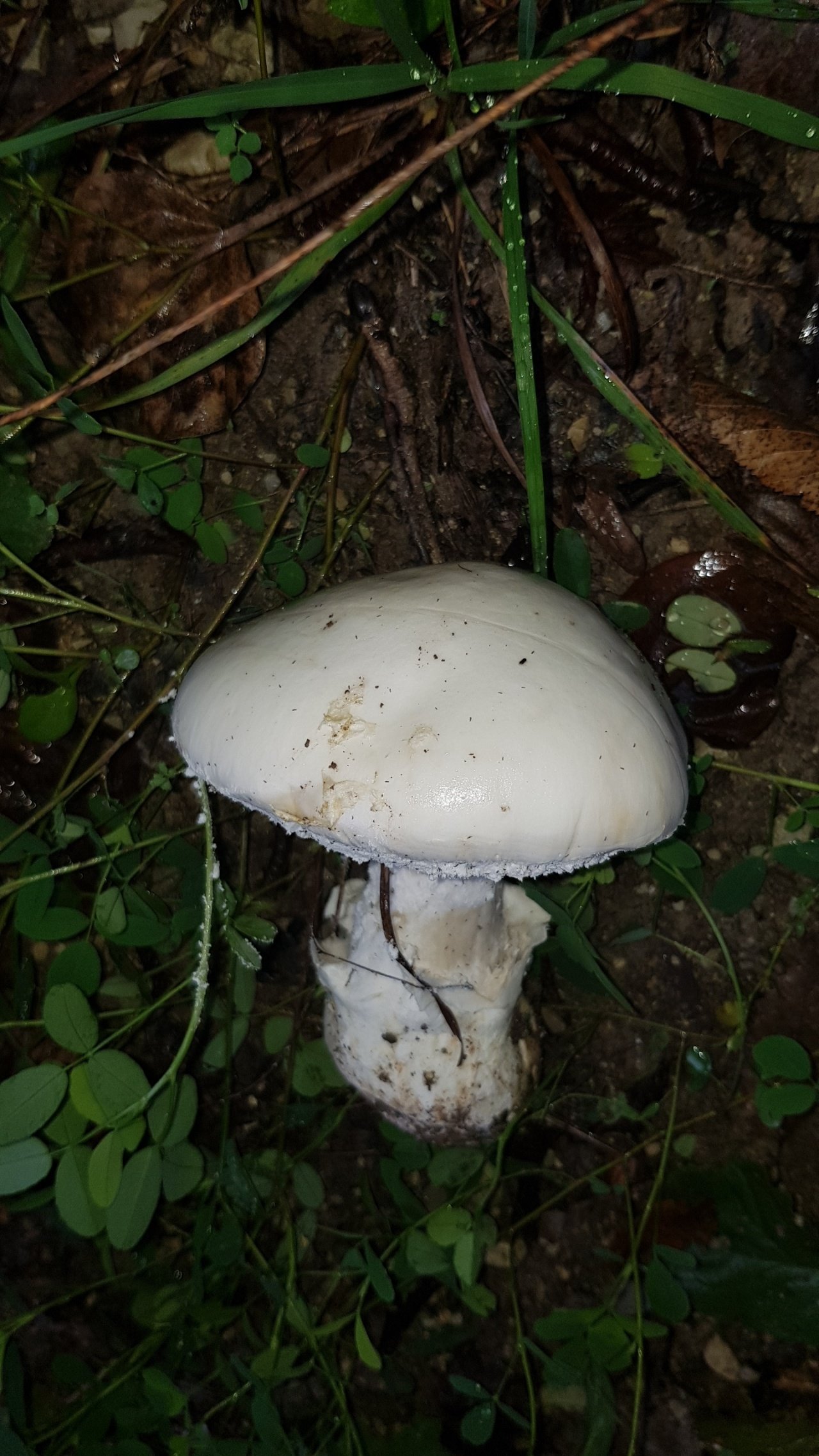
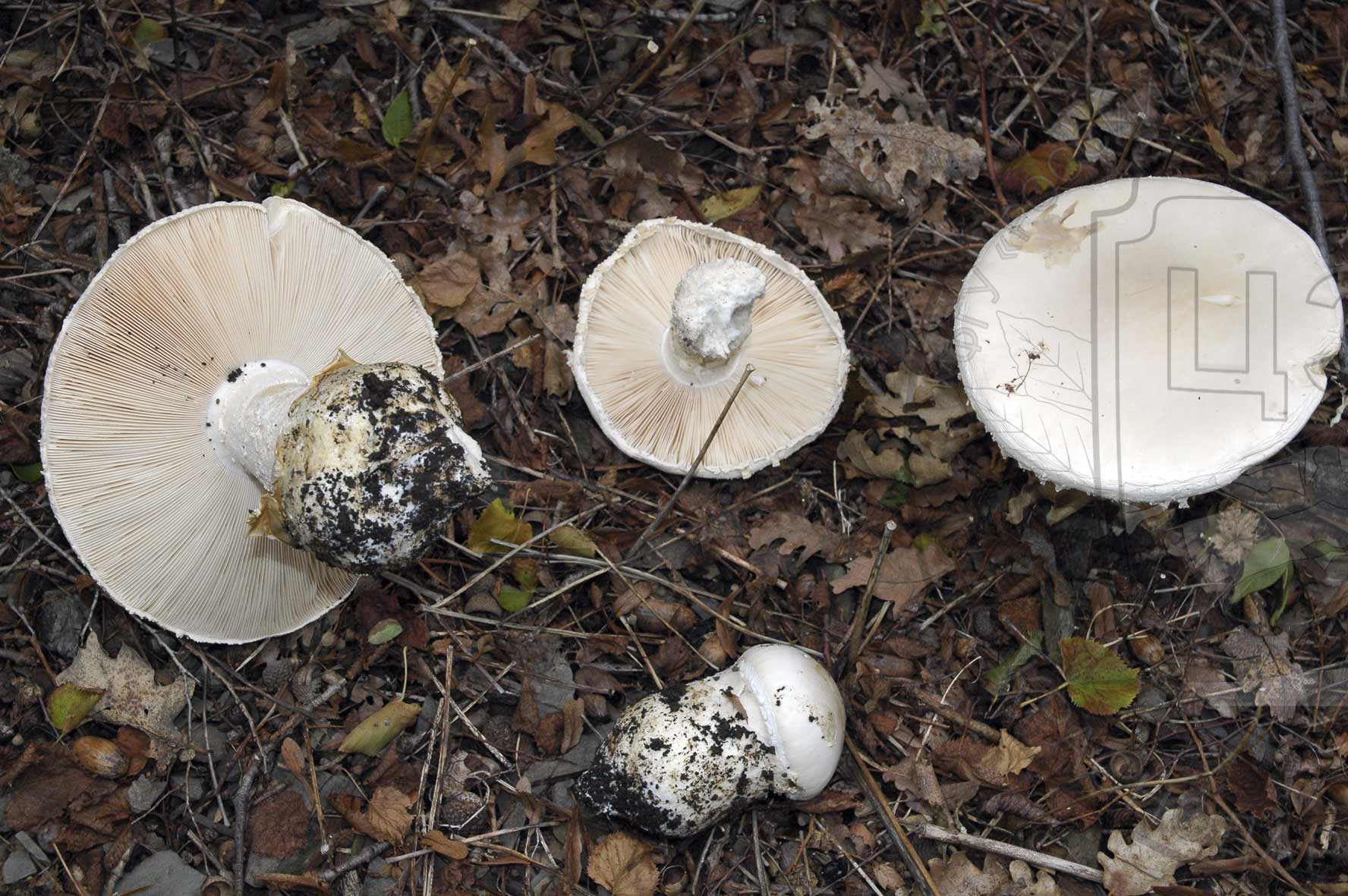
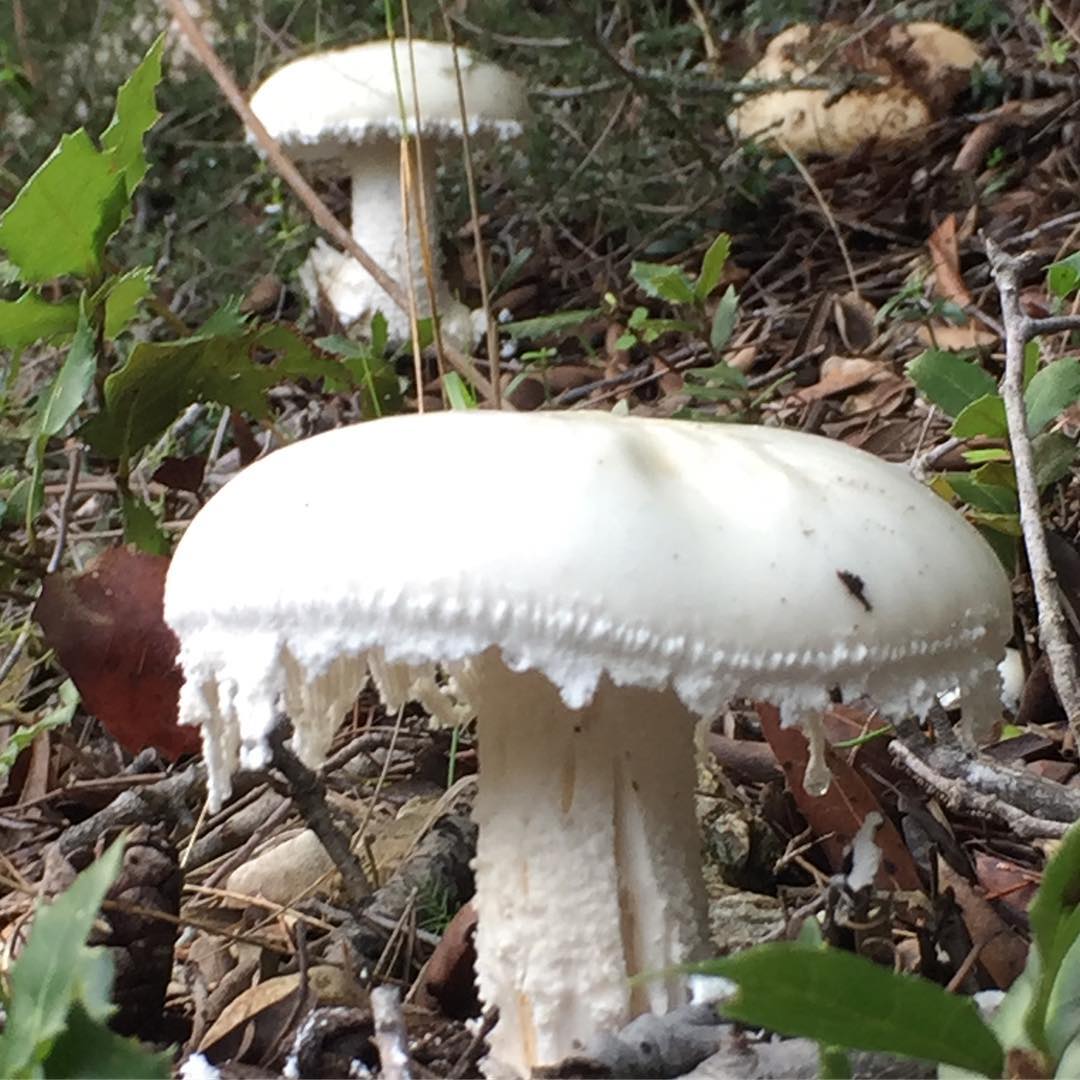
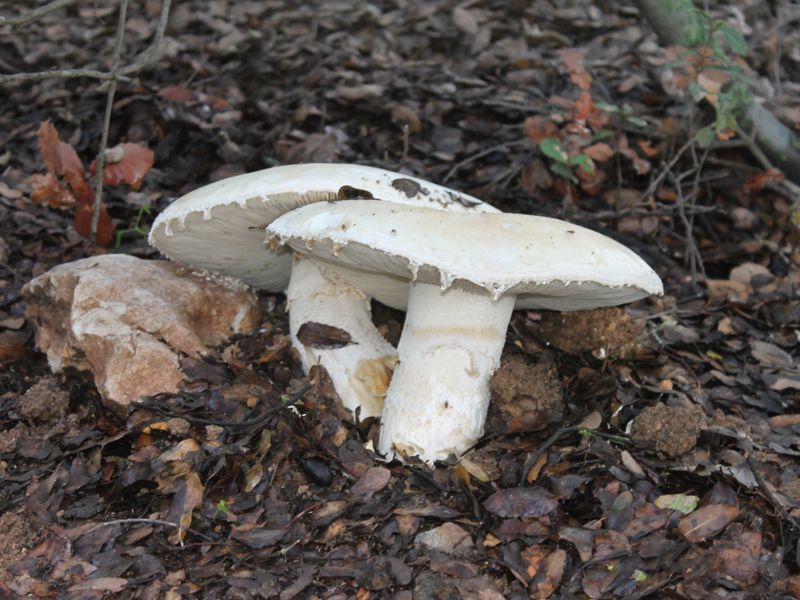
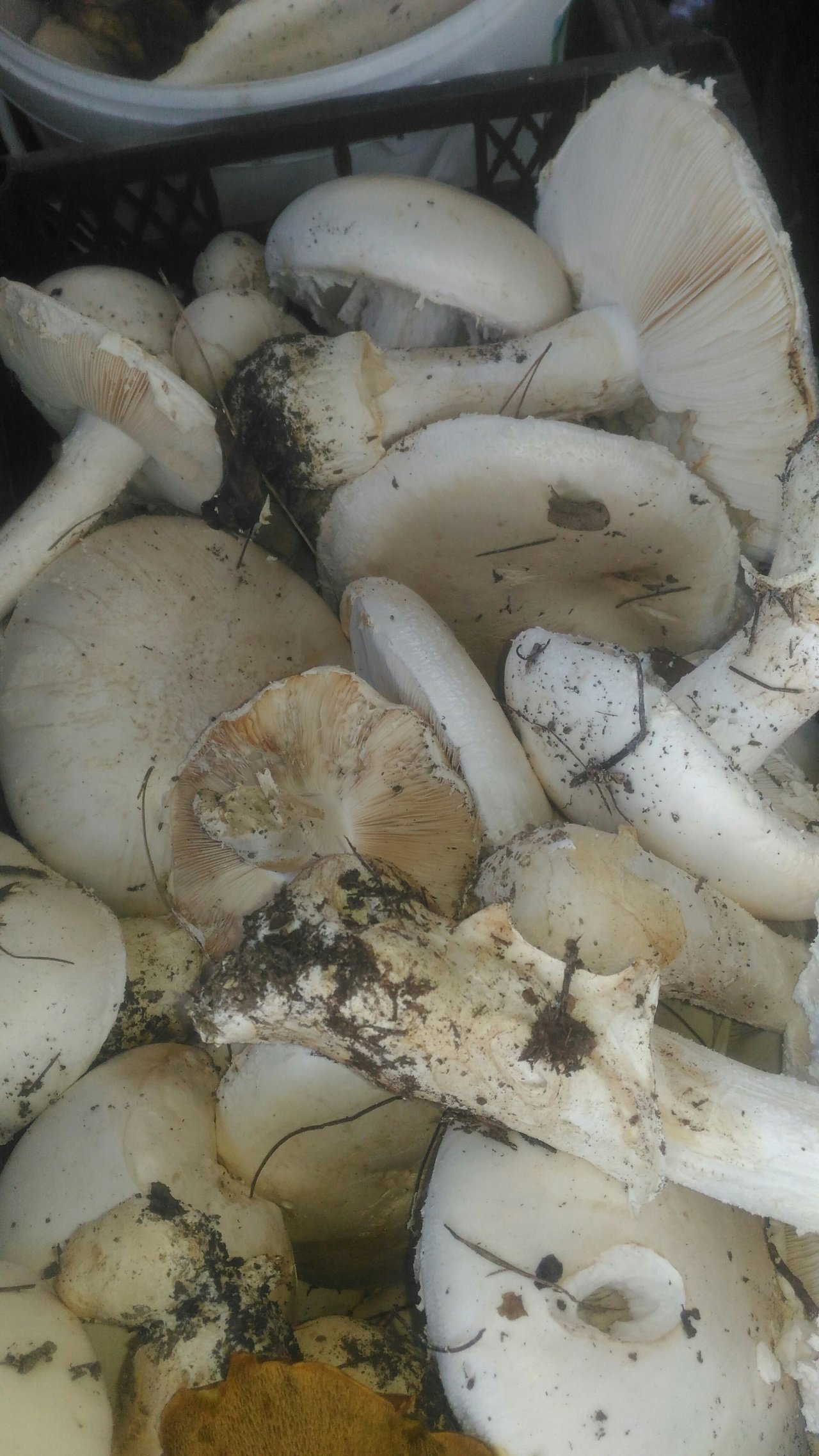
Amanita ovoid (Amanita ovoidea)
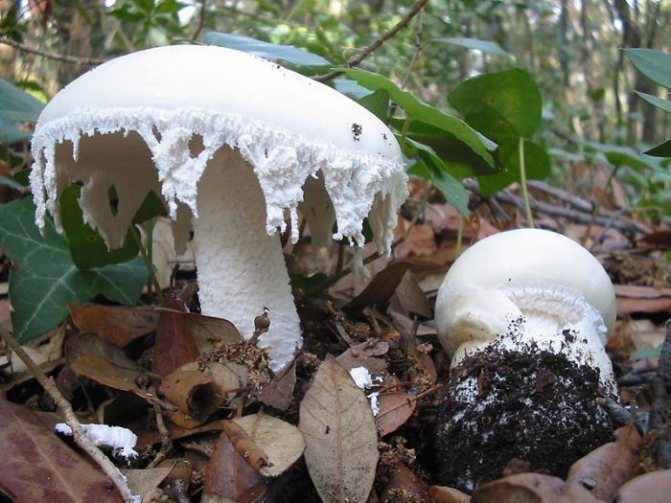

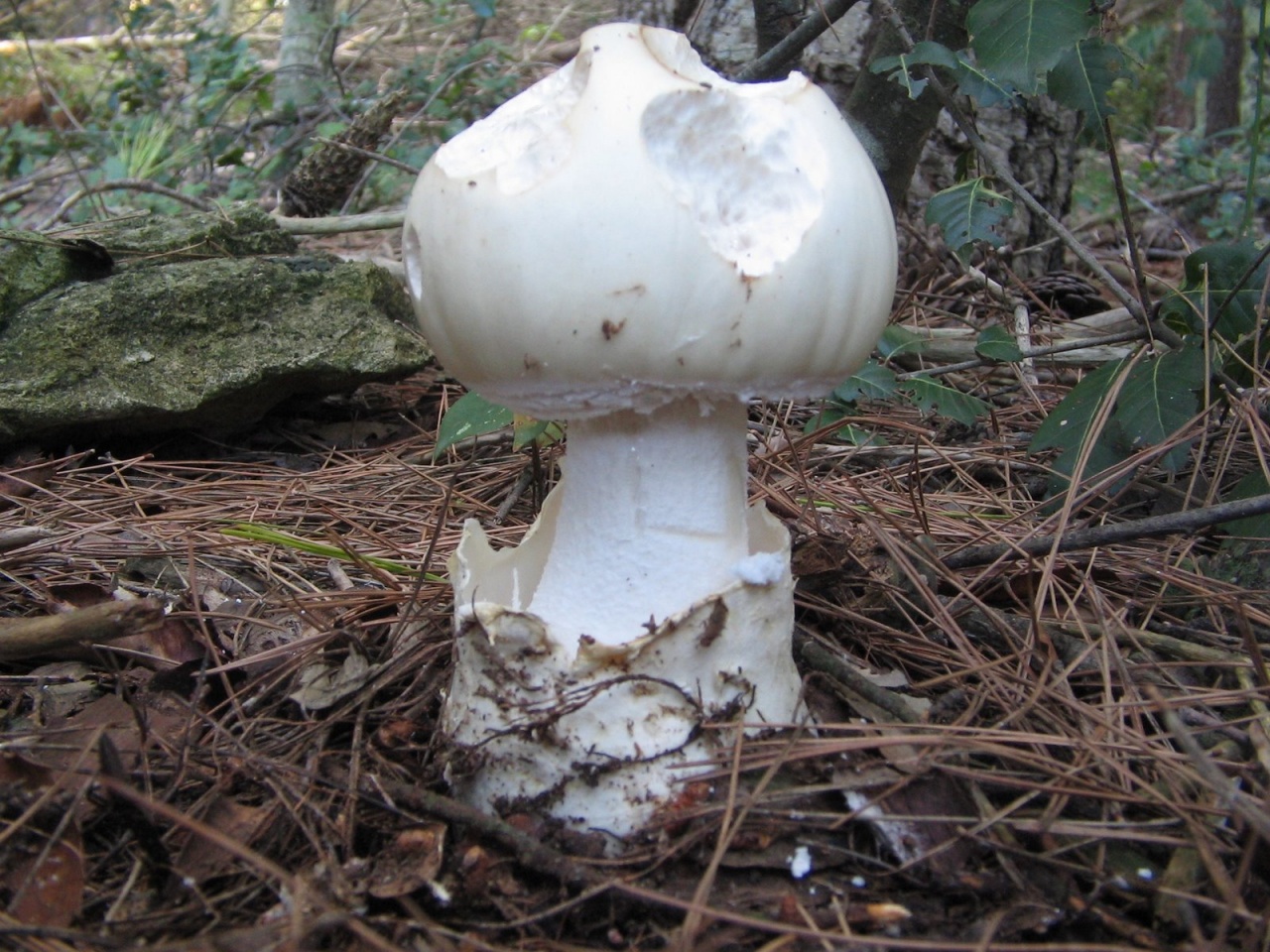
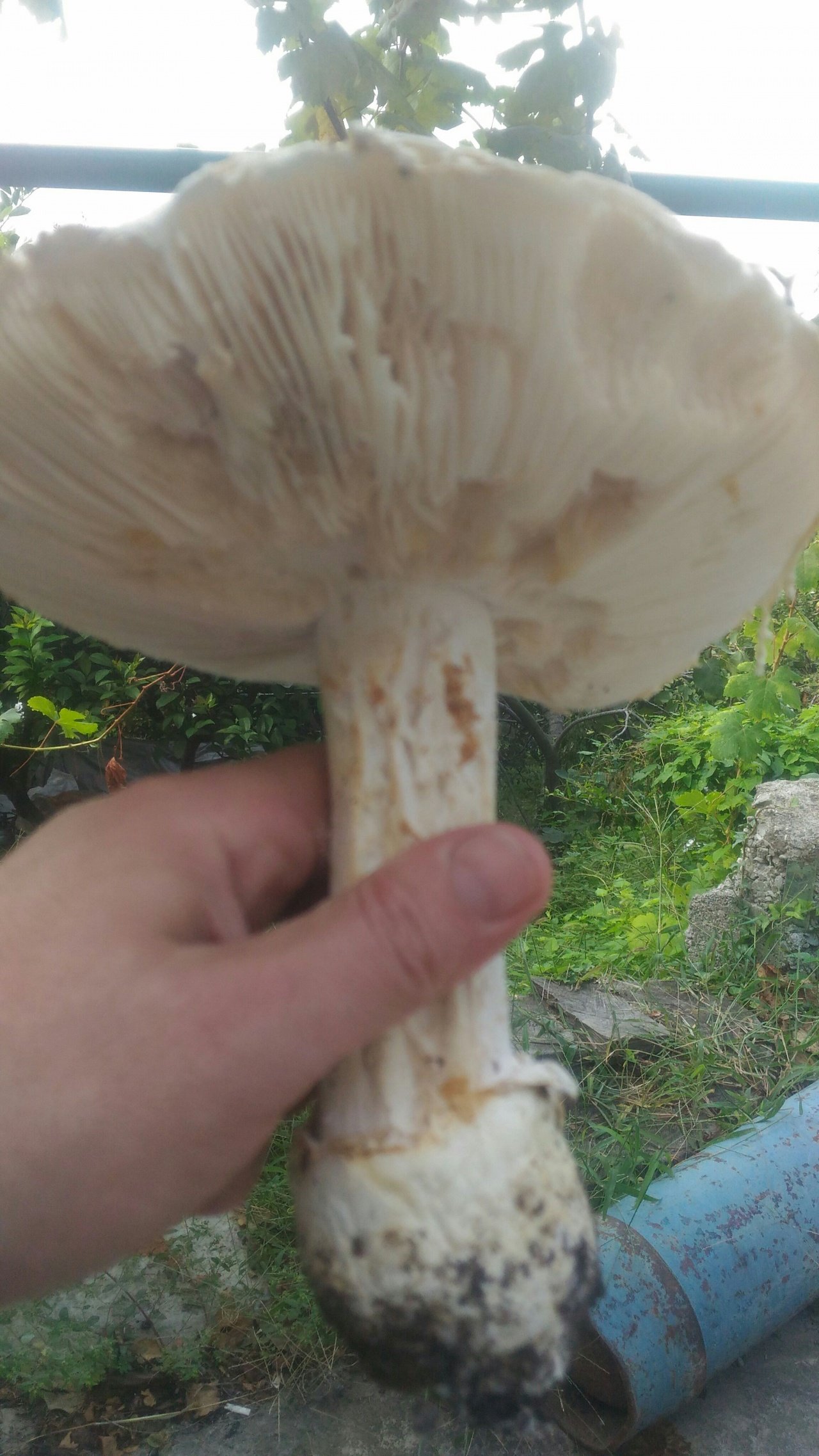
The cap is 6-20 cm in diameter, fleshy, ovoid, semi-rounded, later convex-spread, the edge is even. The skin is white or off-white, the surface is shiny, dry, in young mushrooms in white flakes. The pulp is white, dense, does not change color on the cut, smell and taste are poorly expressed. The leg is solid, dense, 10-15 cm high, 3-5 cm thick, expands towards the base. The surface is white, with a flaky powdery coating.
Grows in deciduous and coniferous forests of Europe, the Mediterranean, the British Isles, Western Siberia, Japan. Fruiting begins in August and ends in October.
Edible mushroom.
Amanita mushrooms.
Usually, hearing the word "fly agaric" people think exclusively of the red fly agaric. However, this is just one representative of the Amanita genus. In fact, this genus is represented by many species, among which there are both deadly poisonous and edible mushrooms, some of which are even considered a delicacy. There is still no unified system for the classification of fly agarics.

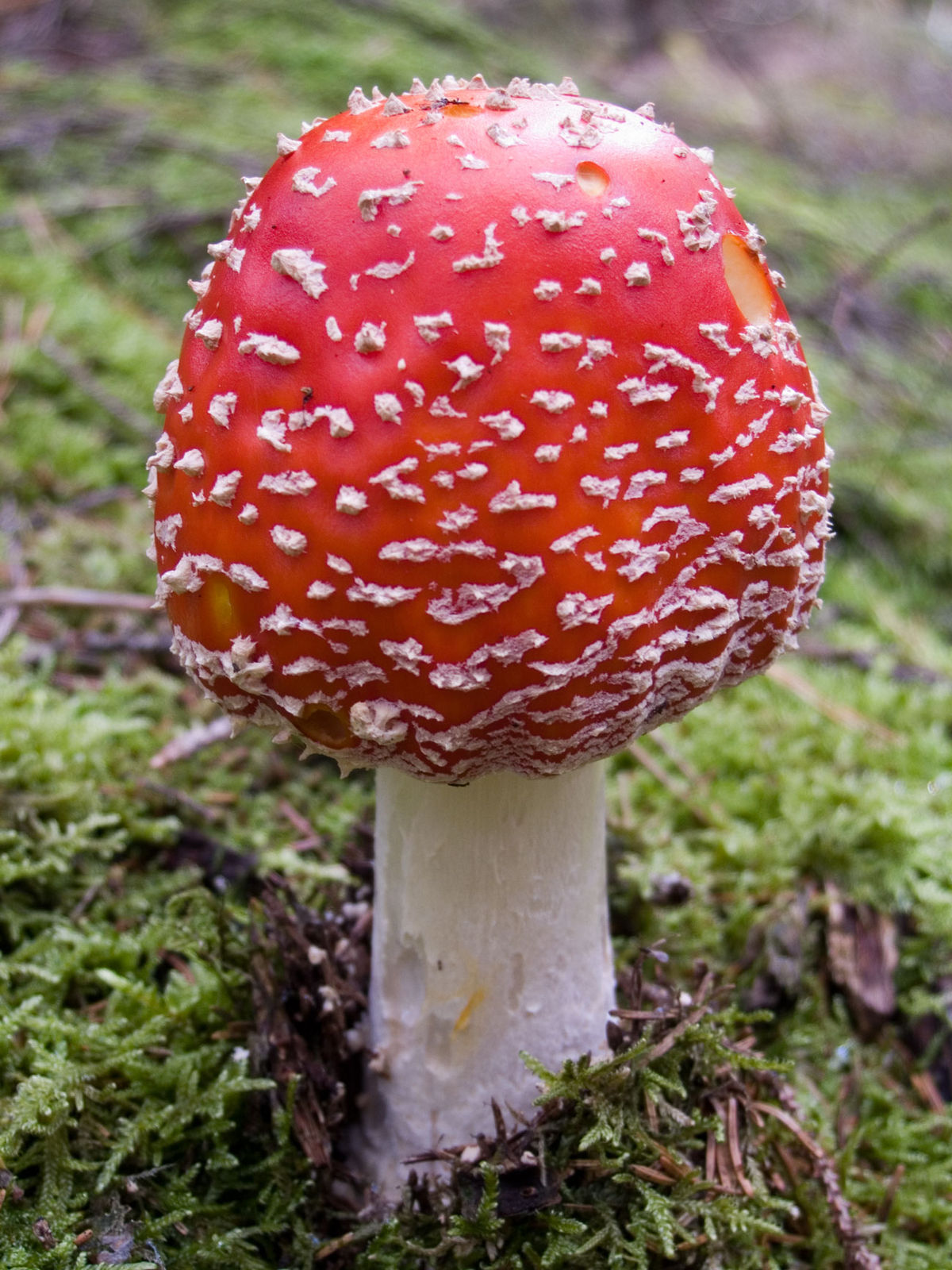
Amanita muscaria red
Below we list the most famous representatives of the amanita genus:
- Fly agaric Vittadini (Amanita vittadini)
- Amanita poisonous / Amanita white smelly / Amanita white grebe / White grebe / Amanita virosa
- Amanita white / Amanita spring / Spring toadstool (Amanita verna)
- Pineal fly agaric (Amanita strobiliformis)
- Amanita muscaria / Amanita thick (Amanita spissa / Amanita cinerea / Amanita ampla)
- Amanita solitaria / Amanita boudieri
- Amanita muscaria / Amanita pink / Amanita gray-pink (Amanita rubescens / Amanita rubens)
- Amanita muscaria (Amanita regalis / Amanita muscaria var.regalis / Amanita muscaria var.umbrina / Amanita umbrina)
- Amanita muscaria / Amanita porphyry / Amanita muscaria (Amanita porphyria)
- Amanita white / Amanita green / Amanita phalloides
- Amanita muscaria / Amanita pantherina
- Amanita ovoid (Amanita ovoidea)
- Amanita muscaria (Amanita muscaria)
- Amanita pearl / Amanita bright yellow (Amanita gemmata)
- Float yellow-brown / Orange fly agaric (Amanita fulva)
- Fly agaric (Amanita flavipes)
- Amanita thick / Amanita high (Amanita excelsa)
- Amanita muscaria / Amanita muscaria (Amanita echinocephala)
- Amanita toadstool / Yellow pale toadstool / Amanita lemon / Amanita lemon yellow / Amanita yellow-green (Amanita citrina / Amanita bulbosa / Amanita mappa)
- Amanita muscaria / Strange float (Amanita ceciliae)
- Far Eastern Caesar mushroom / Amanita caesareoides
- Imperial Mushroom / Caesar Mushroom (Amanita caesarea)
- Fly agaric (Amanita franchetii)
- Gray float (Amanita vaginata)
- White float (Amanita alba)
- Saffron float (Amanita crocea)
- Amanita battarae