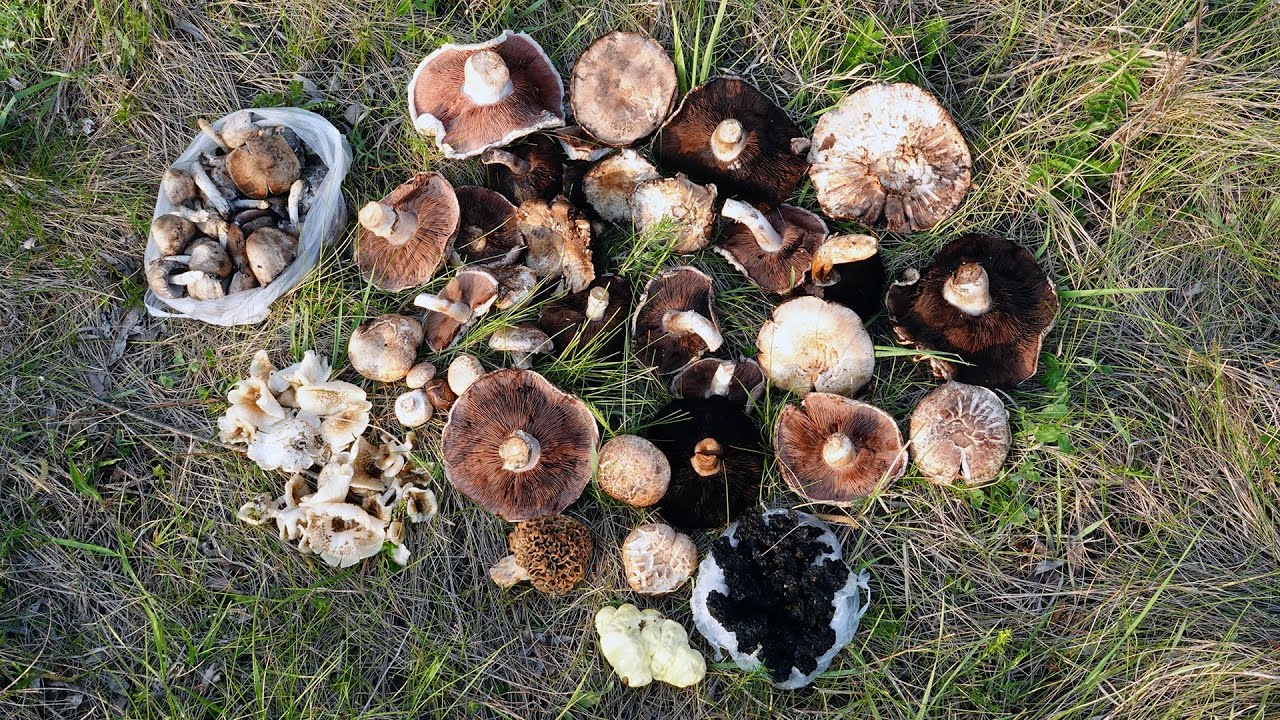
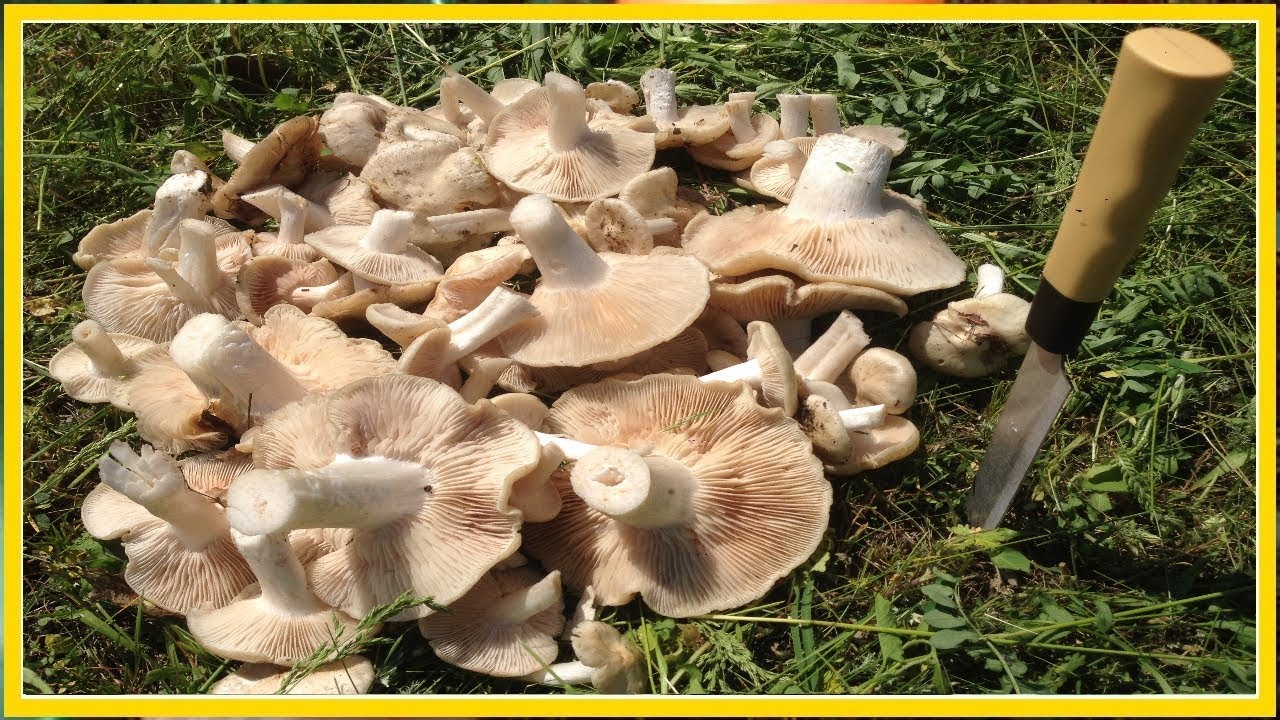
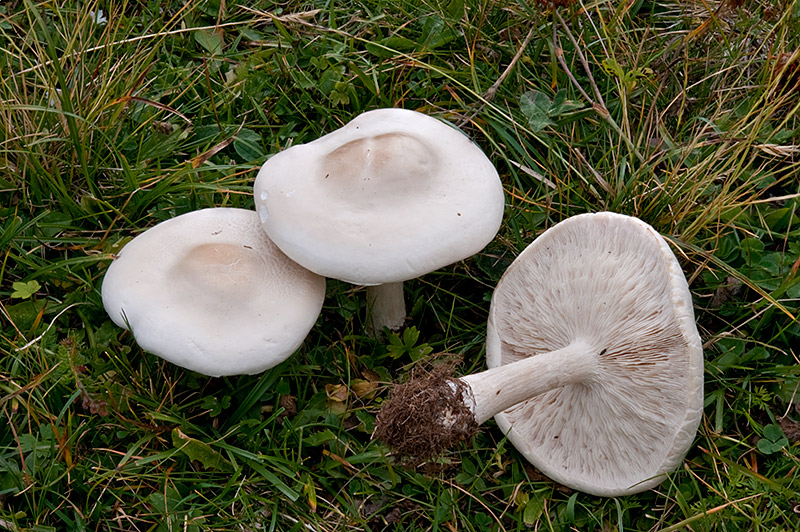
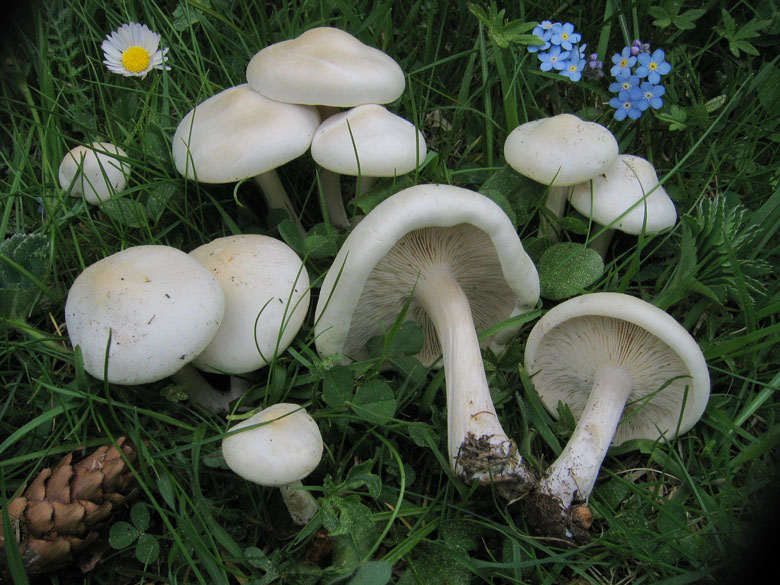
Ecology and habitat
Cosmopolitans found on all continents. Humus or woody saprotrophs growing in meadows, as well as in coniferous and deciduous forests.
- Melanoleuca albifolia Boekhout 1988
- Melanoleuca arcuata (Bull.) Singer 1935
- Melanoleuca atripes Boekhout 1988
- Melanoleuca brevipes (Bull.) Pat. 1900 - Melanoleuca short-legged
- Melanoleuca cinereifolia (Bon) Bon 1978
- Melanoleuca cognata (Fr.) Konrad & Maubl. 1930 - Melanoleuca related
- Melanoleuca graminicola (Velen.) Kühner & Maire 1934
- Melanoleuca grammopodia (Bull.) Murrill 1914 - Melanoleuca striped
- Melanoleuca humilis (Pers.) Pat. 1900
- Melanoleuca iris Kühner 1956
- Melanoleuca langei (Boekhout) Bon 1990
- Melanoleuca melaleuca (Pers.) Murrill 1911 - Melanoleuca black and white
- Melanoleuca niveaMétrod ex Boekhout 1988
- Melanoleuca oreina (Fr.) Kühner & Maire 1934
- Melanoleuca phaeopodia (Bull.) Murrill 1914
- Melanoleuca polioleuca (Fr.) G. Moreno 1934 - Melanoleuca multicolored
- Melanoleuca politoinaequalipesBeguet ex M.Traverso & Zotti 2002
- Melanoleuca rasilis (Fr.) Singer 1939
- Melanoleuca schumacheri (Fr.) Singer 1943
- Melanoleuca strictipes (P. Karst.) Jul. Schäff. 1951
- Melanoleuca stridula (Fr.) Singer 1943
- Melanoleuca substrictipes Kühner 1978
- Melanoleuca tabularis (Pers.) Konrad
- Melanoleuca turrita (Fr.) Singer 1935
- Melanoleuca verrucipes (Fr.) Singer 1939 - Melanoleuca verruciform
- Melanoleuca vinosa (G. Stev.) E. Horak 1971
Treatment
- Treatment of local local injuries consists of timely detection and surgical intervention. Removal is most often performed under infiltration anesthesia. For excision of large formations, it is possible to use general anesthesia. In addition to malignant tumors, there are a number of pre-melanoma diseases in which a surgical method is indicated.
- Local-regional damage. Treatment includes excision with an enlarged area and lymphadenectomy of the affected lymph nodes. Varieties of unresectable, transiently metastatic tumors are subjected to isolated regional chemoperfusion. In certain cases, a combined approach has proven itself well, with additional therapy that stimulates the immune system.
- Treatment of distant metastases is performed with mono-regimen chemotherapy. Certain types of mutations are exposed to targeted targeted drugs.
What does melanoma look like in the photo?
Nodular (diminutive from the Latin "nodus" - node) formation is less common (14-30%). Most aggressive form. Melanoma cancer is characterized by rapid growth (from 4 months to 2 years). It develops on objectively unchanged skin without visible damage or from a pigmented nevus. Vertical growth. The color is uniform, dark blue or black. In rare cases, such a tumor that resembles a nodule or papule may not be pigmented.
- Malignant lentigo.
The disease affects elderly people (after 60 years) and is detected in 5-10% of cases. Open areas of the skin (face, neck, arms) capture nodules of dark blue, dark or light brown color up to 3 mm in diameter. Slow radial tumor growth in the upper sections of the skin (20 years and longer before vertical invasion into the deep layers of the dermis) can invade hair follicles.
Definitioner
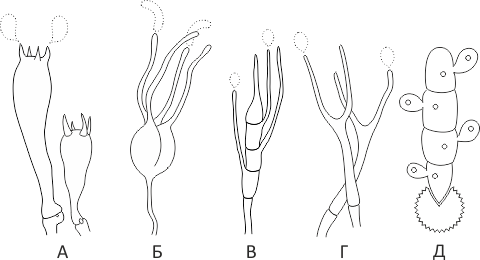
- Basidia (Basidia)
-
Lat. Basidia. A specialized structure of sexual reproduction in fungi, inherent only in Basidiomycetes. Basidia are terminal (end) elements of hyphae of various shapes and sizes, on which spores develop exogenously (outside).
Basidia are diverse in structure and method of attachment to hyphae.
According to the position relative to the axis of the hypha, to which they are attached, three types of basidia are distinguished:
Apical basidia are formed from the terminal cell of the hypha and are located parallel to its axis.
Pleurobasidia are formed from lateral processes and are located perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which continues to grow and can form new processes with basidia.
Subasidia are formed from a lateral process, turned perpendicular to the axis of the hypha, which, after the formation of one basidium, stops its growth.
Based on morphology:
Holobasidia - unicellular basidia, not divided by septa (see Fig. A, D.).
Phragmobasidia are divided by transverse or vertical septa, usually into four cells (see Fig. B, C).
By type of development:
Heterobasidia consists of two parts - hypobasidia and epibasidia developing from it, with or without partitions (see Fig. C, B) (see Fig. D).
Homobasidia is not divided into hypo- and epibasidia and in all cases is considered holobasidia (Fig. A).
Basidia is the place of karyogamy, meiosis and the formation of basidiospores. Homobasidia, as a rule, is not functionally divided, and meiosis follows karyogamy in it. However, basidia can be divided into probasidia - the site of karyogamy and metabasidia - the site of meiosis. Probasidium is often a dormant spore, for example in rust fungi. In such cases, probazidia grows with metabasidia, in which meiosis occurs and on which basidiospores are formed (see Fig. E).
See Karyogamy, Meiosis, Gifa.
- Pileipellis
-
Lat. Pileipellis, skin - differentiated surface layer of the cap of agaricoid basidiomycetes. The structure of the skin in most cases differs from the inner flesh of the cap and may have a different structure. The structural features of pileipellis are often used as diagnostic features in descriptions of fungi species.
According to their structure, they are divided into four main types: cutis, trichoderma, hymeniderma and epithelium.
See Agaricoid fungi, Basidiomycete, Cutis, Trichoderma, Gimeniderm, Epithelium.
Signs of skin melanoma: photo
The first signs of skin melanoma, photo.
Signs of skin melanoma that you should pay attention to in order not to miss the development of an insidious disease:
- The skin pattern is not determined in a mole.
- A non-healing wound appears at the site of the nevus.
- The mole grows vertically.
- Small spots appear next to the nevus, which are similar in color.
- There are no hairs on the mole.
- The tissue around the mole is inflamed or the mole itself is inflamed.
- Changes in the tissues of the surface of the mole - peeling, itching, swelling, the formation of a nodule on the surface.
- Pigmentation from the nevus passes to the surrounding tissue.
- The mole becomes soft or glossy.
The first signs of the development of melanoma are the horizontal growth of the nevus, which does not go beyond the boundaries of the epithelium. If the mole grows vertically, it is a sign of an aggressive, metastatic tumor.
Melanoma of the skin: life projections
Melanoma skin cancer. Photo
Melanoma develops from specialized melanocyte cells that produce the pigment melanin. Melanocytes are responsible for the color of the eyes, hair, skin, and are responsible for protecting the body from ultraviolet rays. Most often, a malignant neoplasm is localized on the skin, less often in the area of the mucous membranes of the rectum, vagina, oral cavity, and also a tumor can form on the retina of the eye. Melanoma is rare, but mortality from melanoma is high - the tumor is prone to metastasis and the formation of secondary foci.
In the oncology department of the Yusupov hospital, patients will be able to receive qualified advice from a dermatologist, oncologist, undergo skin melanoma diagnostics, and undergo treatment for the disease. The oncology department is equipped with modern equipment; the hospital treats malignant diseases using innovative methods with the use of modern medicines.
False doubles
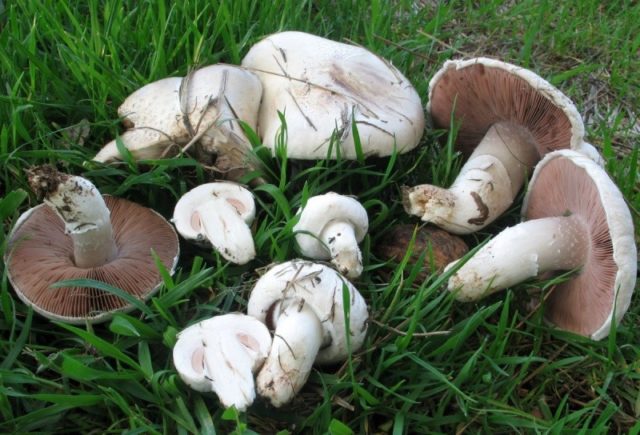
Inexperienced mushroom pickers often confuse straight-footed melanoleucca with mushrooms
It is important to remember that the first mushroom is almost never found in the forest, its habitat is mountainous terrain. While the champignon is an inhabitant of coniferous, deciduous and mixed forests in the plain
The champignon has whitish rings near the cap, the leg is thick. Its plates are gray-pink, in old mushrooms they are black. In melanoleuca, straight-legged plates are white.
Also, the straight-legged melanoleuke is similar to some representatives of the Ryadovkovy genus, for example, the striped or short-legged melanoleuca. The latter mushrooms are distinguished by a darker color, the surface of their caps is smooth and glossy.
The pale toadstool is a poisonous, deadly human counterpart of the straight-footed melanoleuca. The main difference between the inedible species is the presence of a dense sac at the base of the leg in the form of an egg.
The cap of the toadstool is not pure white, but with a yellowish or greenish tint.At first it is bell-shaped, later it becomes prostrate. In the upper part of the thick leg, almost under the cap, there is a film ring.
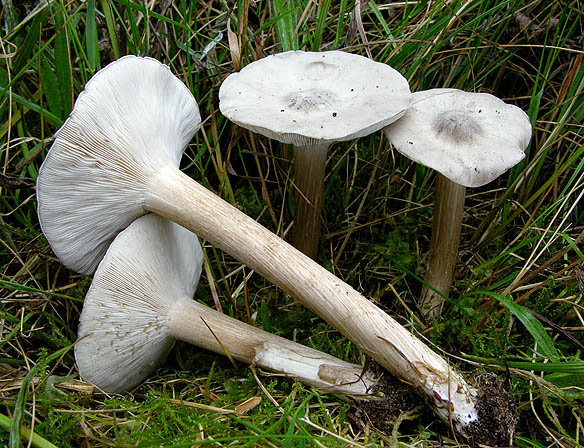
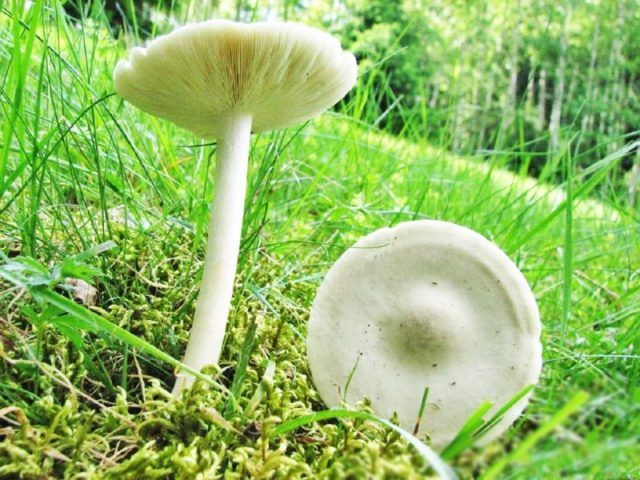
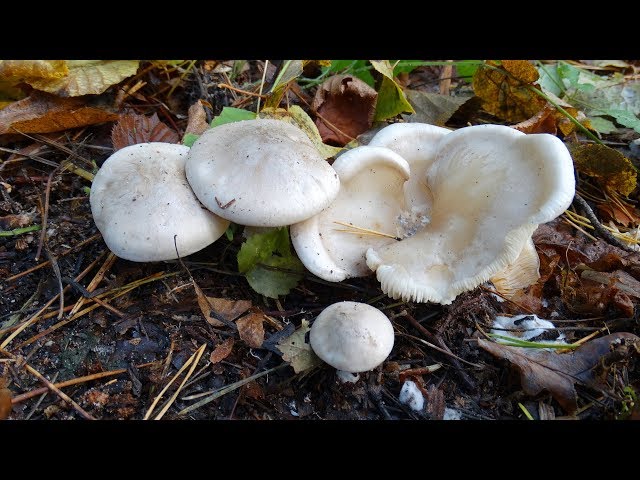
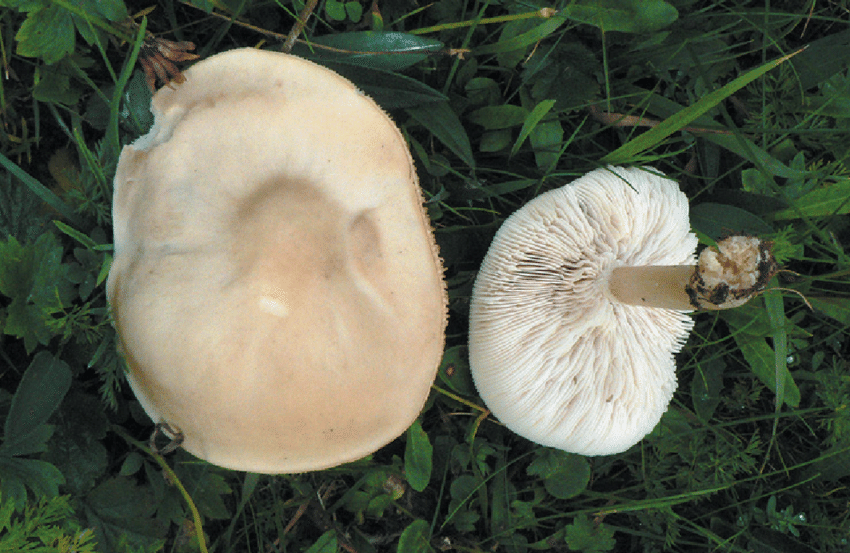
How straight-legged melanoleuks look
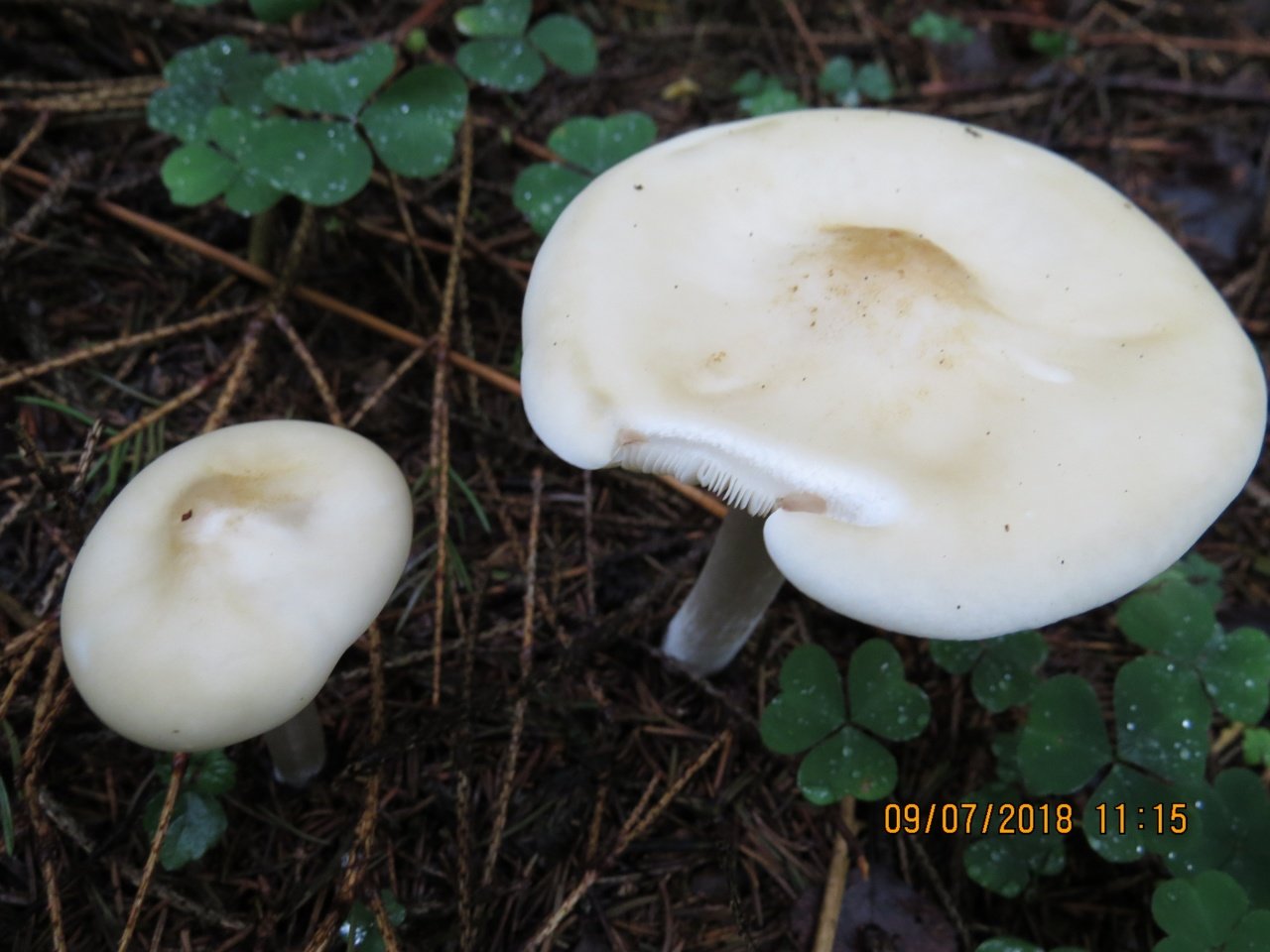
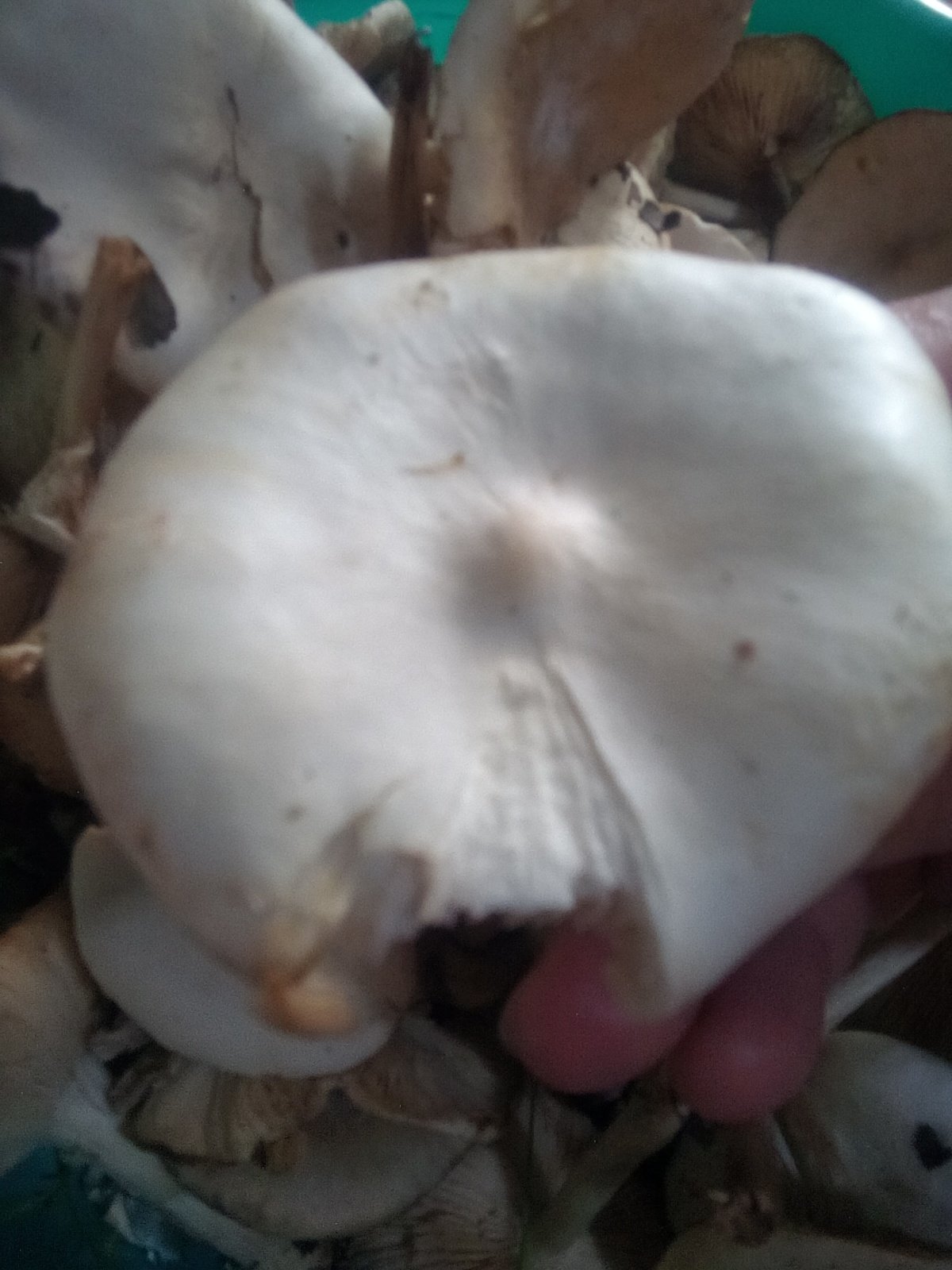
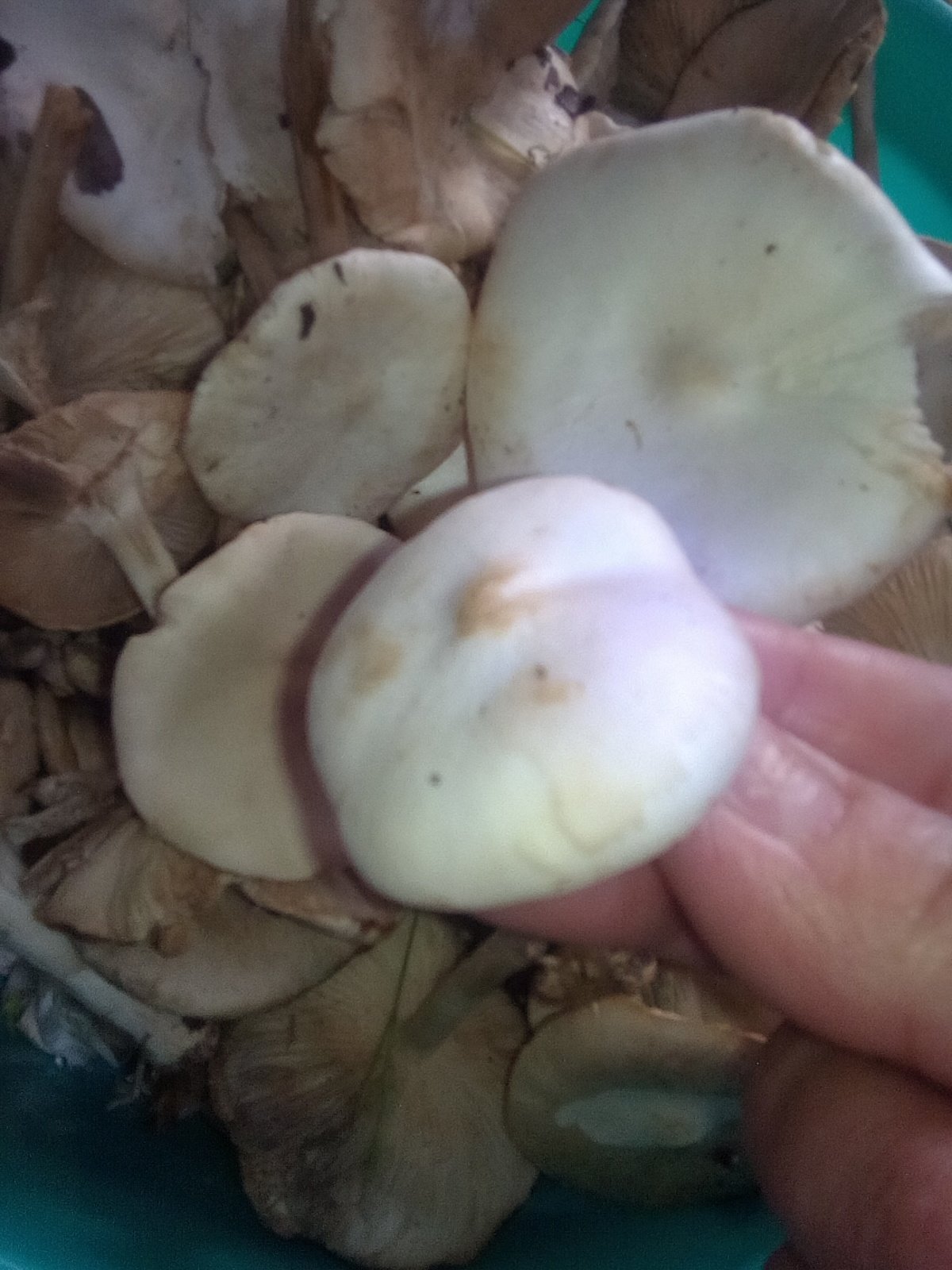
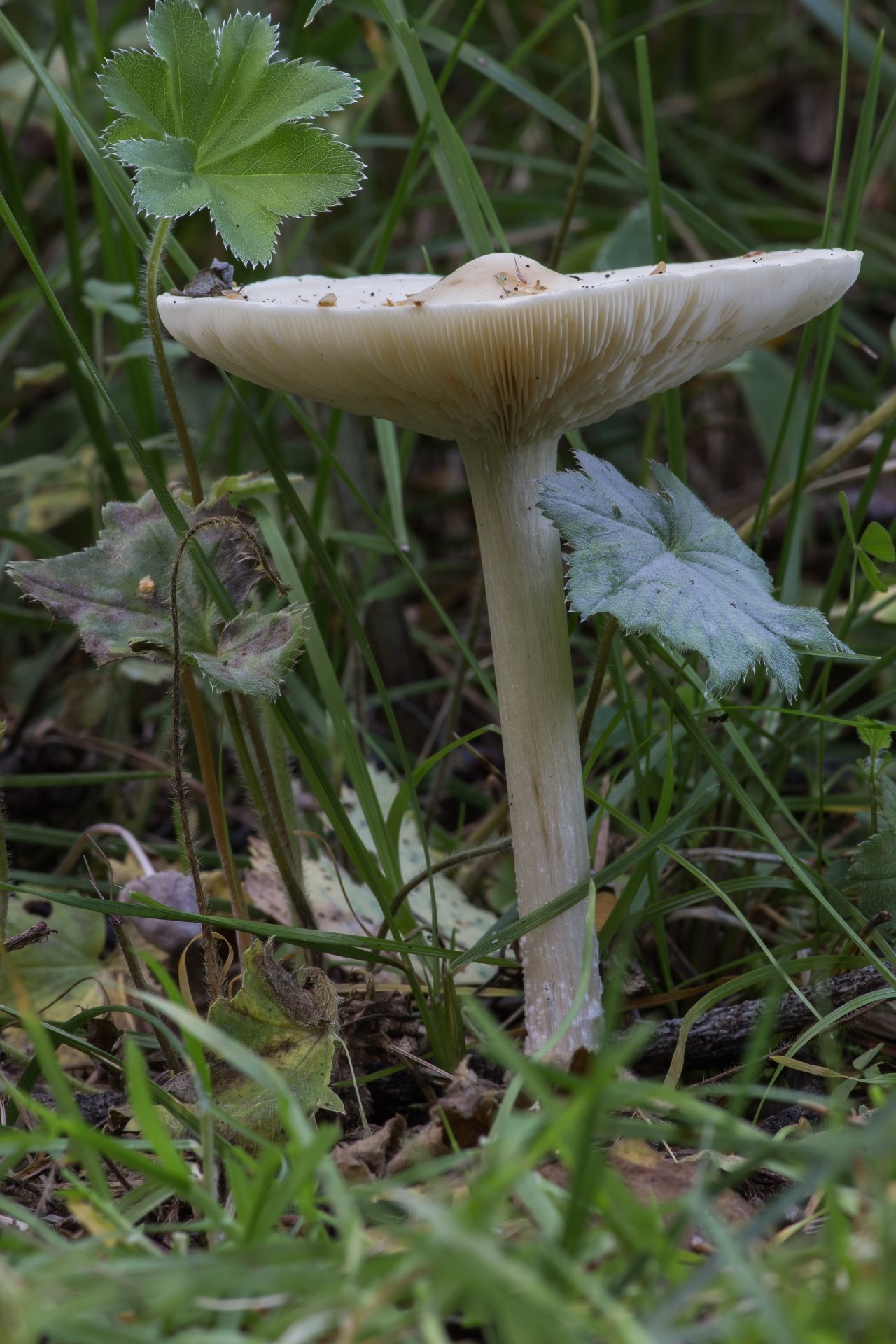
The cap is flat, in young specimens it is slightly convex, in the very center there is a small tubercle. Its diameter does not exceed 10 cm. The color of the cap of straight-legged melanoleuca is white, with a slight gray tint, in the center there is a dark spot. The surface is velvety, dry, smooth.
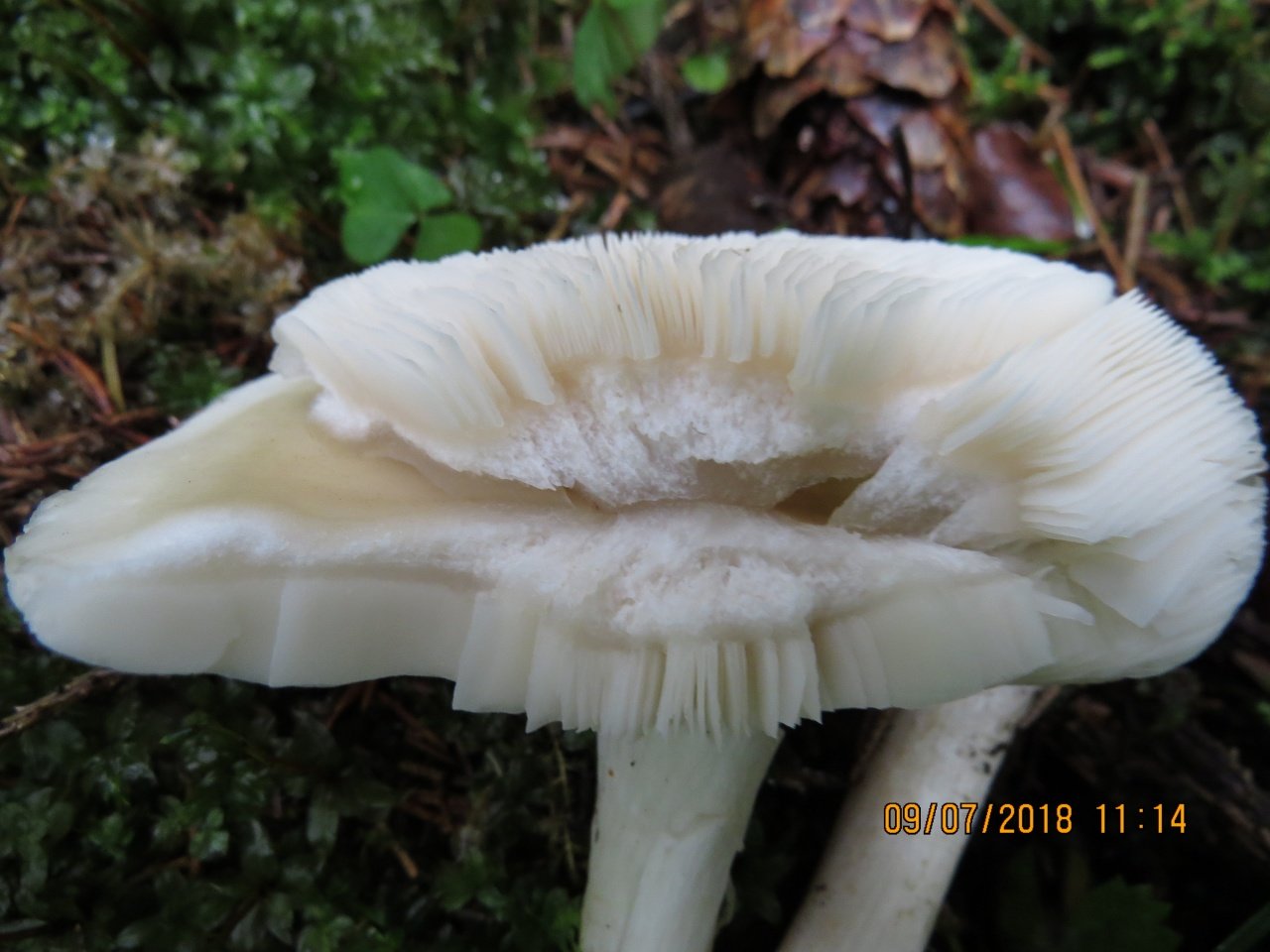
The bottom part of the cap is lamellar. Permanent, pale pink plates grow to the stem.
A thin, long leg of a straight-legged melanoleica is located clearly in the very center, slightly broadened towards the bottom. Its diameter does not exceed 2 cm, length - 10 cm. The color is white or pale gray.
The flesh of straight-legged melanoleica is white, dense, with a specific, barely perceptible flour smell.
Spores are thin-walled, colorless, odorless, elongated. Small warts are located on their surface. Spore powder of straight-legged melanoleuca pale yellow or cream.
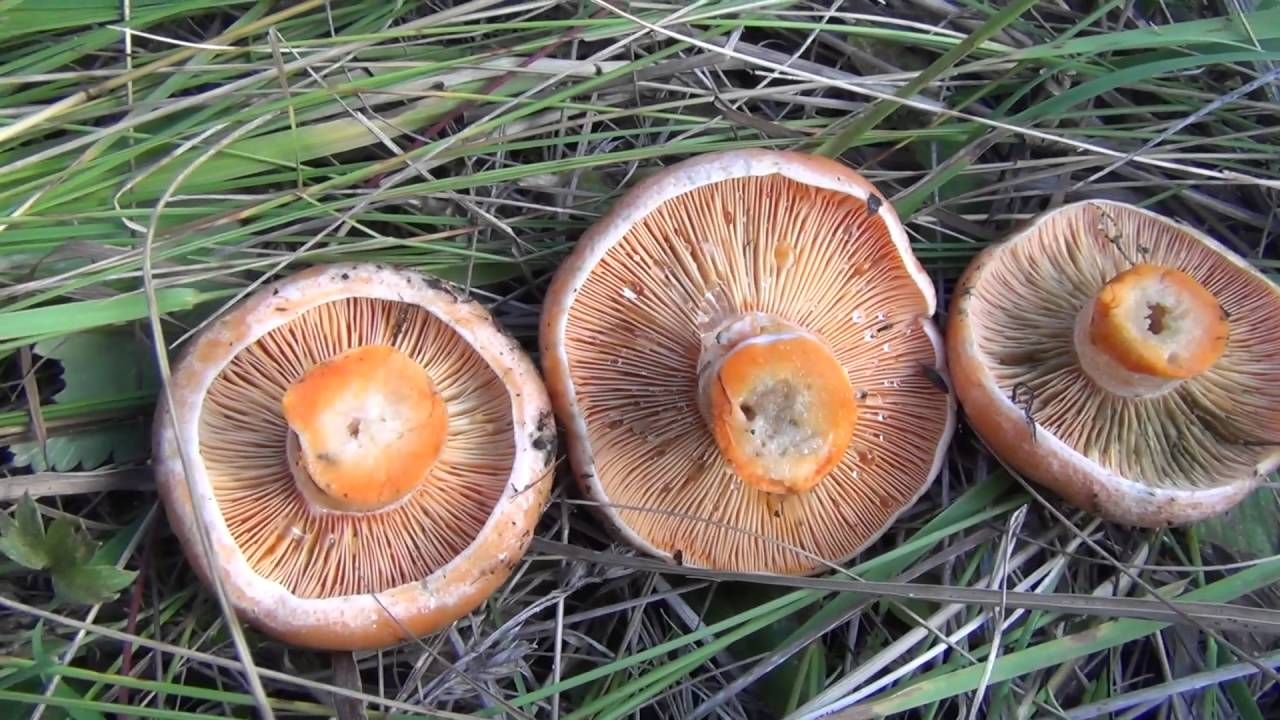
Melanoleuca black and white
Melanoleuca black and white (lat.Melanoleuca melaleuca).
Other names:
- Melanoleuca cognata
- Melanoleuca vulgaris
- Melanolevka ordinary
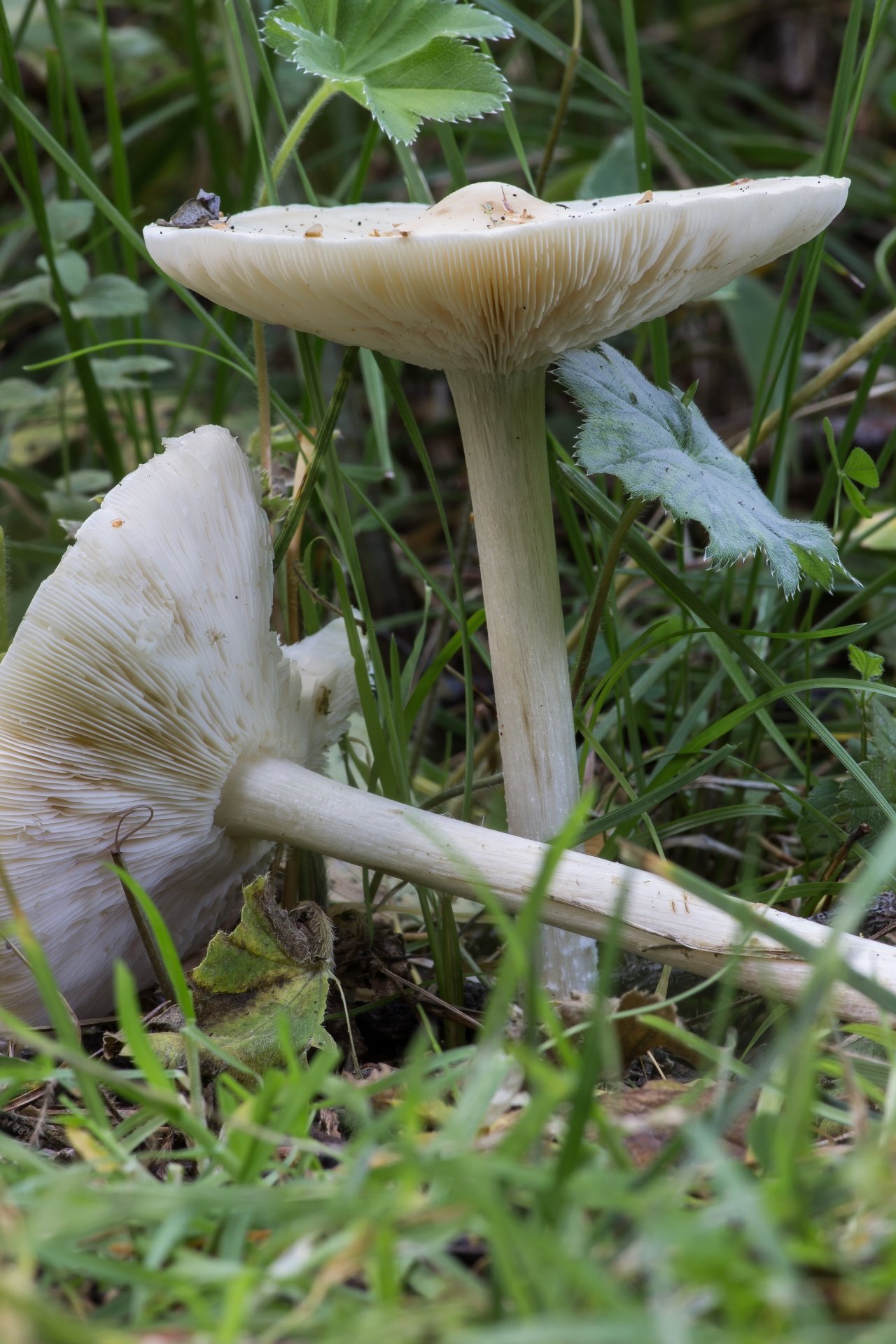
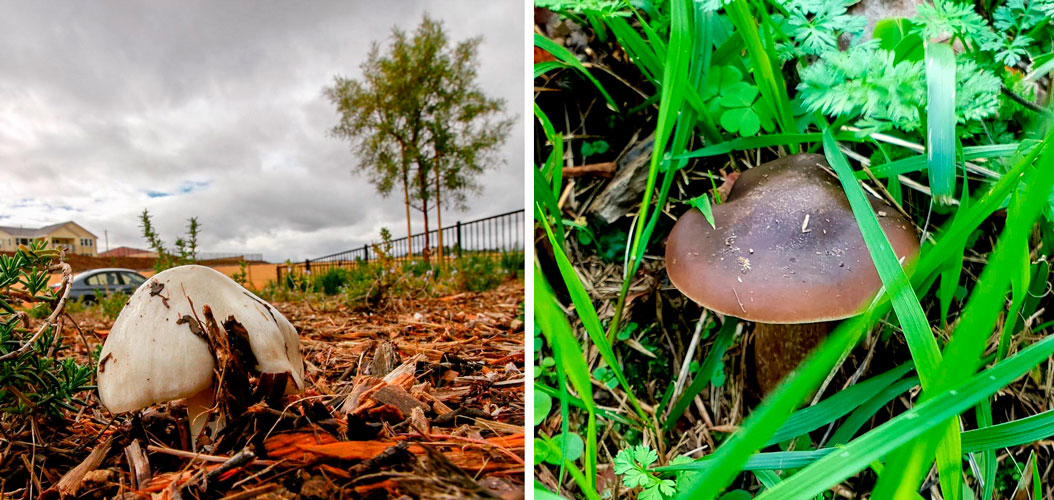
Melanoleuca black and white is an edible lamellar mushroom that grows singly from late July to mid September. Most often, it can be found in open areas of mixed and deciduous forests, in gardens, parks, meadows and along roadsides.
Hat
The cap of the mushroom is convex, in the process of growth it gradually flattens, becoming prostrate, with a slight bulge in the middle. Its diameter is about 10 cm. The surface of the cap is smooth, matte, with a slightly pubescent edge, painted in a grayish brown color. In hot dry summers it fade to a pale brown color, retaining its original color only in the center.
Leg
Stem thin, rounded, 5-7 cm long and about 0.5-1 cm in diameter, slightly widened, with a root nodule or curved to the side, dense, fibrous, longitudinally ribbed, with longitudinal black hair fibers, brownish-brownish. Its surface is matte, dry, brownish in color, on which longitudinal black furrows are clearly visible.
Pulp
The flesh in the cap is soft, loose, elastic in the stem, fibrous, initially light gray, brown in mature mushrooms. Has a subtle spicy scent.
Places and times of collection
Melanoleuca black and white most often settles on rotting brushwood and fallen trees in forests.
In deciduous and mixed forests, parks, gardens, meadows, glades, forest edges, in light, usually grassy places, along the roadsides. Singles and in small groups, not often.
In the Moscow region, it is often found throughout the entire region from May to October.
Edibility
It is considered an edible mushroom, used fresh (boiled for about 15 minutes).
No poisonous species are found among representatives of the genus Melanoleuca
It is better to collect only caps that can be boiled or fried, the legs are fibrous-rubbery, inedible.
The mushroom is edible, little known. It is consumed fresh and salted.
Melanoma of the skin ICD 10
Melanoma of the skin ICD 10 is located under the codes C43-C44. Codes include:
- Malignant melanoma of the lip (excluding the red border of the lips) (C43.0).
- Malignant melanoma of the eyelid (C43.1).
- Malignant melanoma of the external auditory canal and ear (C43.2).
- Malignant melanoma, unspecified, other parts of the face (C43.3).
- Malignant melanoma of the neck and scalp (C43.4).
- Malignant melanoma of the trunk (C43.5).
- Malignant melanoma of the upper limb + shoulder joint (C43.6).
- Malignant melanoma of the lower extremity + hip joint area (43.7).
- Malignant melanoma that goes beyond one or more sites listed above (C43.8).
- Unspecified malignant melanoma (C43.9).
Clinical classification. Types of melanoma
Melanoma manifests itself in various forms, there are 3 main types:
The tumor is of melanocytic origin.The most common disease (from 70 to 75% of cases) among people of the Caucasian race, middle age. Relatively small, complex shape with uneven edges. The color is uneven, reddish-brown or brown, with small blotches of a bluish tint. The neoplasm tends to be a tissue defect accompanied by a discharge (usually bloody). Growth is possible both on the surface and in depth. The transition to the vertical growth phase can take months or even years.
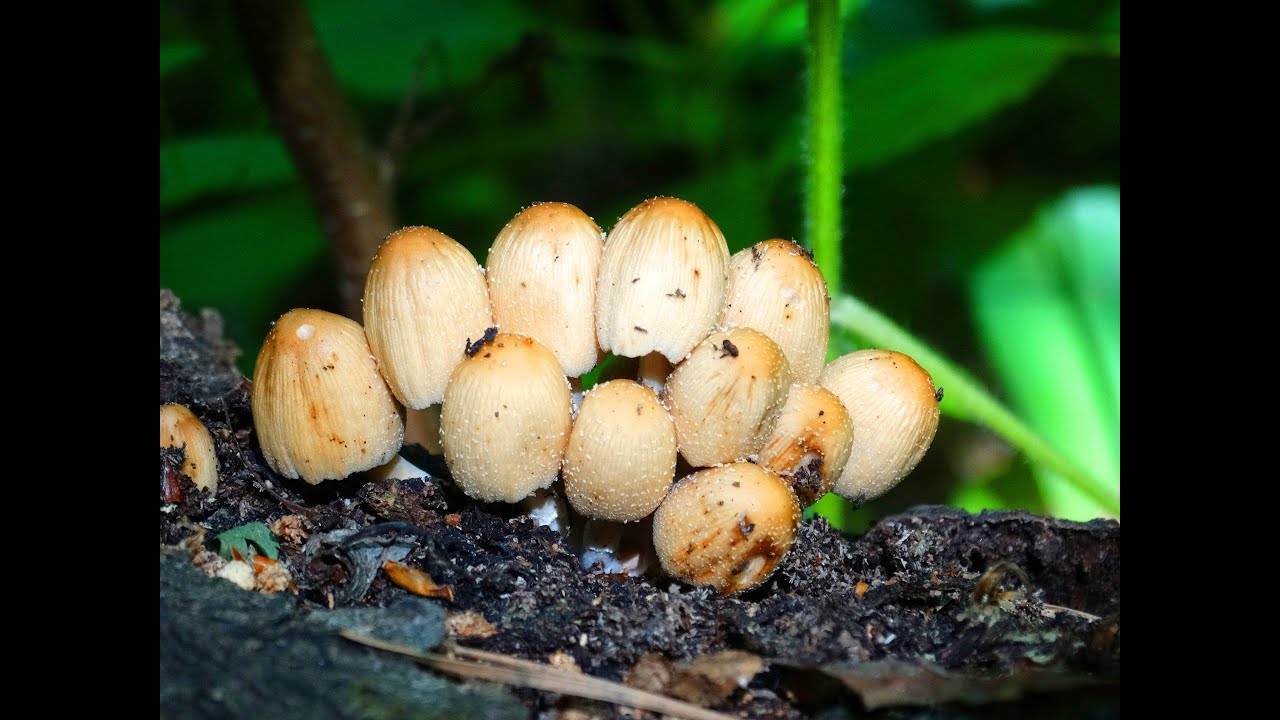
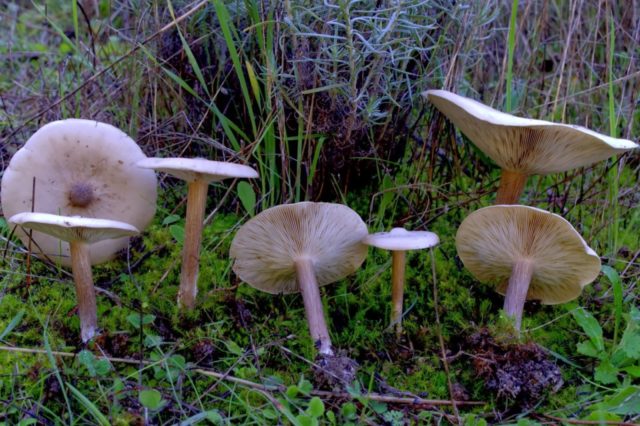
Melanoleuca short-legged (Melanoleuca brevipes)
Synonyms:
- Agaricus brevipes
- Gymnopus brevipes
- Tricholoma brevipes
- Gyrophila brevipes
- Gyrophila grammopodia var. brevipes
- Tricholoma melaleucum subvar. brevipes
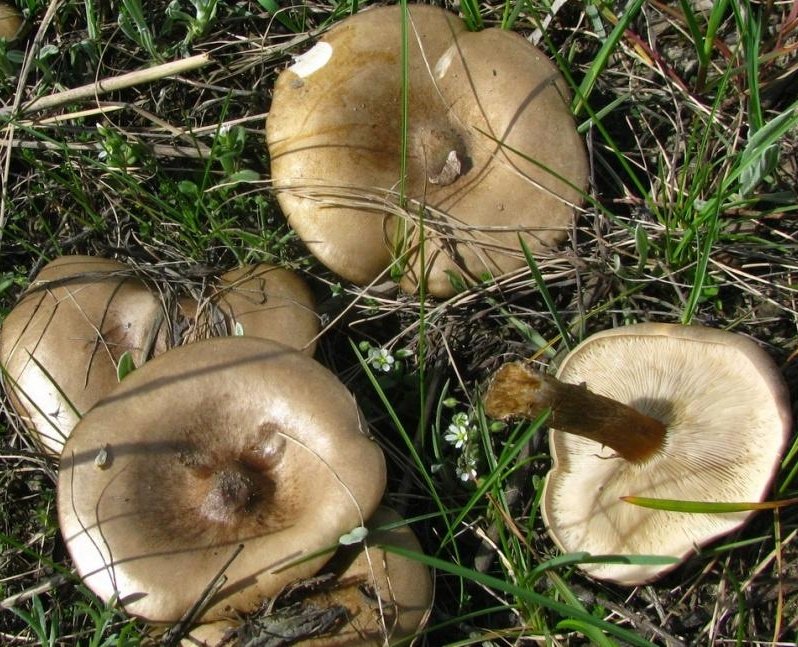

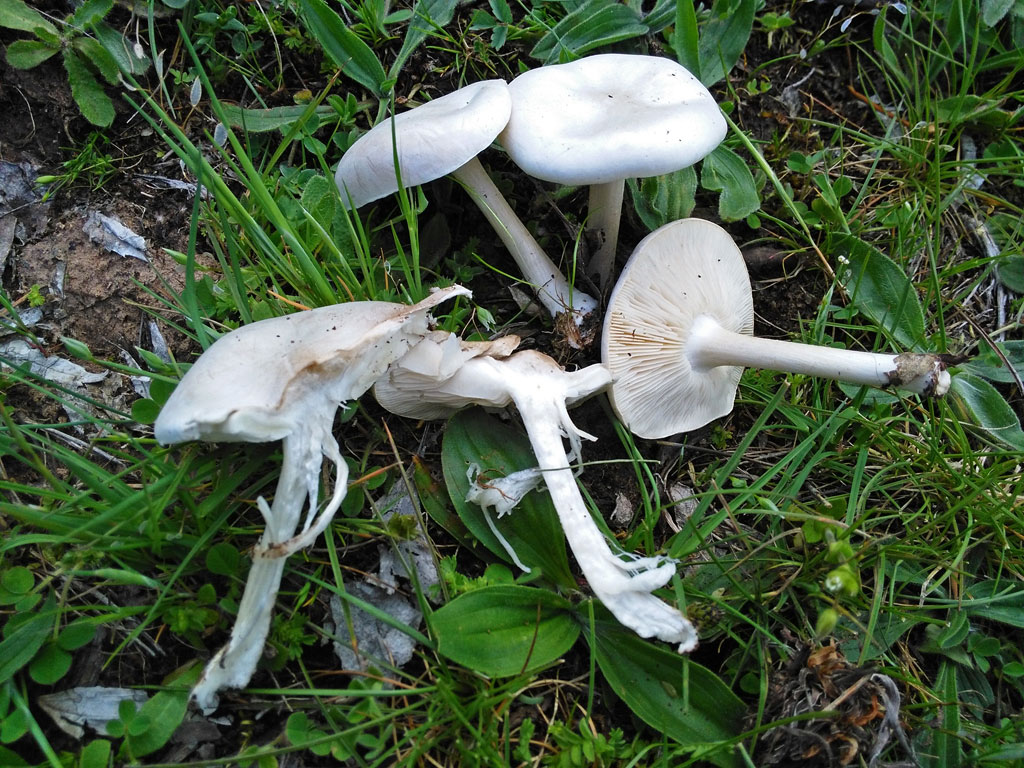
In a genus filled with hard-to-identify fungi, this melanoleuca stands (Or, better to say, “crouches”? In general, stands out) from the crowd with its gray hat and seemingly truncated leg, which seems disproportionately short for such a wide hat, much shorter than most members of the Melanoleuca genus. Of course, there are differences at the microscopic level as well.
Description
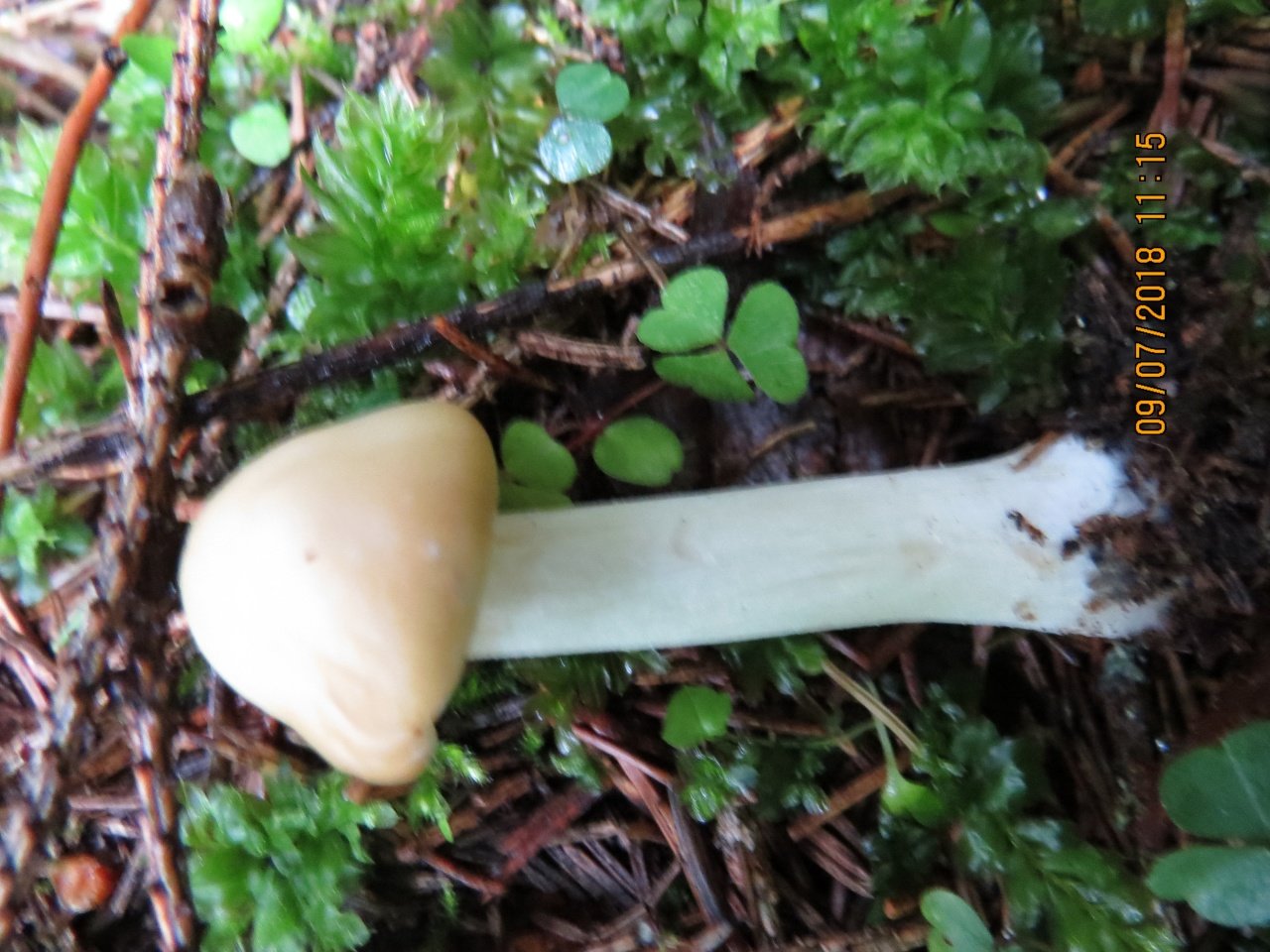
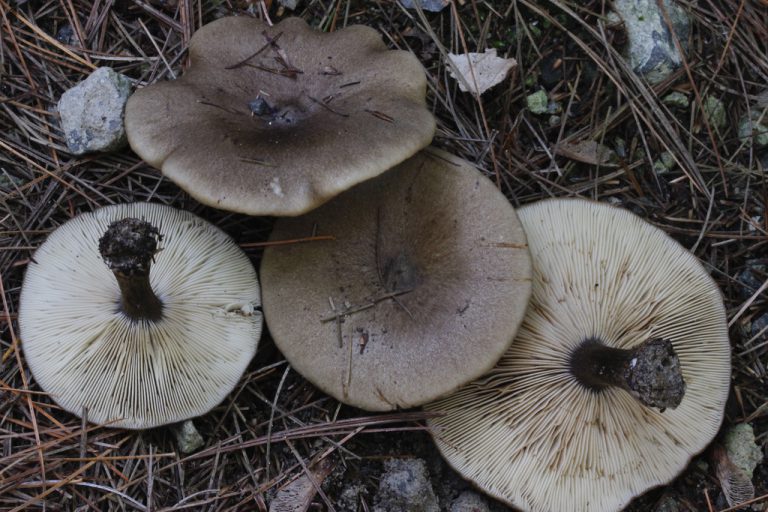
Hat: 4-10 cm in diameter, according to various sources - up to 14. Convex in young mushrooms, rather quickly becomes prostrate, sometimes with a shallow central bulge. Smooth, dry. Dark gray to nearly black in young specimens, turns gray over time, pale gray, and eventually fades to a dull brownish gray or even light brownish.
Plates: adherent, usually serrated, or almost free. White, frequent.
Leg: 1-3 cm long and thick 1 cm or slightly more, whole, dense, longitudinally fibrous. Sometimes twisted, in young mushrooms it is often in the form of a club, it evens out with growth, a slight thickening may remain at the base. Dry, cap color or slightly darker.

Flesh: Whitish at the cap, brownish to brown at the stem.
Smell and taste: Faint, almost indistinguishable. Some sources describe the taste as "pleasant starchy".
Spore powder: White.
Microscopic features: spores 6.5-9.5 * 5-6.5 microns. More or less elliptical, decorated with amyloid projections ("warts").
Ecology: probably saprophyte.
Habitat and fruiting period
Fruiting in summer and autumn, some sources indicate - from spring, and even from early spring. It is found in grassy areas, on pastures, forest edges and on soils with a disturbed structure, often in urban areas, parks, squares. It was noted that the mushroom is widespread in Europe and North America, probably not rare in other regions of the planet.
Edibility
A little-known edible mushroom of average taste. Some sources attribute it to the fourth category of edible mushrooms. It is recommended to boil it before use.
Similar species
It is believed that thanks to such a disproportionately short stem, Melanoleuca short-legged simply cannot be confused with any other mushrooms. At least not with any spring mushrooms.
Photo: Alexander.
Melanoleuca short-legged
| Group: | Lamellar |
|---|---|
| Plates: | Grayish white |
| Colour: | Gray, black, taupe |
| Info: | Bump in the center of the cap |
| Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
|---|---|
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Agaricomycetidae |
| Order: | Agaricales (Agaric or Lamellar) |
| Family: | Tricholomataceae (Tricholomaceae or Ordinary) |
| Genus: | Melanoleuca (Melanoleuca) |
| View: | Melanoleuca brevipes |
Edible mushroom (some sources indicate as conditionally edible) 4 flavoring categories.
The genus to which Melanoleuca short-legged belongs has many fungi that practically do not have significant differences and are distinguished only with the help of a microscope. She is perhaps the only exception to them. It is rather difficult to confuse it, since it has one very characteristic feature - a disproportionately short stem, the size of which is always smaller than the diameter of the mushroom cap.
It cannot be said that Melanoleuca short-legged was especially valuable prey. There is still no consensus about its fresh use. But, apparently, it is worth considering it still edible, as new sources indicate.
Melanoma of the skin: symptoms and signs with a photo
Photo of vertical melanoma on the back
In men, melanoma of the skin of the back most often develops. Superficial and nodular melanoma develops on the back, superficial melanoma is more common. Superficial melanoma is located in the upper layer of the skin, has uneven edges of the tumor, and can have a different color. The prognosis is good in most cases. Nodular melanoma looks like a pedunculated polyp, the color of the tumor dark - brown or black, the shape of the tumor is symmetrical, this type of tumor can ulcerate.
There are non-pigmented forms of melanoma, often melanoma on the back is a secondary focus of a cancerous tumor. Symptoms of skin melanoma are the asymmetry of the sides of the mole, uneven color, the diameter of the formation over 6 mm, the change in the size, color and shape of the nevus, and the blurred edges of the formation. The prognosis is unfavorable for the vertically growing type of skin melanoma indicated in the photo.
What does skin melanoma look like? Photo - 54 pcs.
What does melanoma look like? The appearance on the surface of the skin of a small spot, a gray-yellow nodule, or a shiny plaque. In the early stages, the disease has no subjective manifestations and does not cause any discomfort. With an increase in the tumor, it can begin to itch, itch, there is a feeling of discomfort, tingling. Further in the middle of the neoplasm, a small weeping ulcer may appear. Sometimes it starts to bleed or crust over. The middle of this formation can heal, but at the same time the tendency to peripheral growth remains. On palpation of the base of this neoplasm, some tissue compaction can be felt, although there are no signs of inflammation.
Just a terrible and terrible disease. It should be treated immediately as soon as melanoma is suspected. It is good that we have experienced doctors who can help and cure this horror.
Please give me the coordinates of good doctors.
Tell a specialist in the treatment of melanoma in St. Petersburg.
Collection rules
It is better to pick mushrooms in wet weather, after a long rain. Melanoleucus can be found in mountainous areas or in pastures, in the soil or on plant debris.
Melanoleuca grows in large families: if you see one mushroom, then there are others nearby.
The mushroom leg of the straight-legged melanoleuca can be twisted or cut off; this does not affect the fruiting of the mycelium.
For fragile, straight-legged fruit bodies, wicker willow baskets are suitable, in which the pulp does not crumble, the aroma and freshness are preserved.
It is not recommended to cut old, rotten, darkened specimens of straight-legged melanoleuca. It is better to eat small, white, dense mushrooms.
They put straight-legged melanoleucus in the basket only if there is complete confidence in its edibility. At the slightest doubt, it is better to refuse an incomprehensible copy.
Description
Hat
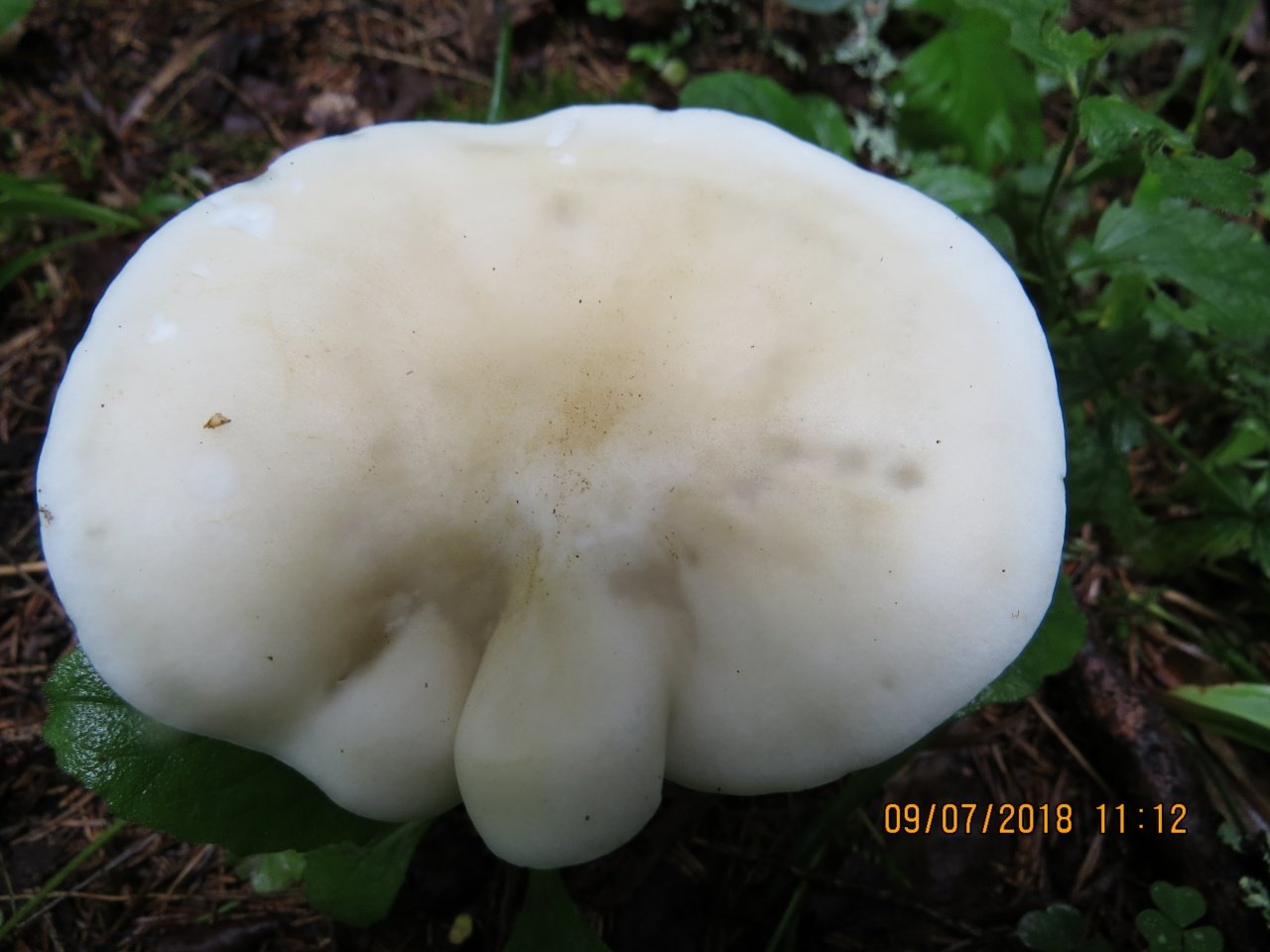
In a young mushroom, it has the shape of a hemisphere, then gradually straightens out, becoming almost flat, depressed in the center, with a small central tubercle. It grows in diameter about 10 cm, sometimes up to 14 cm.
The structure of the cap is dense, elastic. The outer edge is almost always curled inward. The surface of the cap is smooth, matte, dry. The color of the young mushroom is deep gray, almost black. As it grows and ages, the cap gradually lightens, becoming light gray or gray-brown at the end of its life cycle.
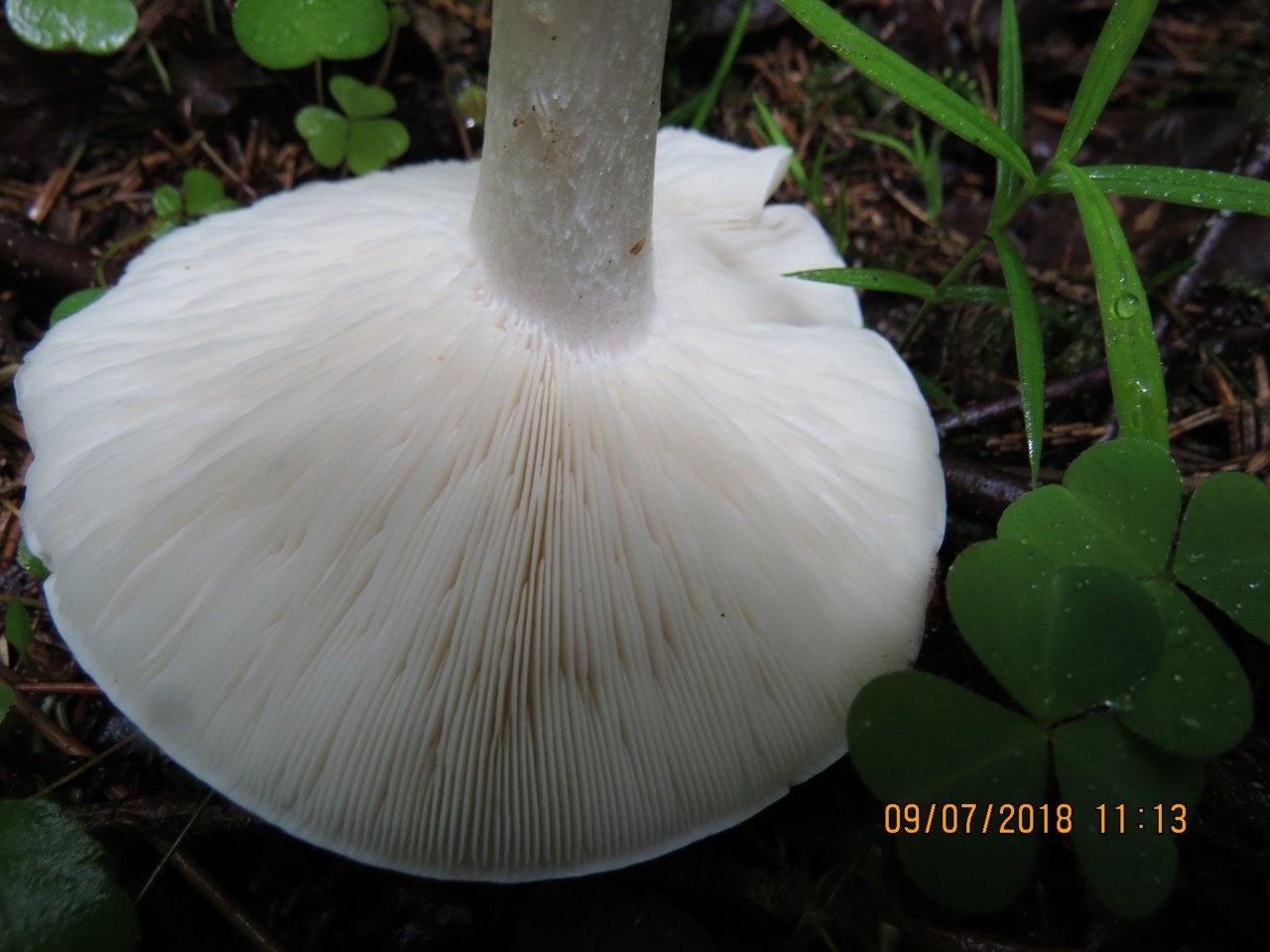
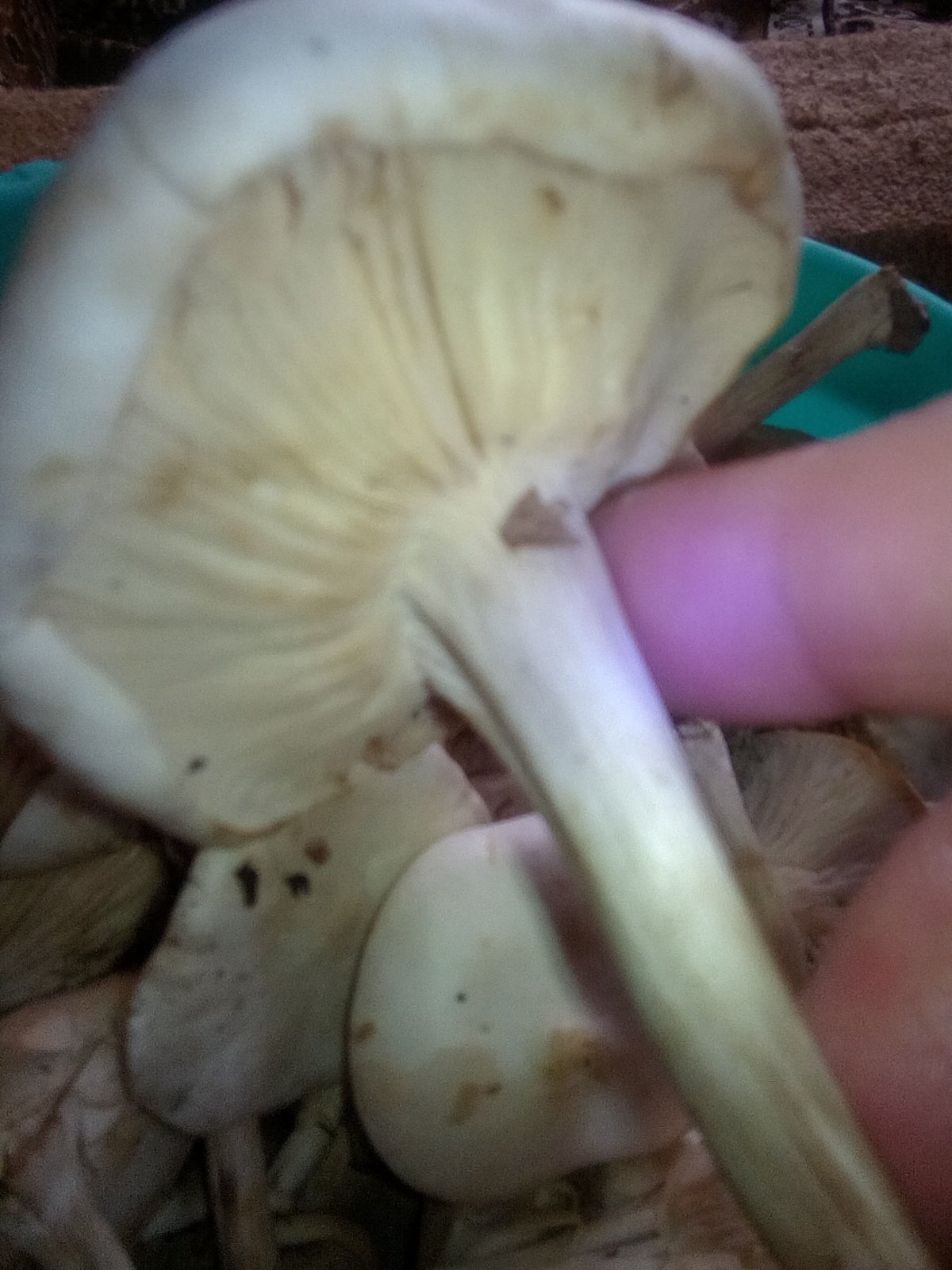
Spore-bearing layer
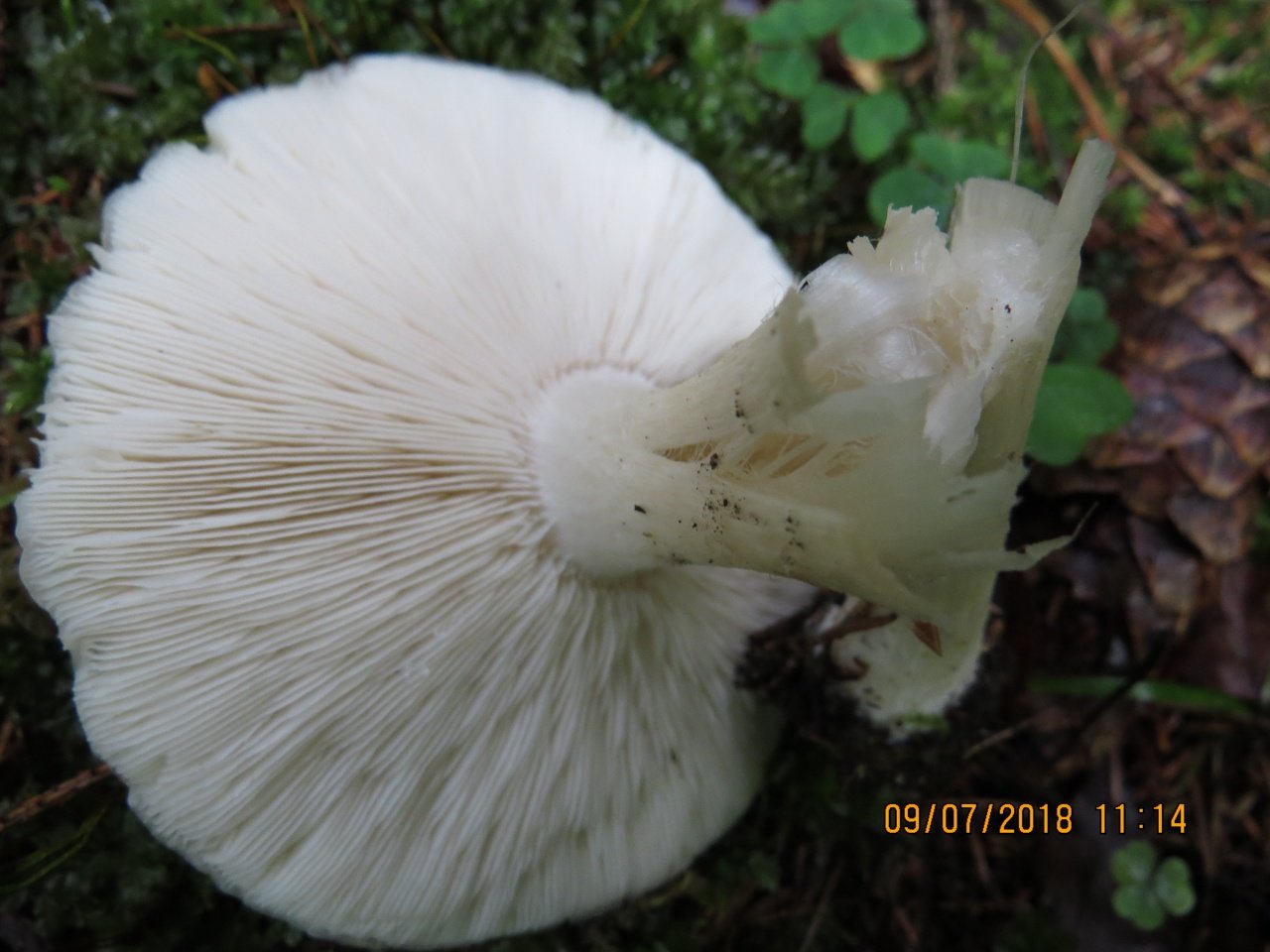
Lamellar. It is colored grayish-white; it darkens a little by old age. The arrangement of the plates is frequent, the plates themselves are wide, adhered to the pedicle by a tooth. Spore white powder, ellipsoidal spores.
Leg
It grows in length only up to 3-4 cm, in diameter about 1 cm. The structure of the leg is dense, with longitudinal fibers, rather hard. The pulp is solid, without voids and cavities. Sometimes, especially in young mushrooms, it has an irregular shape, twisted or bent. Colored a tone darker than the cap.
Pulp
The hat is white, elastic. If damaged, it does not change color, does not emit milky juice.In the leg it is colored brown in different intensities, solid. Has a neutral taste and a weak flour aroma.
Distribution and collection
Melanoleuca short-legged often settles near human habitation. Prefers open grassy terrain, often grows on abandoned agricultural land, on pastures and pastures, on the side of roads and paths, in parks and squares. It grows most often in small groups. The geography of distribution is quite wide, this mushroom can be found throughout the temperate forest belt of Russia. It is rare.
Diagnostics
- Visual method. Examination of the skin using the "rule of malignancy".
- Physical method. Palpation of accessible groups of lymph nodes.
- Dermatoscopy. Optical non-invasive superficial examination of the epidermis using special devices that give 10-40 times magnification.
- Siascopy. Hardware spectrophotometric analysis, which consists in intracutant (depth) scanning of the formation.
- X-ray.
- Ultrasound of internal organs and regional lymph nodes.
- Cytological examination
- Biopsy. It is possible to take the whole formation or part of it (excisional or incisional).
Collection rules
Fruit bodies ripen from early summer to September. The short stem of the mushroom "sits" loosely in the ground, so it will not be difficult to remove it from there.
When collecting melanoleuca, important rules must be followed:
- it is best to go to the forest for mushrooms in the early morning, until the dry dew begins;
- warm nights after heavy rains - perfect weather for a wonderful mushroom harvest;
- it is not necessary to collect rotten, overripe, withered, mechanically or insect damaged specimens, since they have already begun to release toxins;
- an excellent container for collecting mushrooms - wicker baskets that provide easy access to air, polyethylene bags are definitely not suitable;
- The short-legged melanoleucus is best cut with a knife, but it is quite possible and careful to pull it out, slightly twisting and swinging it from side to side.
Although it is a non-poisonous mushroom, it should not be tasted raw.
The first signs of melanoma
Melanoma is the acquisition by cells of unfavorable signs of malignancy (malignancy properties), expressed by various symptoms.
For the convenience of memorizing the signs of melanoma, the "FIGARO" rule is used:
Form - swollen above the surface;
Change - accelerated growth;
Borders - openwork, irregular, indented;
Asymmetry - lack of mirror similarity of two halves of education;
Size - a formation with a diameter of more than 6 mm is considered a critical value;
Coloring - uneven color, the inclusion of random spots of black, blue, pink, red.
In general practice, the English version is also popular, summarizing the main, most typical features - the "ABCDE rule":
Asymmetry - asymmetry, in which, if you draw an imaginary line dividing the formation in half, one half will not be similar to the other.
Border irregularity - the edge is uneven, scalloped.
Color - a color different from other pigment formations. Interspersed areas of blue, white, red are possible.
Diameter - diameter. Any formation over 6 mm requires additional observation.
Evolution - variability, development: density, structure, size.
Without special studies, it is difficult to determine the type of nevus, but timely noticed changes in the nature of the spot will help detect malignancy.
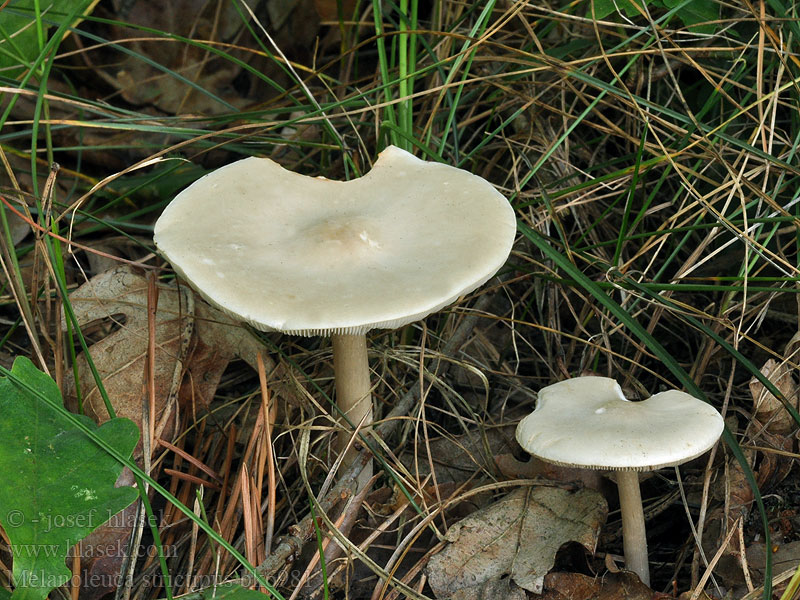
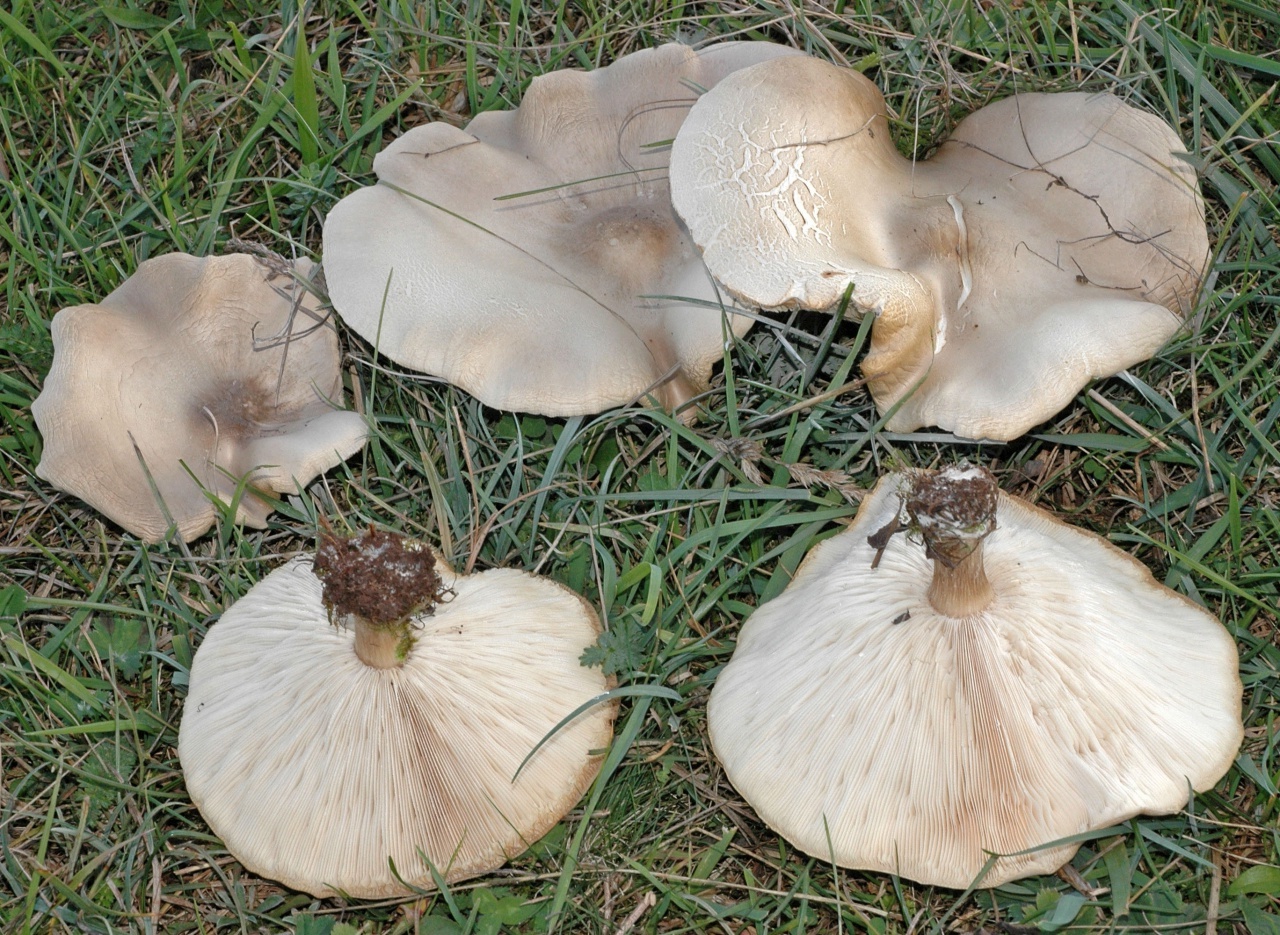
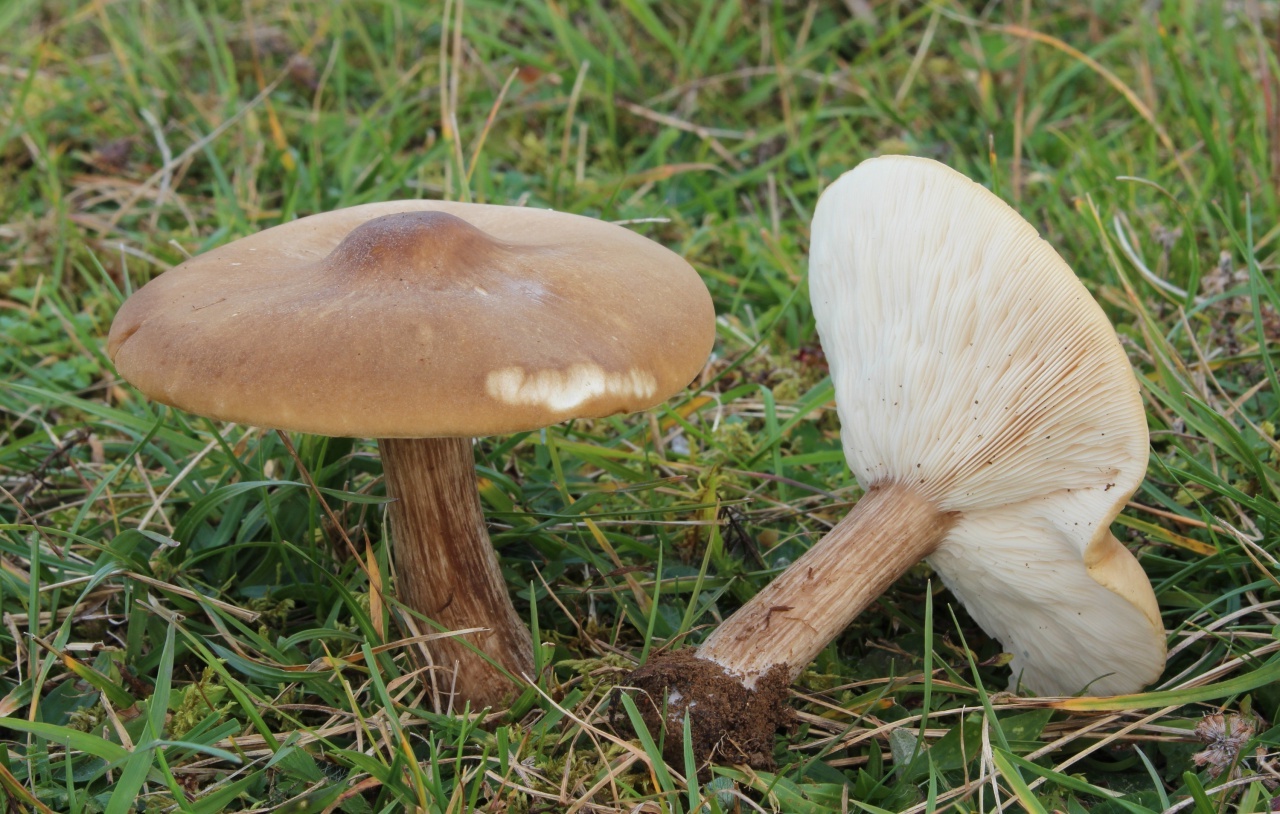
Melanoleuca striped (Melanoleuca grammopodia)
Synonyms for the main name of the species are Latin terms:
- Melanoleuca grammopodium,
- Gyrophila grammopodia,
- Tricholoma grammopodium,
- Entoloma placenta.
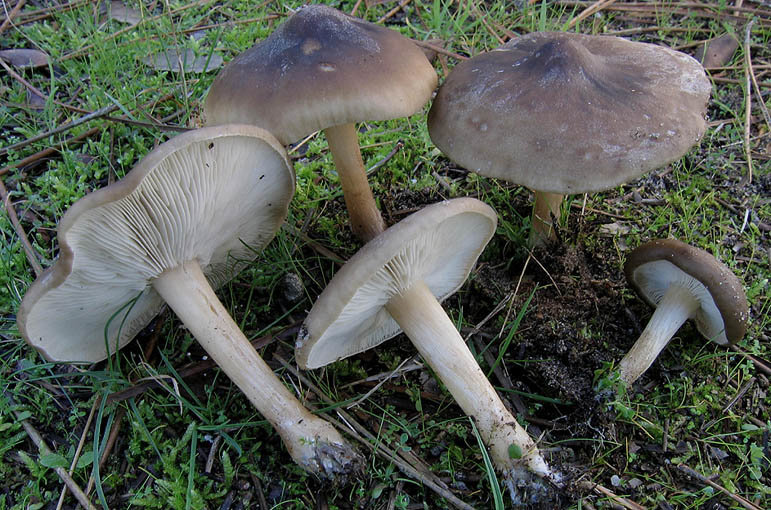

Malanoleuca striped (Melanoleuca grammopodia) is a mushroom of the Tricholomataceae family.
External description of the mushroom
The fruiting body of striped melanoleuca consists of a cylindrical and slightly thickened leg at the bottom, and an initially convex and subsequently outstretched cap.
The length of the mushroom leg does not exceed 10 cm, and its diameter varies within 0.5-2 cm. Longitudinal fibers of a dark brown color are visible on the surface of the leg. If you cut off the leg at the base, then that place is sometimes brown or dark gray in color. The leg is characterized by great rigidity.
The diameter of the mushroom cap can be up to 15 cm. In mature mushrooms, the cap is characterized by a lowered edge, high density, a depressed surface and a characteristic tubercle in the center. The top layer is smooth and matte skin, which can be slightly shiny. The color of the cap of the striped-legged malanoleuca is different: off-white, ocher, nutty. As the mushroom matures, the color of the cap becomes faded.
The lamellar hymenophore, located on the inner side of the cap, is represented by often located, convoluted plates, which can sometimes be forked, serrated and grow to the stem of the fungus. Initially, the plates are white, but later become creamy.
The pulp of the described type of mushroom is elastic, has a whitish-gray color, and in ripe fruit bodies it becomes brown. The smell of the pulp is inexpressive, but often unpleasant, musty and mealy. Her taste is sweetish.
Habitat and fruiting period
Melanoleuca striped (Melanoleuca grammopodia) grows in deciduous and mixed forests, in parks, gardens, pine forests, meadows, meadow areas, forest edges, well-lit grassy places. Sometimes it grows on the side of roads, in groups or singly. When warm weather is established in the spring, striped-legged malanoleucks can appear even in the month of April, but usually the period of mass fruiting of this type of mushroom begins in May. From July to September, small groups of striped-legged malanoleuca or solitary mushrooms are found in spruce forests.
Edibility
The mushroom is edible, it can be consumed in any form, even fresh, without prior boiling. Melanoleuca striped is good when boiled.
Skin melanoma treatment
“Can skin melanoma be treated? How is skin melanoma treated? What medications to use for skin melanoma, are there any contraindications? " - such questions are asked by patients to the doctor. Melanoma treatment is carried out after diagnostic tests of the tumor. Diagnosis is carried out by visual examination, then with the help of dermatoscopy, the doctor examines the site of the tumor lesion. Cells are taken from the affected area of the skin for examination. A histology of the affected and surrounding tissues is performed. With the help of modern methods of examination, CT and MRI, the degree of tissue damage by the tumor is determined.
Melanoma treatment is carried out depending on the stage of development of the disease. At an early stage, complex treatment is carried out. At the later stages of melanoma development, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, treatment with combination therapy are carried out, methods are used to alleviate the condition of a patient with melanoma. It is believed that the use of chemotherapy is ineffective due to the low sensitivity of the tumor to chemotherapy drugs. Surgical intervention is not recommended if a generalized process is identified. If surgery is not allowed, polychemotherapy is performed.
What does skin melanoma look like: photo
Early melanoma may go unnoticed
It attracts attention after changing the color to a darker color of the mole or due to the growth of a tumor. The causes of skin melanoma are various:
- Ultraviolet irradiation. Melanoma often develops in people who like artificial and natural tanning, after sunburn.
- Nevi (moles), melaniform nevus.
- A genetic predisposition to the development of melanoma, for which a specific gene is responsible.
- I and II skin phenotype.The rest of the skin phenotypes are less prone to the formation of a malignant skin tumor. The most susceptible to the development of cancer are people with fair skin, light hair color, blue, gray eyes, freckles.
- Hereditary hypersensitivity to ultraviolet rays.
- Skin injuries, moles.
- Diseases of the organs of the endocrine system.
- Age-related changes.
- A history of skin cancer treatment is a predisposing factor.
Expert opinion
Head of the Oncology Department, Oncologist, Chemotherapist
Melanoma is one of the malignant neoplasms characterized by an aggressive course. Mortality from skin cancer accounts for 40% of all cases of oncology. Diagnosis of melanoma in the Russian Federation is carried out quite often. 9000–10000 disease debuts are detected annually. The tendency towards an increase in severe forms due to untimely treatment, when doctors can only offer palliative therapy, is not encouraging.
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital pay careful attention to the diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. Doctors advise seeking medical attention if suspicious lesions appear on the skin.
In a similar way, you can identify the disease at the initial stages and carry out appropriate treatment. In addition, in the early stages, melanoma is characterized by a favorable prognosis for recovery.
At the Yusupov hospital, doctors conduct a full course of examination, which is necessary to determine the stage of development of skin cancer and all related criteria. As a result of determining an accurate diagnosis, the effectiveness of the prescribed complex therapy increases. The drugs are selected according to the latest European guidelines for the treatment of skin tumors.