Views
The most common types of goldenrod are:
Canadian goldenrod
This plant is capable of reaching colossal sizes for its species, up to one and a half meters in height. The leaves of this variety themselves are also impressive in size, reaching 15 cm in length. It was this variety that was one of the few varieties that became the progenitors of the modern species of large goldenrod. For all other indicators, the Canadian goldenrod practically does not differ from its usual counterpart, with the exception of the absence of toxicity, which favorably distinguishes it from other varieties.
Bicolor goldenrod
The plant is not common in culture, and is a feral species. The stems of this species do not have sufficient rigidity, which provokes the sagging of their tops, especially during the flowering period. The inflorescences themselves have a lingual form of white, and a tubular form of light yellow color, for which the appearance itself received its name.
Bluish gray goldenrod
This variety is notable for its flowering period, which begins in late autumn and ends in early winter. This feature makes the plant dependent on warm climatic conditions, which led to its spread in the United States, especially in states with hot climates, and excluded its free distribution in the CIS countries.
Kutler's goldenrod
The plant has the smallest dimensions of all its varieties, because the length of its stem rarely exceeds 35 cm, and practically has no leaves, with the exception of the basal part, where there are more leaves than other species. Kutler's goldenrod is the progenitor of modern low-growing goldenrods, which are popular as medicinal and ornamental plants.
Dzintra
This goldenrod is notable for the fact that it was bred in Belarus. Plant height reaches 60 cm, and flowering lasts 30-40 days. It is very common as a decorative decoration, and is very fond of florists for its bright inflorescences, contrasting with the rich, dark green color of shiny oval leaves.
The listed goldenrods are only a small part of the vast family of this herb, of which there are more than 16 species only in Russia. Despite such a variety, almost all of them have yellow flowers, and also like sunny and open places, do not grow well in shaded areas, and are practically not found in forests!
Common goldenrod
Common goldenrod, or golden rod (Solidago virgaurea) is a perennial herb from the Asteraceae family with a short woody rhizome. Stems are erect, often unbranched, leafy, up to 100 cm tall. The leaves are alternate or ovate, pointed, serrate along the edge, basal and lower stem leaves are narrowed into a winged petiole, the upper ones are smaller, sessile. The flowers are yellow, in small (up to 15 mm) baskets, collected in a racemose or paniculate inflorescence. Fruits are cylindrical ribbed achenes with a brownish tuft. Blooms in August - September.
It is found throughout the European part of Russia, except for the Far North, in the Caucasus and Western Siberia. It grows in light forests, along forest edges, clearings, clearings, among bushes, in meadows. Prefers soils that are not heavy in texture. In Eastern Siberia and the Far East, it is replaced by closely related species - goldenrod dahurian (Solidago dahurica syn. Solidago virgaurea var. Dahurica) and descending goldenrod (Solidago decurrens), which can be used in medicine due to a similar chemical composition on a par with the main species.
The upper part of leafy shoots, harvested during flowering, is used. It is not at all necessary to grow goldenrod on the site, you can simply collect and dry the upper parts of the shoots with inflorescences in late July and early August. Dried in the shade, laid out in attics or in a dryer, at a temperature not higher than + 35 + 40 ° C. Homeopaths use inflorescences.
We use it in folk medicine and harvested wild. Included in the Pharmacopoeia of Germany and some other countries.
Properties and applications of common goldenrod
Chemical composition: organic acids, diterpenoids, 2.4% saponins, phenolic compounds, phenolcarboxylic acids and their derivatives (coffee, chlorogenic, hydroxycinnamic), up to 012% flavonoids (rutin, quercetin, etc.), coumarins, essential oil.
Pharmachologic effect. It has a strong diuretic effect, it is used for diseases of the kidneys and bladder, especially often for urolithiasis. At the same time, along with a diuretic effect, it exhibits anti-inflammatory and strong antibacterial properties. Contained flavonoids reduce capillary permeability. Effective for urate and oxalate stones. Contraindicated in phosphate stones, as it increases the pH of urine. It is very effective in chronic prostatitis, cystitis and urethritis. Sometimes in fees it is used for impotence and prostate adenoma. Due to its antifungal action, it is effective against candidiasis, and in common parlance - thrush.
In folk medicine, it is used for cholelithiasis, indigestion, rheumatism, gout, associated with impaired uric acid metabolism. Outwardly, fresh leaves are used for abscesses and boils. In Germany, it is sometimes used for diseases of the veins, which is probably associated with a high content of flavonoids and a pronounced anti-inflammatory, vaso-strengthening and antioxidant effect.
Description of the plant

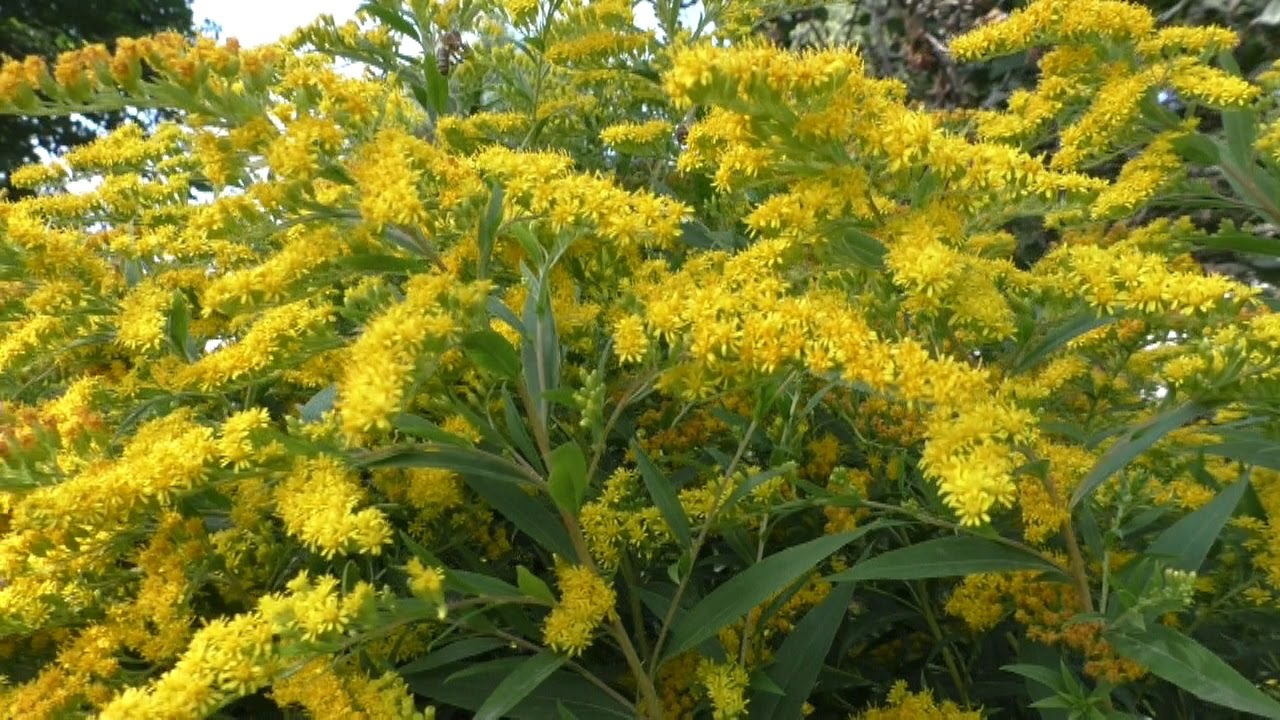
Goldenrod is a perennial brush-rhizome herbaceous plant. The elongated, oblong strong root of the plant goes deep into the ground. On the surface, one can see a little branchy simple shoot, up to 100 cm high. The satiny bark covers the straight stem of the goldenrod. It can be emerald or crimson. The bright green leaves of the herb goldenrod are oval or ovoid in shape, with small serrations along the edges, sawtooth. The lower narrow leaves are more elongated than the upper ones. The narrow leaves of goldenrod resemble willow leaves.
Common goldenrod blooms from May to September. The inflorescences consist of bell-shaped buds, lemon-colored. The flowers are up to 8 mm long. Bells with lemon-colored petals grow along the edges, and in the center they are distinguished by chestnut-yellow colors. The fruit formed after pollination is a cylindrical achene with longitudinal ribs up to 4 mm long.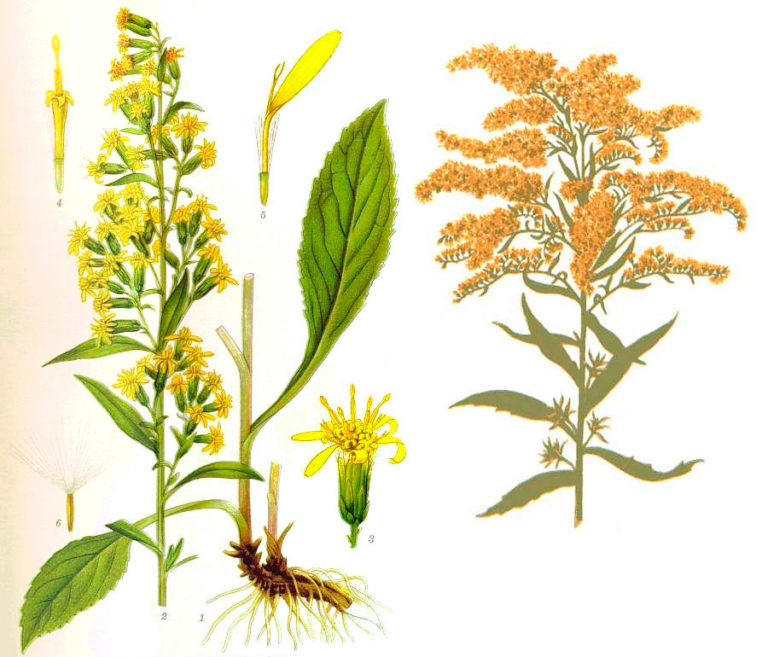
The herb goldenrod is an aggressor plant, one specimen gives up to 100 thousand seeds, germination rate of 95%. In a year, it can move dozens of kilometers, is a full-fledged owner in those territories where he settled.
Goldenrod is used in many industries. Used in veterinary medicine as an astringent. In an industrial way, yellow and brown paints are extracted from goldenrod. The goldenrod plant is highly valued for its beneficial properties and is used in folk medicine.
Types and varieties of goldenrod with a photo
Goldenrod Shorti (Solidago shortii)

A branched perennial plant. It grows up to one hundred and sixty centimeters in height. Leaves are smooth, serrated along the edge, oblong-lanceolate. The panicles are pyramidal in shape, growing up to forty-five centimeters. Baskets are yellowish with a golden tint. The most popular varieties:
Variegata - a plant of this variety has specks and yellowish stains on green leaves.
Goldenrod rugosa (Solidago rugosa)
Rough-stemmed North American perennial goldenrod. It grows up to two meters in height.The stems are rough and smooth. Shoots are reddish brown. Leaves are oval or oblong, serrated along the edge, up to nine centimeters in length and up to two in width. Basal leaves are absent. Baskets are yellow.
Dahurian goldenrod (Solidago dahurica = Solidago virgaurea var.dahurica)
The plant is widespread in Siberia. Grows up to one meter in height. The stems are simple and strong, smooth below, and slightly covered with pubescence above. The leaves are oblong, lanceolate or ovoid, the edge is serrate, the apex is pointed, there are short hairs along the edges and on the veins. There are a lot of baskets, small and have a yellow tint.
Canadian goldenrod (Solidago canadensis = Solidago canadensis var.canadensis)
A perennial plant that grows up to two meters in height. Leaves are bright green, oblong-lanceolate. The baskets are small and have a golden yellow tint. The panicle is pyramidal up to forty centimeters long. Most popular variety:
The patio is a plant that grows up to sixty centimeters in height and does not require a garter. Baskets are golden yellow.
Common goldenrod (Solidago virgaurea)

It grows from sixty centimeters to two meters. Stems are straight, simple or branched. The leaves have a solid edge and are alternately linear-lanceolate or lanceolate. Inflorescences are spicate or racemose. The baskets are yellow.
Goldenrod highest (Solidago altissima = Solidago canadensis var. Scabra)
It grows up to one hundred and eighty centimeters in height. Stems are straight, slightly pubescent. Leaves are lanceolate, toothed edge, parallel veins.
Goldenrod hybrid (Solidago x hybrida)
It includes the following hybrid varieties:
- Goldstral - grows up to one meter in height. Baskets of golden yellow color, gathered in panicles up to twenty centimeters long.
- Kronenstahl - grows up to one hundred and thirty centimeters in height. The baskets are golden.
- Spetgold - grows up to one meter in height. Inflorescences are lemon yellow.
- Frugold - plant height is only twenty centimeters. Inflorescences are yellow.
Reproduction
There are several ways to increase the number of copies:
- Planting bushes in spring or summer.
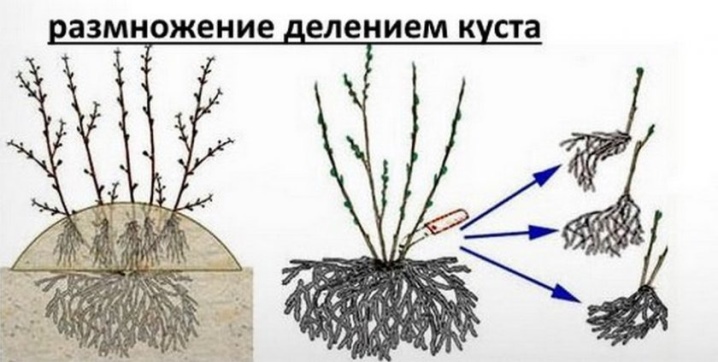
- Cuttings. To do this, in the summer, a couple of young shoots are separated, dividing the root system. You can also trim off a long, annual shoot and root it later.
- Another way is to cut off the shoots from the bush during flowering. This will stimulate dormant buds and allow new growth to grow.
- Seminal. The collected planting material is sown in the ground at 18-22 ° C. After 2-3 weeks, the first shoots can be observed. It is worth noting that the seeds, thanks to their crests, fly around and give new growth, gradually turning into thickets. To avoid this, young shoots must be removed, and the panicles must be cut off after flowering to prevent the seeds from ripening.
Botanical description
What is Canadian goldenrod? The photos and descriptions below introduce us to this perennial herb.

what are the stems
The plant has alternately placed pointed lanceolate leaves, on which three veins can be seen. The lowermost green plates are serrated-toothed. These leaves extend from the stem with short petioles. At the top are sessile whole-edged leaves.
In the second year of life, starting in mid-summer, the plant begins to bloom. This condition continues for one and a half to two months. What can be observed while doing this? At the very top of the stems, paniculate inflorescences-baskets, which consist of small yellow flowers, begin to form. 5-6 of them are reed, and 6-8 are tubular. They contain five stamens with a lower ovary. By the end of August, the canadian goldenrod begins to form cylindrical achenes-fruits. They contain small seeds with a small tuft, which are brown in color.
The plant is an excellent honey plant. Its reproduction occurs both with the help of the wind and in a vegetative way (by cuttings or part of the rhizome).
In Russia, you can find two varieties of goldenrod - Canadian and ordinary (golden rod). The cultivation of the plant is carried out for decorative and medicinal purposes. At the same time, such a species as canadian goldenrod exhibits stronger healing properties, much more effectively affecting the patient's body.
The root system of a plant has the ability to grow independently. At the same time, Canadian goldenrod (see photo below) gradually displaces and drowns out a huge number of species of other plants.

For example, in China, this is considered a serious agricultural problem that needs to be addressed in order to preserve the crops planted in the fields.
Wintering
As mentioned above, Goldfinger Potentilla is considered an unpretentious plant, it tolerates the cold season remarkably and does not need complicated care. In this case, it is necessary to adhere to the minimum agricultural technology when growing the variety.
Since the flower is naturally resistant to temperature fluctuations, it is not necessary to cover the plants for the winter. You can also leave the plant at the planting site without digging out and transferring the shrubs to a greenhouse or a warmed place. With the onset of winter, the shrubs are left in the open air without any changes. In this state, they are waiting for the arrival of spring.


Description
Two varieties are most popular: the Canadian goldenrod (photos are presented below) and ordinary. Let's take a closer look at the appearance of each of them.
Common goldenrod
It is a herbaceous plant, a perennial belonging to the Asteraceae family. Basically, he prefers to grow in clearings, in thickets of bushes, on forest edges, river banks, hilly slopes. In adulthood, the height of the golden feather reaches 0.8-1 m.
The root system is superficial, fleshy. There is a single erect stem, sometimes colored reddish. The top of the plant branches, although the stem itself is practically not covered with foliage. The latter has a regular arrangement, a serrated edge and a sharp and oblong-elliptical shape. What is noteworthy is that over its entire area the scabbard has insignificant pubescence.
At the end of summer, from July to September, racemose or panicle inflorescences are formed on the top of the stem, including a large number of bright yellow flowers. At the end of flowering, from August to October, a fruit is formed containing ribbed cylindrical seeds with a tuft.
Canadian goldenrod
This type of plant also belongs to the perennial forms of Asteraceae. It is found mainly along roads, in glades, swamps, forest edges, river and lake shores. As for the soil, moderately moist areas are a favorite place, but at the same time, the plant develops well in slightly moist and even swampy areas.
The root is short, pivotal. The stem is identical to the previous variety of goldenrod, only it is colored in tones from light to dark green, and the plant height reaches 1.4 m. There is also a slight pubescence. On the stem, the leaves of a linear-lanceolate shape are alternately located, and at the bottom they have serrated edges and a short petiole, and closer to the apex - sessile and entire.
Flowering occurs with the blooming of bright yellow small (3-5 mm) bisexual buds and the further formation of a cone-shaped panicle up to 20 cm. In the middle of the panicle, flowers are tubular, and pseudo-lingual at the edges. At the end of flowering, narrow-cylindrical fruits are formed in the form of a ribbed achene, with a white tuft.
Goldenrod hybrid
There is also such a type of plant, but it is less popular. Differs in compact size and beautiful foliage. It was this specimen that gave life to other varieties, such as goldtanne, spatgold, fearlencron, perkeo.
Description
Golden bunches of solidago can be seen on the territory of the Caucasus, it grows in the Far East, and in Western and Eastern Siberia, however, it is called differently everywhere. The representative of the Astrov family, translated as “healthy”, “strong”, is called both “ordinary” and “Daurian”. In nature, there are about 120 species of this plant, however, on the territory of Russia only more than 20 are cultivated. Goldenrod is a wonderful honey plant, bees love it very much. Healers and craftsmen use this useful plant as a coloring, medicinal and tannin substance. Particularly popular are Canadian goldenrod, Cloth of Gold and Goldking. It is thanks to this variety that new garden crops have appeared: blue-gray goldenrod, two-color, Kutlera, Shorty, etc. The first is a bush that reaches 2 meters in height, with flowers resembling golden yellow baskets.
It should be noted that goldenrod is a very useful flower from the point of view of medicine. Moreover, for various types of disease, all parts of the plant are used - both shoots and leaves, and roots. The most popular in this regard are the Canadian goldenrod and the golden rod, which grow in abundance in meadows and fields. The chemical composition of the plant includes acids, organic and phenol carboxylic acids, as well as their derivatives plus essential oils and diterpenes.
Common goldenrod is a rhizomatous plant, reaching a height of 60–120 cm. It has erect stems, branching in the upper part, possibly with pubescence. The leaves are ovoid or oval in shape, with a jagged edge.
In the upper part of the stem, the leaves are sessile, and in the lower part, petioled. The flowers of this plant form inflorescences of bright yellow color, which make up complex inflorescences - brushes or panicles. Most often, the inflorescences are long - up to 35-40 cm.
There are many other types of goldenrod. The most popular of these are the canadian goldenrod and hybrid goldenrod.
This plant is currently popular in folk medicine and is used to treat various diseases. Its components are even found in pharmaceuticals manufactured by the pharmaceutical industry.
The hybrid goldenrod is compact. His bushes are columnar in shape with a height of 60-150 cm.
Goldstrahl (golden inflorescences, in the form of a short panicle, height of bushes 70 cm),
Baby Gold (inflorescences are bright yellow, bushes 65 cm high),
Perkeo (inflorescences are light yellow, bushes 60 cm high),
Strahlenkrone (inflorescences are bright yellow, bushes height 80 cm).
Goldenrod is low in height, reaching only 40-60 cm. Its inflorescences are compact and bright yellow.
Goldenrod bluish-gray can be 30–120 cm high. It has little branching stems that form a spreading bush. Complex inflorescence - brush. This plant blooms for a long time, almost before the onset of winter.
Cutler's goldenrod is distinguished by a large number of leaves on the stems. It reaches a height of 30-50 cm. Inflorescences are golden-yellow in color.
The variety of varieties of goldenrod allows you to create flower beds of various heights, including multilevel ones, with a long flowering period.
How to plant?
To grow Fortune's euonymus, you need to be able to propagate it correctly. This procedure can be done in two ways:
- vegetative reproduction;
- use of seeds.
The second option is less convenient and does not guarantee the receipt of a new plant with all the characteristics of the mother, therefore gardeners prefer to use the vegetative method.
Another breeding option is the use of cuttings. To do this, the shoot is cut into pieces of about 10 cm and planted in specially prepared soil, after which the cuttings gradually germinate
In this case, it is important to use not yet lignified material, which is treated with a growth stimulator before planting in the substrate. In order for the growth of the cutting to be as fast as possible, it is better to place it in a peat-sand mixture, and then cover the entire container with a film
A month later, the root system will already be formed, and the cuttings must be planted in individual containers in which they will survive the winter, and only then they can be transplanted into open ground to a permanent place.
The simplest way of reproduction is to divide the bush, in which the plant is divided into several parts, the cuts are treated with charcoal and planted in new places. Planting euonymus is recommended in April or May, for which a trench or pit is dug, depending on how exactly the culture will grow. For the bush to take root, the hole must be almost twice as large as the root system. The bottom of the pit should be covered with drainage, the height of which will be up to 15 cm. The soil with which the roots will be covered should be prepared. The earth is mixed with sand and humus, in addition, peat and mineral composition are also introduced.
After planting, the plant is well watered, the soil around it is mulched with sawdust, leaves or peat. For the bushes, you need to find a sunny place, prepare supports for fastening and organize proper maintenance.

Goldenrod properties: harm and benefit
The healing properties of goldenrod

The healing properties of goldenrod are used in both traditional and informal medicine. The composition of such a flower includes organic acids, coumarins, essential oil, phenol carboxylic acids and their derivatives, flavonoids rutin and quercetin, saponins, glycosides, alkaloids and terpenoids. Thanks to this composition, the plant has a powerful anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant, diuretic, antispasmodic and wound healing effect.
In alternative medicine, this plant is used for improper exchange of uric acid in the body, scrofula, jaundice, cutaneous tuberculosis, indigestion and gallstone disease. It is also used in the treatment of stomatitis, bleeding gums, tonsillitis, gingivitis and to eliminate unpleasant odor from the oral cavity. This flower disinfects wounds and accelerates their healing, therefore it is used for edema, suppurating inflammation of the skin and fractures.
Means made on the basis of goldenrod are used in the treatment of oxalate and urate stones, prostatitis, urethritis and even impotence. Gynecologists recommend taking them to women suffering from cystitis or candidiasis.
The rhizome of such a plant is also used as a healing raw material. It can help in the treatment of skin diseases and burns, as well as to eliminate the effects of stomach ulcers and hepatitis. It is also used to increase sexual activity, to treat urological diseases, to eliminate intoxication of the body caused by food poisoning. Goldenrod root also helps treat diarrhea in pets.
Goldenrod honey also has medicinal properties. It has an antimicrobial effect, it is used to increase the body's immune forces, and also to normalize metabolic processes. Compresses are made from such honey, which can help with skin inflammations, and they also eliminate swelling well. It also helps great during the treatment of sinusitis, tonsillitis and rhinitis, as well as meningitis.
In pharmacy kiosks, an extract of goldenrod from fresh inflorescences is sold; it is recommended to take it to normalize the work and restore the urinary system.
295 Goldenrod - for the kidneys and more ...
Contraindications
The plant itself, as well as the products made on its basis, cannot be used during pregnancy and during breastfeeding, and it is also forbidden to use them for people suffering from glomerulonephritis.
Such funds, as well as goldenrod honey, should be used very carefully by people who are allergic to ragweed and insulin dependent. It is also forbidden to use them at high pressure and during exacerbation of kidney disease.
































