What kind of care you need to provide
After planting the seedling in the open ground, a multi-stage process of caring for the plant begins. One of the main activities is watering, which is carried out 2-3 times per season. If the summer is dry and hot, then you can increase the irrigation of the bush. For irrigation, use ordinary clean water.
Young seedlings need protection for the winter. To do this, you need to cover the ground near the trunk with foliage and geotextiles, and the thin trunk is tied to a peg installed next to it.
In the summer, the plant is fed. Mullein diluted in 10 liters of water and 10 g of superphosphate is sufficient for this purpose. It is possible to use Kemira Universal and other components in the second year of the growth of the bush.
With proper care, young bushes bloom very quickly.
Pruning is one of the main steps in plant care, allowing you to give the bush the desired shape. In spring-flowering varieties, after flowering, dry shoots and old branches are removed with sharp garden shears.
The bushes are pruned regularly, but carefully.
Summer-flowering bushes are pruned from the fourth year after planting. Make a radical haircut, removing the old lower and upper shoots. If you eliminate only the tops, then the new shoots will be thin and with small inflorescences.
It is important to remember that in the early years it is impossible to cut the bushes too much. Only dry, damaged branches are removed
Solving possible problems when growing Japanese spirea
Most varieties of Japanese spirea are unpretentious and do not require special care.
If there are problems with growing, then you should pay attention to the conditions in which the bush grows
Spirea in the process of growth and flowering is subject to the following problems:
- defeat by aphids, rosaceous miner, leafworm is possible from mid to late summer. In such cases, an inspection is carried out, the affected areas are identified and the plant is sprayed with solutions such as pyrimor - 0.1%, kronephos - 0.3%, etafos - 0.2%, hostaquik - 0.1%;
- to combat spider mites, celtan, fosalon, metaphos, phosphamide, acrex are used. It is best to start processing before three ticks appear;
- if branches and leaves begin to dry at the height of the season, then you need to make sure that there is sufficient watering and the quality of the soil. If necessary, add top dressing, water the plant.
These problems are the main ones, and it is possible to prevent the impact of pests with the help of regular irrigation of the bushes.
Plant propagation methods
If reproduction of Japanese spirea bushes is required, then different methods are used for this
In each case, it is important to use high-quality basic planting material, as well as prepare the soil on the site and in pots
Reproduction is carried out by the following methods:
- planting with seeds is not used for varieties such as Billard, Van Gutta, Bumalda. Other species can be propagated by seeds, and for this they are placed in early spring in containers with high-quality and loose soil. The hardened sprouts are planted in the soil on the site, but after pinching the main root. Young plants are thoroughly watered, and when it gets cold they are covered with a transparent plastic container;
Young shoots are covered from the cold
Cuttings are kept in water for several days.
Part of the branch is sprinkled with earth, and part is attached to a peg
All of these methods are simple to perform, but it is important to determine the planting site of the resulting bushes. When propagating by layering, the plants will be located next to each other, which should be taken into account if the landscape design of the site is important
Video: summer pruning of Japanese spirea bushes
The choice of variety, planting, reproduction and caring for Japanese spirea do not differ from the cultivation of many other ornamental and fruiting shrubs. Moreover, all stages of plant care are required, because it is then that the bushes will decorate the garden.
Diseases and pests of spirea
Spirea diseases
Spirea can be affected by gray rot and all sorts of spotting. This usually happens due to poor care or poor location. In the fight against fungal diseases, fungicidal preparations Fitosporin-M, Fundazol, Ditan-M45, colloidal sulfur, Bordeaux liquid or other drugs of a similar effect are used. Do not wait until the disease covers the entire bush, start processing at the first manifestations of the disease.
Spirea pests
Of the pests of spirea, the most dangerous are sucking - aphids and putin ticks, since they are carriers of incurable viral diseases. Both aphids and mites feed on the plant cell sap. Aphids form whole colonies on spirea leaves. It causes the greatest harm to the plant from June to August. At the beginning of the growing season, granulated Pirimor is used to control aphids by introducing it in an amount of 15 g / m² into the trunk circle to a depth of 2-5 cm. Further, the spirea is treated on the leaves with Actellik, Fozalon, Pirimor or Etaphos. The best results are obtained by alternating biological products and insecticides.
Spider mites can concentrate on one leaf of spirea in an amount of up to 300 pieces. In one season, this pest gives 8-10 generations. Leaves affected by ticks turn yellow ahead of time, dry up and fall off. The most obvious harm from a tick is in July-August, especially during a prolonged drought. In the fight against ticks, not insecticides are used, but acaricidal or insectoacaricidal preparations - Fozalon, Karbofos, Keltan, Phosphamide and the like, since these pests are not insects, but arachnids. Treatments begin as soon as signs of the presence of mites on the spire are found: small yellow spots on the underside of the leaves and the thinnest cobweb.
In addition to the described pests, the plant can be annoyed by rosaceous miners and rosaceous leafworms, the caterpillars of which damage the leaves of the spirea. The same drugs are used against these insects as against aphids.
In general, the fight against diseases and pests is carried out in an integrated manner, primarily performing agricultural techniques, creating the necessary conditions for the growth and development of spirea and providing it with good care. Preventive measures are also of great importance, skimping which can cost you more than buying pesticides: a plant affected by a viral disease has to be destroyed.
Appearance and biological features
Plants of this genus can grow both small (up to 15 cm) and tall (up to 2.5 m). The branches of the shrub are erect or creeping. The color ranges from light to dark brown. The roots are shallow, fibrous. During flowering, the spirea is covered with numerous small flowers in inflorescences of various shapes. The color of the petals is from snow-white to crimson. Spirea inflorescences can be located both along the entire shoot, and on its upper part or at the end of a branch. The plant propagates by seeds, cuttings, dividing the bush, layering.
Spirea does not need pruning. It is carried out exclusively for decorative purposes in order to give the bushes a more aesthetic appearance. The crown of a plant can be dense and dense or slightly "sparse", but it always looks attractive. The branches bloom right down to the ground, so there is no unsightly "bare feet" effect.
The shrub is hardy, adapts well to various climatic conditions, so it can be grown not only in the south or in the middle lane, but also in the northern regions. If the spirea freezes under severe frosts, then after pruning it completely recovers and blooms in the same year. For the normal development of the plant, a few hours a day of direct sun, top dressing, and good soil are enough. You don't need to cover it for the winter.

Spirea blooms on shoots that grow during the same year, so pruning does not spoil its appearance
Common pests of Spirea Bumald and the fight against them
Spirea Bumald has a high resistance to various pests, but "natural immunity" will not fully protect the shrub from such a problem
Therefore, it is important to study in detail the information regarding pests.
Quite often, aphids can be found on such shrubs. During the flowering periods, the most real invasions of pests are observed, which fill the entire surface of the leaves. You can cope with the problem with the help of drugs based on bitoxibacillin. Any of them is introduced into the soil in the spring, when planting a shrub. If aphid infestation has already occurred, then the foliage should be sprayed with a solution of bactericidal soap. If necessary, the procedure is repeated several times.
Pests destroy the foliage of the bush
Often, the leaves of the plant are damaged by small caterpillars - this usually happens in mid-spring, when the soil is just beginning to warm up. You can deal with them using the same methods as in the case of aphids. At the end of June, you can often see a pest on the foliage - a pink-colored mineral. After a few weeks, he burrows into the depths of the earth and crawls out only for the next season. Basically, such pests are burned only together with the affected leaves, which must first be removed.
Leaf damage by miners
The spider mite poses a great danger to the plant. Such pests hibernate under cover of foliage, and in the spring season they begin to activate and braid the leaves with their cobwebs. The peculiarity of ticks is that they multiply rapidly, they lay their eggs every day. From the invasion of spider mites, the shrub itself suffers greatly, and its decorative effect - it looks lifeless. To cope with such a problem, you should purchase carbophos spraying agents in advance.
In addition to various pests, fungal diseases are very dangerous for the shrub. You can cope with them by treating the plant with Fitosporin solution.
Planting and leaving
The best planting material is a container seedling that can be planted throughout the growing season. The plant needs fertile soil, it prefers sod and leafy soil with a neutral reaction or slightly acidic soil, in which it quickly develops and grows. Therefore, as a nutrient substrate for the hole, you can use simple garden soil, adding peat and sand to it. Sand compositions are enriched with a small amount of clay and mineral complex fertilizer "Aba".

The process of planting a pink spirea has its own characteristics, and they are associated with the time the shrub is placed in the open field. Plants planted in springtime can bloom during the hottest period, so planting a crop, preferably before the foliage is fully blooming. Saplings with damaged, dried out roots are unlikely to adapt and take root. Soaking dry roots in cold water for 24 hours can sometimes help.

In autumn, meadowsweet is planted, or rather, planted when dividing adult bushes. For this, specimens that bloom continuously for 3 seasons in a row are suitable. In general, late types of pink spirea should be planted in autumn. The planting process consists of several stages:
a planting pit is prepared in advance with a depth of 60-70 cm and is spacious enough for a branched root system;
the bottom of the hole is covered with drainage material - broken brick, gravel or expanded clay, its layer should be about 20 cm;
before planting, the roots are checked for rot, cleaned, shortened too long shoots;
over the expanded clay, the prepared fertile mixture is poured in the form of an elevation;
meadowsweet roots are lowered in the center onto a mound and straightened, then carefully fill the hole with earth, paying special attention to the voids;
the root collar is located in line with the soil surface;
the trunk circle is watered with a large amount of settled water (about 35 liters);
complete the planting with mulching - the ground near the roots is covered with peat by 7 cm.




Further development of the plant depends on caring for it. Watering the plant, the roots of which are at a shallow depth, requires special attention. On hot summer days, the shrub must be watered when the soil surface dries up, adult plants need watering twice in 30 days
Before irrigation, you must carefully loosen the soil, and after that, mulch to maintain moisture for a long time.

For pink spirea, periodic pruning is relevant, since the shrub is growing rapidly. In the spring, damaged shoots and frozen branch tips are cut off from the bush by 1/3. This procedure is combined with a decorative haircut, during which the crown is removed from thin branches and the symmetry of the aerial part is restored. In the fall, the branches are shortened to enhance flowering next year, once every 7 years, the shrub is completely thinned out for the purpose of rejuvenation.

The subtleties of growing an ornamental shrub
The right place for planting is the key to successful cultivation of meadowsweet. The duration and intensity of flowering depend on the amount of sunlight received, so the Wangutta spirea seedling should be planted in an area open to the sun.
Preparation of planting material and site
Quality planting material can be purchased at garden nurseries. In this case, the plant must be examined for the presence of mechanical damage to the shoots, traces of the presence of insects and signs of disease. The cut of the shoot should have a light green tint, the root shoot is colored milky white.
Dry and damaged roots are removed before planting. The root of the seedling is first dipped into a container with water, then into a clay mash with the addition of a biostimulant for root formation. You can use drugs "Kornevin", "Heteroauxin" or "Epin".
The site for planting is preliminarily cleared of weeds and other vegetation. Disinfection of the soil is carried out using a weak solution of potassium permanganate. If the soil is depleted, it is recommended to increase its fertility. For example, you can use a soil mixture of leaf and sod land, peat and humus. All components are taken in equal amounts, wood ash (no more than 1 kg) and superphosphates (20-30 g) are added to them.
Planting recommendations
Spirea Wangutta can be planted in open ground in spring and autumn. According to experienced gardeners, an autumn planting is better, since the seedling manages to get stronger during the winter.
The holes for planting seedlings are prepared in advance. The bottom is laid out with drainage materials, then a nutritious soil mixture is laid. When planting, make sure that there are no damages and creases of the root processes.
The distances between the holes depend on the chosen spirea planting scheme. For example, when forming a hedge, we recommend that you adhere to an interval of 1-1.5 m.
Author's advice
 General rules for planting a Wangutta spirea seedling
General rules for planting a Wangutta spirea seedling
How to propagate
The seed method of reproduction of the Wangutta spirea is extremely rare. Most often, the culture is propagated by dividing the bush or by grafting.
At the end of the flowering stage, cuttings are cut. The average length of the cutting is 15 cm. It should have several leaves and healthy buds. The cuttings are buried in a nutrient substrate, covered with a glass cover and placed in a greenhouse. Periodically, the plants are ventilated and irrigated. Planting cuttings in the ground is carried out next spring.
The propagation algorithm by dividing a bush is very simple. When the shrub has faded, it must be carefully dug up. The root system is cleaned of clods of earth and divided into several equal parts. In this case, the root is examined for traces of rot and other damage. Injured and rotten roots must be cut to living tissue.
Watering and feeding
Spirea Wangutta is highly drought-resistant. The plant needs frequent and abundant watering only during hot and dry periods.
Please note that the topsoil must be dry. With an excess of moisture in the soil, the bush loses its decorative effect
Unlike other flowering crops, meadowsweet does not require frequent feeding. The deciduous shrub is fed once per season. Mineral complex compounds or superphosphate are introduced into the pre-moistened soil.
Pruning after flowering
The next step in leaving is pruning the shrub. The formation of the crown is carried out at the end of flowering. The plant can be shaped like a ball, rectangle, triangle and other options.
Sanitary pruning is done in the fall. At this stage, dry branches and shoots damaged by bad weather or insects are removed.
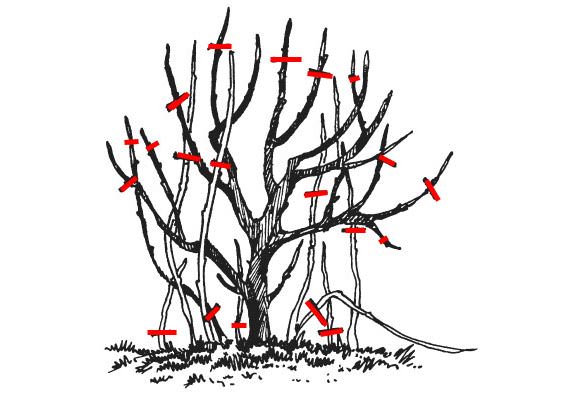 Scheme of rejuvenating pruning of an ornamental shrub
Scheme of rejuvenating pruning of an ornamental shrub
Do I need to shelter for the winter
Spirea Vangutta is a winter-hardy ornamental shrub. There are cases when meadowsweet withstood a drop in air temperature to -40 ° C. It can be concluded that Vangutta is suitable for growing in the northern and central regions of Russia.


