Preparing roses for winter
The flowers of roses are varied and delightful. But from the buds grown in the gardens there is no riot of colors and splendor without human assistance. In pursuit of the beauty and health of roses, gardeners pull out dead and unhealthy branches, form young shoots, a crown and numerous flowers. Therefore, pruning for the winter is an indispensable matter before covering a plant for wintering.
Autumn cutting is carried out in order to increase frost resistance, supply the shoots with light and consolidate the immunity of plants to diseases. Unripe processes rot under the shelter. Therefore, in the last days of October, they pull out unripe, dried, damaged, thickening shoots of the rose bush and cut the remaining stems under the height of the shelter. The bushes are not cut until the night frosts, since pruning stimulates the growth of the shoots. Frost-resistant hybrids of wrinkled roses winter without shelter and these bushes are not cut off for the winter.
Pruning rules
To cut rose bushes for the winter correctly, adhere to the following rules:
- Cut out unhealthy branches, flowers and foliage. Three-year-old shoots are considered old: they have many side shoots, and the bark is dry. Three-year-olds no longer grow and must be removed. The leaves are certainly removed before winter, since under the shelter the crown mates and gives rise to the disease of the flower entirely. To prevent fungal diseases, before winter, the flower is treated with a composition with Bordeaux liquid.
- When cutting, plants leave five strong shoots.
- Unripe shoots are cut out, because after the flower is closed for the winter, the shoots begin to mate.
- Cut branches are removed from under the bush and burned, since cuttings are carriers of diseases.
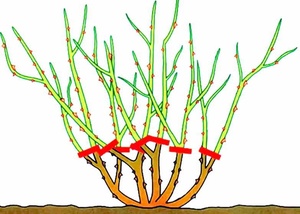
The buds of plant growth are placed in the axils of the leaves, the higher the location, the faster these buds grow. At the bottom are dormant buds that pass a couple of stages before germination. Cut the stem obliquely to the outer bud. The bud looks outward of the bush, and not inward, and the sprout will grow from the side, the bush will increase in breadth. The distance between the kidney and the cut is half a centimeter.
Plants are trimmed to the white core of the shoots. It happens that a pair of processes grow from one kidney, in this case, a healthy sprout is preserved. When pruning roses, they form a bush with single shoots. They do not allow the plant to thicken, since it needs sun and air to form.
Cutting time
Park and ground cover varieties are not cut off, climbing ones are cut off a little. Pruning strengthens the plant, raises cold resistance, improves the air exchange of the crown. Pruning of roses in autumn is performed before hiding flowers for wintering in the last days of October or in the first days of November. Prepare tools - garden tools must be sharpened and sterile.
Both mature and barely planted bushes are cut in the fall. First, cut out dry, unhealthy, old and frail stems, cut flowers and buds, remove the crown to the last leaf. Retain 3-5 strong developed processes, equidistant from each other. Unripe shoots are removed, because under cover these shoots mate and destroy the entire rose bush
It is important to know to which length the shoots should be cut, taking into account the specifics of the species:
- Polyanthus, hybrid tea and floribunda are cut to four or five lower developed buds.
- Cascading standard roses are shortened in the first season, keeping shoots 15 centimeters long, and in subsequent years, faded shoots are cut off, and young shoots are cut.
- Grandiflora and remontant varieties are cut keeping 5 buds each.
- Old English and shrub varieties are reduced by 3/4 or 2/3 the length of the shoots.
- Park varieties, frost-resistant, and these bushes are subjected to sanitary pruning, old, damaged and frail branches are removed, and young healthy shoots are slightly reduced.
After pruning, the leaves are removed, a glove is pulled on and a hand is made to move along the shoots from bottom to top, so as not to damage the buds.
Step-by-step planting procedure for beginners
An experienced florist can easily plant a rose in the ground with his eyes closed. But it will be useful for a beginner to give some advice on this procedure.
Choosing the right place
In general, the rose is a rather picky plant. Therefore, you need to choose a site for planting it responsibly. It is advisable to avoid the lowlands - cold snow water accumulates here in the spring, which can chill the roots. Roses also do not tolerate cold winds, so it is best to plant them under the protection of some object - for example, on the south side of a house, garage, shed or dense hedge.
Attention! The optimum temperature for germinating seedlings is from +18 to +25 degrees Celsius. The ideal place is a slightly shaded area that is well lit only in the morning.
Otherwise, on a hot summer day, a bush rose can get sunburn.
The ideal spot is a slightly shaded area that is only well lit in the morning. Otherwise, on a hot summer day, a bush rose can get sunburn.
Soil preparation
Everything is quite simple and standard here - if the soil is depleted, then it will not be superfluous to apply a little mineral fertilizers. When digging a hole, it is advisable to get rid of large stones, old roots and other obstacles.
If the plants on the site suffer from high humidity, then you should take care of drainage - drainage of water so that the roots of the rose do not rot.
Planting a seedling

Planting a rose seedling in open ground
Too large a pit for planting hybrid and other roses is not needed - a size of 40 × 40 cm is enough with a depth of 30-40 cm.It is advisable to cover the bottom with a layer of drainage - expanded clay or pebbles are suitable - about 10 cm high.
The rest of the volume must be covered with a mixture of compost and chernozem - on such a substrate, the rose will grow rapidly and bloom profusely.
The planting procedure itself is very simple. It is necessary to dig a suitable hole so that the entire root system is located without deforming. The seedling is lowered into it and, holding it with one hand, you need to fill up the earth, keeping the roots in a straightened state. After that, the earth is compacted a little. And that's all, the landing can be considered complete.
Watering the seedling after planting
Immediately after planting, it is advisable to water the seedling abundantly - this helps to strengthen it in the ground. In addition, if the yard is especially hot in May, then it will not be superfluous to shade the bush a little so that it does not dry out before the root system takes root in a new place.
Top dressing of a young bush
With feeding, everything is quite simple. Immediately after planting, you can add some phosphorus fertilizers dissolved in water - thanks to this, the root system will develop more actively.
After a few weeks, when the leaves appear, you can also use nitrogen fertilization to increase the volume of the green mass.
Attention! Nitrogen fertilizers cannot be used in the second half of summer, so that the plant begins to prepare for wintering. Finally, in early to mid-September (in the northern regions and in Siberia at the end of summer), fertilize again with phosphorus fertilizers so that the rose can easily survive the winter
Finally, in early to mid-September (in the northern regions and in Siberia at the end of summer), fertilize again with phosphorus fertilizers so that the rose can easily survive the winter.
Care and fertilization
 It is not for nothing that climbing roses are considered one of the most capricious plants - growing and caring for them really requires a lot of attention. Therefore, from the moment of planting, you need to carefully monitor and care for the plant in order to ensure the normal development of the bush.
It is not for nothing that climbing roses are considered one of the most capricious plants - growing and caring for them really requires a lot of attention. Therefore, from the moment of planting, you need to carefully monitor and care for the plant in order to ensure the normal development of the bush.
Immediately after planting, if the plant was planted in spring, it must be covered with a transparent film, but ventilated every day, leaving it open for at least an hour. The film is only needed while frost is possible. The land around the bush must be constantly loosened and hilled to retain moisture, and also weeded so that the weed does not interfere with growth.
Anyone who decides to decorate their garden with them will have to learn how to properly fertilize and prune roses. Every year, after the winter insulation is removed from the bush, it is necessary to cut off the old, dried up shoots. For beauty, you can prune the bush as you like, the main thing is not to touch the main vines. A few useful rules to help you properly prune a bush:
- Be sure to cut with a pruner or sharp knife. You can pre-disinfect the blades with manganese.
- The cut should be 1 cm higher than the upper bud (unless the goal is to cut off an unnecessary shoot).
- You need to cut the bushes in sunny weather, they must be dry.
- The cut must be done at an acute angle. This is necessary so that the water can roll off without lingering on the cut.
- It is imperative to process the cuts with garden varnish or Novikov's liquid.
Such plants do not require frequent watering, so it is enough to water them with 15 liters of water once a week. It is possible more often, but then it is necessary to use smaller volumes of water for each watering, for example, when watering twice a week - no more than 7.5 liters at a time. Of course, watering must be done with the correction for the weather: in dry summers, you can use 20 liters of water.
Fertilizing climbing roses also requires attention. In different periods of a plant's life, it should be fertilized in different ways, but the first three years are especially important for normal growth.
In the first year, the plants should not be fertilized throughout the summer, since during planting the land was already fertilized with manure. Before preparing for winter, perhaps in the middle of autumn, it is enough to treat the soil with potash fertilizers so that the plant can withstand frosts more easily.
In the second year, it is possible (and even necessary) to use both mineral and organic fertilizers, and it is necessary to alternate them, enriching the land in turn with different substances.
Preparing for winter
 Roses should be covered when the air temperature begins to drop to -5 ° C, but not before. The fact is that if you cover the bush at positive temperatures, debate may begin, or the bush will continue to grow. Before you close it with insulation, you need to cut off all dried shoots, then remove the vines from the support and put them on a litter. You cannot put vines on bare ground.
Roses should be covered when the air temperature begins to drop to -5 ° C, but not before. The fact is that if you cover the bush at positive temperatures, debate may begin, or the bush will continue to grow. Before you close it with insulation, you need to cut off all dried shoots, then remove the vines from the support and put them on a litter. You cannot put vines on bare ground.
When the extra shoots are cut off and the vines are folded on a litter, they must be tied up and covered with any waterproof insulation, be it roofing material, polyethylene or any other material that does not allow moisture to pass through. The base of the bush must be covered with earth to protect it from frost. All this should be done in dry weather. Shrubs, vines and shoots must be dry.
Supports and fixtures
There are many ways to shape your bush. Various arches, nets, pillars and cones for almost every taste
There are no rules or restrictions here, so the gardener has complete freedom of action in this matter, however, when choosing a support, it is important to pay attention to its following qualities:
- Compactness. The task of any support or suspension is not only to give the bush the correct shape, but also to compactly place the plant on the site. If the support does not fulfill this purpose, other options can be considered.
- The size. Each variety has a different length of the vine, this must be taken into account when buying or making a support, otherwise it may turn out that most of the arch or support pillar is bare, and the shoots barely reach its middle.
- Reliability. Climbing roses at their peak of flowering can weigh very, very decently, so the support should easily hold the plants and have a margin of safety in case of abundant growth.
Any support or structure should harmoniously fit into the overall look of the garden, without violating the integrity of the design.
Rambler (small-flowered roses)
Plants in this group form long, thin, arc-like shoots, 3 to 15 meters long. The formation of flowers occurs on the shoots of the last year, therefore, it is necessary to especially carefully cover the roses for the winter.
The flowers are small, up to 3-4 cm, of various colors. Usually, rambler roses have little or no aroma, but everything is compensated by abundant flowering.
Almost all varieties of the group bloom once, forming flowers along the entire length of the stems. Rambler are appreciated for their unpretentiousness, frost resistance, ease of organizing wintering of plants.
Super Excelsa
A variety from the rambler group, it has a long flowering. The bush forms shoots up to 3-3.5 meters, the width of the bush is up to 2 meters. The formation of flowers proceeds along the entire length of the stems, therefore, the leaves of the plant are often not visible behind the number of flowers.
On one shoot, from 3 to 10 flowers are formed. The roses reach 4 cm in diameter, the color is crimson-red.
Florists of the Moscow region note the high resistance of Super Excelsa to black spot, powdery mildew.
Snowgoose
Incredibly beautiful, as if covered with snow, the blossoming Snow Goose rose bush attracts everyone's attention. Small dense flowers are collected in large clusters, each up to 4 cm in diameter
In a brush - up to 20 flowers. The color is pure white.
The shoots of the bush grow up to three meters in length. The plant is vigorous, branched, with shiny small dark green foliage. There are few thorns.
The variety is used for vertical design of supports, suitable as a ground cover rose. Resistance to infections, freezing temperatures is high. In the middle lane, Snow Goose is sheltered for the winter.
Rambling Rector
A popular variety from the rambler group, it was first introduced in the nursery in Newry (Ireland). On the vigorous shoots of the plant, a lot of semi-double small creamy-white roses are formed. The diameter of the flowers is up to 3-4 cm. The aroma is weak, with a musky note.
Scourges in the climatic conditions of central Russia grow up to 3.5 meters, in the south - up to 5 meters. The leaves are small, pale green, beautifully shaped.
Flowers are collected in inflorescences of 15-50 pieces. In the sun, the petals quickly fade, acquiring a pure white tint. The variety can be cut well, often grown as a scrub (shrub).
Bobbie james
Surprises with lush flowering and strong pleasant aroma. Belongs to the group of ramblers with white flowers, forms many inflorescences-brushes. One brush contains 6-15 flowers.
The bush is vigorous, a large enough area is required for growing. Bobbie James blooms once, usually from mid-June to late July or early August, suitable for arbors, arches, pergolas, building walls, fences.
Advantages of the variety:
- frost resistance;
- high immunity to diseases;
- easy care;
- unpretentiousness to nutrition and soil types;
- resistance of flowers to fading and precipitation.
The Bobbie James variety from English breeders has been successfully grown by flower growers in the Moscow region for many years.
Super dorothy
Of the re-flowering ramblers, the favorite of mid-lane growers is the Super Dorothy variety. Bred in Germany, it is characterized by increased winter hardiness, resistance to infections.
Sprawling bush with thin thornless shoots up to 3-4 meters long. Flowers are small, pompom type, collected in brushes of 20-40 pieces. The color is bright crimson.
Note! In this variety, the flowers fade in the sun, so it is advisable to provide for a light partial shade.
Flowering begins late, but continues until the coldest days. The shoots are soft, pliable, so Super Dorothy is suitable for decorating any supports and structures. Due to its increased resistance to subzero temperatures, the variety winters well in the conditions of the Moscow region; in mild winters, shelter is not required.
Care features
In order for the climbing rose "Casino" to be healthy and delight its owners with regular and abundant flowering, you should take care of it, guided by the recommendations listed below.
Watering
Moderate watering is optimal for roses of the described variety, while they do not tolerate excess moisture. In the absence of rain, a young plant needs about 20 liters of water once a week, and adults - 1.5 times more. If precipitation occurs, the owner of the "Casino" rose should take into account the degree of their intensity.
Top dressing
One of the most important requirements, the observance of which contributes to the rapid growth of the climbing rose in question, is the timely and regular application of fertilizers. In spring and early summer, the plant needs to be fed with organic matter mixed with potassium and phosphorus supplements. At the same time, spraying with preparations containing manganese, boron, copper and other trace elements should be carried out.
Garter
Tying up the bush should be done from the moment it is planted. To do this, you need to install the support grid at a short distance from the wall or drive into the last hooks to pull the wire.
The main shoots of the rose must be placed horizontally or in a fan, vertical orientation is desirable for the lateral ones. The plant is tied to a support using a strong wire with a soft polymer coating to avoid damage to the stems.
Pruning
The procedure in question is carried out in the spring, during the formation of buds in the lower part of the bush. It involves the removal of shoots that have not survived the winter. It is advisable to cut the casino rose in summer, as getting rid of wilted flowers stimulates re-flowering. If the bush has grown too much, its excess shoots must be removed in the fall.
Upon completion of the described procedure, all sections should be thoroughly powdered with crushed charcoal or activated carbon. This action accelerates the healing of wounds, drying them and preventing the development of pathogenic microflora.
Shelter for the winter
Given the negative effect of severe frost on the plants of the presented variety, with the onset of persistent cold weather, they must be carefully covered. To solve this problem, spruce branches are ideal - branches of coniferous trees, which are placed above the rose removed from the support and between its shoots.
Above, you need to install a wire structure, elevated above the covered plant by about ¼ meter. Such a frame should be covered with polyethylene and a material with good thermal insulation properties, leaving several ventilation holes.
Diseases and pests
Despite the high resistance of the "Casino" rose to pathogenic microflora and pests, in some cases it may suffer from their harmful activity (as a rule, due to violation of agricultural practices). The variety in question is most often worried about two diseases.
- Powdery mildew. The cause of the misfortune is fungal microflora, the development of which leads to the appearance of a whitish-gray plaque on the stems and leaves. To get rid of it, it is necessary to remove all affected areas of the plant, and treat the rest with a systemic fungicide.
- Bacterial cancer. A characteristic sign of the disease is the appearance of large growths on the roots and neck. Counteracting the disease involves the careful removal of pathological formations and the treatment of problem areas with a solution of copper sulfate.
Thus, the climbing rose "Casino" can be safely recommended to every gardener who is in search of a spectacular and unpretentious decoration of his site. This variety has met the expectations of the overwhelming majority of owners from the moment of its inception to the present day.
More information about the climbing rose "Casino" is waiting for you in the video below.
Features of caring for ground cover roses
Compliance with the basic rules of care allows you to get healthy and beautiful flowers.
Watering rules and humidity
Roses prefer moderate watering once a week. To avoid sunburn, the procedure is performed in the morning, directing the stream under the bushes.
Important! In the fall, watering is stopped to allow the flowers to enter a dormant state.
Top dressing and soil quality
Loamy soils of weak acidity (pH 5.5-6.5) are suitable for roses. Feeding begins 14 days after the appearance of the first leaves (nitrogen fertilizers and organic matter are used). After a month, the procedure is repeated. In autumn, roses are fed with phosphorus-potassium supplements.
Pruning and replanting
This species does not need regular pruning. Florists recommend slightly pruning the shoots in the first year to make the bushes thicker, as well as shorten the shoots to 30 cm every 5 years to rejuvenate the bushes.
In the process of caring for a creeping rose, you should cut off dead and diseased stems with leaves, and also remove dried buds.

Pruning is carried out twice a year - in autumn and spring.
The parts of the shoots remaining after pruning are used for cuttings. To do this, choose a trim of a creeping rose with five leaves, the stalk is placed for 1 day in water with potassium permanganate, and then in the soil under a hood. After rooting, it is transplanted into a pot or open ground.
Transplanting flowers is carried out for reproduction purposes, as well as when moving to a new place.
To propagate a creeping rose, in the spring the shoot is bent to the ground and fixed in the place of the deepening with nutritious soil. One of the buds on the cut is placed in this hole for subsequent rooting. In the fall, the rooted seedling is separated from the mother bush and transplanted.
Note! Florists advise to cut tall bushes with strong stems, and creeping roses, which prefer to creep, propagate by layering. When transplanting an adult flower, the bush is dug up with an earthen lump (the more lump, the better)
The process facilitates pre-watering. For convenience, the shoots are tied with a rope. After digging, the bush is placed on cloth or other material to move to a new location.
When transplanting an adult flower, the bush is dug out with an earthen lump (the more lump, the better). The process facilitates pre-watering. For convenience, the shoots are tied with a rope. After digging, the bush is placed on a cloth or other material to move to a new location.
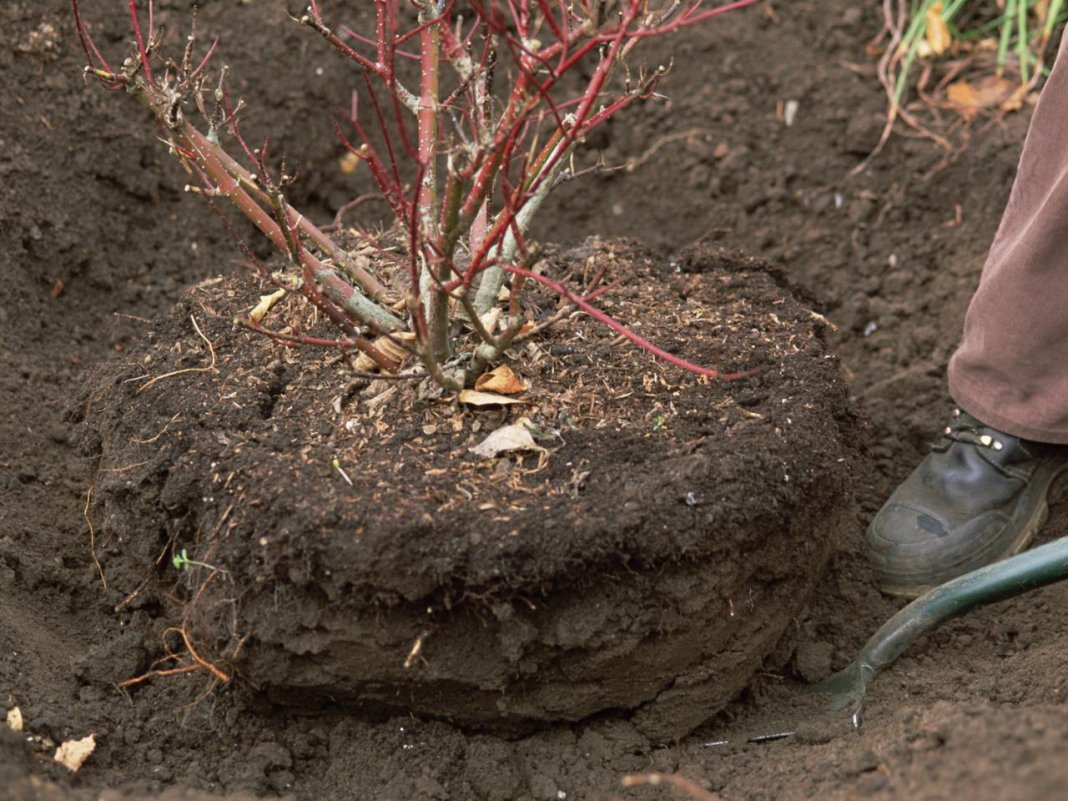

The transplant is carried out not only for reproduction
Features of wintering a flower
Many varieties of the creeping rose survive the winter without shelter in the south of the country and in central Russia. However, if a thermophilic rose is grown, additional protection is provided. The same goes for flowers in the northern regions.
As a covering material, spruce branches and dry leaves are used, which do not lend themselves well to decay (oak, fern, etc.). Before covering, the bushes are huddled.
Recently, an air-dry shelter is gaining popularity - the creation of a frame around flowers from metal arcs or boards, on which a special material is pulled (spunbond, geotextile, etc.). They are also simply wrapped in bushes for insulation.
Important! It is not recommended to use polyethylene and plastic for shelter. Lack of air circulation can lead to damp bushes and rot

Air dry shelter
Where to get seedlings
The next important question to be answered is where to get suitable seedlings. In fact, there are only two options here, and both are worth talking about.
Buying ready-made seedlings, how to choose the right one

Cuttings of roses
The most common option is buying. Looking into a store or a rose garden, you can almost always see a rich assortment of plants. There will certainly be climbing and tree-like, frost-resistant and delicate varieties. And the cost for most varieties is not too high. It remains only to decide which of the plants on sale is worthy of decorating a rose lover's garden.
Also, do not forget about the health of the plant. The seedling must meet the following requirements:
- No rot and dry areas.
- Developed root system.
- Age 2-3 years old.
- Healthy, green stems free from blemishes or damage.
If you choose the right plant, then caring for roses in the spring in the country in an open area will not cause unnecessary problems.
Growing seedlings yourself
However, some gardeners are interested in growing seedlings with their own hands, and not buying in a store.
The easiest way to get a seedling is cuttings. True, this will take a couple of years, but you can save money and, on the contrary, earn a certain amount if you sell them successfully.
Important! For pruning, use only a good pruner, which will carefully cut the branch without causing unnecessary damage. The procedure is pretty simple:
The procedure is pretty simple:
- Select a healthy, sturdy branch and cut off a stalk about 20-25 cm long.
- Immerse it in water with a dissolved root growth stimulant.
- After the first roots appear (2-3 cm is enough), transplant into a pot and keep in it for a year or two until a strong root system appears.
After that, the seedling can be planted in open ground, sold or donated to friends.
How to plant climbing roses
Pruning and planting roses
In order for climbing roses to take root well, take root and bloom profusely, they need to be planted at a certain time. Optimal planting dates:
- for central Russia and the Moscow region - spring (late April - late May) or autumn (early September - mid-October);
- for the southern regions - spring (early April - early May) or autumn (early September - mid November);
- for Siberia and the Urals - late spring - early summer.
Climbing shrub seedlings are sold with open and closed root systems. The latter are in containers, planted in the ground along with a lump of earth. Checking their roots and soil for infection will not work. If you bought seedlings from an unverified seller, take the following steps to preserve them before planting:
- Water the soil in the pot with Aktara insecticide (4 g / 5 l of water).
- Spray the above-ground part with Ordan fungicide (5 g / 1 l of water).
- Place the containers in a room with a temperature not exceeding +3 ° C.
Seedlings with an open root system are planted in a permanent place no earlier than the next day after purchase. Do not leave them in the air (wrapped in polyethylene or open). How to preserve and prepare open-rooted seedlings for planting:
- Soak the plant in water overnight.
- Take out, cut off healthy roots up to 30 cm, damaged, diseased and weak - remove completely, rotten - shorten to a healthy place.
- Cut the aerial part to 30 cm, remove broken, weak shoots.
- Cut off the leaves and buds below the scion.
- Sprinkle the cut sites with crushed activated carbon.
- Disinfect the roots by dipping in a 3% solution of copper sulfate (30 g of substance per liter of water).
- Treat the root system with a growth stimulant (Kornevin, Etamon, Phosphobacterin).
Seat selection
Climbing roses are best grown on the south or southwest side. Ideal location:
- Well lit, even, slightly sloping and slightly shaded in the afternoon.
- Ventilated but protected from drafts and strong winds.
- Dry. Damp, waterlogged soil will cause root rot.
- Near the wall, arch, fence. So that the roots and the aboveground part have enough room for growth, plant the rose at a distance of 50–100 cm from the support (depending on the variety) and half a meter from other plants.
Soil preparation
The area for growing climbing roses is prepared 4-6 weeks, ideally half a year before planting. It is recommended to plant shrubs in an area with drained fertile soil or loose loam. How to prepare the soil:
- Dig the ground to a depth of 50–70 cm, remove the roots of the weeds.
- To increase fertility, add humus, peat compost or humus (10–20 kg / 1 m²) to the soil.
- If the soil is clayey, dilute it with a mixture of coarse sand, humus, compost, turf and leafy soil (6: 1: 1: 1: 1). Mix the sandy soil with clay, turf, humus, compost (2: 2: 1: 1).
- If the soil acidity level is high, add dolomite flour (0.5 kg / 1 m² of soil) to the planting soil mixture.
- On chalky soils and areas where other types and names of roses used to grow, remove 50–70 cm of the top layer of the earth or dig a hole (60 × 60 × 45 cm). Replace the soil with a soil mixture of an equal amount of turf, peat with the addition of 500 g of bone meal for every 2 buckets of the composition.
Landing
Planting a rose
How to plant a climbing rose:
- Dig a hole 50 × 50 cm in size, 60–65 cm deep, at a distance of 2–2.5 m from the same rose bushes, half a meter from the wall (support) and other plants.
- Pour some soil mixture at the bottom, form a mound.
- Spread the roots of the seedling, place in the hole so that they do not curl up. If you plant a bush near a support or wall, place the root system in the opposite direction from the structure.
- If the seedling has a closed root system, remove it from the container and plant it along with the existing clod of soil.
- Fill the hole with soil 2/3, tamp.
- Pour in 0.5 buckets of water to remove the voids.
- Fill the remaining space with soil mixture, deepening the grafting site by 10-12 cm. Tamp it a little, pour in another 0.5 buckets of water.
- When the liquid is absorbed, add the planting mixture. Spud the seedling, covering the stem 20 cm in the spring and 25-30 cm in the fall.
- Mulch the tree trunk circle with needles.
- For better rooting, cover the seedling with foil, creating a greenhouse effect. Lift the plastic to ventilate every day.
- After a week, remove the shelter, tie the branches to the support (if the view requires it).


