Pruning
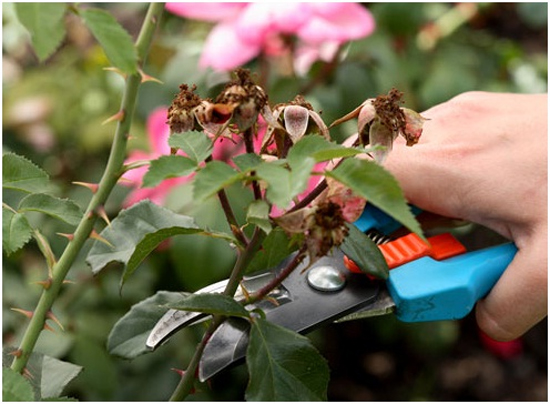

Rose pruning process
Purchased seedlings, as a rule, are grafted plants, the growth and resistance of which is ensured by a viable and hardy rose hip. This powerful base often stubbornly produces its own shoots that must be monitored and cut mercilessly throughout the growing season.
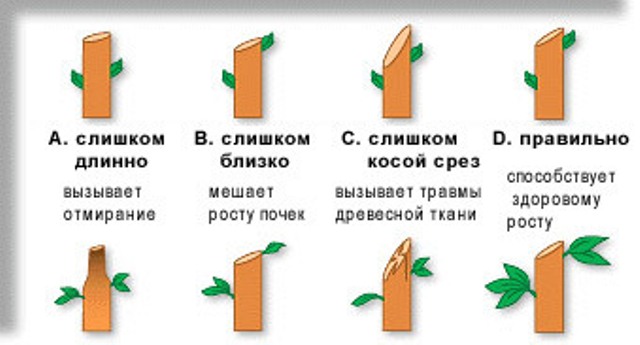
Correct cut of roses
Pruning your own stems of varietal roses can be of three degrees:
- Up to four buds from the base of the shoot. It is used for spring seedlings, rejuvenation of old plants and as a last shock therapy for underdeveloped bushes.
- Up to seven buds from the base. By shortening the stems in this way, you get strong young growth and abundant flowering of the bush.
- Affecting only the ends of the stems. This method is used as a light formative to stimulate flowering.

How to cut roses correctly
In addition, pruning roses has its own seasonal specifics:
- In the spring, after being freed from the winter shelter, weak, dead, thickening shoots are removed.
- In the summer, sparing pruning is carried out, removing wilted flowers and inflorescences to the first viable bud.
- In the fall, in the middle lane, the shoots are shortened to the height of the winter shelter. In warmer climates, serious fall pruning is not done.
When and how to plant roses
It is advisable to purchase seedlings in September - October. In the spring there is a risk to buy last year's planting material.
To protect new plantings from diseases, it is not recommended to plant them in the place of previous roses.
Planting technology for rose bushes:

Place the seedling in water before planting.

Dig a planting hole 50 × 50 cm in size and 10 cm deeper than the size of the roots, together with an earthen lump

Loosen the ground at the bottom of the pit
- Mix the excavated soil with the compost at a 3: 1 ratio. Add wood ash.
- Pour one bucket of heteroauxin solution into each well. Dilute the drug according to the instructions.

Place the seedling in the hole and cover with fertilized soil, holding it. The main thing is that all the roots are straightened.

Make a watering groove around the trunk

Do the next watering two days after planting.
The optimal distance between varieties of roses is 1-2 m.

How to cross-stitch correctly (for beginners): a step-by-step description of the stages, reading diagrams, and also what materials are needed (Photo & Video)
Diseases and pests
The cultivation of roses is also accompanied by the appearance of various diseases:
Powdery mildew affects the plant mainly in summer and can appear outdoors and in the greenhouse. On the shoots, leaves, a white bloom appears, which gradually turns brown. The shrub begins to disappear, dry out
To eliminate it, it is important to carry out a special treatment with fungicides.
The appearance of rust from the spores of the fungus on the leaves and shoots of the plant.
Black spots may appear on rose leaves in late August.
Pink rust (orange pads). The disease develops rapidly and requires treatment with insecticidal substances.
Rust with asterisks often appears on rose leaves in summer.
With the further development of the disease and the absence of preventive measures, the plant turns yellow and disappears.

Rust on foliage
Pests that harm park roses: rose borer, aphid, broomstick, rose cicada, leafworm, spider mite, click beetles. Methods of dealing with them are timely feeding, proper watering, regular loosening, mulching the soil. If the disease is already progressing, then treatment with insecticides for a specific purpose is required.
If you provide the park roses with proper care, they will delight the gardener with a lush, bright flowering, a wonderful aroma throughout the warm season. To do this, you need to water them generously, instantly respond to the appearance of signs of disease, and prune.
Why on the site, and not at home?
Potted roses are bad at home. They suffer from pests (spider mites), dry air and other problems. It is difficult for an amateur flower grower to choose a suitable irrigation regime, to provide a difference between night and daytime air temperatures, not to overdose fertilizers, etc. An exhausted potted rose loses its dried leaves and then dies. Only a few amateur flower growers successfully grow this garden plant in their rooms.

A compromise option is planting a potted rose in a container, which is transferred to the basement for the winter, on a warmed loggia, or placed on a windowsill. This is also a troublesome task.
A potted rose transplanted into the open ground of a site feels completely different. It comes to life, endures heat and drought, blooms for a long time even in a cool rainy summer.
I transfer the whole bush from the pot, without dividing it into parts, so as not to ruin the recently rooted cuttings. They (thanks to accelerated technologies) have already begun flowering. The rose will develop a good root system over time. And the pruner will relieve it of thickening and remove weak shoots.
Transplanting potted roses in the fall often leads to the death of the plant. The rose purchased at this time is safer to hold for some time on the windowsill, without removing the transparent packaging for a week. Moisten the soil only through the pallet. You can gently (without damaging the roots) transfer the bush into a larger pot by adding fresh soil. We'll have to take care of the rose as a rather complex indoor plant. Treat for spider mites, shorten the shoots, and after a while put them out for the winter in a suitable place, preventing the soil from drying out. Experienced indoor rose lovers say that they need to be watered with almost hot water through a sieve of a watering can or a shower.
In May, a potted rose can already be transplanted into a flower garden. With a temporary cold snap, it is better to cover it with light lutrasil. Phytohormones, for example, Epin, will help cope with stress. I wrote about some features of its use in the article "Speckled leaves, drying out of branches and other diseases of edible honeysuckle."
Calendar of works in the rose garden

Beautiful roses require constant care
By seasons, rose care is distributed as follows:
| Season | Actions |
|---|---|
| Spring | Transplantation, preventive spraying with Bordeaux liquid, sanitary and stimulating pruning, complex mineral dressing. |
| Summer | Watering, weeding, mineral and organic fertilizing, loosening, removal of wilted inflorescences, prevention of diseases, destruction of pests. |
| Autumn | Loosening, weeding, preventive "Bordeaux" spraying, pre-winter pruning, hilling. |
| Winter | Protecting bushes from rodents, covering shelters with snow. |
Timely, complete care will ensure the intensive growth and lush bloom of garden roses of the most exquisite varieties.
Fertilizer for roses in summer
To set buds and extend the flowering period, roses need phosphorus and potassium. Also, magnesium has a positive effect on the appearance of prickly beauties, which affects color, iron, as a protection against chlorosis, manganese and boron. But nitrogen should be added to the soil only in the spring, because it postpones the flowering process, promotes foliage growth and weakens the bushes in the face of diseases.
Fertilizers can be applied in liquid or dry form. Whichever method you choose, first pour abundant soil around the bush and fertilize not the center of the rose, but the soil at a distance of 10-15 cm from the stems.
Throughout the summer (once a month) roses can be fed with a solution of 10 g of superphosphate and potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water. In July, 500 g of chicken manure and 10 g of nitrophoska, as well as 2 glasses of ash, are added to the solution.
Fertilizing roses after flowering is important for the next season. So that the bush does not weaken from bearing lush inflorescences, in the fall, add a mixture of 16 g of potassium monophosphate and 15 g of superphosphate dissolved in 10 liters of water under it. It is worth watering the bushes at the rate of 2 liters of fertilizer for an adult bush and 1 liter for a bush of the first year of life.
You can also carry out foliar dressing of roses during flowering. For her, use specialized preparations, for example, Bud Plus, diluting 1 sachet of the product in 2 liters of water.
The method of propagation of the rose plant by dividing the bushes and layering
Reproduction by dividing the bushes. This method of propagation of rose bushes is applicable to native-rooted species and is common mainly among amateur gardeners. In the middle lane, it is best to divide the bushes in the spring, in the south - in the fall.
When dividing, the rose bush is carefully dug out, the excess soil is shaken off from the roots, the root necks are cleaned of soil. Then, with hands or a shovel, carefully divide the bush into several parts without damaging the root system.
Each part should have intact shoots and its own roots, which are shortened by 1/4 of the length, after which the plants are planted in a permanent place.
When dividing, it is necessary that at least one healthy kidney remains in each part of the root. It is best to divide the bushes in cloudy weather and protect the roots from drying out.
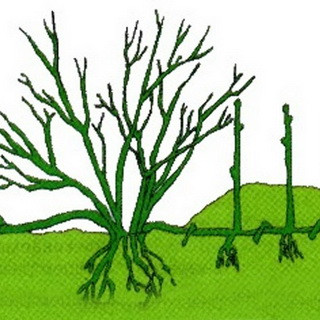

Reproduction by layering. This method of propagation of roses has long been practiced in amateur floriculture, since it can be used to obtain new rose bushes from both grafted and rooted plants, it is especially good to propagate ground cover and climbing roses with it. For reproduction by layering in early spring, relatively long annual shoots are selected, bend them down, laid in grooves 6-8 cm deep, attached and covered with loose nutrient soil. The ends of the shoots are not covered with soil, the top of the shoot should be free.
In the middle or at the end of June, new shoots appear from bent shoots, and adventitious roots begin to grow at the nodes in the ground. The next spring, the cuttings are separated from the mother plant and the rooted shoots are planted for a year to grow.
What can you combine roses in a flower bed with?
Of course, the queen of flowers plays the role of the main violin in any flower garden. But its charm can be enhanced with the help of properly selected "companions".
Roses in combination with annuals and perennials
The main rule in this combination is that the neighbors should be low, located at a certain distance from the rose bushes and not grow too much.
Of the annuals, verbena, kosmeya and levkoy are good neighbors for roses. Of the perennial flowers, it is best to give preference to lavender, veronica, delphiniums and dim varieties of asters. Bulbous primroses, chrysanthemums and any short plants with flowers of not very bright color will also look very beautiful next to rose bushes.
Roses combined with ornamental shrubs
Against the background of lush greenery of ornamental shrubs, roses look even more charming. The classic combination is flower beds with roses and conifers. Also very popular are combinations of roses with box trees, hydrangeas and clematis.
Roses combined with herbaceous plants
Perennial and annual grasses get along well with roses and do an excellent job with their main task - they cover the lower part of the bushes, exposed land and dark corners. The universal "soldiers" here are the hosts, the spikelet, fescue, and turf pike. Ferns also go well with roses, but their development must be limited, otherwise over time they will become real aggressors.
The lower part of the bush of many types and varieties of roses is not very attractive. To hide this flaw, plant low ornamental plants and flowers next to them, which will serve as a kind of frame.For pastel-colored roses, lavender, boxwood, woolly cineraria, and sea cineraria will be excellent companions. Plants with golden and purple leaves and flowers are suitable for bright roses, for example, Thunberg barberry, rosemary santolina, curb aster, etc.
How to properly care for roses
If you provide garden roses with proper care and feed them on time, they will delight their owner for a long time with lovely fragrant flowers and lush green foliage.
Features of feeding
The best fertilizer for roses is manure, and especially horse manure (must be at least 6 months old). The fresher chicken and pork manure will only bring harm to this flower. The fact is that it is very sour and can simply burn the plant. And fresh horse manure helps to block nitrogen in the ground.

During budding, calcium nitrate diluted in water is used as a top dressing (a full tablespoon of the substance is taken for 10 liters). When the rose begins to grow actively, it should be watered with a solution of mineral fertilizers, infused mullein, herbal infusion or a solution of chicken droppings every 1.5–2 weeks. It is best to apply fertilizers dissolved in water and after the plant has been watered. From the 3rd week of July, it is no longer necessary to feed the plant, as it begins to prepare for winter.
Roses, like all other plants, very poorly tolerate excessive cold, heat or long rains. To help them, you can spray the plant with epin, sodium humate, zircon, or ecosil. If the flowers are overfed, then a lot of foliage will form, and, on the contrary, there are few buds.
How to water properly
Watering should be infrequent, namely, once every 7 days. However, if the summer is very hot and dry, the amount of watering doubles. A bucket of warm water is poured under the root of one bush (do not pour on the leaves). Watering should be done so that the soil is saturated to a depth of 20-30 centimeters.

If the rose bushes will not be watered for a long time, then the soil under them should be covered with plucked grass, humus or bark from a tree.
If the plant lacks moisture, the flowers will become smaller. If it is in excess, then the foliage will begin to turn yellow. It is also recommended to loosen the soil after each watering.
Pests and diseases (control methods)
Rose bushes are susceptible to diseases such as powdery mildew. For prevention, spray the foliage with a solution made from regular soda (40 grams) and water (1 liter). It is necessary to spray 2-3 times in spring (with a break a week), and in June.
If aphids appear, then 10 liters. Dissolve a bar of laundry soap with water and put 2 sprigs of wormwood. Boil this mixture for 10-15 minutes. After it cools down, process the foliage. Repeat the procedure after 7 days. In the event that the aphid remains, then spray the rose with a systemic poison, for example, Aktara.
Nasturtium and lavender repel aphids, so it can be planted near roses. Close-planted garlic and onions will help keep the roses from getting sick and make the flowers more fragrant. Marigolds and calendula will protect from beetles.
If cracks appear on the stems, buds on the foliage have ceased to form and spots have formed, then the infected branches must be carefully cut off, and the plant should be sprayed with infusion of wormwood, nettle and horsetail.
Pruning features
Shoots that grow inward are subject to pruning. As a result, the bush will have many new shoots. And if the withering flowers are removed in time, then the next flowering will be more abundant than the previous one.
Louise Odier rose propagation
This species, like all roses, reproduces:
- Layers. In the spring, a small groove is dug next to the bush. The lateral shoot is tilted to the ground, laid in a recess, pinned with a hairpin or wooden slingshot where there is a bud with leaves, covered with earth, watered and looked after, like the whole bush. In autumn, the shoot is cut off with a pruner from the main plant, dug up and divided into pieces so that each has a root.Sprouts are rooted in home flower pots, and planted in a permanent place in the spring.
- Root shoots. Like all roses, Louis Audier produces root shoots. They choose one of the most distant from the mother bush, rake off the ground from the roots, cut the root connecting the shoot with the main plant with a sharp shovel. The shoot is dug up and planted in another place for growing.
- By dividing the bush. An adult bush is dug up, divided with a shovel into several parts and seated in places prepared in advance. Before planting, the roots for disinfection are dipped in a thick solution of potassium permanganate or the pruning sites are sprinkled with ash, the inventory is treated with bleach.
- By cuttings, however, according to gardeners, the Louise Odier rose does not reproduce well in this way. Cut off freshly faded shoots with a pruner. Cut into several pieces so that each has 3-4 buds. Before planting, a special pruning is done. Above the kidney, cut in a straight line, under the kidney - at an angle of 45 degrees. The leaves are cut off, the twigs are soaked for 40 minutes in a solution of Heterooxin (stimulant). Then the cuttings are planted in nutritious soil (you can in a flower pot at home), watered, covered with plastic bottles or glass jars. The offshoot is sprayed every day without watering for 30 days before root formation. If the planting is carried out in the garden, for the winter they are covered with spruce branches, dry foliage and lutrasil with small holes, and when the heat comes, the seedlings are sent to a permanent landing site.


