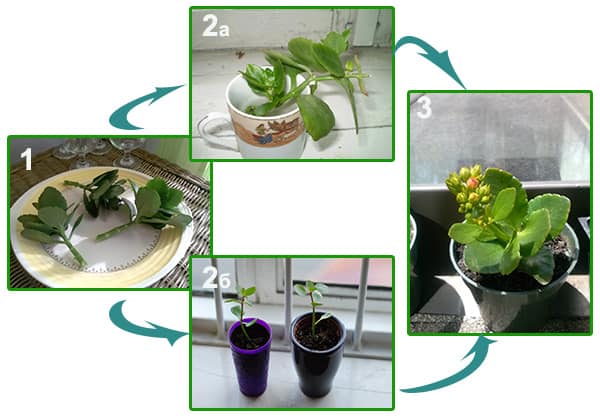
Reproduction of Kalanchoe by cuttings: features of the procedure
At home, you can propagate Kalanchoe yourself using leaves, offspring, buds, cuttings, children. Each of the methods has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Some of them are suitable for those who are just starting to grow these flowers in their home, others are acceptable for already experienced florists. But this does not mean at all that novice flower lovers cannot use one or another option for propagating a plant they like: the information provided will help you understand how the process itself takes place and how to avoid possible mistakes.
How this happens, what is needed for each breeding method, what should be remembered when performing the procedure - about this and much more below. article: → "Peculiarities of propagation of begonias by cut cuttings"
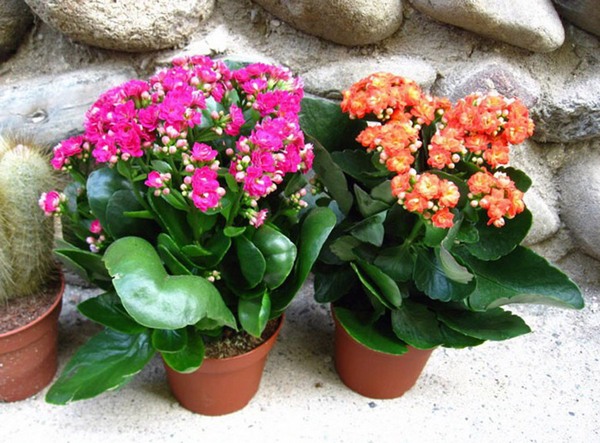
Types of Kalanchoe with a photo
The genus has about 20 species. Many types of Kalanchoe are grown at home.
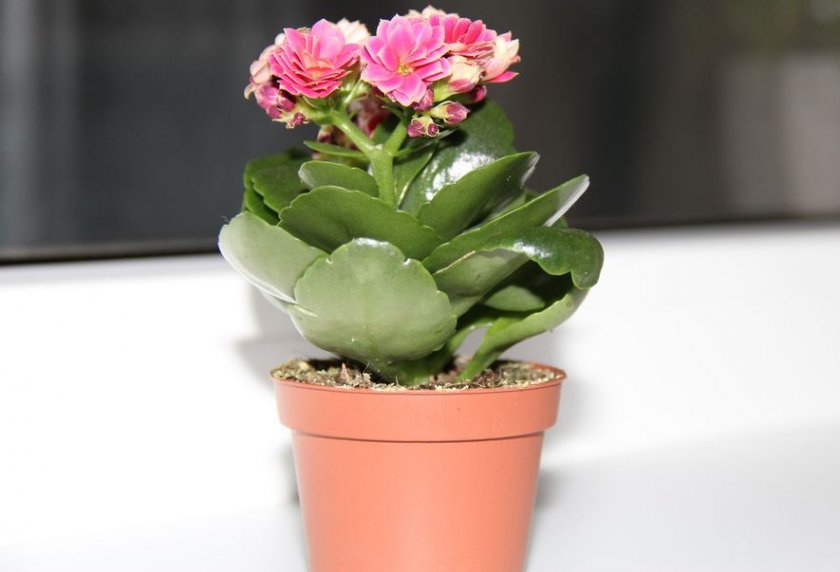
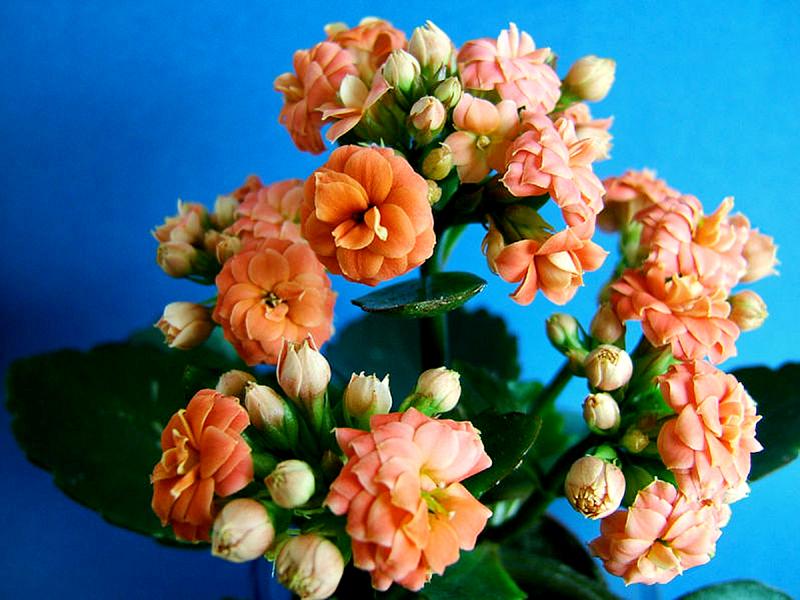
Kalanchoe blossfeldiana

This species is famous for its numerous flowers, collected in an umbrella-shaped inflorescence. Flowers are located on long peduncles and are distinguished by a variety of colors. The plant to care for is very unpretentious.
Kalanchoe manginii (Kalanchoe manginii)
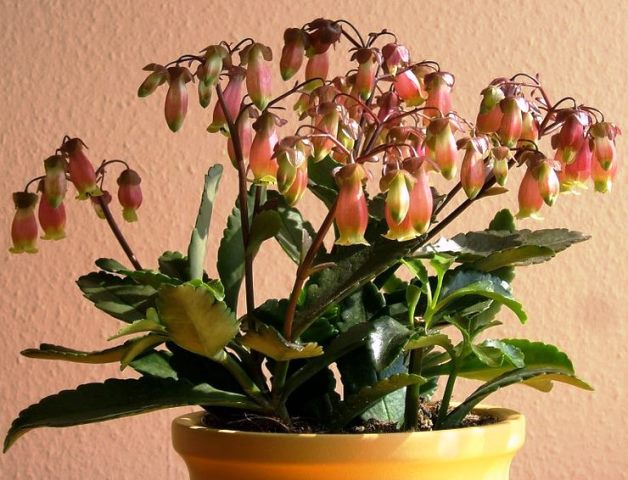

Ampel view. The flower is miniature (up to 15 cm) and is distinguished by exotic inflorescences that resemble small bells. Flowering usually occurs in spring.
Kalanchoe daigremontiana

This species blooms quite rarely, exclusively in winter. Plant height reaches 50 cm. It has a straight stem and long (up to 10 cm) green triangular leaves. The leaves are strewn with many purple spots.
Kalanchoe pinnata (Kalanchoe pinnata)

It is considered the most hardy species. It is distinguished by its height, reaching 1 m. The color of the flowers is unusual: white tones, smoothly turning into green. The juice of this type of Kalanchoe is sold at the pharmacy.
Kalanchoe bentii
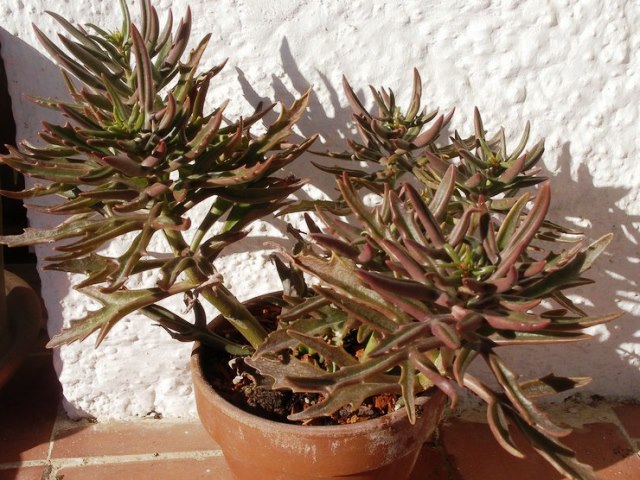

The species is represented by dwarf shrubs, reaching a height of 1 m. Leafy platinum is up to 50 cm long, rather thick and weighty. White flowers are collected in umbrella inflorescences. Flowering occurs in mid to late spring. It tolerates cultivation in cool rooms.
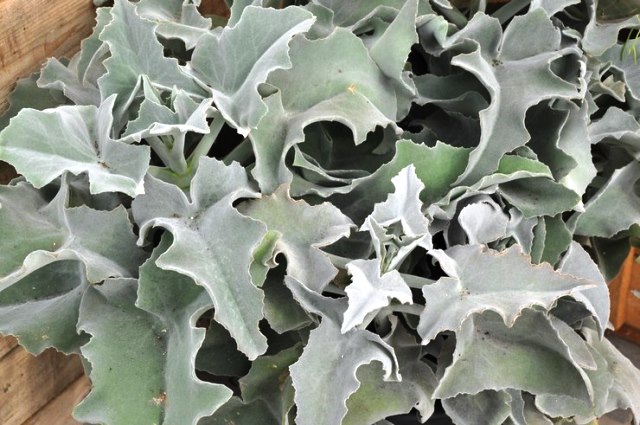

The species is represented mainly by shrubs. The leaves are serrated and covered with small hairs.
Kalanchoe felt (Kalanchoe tomentosa)

Representatives of this species are semi-shrubs. Stem erect, leaves with small hairs. Miniature flowers are collected in umbrella inflorescences.
Kalanchoe grandiflora (Kalanchoe grandiflora)
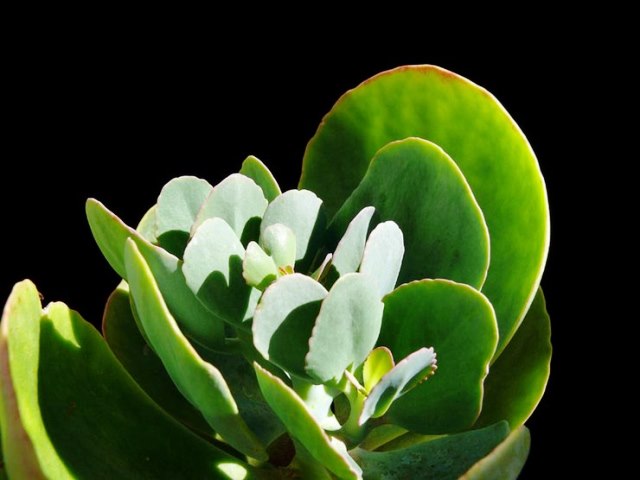

The species is also known as Kalanchoe marmorata. These are mainly semi-shrubs, reaching a height of 50 cm. Leaf plates are green. In direct sunlight, the leaves may turn pale red. Yellow flowers are collected in an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, have a pleasant aroma. Flowering begins in late spring.
Kalanchoe paniculata (Kalanchoe thyrsiflora)
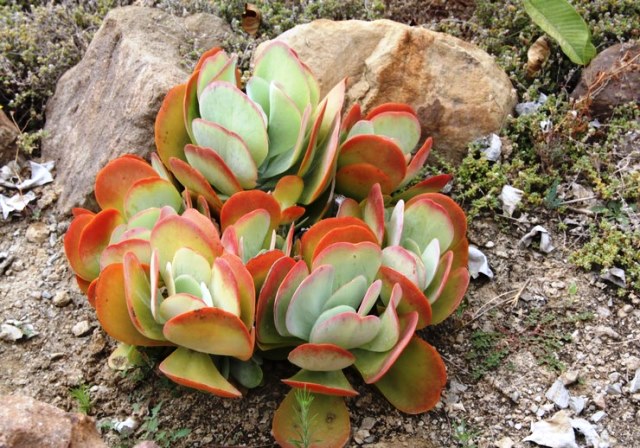

Plants of this species reach a height of 50-60 cm. At the base, the leaves are densely packed, closer to the top - the leaves become smaller and less frequent. Flowers are yellow. Flowering occurs in late spring.
Flaming Kalanchoe (Kalanchoe flammea)
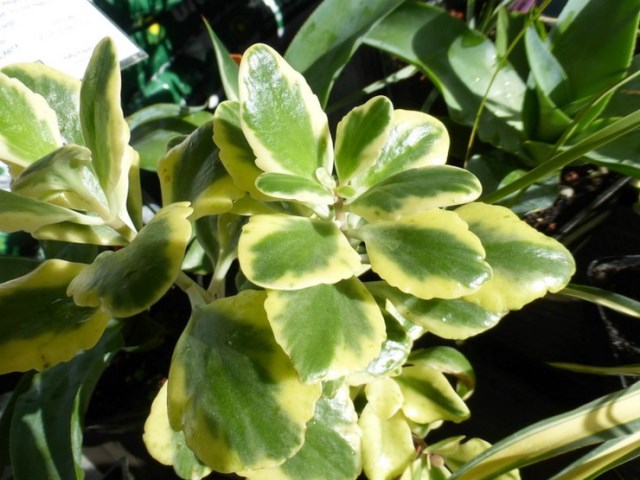

The species is known as the glaucous Kalanchoe (Kalanchoe glaucescens). Plant height reaches 40 cm. The leaf plates become wider and larger closer to the top of the plant. The leaves are round green with a white tint around the edges. Orange flowers are collected in umbrella inflorescences.
Kalanchoe tubular (Kalanchoe tubiflora)

The species is represented by dwarf shrubs, reaching a height of 70 cm. Leaf plates of gray-green color, narrow, elongated. The leaves of the plant are strewn with brown spots.
Kalanchoe dissected (Kalanchoe laciniata)
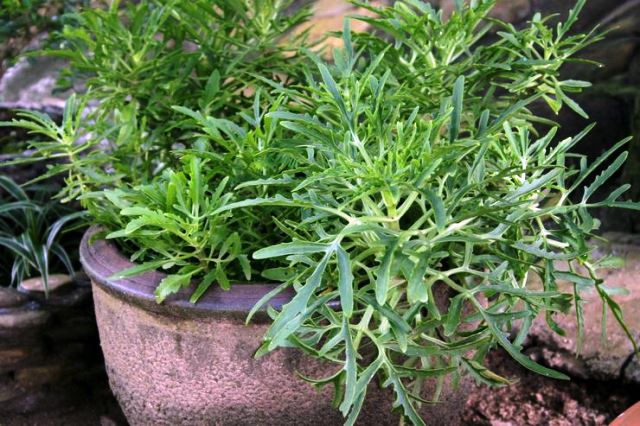

The species is also known as lobular Kalanchoe. The stems of the plant eventually sink down under their own weight, shedding leaves at the base. Green leaves have a dissected shape. Flowers are yellow or orange.
Kalanchoe Kalandiva
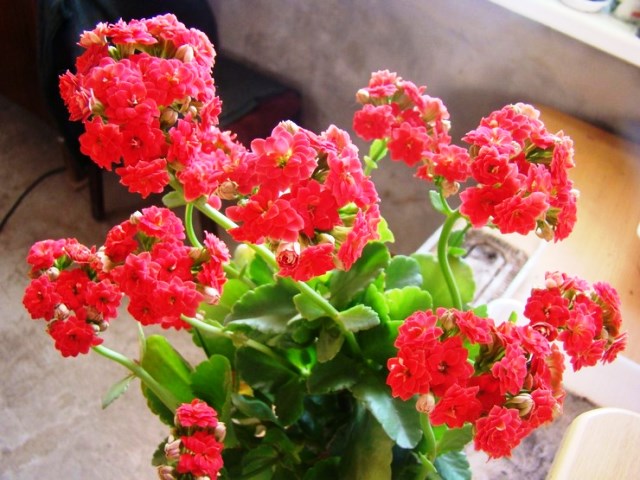

The species was obtained by selection.Differs in modest size and six-month flowering period.
The Kalanchoe plant is easy to care for at home, even beginners can do it. Subject to certain rules, the flower will constantly delight with its appearance and beauty.
"Questions and answers"
- What branches are best to cut off for propagation?
Too old twigs, which have already managed to become a little lignified, are not suitable, so they will take root for a long time. But young Kalanchoe twigs will very quickly get used to the new soil, so the best option for reproduction is young Kalanchoe sprouts.
- Why isn't my Kalanchoe blooming?
In fact, there can be a huge variety of reasons. But the most popular ones are: too large a pot volume, poorly chosen place for a plant, improper care. Most often, people plant Kalanchoe in large pots. Try to change the container, perhaps after that the plant will bloom after a while.
- Can Kalanchoe be propagated in water?
Sure! This is one of the most popular and easiest ways. the main thing is to choose the most suitable shoot and monitor its maturation in water. For faster results, you can use special root growth stimulants.
Rate the quality of the article. We want to be better for you:
Growing Kalanchoe
First you need to pay attention to the choice of a pot for planting this plant. What kind of pot is needed for the Kalanchoe? It is advisable to choose a pot that has small protrusions at the bottom so that there is a small space between the pan and the bottom of the pot.
This will help prevent moisture stagnation.
The next thing to prepare is the soil. So, what kind of soil is needed for Kalanchoe?
The soil mixture is made from three equal parts:
- Humus;
- River sand;
- Leafy land.
What kind of soil is needed for Kalanchoe? Store soil is suitable for succulents with a small addition of sand.
The required composition of the soil for Kalanchoe:
- 3 parts coarse sand or perlite;
- 2 parts of sod land;
- 2 parts of humus (leafy earth);
- 2 parts of peat.
The soil should not be heavy; good drainage is essential.
It can be broken bricks or, for example, pebbles.
After the soil for the flowering Kalanchoe is prepared, the plant itself must be planted.
Kalanchoe is a light-loving plant, after planting it is placed in a sunny place.
Watering the Kalanchoe is recommended no more than twice a week. The soil should not dry out. There should be no excess moisture either, so the water from the sump is periodically drained.
Water for irrigation is preliminarily settled, its temperature should be room temperature.
Watering must be done carefully so that moisture does not get on the stem, otherwise, it can rot. With the onset of cold weather, and, up to warming, watering the Kalanchoe is reduced
The humidity in the room should not be too high, the plant from this will begin to wilt and lose its presentation
With the onset of cold weather, and, up to warming, watering the Kalanchoe is reduced. The humidity in the room should not be too high, the plant will begin to wilt from this and will lose its presentation.
For the normal functioning of the plant, timely loosening of the earth and feeding is required about once a month. The room temperature must be at least 16 degrees.
Kalanchoe is a thermophilic plant. It can easily cope with the summer heat with timely watering.
In the first year, the plant blooms all winter. True, for this you need to regularly get rid of wilted flowers. But in order for the flowering to repeat the next year, the flower needs rest in the autumn.
It must be removed away from bright light and provide a so-called night period of up to 14 hours. In the evening, cover the flower with a cloth to protect it from the light.
Growing Kalanchoe at home does not require much effort, you just need to comply with certain conditions.
All methods of reproduction by complexity
Vegetative breeding methods of Kalanchoe are not too complicated and laborious. The most common method of reproduction of Kalanchoe at home, which allows you to quickly get an adult plant - by cuttings.
Kalanchoe cuttings take root without any problems. During spring pruning, they are harvested in large quantities. From a large overgrown bush, you can get 10-15 young specimens, and in some cases even more.
It is just as easy to propagate Kalanchoe by offspring. Offspring - the same cuttings, but already rooted in the ground near the mother plant. From them, you can quickly get adult copies. The only difficulty is that not all plants produce offspring. If they are formed, then rarely and in small quantities, therefore this method is less productive than cuttings.
Reproduction by children is more laborious than cuttings. Children are already small plants with roots. But to get a medium-sized plant from a baby, you need to spend at least 2 years. Kalanchoe is propagated in this way when it is necessary to obtain a large number of young plants.
Growing a plant from a leaf is similar in labor intensity to growing a Kalanchoe from children. Usually, leaf blades of those species that do not give children are rooted. A very small plant grows from the leaf, which will take a considerable time to build up green mass.
And of course the most difficult and time-consuming process is growing from seeds. In room culture, it is usually not used, since there are other, much simpler and faster ways of breeding Kalanchoe.
Why the Kalanchoe stalk does not take root
When breeding succulents by cuttings, it should be remembered that in nature, the peak of reproduction occurs in spring, when daylight hours in the tropics increase, there is no excessive heat with extreme humidity. Therefore, at home, you do not need to be too zealous with leaving: watering too much and placing the seedling in the sun.
Kalanchoe is considered a very flexible flower among florists. It grows well on poor soils, tolerates the lack of watering.
Succulents have such a developed mechanism for maintaining generic numbers that they are able to take root in harsh conditions. Kalanchoe needs only light, a little moisture and warmth. This should be the starting point for propagation by leaf and cuttings.
Features of breeding domestic succulents
Reproduction of Kalanchoe is carried out by several methods:
- cuttings;
- with the help of children;
- leaflets;
- offspring;
- buds sitting in the axils of the leaves;
- seeds.
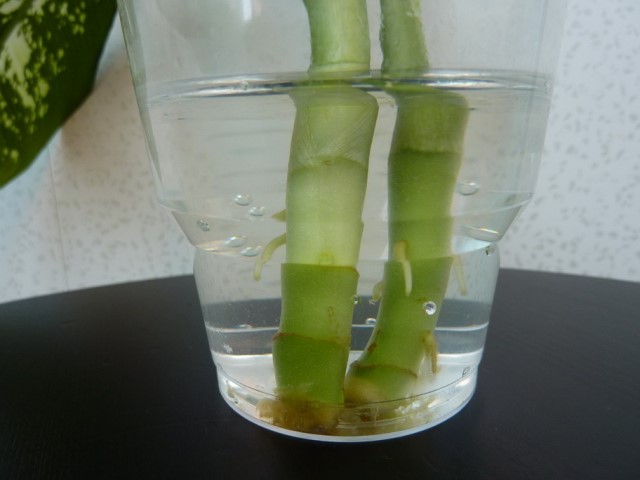
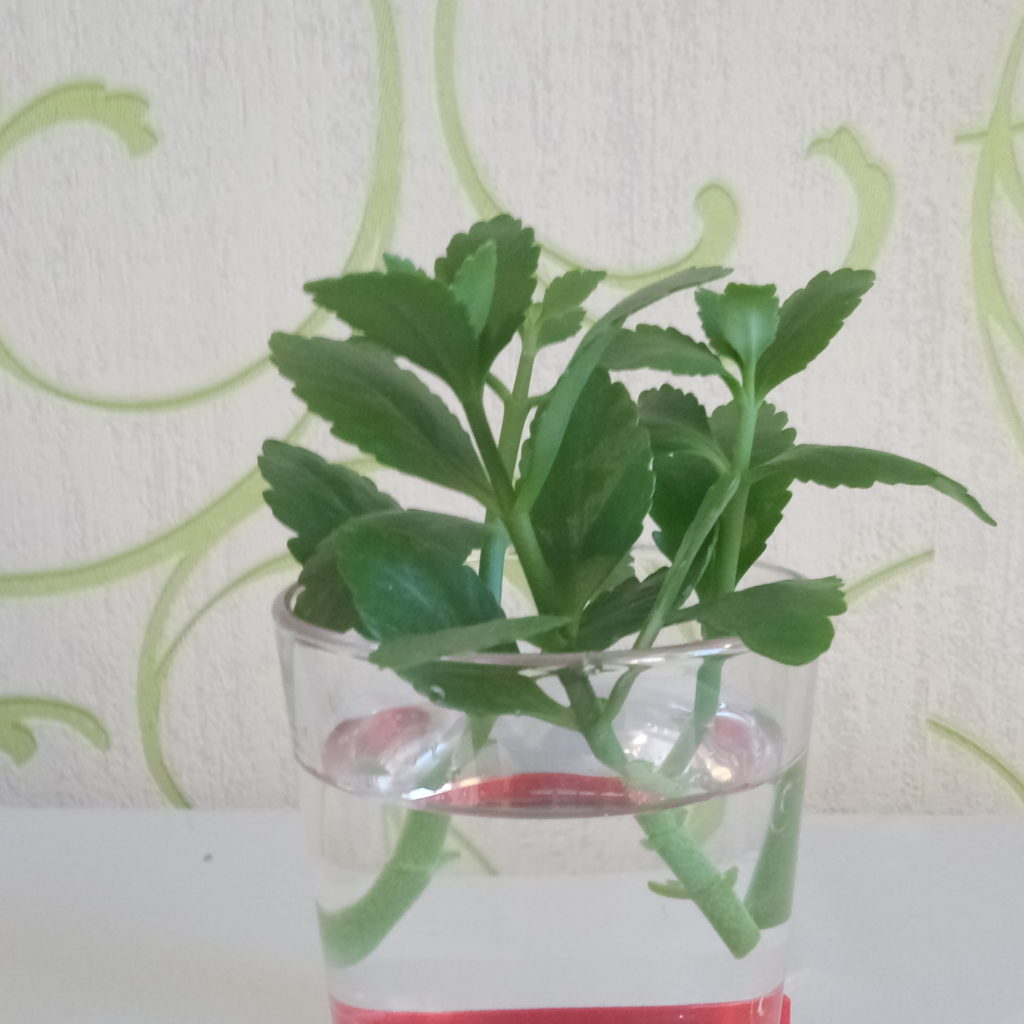
Cuttings in water
For cuttings Kalanchoe cuttings are prepared and rooted as follows:
- Cuttings are cut from the developed strong apical shoots from 8 to 12 cm in length.
- For rooting, the cut material is first dried for 24 hours.
- The foliage is removed from the bottom of each shoot.
- Place the cuttings in water up to about half their length.
- Do not allow exposure to abundant solar radiation on the planting material.
- After 2-3 weeks, the cuttings are ready for planting.
At home, reproduction of Kalanchoe does not present any difficulties, since often the planting material quickly and easily takes root, regardless of the season. You can get young seedlings in several ways:
- Planting cuttings or leaves, parts of leaf plates;
- Sowing seeds obtained from inflorescences;
- Children or offspring.
The simplest ways of reproduction of Kalanchoe are cuttings and rooting of leaves, because in this case, young seedlings turn into flowering bushes the next year. Sowing seeds is justified only if you need to get a large amount of planting material.
Kalanchoe reproduces in different ways depending on the species:
- Rooting leaves and cuttings, planting offspring and children are suitable for the pinnate, tube-flowering and Kalanchoe Degremon.
- Varieties of Blossfeld, Mangin can be propagated by seeds, cuttings or offspring.
- For felt Kalanchoe, it is good to use sowing seeds, planting cuttings and leaves.
How is Kalanchoe characterized
The peculiarities of the Kalanchoe can be called thickened fibrous roots, fleshy, sometimes woody stems and thick succulent leaves arranged in a spiral opposite or in whorls of three, but, again, spiral.
The leaves themselves can be either petiolate or sessile, but either petioles or leaf plates in all species have a stem-embracing base. The shape of the leaf plate varies quite strongly from type to type, it can be simple or feathery, smoothly edged or with a jagged edge.
Its thickness is highly variable: from flat to cylindrical, and its sizes vary from small leaves to healthy "burdocks". Peduncles in all species are apical or appear from the leaf sinuses located near the tops. In most Kalanchoe, they are leafy, the flowers are four-petaled.
How to propagate Kalanchoe
There are five main ways of breeding Kalanchoe at home:
- Children.
- By the kidneys.
- Offspring.
- Cuttings.
- Leaves.
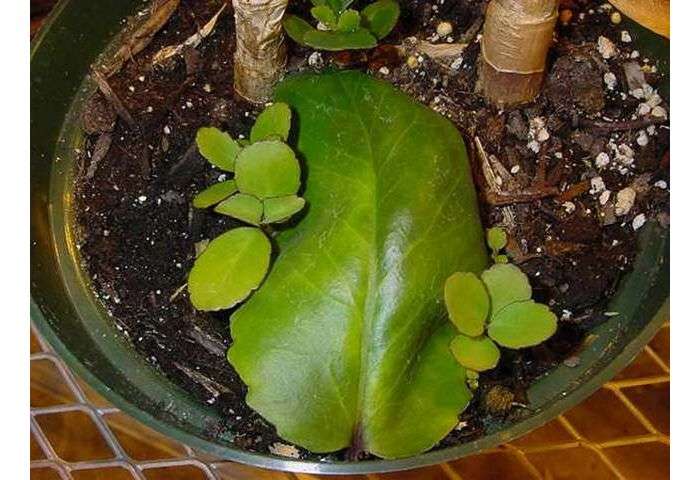
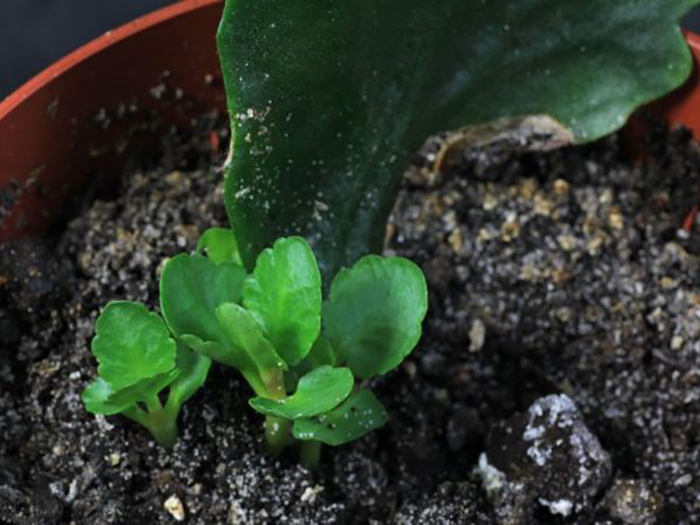
Brood leaf buds are called babies. They look like small plants with a formed rosette of two leaves and roots. Babies are formed on the leaves only in "viviparous" Kalanchoe.
The babies, having reached their optimal size, fall to the ground and take root on their own. The baby, in fact, is already a full-fledged plant that can be planted immediately into the ground.
Reproduction by kidneys. This refers to the axillary buds. In some species of Kalanchoe, after flowering, not only the flower itself, but also the leaves fall off. In place slightly above the sinus of the fallen off leaf, a bud begins to hatch. It is easy to recognize, it looks like a head of cabbage, only very small.
After a stem of at least 1−2 centimeters is formed from the kidney, it can be carefully cut and planted in soil with a high sand content. In such soil, the stem will quickly give roots and will feel great.
Reproduction by offspring. In order for these offspring to appear, the plant must be stimulated to this. After the plant has bloomed, you need to pinch the top of the stem. After that, an offspring will grow up next to the mother, which is used for reproduction.
As soon as the offspring gain strength and are as tall as one-third of the mother, they can be separated. It is necessary to separate carefully so as not to damage the roots. The offspring must be placed in soil with a high content of sand and peat, in such a soil they quickly gain strength and growth.
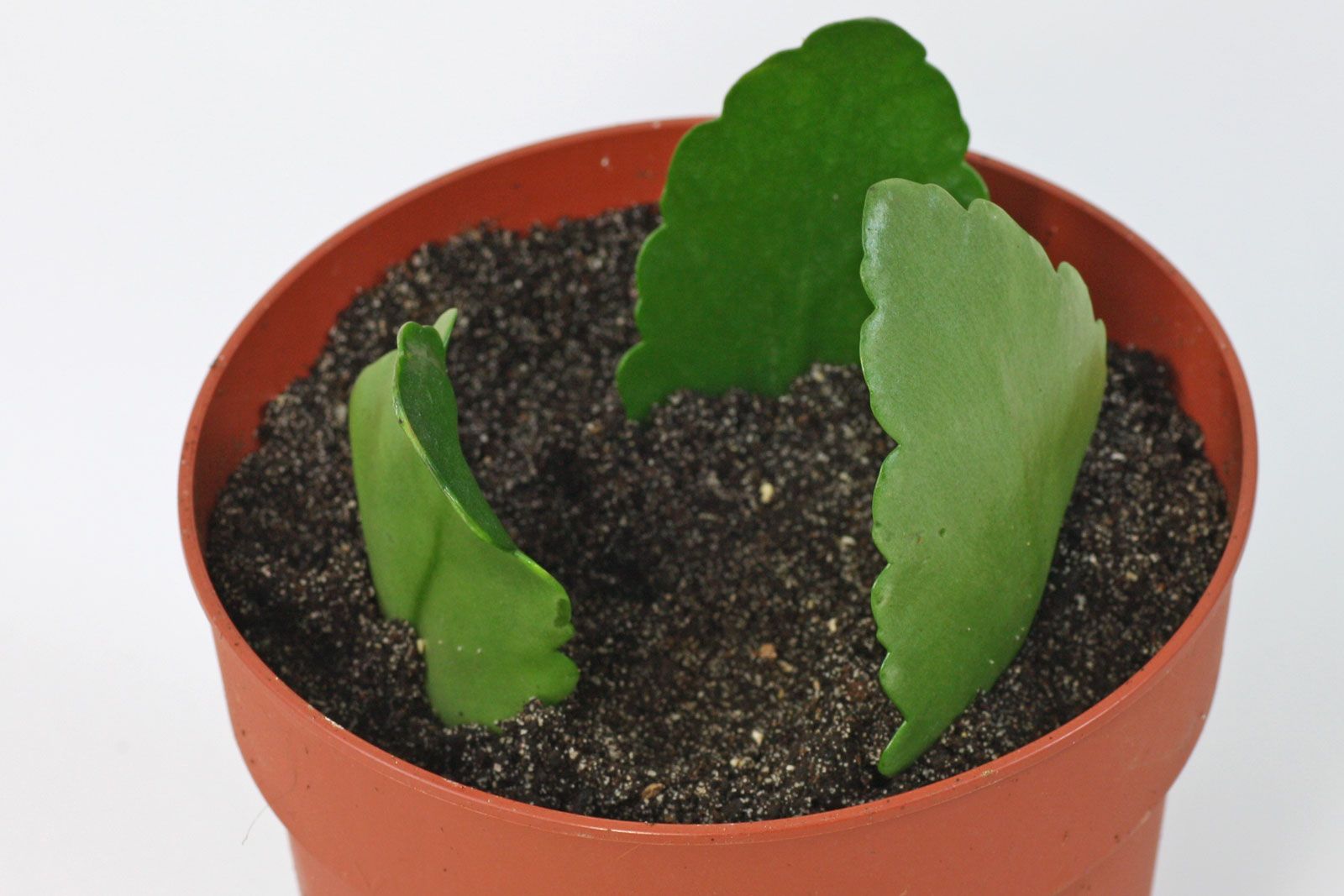
Reproduction of Kalanchoe leaf
Leaf rooting can be called a way for the lazy. The easiest way to get a seedling is to leave the fallen leaf lying under the mother plant and forget about it. But with this approach, there is a risk that the Kalanchoe will grow stunted or sick.
Reproduction by leaves is carried out in several stages:
- Choose a healthy leaf that is firm to the touch - free from spots, tears, or dry marks.
- Use a sharp tool to cut the leaf plate.
- Dry the slices for several hours, if the leaf is large, fleshy - up to 2 days. Avoid direct sunlight when doing this.
- Lightly press the prepared leaf into the substrate vertically or at an angle.
- If the leaf is small, there is a risk that it will dry out faster than take root - cover it with a transparent greenhouse. This will reduce moisture evaporation.
For propagation by leaves, the same substrate is suitable as for cuttings. After about 3-4 weeks, small buds will begin to grow along the edges of the leaf. When the babies grow up and take root, they can be separated from the mother sheet for seating in separate pots.
Reproduction of Kalanchoe by brood buds (children)
The advantage of succulents is that they can be propagated in many different ways. Some species are called viviparous. This name was not given by chance.

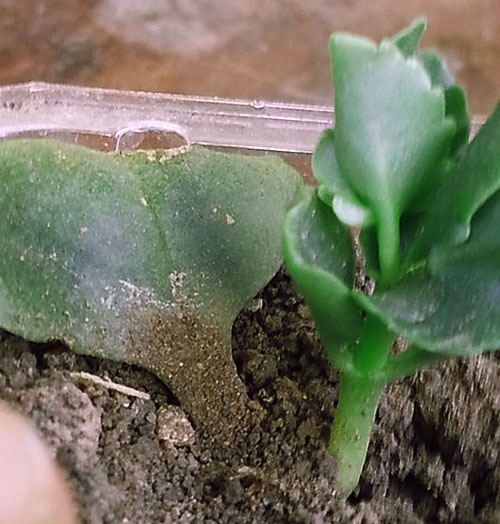
A miniature specimen with roots grows at the edges of the toothed leaf plates
If the babies are not ripped off, then over time they themselves will fall away from the mother plant. Then they will calmly germinate in the soil. Collecting the buds is very simple: it is enough to gently run your hand over the sheet.
Children need to be planted in a shallow flat pot in the ground intended for planting succulents. They have roots and therefore do not need additional germination measures. It is enough to dig a shallow hole, carefully put the kidney there and lightly sprinkle the roots with earth.
As soon as the children get stronger and grow up, they are separated from each other and transplanted into other pots.
Reproduction of Kalanchoe brood buds
Among the numerous species of Kalanchoe, there are so-called "viviparous" plants, in which brood buds are formed between the teeth of the leaf plate - babies, miniature, but full-fledged plants with two pairs of true leaves and roots 1-1.5 cm long. Until a certain point, they develop on mother leaf, then fall down on the soil mixture and take root very quickly.
The grown miniature Kalanchoe is transplanted into separate pots filled with a drainage layer at the very bottom and soil mixture for succulents. Some growers practice this method easier - they pick the plant from the leaf in their hand or a small bowl. Once formed, they detach from the leaf easily and pour into the palm of a hand, it remains only to distribute them evenly over the surface of the earthen coma in a separate pot.
Reproduction by brood buds is used for species of Kalanchoe Degremon, pinnate and tubular-flowered.