Interesting features of viburnum
- Almost all the fruits of viburnum varieties are edible, tart on the palate, mostly bitter, but there are also sweet ones.
- The viburnum harvest has beneficial properties: it is rich in phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, iron, copper, manganese, iodine, vitamins A and C.
- Berries have a lot of applications: they make jams, bake pies, use them to make tea, treat themselves, make all kinds of cosmetic masks and scrubs, make alcoholic beverages.
- Almost all components of viburnum (bark, leaves, flowers, berries) are used for medicinal purposes.
- The shape of the crown can be easily changed, since these shrubs tolerate pruning well.
- Plant varieties are often used for the benefit of a person: they are planted on roads to create snow-collecting areas; for strengthening the soil in mountain areas; to attract birds to forests, planting different species of viburnum in plantings; and also planted in public places (often it is a viburnum of the Sargent Onondaga variety).
Having decided to decorate your garden with viburnum shrubs, you can get lost in the variety of varieties. Which variety to choose: dwarf or tall, with ordinary red fruits or with a more original color, with a round crown or a more spreading version? But even having opted for the first variety that comes across, it will be possible to settle an excellent decorative ornament on your site, which also has a lot of useful properties and does not require significant efforts during cultivation.
vote
Article Rating
Diseases and pests of fuchsia
In general, a flower such as fuchsia is practically not susceptible to disease. If the humidity is too high, small dewdrops may form on the fuchsia leaves. Also, the leaves can be covered with powdery spots. To eliminate this trouble, you need to start preparing a mixture of water with foundation, in a ratio of 11: 1. You need to spray the plant with such a solution.
If the leaves turn yellow, this is a signal of chlorine, which indicates abundant watering of the plant. It is also possible that the plant lacks substances such as nitrogen or magnesium.
When dry brown spots appear, you should know that the plant needs molybdenum.
A favorable sign if the roots are white and short. If the roots are densely intertwined with a clod of earth, then this is a signal that the plant needs to be transplanted as soon as possible into a larger pot. If there is no white color in the roots, but on the contrary they are brown and very dark, then this indicates that the plant suffers from root rot. This is also a sign of abundant watering and most likely the plant will need to be thrown away.
Fuchsia is also susceptible to a disease such as rust. It can be recognized by the brown concentric circles at the bottom of the leaf. All leaves that have been affected should be removed immediately. After all, there is the possibility of very easy transfer of disputes: from the wind, insects or human hands. The disease is contagious and spreads easily to healthy plants. It is necessary to check in a timely manner if other fuchsias are not infected. It is necessary to thoroughly wash and disinfect all instruments that were used when working with an infected plant. And you certainly need to carry out the same manipulations with your hands if you accidentally come into contact with infected leaves.
After removing diseased leaves, it is necessary to spray with such preparations as: "Topaz", "Vectra", "Strobi", Bordeaux mixture, cuproxat. Process 2-3 times with an interval of 10 days.
If the white-winged fly is not noticed in a timely manner, then its rapid reproduction will lead to damage to the nearby fuchsias. To combat these harmful insects, special preparations are used, such as: "Angara", "Actellik". There is an option to rinse the leaves with green soap, but this method will only work for small plants.
Possible diseases and pests of the plant
With proper cultivation of fuchsia, no diseases are terrible for it (read about the rules for growing fuchsia at home here, and from this article you will learn about the intricacies of caring for a flower in the garden). But in case of violation of agrotechnical rules, such problems arise:
- When the plant is exposed to direct sunlight, spots form on the leaves. You can save the flower if you rearrange it to another place.
- With waterlogged soil, root decay occurs. It will no longer be possible to save the plant.
- The yellowing of the leaves is the result of depletion of the soil, lack of magnesium and iron. To combat, use spraying with a solution of magnesium sulfate, preparations containing iron. Yellowing can result from improper watering.
TIP: If the plant is affected by a fungus, then use fungicides.
Fuchsia can be attacked by pests such as:
- aphid;
- weevil;
- mite;
- whitefly.
To deal with the first three, you need to use Aktelik or Gaupsin. These are non-toxic drugs for humans. To combat whitefly, you need to isolate the affected plant in order to prevent the spread of the parasite to other flowers. Then carry out the treatment with a drug from the group of neurotoxins. Treat the leaf with a single dose, and the root with a double dose.
Reproduction methods
The choice of a method for obtaining a new generation of fuchsias depends on the material available, the skills of the grower and the results that he expects. Not all methods are equally available - some procedures require more time and effort.
Seeds
Seed propagation looks simple only at first glance. Good quality and right grade material is difficult to buy. Do-it-yourself picking is fraught with the risk that the plant will become over-pollinated and, as a result, fuchsia will grow, which will differ from the original. Of course, breeders use this technique, but for an ordinary grower, such an effect is not always needed. The whole process of growing from seeds consists of several stages.
Planting material is sown in a specially prepared substrate of peat and sand
To reduce possible losses, it is important to pre-treat the seeds with a solution of potassium permanganate and disinfect the soil with steam. Seeds are laid out directly from above, without deepening
So that this order is not violated, bottom watering (through the drainage holes) or spraying from a spray bottle is recommended.
Within two weeks, the substrate must be periodically moistened and created over it the effect of a greenhouse, covering the container with film or glass. To prevent mold from appearing, the surface is ventilated, increasing this gap as the seedlings appear and grow. Then the covering material is removed completely.
After a couple of months, the seedlings can be replanted. They are taken carefully, removed from the moist soil and transplanted into a more nutritious mixture of three parts of leafy soil and one part of peat and sand.


Leaflet
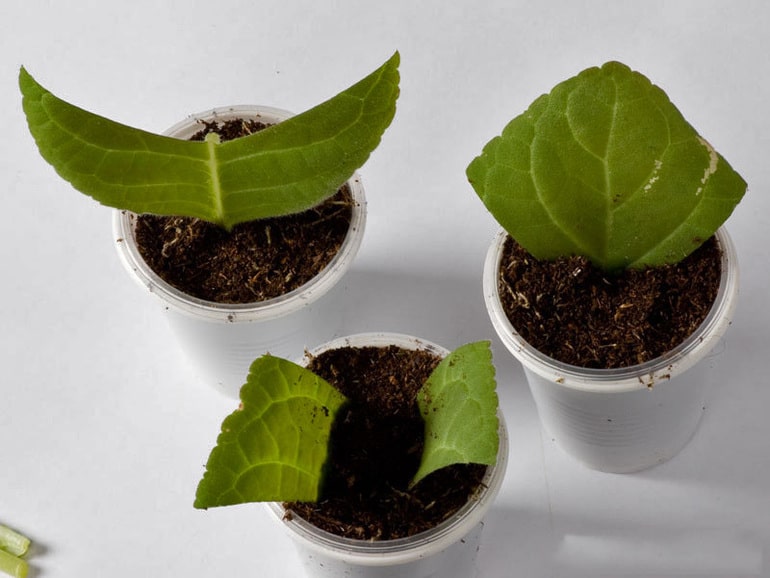
In order to get an exact copy of the fuchsia seen, it is enough to take a leaf from it. However, it must be healthy-looking and large enough. One or even several leaves will not in any way affect the appearance of the plant and its well-being, in addition, this method can be considered quite productive in terms of the possible number of shoots obtained. The procedure in this case is as follows.
- Apply to the cut any remedy that stimulates the appearance of roots. Take a narrow vessel with water, dissolve a tablet of activated carbon in it and place a slice of the workpiece in it.So that the whole leaf does not end up in the water and does not rot, you can use a paper stand with a hole made in it. For prophylaxis purposes, the liquid must be periodically replaced with a fresh one.
- Since the leaf itself acts as a source of nutrition, in this case the roots appear faster than in the case of seeds, and the fuchsia will grow faster. After the roots appear (on average, it takes a week), you can start transferring to the ground. If the roots do not appear within three weeks or mold appears in the water, the leaf must be disposed of.
- The transplanted rooted leaf does not require intensive watering, only light spraying of the soil and maintaining a constant temperature of about 20 degrees. Usually a new shoot will hatch next to the leaf in a few days.


Shank
In addition to individual leaves, you can use parts of the stem - they are also called cuttings. It is this method that is optimal in order to form beautiful plantings of fuchsia in the garden or in a flower bed. To do this, cuttings are cut in the fall, stored in a cool place in the winter - a garage, basement or cellar, and begin to root in the spring.
At home, such a long shelf life is not needed. To do this, with a sharp knife or blade, twigs are cut off from the plant - both small and up to 20 cm long.It is better to choose young, non-lignified shoots, the lower leaves of which must be removed. In this case, it is best to start rooting right away and use one of the following options.
- Wait for the roots to appear in the water, as in the case of leaf propagation described above. They can take from 5 to 10 days to appear.
- Use substrate, perlite, coconut briquettes or peat tablets. The selected substance is placed or poured into a small container - a container, glass or pot with good drainage holes. Then moisten, make a small indentation, stick in the stalk and lightly tamp. If the leaves touch the ground, container walls or covering material, rot may form on them.
The appearance of roots in the soil is evidenced by the appearance of new leaves. If all goes well, the cutting is transferred to a permanent pot. Thus, the time required to obtain a large fuchsia is reduced to a minimum.


How to do it right?
Rooting fuchsia cuttings is easy and simple. The main thing is to adhere to certain instructions, which will allow you to get a large percentage of accepted seedlings in a short time.
The grafting method involves several stages:
The optimum size of cuttings is 10-12 cm with the top and lateral two or three pairs of leaves. The cut is made with a sharp knife diagonally. Exclusively at the end of the flowering of fuchsia.
After the performed operation, the trimmed part should dry out within 10-15 minutes.
We process the cut with a preparation to stimulate root formation. It can be: "Kornevin", "Zircon", "Epin", "Heteroauxin".
The stalk should be placed in a container with the chosen medium: In a plastic cup with water, after removing the lower leaves. When they come into contact with water, decay processes can develop, which eventually spread to the entire process. Water needs soft, filtered water. The term for root formation is on average 2 weeks.
Can be planted in a planting palette filled with substrate (sand, sawdust, vermiculite). The filler must be pre-moistened.
A peat tablet is also suitable. It should be saturated with hot water, as it swells faster. In a peat tablet, plants immediately begin to actively develop, 99% of the cuttings take root safely.
Plant immediately in a damp, loose earthy mixture. The soil should include most of the sand, vermiculite.
Create a greenhouse effect. Cover the containers with glass, transparent foil. Such a greenhouse requires regular ventilation and removal of condensate.
Place the cutting in a sunny spot where it is light but not too hot. The air temperature inside the greenhouse should not exceed + 25 ° С.
As needed, the stalk is moistened, preventing the soil from drying out.
After the roots appear, the process requires a transplant. A long delay with this, in the future, can negatively affect the plant.
Small plastic cups or small pots are great containers.
For transplanting, a specially prepared soil with a neutral pH is chosen. Drainage is laid at the bottom of the flowerpot
It is worth lowering the plant into the ground carefully, the roots are very fragile so as not to break. Then fuchsia should be watered with settled warm water.
Do not forget to stick markers on the cups indicating the variety.
The plant will fully take root when it grows.
Watch a video about fuchsia cuttings:
How to plant correctly
Before starting planting, the plant is treated with a growth stimulator.
A small hole is made in the soil, where the treated cutting is then planted. Planting is carried out in such a way that the bottom row of leaves does not come into contact with the soil.
After that, you need to slightly moisten the soil, and then create greenhouse conditions for successful rooting. A plastic bottle, cut in half, or a plastic bag will work for this.
The plant should be placed in a bright room, but not under direct sun, the temperature should be cool enough, 18 - 22 degrees.
So that the petioles do not start to rot, you should not forget to open them for a few minutes every day for airing.
Rooting occurs in about 15-30 days.

After the rooting of the cuttings, it is necessary to gradually begin to harden the plant, opening the shelter for several minutes, gradually increasing this time. This is necessary in order for the sprout to gradually adapt to environmental conditions.
How to root cuttings in peat tablets
Rooting fuchsia in peat tablets is very simple and convenient. The survival rate of cuttings is very high, and in the future they grow well in such a substrate. In addition, this material is very economical and does not take up a large storage area.
For rooting in tablets, the apical parts of the plant and young stems should be cut off. If the shoot is too large, then you can cut several cuttings from it.
The landing algorithm is as follows:
- The peat tablet is allowed to soak in water for a while. Fifteen minutes is enough for it to swell and increase in size.
- The prepared stalk is cut with a sharp knife a centimeter below the last leaves. At the same time, you do not need to touch the leaves, if they are not very large. Otherwise, they are shortened slightly to avoid evaporation of moisture.
- The cut site is treated with special preparations for better root formation, and if they are not at hand, then you can lubricate the cut with ordinary honey.
- The petioles must be buried in peat without touching the lower internode. After that, the substrate is slightly compacted, otherwise the sprout will not hold well.
- The design with a tablet and a handle in a jar or plastic cup is covered with a transparent film on top to create comfortable rooting conditions.
- The plant does not need watering, since a tablet soaked in water will keep it for a long time. The only thing to do is to ventilate the greenhouse every day to avoid rot and mold.
Rooting usually takes 15-20 days, but sometimes the process can take 30-35 days. If the sprouts are green and strong, then rooting will definitely occur.
This will be evidenced by the appearance of new leaves. Then the shelter is removed, and they are closely monitored so that the soil does not dry out. Young fuchsia needs regular, but very moderate watering.
How to root cuttings in a glass of water
The rooting procedure in water is not at all complicated.The stalk is cut in the specified way, put in a glass of water and wait for the roots to appear.
- It is advisable to put activated carbon or root in the water.
- In the spring, the roots are formed in a week. And if you had to take up rooting in the fall or winter, then the process can take a month.
- Using this method of rooting fuchsia, it is better to cut off all the leaves from the twig, leaving only one, this will consume less moisture.
When the roots that appear have grown a couple of centimeters, you can plant the plant in the prepared substrate.

How to root fuchsia cuttings in perlite
- It is necessary to prepare a plastic cup, pour a substrate in the form of perlite or vermiculite into it and spill it lightly with water.
- Place the cut petiole in the container slightly at an angle, which promotes better bore formation.
- The structure should be covered with a bag or plastic container to create a greenhouse.
- When the roots grow, you can start transplanting seedlings into prepared containers with soil.

How to transplant cuttings
It is better not to take a large pot for transplanting fuchsia seedlings. If the root system has not entangled the entire clod of earth, then there is a great opportunity to overmoisten the plant.
It is best to take the smallest pots for a start, and when the roots grow, carefully transfer them into a two centimeters larger pot.
The transplanted fuchsia should be placed in a plastic bag for several days to make it easier to cope with the stress of the transplant, remembering to periodically air it.

Diseases and pests
spots will form
However, this trick will not work with excessive watering, if root rot is allowed. In this case, unfortunately, it will no longer be possible to save the plant. Neither a decrease in watering nor a transplant will help. Even cuttings taken from this fuchsia are unlikely to take root.
One of the reasons for the yellowing of leaves (if only this is an unnatural process) is a lack of iron and magnesium, that is, depletion of the soil. To combat this phenomenon, you can try spraying the flower with sodium sulfate solution. Feeding with preparations that contain iron can also help.
Leaves may turn yellow due to sunburn caused by spraying the plant during the day or improper watering. For rust (fungus) infections, fungicides should be used.
Fuchsia can be attacked by pests, among them:
- whitefly;
- spider mite;
- weevil;
- aphid;
Gaupsin or Aktelikom "Aktara" means
Care
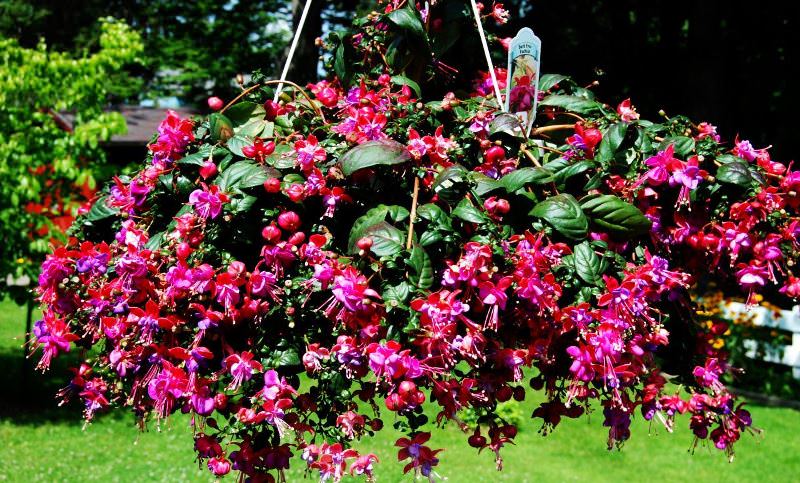
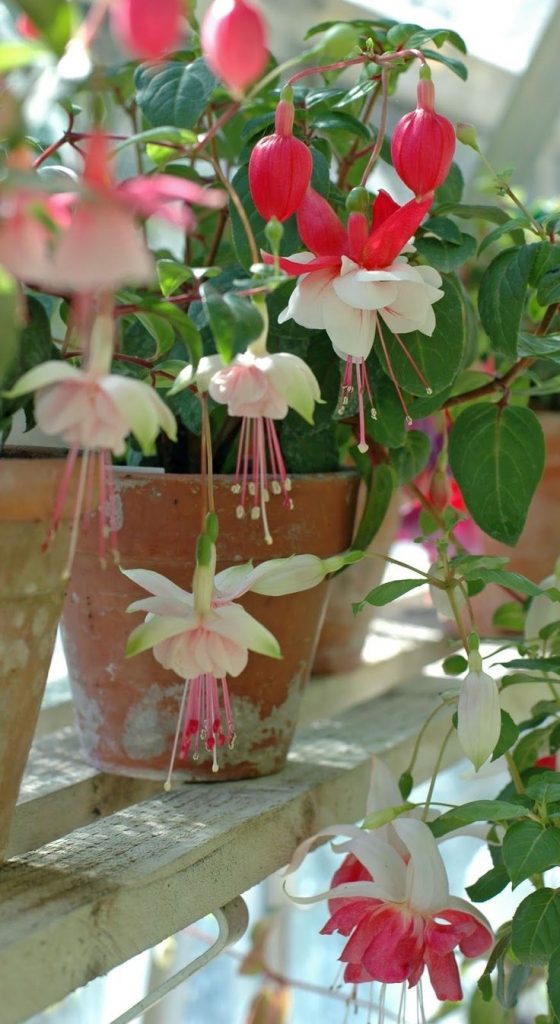
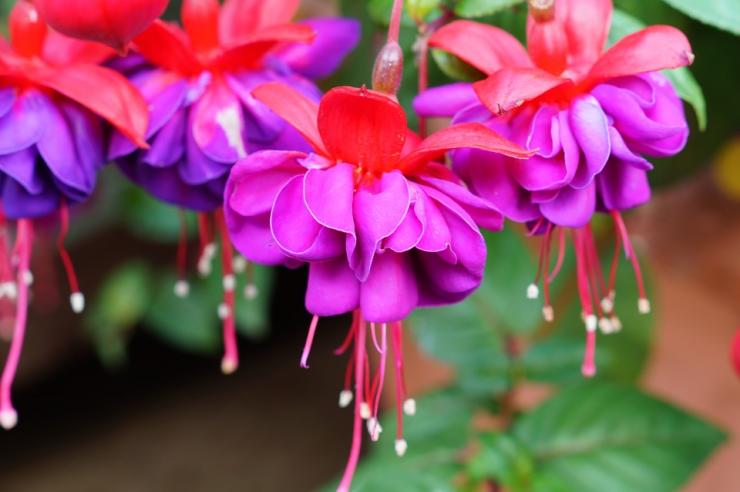
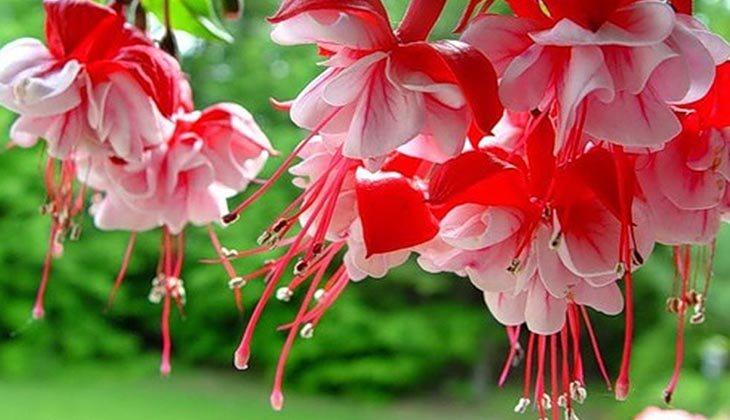
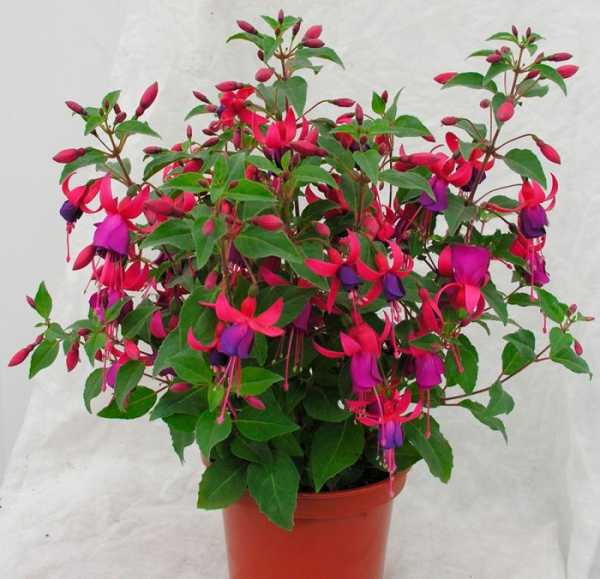
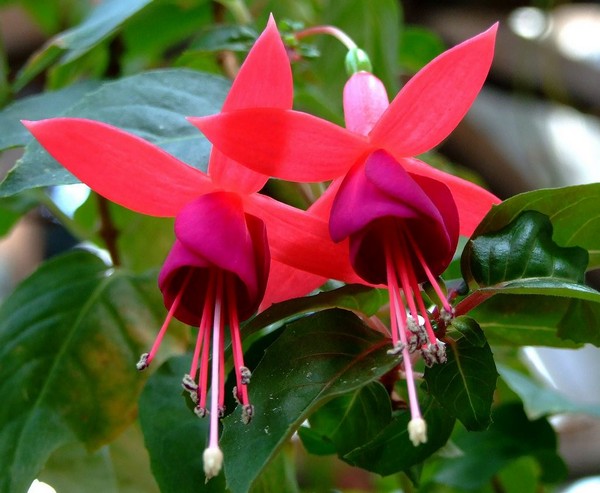
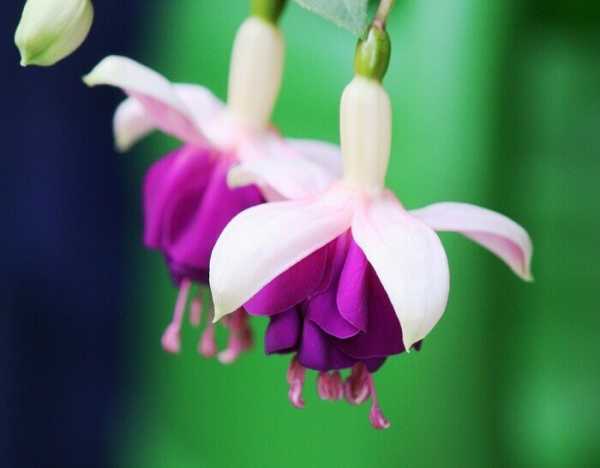
Fuchsia has a huge number of hybrid forms with straight and pyramidal stems, there are ampelous varieties and spreading, hanging, climbing, in the form of bushes and bonsai. Fuchsia blooms profusely and for a long time with beautiful lantern flowers. We will tell you how to care for room fuchsia at home:
Temperature
 A comfortable temperature for growing fuchsia at home is 18 - 22 ° C in summer and no higher than 18 ° C in winter. If the temperature is above or below these limits for a long time, the decorative effect of fuchsia may suffer. The buds will begin to fall off, the leaves will become smaller and lighter. The plant will slow down its development. There will be a risk of infection with diseases and pests.
A comfortable temperature for growing fuchsia at home is 18 - 22 ° C in summer and no higher than 18 ° C in winter. If the temperature is above or below these limits for a long time, the decorative effect of fuchsia may suffer. The buds will begin to fall off, the leaves will become smaller and lighter. The plant will slow down its development. There will be a risk of infection with diseases and pests.
When the temperature drops during the active growing season of fuchsia below the comfortable one, the same effect will be observed. The plant is guided by the ambient temperature. When it is warm and light, the flower actively develops and blooms profusely, usually from spring to autumn. In late autumn and winter, when it gets cooler and less sunlight - the development of the fuchsia flower stops, the buds stop forming - the fuchsia is getting ready for rest.
Location

It is better to place vases with fuchsia on the windowsills of the east and north sides of the room. Even here, the flower must be protected, if necessary, from direct sunlight with blinds or curtains.On the north side windows in the spring, perhaps the fuchsia will lack lighting. We'll have to provide the bushes with illumination using a phyto lamp or fluorescent lamp for up to 12 hours a day.
On the southern windows, especially in summer, fuchsias will be too hot. It is better at this time to take out a flowerpot with a flower in the garden under the trees or on the balcony, where the sun's rays will illuminate the fuchsia only early in the morning. At noon and until evening, fuchsia feels better in partial shade. During flowering, it is advisable not to rearrange the flower from place to place and not turn it towards the light in different directions. Fuchsia does not like this, and can simply shed all the buds.
Watering

Proper watering is the most important part of blooming fuchsia care. Many factors affect the frequency and amount of watering a flower:
- Pot location
- Fuchsia variety
- Stage of her growth
- Soil composition
- Pot size and type
- Weather
Fuchsia can survive for quite a long time without additional nutrition, but not without water. Fuchsia should be watered regularly. Make sure that the soil is well saturated with moisture every time. The next watering should not be earlier than the topsoil dried up from the previous watering. Excess water from the pan must be drained to prevent moisture stagnation in the roots of the plant.
A flowering plant has a great need for moisture. Watering in the summer will have to be frequent and regular - every 3-4 days, and sometimes more often.
In autumn, watering is gradually reduced to once a week, and in winter it is watered no more than once or twice a month.
Top dressing

You need to feed fuchsia regularly, once every two weeks.
This is especially important during the active growing season, from April to the very fall. For feeding, complex fertilizers are used for decorative flowering plants.
Watering with liquid fertilizers must be done on wet soil. Top dressing helps fuchsia grow green mass and form countless buds. You can also apply foliar dressing of fuchsia on the back of the leaves.
Young, freshly planted fuchsia bushes do not need to be fed, since they are planted in a well-prepared soil filled with all the necessary microelements and organic matter. The same rule applies when transplanting a plant into a larger pot with new nutrient soil. Top dressing should be resumed, somewhere, a month after transplantation.
Air humidity and spraying

For fuchsia, air humidity is comfortable in the range of 50 - 60%. Too dry indoor air will lead to yellowing and wilting of fuchsia leaves and buds. You can increase the humidity of the surrounding air using wide containers of water, placed next to the fuchsia. You can also put a flower pot in a tray with damp pebbles or expanded clay.
On hot summer days, fuchsia will be saved from the heat by regular spraying with settled water at room temperature in the morning and evening hours. It would be nice to take the fuchsia out into the fresh air in the garden, in the shade under the trees, or at least on the balcony, where the sun's rays only fall in the morning hours. But we must remember that this must be done carefully - after all, fuchsia does not like when it is moved from one place to another during flowering.