Forsythia care
Caring for an unpretentious forsythia is quite simple. She needs moderate watering, loosening and weeding of the trunk circle, feeding for the formation of flower buds and pruning.
Watering
The bush does not need a special watering regime. In a rainy summer, forsythia bushes are not watered at all, it has enough moisture from precipitation. In drought, especially in hot windy weather, the soil must be moistened. Enough watering 1-2 times a month (1 bucket under the bush). After watering, the soil must be deeply loosened (on the bayonet of a shovel), removing all weeds and covered with compost.
Top dressing
Feeding forsythia is carried out three times per season:
- In early spring, along the near-trunk circle, it is necessary to carefully spread a layer of rotted manure so as not to touch the trunk and branches, then water well. Such organic feeding will ensure active growth and future lush flowering of the plant.
- In April, a complex mineral fertilizer is applied to the soil (60-70 g per 1 m²)
- After flowering, the shrub must be fed with all-purpose kemira (100-120 g per 1 m²). In this period, the flower buds of the next season are laid.
Pruning forsythia
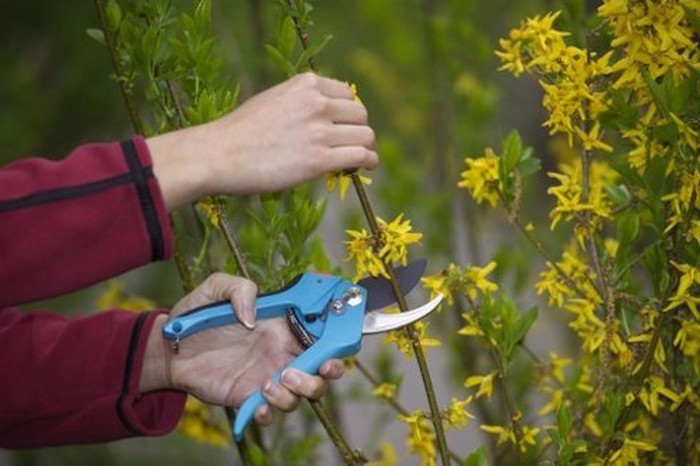
One of the important activities that is necessarily included in the plant care program is pruning. Correct pruning forms a beautiful, spreading bush crown, stimulates the growth of young shoots. The time for pruning forsythia is after flowering. Young shoots must be shortened by a third over a strong bud. It is not recommended to cut off old shoots completely, but to leave a "stump" to stimulate the growth of young shoots. In addition, forsythia requires regular pruning of the branches creeping on the ground, as they take root very quickly. Once every 4 years, the shrub must be rejuvenated in order to achieve abundant flowering. All old branches are removed at the root, a few strong young branches remain.
Pruning forsythia in the fall consists in removing excess, damaged branches. Pruning should be done in early fall, so that the cuts have time to drag on for winter.
Propagating forsythia by green cuttings
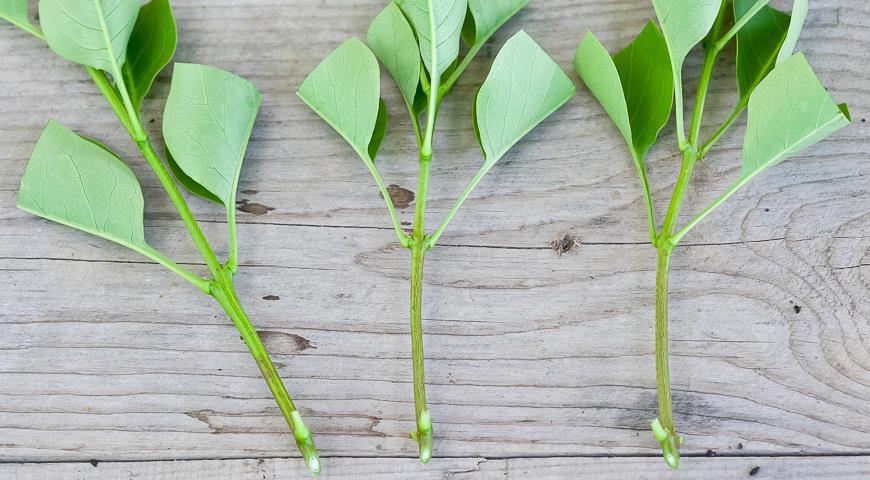
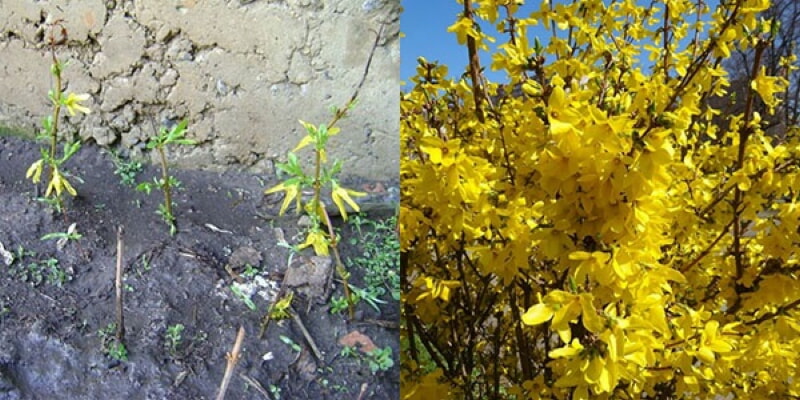
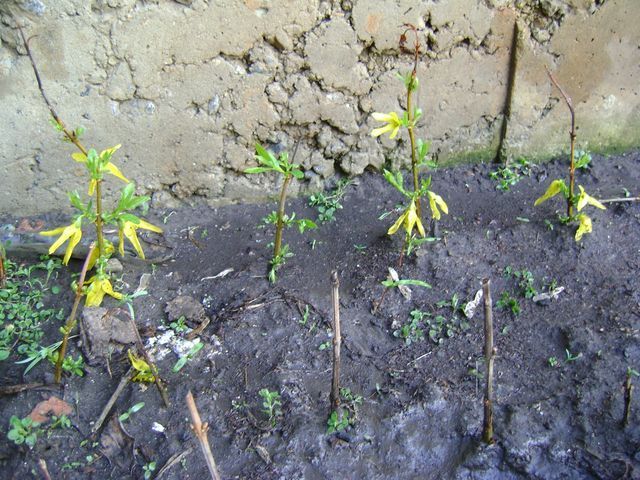
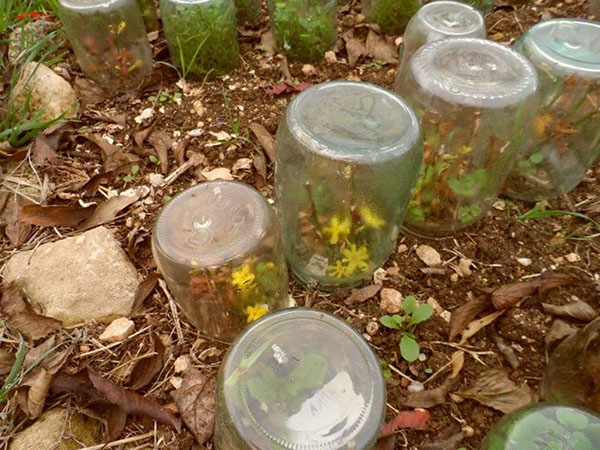
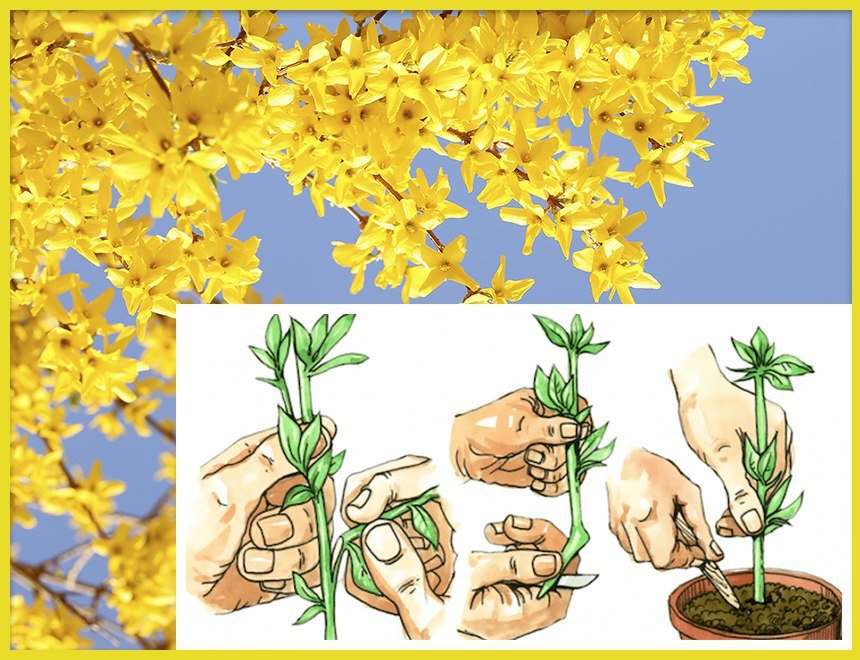
Reproduction of forsythia by green cuttings also involves the use of young shoots, which are not more than one year old. They need to be harvested after the end of flowering, in the interval between the end of May and the beginning of June. This plant is good because almost all green cuttings root perfectly if you keep the soil moist. For cuttings, select those shoots that are just beginning to lignify. Its optimal length is 20 cm. Do not remove the leaves from the cut off branch under any circumstances! They will become a kind of signal that will help you understand whether a new seedling has taken root or not. As soon as the leaves wilt and darken, the cuttings of forsythia can be stopped in the summer, since it has not given roots.
Planting cuttings should be carried out in a pre-moistened and loosened soil. The best way for this is a mixture of ordinary fertile soil with sand - such soil is sufficiently nutritious and, most importantly, light, which does not interfere with the germination of roots. Cutting of forsythia continues at the next stage - planting. It is not necessary to deepen the seedling more than 5 cm into the ground, and try to position it obliquely. Planting is carried out not only in a seedling box, as it takes root well in a regular bed, if everything is done correctly. In order for rooting to go faster, you need to cover the planting material with a film. The roots of the cuttings are formed after a month, but care should be taken that they do not die throughout the summer.Reproduction of forsythia by cuttings does not require special skills from the summer resident, and no one will have any problems with caring for young, taken shoots. So, in the heat, you need to equip them with shading and water them with a watering can, since without a nozzle, the soil can be easily washed off. Adult forsythia is indifferent to moisture and does not require a lot of it, but if you are rooting young cuttings, then water is very important here. It is necessary to ensure that the inside of the soil remains moist constantly - this is the most important guarantee of the success of the entire event. Within a month, the established shoots can be transferred from a shaded garden bed or nursery to a permanent place (always with a lump of earth!). Some experienced summer residents recommend leaving forsythia in this place until next spring and replanting it only a year later. Then she will have time to build up a strong root system.
Regardless of whether you leave a young bush in the old place or transplant it to a new one, it will definitely need to be covered. Otherwise, it will surely freeze out, and then your efforts will be in vain.
How to plant?
Forsythia cuttings can be planted indoors and outdoors. Usually, they land in a closed one immediately, in which they take root faster. In any case, for better rooting, it is recommended to place the cuttings in a special solution, for example, in Kornevin, before planting. It is necessary to leave it in the solution for an average of 4–5 hours, but it can be longer.
Indoor
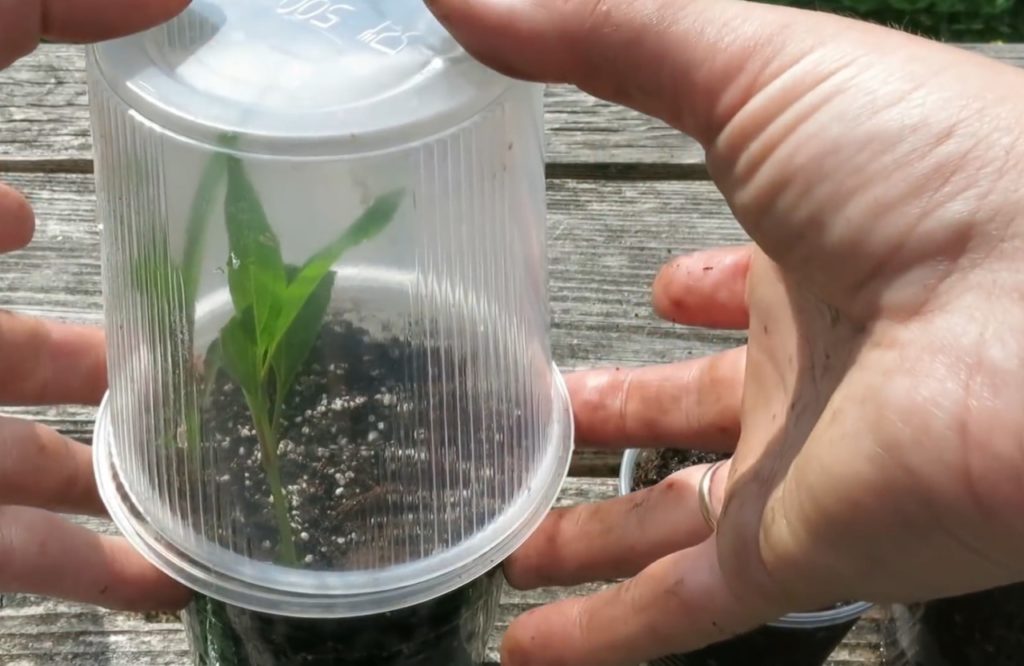
For planting green cuttings of forsythia in closed ground, you should prepare loose soil that allows air to pass through well. The cuttings should be planted at a distance of 5–8 cm from each other and to a depth of no more than 5 cm. It is best to plant them in a transparent container, since the developing roots will be best seen in it. It is recommended to cover the cuttings on top with a glass jar or a large plastic glass, you can use a bottle to create a kind of greenhouse in which the rooting of plants will be fastest.
The cuttings should be regularly ventilated and watered, while using a small watering can, if after a month the roots are visible on the shoots, then the plants can be safely transplanted to their future permanent residence.
In open ground
Lignified cuttings that have been stored in a cold place all winter should be properly planted in the ground. This is done in the spring. It is best to choose warm weather and decide on a place in advance. Before planting, the cuttings are updated. Next, you should dig a small hole and pour it with water. After the water is completely absorbed, a young plant should be placed in it to a depth of no more than 10 cm. 2-3 buds should be left on the surface. Tamp. If several cuttings are planted at once, the distance between them should be about 5-8 cm.
With the arrival of the first frosts, young plants should be covered, since in a short time they will not have time to grow and get stronger.
Reproduction of forsythia in water in the spring is extremely rare. Most of these plants do not take root, and therefore very few people undertake experiments. Nevertheless, this is done quite simply.
- Green cut branches are placed in small cups of water, where a plant growth stimulator is added in advance.
- After the appearance of the first roots, the plants are transferred either to the open or to the closed ground. But "growing" should still be carried out, creating a greenhouse environment, that is, cover the plants with a jar or bottle.
- In autumn, mature plants can be safely transferred to a permanent place of residence, giving preference to less sunny areas of the garden.
It is worth noting that the technique of planting spring and summer cuttings in indoor and outdoor ground is no different. But in all cases, it is advisable to cover young plants with a jar, constantly water and ventilate them, and it is also recommended to shade the area when it comes to open ground.
What varieties are popular
In nature, bushes can be found in East Asia and in the territory of the former Yugoslavia:
- Not too large shrub - 1-3 m in height and about 2 m in width.
- Shoots are covered with gray, hardy bark.
- Leaves are oval in shape with denticles at the edges. Fully bloom after flowering. They are located opposite each other along the stem.
- The flowers are shaped like a bell, painted yellow, each of them has 4 petals. The flowering period lasts a long time - about three weeks.
- The fruits are presented in small boxes, each of which ripens several seeds with wings.
 European
European
In the gardens of Europe, you can find several varieties of the plant. European - shrub up to 2 m tall with vertical shoots. Flowers are single. Giralda - differs from the previous species in twisted flower petals and their larger sizes. Drooping - grows up to 3 m. Shoots sag down. The yellow flowers form bunches. Popular varieties:
 Giralda
Giralda
- variegated - differs in green leaves with a yellowish pattern, her flowers are yellow;
- Fortune - the leaves of the variety are narrow, the flowers are yellow;
- purple-stemmed - this plant has purple stems and blossoming leaves.
- dark green - reaches 3 m in height. Shoots grow upward. Large leaves, dark green. The flowers are greenish.
 Drooping
Drooping
Intermediate - the leaves are oblong, dark green. The flowers are bright yellow. Varieties:
- Beatrix Farrand - tall (up to 4 m) shrub with yellow flowers;
- Denziflora - the plant reaches 1.5 m, with twisted petals;
- Spectabilis is a bush up to 1 m in height and up to 1.2 m in width, the flowers are bright yellow, the green color of the leaves changes to purple by autumn.
White - stands out from all the unusual white flowers with a yellow throat, which at the bud stage have a pink tint. The undersides of the leaves are purple. Ovate - endowed with yellow single flowers that bloom on the bush earlier than other species. The leaves are green with a purple tint. Common varieties:
Spring Glory - the flowers are bright yellow, large, the leaves are green in spring, and in the fall they become variegated with a purple and yellow pattern;
 White
White
- Tetragold is a low (up to 1 m) shrub with yellow, rather large (up to 3 cm in diameter) flowers;
- Goldsauber - golden yellow flowers, large, bloom in mid-April.
Reproduction of shrubs by cuttings
Reproduction of shrubs by straight, or green, cuttings
This is the most convenient and commonly used method for cutting shrubs. Cuttings are taken from the shoots of the current year, which have finished or are finishing their growth, but have not yet had time to woody. They are also called green or summer.
Cuttings are cut from young plants. It is advisable to use old mother plants only the next year after the rejuvenating pruning carried out this year.
green hydrangea stalk
For cuttings, side shoots are used, formed on the growths of the last year, in the lower tier of the illuminated part of the plant. It is better not to take vertically growing shoots and tops for reproduction.
Planting green cuttings is not delayed, it is desirable to carry it out as soon as possible. But, if transportation is necessary, the cuttings are placed obliquely in a container with moist sphagnum.
In such packaging, they can be stored in the refrigerator, but no longer than two days. In any case, at all stages of working with green cuttings, they must not be allowed to dry out: cut shoots can also be placed in the water in the shade.
This breeding method is suitable for:
Horticultural crops: actinidia, barberry, privet, weigela, hydrangea, dogwood, viburnum, clematis, vesicle, lilac, henomeles, mock-orange, spirea, honeysuckle, currant, rose.
Indoor crops: hibiscus, large-leaved hydrangea, oleander.
Reproduction of shrubs by semi-lignified cuttings
These are shoots that are already covered with bark. Such cuttings are taken starting from the end of June: the tops of semi-lignified shoots of the current year are cut off and cut into cuttings with two internodes. The lower leaves are removed. The cuttings are dusted with a root formation stimulator and planted in pots in a mixture of peat and sand in equal amounts. After 2-3 months, roots are formed on them.
semi-lignified spirea stalk
This breeding method is suitable for:
Horticultural crops: hydrangeas, spiraea, rhododendrons, barberry, heather, hemlock, holly, juniper, magnolia, privet, viburnum, dogwood, forsythia, honeysuckle, abelia, broom.
Indoor crops: azalea, camellia, ivy, gardenia, oleander, hibiscus, large-leaved hydrangea.
Reproduction of shrubs by cuttings with a heel (heel)
A variety of semi-lignified cuttings are lateral branches that grow in mid-summer on the already overwintered shoots. They are not cut off, but torn off with a heel - a piece of root or bark with a thin layer of wood. The heel is obtained when the shoot is not cut off, but broken out from the base.
viburnum stalk with heel
This breeding method is suitable for:
Horticultural crops: chubushnik, varieties of barberry Thunberg, thuja, juniper.
Reproduction of shrubs with hammer-shaped cuttings
The base of the cutting is the same lateral branch on last year's escapeas with heel cuttings. Only the stalk does not come off, but is cut out with a part of the lignified branch, which protects the stalk from decay.
hammerhead cuttings of maiden grapes
This breeding method is suitable for:
Horticultural crops: maiden grapes.
Reproduction of shrubs by lignified cuttings
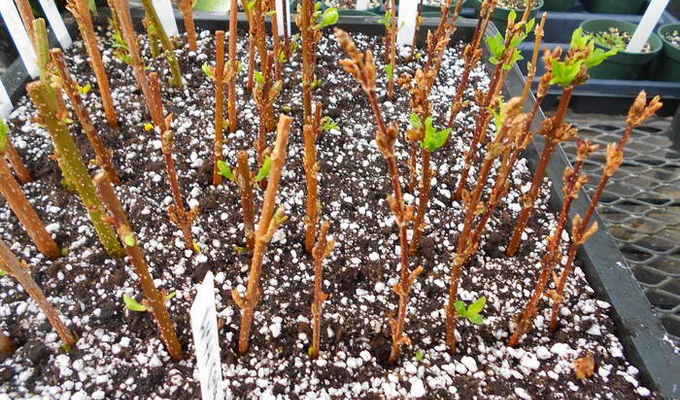
These are taken from matured annual shoots with normal bark. Cuttings are harvested in autumn after leaf fall or early spring, and cuttings collected in spring are immediately planted for rooting, and autumn cuttings can be planted both in autumn and spring (then they are stored in a refrigerator, basement or in the snow before planting).
woody currant stalk
Lignified cuttings root more slowly and with a lower percentage of success, but you have to take less care of them (no need to water, spray), so this method is convenient for many.
This breeding method is suitable for:
Horticultural crops: poplar, hydrangea, snowberry, forsythia, mock orange, fruit grapes, abelia, hemlock, holly, juniper, privet, forsythia, euonymus, broom.
Indoor crops: camellia, ivy.
comparison of types of cuttings
Forsythia in landscape design
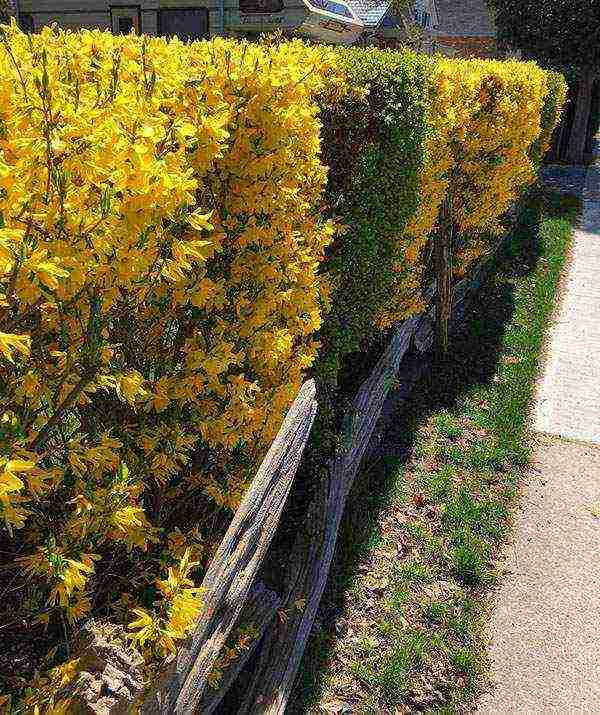
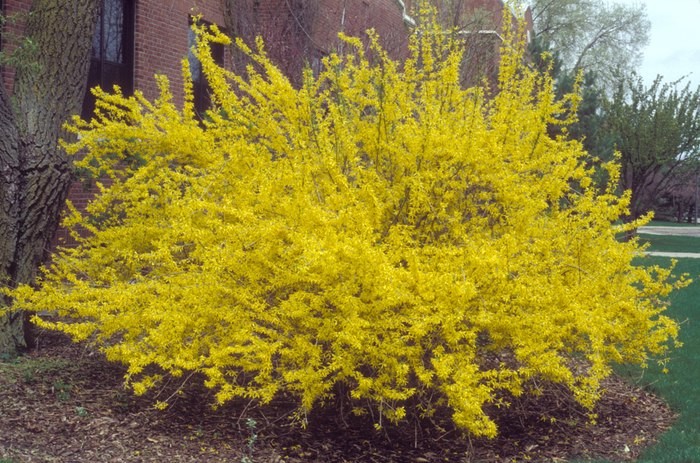
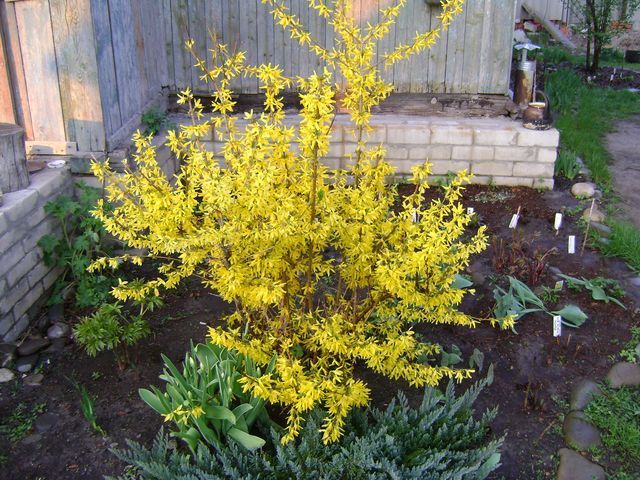
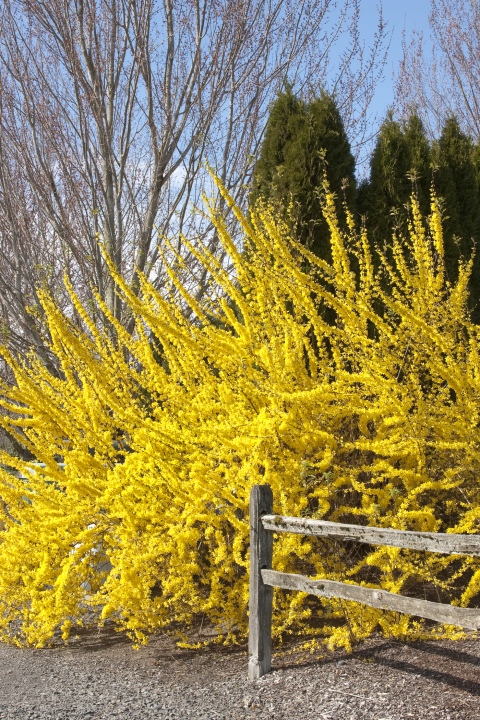
Forsythia looks great against a dark green background of conifers: juniper, thuja, spruce, as well as against a green lawn. It looks great as a single plant - a bright golden spot in a spring garden, and in group plantings with other flowering ornamental shrubs. The drooping forsythia looks especially elegant and delicate; it is used to decorate slopes, alpine slides, hedges and buildings.




Forsythia is an attractive and unpretentious shrub that adorns any area with a luxurious golden flowering at a time when many trees and shrubs have not yet woken up from their winter sleep. Having created favorable conditions for the growth and development of forsythia, you will enjoy its unusual beauty for many years.
Forsythia - propagation by cuttings in spring
Forsythia is a perennial shrub belonging to the olive family, which blooms luxuriantly in early spring with a huge number of bright lemon-yellow flowers. The flowering of this shrub can be observed in early spring, namely from March to April. The blooming forsythia stands out the brighter and more saturated against the background of the garden just beginning to wake up after the winter. A feature of this plant is that only after the flowering period, the bush releases young leaves.Many gardeners want to see this bush on their site, because it is a kind of confirmation of the onset of spring. This is easy to do, because the propagation of forsythia by cuttings in spring is very simple.
Breeding options for forsythia
The most productive way to propagate this plant is by sowing seeds. This option will allow you to grow several healthy and strong bushes at once. However, this method is suitable only for those who are ready to wait for the bush to grow and get stronger. It may take several years until the first flowering of the plant.
But there is another way - reproduction of the forsythia bush with green and lignified cuttings, or layering.
Propagation of forsythia by layering
In order to reproduce the shrub through layering, you need to select a young flexible branch of forsythia, which grows in the lower part of the bush, at the end of summer or at the beginning of autumn, bend it to the ground and dig in with fertile soil. The young shoot will take root after a while. To speed up this process, you can slightly cut the bark on the branch in the place that will be covered with earth. With this option for breeding forsythia, as early as next spring, you can cut off the shoot from the main bush and, if desired, dig it up and transplant. The bush, propagated through the layers, will bloom in a year.
Propagation of forsythia by cuttings
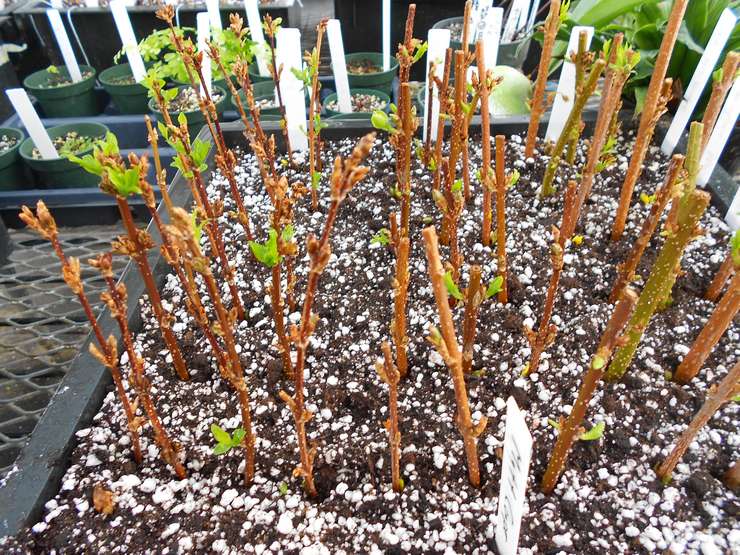
Forsythia can be successfully propagated using lignified cuttings. For this, in late autumn or winter, during the dormant period of the plant, it is necessary to prepare the material. Thick annual shoots of the bush, about 15 cm long, are perfect.Until spring, the cuttings should be stored in a cool cellar or on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. In the spring, cuttings can be planted in a greenhouse or immediately on a garden bed, having previously updated the slices.
Reproduction of forsythia is also remarkably carried out by green cuttings. In this case, the material must be prepared in late spring or early summer, when the flowering of the plant has already ended. You can plant cuttings in the ground immediately if the weather is not very hot, or you can wait until autumn.
Cut branches take root surprisingly quickly. When forsythia is propagated by cuttings, you can leave them in the water and they will soon take root and be ready for planting. For green cuttings, soil mixed with sand is suitable. It can be planted either directly in open ground or in separate boxes. Prepared cuttings must be deepened by
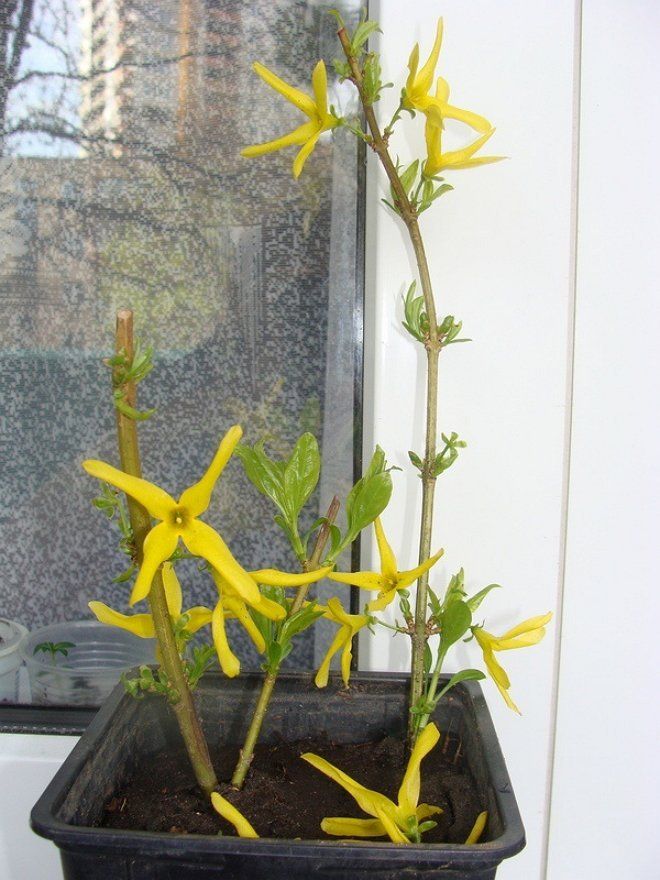
Reproduction of the forsythia bush through grafting is very effective - the cuttings will take root in one month. Until the plant takes root, it must be looked after. Cover young forsythia from a lot of direct sunlight in hot weather, and keep the soil moist. These actions will help the plant take root faster. When this happens, you can transplant the bush, but experienced gardeners are advised to wait and let the young bush overwinter under a cover of spruce branches or straw, and only then, in early spring, transplant to a permanent place.
Follow-up care after transplant
It is not enough to know how to root forsythia with cuttings to obtain an attractive shrub for decorating a garden.
It is also important to observe proper care after transplanting to a permanent location of the plant.
Preparing the soil for transplanting a seedling
A yellow shrub in the spring requires a properly selected soil. The culture does not tolerate acidic and heavy soil. It is also necessary to avoid places with a closely located water table. Before planting a seedling, you need to mix the soil from the planting pit with humus and sand in a 1: 1: 2 ratio.
Additional Information! Before planting, a drain is placed in the pit. For this, large crushed stone is used.
Watering
Moisture is essential for the development of the shrub. Water the seedling as the soil dries.After the seedling gets stronger, the frequency of watering is reduced to 1 time in 2 weeks.

Seedling care
Fertilization
In order for the flowering of the culture to be exuberant, fertilizers must be applied. In the first year after planting, top dressing is not used. In the second year in the spring, after awakening the buds, nitrogen fertilizers should be used. To increase the color, potassium-phosphorus fertilizers are used, which stimulate the formation of buds. After the bush stops blooming, fertilizing is reduced. Complex fertilizers can be used in summer. At the end of summer, organic fertilizers are used.
Pruning bushes and sheltering for the winter
Autumn is the period when you need to prepare the culture for the first frost. A few weeks before frost, you need to cut the bush. All branches are shortened, and damage to the crop is removed.
The bush must be carefully tied with twine and bent in the ground. The root is covered with a mixture of humus and foliage
Branches - fallen leaves or agrofibre.
Autumn harvesting of cuttings
Interesting! In the spring it is necessary to open the bush. Otherwise, mold may develop on the bark.
Forsythia is a spring shrub that will decorate any garden. Propagated by cuttings, seeds and cuttings. The last method is the most common, as you can get the required number of seedlings. Reproduction of culture by cuttings in the summer allows you to plant young shoots in open ground. Experienced gardeners recommend seedlings for seedlings from 1 year old.
Follow-up care
Forsythia does not need special attention of the gardener, as it is an unpretentious representative of the flora. The culture requires minimal maintenance activities. Adult forsythia practically does not need to be watered, with the exception of dry weather for a long time. To irrigate golden lilacs, 12 liters of water are enough. After the procedure, you can begin to loosen the trunk circle.
So that the culture does not lose its decorative qualities, it is worth constantly destroying the weeds that grow nearby. This event helps to protect shrubs from diseases and pests. Golden lilac needs feeding three times per season:
- during the awakening of the culture, it is worth spreading a little manure and watering the area abundantly;
- in mid-April, you need to fertilize forsythia with minerals;
- after flowering it is necessary to use "Kemira".
Forsythia is good at sanitary and formative pruning.
Sometimes there are lesions of the culture with moniliosis and bacteriosis.
Growing forsythia at home is a simple process. The main thing is to propagate the culture correctly and accurately. In spring, summer and even autumn, gardeners can start harvesting material, which will subsequently allow them to decorate their territory with a decorative bright representative for many years.
You can watch the breeding of forsythia in the video below.