What to plant next to in a flower bed?
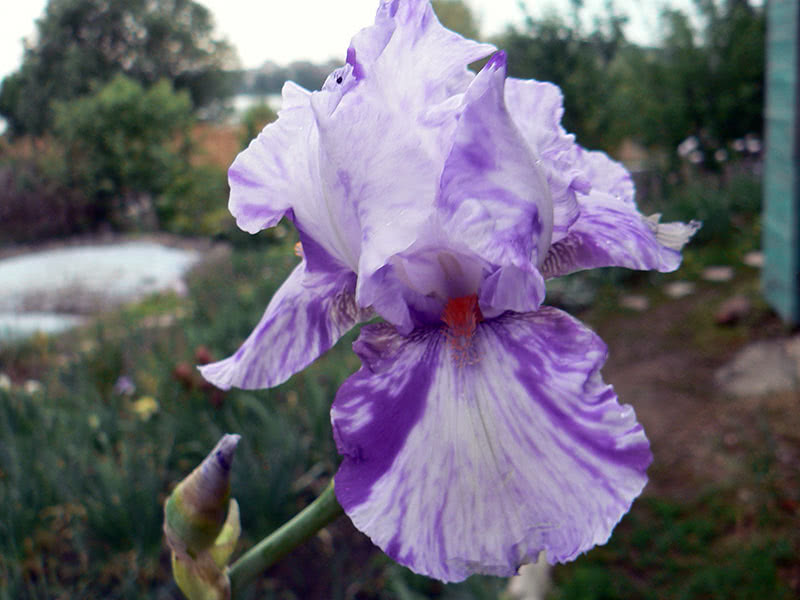
Irises are used mainly for decorating flower beds on the site, while many schemes are presented, each of which is in demand. If we consider blooming irises, then you can use different color schemes. The combination of one- and two-color irises looks very stylish and impressive, while one of the shades can be matched to the tone of monochromatic plants.
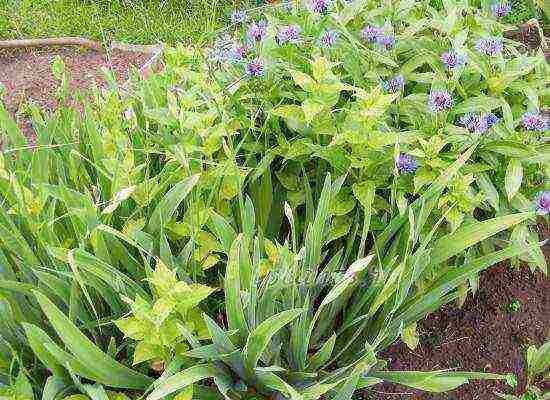
A pond lined with irises looks pretty nice. In addition, plants have a positive attitude to moisture. Irises can be combined with other flowers. They look great in various ensembles, but there are exceptions.

So, it is worth adhering to the following recommendations:
if irises of similar tones are planted, then they do not look very good, therefore, when planting seeds, attention should be paid to the color versions of future plants;
it is not necessary to plant varieties with bright and pale colors together, since the latter will be lost against the background of the former;
if two-color variants grow together, but of different varieties, it will seem variegated and disharmonious;
do not plant irises of different dark tones next to each other.

Irises should be combined in flower beds with the following plants:
- lupins and delphiniums;
- lilies and poppies.
Important! Since the root system of these plants develops at different soil levels, they feel great around. Such a composition will decorate the flower bed, so it is better to place it in the center.
And along the edges you can arrange forget-me-nots, marigolds or pansies.
Do not forget about roses, because iris greens perfectly cover the stems of roses, thereby providing good growing conditions. If you plant irises in artificial reservoirs, then a hosta, a bathing suit, will fit in the neighborhood, but you can also plant any moisture-loving plant. With the help of irises, you can create amazing and unforgettable compositions.
For information on how to plant irises, see the next video.
How to care for irises in the garden
Iris requirements are minimal. If you follow the instructions on the rules for planting and caring for irises, then you can easily grow beautiful ornamental plants in your flower bed.

After planting, it is imperative to weed the flower bed from weeds several times and loosen the soil
Note! Be very careful when loosening the soil. The fact is that the root system of the flower is located close to the surface of the upper soil layer. Sloppy work can damage the roots of the cockerel
Careless work can damage the roots of the cockerel.
Watering mode
Iris flowers love moisture, so on dry days they need to be watered daily. In other cases, 3 times a week will be enough.
Important! Drops should not fall on iris leaves
How to feed irises in spring for lush flowering in the garden
To achieve lush flowering, it is recommended to apply mineral fertilizers to the soil. Top dressing is usually done three times. The first time in early spring, then at the time when the buds begin to form, and the last time after the iris has faded.
For each top dressing, supplements of different composition are selected. For spring, nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers are suitable. The second time the plant needs more nitrogen and potassium. And after the end of flowering, it is worth adding more phosphorus to the soil.
Features of care during flowering
During the flowering period, the plants are especially stretched in height. To prevent the wind from breaking the stems, it is recommended to tie the irises to the support.

You can watch flowering in late spring or early summer.
Note! No need to feed irises during flowering
Preparing for winter
In order for the plant to successfully survive the winter, it is necessary to perform a number of measures aimed at preparing for wintering.
First, you need to prune the stems. This procedure will help to preserve the spectacular appearance of the plant for a long time. Secondly, do not forget to make mineral fertilizing, because in winter the plant will receive less nutrients. Thirdly, killer whales need to be hidden from the cold for the winter. For this, film or polyethylene is suitable, which will allow you to keep warm. The shelter is removed already in the spring, when the possibility of frost is minimized.
Some varieties are recommended to be dug out for the winter. They need to be dried and the roots hidden in a dry ventilated room. After the soil warms up to at least 10 ° C in the spring, it will be possible to transplant the roots into the ground.
Pruning
After the irises have faded, pruning must be done. To do this, with a sharp tool, you need to remove flowers that have ceased to bloom, along with a receptacle or even a stem. The procedure should be repeated in the spring, cutting off the leaves that have withered or dried up.
Note! When removing parts of the plant, it is important not to damage the leaf plates.
When is it better to plant daffodils: planting dates at different times of the year
Planting daffodils can be carried out at different times of the year, depending on this, it will have its own specifics:
- Late summer and early fall planting are two of the preferred options that most seasoned gardeners recommend. You can start planting these flowers from mid-August and during the first few weeks of September, since during this period the most active growth of root shoots is observed.
- Spring planting is also acceptable, but it is practiced in most cases if, for some reason, a good time was missed in the fall. Without fail, it must be preceded by keeping the planting material in fairly cold conditions for 2-3 weeks. To do this, you can put it in the refrigerator, but it is necessary to avoid placing it in the freezer, since too low a temperature can destroy the tubers. Without observing these measures, in fact, it is never possible to get a strong and resistant to adversity plant, which will negatively affect the quality of its flowering. The most optimal time for planting is in mid-April, when the last snow melts. It is not recommended to delay with this process, as this will lead to the fact that the plants will lag behind in their development and flowering may be completely absent for two seasons.
Where to plant
Certain attention will need to be paid to the choice of a place in which it is planned to plant daffodils. Some of the criteria that influence this process are discussed below:
- Most varieties of daffodils are not demanding on the degree of lighting and tolerate partial shade much better than direct sunlight throughout the day. However, you should not completely deprive them of natural light either, so it is not recommended to plant these flowers near large structures, buildings, structures, too large bushes or trees. The only exceptions to the rule are certain light-loving varieties, which must be planted in open areas in order to obtain the maximum amount of sunlight.
- The soil also does not really matter, but it should not be too depleted, because with an acute shortage of the required amount of nutrients and a set of useful chemical elements, daffodils stop blooming and lose vitality.
- There should be no drafts in the chosen place, moreover, it must be reliably protected from cold winds.
- It is better to avoid light sandy soils, since after the onset of cold weather they practically do not retain heat in themselves, which can lead to freezing of the planting material. The rest of the soil characteristics, for example, the acidity level or its structure, are not of fundamental importance.
- A place with drained loamy soil will be the ideal solution, since it is these conditions that are most suitable for growing any bulbous type of plant.

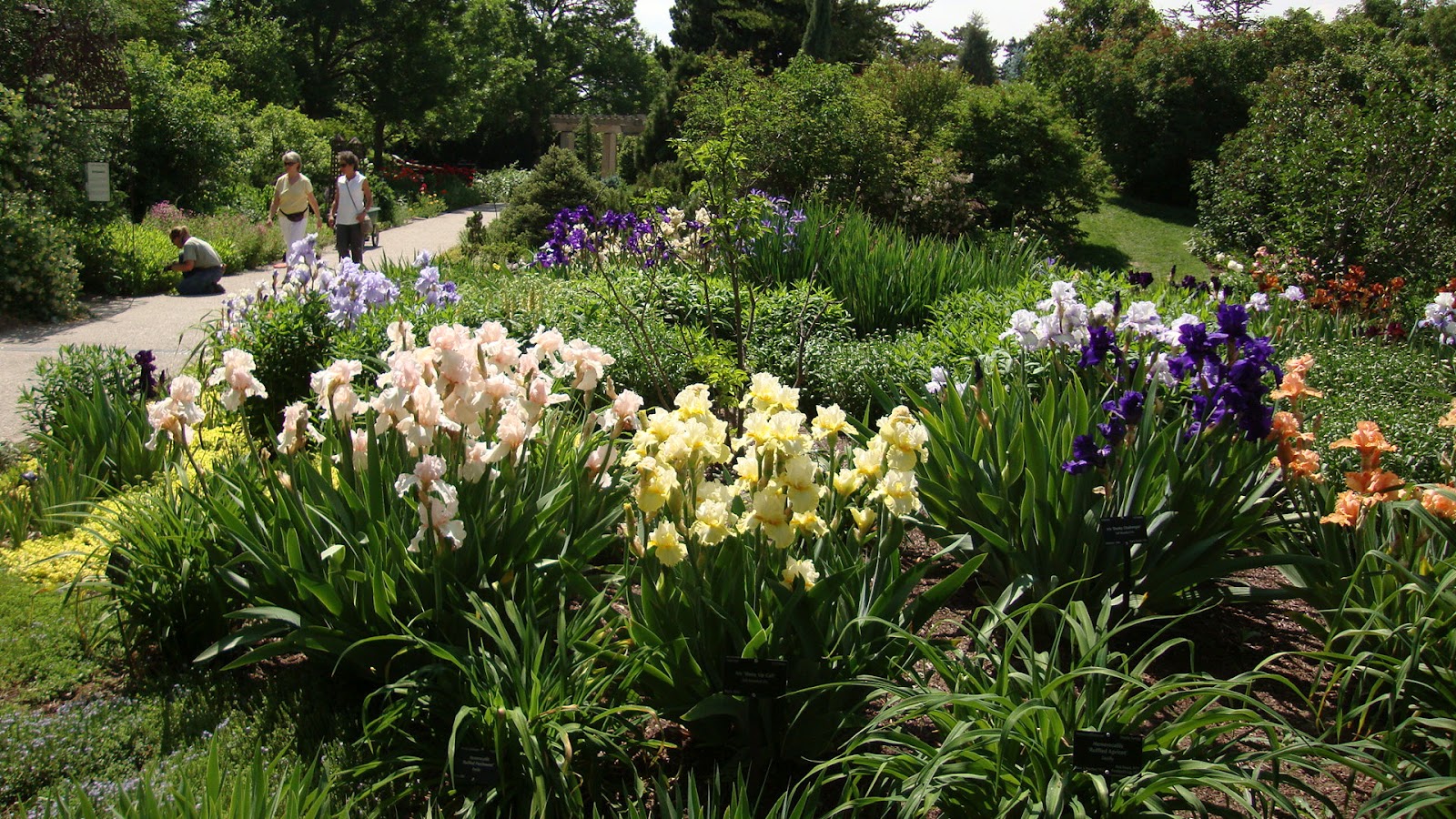
Successful combinations with other colors
Irises can be combined with a variety of plants. The result is an excellent composition.
Spirea
This plant is distinguished by small flowers of different shades. They can be crimson or pure white. Inflorescences are distinguished by a spike-shaped, pyramidal, paniculate shape.
Ephedra
These crops are shrubs. They differ in different sizes - from 2 centimeters to 5 meters. Plants decorate small leaves. They bloom in June-July.
Lupine
The plant is characterized by an apical inflorescence, which includes many flowers. They differ in different shades - white, pink, yellow. There are also purple, red, cream inflorescences.
Pansies
The upper and lower petals differ in shade. There are flowers with yellow, purple, blue petals. They are also blue, white. Plants are monochromatic and spotted.
Delphinium
The flowers are blue, purple, white. They form decorative pyramidal inflorescences. The plant is 4 to 45 centimeters long.

Poppy
The culture is characterized by large flowers. Most often they are red. Less common are white and yellow inflorescences.
Day-lily
The daylily is characterized by large six-part flowers. They can be yellow, orange or reddish brown. Inflorescences include several flowers.
Juniper
This is a beautiful shrub that grows up to 1-3 meters. In the gardens, tree-like plants are also found, reaching 4-8 meters. The leaves are needle-shaped or scaly-shaped.
Barberry
This plant is deciduous or evergreen. Semi-evergreen crops are also found. Barberry is decorated with thorns and leathery leaves. The culture is characterized by small fragrant flowers of orange or yellow hue.
Forsythia
It is a small tree that reaches 1-3 meters. The plant is covered with trifoliate plates. They are oval in shape and reach 2-15 centimeters in length. The culture is characterized by rich yellow flowers. They resemble a bell in shape.
Hosta
This plant is characterized by a spectacular appearance. The hosts are distinguished by attractive leaves. The flower is considered versatile and unpretentious to care for. It easily tolerates cold and drought.

Astilba
The plant is distinguished by small openwork flowers that form apical inflorescences. They have a red, white, lilac, pink hue. Flowering lasts from June to August. Varieties with drooping inflorescences look especially attractive.
Peas
The flowers resemble moths in shape. The plant is characterized by lush flowering. It starts in July. With proper care, flowering lasts until frost.
Saxifrage
The plant is characterized by long creeping stems. In height, the culture reaches 5-70 centimeters. Leathery leaves have different shapes - pinnate, oval, diamond-shaped. In May-August, small flowers appear on the saxifrage. Most often they have a white tint, but sometimes there are red, pink, yellow varieties.
Phlox
There are many types and varieties of phlox, which differ significantly from each other. Flowers can be 2.5-4 centimeters in diameter. They are characterized by a tubular-funnel shape. Most of the plants are perennials.
Currant
It is a perennial shrub that can be spreading or compact. In height, it reaches 100-200 centimeters.The green fluffy leaves turn brown with age.
Gooseberry
This is a small shrub that is no more than 1.2 meters in height. The plant is complemented by spines and petiole leaves of a round or heart-ovoid shape. The fruits are oval or spherical berries that ripen from June to August.

Thuja
It is an evergreen tree or shrub. Young plants have soft, pale green needles. Adult crops have scaly needles of a rich green color.
Derain
This is an ornamental culture that belongs to the Kizilov family. Under natural conditions, the plant reaches 4 meters. Young branches are green in color and then turn reddish.
How to plant flowers in the fall
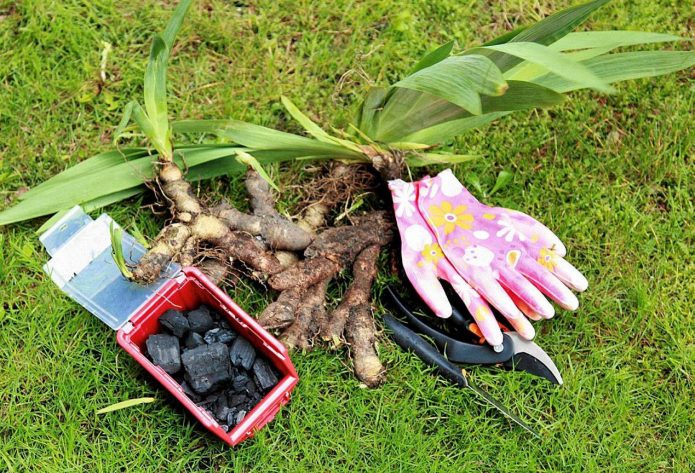

It should be borne in mind that not all iris varieties can take root in any region - some will not be able to grow in cold climates
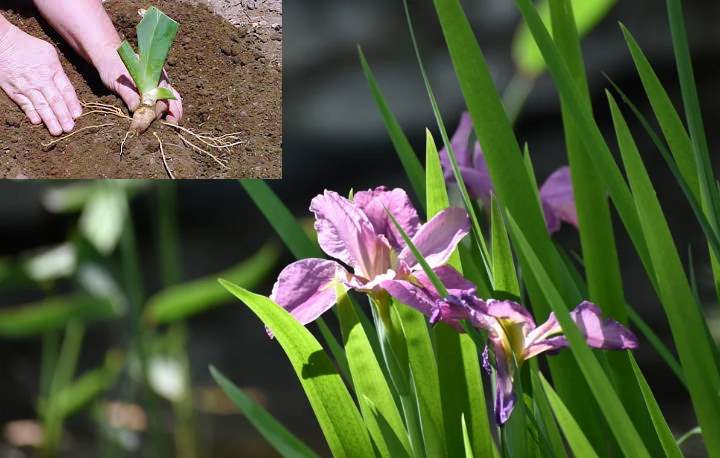
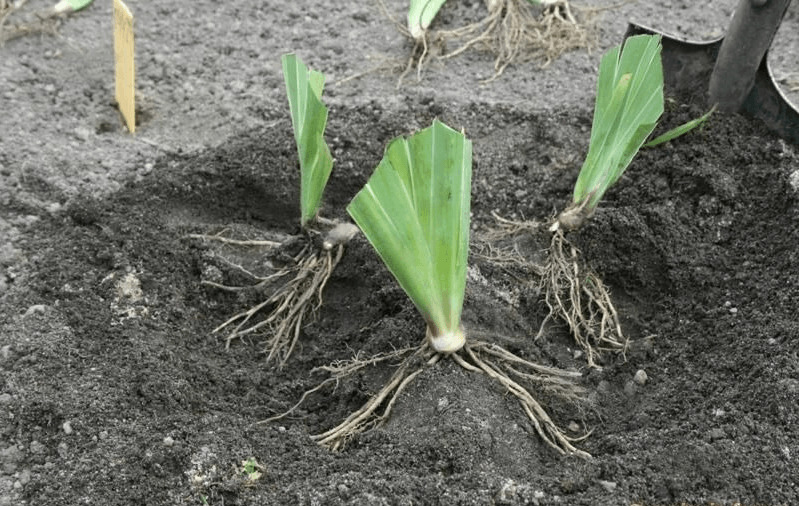
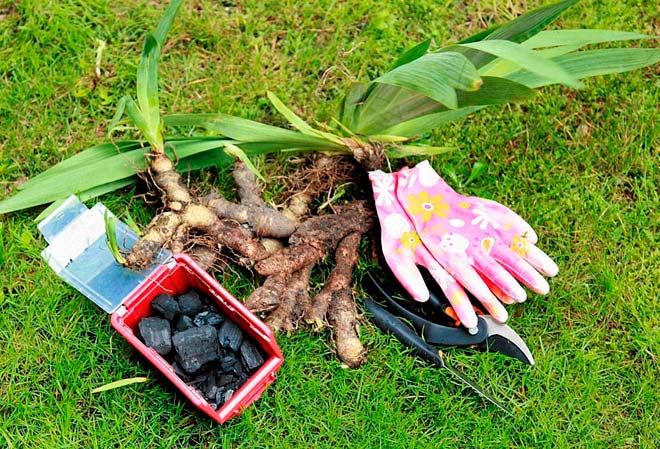
Different varieties of irises are used for planting. They can be bulbous and rhizome. The latter are planted by dividing the rhizome. There are also bearded, dwarf, Siberian irises. Most often, rhizome plants are found in flower beds. The planting features of different varieties are not very different.
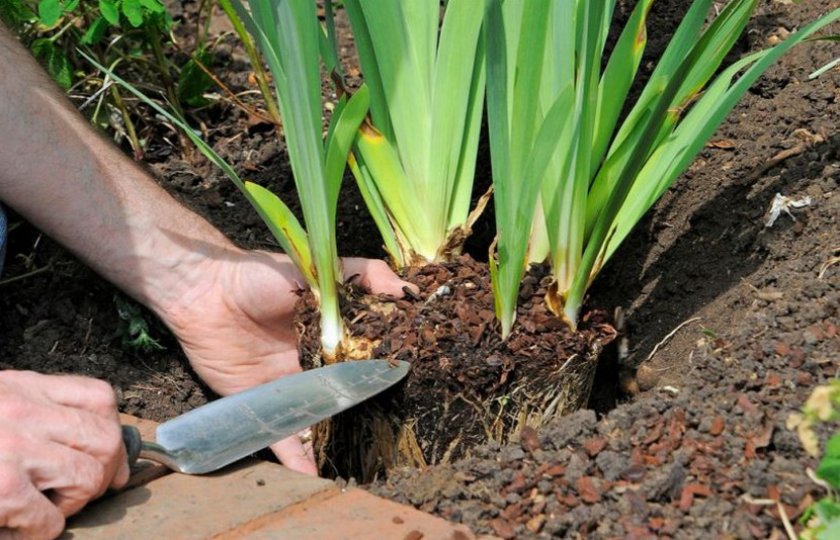
2–3 weeks before transplanting, the plant is stopped fertilizing and almost never watered. You need to dig out the bush with a pitchfork, retreating a short distance so as not to damage the rhizome
They extract it with a large clod of earth, and then carefully divide it
How to choose a landing site

Excess moisture in the ground will lead to brown spots on the leaves.
The place must be chosen correctly so that the irises grow well. The most important things to consider are humidity and light levels. Flowers do not like an abundance of moisture - from this, their roots can rot. Therefore, it is advisable to choose a high place where groundwater does not accumulate, and in the spring the snow melts most quickly. For the same reason, it is recommended to slightly raise the bed with irises. Only a few varieties prefer an abundance of moisture, for example, marsh iris.
Therefore, you need to find a plot in the garden with a minimum amount of shade. But you shouldn't choose a very open area, exposed to winds.
The soil on the site should be slightly acidic, loamy. If it is very sandy, be sure to add clay. And to reduce acidity, it is recommended to dig it up with ash or chalk.
Garden and soil preparation

Clay soils with low pH are not suitable for irises
It is advisable to prepare the garden a month before planting. It should be free of weeds and neutral soil is preferred. You can fertilize it with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, ash or humus. You should not apply nitrogen fertilizers or manure, as this can activate plant growth, which is not necessary at all before winter.
The soil should be watered well several times so that it compresses and settles. All preparation is completed 1-2 weeks before landing.
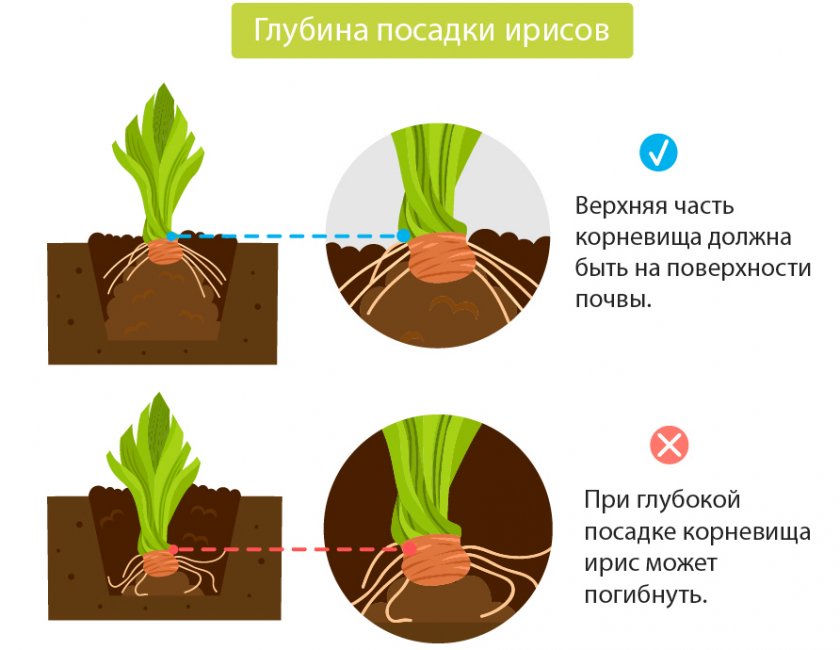
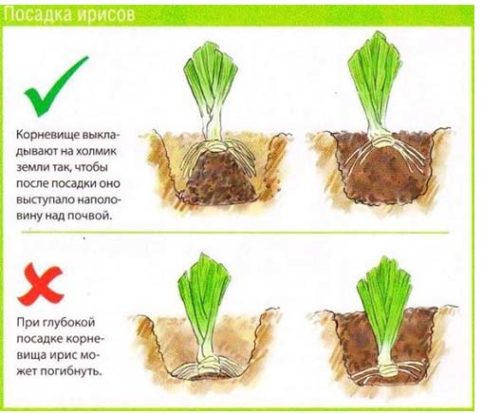
The holes are made to a shallow depth, since irises they do not like the rhizome to be completely covered with earth. The distance between the pits is made from 30 to 70 cm. It depends on the variety of plants. For undersized, 20-30 cm is enough. The higher the flowers, the more space they need.
How to choose planting material
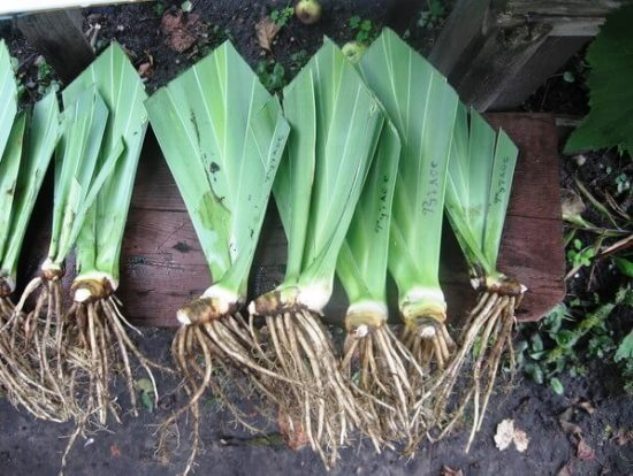

For planting, it is better to choose one-year-old shoots with a height of about 6 cm
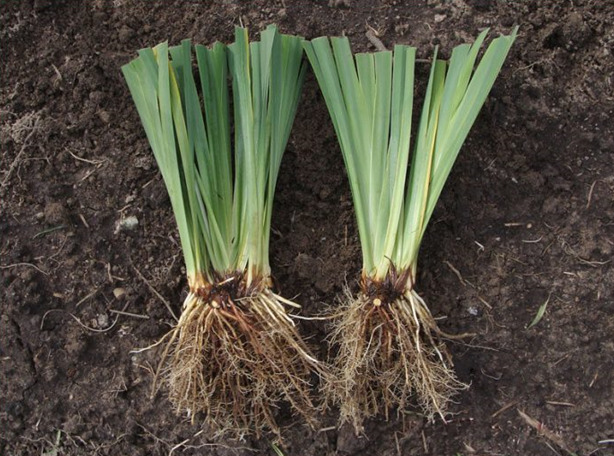
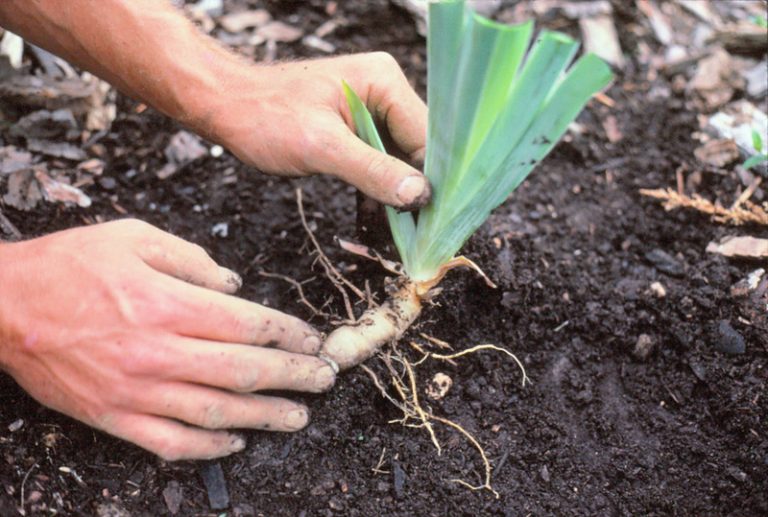
If the layers are taken from your bush, it is important to properly divide it. This should be done with sharp instruments so as not to damage the kidneys.
Each division should have a root piece of at least 10 cm, several young buds and lateral roots. They need to be pruned to 10 cm. Each layer should have green leaves, which are pruned with a "house".
Before planting, the layering must be disinfected by holding it in a solution of potassium permanganate for 10–20 minutes. Then dry well in the fresh air, preferably for several days. Sections can be sprinkled with ash to prevent rotting.
When buying bulbs for planting, you need to pay attention to the following important characteristics:
- root. It should be juicy, strong, without damage;
- the presence of kidneys. There should be several on the sides;
- leaves. They should be green with no rot.
The technology of planting irises in autumn in open ground
For transplant, you need to choose a dry, clear day. After preparing the beds and choosing planting material, you need to correctly follow the main stages of planting.
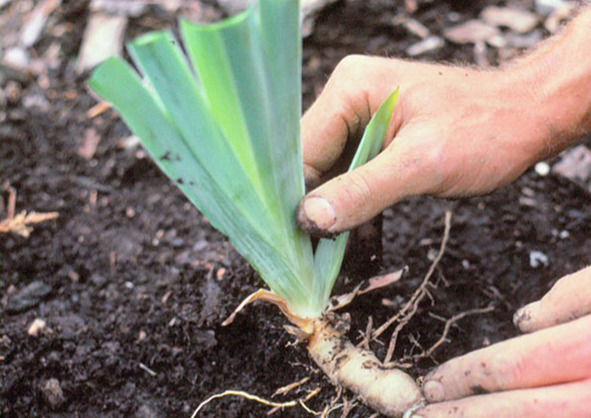
- Dig a hole no more than 10–12 cm deep. Make a small mound in the middle.
- Place the iris seedling on a mound, spreading the roots along the slopes and spreading them out.
- Sprinkle with earth and compact slightly. Make sure that the neck of the root and part of the rhizome remain in the air.
- Water the plant so that water does not fall on the leaves.
How to plant irises in open ground
You can plant irises until the end of September
It is important to find a well-lit area for them. An ideal place would be a flower bed or flower garden that is illuminated by the sun for at least 6 hours
You can spot them on a high bed or slope with good drainage. Some varieties can be grown in shaded areas that are well ventilated.
Once you have decided on the location, you need to pay attention to preparing the soil. It is better that it is slightly acidic (pH level 6.8)
Add sulfur to the ground (per 10 sq. M. 1 kg). This should be done to a depth of 10-12 cm.
It is important to apply the substance no later than 1 year before the planned planting of flowers. If the soil is acidic, you can correct the situation by adding lime
The dosage depends on the pH level. For loamy, clayey and sandy soils, about 0.2-0.3 kg of the product may be required.
The next step involves the correct location of the irises in the selected area. We recommend that you use a proven scheme. Place flowers at the tops of an isosceles triangle, keeping a distance of 30-50 cm between them. To activate the process of plant development, apply appropriate fertilizers to the soil. It needs to be nourished after loosening to a depth of 20 cm. Nitrophoska and diammophoska are suitable fertilizers (maximum 90 g per 1 sq. M.).
Once you complete all this work, it's time to decide on the depth of planting flowers. They must be planted in shallow holes that are slightly lower or at ground level. Pour some earth on the bottom, place the rhizome on it at a slight angle and straighten the roots. The fan of leaves should be directed towards the south. This will allow the bush to develop symmetrically. Fill the hole with earth.
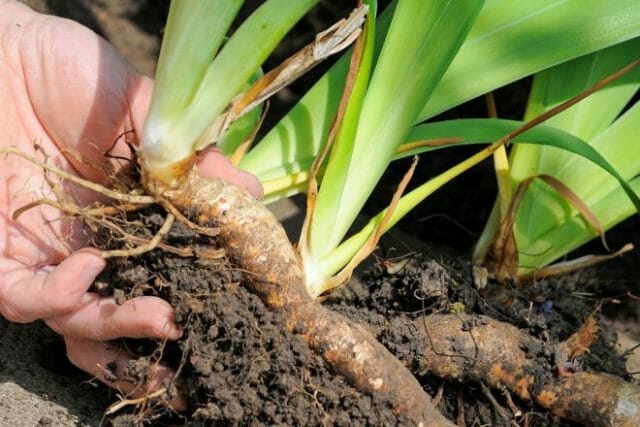

Cultivation of irises - when is it better to plant and transplant bearded irises, is it necessary to cover irises for the winter, how to deal with pests
When is the best time to plant and replant bearded irises?
Planting and replanting bearded irises is possible throughout the growing season. Even in the midst of flowering, plants take root well, but the best time is right after flowering. At this time, the active growth of roots begins in irises. The planting unit (delenka) is an annual link of the rhizome with a diameter of 1-2 cm and a length of no more than 3 cm, with a fan of leaves cut by 1/3, and a bunch of roots 5-7 cm long ...
Iris bulbs are dug up and nests are divided no earlier than 4-5 years after planting. They are planted in September-October to a depth of 5 cm at a distance of 15-25 cm.
In what areas is it desirable to plant?
When planting irises, the choice of location is important. It must be remembered that these flowers are plants of the first half of the day. They do well if they are illuminated by the sun before noon, and bloom profusely if the neighboring large plants (trees and shrubs) do not take moisture away from them. Therefore, it is advisable to allocate well-lit areas for irises with a slight slope to the southern and south-western sides, from which snow is not blown off in winter. Soils are preferable of light texture, well-drained, with acidity closer to neutral. To improve the mechanical composition of loamy soils, before the autumn digging, manure, peat or compost (1-2 buckets per 1 square meter) and at least a bucket of river sand are introduced into them.Sandy soils require the addition of organic matter and a small amount of clay.
How to propagate varietal irises?
Varietal irises are propagated by dividing the bush. Plants to be divided are usually dug up with a garden pitchfork. The rhizomes are shaken off the ground and cut so that each annual growth has a bunch (fan) of leaves. To reduce evaporation, the leaves are shortened by 2/3 of the length, and the roots by 1/3. Old links of the rhizome that do not have good roots and leaves should not be thrown away, since they have dormant buds, which, after planting, will start to grow and provide additional planting material. They also need to be inspected, damaged parts removed and processed along with the cuttings. All sections are made with a sharp knife so that the wound surface is smooth.
Freshly cut cuttings for disinfection for 10-15 minutes. placed in a dark solution of potassium permanganate. Then they are dried and added dropwise before planting.
How to care for garden irises during the period of intensive secondary growth?
From mid-July to mid-August, new shoots are formed, rhizomes grow, flower buds are laid and formed. At this time, the consumption of phosphorus and potassium increases in plants. Top dressing with superphosphate (50-60 g / m2) and potassium salt (20-30 g / m2) is carried out on wet soil, followed by light loosening
It is important to remember that exceeding the dosage is dangerous for iris rhizomes. Excess nitrogen in the second half of summer causes fattening of plants and their death in winter
Do I need to cover irises for the winter?
With the onset of the first frost, the leaves are shortened by 1/3. When temperatures are below freezing, the irises are covered. To protect the plants not only from frost, but also from damping off, they put a dry shelter or use non-caking material. You can cover the irises with dry sphagnum moss, and on top of it - huts of spruce branches (in the absence of moss, you can take a dry leaf, but under it you must definitely put a bunch of short branches). In the spring, as soon as the snow melts, the moss must be slightly agitated to provide air access to the plants. Remove the shelter when the soil thaws.
How to deal with pests?
In early spring, the most dangerous for irises is the moth caterpillar: it gnaws at the leaves and flower stalks. Its activity is especially harmful in dry springs. For prophylaxis, granosan is introduced into the soil at the base of the bushes. Ottrips nesting in the leaf axils are helped by multiple spraying with a solution of karbofos or chlorophos (20-30 g per 10 l of water). In the second half of summer, in wet weather, naked slugs appear, eating leaves. To scare them off, sprinkle the soil around the plants with superphosphate. In warm, humid periods, bacterial rhizome rot is especially dangerous for irises. In case of damage, decaying areas are cut out to healthy tissue, and the sections are washed with a strong solution of potassium permanganate and covered with Novikov's liquid ("green" with glue). The causative agent of rot dies in direct sunlight, so the cut can be dried in the sun.
In late summer and early autumn, iris leaves are often covered with brown rust spots. Such leaves are cut and burned. The disease can be prevented by sprinkling the plants with Bordeaux liquid in the middle of summer.
.
How to prepare bulbs for planting
Bulbs for planting irises are purchased at the store. You can also use your own planting material. It should be checked for quality. Do not plant damaged or rotten bulbs in the ground. It is necessary to soak the iris bulbs in advance in a growth stimulator. For disinfection of planting material, solutions of potassium permanganate or antifungal drugs are used. After processing, dry the bulbs for 30 minutes.

Site selection and preparation
Iris bulbous varieties should be planted in areas:
- well lit, or better a little shaded;
- with nutritious and loose soil;
- neutral in acidity;
- where groundwater is deep.
When the soil under the irises is sandy, humus can be added. In heavy soil - wood ash, sand. It is advised to neutralize the acidity of the soil with crushed eggshells, lime.
In what time frame do you need to plant
Experienced flower growers believe that the planting of irises will be more successful in the fall. Flowers take root best of all at a temperature of +15 degrees. For distillation, it is advised to plant in early February. Then by the spring they will receive delicate bouquets.
Landing scheme
Before planting the bulbs, they dig up the earth, loosen it. It is best to fertilize poor soils with nitrogenous complexes. The holes are made small. The burial depth of iris bulbs depends on the size of the planting material. Large ones are placed at a depth of 6-7 centimeters, small ones - 3-4. The upper part of the root system should be left above the ground, not buried. You can place the bulbs next to each other. If the plantings are single, then the distance between the flowers should be 10 centimeters.