How to get rid of?
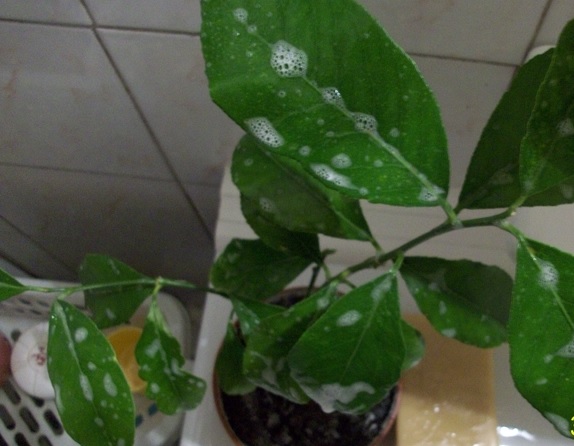
 You can fight these insects using different means. The easiest way to get rid of pests is natural cleaning, which involves washing and rubbing the flowers regularly. To do this, use ordinary water to which a few drops of a mild dish detergent are added. The sponge is moistened in water and individual leaves are wiped with it, after which water is sprayed from a spray bottle all over the plant, especially trying to get to the lower part of the leaves. You should also process the pallet, pot and windowsill.
You can fight these insects using different means. The easiest way to get rid of pests is natural cleaning, which involves washing and rubbing the flowers regularly. To do this, use ordinary water to which a few drops of a mild dish detergent are added. The sponge is moistened in water and individual leaves are wiped with it, after which water is sprayed from a spray bottle all over the plant, especially trying to get to the lower part of the leaves. You should also process the pallet, pot and windowsill.
If after a week the spider mites do not disappear, the soap solution is applied again. Not all plants tolerate such a remedy equally well, therefore, it is necessary to test the flower before applying it. To do this, a soap solution is applied to a small part of the sheet and the reaction is monitored.
Since the spider mite does not tolerate high humidity, it is possible to fight it with the help of frequent watering and spraying of the flower. After each moistening, the plant is covered with a transparent bag and left for several days. In conditions of high humidity, the insect dies. To avoid the greenhouse effect and the flower does not get sunburn, it should be placed in a shaded place.
Preparations such as acaricides help well to rid the plant of this small pest.
But it is necessary to handle flowers with this tool very carefully, because it is unsafe for people and animals. Sparing acaricides include:
- Fitoverm;
- Vermitek;
- Aktofit.
Such drugs contribute to the destruction of dormant female spider mites and eggs of future larvae, therefore they are used repeatedly to achieve the desired result. If the temperature in the room is below +18 degrees, these drugs will be ineffective.
The plant can be sprayed with chemicals such as:
- difokol;
- dienochlorine;
- azocyclotin;
- fenbutatin.
It is not recommended to use the same remedy more than four times, since spider mites begin to get used to it and develop immunity.
You can make your own special herbal tea at home, which is used as an acaricide. To do this, take 1 tbsp. l. ground cinnamon, 1 tbsp. l. ground cloves and 2 tbsp. l. Italian seasoning. All ingredients are mixed and poured into 1 liter of water, then brought to a boil, cooled and 2 tbsp. l. chopped garlic. It is filtered, after which liquid soap is added to the tea and poured into a spray bottle. The lower part of the leaves is sprayed with this solution every three days for two weeks.
At home, essential oils and organic salts help well against spider mites. Rosemary oil is used as an organic pesticide. It is necessary to dissolve a small amount of oil in water and spray on infected flowers. The peculiarity of such a remedy is that it has a destructive effect on ticks, but leaves other insects alive.
Potassium salts and fatty acids are abrasive. They should be used in the evening to keep the flowers hydrated longer.
The following insects are considered good helpers in killing spider mites:
- ladybug;
- predatory thrips;
- lacewing larva.
Since pesticides kill all insects in a row, the spider mite population begins to grow because of this. Therefore, it is better to avoid using pesticides such as imidocloprid, malathion and carbaryl.
Preventive measures
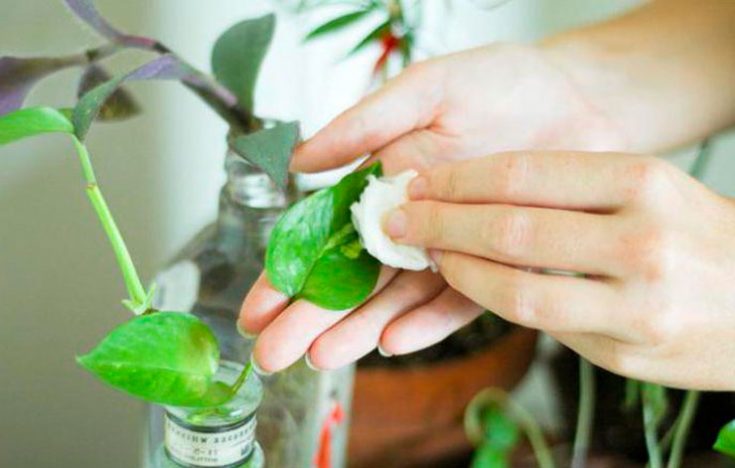

Almost all types of mites, with the exception of a few species, do not tolerate excess moisture.Many growers are focused on this feature and successfully prevent the appearance of the parasite.
With proper care of indoor plants, it is possible to quickly recognize this dangerous pest and destroy it in time. Therefore, there are proven methods to prevent the appearance of various parasites. For example:
- Every three days it is recommended to wipe the leaves of indoor flowers and other ornamental plants with a damp cloth. To do this, you need to take hot water and rinse the rag well each time.
- Do not let the soil dry out.
- Constantly remove fallen leaves from the flowerpot, which can serve as a shelter for ticks.
- Flowers are regularly fertilized and the desired temperature and humidity are maintained. If the plant is strong and healthy, then it may be too tough for even ticks.
Novice growers believe that you can get rid of ticks by submerging the plant completely in water. In fact, this is not the case. Firstly, you can harm the flower itself, and secondly, an air bubble forms around the tick. Of course, if you keep a flower in water for several hours, then the effect will be obvious, but it is unlikely that any flower can withstand it. The most effective method is rubbing the leaves with hot water, but this method will not be effective if many spider mite colonies are found on the plant.
In order not to spend a lot of effort and energy on fighting flat pests, it is better to adhere to certain rules for caring for indoor plants. If you really like flowers so much and you can't live without them, then you need to take care of them properly.
Danger of mites for indoor plants
To understand why this pest is dangerous, it is necessary, first of all, to understand: what does a tick do when settling on plants? Living on the leaves, he slowly feeds on the liquid component of their cells, gnawing holes. Because of this, the leaves change color, and over time they begin to dry and die off.
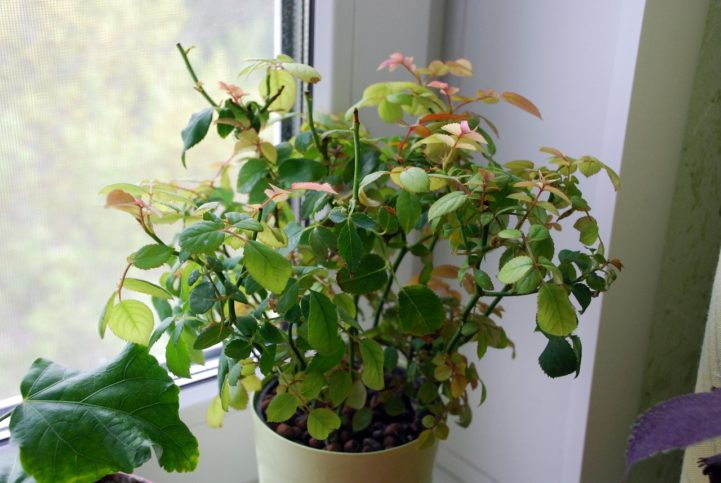

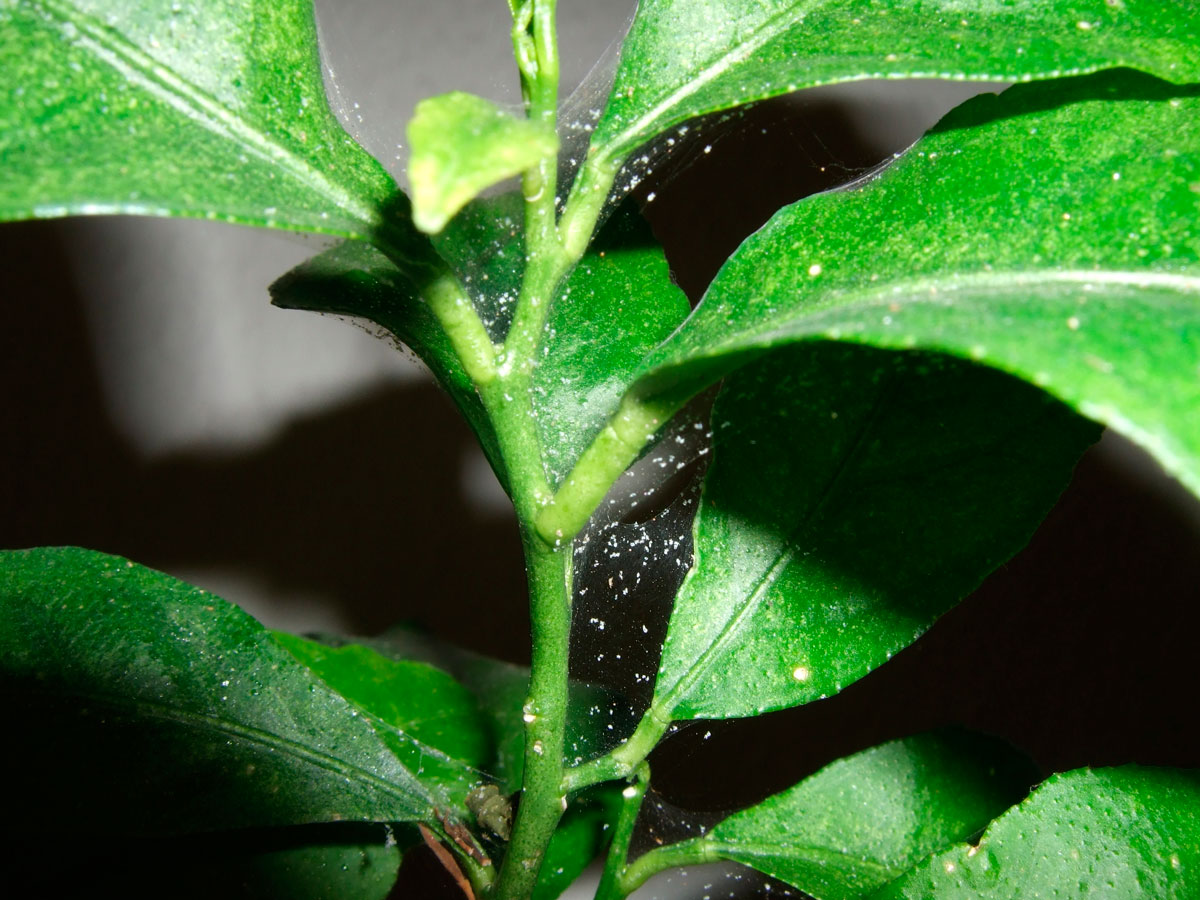
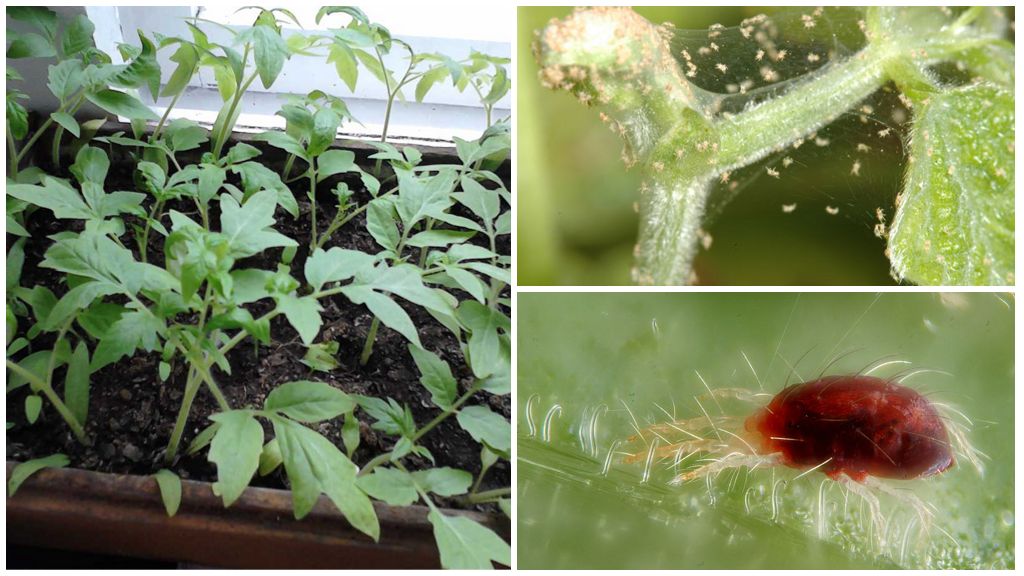
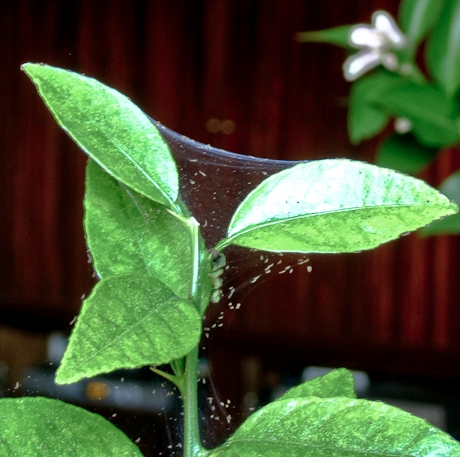
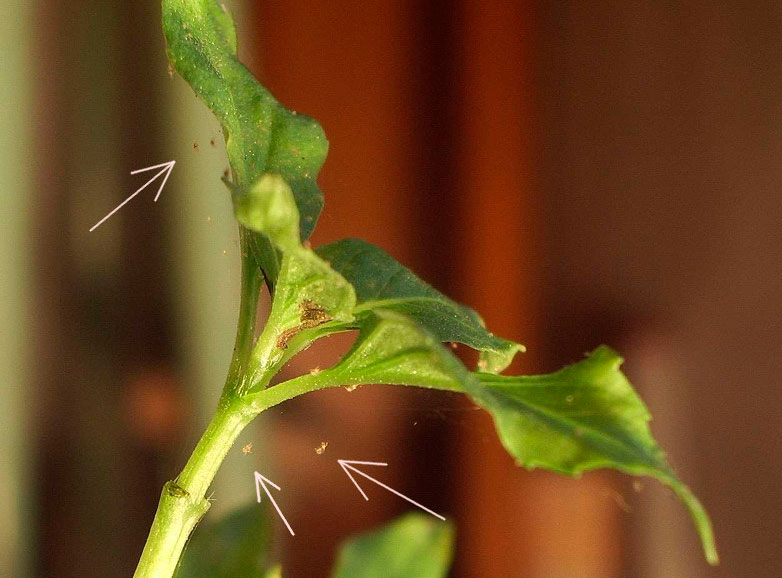
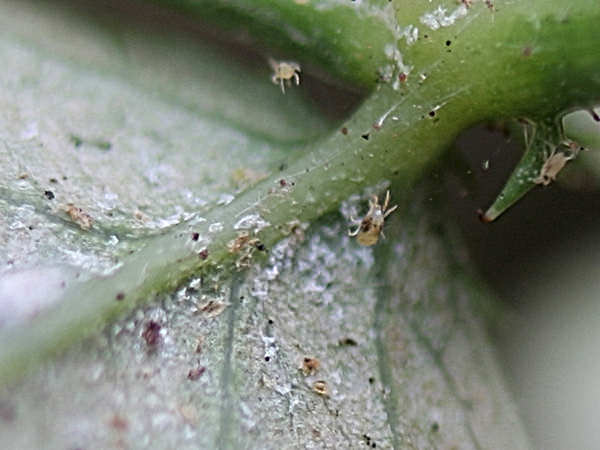
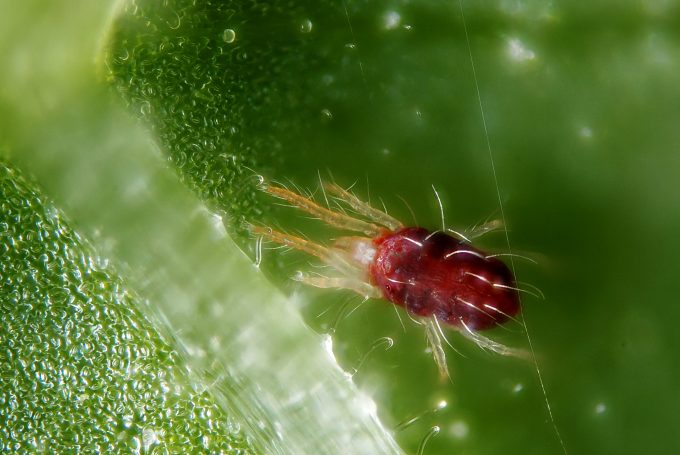
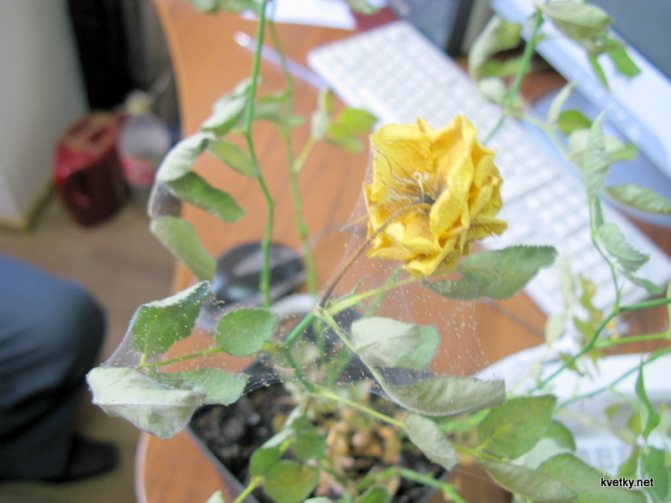
Spider mite infested plant
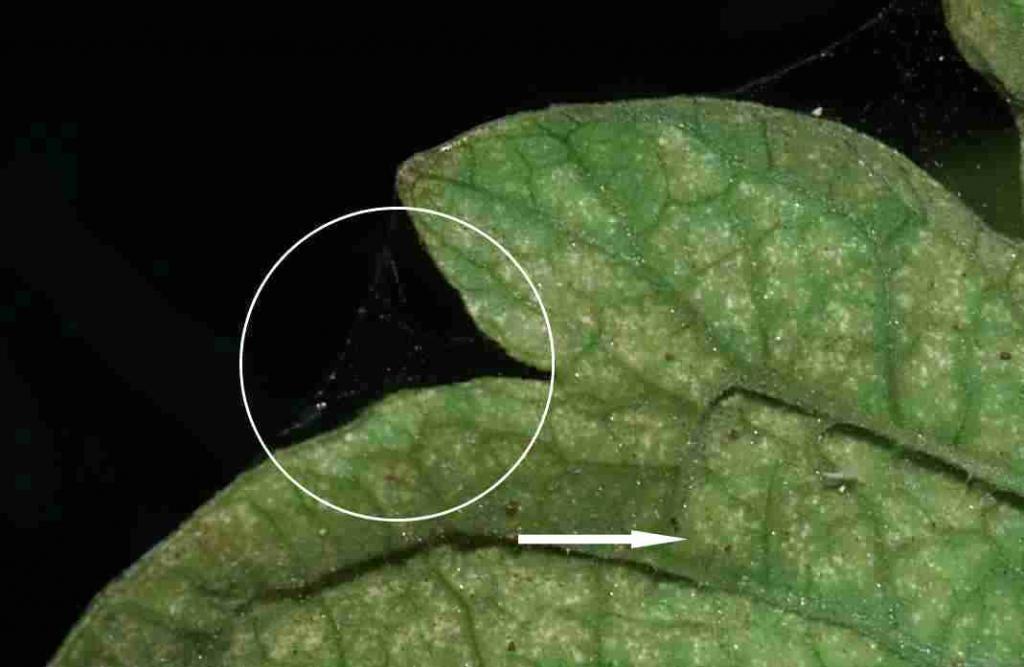
This type of mite was called spider mite, since the leaves affected by it are braided by the pest with a thin cobweb
If you do not pay attention to this and do not take timely measures, then the plant is doomed to death.
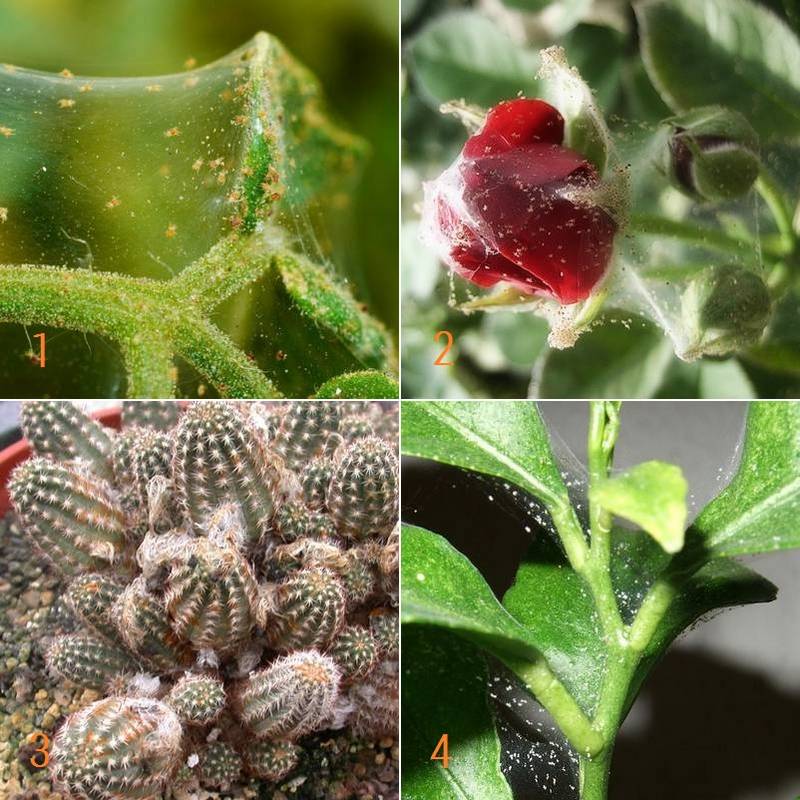
Also, most ticks prefer to destroy the flowers of plants. Their favorite flower is the indoor rose. Having settled on it, the mite gradually destroys all beauty, harming the decorative properties of the houseplant. These are the main signs of the appearance of a tick on plants. Noticing any deviation from the above, immediately start fighting the pest. So, you found a spider mite on your indoor flowers: what to do next?
Prevention measures
The main factor in the appearance of spider mites is dry air, so the best warning is to spray water on plants during dry weather. In this case, you need to ensure that water does not accumulate in the core of the stem.
Pay special attention to plants during the winter season, as water evaporates slowly due to the reduced day length and low temperatures. To get rid of the parasite, the plant should not be immersed in water, since when in contact with water, ticks acquire armor in the form of air bubbles.
To get rid of the parasite, the plant should not be immersed in water, since when in contact with water, ticks develop armor in the form of air bubbles.
A homemade solution will help prevent infection.
- To prepare it, you need to mix 20 g of cinnamon, 40 g of Italian herbs, pour 1 liter of water.
- Boil, cool and add 40 g of chopped garlic.
- You can also add 2-3 drops of soap.
For prevention purposes, process the leaves every 2 days for 2 weeks.
Nuances of prevention at the site:
- Regular cleaning of garden tools with disinfectants.
- Deep digging of the soil in the fall.
- During the fruiting period, regular weeding and subsequent loosening.
- Compliance with the advice of crop rotation.
- Regular watering (as the earth crust dries up), soil mulching.
- Daily inspection of leaves for contamination. If traces of the parasite are found, cut off and burn the infected leaf.
Getting rid of spider mites can be a lengthy and onerous task. Try not to create conditions that are beneficial for the reproduction of the parasite (heat, moisture, dryness).
At home, do wet cleaning, observe sanitary standards, wipe dust not only on cabinets, but also on leaves. On the site, regularly ventilate the greenhouse, get rid of weeds in time.
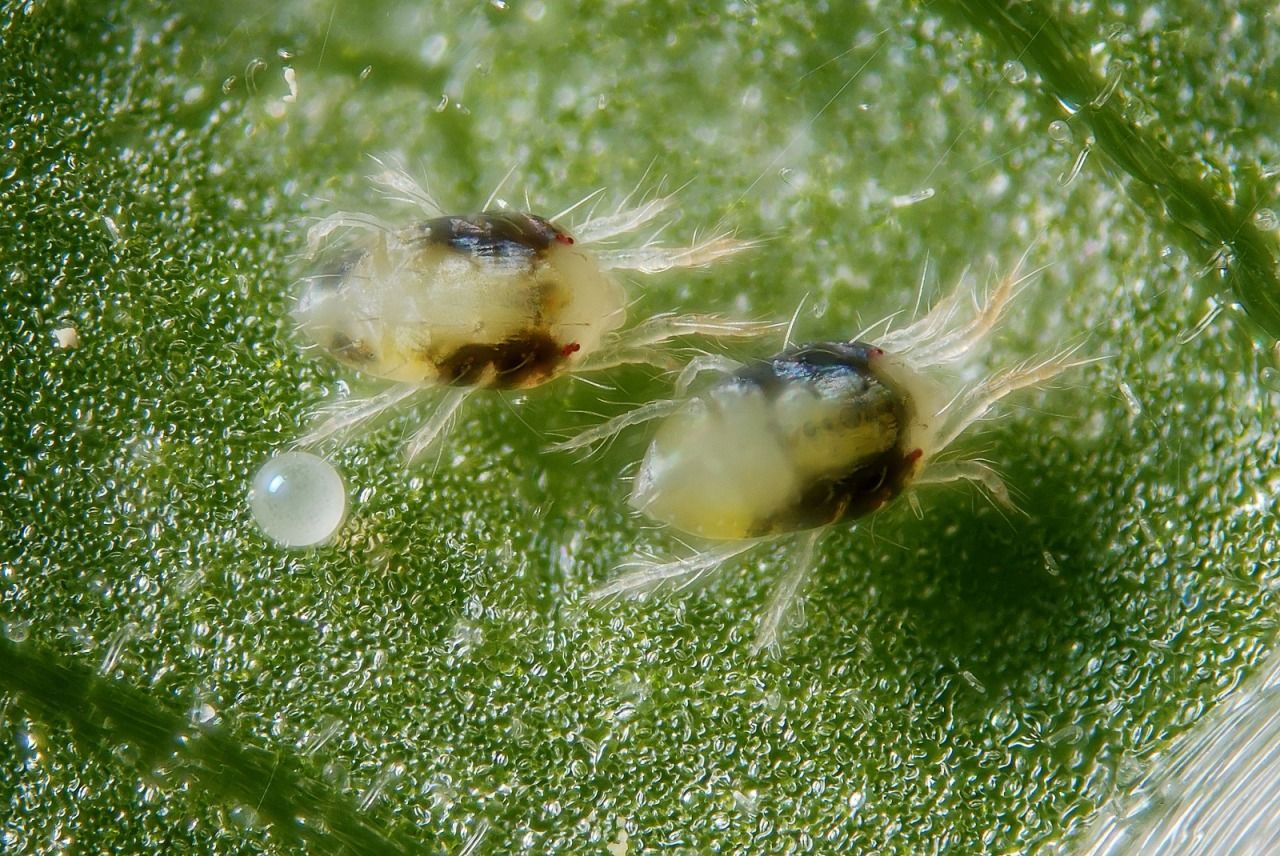
Spider mites
Tetranychus telarius form a cobweb, but the grower cannot always see it right away. Sometimes it is so small and thin that it is clearly visible only with a huge accumulation of mites, or when the plant has already completely dried out. Therefore, if you find suspicious spots on the leaves, do not seek to look for cobwebs, look for the skins that remain from the molts - they are usually gray or almost white in color, you can see them on the back of the leaf, they look like fine dandruff. This is due to the fact that the common spider mite lives mainly on the back of the leaf, and weaves a cobweb between the veins, if you look closely, you can see it with a magnifying glass along the central vein. But if nothing was found, this does not mean that there are no ticks.
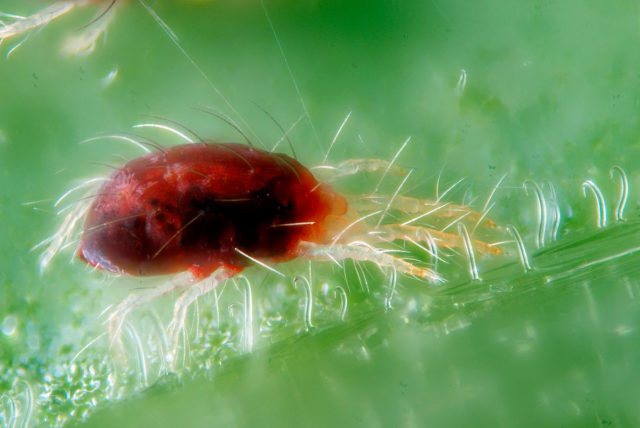
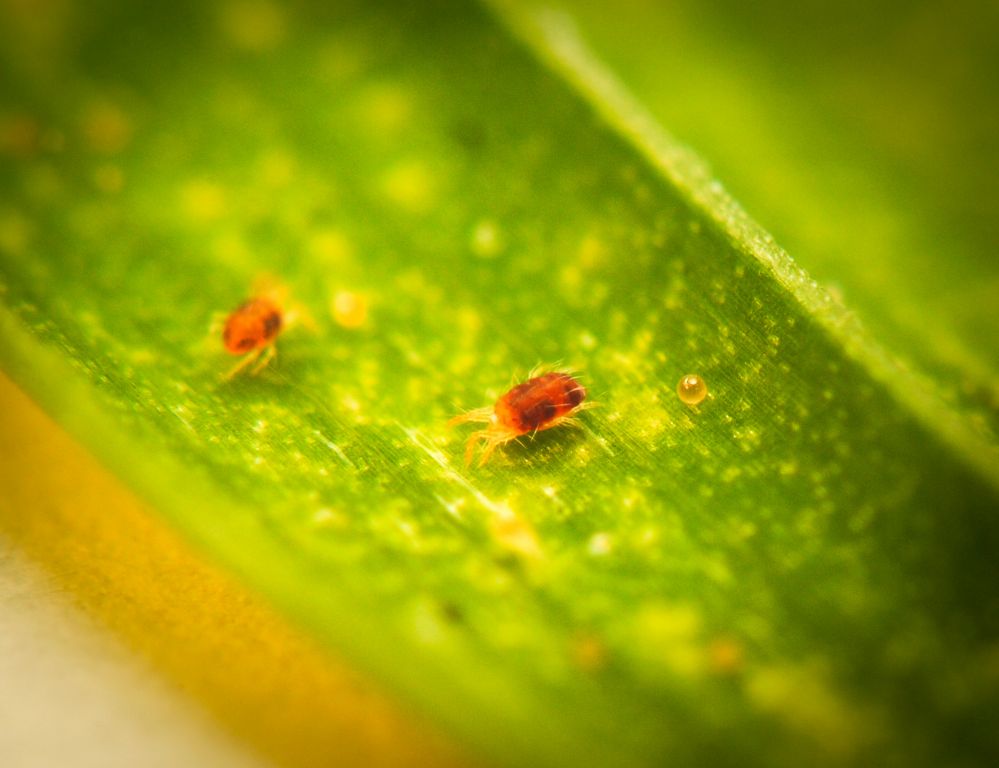
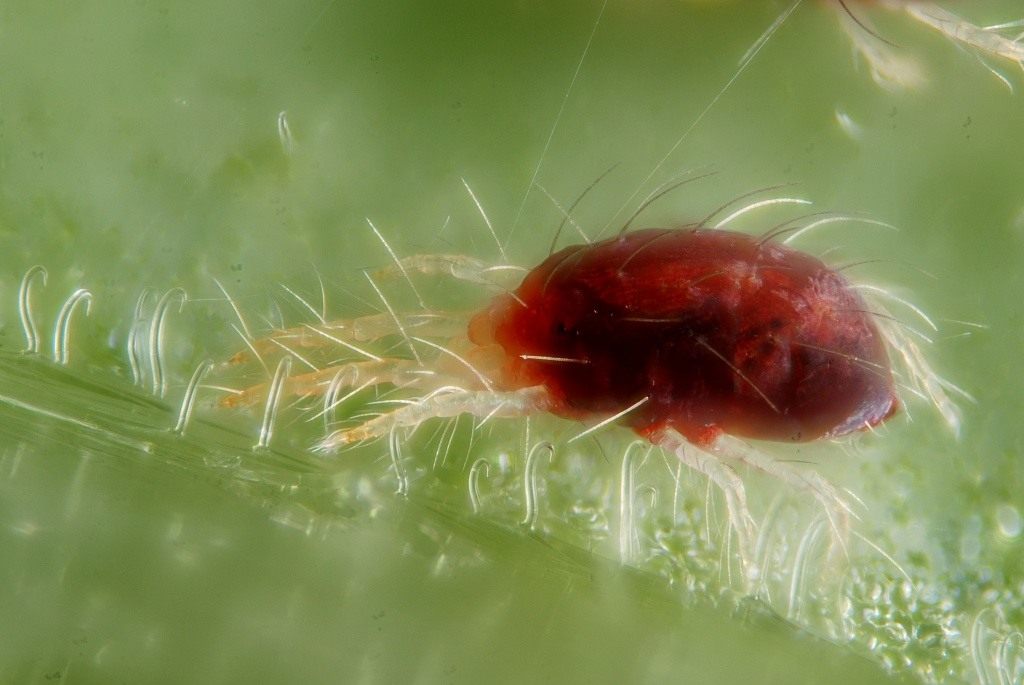
 Common spider mite under a microscope.
Common spider mite under a microscope.
 The cobweb is visible between the leaf plate and the central vein.
The cobweb is visible between the leaf plate and the central vein.
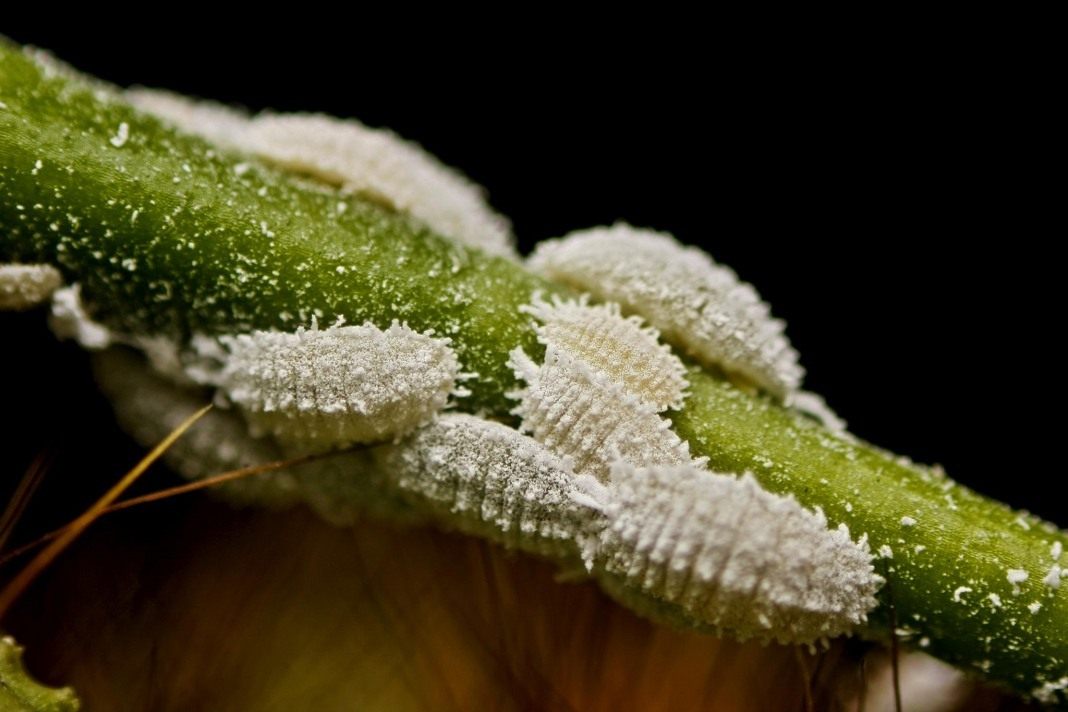
 The skins on the back of the sheet are white.
The skins on the back of the sheet are white.
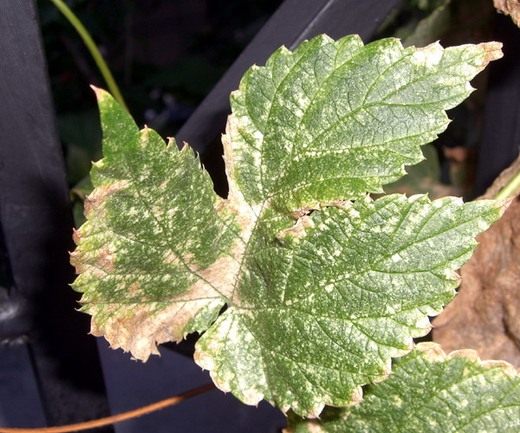
Typical signs of damage: point punctures, whitish or yellowish, are visible in the lumen of the leaf. At first there are few of them, but gradually they merge into spots. The leaves turn pale, acquire a grayish or pale yellow tint. Then the leaves dry out, completely lose their color. This is a typical picture, but in some cases, the leaves turn red or take on a bronze tint. In some plants, the leaves do not change shape even when the spots are large, in other cases they are strongly deformed, curled.
Keep inspecting the plant every day, as ticks multiply rapidly under favorable conditions. The female lays over 150-200 eggs during two to three weeks of life under favorable conditions. The duration of generation is 2-3 weeks, at the same time all stages of development are present on the plant: eggs, larvae, nymphs, females and males. The entire path of metamorphosis (from larva to adult tick) at an average temperature of 20-24 ° C, usually takes no more than 10 days, at temperatures above 32 ° C, the rate of regeneration is reduced to a week. The rate of "maturation" of a tick egg is 1-3 days.
Sexually mature individuals have a greenish color, are hardly noticeable on the leaves. With a decrease in daylight hours (from August), in dry hot weather, females appear, preparing for winter. They stop feeding on plant sap, acquire a reddish-brownish color, and look for more discreet places where they can hide (in the upper layers of the soil, under fallen leaves, in cracks in the bark). At the same time, females secrete a large amount of cobwebs, this is especially noticeable on garden roses - in a few days they become entwined with cocoons of cobwebs. If the temperature does not drop below 10-12 ° C, then the spider mites will not hibernate, but will continue to actively reproduce (this is the minimum temperature at which the vital activity of the mites is still ongoing). It is sad that even prolonged freezing does not kill spider mites. Mite eggs can survive in soil or other secluded places (for example, straw, compost heap, window frame crevices) for years.
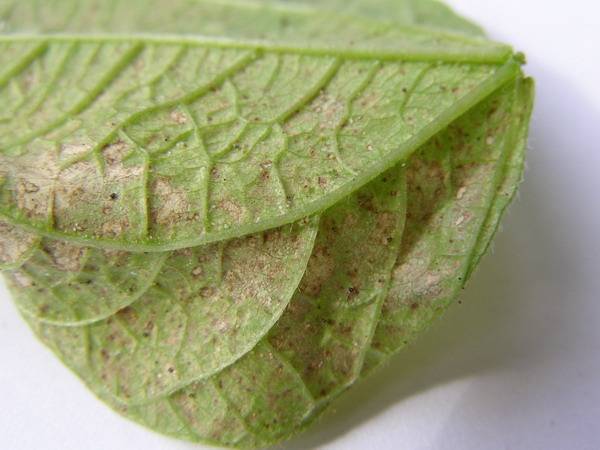
 On plants with dense leaves (citrus fruits), only vague yellow spots are visible on the outside.
On plants with dense leaves (citrus fruits), only vague yellow spots are visible on the outside.
 On plants with more delicate leaves (balsam in the photo), the leaf is translucent, the traces of a tick are visible through and through.
On plants with more delicate leaves (balsam in the photo), the leaf is translucent, the traces of a tick are visible through and through.
 Ticks love roses especially, we can say that the concept of "rose" and "tick" are inseparable. There is nothing to heal here.
Ticks love roses especially, we can say that the concept of "rose" and "tick" are inseparable. There is nothing to heal here.
Six-legged ticks
Phytoptipalpus paradoxus, another subfamily of tetranychid ticks, differs in that they have only three pairs of walking legs. These species of herbivorous mites have evolved over time. The fact is that the formation of the cuticle and hatching from the egg in ticks occurs at a time when the fourth pair of legs is not yet developed in the embryo. A six-legged larva with a shortened abdomen hatches - the last segments and genital valves are underdeveloped. As a result of mutations during evolution, in some adults, the abdomen developed normally, but the last pair of legs did not develop. As a result, the trait was fixed, and a subfamily of six-legged spider mites was formed. All three pairs of legs they have are very short, and the body is much wider than that of an ordinary spider mite, almost round. Six-legged ticks lack the prelarva stage in their life cycle.
Signs of plant damage
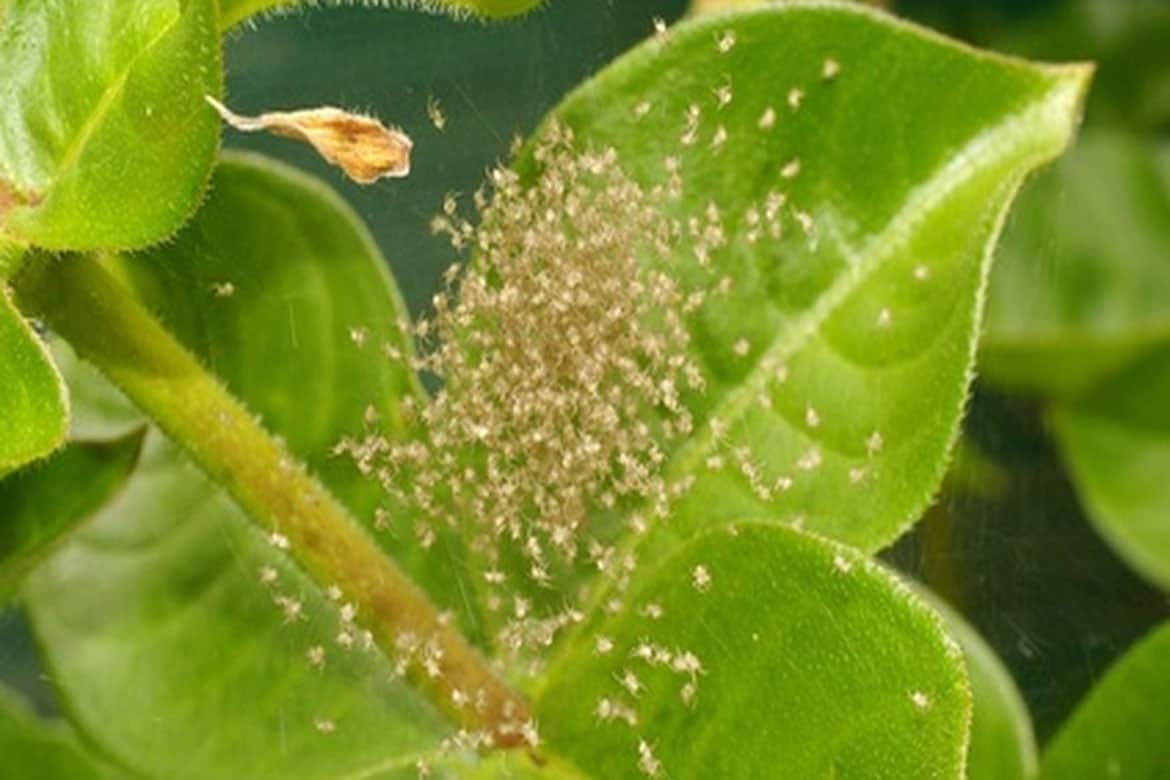
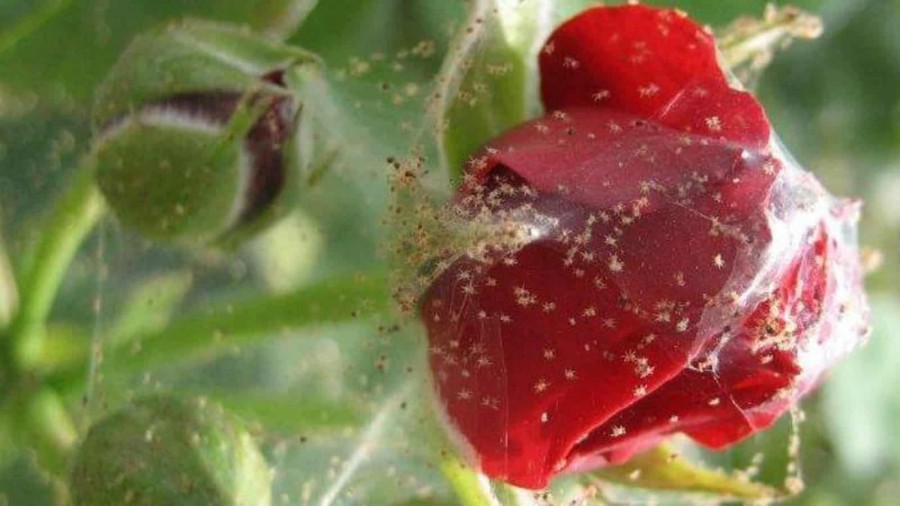
Specialists call the spider mite the ideal pest. It is able to multiply very quickly, is omnivorous and at the same time easily goes into diapause if conditions are not too favorable for life. The clutches left by the female and covered with cobwebs can be found on the walls of the containers, on the leaves from below, as well as in the ground itself. The eggs have a smooth shell. They can remain viable for several years without dying due to unfavorable conditions, but simply slowing down their development.
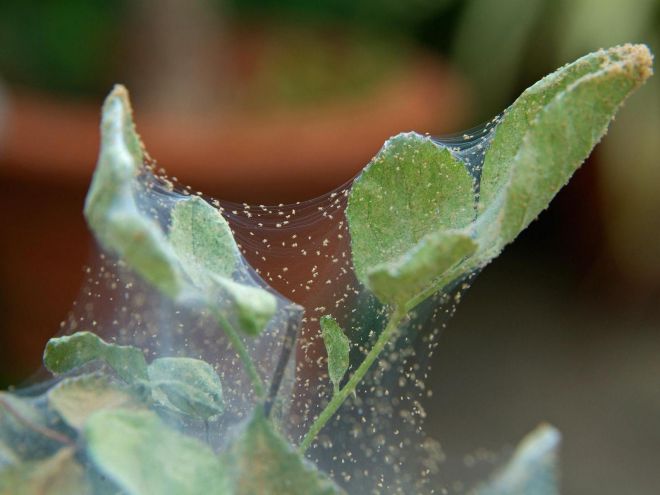
If the infection is very severe, the plant will be visibly enveloped in such a net that collects dust and excrement from these small animals. However, some varieties of the pest practically do not weave a web.

Eggs are another sign of infection, but it should be noted that they are very difficult to see. The fact is that the diameter of each is less than a millimeter, in addition, they are very light or even translucent. They are located in small groups, from 1 to 3 eggs in each, and are covered with a protective layer of cobweb, which creates the most suitable conditions for development. It takes 3 days for the larvae to appear.
Such a mite eats plant sap. He can get it from anywhere in the flower. Small light spots appear on the affected area, they are best seen on the leaves. This leads to a slowdown in photosynthesis and disruption of intercellular structures, respectively, their proper functioning becomes impossible.
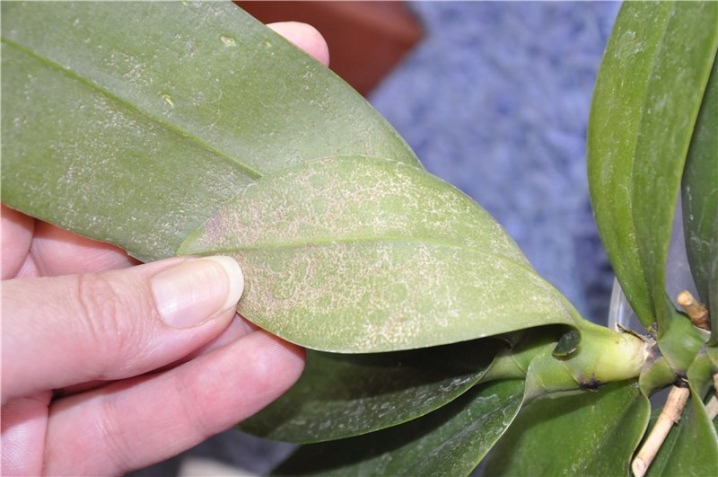

These spots grow over time and lead to yellowing of the leaves. They dry out in small areas, and also become sluggish and inelastic. A spider web plaque forms on top.
Finally, the last stage can be called leaf fall. The spots on their surface join together, the leaf plate dries and falls off. The more pests are on the plant, the faster they are able to destroy it.
Traditional methods of dealing with spider mites
Folk remedies are widely used in the practice of getting rid of pests, since they are available and not as dangerous as chemicals.
Alcohol

Alcohol treatment is suitable for plants with large leaf blades. In this method, the leaves affected by the pest are wiped with a cotton pad or an alcohol napkin. It does not cause burns, as it evaporates quickly, without having time to cause harm. The method is quite effective.
Colloidal sulfur
A 1% emulsion is made from sulfur powder or paste, with the addition of water. For better adhesion, you can replace the water with a soapy solution. It is desirable to carry out the treatment by wetting, since the particles of the emulsion do not dissolve and will clog the hole of the sprayer. After a couple of days, the white bloom is washed off with running water.
Kerosene
You can add a small amount of kerosene to the soap solution - treat the plant with this composition. Then it is washed with running water.
Tobacco infusion
For 1 liter of boiling water, take 50 grams of dry raw materials or tobacco dust. The prepared, strained infusion is sprayed with plants from a spray bottle.

Flat heifers
Squattle Tenuipalpidae - or false spider mites (not to be confused with the flat beetle Cucujidae), the genus Brevipalpus Brevipalpus and Tenipalpus Tenuipalpus. In size and shape, they are very similar to spider mites, they also sit on the underside of the leaves, and move slowly. Their sizes are very small, from 0.1 to 0.4 mm.
If these images are not enough for you, you can see another spider mite photo.
In many species, colonies consist only of females, which hatch from unfertilized eggs. Development takes place in three stages: larva, protonymph and deutonymph. Maturation from egg to adult tick is 12 to 24 days. The eggs of some types of flat beetles can be seen with the naked eye and appear as reddish-orange clusters. The larvae of flat beetles are six-legged, orange-red, translucent, nymphs are opaque, dark spots appear on the body. Adult mites are brown, eight-legged with a flattened body. Adult females live for 5 to 6 weeks, producing 6-10 generations per season. Many flat beetles have a pause (dormancy) of 1-2 days between molts, at which time they do not feed, they remain on the leaves in a motionless state.
 Squat beetles are brown, but very small, similar to brown grains.
Squat beetles are brown, but very small, similar to brown grains.
 Puncture points where flat beetles stick are dark dots.
Puncture points where flat beetles stick are dark dots.
 Cobwebs do not form flat heifers. They do not suffer from high humidity.
Cobwebs do not form flat heifers. They do not suffer from high humidity.
Plants affected by flat plants differ in the nature of the spots. The fact is that most flat beetles have toxic saliva, which, when it enters the tissues of the plant, causes necrosis. Therefore, brown or gray-brown spots appear on the upper side of the leaf. First, small, punctate, 1-2 mm, then increasing in size. The leaves are often deformed, and in plants with dense fleshy leaves (Saintpaulia, Gloxinia), the edges of the leaves begin to tuck inward.
Worst of all, flat beetles are the main carriers of viruses (mosaic and annular spotting). But even worse is that the ideal conditions for the reproduction of flat beetles are a temperature range of 25-30 ° C and a fairly high air humidity, at least at 70-80% of air humidity they feel comfortable, while spider mites with such humidity inhibit development ...
Temperature dependence of the tick metamorphosis rate:
- at an ambient temperature of 15 ° C: eggs ripen for about 2 weeks, about another week for each subsequent stage: larvae, pronymphs and deutonymphs, only 33-36 days from egg to adult.
- at an ambient temperature of 20 ° C: eggs ripen for about a week, about 3 more days for each subsequent stage: larvae, pronymphs and deutonymphs, only 2 weeks from egg to adult.
- at an ambient temperature of 30 ° C: eggs ripen for about 3 days, about 1.5 more days for each subsequent stage: larvae, pronymphs and deutonymphs, just a week from egg to adult.
Signs of the appearance on the plant
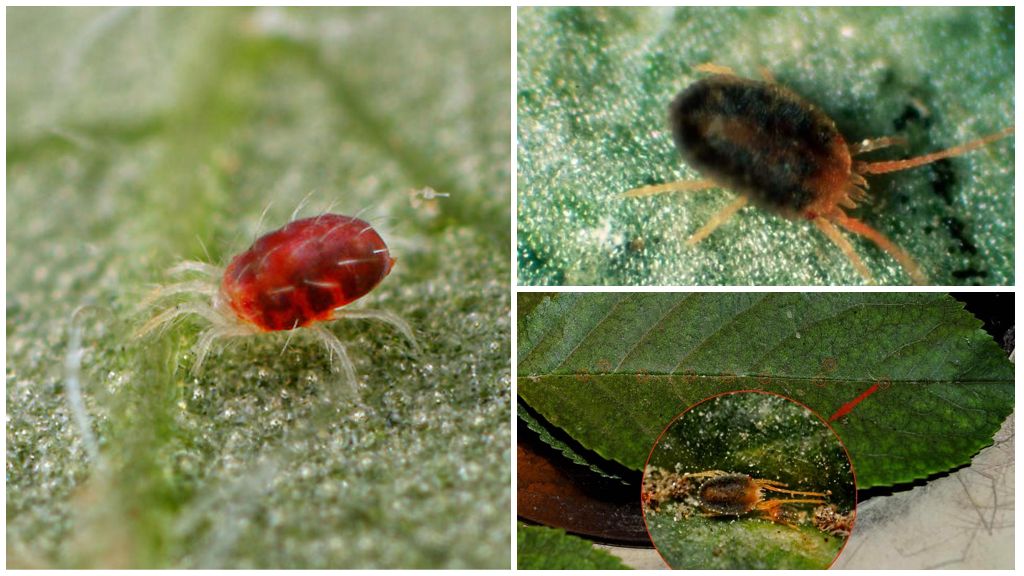
The body size of the animal (this is not an insect, belongs to the arachnids) is from 0.2 to 1.2 millimeters, rare species reach 5 millimeters. In most cases, it is difficult to notice a pest that has appeared; it is usually identified by a changed plant species. Ticks are dangerous with a short life cycle, it lasts only 8-40 days. Within 7-8 days, an adult develops from the egg, ready to reproduce. Adult ticks have 8 legs, body color varies from whitish and yellow to reddish-brown in different species.
> The female makes clutches on the bottom of the foliage, in the ground, on the walls of the pots. She covers them with cobwebs. The eggs are well protected by a smooth shell; under unfavorable conditions they do not die, but slow down development, retaining their viability for several years. Nature has created an ideal pest - it multiplies quickly, goes into diapause under unfavorable conditions, eats everything. A spider mite infection can be identified by the appearance of the affected plant.
Eggs
It is difficult to notice the eggs of ticks, their size is less than a millimeter. They are white or translucent, covered with a dense shell. The female lays them out in small groups (1-3 pieces), braids with cobwebs to protect and create favorable conditions for development. Larvae appear after 3 days.
Thin spider web
The main sign of the appearance of a tick is a cobweb, which is massively woven by adults in the lower part of the foliage. Colonies of eggs, larvae and ticks are hidden under its clusters. Some species of these arachnids hardly weave a web.
Yellowing of leaves
The tick feeds on plant sap, sucking it from anywhere on the ground. A small white speck forms at the puncture site, best seen on the leaves. Cells cease to function normally, photosynthesis slows down, the conductivity of intercellular structures is disrupted.
Small specks grow, the leaf dries up in separate areas, turns yellow, becomes lethargic, loses turgor and elasticity. The houseplant takes on an unhealthy appearance - the leaves are yellow and sluggish, entangled in cobwebs.
Falling and dryness of leaves
Loss of foliage is the last stage of infection. Separate spots on the plates join, the sheet dries and falls off. When photosynthesis is disturbed, the defenses of plants are reduced. Large colonies of ticks literally suck all the strength out of the flower. They attack ovaries and buds, deform even strong stems. One skeleton remains from the flower.

Pest control methods: what products can be used, processing features
At home, it is difficult to apply agrotechnical and biological methods.
destruction of arthropods. Predominantly use acaricides or folk
funds. In addition, if a tick appears on flowers, and other methods of control do not
help, consider the option of transplanting with a complete replacement of soil (remove
only the top layer is impractical). The flower is washed.
At the initial stage, you can remove the leaves where the pests live, and there are signs of infection. In addition, it is necessary to disinfect the pallet, all containers, as well as the surfaces around the area where the plant is affected. There can be parasites on the curtains too.
Chemical
Possible methods of delivery of the poisonous substance to the ground parts of flowers:
- soaking in solutions containing acaricides;
- spraying the product by means of a spray bottle;
- applying the substance to all leaves with a rag.
 Chemicals are sprayed with a spray bottle.
Chemicals are sprayed with a spray bottle.
Table: Examples of chemicals,
used on indoor plants. How they affect, how much they cost
Signs of the appearance of a spider mite on indoor plants
You can understand that a parasite has appeared by a number of nonspecific signs:
- white blotches over the entire surface of the leaves at the initial stage of the development of the disease, they arise due to the introduction of the most protruding part of the oral apparatus into the plant tissue;
- spots of a different shade are formed (light, brown) - a sign of a violation of internal processes;
- young flowers stop growing;
- the shape of the leaf, its texture changes;
- flowers fall;
- leaves dry up;
- from the back you can see white formations - pest eggs, they are microscopic (less than 0.2 mm).
So, the appearance of arthropods is assumed if a cobweb is noticeable (one of the main specific signs). Also in the lower part of the sheet, moving microscopic points (less than 0.5 mm) are striking. This is an imago, the offspring of arthropods are much smaller.
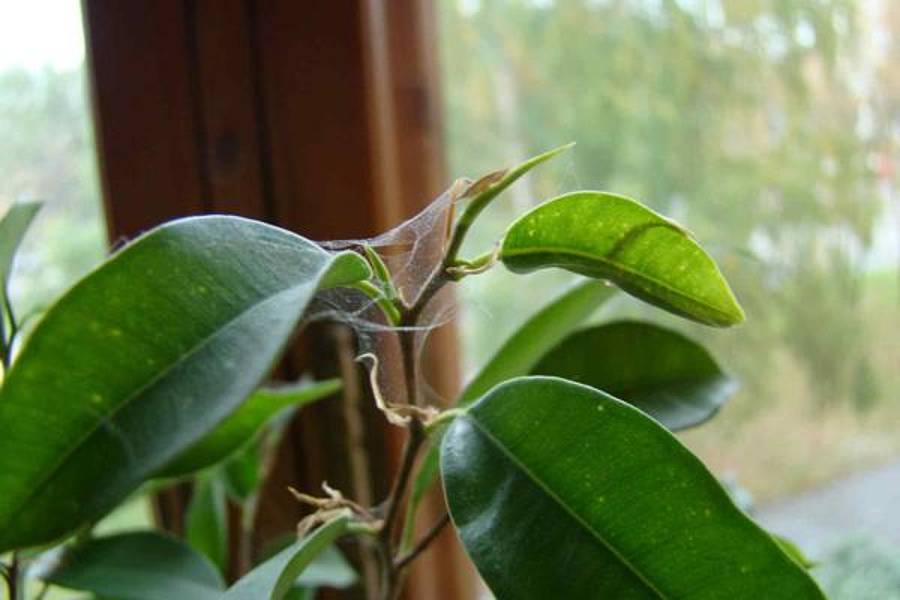
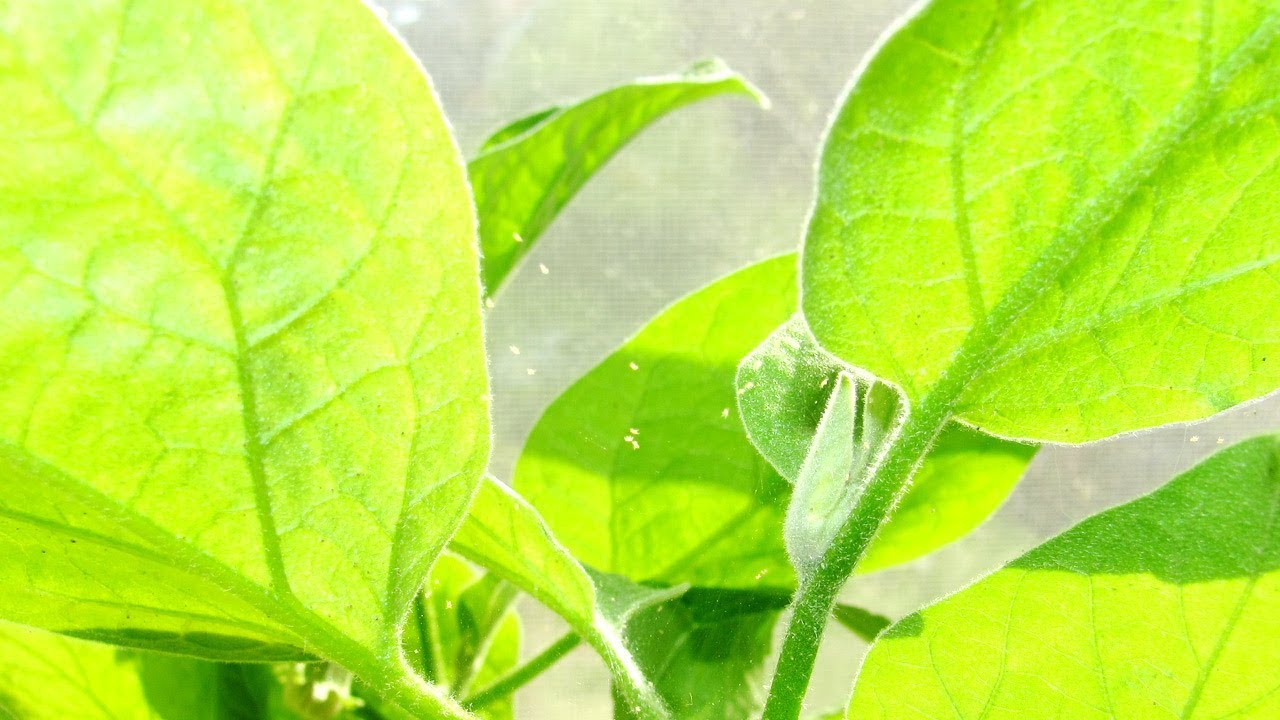
White spider web on indoor plants
Fine fibers can be seen between the stem and the base of the leaves. The threads are white, the web itself is transparent. It is formed as a result of the release of a special secret, which instantly freezes. This leads to the appearance of threads. The cobweb becomes noticeable when there are a lot of flower mites.
In the last stages of the development of the disease, it is visible how parasites crawl along this grid, which allows you to immediately determine the cause of the deterioration of the condition of the flowers.
 When there are a lot of ticks, the cobweb is more noticeable.
When there are a lot of ticks, the cobweb is more noticeable.
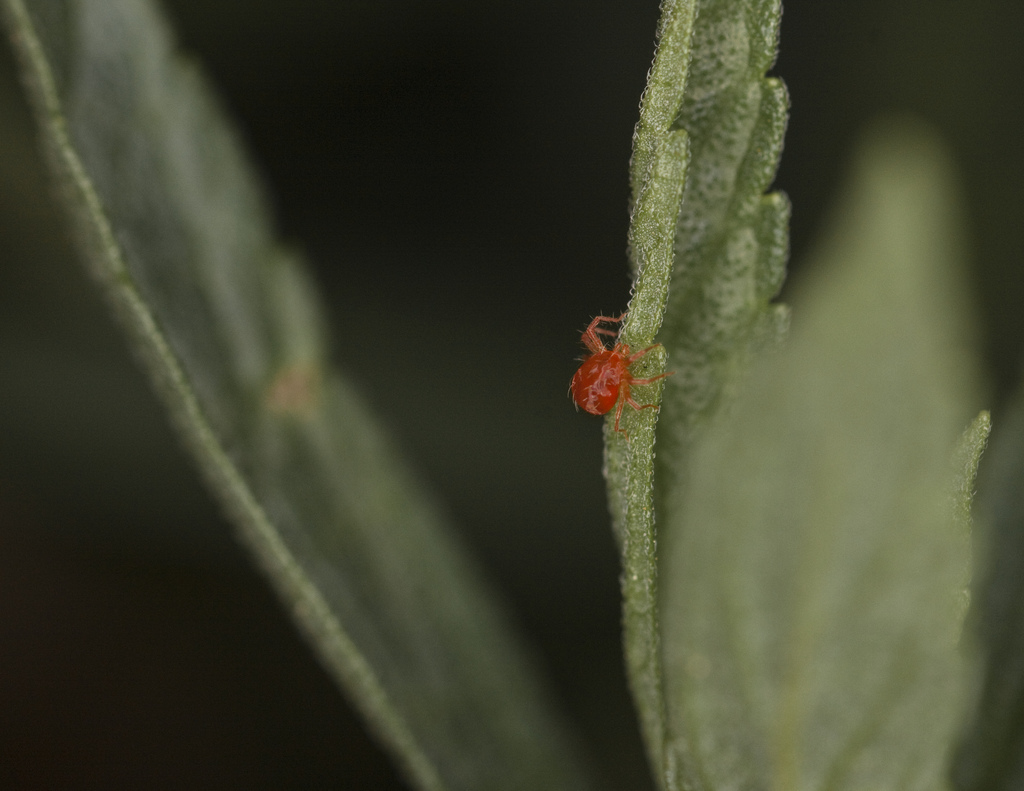
White spiders on indoor flowers
The shade of the outer covers of ticks varies from light yellow to
brown. There are green and red pests. Color helps to recognize
type of parasite, since there are a large number of individuals representing
common group of spider mites. In addition, traces of habitat remain on the leaves.
pests: shells that are shed by larvae and nymphs in the process of molting, they
light color; waste products in the form of tracks with a silvery sheen,
spots of white.
 The color can vary with the age of the spider mites.
The color can vary with the age of the spider mites.