Winter preparation process
A month before the hiding of roses, immediately before the onset of cold weather, it is worth taking care of their future fate. A suitable period for hilling bushes. In the flower garden, it is necessary to remove all unnecessary, that is, to weed. Excess grass and weeds only draw out the useful properties of the earth, which are already very few in the fall.
Remove fallen leaves from trees. Loosen the soil around each bush a little. This should be done carefully so as not to damage the roots of the plant. Cover the bushes themselves with half of the earth. Thus, they will better endure frost. And most of the bushes will not be affected.
1. Pruning roses
Pruning certainly takes one of the important steps. That is why, it is worthwhile to carefully approach this issue. Pruning takes place in September. But more often, of course, it all depends on the weather. You can also prune in October if the weather was still warm before.
Pruning roses allows the bush to breathe with renewed vigor. Provides oxygen. Removing old shoots, new ones are born. Uncut roses are subject to freezing. If the rose is not trimmed, then the chance to survive the winter is practically scanty. Most likely, such a bush will simply freeze. Cut bushes can be easily sheltered from frost.
When pruning a rose, it is necessary to leave 20-25 cm from the ground. If this is a tea rose, then this rule is no longer valid. Pruning the stems should be 30 cm. To make the flowers even larger, then cut off to 15 cm. Pruning occurs at an angle of 45 degrees.
Cutting methods:
- Radical. Leave 20-25 cm. Dead branches are also cut.
- Lightweight. Delicate varieties are a priority. Only the upper shoots need to be cut.
- Moderate. Cut off as many stems as possible. This is predominantly for roses that curl.
2. Prevention of disease
The increased soil moisture has always attracted all kinds of pests. Also, with the constant planting of plants, pests will not keep themselves waiting long. When buying and planting new plants, make sure it is not contaminated.
Types of rose disease:
- Non-infectious.
- Infectious. Fungal, viral, bacterial. These are: powdery mildew, burn, spotting and so on.
For the prevention of diseases, top dressing is the best fit:
- 1 tbsp. l. For 10 liters of water. Top dressing station wagon. Spray the plants.
- Potassium nitrate. Well suited just before flowering buds.
- Ash. Also good for pests.
- Infusion of mullein for 10 kg of the mixture. Held once every two weeks.
- Bordeaux liquid solution 1%. Once a week.
- 3% ferrous sulfate. Spray the bush with a sprayer.
- Burgundy mix. Also effective in prevention.
- Soda ash 50 grams per 10 liters of water with the addition of 50 grams of laundry soap.
- Colloidal sulfur. One hundred grams per 10 liters of water.
- Topsin m. 10-20 gr per 10 liters.
Also, potassium dressing will help prevent unwanted diseases of such an exquisite plant.
The plant should be taken care of in advance. Since there is a constant threat of infection
Therefore, you should pay attention in time to suspicious spots on the leaves.
3. Shelter roses for the winter
Not all flowers are suitable and can survive frost. Each flower is as individual as a person. Some options are frost-resistant, while others, on the contrary, are very sensitive. But most often the bushes freeze out due to improper preparation for the winter. Many hostesses make a mistake. And as a result, unpleasant consequences occur. Indeed, many gardeners put a lot of effort into their works.
To cover the plants, you need to wait for stable weather. It's good if the weather is already stable outside. In this case, the soil must be only dry. If the soil is wet, then it is worth waiting for a few days.
You should never rush to cover your roses. If you cover them ahead of time, then at a sharp positive temperature, they will begin to bloom. Which is highly undesirable before the onset of cold weather. And if you cover them later. Then most of the bushes will simply freeze.
Before sheltering, it is necessary to collect all the leaves near the plants themselves and gently dig up the ground with small pitchforks. To huddle the bushes, making a mound of 15-20 cm. And after that, you can go directly to the shelter.
Shelter types:
- Normal. This method is simple. It is necessary to cover the trimmed bushes with earth up to half. Thus, the root system and half of the sticks will be covered.
- Special fabric. Such fabric is sold in shops, everything for the garden and vegetable garden. If you are not sure which one to buy, then the consultant will be happy to help you in choosing and tell you which one is best for you.
In any case, it is simply necessary to cover plants, and even more so roses. Then next year they will delight you with their beauty.
Climbing rose propagation
There are 5 ways to propagate climbing roses:
- seeds;
- cuttings;
- layering;
- dividing the root;
- inoculation (budding).
Cuttings
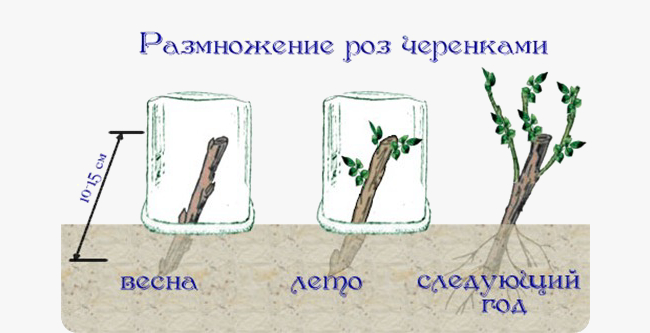 Cutting roses
Cutting roses
This method of reproduction always gives 100% result. Cuttings are cut in summer, spring or autumn (during pruning). Faded and flowering shoots are suitable for harvesting them. How to breed a climbing rose by cuttings:
- In summer, spring or autumn, cut 15 cm long cuttings from semi-lignified shoots. Leave 2-3 internodes on each.
- Cut the bottom of the cutting at an angle of 45 °, stepping back 5 cm from the bud. From above, 1 cm above the kidney, make a cut at an angle of 90 °.
- Remove the lower leaves completely, cut the upper ones in half.
- Fill the pots with a mixture of disinfected sand, peat, humus (1: 1: 1). Deepen the cuttings 2 cm. Cover with a jar or plastic wrap.
- Place containers in a room with a temperature of + 23 ... + 25 ° С, shade from direct sunlight.
- Ventilate and water the seedlings periodically.
- Remove the jar (polyethylene) after 2-3 weeks.
- Transplant the young plants to a permanent location according to the optimal time for planting roses for your region. Treat them like mature shrubs.
Budding
 Step by step budding
Step by step budding
Grafting of climbing roses is carried out on a rose hip. The first plant acts as a scion, the second as a stock. The procedure is carried out in the second half of July or early August. Before grafting, the dog rose is watered abundantly with warm water. How to propagate a climbing bush by budding:
- Make a T-cut at the root collar of a 3-year-old stock, pulling the edges of the bark slightly.
- From the scion, cut off the bud (eye) along with the bark and a small piece of wood.
- Insert the bud into the rootstock incision, press firmly, wrap with budding film.
- Spud the rose hip bush so that the soil covers the grafting site by at least 5 cm.
- After a month, loosen the film, and in the spring - remove it completely.
- For the first year, do not let the grafted rose bloom, cut off the buds that appear.
- Take care of the grafted plant as well as others: water, fertilize, mulch, cover for the winter.
Growing from seeds
 Disinfection of pink seeds
Disinfection of pink seeds
To propagate a climbing rose in this way, purchase high-quality, pickled seed from the store. Collecting seeds yourself is not recommended. Plants obtained from them will not carry the varietal qualities of the mother bush. How to grow a climbing rose from seeds:
- In mid to late February, fill the seed with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- After half an hour, remove, place between 2 sponges soaked in the same substance. Wrap the resulting "sandwich" in plastic, put in the refrigerator, in the vegetable compartment.
- Inspect the seeds from time to time. If mold appears, rinse them, replace the cotton pads with new ones (also moistened with hydrogen peroxide).
- After 40-50 days, plant the sprouted seeds in plastic cups with soil mixture for roses, deepening by 1 cm. Cover with foil, place on a windowsill.
- Open the polyethylene daily for airing, and after emergence, remove it completely.
- Water the seedlings as the soil dries up.
- In the spring, take the cups outside, put them in a lighted place protected from the wind.
- After 2 months, buds will appear on the seedlings that need to be removed.
- In April - May, prepare the holes and transplant the young plants to a permanent place. After planting, treat them as if they were mature shrubs.
Reproduction by layering
 Roses propagation scheme by layering
Roses propagation scheme by layering
How to propagate a climbing rose by layering:
- In the spring, after removing the shelter for the winter and pruning, make a small incision above the bud of one of the shoots.
- Next to the bush, dig a ditch, 7–10 cm deep. Pour a layer of humus on the bottom, and then - earth.
- Bend the shoot, put it in the groove, fix it with metal brackets and fill it with soil. Leave the top outside.
- Treat the cuttings as if they were mature plants.
- By the fall, a sprout will appear on the shoot, which can already be transplanted. If winters are cold in your area, postpone this procedure until spring.
- Then separate the branch from the mother bush, cut off the layers and plant in a permanent place. Provide the same care as for adult flowers.
Beauties from Canada
These park roses grow comfortably in cool climates. They bloom well in the capricious Russian summer. In the south of the country, Canadians are too hot, they languish from lack of water. Roses hibernate without shelter, withstanding for a short time even the cold of about thirty-five degrees.
Several of the most common varieties in our country:
- John Davis. Large light flowers have a classic shape and look very elegant. A bush with a height of two and a half meters, pleases with its beauty all summer until the cold weather. It is impossible not to notice it - a subtle scent will invite you to admire pink park roses.
- John Franklin. It grows into a neat bush a little more than a meter high. Reddish roses, similar to double carnations, are collected in small inflorescences. A very pleasant light smell is the hallmark of the variety. Blooms all summer.
- Morden Sunrise. Large flowers, about eight centimeters in diameter, are painted in a pleasant orange color with a pink blush. The bush grows no higher than one meter, but despite its growth, it is very resistant to many diseases.

Views
- Dwarf. Such trees are from 0.3 to 0.5 m in height.
- Half-stamp options. Their height can reach 0.8 m.
- Ordinary boles. Such options have a height of up to 1.3 m.
- High-standard roses. They are "weeping" trees up to 3 meters. These are the largest standard roses.
It should be noted that grafted roses retain their properties. For example, the cascading varieties in the standard version are “weeping” trees.
Plants on a trunk look great in any landscape design, for example, in group plantings, on lawns or on multi-tiered cascading compositions.


According to the recommendations for the stock, it is better to choose a rosehip, as it is the most resistant. The specimen must have a strong root system and flexible shoots.
When buying a ready-made stem, it is imperative to study the description for it, which contains a detailed algorithm for care actions and describes which plants were grafted.
It should be remembered that decorativeness is highly dependent on the quality of the original seedling, so it must be carefully inspected. It is better to purchase an escape in special stores, where you can consult with a good specialist - this way you can be sure that quality products are being purchased.


You need to ask about the age of the seedling.It is better if he is 2 years old, since during this period strong roots and trunk are formed. If dry shoots or cracks are seen in the root system, then it is better not to take such a stock - the stem should be even and smooth.
The trunk diameter is determined based on the type of tree. For example, for "weeping" types, the best option would be a diameter of up to 2 cm, the rest - up to 1 cm. The crown must have at least two vaccinations - in this case, it will become lush.
The substrate must be fresh and moist. If moss, weeds grow on it, or it is completely dry, it means that the escape was poorly cared for - it is better not to purchase such products
It is important that the root system is closed

It is worth deciding in advance on the grafted variety and familiarizing yourself with the requirements for its care, as well as with climatic characteristics.
Decorative views
The group of park roses includes all species of decorative rose hips. They bloom much earlier than cultivated varieties - from about the beginning of June. They have a pleasant scent. And in August they are decorated with orange fruits.
In Russia, species rose hips are widely used in cities to decorate parks, squares, areas near houses:
- Wrinkled rose (Rosa rugosa). The bushes are pyramidal in shape and reach one and a half meters. The plant's name is justified by its wrinkled, shiny foliage. Dark pink flowers, up to ten centimeters in diameter, smell fragrant. Such enjoyment begins early in June and continues throughout the month.
- White rose (Rosaalba). Gorgeous spreading bushes about two meters high are visible from afar. At the end of May, they are covered with countless buds, which open into flowers with a diameter of six centimeters, clustered in bunches in loose inflorescences. The delicate scent of roses is carried by the warm wind far from the plant.
- Thorny rose (Rosa spinosissima). A very unpretentious plant. The height of the bush can be from seventy centimeters to two meters.
Its flowers are not double, milky white, with bright yellow stamens. Pleasant aroma. Blooms in May. The stems are covered with many small thorns.
Thanks to the painstaking work of Canadian and English breeders, varieties of park roses with large double flowers have been bred. New plants are not sissy at all. They steadfastly resist most diseases, quite confidently endure the difficult Russian winters.
Covering material for roses for the winter
From freezing in winter, rose bushes will be protected by such covering material as:
- lutrasil;
- geotextile;
- polyethylene film;
- spunbond;
- flying foliage;
- rags and burlap;
- plywood and boards;
- spruce branches;
- unnecessary coats or blankets.
The choice of a suitable covering material is influenced by the method of shelter, as well as the variety of roses. Large, powerful bushes can only be covered with spruce branches or foliage. And thermophilic varieties need a better shelter. For them, it is necessary to install frames that are covered with film, while the stems are additionally tied with rags and bags.
To cover several bushes at once, film is most often used, but it is better to opt for lutrasil, geotextile or spunbond. They cover a frame made of wood or metal. These materials will save the bushes not only from frost, but also from damping off, as they are able to remove fumes.
Pay attention to the density of the covering material, it should be at least 200 g / m2. In this case, the material is folded in several layers.
The edges of the non-woven shelter, which is stretched over the frame, must be pressed with stones, boards, etc. When covering with a film, you need to leave several air vents for ventilation. And when using lutrasil, spunbond and geotextiles, this is not required. On the contrary, their edges are firmly pressed against the soil surface so that there are no holes.
If you are covering climbing roses with non-woven fabric, then their lashes do not need to be laid on the ground. First, the hilling of the base of the bush is carried out to a height of about 0.3 m.After that, the shoots are wrapped in several layers of covering material, which is fixed with ordinary clothespins or a stapler and staples.
How to cover roses
A step-by-step guide to sheltering roses for the winter
Stage 1: preparing roses for wintering correctly
1. At the end of summer, you need to stop nitrogen fertilizing, which provoke the growth of shoots. Before autumn, you can occasionally fertilize flowers with potash mixtures, which contribute to the stiffness of the stem. The last feeding should take place no later than September (in warm climates - the end of September). The most successful composition for pre-winter fertilization is potassium-magnesia. Such a simple care of roses in the fall will bear fruit.
2. Before the shelter, the roses must be allowed to ripen. To do this, you must stop cutting flowers into bouquets 3-4 weeks before hiding. This also applies to young roses of the first year, the buds of which you have cut all summer. Before winter, they must be allowed to bloom in order to end the growing season naturally.
3. Almost all garden varieties of roses do not have a natural period of foliage. Therefore, all leaves must be cut or torn off. This will not only put the plant into a dormant state, but also rid it of potential foci of infection.
4. Directly before the shelter, the bushes should be treated with a fungicide or a solution of ferrous sulfate in order to disinfect all aerial parts of the plant. The soil under the roses should be cleared of fallen leaves, weeds and any other debris.
Stage 2: Bending or Trimming
You can not cut off park and weaving varieties. Climbing roses and some shrub varieties that are sensitive to cold should begin to be bent to the ground in advance, as laying on the ground can immediately damage or break the stiff stems. So, 3-4 weeks before the shelter of the rose, you need to start putting it on the supports, which gradually sink lower and lower.
Curl or trim park roses?
Many growers like to cover roses without cutting, citing the fact that this way the plant tolerates winter better. In addition, the risk of throwing out new shoots is significantly reduced, and the bush itself wakes up and blooms earlier in the spring. However, opinions are not unambiguous, because in conditions of harsh winters the plant winters the better, the smaller its aboveground part. There is one more point - the upper part of the stems can contain bacteria and rot, which is dangerous for the plant as a whole. Therefore, we are for pruning!
How to bend the bushes correctly?
- If the stems are dense and not flexible, then they need to be bent in several stages, as mentioned above. Old construction rods or rods can be used to bend the branches. They easily enter the ground, bend well and serve for many years.
- In order for the stem to bend without damage to the plant, you can dig the root of the rose with a pitchfork. It is not necessary to dig up the bush too much, make 2-3 incomplete digging so that the stem becomes mobile. Now he will better lie on the support for shelter.
- The bush must be bent towards the side of the graft in order to avoid the breaking load on the stem in this place.
Standard and all climbing roses are removed from the support and laid on the ground.
Stage 3: Covering
How to properly cover roses for the winter? This can be a ditch, an air-dry type of shelter, or a wrap.
- The bushes are dug in as follows: we spud the roots of the prepared rose with earth by 20-40 cm of the height of the stems; the upper shoots of the bush are covered with dry foliage or covered with spruce branches. You can completely bury roses in the ground;
- The air type of shelter provides for the insulation of the root with foliage or needles and the construction of an air dome over the rose made of plywood, plastic or other suitable materials;
- Some growers use a method of wrapping roses with geotextile fabric or other thermal insulation material.
How to propagate garden roses outdoors by cuttings
Cuttings. As mentioned above, the method of propagating rose plants by cuttings in amateur gardens is the most promising and simple. Roses grow and bloom with this method of propagation no worse than grafted ones.It is very important that there is no danger of losing the variety, since even with the complete freezing of the aboveground part of the bush, new shoots appear from the root collar of the plant in the soil, and the variety is fully restored. Own-rooted rose seedlings can be obtained both as woody stem cuttings and green ones.
Roses can be propagated by green cuttings in early summer. Before propagating roses in the open field in this way, you need to prepare cuttings of mother plants. For spring cuttings (March - April), cuttings are used from plants growing in winter gardens or greenhouses, and for summer cuttings (from late June to mid-August), cuttings are cut from roses growing in the open ground. Cuttings should be cut from well-developed lignified or semi-lignified shoots, the thickness of which is in the range of 0.4-0.6 cm (pencil thickness). To reduce evaporation, the lower leaves are removed, the upper ones are shortened by 1/3. Before setting for rooting, cut cuttings are placed in water at room temperature for 24 hours. Cuttings should be rooted in homemade greenhouses or boxes under glass, at a temperature of 20-25 ° C. Cuttings are planted in sand to a depth of 1.5-2 cm. After rooting (after 20-25 days), the seedlings are transplanted into pots or film containers, in which they are grown and hardened at a temperature of 4-6 ° C.
Propagation by lignified stem cuttings. Many gardeners are interested in how to propagate a garden rose with lignified stem cuttings correctly and efficiently. In the fall, after pruning the roses, a large number of lignified shoots are thrown away, most of which can be used for autumn cuttings. Cuttings with developed buds are stored in moist sand at a temperature of 3-4 ° C. At the end of April - May, cuttings 10-15 cm long with 3-4 buds are cut from well-preserved shoots. The cuts should be oblique and made with a sharpened knife. Cuttings are planted in boxes or beds. Rooting medium and air temperature are the same as for green cuttings.
Cultivation of planting material for standard roses. Growing planting material of standard roses requires much more time (3-5 years) and labor than growing seedlings of bush roses. Rosehips serve as stock for the stem. As the dog rose grows, all buds that have started to grow or lateral shoots that are starting to grow are periodically removed from its lower part - they easily break off when pressed with a finger. In the second or third year, 2-3 strong shoots (renewal shoots) are formed from the dormant buds of a growing rose hip, by the end of summer they grow up to 1.2-1.5 m, sometimes up to 2 m.In the fall, the bushes are dug out, all the shoots are cut out, leaving one - the tallest and most direct. This will be the stock stock. Budding in the middle lane is best done with a sprouting eye in May - June. It is carried out at the desired height. For the winter, the rootstock with grafted eyes is added dropwise and stored at a temperature of 1-2 ° C. In the spring, the plant is planted on the site, with the beginning of sap flow, pruning is carried out, for which the top of the stem is cut off 1-2 cm above the grafted kidney. The cut is covered with garden pitch. With the beginning of the growth of the shoots, the formation of the crown begins. To maintain the rose, the stem is tied to a stake, the end of which should be at the level of the graft.
In spring and summer, pinching the tops of the shoots, they form the crown of a standard rose, as they grow, they remove wild growth, and in the second half of summer they give the opportunity to bloom.
In the selection of photos presented below, you can see the work on the propagation of roses and the further care of this flower:


