Caring for jatropha gout and kurkas at home
In care, the jatropha houseplant is completely unpretentious. It prefers to grow in a sunny place at room temperature throughout the year. It tolerates dry indoor air well. The substrate is prepared from sod and leafy soil, humus and sand (1: 1: 1: 0.5). You can use a ready-made cactus substrate.
Despite the fact that this succulent tolerates high temperatures and loves bright light, at first it must be protected from exposure to sunlight, since the leaves can get burned. In cases when there was no sunny weather for a long time or the succulent was just acquired, it must be gradually taught to light and sunlight. True, the gout jatropha, on the contrary, loves direct sunlight, but experienced flower growers recommend hiding it from the midday sun.

Indoor jatropha is afraid of drafts, so you never need to leave it in the room when ventilating it, and even more so to take it out into the fresh air. In summer, when caring for a jatropha flower at home, you should provide it with moderate. When the leaves fall off, watering is almost stopped until early spring. Jatropha is fed with fertilizers for cacti. The main advantage of growing jatropha at home is that it easily tolerates dry conditions. A succulent plant does not require high humidity conditions, dry air and occasional watering do not affect the condition and appearance of green leaves and inflorescences of the succulent. But you still need to monitor the quality of water: as for any indoor plants, it should be well-settled and soft, jatropha should not be watered with cold water.
What an indoor jatropha flower looks like can be seen in the photo below:
Here indoor culture is presented during the period of flowering and rest.
The genus Jatropha - Jatropha is a plant from the Euphorbiaceae family.
Homeland:
Central America. Flowering time: May - June.
The name Jatropha comes from the Greek words jatrys, doctor and tropha, food, and refers to the medicinal properties of some of the genus (eg Jatropha curcas).
The genus of Jatropha
(Jatropha
) includes about 175 plant species found in the tropics and subtropics of the Old and New Worlds. Some of them are grown as ornamental plants in tropical gardens and as indoor plants.
The natural habitat of the jatropha plant is Central America, but today it grows in many tropical and subtropical regions, including India, Africa and North America. From the Caribbean, jatropha has spread as a valuable plant for hedges in Africa and Asia by Portuguese traders. Like many other representatives of Euphorbia, jatropha contains compounds that are highly toxic.
Look at the photo - the jatropha has an unusual bottle-shaped stem, and this is not the only original feature of the perennial plant:
The decorative qualities of this plant were highly appreciated by fans of succulents, exotic plants and bonsai.
Diseases and pests
The following pests can spoil the appearance of the plant, and sometimes even provoke its death:
- aphid;
- false caterpillars;
- nematodes;
- root worm.




Fungal diseases can also harm sedum, the first signs of which are the appearance of dark spots on the leaves. All damaged areas must be removed, and the plant must be treated with fungicides. Morgan's sedum is a very beautiful succulent that has an unusual appearance.With the help of this plant, you can decorate both interiors and open loggias and balconies. Due to the fact that sedum is a southern flower, before purchasing it, you must carefully study the features of its planting and care. Only by observing all the rules and recommendations of experienced gardeners, you can grow a beautiful and healthy flower that can surprise all family members.

For information on how to properly care for Morgan's stonecrop, see the next video.
How to plant in open ground?
Sedum is planted in open ground with seedlings, which are purchased in the store or grown independently. To do this, in early March, soil is poured into a small container, the seeds are laid out, a little sprinkled with a substrate and slightly moistened. Then they are covered with polyethylene, put into the vegetable tray of the refrigerator and kept for 2 weeks.
Next, the container is placed in a well-lit warm place, from time to time sprayed from a spray bottle, preventing the soil from drying out. Every day for 15-20 minutes the film is removed, allowing the planting to breathe.




Around the second half of May, when the threat of night frosts has completely passed, the seedlings are transplanted into open ground. To do this, in the prepared area, pits are dug up to 20 cm deep and drainage from expanded clay, crushed stone or broken brick is laid on their bottom. A nutritious mixture made from sand, turf and humus, taken in equal shares, is poured on top, small depressions are made in the substrate and seedlings are planted.
The distance between adjacent holes should not be less than 20 cm, otherwise the plants will be too crowded. Then the plantings are watered with warm settled water and transferred to a general care regimen. Young stonecrops begin to bloom after 2-3 years.


How to grow sedum from seeds and cuttings
The plant can be propagated by stem cuttings, layering, seeds, as well as mature leaves. With seed propagation, the first shoots appear in 10-15 days, the cuttings take root in 15-20 days.
It must be said that the leaves of stonecrop are rather fragile and, breaking off from the stem, quickly take root.
When stonecrop propagates, the rhizomes are separated after 2 months and give a lot of hanging stems that cover the walls of the pot.
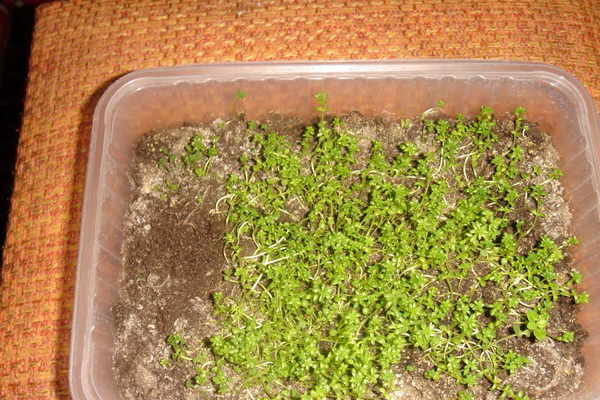

Sowing seeds is carried out in spring or autumn in bowls or boxes, which are covered with foil. Seedlings are very small. When 1-2 true leaves appear, they dive into pots. Young plants bloom in the 2-3rd year.
Many flower growers do not deepen the seeds, put them superficially in spring or before winter, in bowls or boxes, which are dug into a garden bed or put in a greenhouse. Seedlings are very small. When 1-2 true leaves appear, they dive into boxes or beds. Young plants bloom for 2-3 years. Four - five-year-old bushes are divided at the end of summer or in spring into divisions with 2-3 buds, a piece of rhizome and roots.
In the spring, at home, stonecrop houseplants are propagated by leaf cuttings. They are preliminarily dried for several days and planted in clean sand washed with water. Stem cuttings should be immediately planted in pots with medium-heavy, water- and air-permeable soil.
In stonecrop, during the flowering phase, stem cuttings 10–15 cm long are cut and rooted in wet sand. After 20-30 days, they take root.
Vegetative propagation of ixora
How to root Ixora from a cutting photo
In room conditions, Ixora is propagated mainly by cuttings:
- Cut the cuttings in the spring from semi-lignified shoots (material for rooting remains after pruning).
- You can root in water: dust the cut of the cutting with Kornevin, place 2-3 cuttings in a jar or vase, after dissolving a tablet of activated carbon or adding a couple of drops of phytosporin per 100 ml of water, put in a warm place with diffused lighting.
- Full-fledged roots will form in 3 weeks, then they can be planted in separate containers with soil for adult plants.
Ixora stalk rooted in the substrate
Also, cuttings can be rooted in wet vermiculite or directly in the substrate for rhododendrons. Deepen the cuttings by 0.5 cm, cover the common container on top with a transparent bag or a piece of glass, each cuttings can be individually protected with a glass glass, jar or cut plastic bottle, the shelter will need to be lifted daily for airing. The lighting should be diffused, the temperature should be in the range of 25-30 ° C, bottom heating is desirable. When the cuttings grow, they can be planted separately.
After planting rooted cuttings, pinch the tops of the shoots, repeat the procedure when the young shoots reach a height of 15 cm.
Very rarely, Ixora is propagated by layering. It is difficult to bend the branches to the soil, therefore, propagation by air layers is used:
- Closer at the top of the shoot, make a circular cut of the bark in the form of a wide strip, wrap this place with wet vermiculite, wrap it with cellophane on top, leaving holes for air to penetrate.
- Shorten the leaves on the cutting by ½ the length, moisten the vermiculite as necessary, add water (add rooting stimulants to it) with a syringe.
- When good roots are formed, the young plant can be cut off and planted separately.
Reproduction
Like all types of hare cabbage, stonecrop reproduces well in a vegetative way: by leaves or stems. It is best to carry out cuttings in early to mid-July.
At this time, the plant feels great, and there is just enough time until autumn for the cuttings to take root well and get stronger.
Before planting the cuttings, they are dried in a cool place. After planting, it is sparsely watered in order to compact the soil between the plants.
In addition, young stonecrops need oppression, since, unlike adults, they cannot yet withstand direct sunlight.
Landing in open ground should be carried out no later than the beginning of September. Otherwise, young growth may not have time to take root before the start of frost.
It is advisable to plant cuttings of caustic sedum immediately in a permanent place of growth. As already mentioned, plants of this species do not like frequent transplants.
Stonecrop propagation by seeds is possible, but rather problematic. A greenhouse is required for reproduction and growth is very slow. The dive is carried out after the appearance of two true sheets. The sedum, grown in this way, blooms only after 3 years.
Adult and large enough plants are successfully propagated by dividing the root system.
Diseases and pests
- Exposure of the stem or stretching. The reason is lack of light, mechanical damage.
- Root rot. May arise from heavy watering or cold winters. We reduce watering, and in the spring we cut the plant.
- Leaves dry out - not enough moisture.
- Nematodes are small roundworms. Treatment - treatment of the plant with solutions of laundry soap, with extensive damage - treatment with actellik.
-
Root bug - affects the root system, the plant withers quickly.
The plant should be transplanted by removing the damaged roots, the rest should be treated with tobacco or infusion of pharmacy calendula.
In general, Morgan's sedum lives well for 6 years, after which the plant should be updated.
In folk medicine, the juice of this plant is used as a healing agent for wounds and burns, but if there are children at home, it is better to hang it higher, if it gets into the stomach, it can cause upset and vomiting.
1 Botanical description
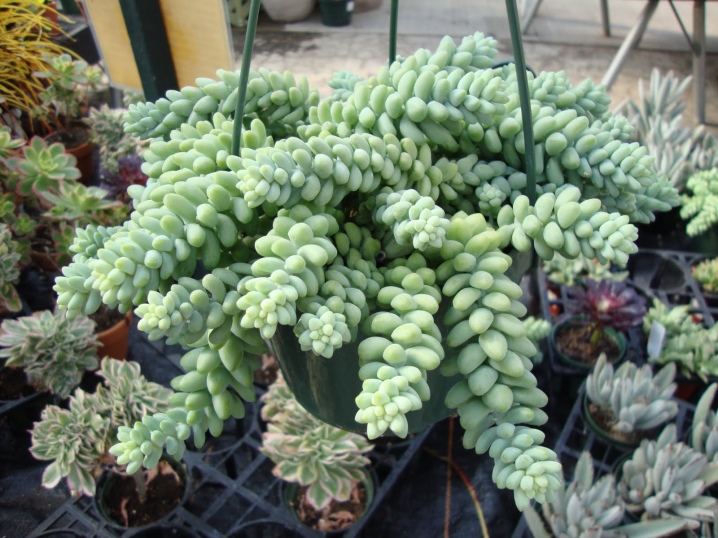
The sedum Morgan (Sedum Morganianum) is a striking representative of the group of succulents grown at home. Its botanical description clearly characterizes the second name, which the flower growers dubbed sedum - donkey or monkey's tail. Indeed, the spectacular stems, reaching a length of 0.6-1 m, resemble the tail of an animal. Long hanging shoots are strewn with fleshy cone-shaped leaves covered with a waxy bloom. This bluish bloom protects the flower from sunburn.Inside the leaves, which look like claws or fangs, are the moisture reserves necessary for the plant to survive.
During flowering, pink or purple small flowers appear at the ends of the shoots. An adult specimen looks very elegant, since several flowers open at the same time on each shoot.

The root system is superficial and does not grow strongly even when the sedum reaches an impressive size.
Types and varieties of indoor sedum
The sedum plant has worked well as a perennial garden plant, but it also grows well and grows indoors. It must be remembered that this plant does not like abundant watering and that it should have a dormant period in winter. In the summer, stonecrop can be safely taken out into the street, planted in pots that decorate the balconies - the warm summer air will only benefit the stonecrop.
Adolf's sedum (Sedum adolphii)
It has green fleshy leaves with a light bloom. The shape of the leaf in some of the distributors is similar to the Nussbaumer sedum, only the color is different. There are also plants with wider leaves. It takes on a reddish tint in bright sunlight.
 Adolf's sedum
Adolf's sedum
Sedum Morganianum
Indoor plant. The stems hang down from the pot and are densely covered with round, elongated, slightly pointed leaves that vaguely resemble bananas. Perhaps that is why his nickname is "Monkey Tail". The color of the leaves is bluish green. The leaves easily break off the stem, even from a slight touch when moving the pot from one place to another, but the leaves also easily take root.
 Morgan's sedum / Blossom
Morgan's sedum / Blossom
Sedum burrito
This species is easily confused with morgan sedum. Its difference is in the color of the leaves - stonecrop burrito has a bright green color, and the shape of the leaves is not pointed, but rounded.
 Sedum Burrito
Sedum Burrito
Sedum Stahlii - Stahl
It does not hang from the pot, but grows upward, the shoots can reach 15-20 cm in height, the leaves are tightly attached to the stem, have an ovoid shape. The color of the leaves is brownish red.
 Sedum of Steel
Sedum of Steel
Sedum mexicanum
Ampel plant with long shoots. Its leaves are elongated, thin, needle-like. This plant blooms with yellow flowers. Gardeners love to use this flower to decorate summer planters on balconies along with annual flowers.
 Sedum Mexican / Blossom
Sedum Mexican / Blossom
Sedum Sieboldii
This is an ampelous plant, with long, about 20-25 cm, stems. Its leaves are bluish-green (some varieties have a different color), round in shape. It is well suited for outdoor hanging pots, for decorating rockeries and alpine slides in the summer. However, this type of sedum does not tolerate frost well, so for the winter, bring it indoors where the temperature will not drop below 10˚. The heat in winter will also have a bad effect on this flower, since winter is a dormant period for it. In the fall, it will shed its leaves, and in the winter it should be placed in a cool place in partial shade. Watering during this time of year should also be kept to a minimum.
 Siebold Sedum / Blossom
Siebold Sedum / Blossom
Nussbaumer sedum (Sedum nussbaumerianum)
This sedum grows in a small bush, with pointed fleshy leaves of a lemon-pink hue.
 Nussbaumer's sedum
Nussbaumer's sedum
Red sedum (Sedum rubrotinctum)
A well-known indoor species native to Mexico. A distinctive feature is the red, fleshy leaves. The plant acquires a rich red hue in bright sunlight. Blooming with yellow flowers with a short pedicel.
 Sedum red-colored
Sedum red-colored
Features of home care
Most varieties of sedum are suitable for keeping in a home environment. They are able to exist even in the harshest conditions, so they will not cause unnecessary trouble. It is necessary to follow simple rules, and then the indoor sedum flower will delight its owner for more than one year.

Sedum is ideal for home maintenance and for decoration of territories.
Temperature
The sedum is thermophilic and tolerates heat well, therefore, in the summer, the temperature should be at least 25-28 ° C. In winter, it is enough to adhere to 10-15 ° C. At higher temperatures during the cold season, sedum shoots can stretch and deform.
Lighting
Sedum is photophilous. It is recommended to place the plant in the sunniest part of the apartment so that it gets enough light. In winter, you can take it out on a windowsill or a heated balcony. For a frost-resistant succulent, a cold zone is also suitable.
Note! You can use phytolamps when there is not enough sun. If you miss this moment, the sedum will stop blooming and fade.
Watering
The plant does not need frequent watering. Its main feature is the ability to accumulate water in the leaves. In summer, the frequency of watering should not exceed twice a week, and even less often in winter - once every two weeks. Water is used at room temperature, settled. With a lack of moisture, leaves may fall off, with excessive moisture, the plant will die.
Air humidity
Sedum feels great in dry warm air. There is no need to spray it in order to moisten it, it is only necessary to remove dust from the surface of its leaves. In conditions of high humidity, sedum leaves can undergo a decay process.
Soil and top dressing
Sedum primer can be purchased at the store, special for succulents. You can also make it yourself:
- mix turf and leaf species with river sand, add small pieces of brick and coal;
- add rotted foliage and sand to 2 teaspoons of peat.
In the spring-summer period, feeding is carried out at intervals of 1 time per month. Mineral fertilizers are suitable for cacti, the amount is calculated according to the attached instructions. Autumn and winter are the dormant period of the succulent.


