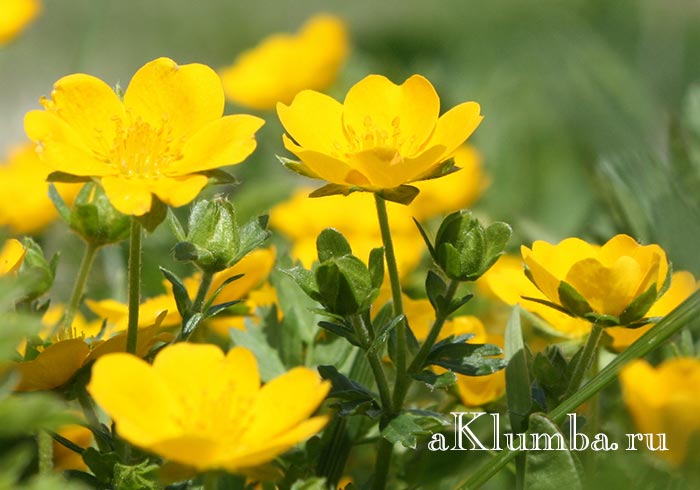
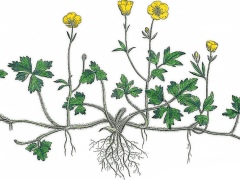
Planting buttercups with tubers
We made a general description of the buttercup family, examined the main types and features of growing plants from seeds. However, this method is rarely used. A more common method of growing garden buttercups is to plant rootlets. They are sold in flower departments, but can also be obtained independently by digging up tubers and dividing the root system.

Buttercup tubers
Planting material is chosen, paying attention to even minor details. Traces of pests and mold, other defects indicate that they are trying to sell you roots of dubious quality
The germination rate will be low.
- Since the planting material is offered in a dried form, it must be well prepared before planting. For example, immersion in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 40 minutes is a good prevention of diseases.
- Then each root is wrapped in wet gauze and left for a couple of hours. The procedure is repeated once more, but the roots in a wrapped cloth or gauze are placed in a bag and placed in a cool place overnight.
- After such simple manipulations, the roots swell well and become like octopuses. In this form, garden buttercups are completely ready for planting and care.
Popular varieties
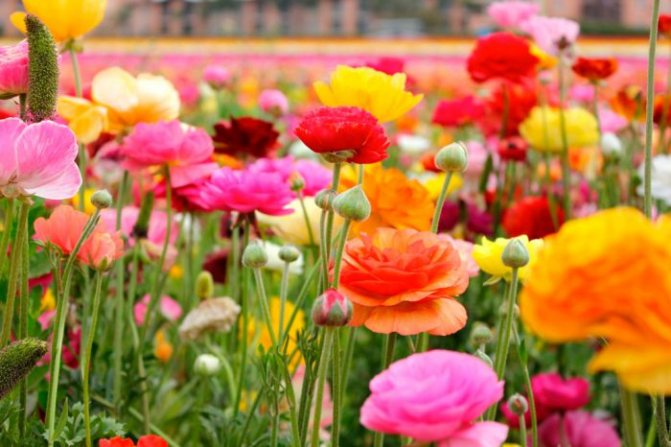
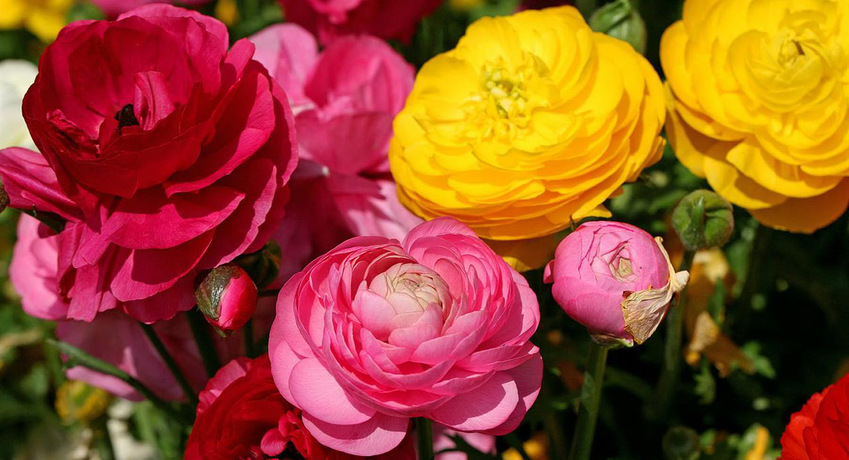
The appearance of ranunculus has quite a few options, but the plants are divided into several groups according to the shape of the inflorescences:
Asian ones are similar in description to multi-colored roses, they are distinguished by high thermophilicity, although some hybrids are quite capable of growing in a rather cold climate;
turban or African with large spherical flowers that have a dense double shape;
Persian ones have simple or semi-double buds of small size, peduncles are also low;
French ones have semi-double flowers, the petals are arranged in two rows;
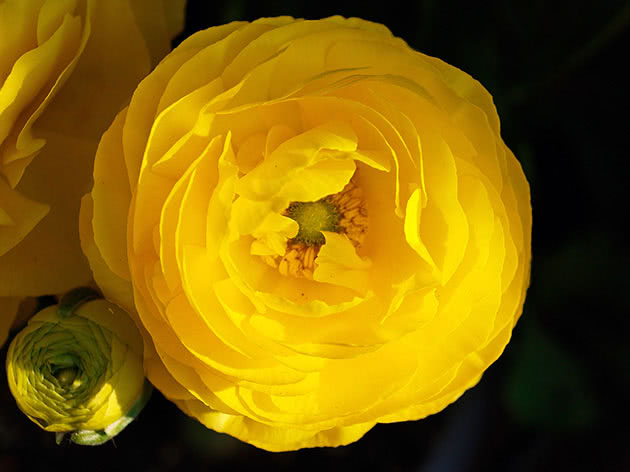
peony are distinguished by large, about 10 cm, double inflorescences.
There are quite a few varieties of garden buttercup, both wild and cultivated. Among the most famous and common varieties of ranunculus, the following can be distinguished:
Bloomingdale orange bicolor can reach a height of 30 cm, with large inflorescences (about 9 cm in diameter), which are orange in color with a reddish border, the variety is distinguished by a rather long flowering;
Bloomingdale Blue Bicolor does not exceed 25 cm, has white buds with a dark pink border, prefers areas with nutritious soil;
"Bloomingale rose bicolor" has a very beautiful color: white terry inflorescences are decorated with pink edging;
Red is distinguished by an exquisite burgundy color of buds, which are often used to decorate bouquets, the shoots are long, up to 40 cm, the variety blooms at the end of July;
"Pikoti" has several varieties, in which the edges of the petals have a color that is very different from the main color, the shape of the flowers is similar to semi-blooming peonies;
"Pearl Pikoti" - a beautiful hybrid of the previous variety, has white buds with a light purple-lilac dusting on the edges of the petals;
"Double Pink Buttercup" - a hybrid with densely double buds, pink petals are numerous and tight;
"Elegant" has a variety of colors of inflorescences, but the most spectacular are flowers with white petals having a burgundy top or yellow-lemon buds with purple streaks along the edges;
"Festival" is distinguished by numerous, densely folded petals with a contrasting center of green color, the color of the buds can be different: pink, cream, lemon or white;
"Pon-pon" has inflorescences resembling lush pom-poms in their appearance, which stand out for their beautiful mixed colors: red with light green, snow-white with delicate purple transitions;
"Carousel" is distinguished by a different color of the buds, in which the core is green, the variety propagates exclusively by seeds, since no shoots are formed on the rhizome;
"Success" is a very disease-resistant variety and is characterized by a rather long flowering period, large buds have different colors;
"Flamenco" stands out for the unusual appearance of the buds: yellow petals have a bright red border;
"Andrea" has dense spherical double inflorescences about 8 cm in diameter, flowers are brightly colored and serve as a real decoration of the flower bed;
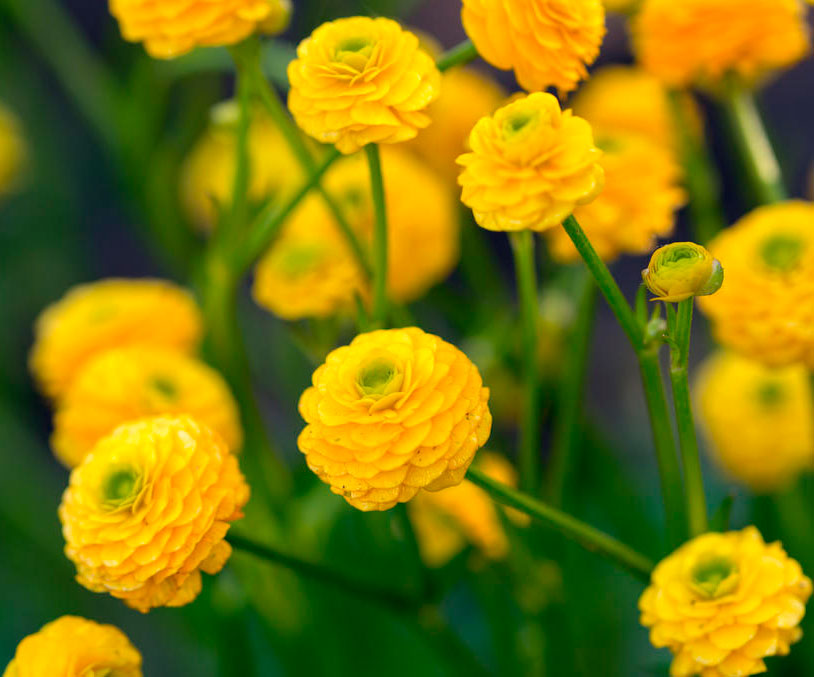
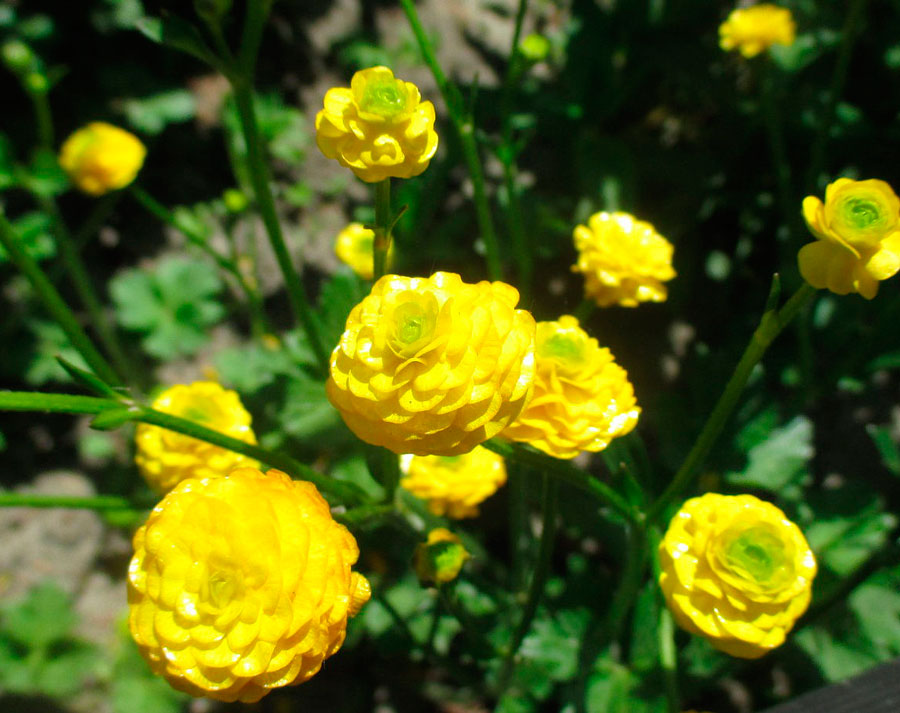
"Victoria" does not differ in height (up to 30 cm), small buds are painted in bright yellow, in shape they are very similar to roses;
"Blossoming Valley" with large bright red double-type flowers, reminiscent of rose bushes, prefers cultivation plots with a light shadow;
"Yellow" stands out with rather large lemon-yellow buds that look like balls.
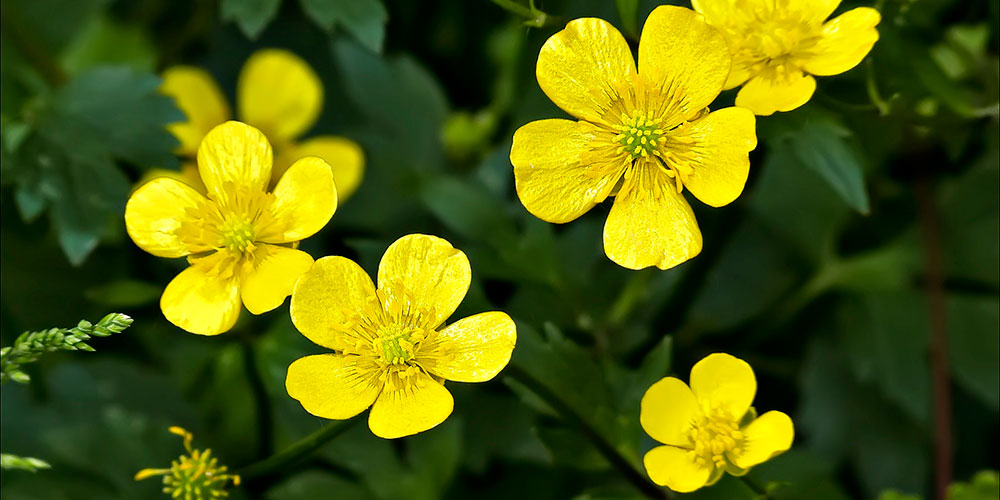
Often, flower growers prefer to plant a mix of buttercups, because in one sowing you can grow a bright multi-colored meadow of flowers.
Views
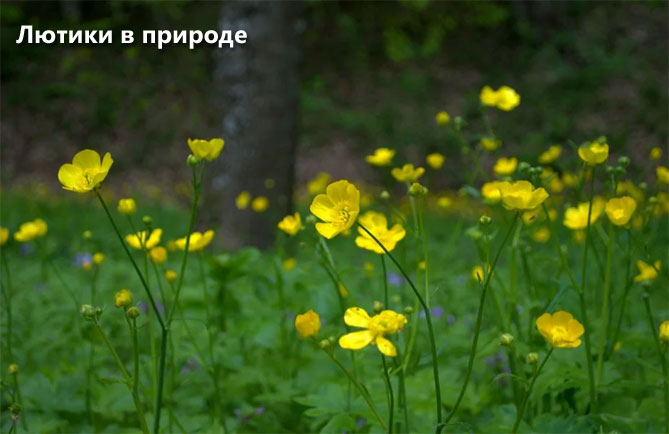
More than 40 species of ranunculus grow in the Russian open spaces. Profusely blooming buttercups give the natural landscape a vibrant color. Description of some species representatives:
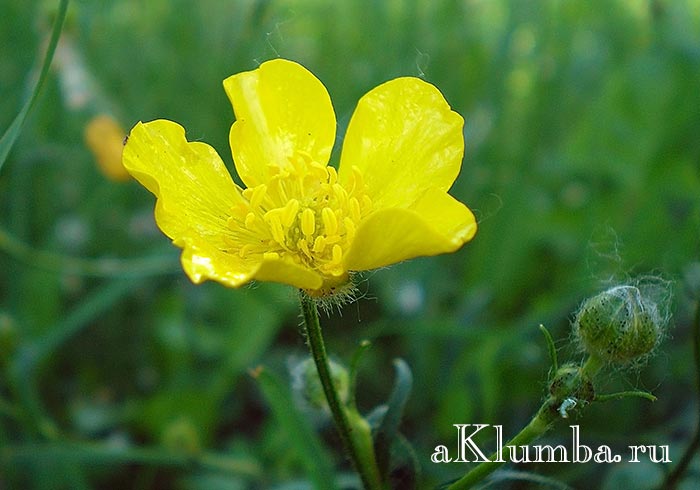
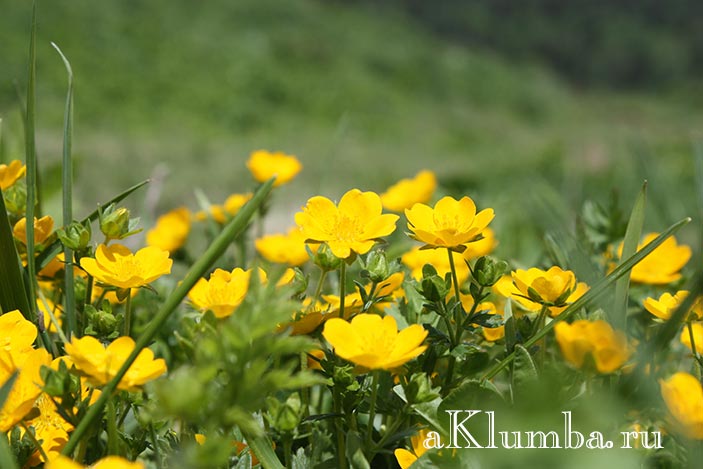
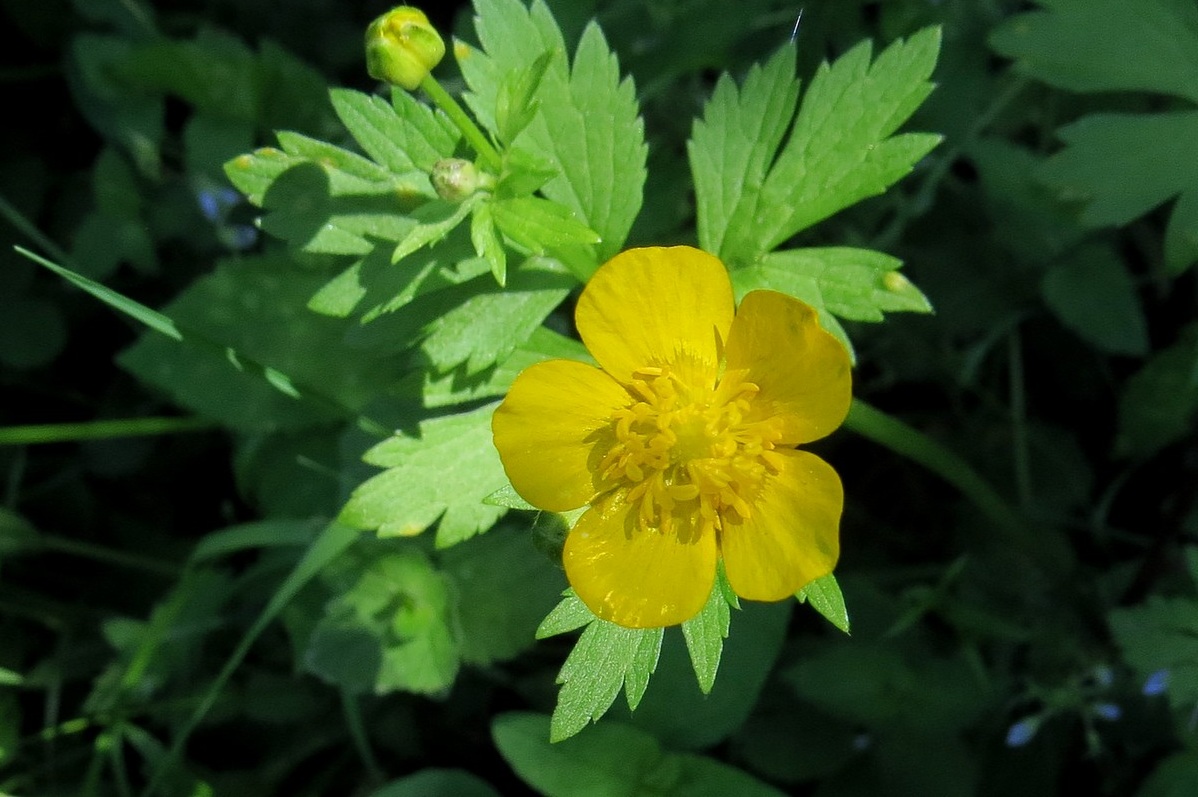
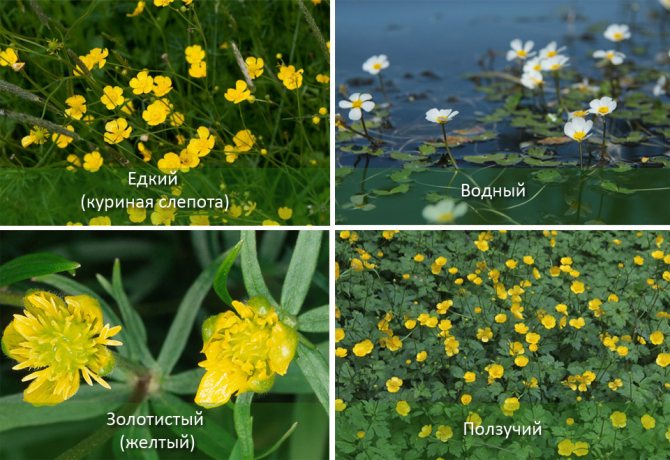
- Ranunculus sarmentosus Adams (scion) is a perennial plant with a creeping stem that takes root in stem nodes, forming new shoots. Long-petiolate rounded leaves are collected in basal rosettes. Flowers are yellow, single, five-petalled. The culture is widespread on the seacoasts of the Far East, in the vastness of Siberia, Mongolia, and China.
- Ranunculus acer L. (acrid). Perennial reaches 1 m in height. It is popularly known as night blindness. The stem is pubescent with hairs, basal leaves on long petioles with a palmate-divided leaf plate. The flowers are five-petal, bright yellow on long stalks. Stem leaves are sessile, tripartite. Representatives of this species are distributed along the banks of rivers, in meadows, forest glades of a temperate climate.
- Ranunculus sceleratus L. (poisonous) has a stem 50 cm long, thickened tripartite leaves with an oblong lobe. The pubescent peduncles bear small yellow flowers with a diameter of 10 mm, which have sepals longer than the petals. On an elongated receptacle, many leaflet seeds ripen. The flowering period of the culture is May-June.
- Ranunculus repens L. (creeping) is a perennial with a short rhizome and a creeping thick, pubescent stem measuring 40 cm. Leaves are of two types: basal petiole, formed at the nodes and upper sessile, lanceolate. The diameter of the flower corolla is 2–3 cm. The color of single flowers located at the top of the stem is yellow. There are subspecies of culture with a semi-umbrella inflorescence. Ranunculus blooms in June. Distributed in humid shaded areas along river banks and in swamps.
- Ranunculus polyanthemos L. (multiflorous) - perennial up to 80 cm in height. It has a branched ribbed stem, leaves and yellow flowers are pubescent with prominent whitish hairs. A poisonous plant with a pungent odor is common in dry meadows and forests. Buttercup yellow blooms from June to August. Used in folk medicine for the preparation of tonic, wound healing and pain relievers.
- Ranunculus flammula L. (burning) - perennial with a long stem (50 cm), broad basal leaves on long petioles and sessile stem small leaf blades. It has single yellow apical flowers with a diameter of 8-12 mm. The flowering period is from May to September. It grows near the reservoirs of central Russia and Western Siberia.
Breeders have bred many varieties of ranunculus, taking as a basis the simplicity of wild representatives of the genus and improving its aesthetic qualities. Ornamental garden buttercup often has a powerful stem and double flowers of different shades, which allows florists to actively use it to compose beautiful bouquets. The most popular ranunculus varieties among florists are:
- terry buttercup;
- Bloomingdale Rose Bicolor;
- Pearl Pikoti;
- Double Pink Buttercup;
- Flore Pleno;
- Masha.
 RANUNCULUS (LUTIC). AFTER 3 WEEKS AFTER LANDING
RANUNCULUS (LUTIC). AFTER 3 WEEKS AFTER LANDING
Watch the video
Diseases and pests
Garden buttercups are an ornamental crop that is rarely exposed to diseases and pest attacks, provided that the correct watering regime is observed. In waterlogged soil, flowers are sometimes at risk of infection with powdery mildew and root rot. When a whitish bloom appears on the leaves and peduncles of the plant, you need to start urgent measures to protect the ranunculus from the spread of the fungal disease.
Infected plant parts should be removed. Fungicide such as "Topaz", "Saprol", "Fundazol" will help to destroy the harmful mycelium of the fungus - the causative agent of powdery mildew. An aqueous solution of the drug must be prepared according to the instructions on the packaging of the product. For those gardeners who do not accept the use of fungicides, there are folk remedies to combat a dangerous disease:
- Soda ash solution. Dissolve 25 g of sodium carbonate in 5 liters of hot water with the addition of 5 g of any liquid soap. The cooled solution is sprayed with flowers and soil 2 times a day for a week.
- Soap and soda solution. 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of soda with 100 ml of boiling water. Dissolve 1 teaspoon of shavings of laundry soap in 4 liters of hot water. Add soda solution. Spray flowers 2 times a day for a week.
The fight against root rot involves loosening the soil around the flower, removing damaged parts of the plant. Surviving leaves and stems should be sprinkled with wood ash for disinfection. The aerial part of garden buttercups is sometimes damaged by cabbage butterflies, and the roots are damaged by nematodes. To repel the attacks of pests on flowers, it is necessary to treat the plants and the surface of the earth with solutions of insecticides (Aktellika, Karate, Nematofagin, etc.)
Growing and caring for the garden
If you decide to grow buttercups, you need to know that soils with neutral or weak acidity are suitable for them. In this case, the soil should be loose and nutritious, moderately moist. Areas with high groundwater levels should be avoided.
How to plant
- To begin with, the garden bed where they plan to plant a buttercup is dug up.
- Then equidistant holes are made at a distance of 15 or 20 centimeters from one another, and a depth sufficient for complete immersion of the roots.
- A handful of sand or vermiculite is placed in each hole before planting.
Favorable weather conditions will allow observing the first shoots 7-10 days after planting. And the period from germination to the appearance of flowers is usually about 75 days. By the end of the summer season, the fruits of the buttercup reach maturity. Now you can collect seeds, there are about 500 of them in each box.
How to care
During the period of development and growth, caustic buttercup does not require special care. It is enough to regularly fight weeds and loosen the soil in the beds. With watering, the main thing is not to overdo it, they moisten the soil no more than twice a week, only if drought occurs. With the arrival of prolonged and heavy rains, the beds are covered with polyethylene. For the ripening of tubers, and in order to exclude decay, in August, watering is reduced to a minimum.
In autumn, after the plant stem has completely dried out, the rhizomes are dug out of the ground. Leaving them in the ground for the winter is excluded, this will lead to the inevitable death of tubers. After removing, the roots should be dried.For the winter, they are buried in containers with peat or simply wrapped in linen and stored in a dark and cool place (for example, a cellar).
4. Reproduction
For buttercup, there are several methods of reproduction at once - by dividing the bulbs, forming air layers and seeds. With generative or seed propagation, the varietal characteristics of plants may be lost.
4.1 Growing from seeds
Most varieties can be propagated using seeds, but with this method of propagation in varietal plants, daughter bushes may differ in appearance from their parents. The germination rate of planting material is often low even with proper storage and sometimes does not exceed 20 percent.
It is preferable to buy seeds from a flower shop, but you can also get your own planting material. In order to obtain high quality seeds, even during the flowering period, the largest brightly colored buds can be marked with colored threads.
Achenes are separated from mother plants after complete ripening. In order to prevent the seeds from spilling onto the surface of the earth on their own, the achenes are pre-tied with gauze or bandage or a nylon sock is put on.
As the achenes mature, they are pruned, and the seeds are sent for drying in a warm and well-ventilated place. Dried planting material is collected in paper envelopes and stored in a cool and dry place.
Sowing seeds is carried out at home in late February - early March or sown in open ground in May. For growing seedlings, small flower boxes are prepared with drainage holes and nutritious and loose soil. The land mixture can be made up of equal parts of peat and river sand.
The soil surface is slightly tamped and moistened with warm water from a spray bottle. Seeds are sown and covered with sifted air earth or a small layer of river sand 4 - 5 mm thick. Crops are re-moistened and covered with glass or a clear plastic cap to create a greenhouse effect.
Every day the plants are ventilated by raising the cap for a few minutes. The air temperature for sprouting should be 10 - 12 degrees Celsius. With the appearance of sprouts (this usually occurs within 2 - 3 weeks), the air temperature is raised to normal room temperature.
The airing time is gradually increased, and with the appearance of the first shoots, the shelter is completely removed.
Bushes develop quickly enough and at the age of 6 - 8 weeks they can demonstrate 3 - 4 true leaf blades. Seedlings are kept at room temperature, in a well-lit place, but out of reach of direct sun. The soil is kept evenly moist.
With the appearance of the first real leaves, a dive is carried out - the flowers are planted in separate cups. A week after picking, buttercups can be fed for the first time with nitrogen fertilizers in a very weak concentration.
Diving can be carried out in peat pots - in this case, the seedlings can be transplanted into the garden directly in them. When each plant can boast 3 real leaf blades and reaches a height of 10 cm, the seedlings can be planted in open ground.
Seed reproduction helps to get many plants at once, but it requires a lot of patience - not all varieties of buttercup will form buds in the first year of life. Most often, during spring and summer, the bushes will grow green mass and an underground bulb, and the first flowers will decorate them only in the second year.
4.2 Subdivision of tubers
Before planting, especially large rhizomes can be carefully divided by hand into 2 - 3 parts. You should not divide the tubers into a large number of parts - even in the best case, the plants will recover for a long time and will bloom only in the second year, at worst they will simply die.
The places in which the wound surface has formed are sprinkled with crushed charcoal or ash and dried
Water such plants after planting with extreme caution, since excess moisture can provoke the appearance of rot. During the season, several daughter bulbs may appear on adult rhizomes - they are separated and planted.
1 Variety
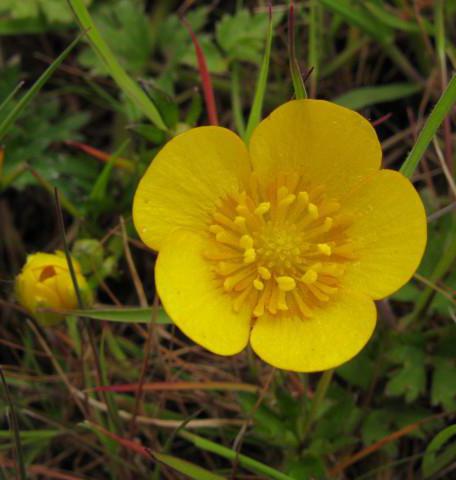
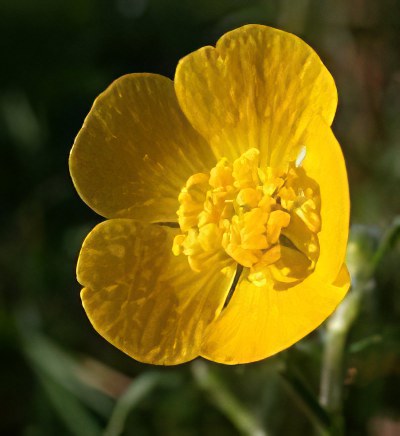
The buttercup flower is extraordinarily beautiful. The shape of the buds ranges from simple to densely double. Buttercup species can be divided into four groups depending on the shape of the inflorescences:
- turban - large densely double inflorescences of a spherical shape;
- Persian - small simple or semi-double inflorescences;
- French - semi-double inflorescences;
- peony - large double inflorescences.

Peony and turban buttercups are most popular with flower growers, because they look great on flower beds and flower beds, in balcony boxes and floor vases, in mixborders and rockeries.
Ranunculus inflorescences, depending on the variety, look like half-open roses and dahlias, spherical chrysanthemums and double peonies. Due to the absence of a pronounced odor, the flower does not cause allergies, therefore it is excellent for cutting.
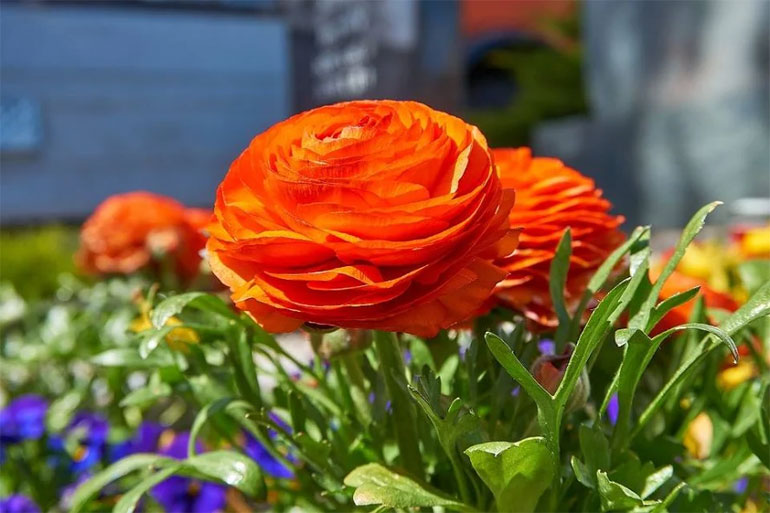
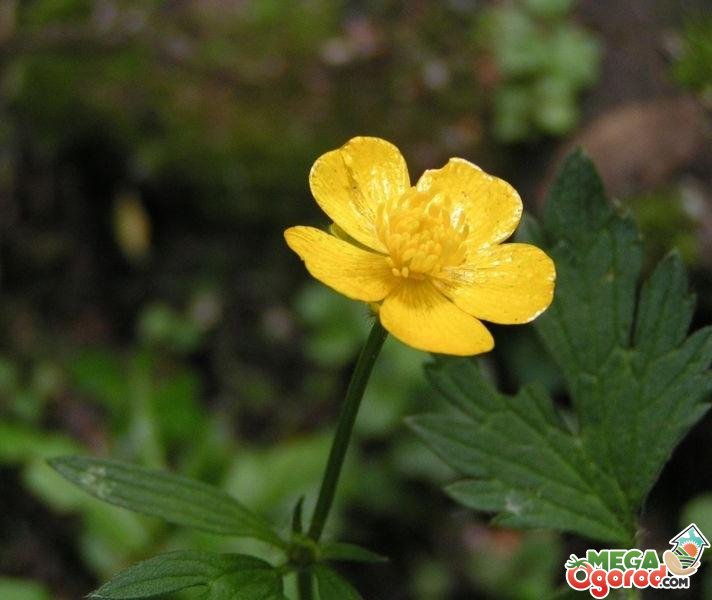
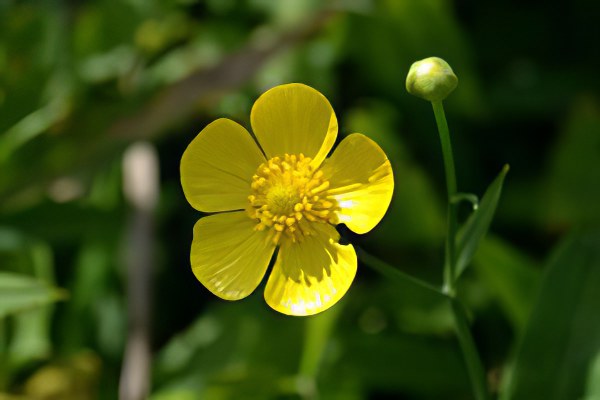
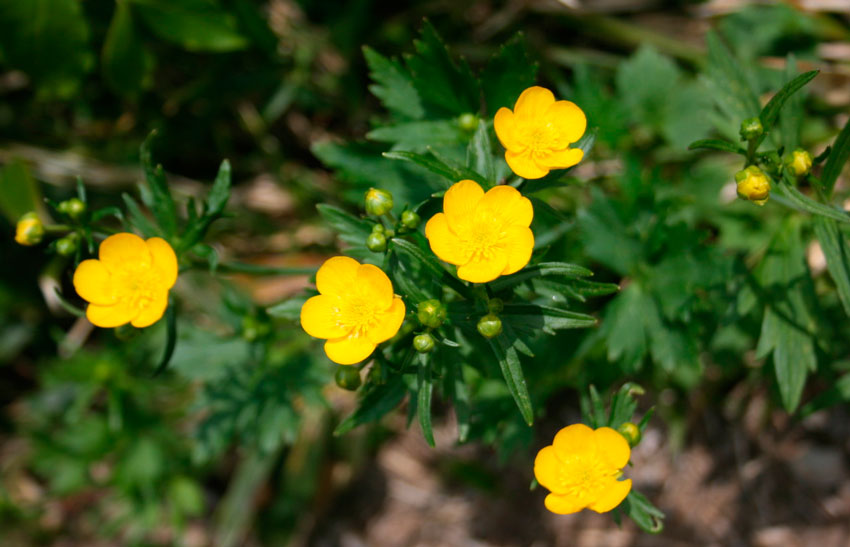
Buttercup belongs to herbaceous perennials, but some growers consider it annual due to the difficulty of storing tubers. A simple weakly branching stem reaches a height of 30-50 cm, and tuberous rhizomes, similar to cones or spiders - 2-2.5 cm. The green parts of ranunculi are strongly pubescent, the leaves are tripartite. The diameter of the inflorescences, depending on the variety, is 4-10 cm. Flowering is short in June, but under favorable conditions, buttercups bloom until early August.

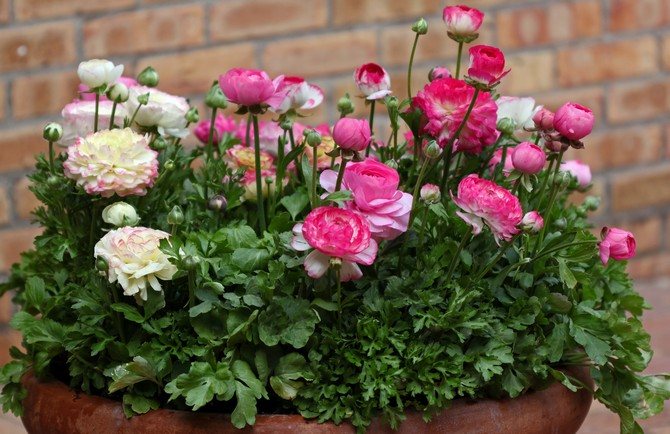
Buttercups garden planting and care
buttercup photo and description
Ranunculus is planted in open ground with no turning onset of heat in order to exclude night frosts. Areas with light shade are well suited for planting, because under the scorching sun, buttercup flowers quickly die. It is imperative to protect the plants from drafts.
As a material for planting, only the rhizomes of the plant in special packaging go on sale. It is better to take responsibility for their choice: check for damage or disease, so that your investments and efforts are not wasted.
Indeed, the survival rate of a plant on your site depends on the quality of the planting material.
buttercup root
Before planting buttercup roots, it is necessary to prepare in a special way:
- to begin with, they are placed for 30 minutes in a strong solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection;
- then, the roots are wrapped in a damp cloth and left to lie in a warm room for two hours. This is necessary to saturate the roots with moisture, because during storage, sellers do not always provide the right conditions, so the goods often dry out;
- at the third stage of preparation, the planting material is tempered in a refrigerating chamber for 24 hours. For this, the roots, without removing the matter, are folded into an oilcloth bag.
The result of proper preparation will be smooth, elastic tubers. They have become much larger than their original sizes, which means that now, with complete confidence, the roots can be planted in the beds.
Rules for the care of Garden Buttercups
Watering Buttercup is necessary once every 3 days, but if the weather is dry. Watering should be moderate. When the air humidity is high, the plants are watered less frequently. In case of prolonged rainy weather, it is recommended to cover the beds with cellophane. In August, watering stops - during this period, the tubers ripen, and excess moisture will provoke their rotting.
Loosening, removing weeds
Buttercup Garden responds well to loosening the soil. Its root system requires good air exchange. It must be carried out after watering. Together with loosening, it is necessary to remove weeds.
Top dressing
The beauty of flowering, the number of inflorescences largely depends on the nutrients in the soil. For this, it is necessary to apply fertilizers in a timely manner.As top dressing, it is recommended to use nitrogen-containing fertilizers (at the initial stage of plant development) and complex fertilizers containing potassium and phosphorus (during the flowering period). Fertilizers are applied once every 15 days.
Digging tubers in the fall
As soon as the stem of the plant dries up, you need to start digging out the bulbs. This usually happens at the end of September. In no case should you leave tubers in the ground for the winter - they will die. After drying the dug tubers, they are buried in peat or wrapped in cloth. Store the seed in a dark, cool place. The optimum storage temperature is approximately + 20 ° C.
Diseases affecting Buttercups Garden
With poor care, Buttercups Garden can be affected by fungal diseases. As a rule, this is due to waterlogging of the soil. Plant roots begin to suffer from rot. This contributes to the wilting of flower buds, the development of powdery mildew. In addition, mold appears on the leaves.
In this case, watering is reduced, and specimens affected by powdery mildew are treated with a fungicide solution designed to combat this disease.
Harmful insects dangerous for Garden Buttercups
Most often, plants are attacked by spider mites, nematodes. In flowers affected by spider mites, yellowish or whitish spots begin to appear on the leaf plates. Such plants are immediately treated with an insecticide.
If Buttercup leaves began to curl into a tube, then this is the first sign that a nematode has settled on the plant. In this case, the roots are urgently treated with a manganese solution, from which the nematode quickly dies.
Caring for the mesembriantemum at home
Growing from seeds
Sowing the seeds of the mesembryanthemum directly into the soil is possible only in the southern regions. In middle latitudes, seedlings of such a plant are first grown, while sowing is carried out in the first half of April. It is not worth sowing seeds earlier, because the seedlings need a lot of light. To grow seedlings, you need a breathable light soil mixture, which should consist of coarse sand, peat and garden soil (2: 2: 1).
The substrate must be disinfected before planting, for this it is calcined in the oven or spilled with a solution of potassium permanganate. Then the surface of the soil mixture is leveled and removed to a warm place for 15 days, during which time the beneficial microorganisms necessary for the plants should multiply in the substrate. The seeds must be evenly distributed over the surface of the soil mixture, which must be pre-moistened, then they are slightly pressed into the substrate, but not covered with the substrate. The container must be covered with glass or foil, and then it is removed to a well-lit cool (15-16 degrees) place before the seedlings appear. After about 7 days, the first seedlings should appear, when this happens, the plants are removed to a cooler place (from 10 to 12 degrees). The mass appearance of seedlings occurs only after 3-4 weeks.
How to water and feed
The development of fragile seedlings is extremely slow, and they also do not have resistance to root rot, in this regard, in order to grow seedlings of such a culture, it must be properly watered. The greenhouse where the seedlings grow should be well ventilated, while the soil mixture should always be slightly damp. To moisten it, you must use a spray. After the plant grows stronger, and they have 2 true leaf plates each, they should be cut into individual containers (plastic cups or pots), which are filled with the same soil mixture, but it should be noted that there should be a lot of sand in it. It is not necessary to feed such a plant during the seedling period.
Landscape design
Beds of decorative buttercups are usually placed under tree crowns, which create a not very dense shade.
decorative ranunculus
They are also planted in a separate group, because the foliage and flowers of night blindness, even decorative ones, are of modest size, which means that the plant will visually “disappear” in conjunction with other cultures. The only acceptable company for buttercups is permissible to consider blue anemones, while always placing it in the background.
Regularly, in order to maintain the aesthetic appearance of the plantations, sluggish inflorescences that have lost their visual appeal should be removed.
As it turned out, buttercup garden cultivation and care prefers simple, with all this, beautiful and attractive compositions are created with its help. But today rarely found in personal plots, due to the fear that the buttercup is poisonous.
But you can and really deserves the attention of gardeners to use ranunculus in landscape design!
Buttercup flower care outdoors

It does not take much time and special attention to care for this garden herb.
Watering should be done regularly, but in moderation. Excess moisture is not allowed. With prolonged rainy weather, the roots of the plant may begin to rot, so you need to use a film cover. At the end of the summer season, watering should be gradually reduced, and then completely stopped (with the appearance of wilting leaves).
For abundant flowering, a good air exchange is necessary for the root system, therefore, loosening of the soil is required.
Good flowering depends on the availability of essential nutrients in the soil. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers (at the initial stage of plant development) and complex fertilizers containing potassium and phosphorus (during the flowering period) are used as top dressings. Top dressing is recommended to be applied twice a month at intervals of two weeks.
In order for the flowering period to be longer, it is necessary to timely rid the plant of dried flowers.
Features of the cultivation of the umbilical cord
In gardening, 3 types of this culture are popular, but the planting of the spring navel is done more often, because caring for it is very simple, it is the most unpretentious of all, it can grow in the shade, it blooms and does not lose its decorative effect even with prolonged drought, requiring only rare watering. Below are tips for successfully breeding omphalodes, after reading which, even a beginner can grow a beautiful groundcover in his garden.

Location. The navel is shade-tolerant, grows successfully and blooms in partial shade. You can plant it under the crowns of shrubs and garden trees: linden, rowan, apple and others. In the sun, under direct rays, it turns yellow and becomes a minor, therefore diffused lighting is preferable. Like any mountain plant in low places it can get wet. To prevent this, it is advisable to plant this plant in higher elevations, or take care of a good drainage layer.
The soil. This culture grows well in any permeable areas. The soil should be slightly acidic, light and nutritious, but too rich soils are contraindicated. Dolomite flour or chalk is added to acidic ones.
Top dressing. Omphalodes does not need top dressing, it is enough to mulch the soil around the bush with humus in the spring.
Watering. When cultivating an umbilical flower, it is fate that all its types are drought-resistant, they easily tolerate hot, dry periods. The bush should be irrigated once a week to maintain its flowering and decorative effect. Weeding is required after watering.
Shelter for the winter. All types of umbilicals, except for the Cappadocian, are highly resistant to frost. This species is prepared for wintering: it is covered with dried fallen leaves, which is not only a shelter from frost, but also a fertilizer.