Dates for planting tulips
The development of a tulip is directly dependent on the external habitat. Temperature has a direct effect on the plant. Since the growing season begins with the first warming, flowers appear early. This is due to the fact that the shoot begins to grow in the fall. This situation is inherent in all primroses.
- Planting small bulbs is best done in early August. This is done for the early development of the plant.
- In this case, young animals need to be watered regularly (2 - 3 times a week).
- Loosen the soil around the plantings (2 times a month).
Large-sized bulbs take root in late September or October. This is done so that the plants have time to adapt before frost. If there are severe winter frosts in the area, you can mulch the surface of the landing site. At the same time, this layer must be eliminated in the spring. It can interfere with the growth and flowering of plants.
Rules for planting daffodils in the fall in open soil
There is nothing difficult in this event, even a novice florist can handle it. Several preparatory procedures need to be done.
Location
- The choice of a site for growing these flowers should be done in the summer. The best place and composition of the soil is loam. But on a different soil, the plant will also grow and bloom successfully.
- The acidity level for daffodils is preferable - 6.5 - 7.0 pH. If the soil in your flower bed contains a high percentage of sand, then over time, the flowers will begin to decrease in size. As a result, the flowering process stops altogether.
- You need to know that in the harsh winter months, sandy soil freezes much faster than others. This can seriously harm the bulb, even destroy it.
Soil composition
- Add the necessary ingredients to the soil first to make your daffodils feel comfortable. If the soil is sandy, then add clay and humus. When the soil is too heavy and oily, then sand should be added at the rate of 20 kg per 1 m2.
- Dig up the area where you are going to plant the daffodil bulbs 3 months before the planting process. Digging depth of at least 25 - 35 cm. Fertilize the soil with rotted manure, humus and compost. Prepare the ground in late spring or early June.
- Humus will need at least 15 kg per 1 m2, and 20 kg of manure for the same area, prepare and apply at least a year before the planned planting. If the flower bed with daffodils is very small, then you can do the following: remove the top layer of soil and replace it with a special fertile one for bulbous garden flowers.
Planting depth
Bulbs are usually found in different sizes before planting. Therefore, they need to be examined and sorted by size. In addition, check for damage, rotten areas. It is better to throw out such planting material immediately so that there is no contamination of other plants.
Experienced experts recommend planting the bulbs according to the classic rule - the depth is 3 onion heights. So, deepen large ones by 15 - 20 cm, and smaller ones by 10 - 15 cm.
But, if you have a task to achieve an earlier flowering, and you want as many babies as possible to form on the mother bulb, then plant it a little closer to the soil surface.
If the flowering of plants needs to be done a little later, and there is no need for an abundance of children, then deepen the bulb a little more when planting.
For larger and more abundant flowering, it is better to purchase varieties of the highest class, and when there is a goal to propagate a rare or favorite variety, it is better to use small bulbs.
Landing scheme
- Choose a place for planting plants that is sunny and well-lit. Although daffodils grow successfully in a penumbra. If the bulbs are large, then space between the planting holes at least 20 cm.When the planting material is rather small, then the distance can be reduced to 8 - 10 cm.
- Pour a small layer of river sand at the bottom of each planting hole. Fix the onion with the bottom down. Press down a little. Make sure there are no voids in the soil.
- Take a handful of wood ash and sprinkle a thin layer on each onion. This will protect the plant from diseases and infections. Then fill half of the hole with a nutritious potting mix. The topmost layer is a mixture of soil and complex mineral fertilizers. The main components are phosphorus and potassium, which contribute to high-quality and abundant flowering.
- Use a dose several times less than that indicated on the package and in the instructions. If the weather is rainy, then watering can be omitted. But in dry climates, it is imperative to moisten the soil.
How to store?
The main task of the grower after digging out the tubers is to preserve them correctly in autumn and winter. Often, especially novice growers are faced with the fact that the bulbs are moldy or prematurely germinated. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly and consistently follow all the rules at each stage.
Preparing for storage
It is precisely the strict implementation of all the recommendations described below that will make sure that mold or mildew will not appear on the flower bulbs.
Immediately after removing the tubers from the ground, they must be sorted. Cut, damaged and too small bulbs are removed - they are not used as seed in the future.


In addition, there are a number of steps to be taken.
- Remove dirt from the surface of the bulbs. If the earth has dried up, then it is carefully separated in pieces, but if it is wet and adhered in a thick layer, then the bulbs are washed. It is best to do this first in hot water, the temperature of which is about +40 degrees, and at the very end, rinse the tubers with a pale pink solution of manganese.
- The outer brown husk is removed from the daughter bulbs and separated from the mother tuber.
- If large bulbs are found to be damaged by fungus, you can try to rescue them. To do this, they are treated with a fungicidal solution, and then dried thoroughly.


Drying
Even if the bulbs have not been previously exposed to moisture, they should be thoroughly dried before storing them.
To do this, the tubers are laid out on a flat surface so that they do not come into contact with each other. Place the onion tray in a dark and cool place with natural ventilation.
It is highly not recommended to dry them near heating devices or directly in the sun. The average drying time is 10 days.


Where and what to store?
Tubers are laid out in a storage container depending on their size - you cannot store bulbs of different sizes together. Here it is worth remembering that the largest tubers survive storage best, but the small ones often begin to disappear during storage, even if the storage conditions are met.
The planting material of tulips is placed in containers in one layer, and on top is covered with a thin layer of sawdust or special moisture-resistant paper.
The optimal storage conditions for bulbs are:
- temperature from +3 to +28 degrees;
- complete lack of light;
- the optimum humidity level is from 55 to 70%.
In an apartment, the best place to store them will be a balcony or a glazed loggia. If we talk about storing bulbs in a private house, then here you can use a basement, pantry or underground
Particular attention should be paid to the absence of freezing temperatures, because frozen tubers are not subject to further planting.


Now that you know all the information about the storage, digging and further planting of tulip bulbs, you can easily grow them at home and keep the seed in excellent condition.
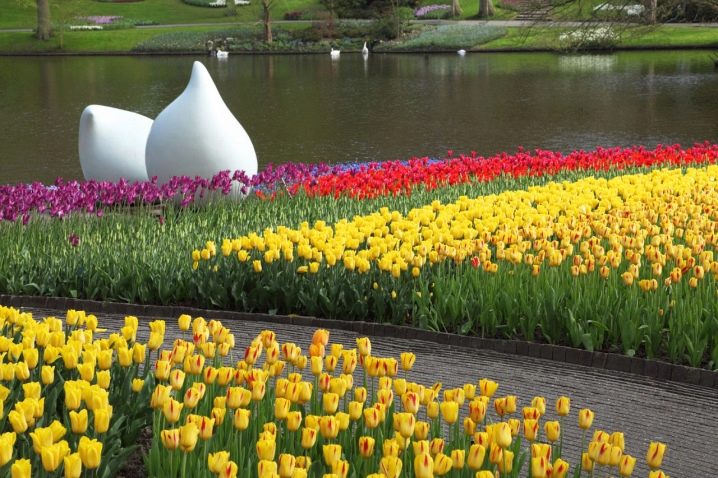

How to prepare tulips for planting?
The preparation of planting material includes several stages:
- Sorted by diameter, small and large bulbs are deepened at different distances from the surface. Also, the distance between the planted plants depends on the size.
- Before planting, visually inspect the material for the presence of fungal and infectious diseases. If you plant a diseased plant with healthy ones, there is a high probability of infection of the rest of the tulips.
- Pretreatment, disinfection of bulbs.
- Processing of the affected material if it is a pity to get rid of.
Inspection, sorting
If the bulbs were not sorted after digging or the acquisition is timed directly to planting, then you should immediately take up the inspection:
- For this, the planting material is laid out on the table.
- Inspect each bulb for external damage.
When the inspection is over, the plants are sorted. Sick bulbs are laid separately. Tulips are also divided by diameter.
Peeling, disinfection
First of all, they deal with healthy bulbs:
- For better receipt of nutrients from the soil and growth, it is necessary to carefully (so as not to damage the planting material) to remove the brown husk.
- Then treat with a weak solution of manganese and leave to dry for 30 minutes.
The upper shell is also removed from diseased bulbs and again examined from all sides.
- If the damage is minor, then remove the affected area with a knife.
- Then it is dipped in a pink manganese solution for 5 minutes.
- Then they are dried in the shade and planted separately from healthy plants.
After disinfection and quick drying, the plants are immediately planted. They do this because the bulbs, saturated with moisture, begin to sprout. If you do not do this on time, then when the plant deepens into the ground, they can break. When this happens, new roots no longer grow and the plant dies.
Instead of manganese, you can use other disinfectants, which it is advisable to inquire about in specialized outlets.
Storage periods
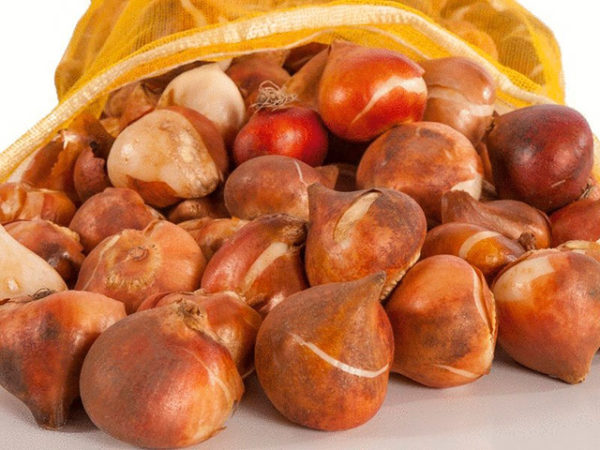

It is difficult to store tulip bulbs at home in winter. The planting material of these flowers is not suitable for long-term storage. It is best to dig up the plants after flowering and store them until digging in the fall. The option with winter storage is suitable only in exceptional cases (for example, they bought plants late in the fall and did not manage to plant them before the cold weather). Subject to the conditions until the fall, the onions are well preserved.
If the storage conditions are violated, the bulbs deteriorate. How to determine:
- droplets of moisture appeared on the surface of the integumentary scales - a signal of dampness and high humidity in the room;
- bulbs shriveled, become soft - the air in the storage is too dry.
In the first case, household heaters are used for drying, while humidifiers and water containers placed in the storage will help to cope with dryness.
Tulips protect from mice and other rodents, not only in flower beds, but also during storage. In cellars, basements, premises are disinfected in advance, baits are scattered, traps are set. To protect tulips from mice, boxes are placed on shelves, hung in bags or stockings on hooks under the ceiling. Observing the simple rules for digging and storing tulips, it is always possible to obtain healthy planting material. And this means that in the spring, your favorite bulbous in the plots will again delight you with friendly flowering.
Storage tips
Store daffodil bulbs in dry, cool places, for example, in a barn, basement, dry cellar. The storage temperature should be about 20 degrees Celsius, without sudden changes. Do not try to store the daffodil bulbs in the refrigerator until planting in the fall, although at first glance, the conditions are suitable there: cool and dark. The air humidity in the refrigerator is so high that daffodils will quickly sprout and become unsuitable for planting outdoors.
Each bulb must be provided with air access, so you need to decompose them in one layer. If there is a lot of planting material, then you can arrange the bulbs in two layers, laying a layer of newspaper or paper between them. You do not need to do more layers, as this will complicate further work with the planting material.
Cardboard boxes or wooden crates are best for storing bulbs. Never use cellophane bags, plastic, plastic or glass containers. The bulbs that you nursed so carefully can simply rot.
Next, periodically review your planting material. Go through each onion, examine it from all sides. If you find diseased or rotting bulbs, throw them away, otherwise they can infect healthy plants.
Storage humidity should be approximately 70%
It is important to ensure that it is not very high or extremely low. If the air in the room where the bulbs are stored is very dry, occasionally spray water around the planting material
Ventilate the room periodically if it is not equipped with automatic ventilation, as the bulbs release a small amount of gas during storage.
The dug out daffodil bulbs actively continue their vital activity: they grow, breathe, and form flower buds. Thus, they need to be stored until planting in the fall for no more than three months.
The optimal planting time is late August and early September. Planting them too early is not recommended, as the plant will start to grow and will not survive the winter well. Later, it is also not necessary, because the daffodils will not have time to form roots, and the unrooted plants will die.
When planting daffodils, choose a spot in your garden where water will not stagnate in spring during floods and in summer during rains.
If you want daffodils to delight you with their flowering as long as possible, plant them under trees in shady places. There, their color will appear in all its glory, will not fade from the bright spring sun and they will bloom for a very long time.
Prepare the holes, the depth of each of them should be equal to three times the height of the onion. That is, if the height of the bulb from the bottom to the crown is 5 centimeters, then the hole must be dug 15 centimeters deep. Now you need to pour some sand on the bottom to ensure drainage, then cover with fertilized soil.
For the winter, you can cover a flower bed with daffodils with foliage or dry grass.
Observing the rules outlined in this article, you can every year admire amazing daffodils from early spring to early summer and enjoy not only contemplation, but also from the very process of caring for your bulbous pets.
For information on when and how to dig up daffodils, see below.
Optimal timing
It is necessary to dig up tulip bulbs after flowering, until the children are disconnected from the bulb nest. There is no single digging time, the optimal time depends on the climatic conditions of the area. You can determine the best period for extracting a plant from the soil by its external features:
- leaves wilted and turned yellow by 2/3 of their length;
- the lower ground part of the plant bends easily, it can be twisted around the finger;
- The covering scales of the bulbous body are brownish brown.
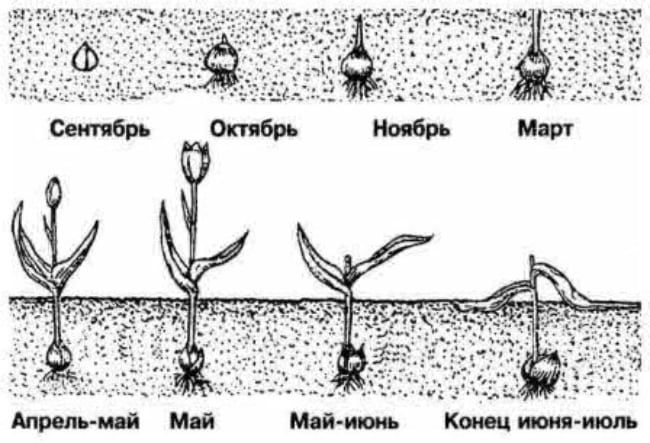 Tulip from planting to digging
Tulip from planting to digging
In the Moscow region, these signs can be observed in early varieties of tulips in late June - early July. Late plant species are dug up 10-14 days later. The timing of the excavation of culture in other regions of Russia may differ by a month. A dry sunny day is chosen for the procedure. In a rainy, cold summer, tulips do not turn yellow for a long time. A florist should act like this:
- after flowering, fertilize the crop (30 g of superphosphate and 15 g of potassium nitrate per 1 m²);
- after 15 days, dig up the onions;
- without cutting off the ground part, place in boxes;
- sprinkle with dry earth;
- transfer the bulbs to a dry warm room for ripening;
- prepare the bulbs for storage.
Why are tulips dug up
 If we proceed from the fact that tulips are originally wild plants, then digging them up after flowering, it seems, is not necessary - they winter well, bloom in spring. But in culture now it is not natural species and "old" hybrids, but new varieties, the quality and varietal characteristics of which are preserved during summer digging and planting in autumn.
If we proceed from the fact that tulips are originally wild plants, then digging them up after flowering, it seems, is not necessary - they winter well, bloom in spring. But in culture now it is not natural species and "old" hybrids, but new varieties, the quality and varietal characteristics of which are preserved during summer digging and planting in autumn.
In addition to botanical (natural) species, varieties bred in the last century, you can not dig tulips from the Foster group (some varieties) and the simplest varieties. If there are few flowers, then in case of their death it is easier to buy new planting material than to store it.
Every year, tulips of rare exquisite species and varieties are dug up, late flowering, once every 2-3 years - resistant varieties, once every 4-6 years - old, simple and unpretentious varieties.
What does digging give:
- the bulb, freed from children, accumulates more nutrients;
- bulbs that have not been dug become smaller, degenerate or go into the ground so deep that the seedlings cannot break through the thickness of the earth;
- without digging, plantings thicken, which leads to a decrease in decorative qualities;
- varietal characteristics are preserved, the quality of flowering improves;
- hybrids, for example, fringed tulips, need a high temperature to form a full-fledged bulb, which cannot be created at a depth of 12-15 cm;
- low-quality planting material can be rejected;
- the soil is renewed, fertilized, freed from weeds, plant residues, dug up, which helps to improve the structure;
- the bulb left in the ground often becomes an object for various infections, the reproduction of pests (in summer it is warm, the soil is moist, which plays a role in the rapid development of the pathogen);
- the plant can be transplanted to another place, freeing the old one for other crops.
Do I need to dig up the bulbs after flowering
By July, tulips and daffodils will bloom, and their leaves will turn yellow and withered. Before the ground part of the plant withers naturally, you do not need to touch the flowers - the bulbs accumulate nutrients, and if the shoots are cut off before the bulb is ready for winter, the flower may later die.
Therefore, you do not need to touch the green leaves of tulips and daffodils.
If you absolutely do not like dry stems, you can simply get out of the situation - plant tulips not in a garden bed, but in containers or in pots that are buried in the ground. After flowering, they can be dug up along with the flowers and removed for ripening in some distant place. There, yellow leaves and stems will not catch your eye.

Tulips require bulbs to be dug up annually
Pay attention to certain subtleties of tulip propagation:
- if you want a specific cultivar and healthy bulbs of this cultivar, choose the most beautiful flower and cut the head off a few days after it blooms. The bulb will begin to develop and grow, since the flower will not waste energy on flowering and the development of seed bolls;
- to find out if the bulbs are ready for digging, dig up one or two - they should have pronounced roots and a brown bulb;
- the bulbs must be dug out on a dry sunny day, since they must be dried;
- dig deep with the shovel to avoid injuring or damaging the bulbs.
After drying, the bulbs must be inspected, the strongest and smoothest selected and sent for storage. First, they need to be stored at a temperature of at least 22 degrees, and at the end of August, move the boxes to a colder room (15 - 17 degrees) and store there until the autumn disembarkation.

In this way, you will always have excellent planting material that will delight you with luxurious flowering.
Unlike tulips, daffodils do not require annual digging - they can grow in one place without transplanting for up to five years. If you intend to leave the daffodils in the old place, then after flowering, simply apply fertilizer, and close to the frost, cover the daffodils with insulating material.
And if you intend to plant plants, then dig up the bulbs immediately after. as the leaves dry up, that is, in July. The bulbs should be peeled, dried, and stored in containers. They should be stored in a cool, ventilated area without excess moisture.
However, it is possible to transplant daffodils immediately after digging up without cleaning and drying. If the site is prepared and fertilized, plant the daffodils and wait for the next year to bloom.
How to prepare material for planting
Bulbs are harvested in flower beds in the fall, bought in markets or in specialized retail outlets. But, regardless of the place of purchase, they must be stored correctly in the winter. Seed material is dried, adhered soil is removed, if it remains. The material prepared in this way for storage is laid out in wooden boxes in one layer. If you put it in two or three layers, the risk of spoiling the onions increases. Put away in a cool place. The storage temperature is around zero. Good ventilation is essential.
In private houses, the bulbs are lowered into the basement or cellar. If they are not there, put them in the lower container of the refrigerator. There they remain viable throughout the winter. Before planting, the seed is taken out and carefully examined. All onions with signs of rot or disease are discarded. They will infect healthy specimens. Recently purchased bulbs are placed in a container at the bottom of the refrigerator for at least 12-14 hours. There they will harden, become hardy and resilient.
Further processing is carried out against pests and diseases. The onions are dipped for half an hour in a pre-prepared solution of potassium permanganate of a weak pink color. You can use a tincture of celandine or any other remedy for diseases and pests.
Before planting, remove the hard husk from each bulb. Once again, carefully examine. The slightest sign of illness or damage is a reason for rejection. The risk of infection of neighbors in the flower garden is too great.


