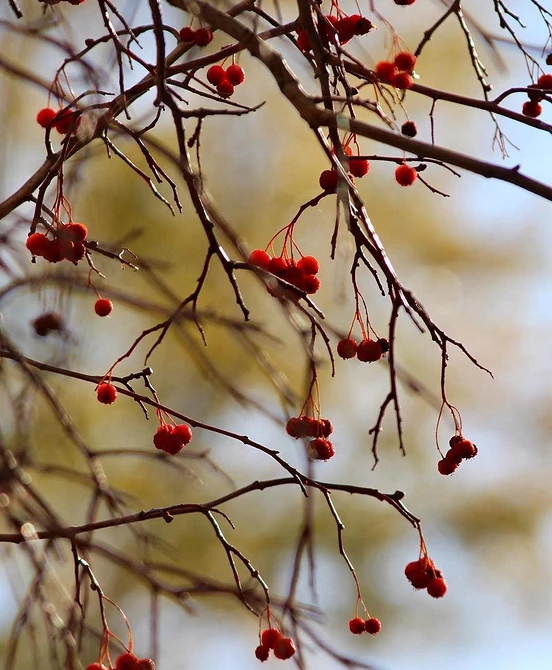
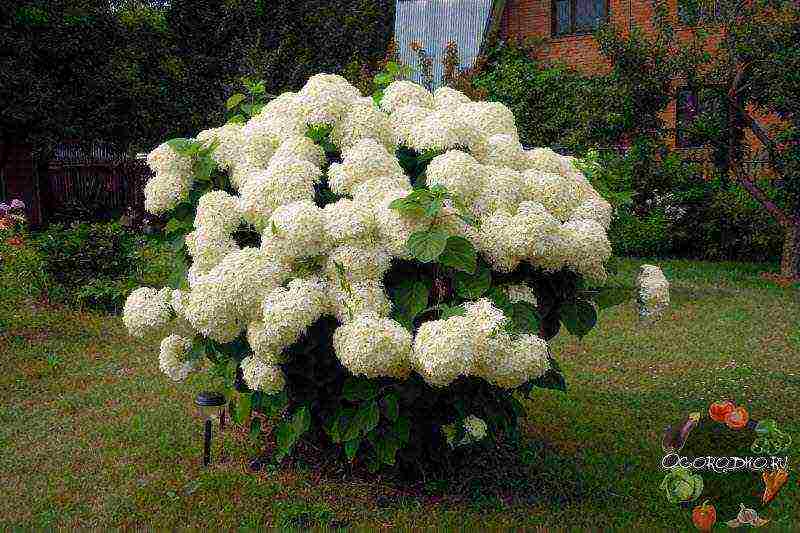4 Hawthorn Blood Red
The most widespread and winter-hardy variety of hawthorn is Blood Red. This bushy tree grows up to 4 m in height. It blooms in May with large pink inflorescences. Despite the not too pleasant smell, flowers are honey plants. Red berries ripen at the end of August and last until frost.
Hawthorn is suitable for creating hedges, but it is also planted alone. The crown can be formed. Pruning is carried out in the spring along with sanitary cleaning.
It is very simple to care for the hawthorn: in the summer it needs one watering every 2-3 weeks, but if it is hot, then a little more often. It is fed once a year - in the spring before flowering.
Instagram @dacha_living
Instagram @ veraslo7

Instagram @life_atmosphere
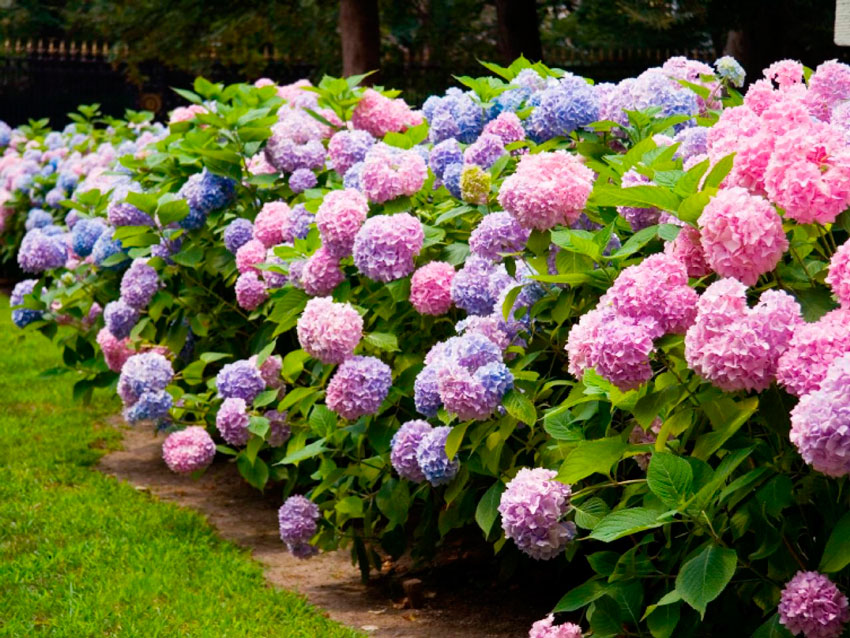
Wintering large-leaved hydrangea
The easiest way to protect low-hardy large-leaved hydrangeas for the winter is to dig and carry them into pots and containers, keeping them either in a cool room with tubs, or on a windowsill in a room with at least 2 months of full shading.
However, constant digging and planting will not allow the plant to build up a normal root system, and the absence of a full-fledged dormant phase will still affect flowering, and the risk of infection with diseases and pests will increase. If you want to keep the macrophylla hydrangea indoors in winter, then it is better to grow it initially as an indoor or garden container plant, the care of which is somewhat different from the general rules.
For successful overwintering in the soil, any macrophylla hydrangea, without exception, needs protection and shelter; even the newest varieties with increased resistance or remontant varieties bloom more luxuriantly due to the ability to release inflorescences on young twigs. Indeed, even in the best hydrangeas, winter hardiness is limited to only 18 degrees of frost. Shelter for garden hydrangeas is often compared to sheltering roses, and they do have a lot in common.
The classic method of protecting large-leaved hydrangea for the winter involves the creation of several layers of shelter:
- in mid-September, leaves are removed from the bottom of the bushes of large-leaved hydrangea to improve lignification, and before the first frost, leaves are removed up to half of the shoots (if it is rainy autumn, then a frame is additionally built over the plant to protect it from waterlogging);
- in late October or early November (if autumn is cold and the first frosts are observed earlier, then in mid-October), the hydrangea bush is spud with peat, using about 1 bucket per plant;
- when the temperature drops greatly, spruce branches or a board are laid on the soil, the shoots of the plant are tilted and pinned;
- the bush is covered with a dense layer of nonwovens;
- from above the bushes are covered with dry leaves;
- non-soaking protective materials (roofing material or film) are laid on the leaves.
Each stage of the shelter is created in a few days, completely closing the hydrangeas only with the onset of stable frosts: damping off threatens the shrub no less than freezing. The holes in the shelter are left until severe frosts, if possible, opening them up during periods of thaw.
Hilling large-leaved hydrangea for the winter. Kathy purdy
There are other options hiding place of large-leaved hydrangea:
- huddled bushes of large-leaved hydrangea are bent to the ground, covered with leaves or covered with spruce branches, and covered with boxes or wooden boxes on top;
- after hilling, spruce branches are laid out around the bushes or wooden flooring is installed, shoots are pinned and the bushes of large-leaved hydrangea are covered with spruce branches or dry leaves, covering from above with non-woven materials; the last layer of shelter is created from peat or sawdust, covered with waterproof materials
Removal of the shelter is carried out gradually, layer by layer, with a difference from 2 to 3 days to 1 week. They begin to remove the shelter in April, and finish only after the threat of spring frost has completely disappeared.
Views
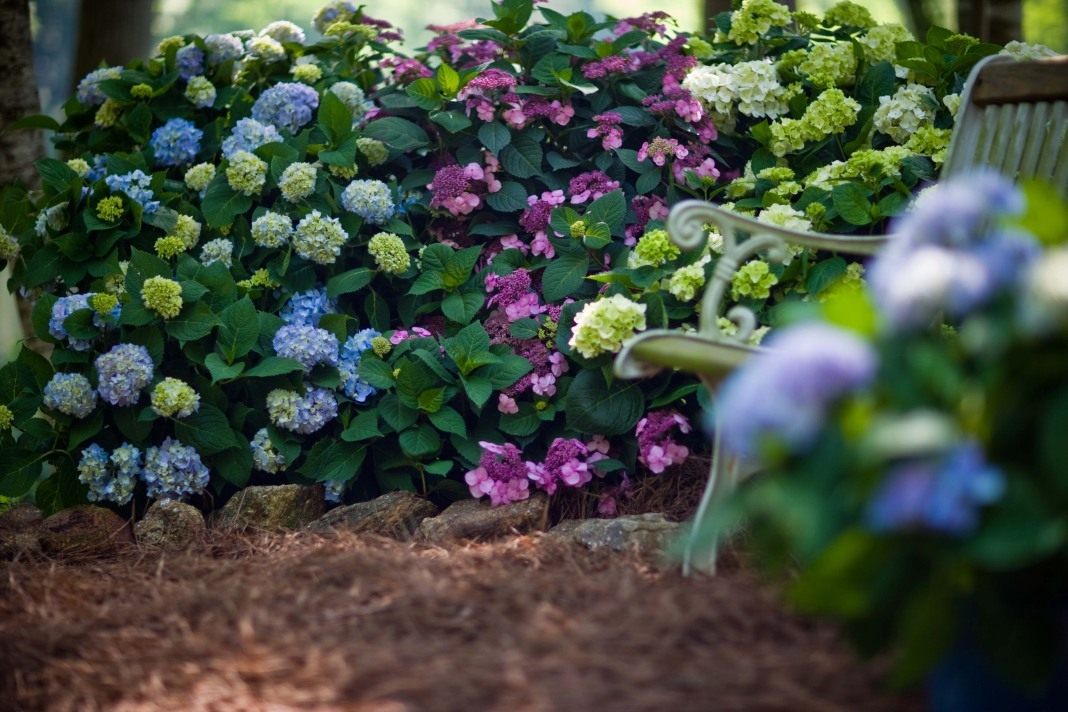
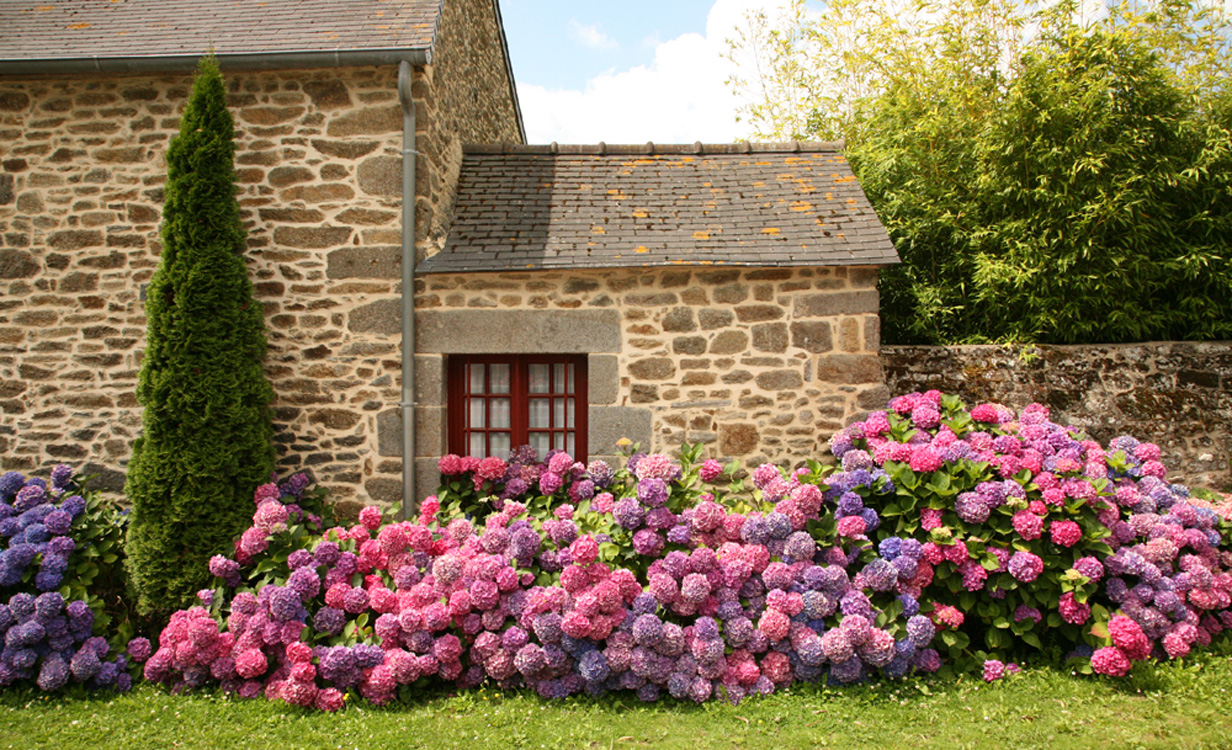
Today gardeners practice growing hardy varieties as well as flowering crops that need additional shelter for the winter. Among the most popular today are several types of hydrangea.
Paniculata
The way this species looks like determines its special popularity. The culture, developing, turns into small trees, which usually will be no higher than 2-3 meters in height. Paniculata (panicle hydrangea) is quite common in Asian countries, as well as in northern Russia. In its natural environment, the plant prefers places near forest edges, in addition, the hydrangea feels good in the thickets of the oak forest. The tree has an elliptical shape, at the bottom the culture seems more lush.
Inflorescences have a paniculate shape
Plants of this species are considered excellent melliferous plants, in addition, in the garden, hydrangea attracts attention with its aroma during flowering. Among the features of this species, it is worth highlighting the property to develop quite actively, in light of which, when growing a panicle hydrangea in a flower bed, it will need to be regularly cut in order to maintain decorative attractiveness
Large-leaved
A perennial species that belongs to the shrub type. These plants reach a height of 2 meters, the shoots of the hydrangea are erect, there is no fruiting. Varieties of this species can have white, blue, pink and even lilac colors of inflorescences, while the leaves are painted in a standard green shade. Plants enter the flowering phase later than everyone else, so you can catch large-leaved hydrangea in bloom from August to November.
Tree-like
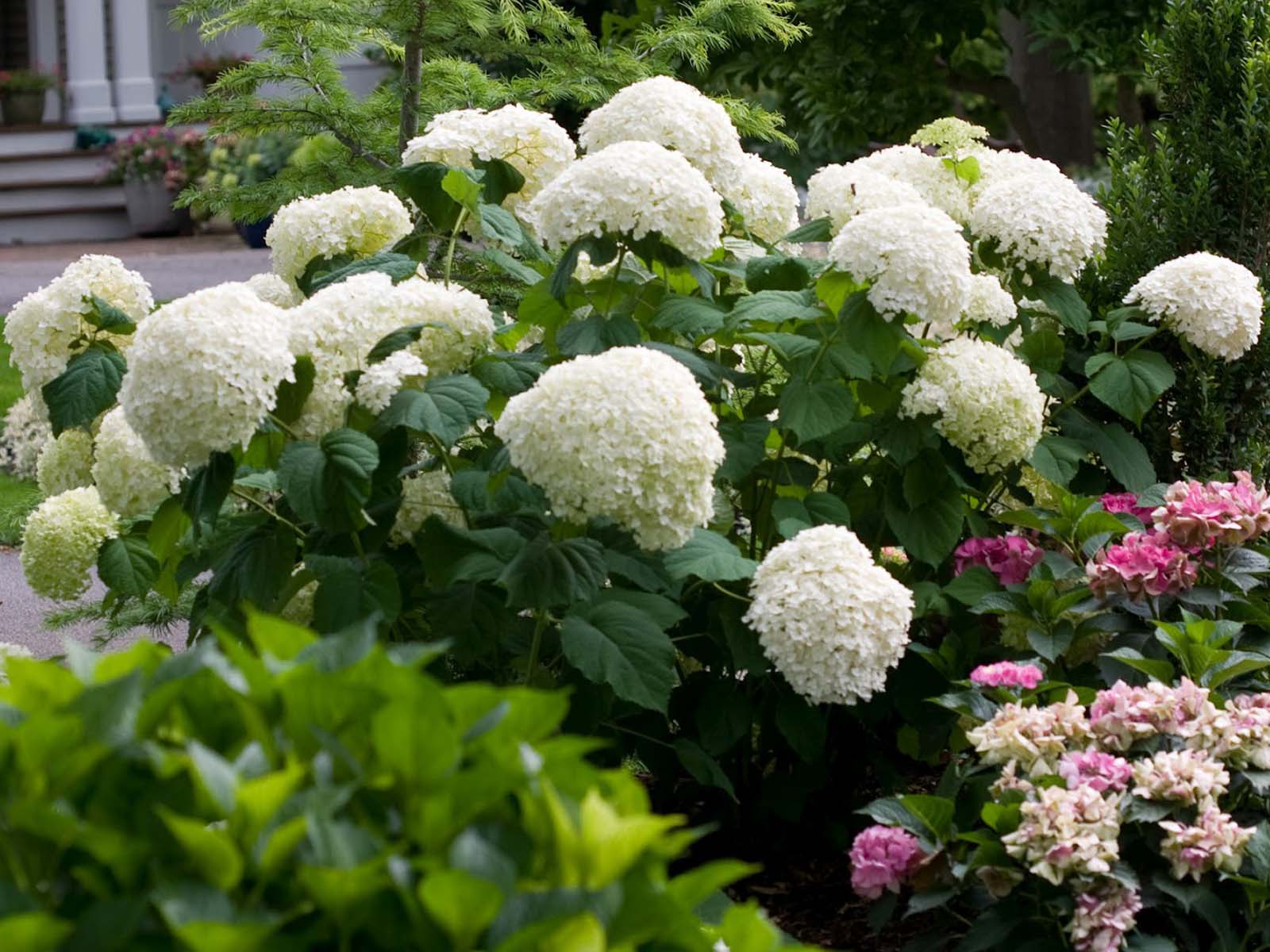
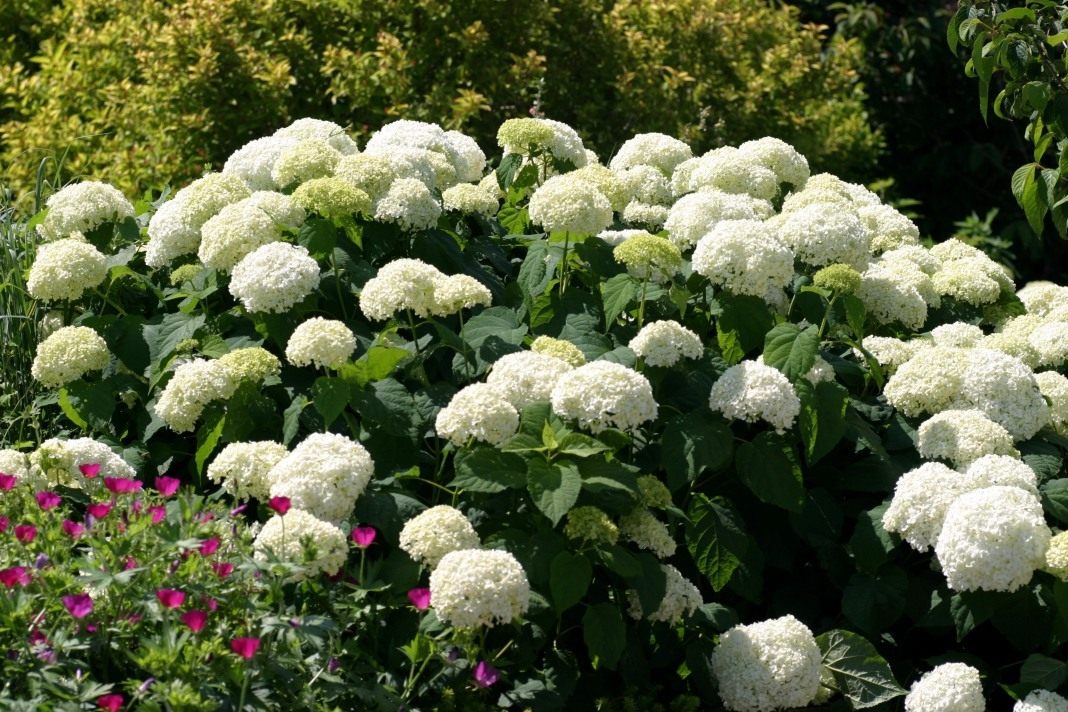
There are several more species names - wild or smooth hydrangea. The culture is notable for its resistance to frost, in light of which it is rather actively cultivated in regions with severe winters. Hydrangea develops in the form of a shrub no more than 2-3 meters high. The shoots of the plant are erect, the leaves are rounded, the varieties are presented in a wide variety of colors.
Pereshkovaya
A culture that has not yet become widespread in domestic front gardens. Hydrangea of this species is a liana, the length of which can reach 20-25 meters. Recommended for vertical gardening, winds well with a high support. Inflorescences are collected in scutes, their color can be white in all shades, as well as in various variations of pink. Another variety that is considered an excellent honey plant.
Dubolistnaya
This is a shrub that grows up to two meters, the shoots of hydrangea are reddish in color. The culture got its name due to the similarity of its leaves with the green mass of oak. The plant blooms with inflorescences of paniculate type, painted in white. The flowering phase occurs in early summer and ends in September.
Radiant
Another species that, in the process of its development, forms a shrub no more than 2-3 meters high. Hydrangea leaves are oval in shape with a pointed edge. It blooms with white inflorescences in the form of shields. Flowering in this species is short, usually lasts one month from June. The culture has an extremely low resistance to negative temperatures, therefore, to obtain a good result, the gardener will need to reliably cover the plant for the winter.
Ash
An upright shrub, usually two meters high. Green leaves are ovoid, in terms of frost resistance, the species shows average indicators.
Serrated
A small tree-like shrub with a beautiful spreading crown. It is an annual with oval-shaped green foliage. Inflorescences in the flowering phase acquire a spherical shape.This version of hydrangea is considered the most beautiful due to the peculiarities of the color - in the middle the flowers will have a blue color, and along the edge their shade becomes close to white. Flowering lasts from July to September.
Hydrangea Sargent
A shrub whose height varies between 2-3 meters. The plant is actively developing in width, flowering falls at the end of summer. Inflorescences repeat the shape of an umbrella, flowers can be painted in purple and lilac tones, after flowering they change color to white. The species is popular due to its frost resistance.
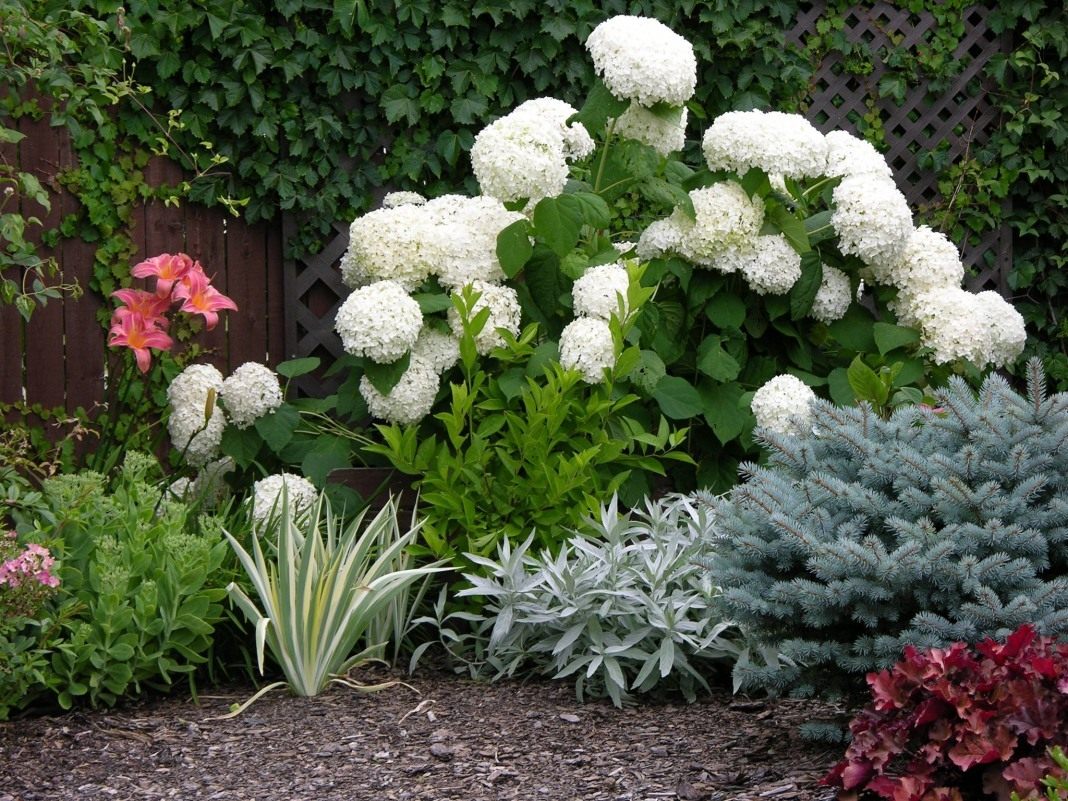
Hydrangea oakleaf: photo and description of varieties
Oak-leaved hydrangea (N. quercifolia) is the most exotic among other hydrangeas. This is a North American plant with a height of 1.5-3 m. Its "highlight" is textured leaves, pleasant to the touch, reminiscent of red oak leaves. Such leaves are the main difference between this form and other species of this shrub.
As shown in the photo, in oak-leaved hydrangea, the edges of each leaf are sharp, with notches:
Leaf size - up to 25 cm. Fresh shoots and young leaves are covered with a light white fluff, which eventually disappears, remaining only on the underside of the leaf. In autumn, the leaves turn purple-red.
Hydrangeas have huge, up to 30 cm paniculate inflorescences with a predominance of sterile flowers, which at first stand like candles, then gradually bend down. Unfortunately, in central Russia, it practically does not bloom. Experts suggest that the matter is not only in the relatively low frost resistance of the shrub (it can withstand a short-term drop in temperature to -29 ° C), but in the insufficient number of sunny days.
Where the climate is milder and there is more sun, varieties of oak-leaved hydrangea are popular:
'Snow Flake'
‘Snow Queen’
‘Garmony’
‘Applause’
‘Snow Flake’ has double flowers
‘Snow Queen’ - white
‘Garmony’ is characterized by spherical or flat large inflorescences up to 20 cm in diameter. The petals are white or creamy.
When describing the oak-leaved hydrangea, it is especially worth highlighting the ‘Applause’ variety, the shrubs of which reach a height of 2 m and have large inflorescences of snow-white color.
Young plants should be covered for the winter or transplanted into a pot and kept indoors as a house flower during this period of the year. In mid-December, the shrub loses its foliage and retires. During this period, it is worth moving the hydrangea to a dark, cool corner of the room and reducing the frequency of watering. Awakening occurs in April - buds begin to swell on the branches of the bush. During this period, the hydrangea must be placed on the windowsill so that the plant receives enough light. It is watered by adding fertilizers to the water. Back to the garden plot, the shrub is planted in May.
With age, the shrub tolerates the cold much better. If your hydrangea, in principle, does not bloom, it makes no sense to preserve the shoots. Then, at the base of the plant, you can simply pour an armful of dead leaves. The bush will freeze almost to the base, but it will surely grow back.
In the southern and western regions of the country, you do not need to dig the hydrangea for the winter, but be sure to cover it. This procedure is performed in dry weather in the fall - in October-November. The branches of the plant must be bent to the ground and covered with non-woven material. The same material or spruce branches are laid under the bent stems. On top of the covering material, it is necessary to sprinkle peat with a layer of about 15 cm, covering it with a film.
The photo shows the types of hydrangeas, with the names and descriptions of which you familiarized yourself with on this page:
Low-growing ornamental shrubs for the garden
Low-growing shrubs are good because they can both create compositions on their own, and serve as an excellent background for other representatives of the garden. Usually unpretentious in terms of conditions and care, undersized shrubs can reduce the number of growing weeds or simply decorate some undesirable area of the territory with themselves.
Usually they include plants, the height of which does not exceed 1 meter, and among them you can find flowering, decorative deciduous, fruit and beautifully flowering all summer, types of shrubs.
Low Japanese quince (Chaenomeles japonica) is an excellent choice for hedges. It has thorns, and from the end of May, arched, sloping branches are covered with bright orange-red flowers, which are replaced by golden fruits. Not afraid of winters and tolerates them well under the snow.
Japanese quince 'Rubra'
Common heather (Calluna vulgaris) is a low-growing evergreen shrub that is valued for its long flowering throughout the second half of summer. Its height does not exceed 60 cm, and the shoots are always directed strictly upwards, due to which a richly flowering crown of a beautiful shape is formed. Heather can grow on any soil, provided there is sufficient light.
Common heather "Annemarie
Wolf (Daphne) - the only drawback of this shrub is that all its parts, including the fruits, are highly poisonous. Although in appearance, this is a rather cute plant, with white fragrant flowers, which are replaced by bright red berries. Prefers fertile soils, places illuminated and does not tolerate drought.
Daphne (wolf, wolfberry) hybrid 'Lawrence Crocker'
Deutzia gracilis is a flowering shrub up to 80 cm high. Its flowers are collected in white inflorescences of 30-40 pcs., And the leaves can be not only green, but also variegated and even golden. It is also noteworthy that the action is practically not affected by garden pests.
Deytion graceful 'Chardonnay Pearls'
The horizontal cotoneaster (Cotoneaster horizontalis) is a slowly growing shrub, which, however, is more than compensated for by its decorative effect. By autumn, green shiny leaves are replaced by purple-orange, which in turn are replaced by coral-colored berries that can delight for a long time, even under the snow.
Horizontal cotoneaster
Cinquefoil (Potentilla fruticosa) is a versatile shrub that can decorate both hedges and curbs. Its bright yellow lights last up to 100 days. Quite unpretentious to growing conditions.
Shrub cinquefoil
Snowberry (Symphoricarpos) - A distinctive feature of this deciduous shrub is its spectacular white or pale pink fruits that persist throughout the winter. A fairly unpretentious plant that prefers limestone soils and tolerates shearing well. Especially interesting for carpet plantings is the Chenot snowberry (Symphoricarpos x chenaultii), obtained as a result of hybridization with. rounded, but it requires shelter for the winter.
Snowberry Chenot
Norway spruce (Picea abies) - contrary to popular belief, it can also be undersized and not exceed 30-50 cm in height. It is to such undersized varieties that "Little Gem" can be attributed, which has a hemispherical dense crown, with dark green needles, and "Echiniformis", which, with its outlines, can sometimes create rather bizarre images. Both varieties are hardy and unpretentious in cultivation.
Norway spruce "Little Gem
The next two species are herbaceous perennials, although they are sometimes called dwarf shrubs.
Apical pachisandra (Pachysandra terminalis) is an evergreen undersized shrub that grows quickly and is ideal for shady areas in the garden. It can be used to green areas under fruit trees, thereby creating carpet plantings. Its small white flowers are collected in ears and appear for a short time - in April.
Apical pachisandra
St. John's wort (Hypericum ascyron) is a plant that does not impose special requirements on the place where it grows, therefore it can be placed in any part of the garden. Its bright yellow flowers, decorative type, delight the eye for a long time. And the harsh winters do not frighten him at all, since, even after freezing, he is able to quickly recover.
St. John's wort large
Top dressing
In order for the Vanilla Freise bush to delight you with lush flowering, it is necessary to provide it with all the necessary nutrients. In shops for gardeners, ready-made mineral complexes for hydrangeas are sold; preparations for azaleas or other flowering plants are also suitable. But it is better not to be limited to industrial "feed", but to add hydrangeas and organic fertilizers, for example, mullein, to the "menu". So, it is organic matter that is preferable for the very first feeding of a plant planted in open ground - it is applied after 14 days.
Further, every year the hydrangea is fertilized according to a certain scheme.
The first feeding is done in the last decade of May, when the buds begin to swell. You can use humus, mullein, or slurry as fertilizer. It is also recommended to feed the plant with nitrogen in the spring - it will stimulate the growth of new shoots.
In June, with the beginning of bud formation, we introduce fertilizers into the hydrangea's diet, containing potassium and phosphorus necessary for flowering. They can be of both organic and inorganic nature. Various herbal infusions rich in vitamins and microelements will be useful for the flower. But nitrogen cannot be given during this period - it will negatively affect the flowering process.
At the end of August, superphosphate fertilizers will become the best "food" for hydrangeas. They contain a large amount of beneficial minerals that will contribute to abundant flowering.
In the fall, we once again supply the soil with phosphorus fertilizers.
Although "Vanilla Fraz" is resistant to cold weather, but in the northern regions, where the temperature in winter drops below -30 degrees, it is advisable to cover the bush. Too strong frosts can lead to freezing of the shoots and, as a result, to poor flowering or even its absence. You can cover the bush with dry foliage and cover it with snow.
Diseases and pests
As a rule, hydrangea is quite resistant to all sorts of pests and diseases. However, it can also become infected with chlorosis, downy mildew, spider mites, and green leaf aphids can appear on it.
Chlorosis is expressed in a sharp lightening of the leaves of the plant, the loss of their natural color. The reason for its development is the excessive content of lime or humus in the soil. To eliminate chlorosis, it is enough to water the plant with solutions of nitric acid potassium and copper sulfate in turn with an interval of three days.
 Hydrangea disease - chlorosis
Hydrangea disease - chlorosis
The cause of hydrangea disease with downy mildew is excess air humidity. For treatment, it is recommended to treat the hardwood surface with a solution of copper sulfate with the addition of soap.
An infusion of garlic will help drive aphids from the plant. It is necessary to prepare a garlic infusion (200 g of chopped garlic in a bucket of water, let it brew for 2 days), add laundry soap (40 g) and irrigate the perennial with this infusion every 5-7 days until the aphids are destroyed.