Vegetative reproduction of kalmia
Vegetative reproduction of kalmia implies several options:
Rooting green cuttings
Calmia cuttings
Not the best way, because the cuttings take root very badly. In early spring, before the start of sap flow, cut the apical cuttings 10-15 cm long, make the lower cut at an acute angle, treat with a fungicide and hold the cuttings in a growth stimulator. Remove the leaves from the bottom, and shorten the rest by 1/3 of the length.
- Plant the cuttings in a shared wide container or individual pots.
- Create conditions similar to germination from seeds: shelter (containers are covered with glass or foil, cuttings in separate containers can be covered with a glass jar or a cut plastic bottle), temperature regime, lighting, ventilation and soil moistening. Take the same rooting substrate.
- When the cuttings take root, the shelter can be removed.
- Plant it outdoors the following spring.
Reproduction by root shoots
This method has worked well. Mature bushes can give rise to roots. They are carefully separated from the mother plant, trying not to damage the root system, and seated.
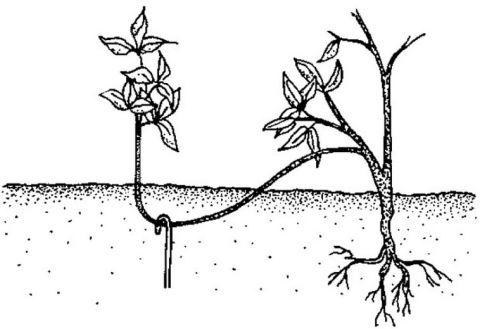
Reproduction by layering
To subsequently get a young plant, it is necessary to dig a hole in the spring, bend the stem to the ground and make a shallow incision - this will be the place of contact with the soil, the top of the stem should remain above the soil surface. Water well and keep the soil moist throughout the season. The next year, the young bush can be separated from the mother plant.
Winter hardy varieties
When grown in the garden, mountain laurel has established itself as a very demanding thermophilic plant. Therefore, not all varieties are suitable for the Moscow region. Of all the variety, the most adapted are:
- "Bandeau" - a shrub develops upward and up to 1.3 m wide, characterized by pale pink flowers with a maroon throat;
- "Carousel" - the variety is a compact, low bush with large white buds, decorated with purple strokes and dots;
- "Elf" - differs in low stems that develop up to a maximum of 80 cm, and snow-white flowers with a scarlet "star" on the calyx;
- "Black Label" - the characteristic features of the variety are medium height, large flowers reaching 3.5 cm in diameter, and white-chestnut color of the buds;
- "Ewa" - is a bush with a widely branched crown, which grows up to 1.3 m in diameter, and delicate pink inflorescences;
- "Bullseye" - blooms in purple buds with a white edging and a "star" at the base.
This selection is able to withstand 35-degree frosts, but young plants require special preparation for winter.
Did you know? Due to its abundant and long-lasting flowering, kalmia is an excellent honey plant. But the delicacy absorbs all the toxic substances of the plant. Because of this, the ancient Greeks called him "insane" and used as a dope in the fight against Xenophon.
Charming garden beauty kalmia: planting, care and photo

When it is time for plants to bloom, the garden becomes a unique place of delight. Especially if a perennial shrub grows in it - kalmia. The plant belongs to the Heather family. It was first discovered in North America. There, the shrub is found in swampy areas, forest edges or dense thickets.
Under natural conditions, kalmia grows up to one and a half meters, although there are also undersized species - about 30 cm. The shrub got its name in honor of the Finnish environmental researcher Pierre Kalm.
Nowadays, kalmia adorns gardens not only in America, but throughout Europe. Thanks to the diligence and painstaking work of botanists, the plant appeared in the Moscow region.
Spreading
In the natural environment, all representatives of the species of Calmia are found in North America, they are observed even in the northern regions of Alaska. They grow in forests, on forest edges, along the banks of rivers and reservoirs, in wetlands.
Plant root formation stimulants
In specialized gardening shops you can buy ready-made solutions of plant root stimulants: Kornevin or Ecosil. However, natural stimulants prepared independently at home are no less effective, which, unlike purchased ones, do not contain chemicals and harmful substances.
One of the most effective stimulants is an infusion of willow branches, which is used as for watering seedlings and soaking seedsand for keeping cuttings.
The potato tuber is an excellent root growth stimulator: cuttings are inserted into half of the tuber and left for several days. This will prevent the cutting from drying out and get enough nutrients. Aloe juice, like yeast, serves as an excellent root stimulator. Water with honey is no less effective.
Kalmia latifolia Peppermint
Calmia in medicine
Due to the presence of toxic substances in the plant, including andromedotoxin, it is not used in medicine in Russia. However, it is used to treat diseases of the digestive tract, skin diseases, syphilis, by the indigenous people of North America.
In homeopathy, calcium is used for diseases of the cardiovascular system, rheumatism, sciatic and intercostal neuralgia.
Diseases and pests
The plant is considered resistant to most diseases of horticultural crops. Nevertheless, in a rainy summer, in conditions of high humidity and high temperatures, kalmia is exposed to fungal infections that affect the root collar, pagons, leaves and peduncles of the shrub.
 With a mild degree of disease, the affected parts of the plant are removed and burned, and the entire bush is treated with one of the fungicides, for example, topaz or benlate.
With a mild degree of disease, the affected parts of the plant are removed and burned, and the entire bush is treated with one of the fungicides, for example, topaz or benlate.
In addition, overgrown dense shrubs are tied up in order to raise the branches higher and provide air access to the root collar and inner crown pagons.
Sometimes on the leaves of kalmia, signs of chlorosis are observed - bleached spots on the leaf blades, leading to a gradual yellowing of the entire leaf, with the exception of the veins.
It is recommended to add iron chelate or sulfate to the soil, following the instructions attached to the package.
The pests were hardly noticed on kalmias, and it is believed that the shrub is resistant to the attack of insects and ticks.
However, some sources mention rare isolated cases of the presence of scale insect colonies on the pagons of kalmiya.
How to care
It only at first glance seems that the capricious kalmiya will exhaust all the strength from you when caring for it. In fact, a flower needs a little attention and knowledge about its requirements for watering, feeding, pruning, preparing for winter. Let's take a closer look at all the subtleties of crop care.
Watering and loosening the soil
This flower loves moisture, but cannot tolerate excess of it. Therefore, the bush should be watered as the upper ball of soil dries up in the near-trunk circle. In hot weather, be sure to moisten the roots and crown of the exotic.
Do this in the morning or evening so that the sun's rays do not damage the foliage. Calmia is enough to moisturize 2-3 times a week. Pour 2-3 liters of water under young shrubs each time, and mature specimens will need about 10 liters. In a drought, sprinkle the crop.

In such conditions, you deprive the flower's root system of oxygen and nutrients. Therefore, do not be lazy to periodically process the area with a hoe and renew the mulch layer as necessary.
Top dressing
After planting a young kalmia seedling, you can forget about fertilizers for the next 2-3 years. Then it is advisable to feed the bush at least once a season with the same interval.It is best to plan these procedures between April and June.
For these purposes, it is best to use mineral complex fertilizers for rhododendrons.
Do not forget to pay attention to the "spring" or "autumn" packaging markings. In the absence of purchased funds, you can use organic
Keep in mind that varietal Calcium hybrids require much lower nutrient concentrations than conventional varieties. In the spring, it is advisable to add a urea solution (1 tablespoon per bucket of water).

Particular attention should be paid to the plant during the flowering period, since the abundant inflorescences greatly deplete the culture. In the fall, it is advisable to feed it by scattering "Kemiru universal" under the crown
Pruning
Considering the slow pace of shrub development, you can relax and enjoy the beauty of its bloom. Over the course of a year, the plant grows weakly and only by the age of 10 reaches its standard volumes, which, depending on the variety, fluctuate between 60–130 cm. The branches of the bush, without human intervention, tend to form a compact, neat crown. Consequently, the plant does not need formative pruning, although it tolerates it easily.

In addition, it is advisable to remove faded buds from the bushes in time so that the plant does not waste energy on their maintenance.
Wintering
Perhaps this nuance is the most important in caring for the North American exotic. The heat-loving broad-leaved squid, despite the grafted frost resistance genes, requires human help at the beginning of its development.
It consists in abundant watering of young seedlings in the fall and mulching of near-trunk circles before the onset of cold weather. Experts recommend using peat and humus as winter mulch. Better to do 10-15 cm flooring.

The crown of the plant also needs to be covered. For these purposes, wooden or roofing frames are used, insulated from the inside with foam. For dwarf specimens, you can use an inverted box without a day. From above, such structures are spud with dry foliage or covered with spruce branches or non-woven material.
Too early to install all these structures is not worth it, because the bush can vanish, and belated actions are fraught with freezing. Therefore, keep an eye on the temperature outside and organize your winter preparations in a timely manner.
In the spring, with the onset of warmth, the culture is gradually revealed. It is not worth filming all the materials at once, since the calmia needs time to adapt.
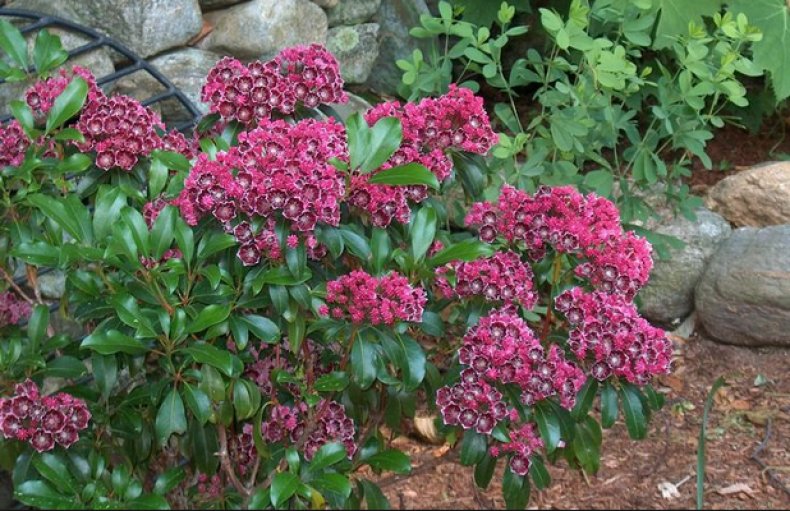

Kalmia (lat. Kalmia) is an evergreen flowering shrub plant of the Heather family. Depending on the species, the height of the plant varies from 0.5 m to 9 m.
The habitat is North America, where some species are distributed up to Alaska. Calmia thickets are found in the undergrowth, along the edges of forests, less often in swamps.
How to choose seedlings when buying
Not only the survival rate of ornamental shrubs, but also their further development depends on the quality of the planting material. Therefore, the choice of seedlings must be approached very seriously and scrupulously.
Of course, it is better to make a purchase in specialized stores and garden centers with an impeccable reputation. Feel free to ask a lot of uncomfortable questions to sellers. On the contrary, you should be wary if they do not have complete information about their product and cannot satisfy your curiosity.
Try to find out as much as possible about the seedling of the variety you like. And then take a close look at its roots and stems. Many retail outlets today sell ornamental plants in closed-root containers.
In this case, it will be enough to assess the general condition of the flower and find out its age.
Experts advise buying exactly potted seedlings, since their root system receives nutrition and is devoid of the risks of drying out. In addition, capricious kalmia reacts very painfully to transplants.Therefore, it is better not to disturb her once again.
Important! Never buy seedlings with spots, blooms, growths, darkened and moldy circles on the roots and stems. It is also worth giving up specimens with mechanical damage .. A healthy seedling always has smooth and even stems
It is desirable that the plant has 2-3 lignified branches with a height of 10 to 20 cm (depending on the shape). Also, its roots should be well branched and fresh.
A healthy seedling always has smooth and even stems. It is desirable that the plant has 2–3 lignified branches with a height of 10 to 20 cm (depending on the shape). Also, its roots should be well branched and fresh.
You can check this by making a small scratch on one of the processes. The light wood that appears indicates the quality of the product
Particular attention should be paid to the place where the root transitions into the trunk. It should have a homogeneous structure, without any suspicious points and breaks.
For cultivation in gardens and parks, choose 2-year-old specimens that have already wintered
They have a sufficiently developed root system and crown, which will contribute to rapid rooting and adaptation to winter.
Diseases and pests
Calmia is a hardy plant. It has resistance not only to frost and drought, but also to most diseases and pests common among cultivated plants. However, it also has its weak points.
So, kalmia does not tolerate too wet, windy and cold weather at all. This can lead to late blight. With this disease, the leaves gradually dry and fall, first the lower ones, then the upper ones. Following them, the stems turn black and rot. If you notice signs of late blight on the plant, you need to remove the infected leaves and cut off diseased stems, and pollinate the calcium with a solution of a copper-containing preparation.


With excessive watering, the bush can infect a fungal disease. In this case, you need to cancel watering until complete recovery, remove damaged parts of the plant, ensure sufficient drainage and treat the bush with fungicides.
A rarer disease for kalmia is chlorosis. When infected with chlorosis, yellow spots appear on the leaves of the plant. In such a situation, it will be necessary to add ferrous sulfate to the soil.


Use in landscape design and selection of partners
There are also some fashion trends in landscape gardening design. And, despite their changeability, interest in beautifully flowering decorative perennials will never lose its relevance.
This also applies to kalmia, even in spite of its poisonous secret, which is hidden behind the refined beauty and tenderness.
In the garden, such a shrub will decorate any area. Many designers like to create eye-catching compositions of calmias and rhododendrons. Different periods of their budding allow a fabulous atmosphere to reign on the site throughout the warm season.
Single shrubs also look good against the background of a green lawn or under the cover of a lush crown of a tall tree. In the Japanese style, it is very common to plant kalmias on alpine hills, especially since the broadleaf species is adapted to rocky conditions.
Garden specimens of these plants are often found as a decoration for alleys, a central entrance to a house or a gazebo. These shrubs are planted in the best areas to create a cozy and festive atmosphere at the same time.
The flower feels good in the neighborhood of all heather cousins, as well as all conifers and marsh crops, wild rosemary, erica, ferns and common whitewash.
Did you know? In medicine, andrometoxin is widely used, which is present in small-leaved calcium. The substance is an integral component of external remedies for skin diseases.
Charming garden beauty kalmia: planting, care and photo
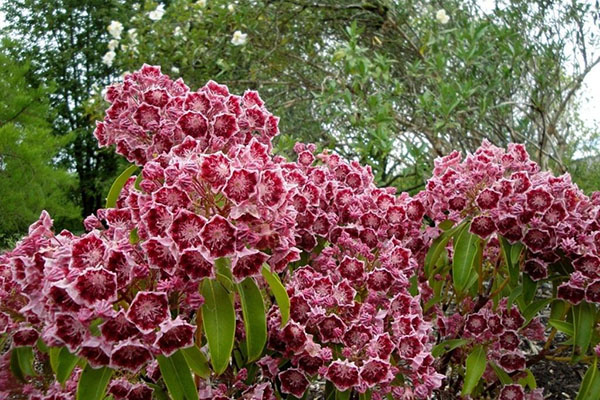 When it is time for plants to bloom, the garden becomes a unique place of delight.Especially if a perennial shrub grows in it - kalmia. The plant belongs to the Heather family. It was first discovered in North America. There, the shrub is found in swampy areas, forest edges or dense thickets.
When it is time for plants to bloom, the garden becomes a unique place of delight.Especially if a perennial shrub grows in it - kalmia. The plant belongs to the Heather family. It was first discovered in North America. There, the shrub is found in swampy areas, forest edges or dense thickets.
Under natural conditions, kalmia grows up to one and a half meters, although there are also undersized species - about 30 cm. The shrub got its name in honor of the Finnish environmental researcher Pierre Kalm.
Nowadays, kalmia adorns gardens not only in America, but throughout Europe. Thanks to the diligence and painstaking work of botanists, the plant appeared in the Moscow region.