Opuntia - cactus with "ears"
The clayey Mexican deserts are considered the birthplace of prickly pears. An ancient Aztec legend says that the current Mexico City, the capital of the country, was formed on the site where a huge prickly pear grew, on which an eagle was sitting, eating a snake. It is this scene from the legend that is captured on the coat of arms of the city. Types of desert "thorns".
Opuntia is naturally endowed with serious means of "self-defense": in addition to large noticeable thorns on the shoots, there are tiny glochidia practically invisible at first glance - thorns with jagged edges at the end.
Flowers emerge from thorny buds and differ not only in color, but also in size. Unfortunately, blooming in the wild, at home, they rarely delight with flowering. This is due to the fact that the buds appear mainly on adults and rather large specimens. However, similar to "cakes", the shoots make the prickly pear cactus already unusual! In the cactus family, this is a very numerous species, it includes more than 190 varieties!
Berger's prickly pear (Opuntia bergeriana) is a tree-like species that grows over a meter in height and blooms with red flowers.
O. bergeriana
Pink-flowered prickly pear (Opuntia rhodantha) amazes with the beauty of bright pink flowers. This variety is winter hardy, therefore it is also found in North America.
O. rhodantha
The mighty prickly pear (Opuntia robusta) lives up to its name, because the diameter of its shoots can vary from 30 to 50 cm.
O. robusta
Opuntia golden, or small-haired (Opuntia microdasys) is a popular species in indoor floriculture, it is distinguished by small needles and hairs, which can be of different colors.
O. microdasys
The white-haired prickly pear (Opuntia leucotricha) is one of the edible species. The shoots are dotted with white bristles, the flowers are usually yellow, and the white fruits are used for food.
O. leucotricha
The main prickly pear (Opuntia basilaris), in addition to its unusual name, boasts a reddish shade of shoots and bright red, or carmine flowers. On the basis of this species, many mini-varieties for indoor floriculture have been bred.
O. basilaris
Shera prickly pear (Opuntia scheerii) is perhaps one of the most beautiful of the genus. Smooth shoots are covered with curved thorns, flowers are in harmony with the olive color of the shoots.
O. scheerii
The pubescent prickly pear (Opuntia tomentosa) is often used as a rootstock (base for a grafted cactus). Rare spines and soft pubescence distinguish it from other species.
O. tomentosa
Opuntia articulatus (Opuntia articulatus) is very original thanks to the unusual shape of the shoots and huge white thorns. It grows only up to 30 cm tall.
O. articulatus
Opuntia subulata (Opuntia subulata) is even more unusual in shape. In indoor floriculture, it is valued for the decorative effect of shoots and thorns.
O. subulata
The cactus is also grown commercially to produce the dye carmine, which is sourced from the bright scarlet fruits of some species. In addition, prickly pear is used in medicine, the beneficial properties of cactus juice make it an excellent antiseptic.
Reproduction of hymnocalycium
Gymnocalycium is propagated by seeds and children, and chlorophyll-free species are propagated by grafting.
Those hymnocalycium that form babies are very easy to propagate: daughter plants are removed from the mother, dried for a day or two, and then planted in a wet mixture of sand and peat. Babies usually form roots very quickly. They take care of the planted shoots, as well as for an adult cactus.
In the photo: Growing hymnocalycium in a pot
However, for most species of hymnocalycium, seed is the main method of reproduction. And for those plants that can be propagated vegetatively, the seed method is more reliable. To grow a cactus from seeds, you will need the same substrate as for an adult hymnocalycium, but the fractions of which it consists should be smaller.
The soil mixture must be disinfected by heating in the oven, after which it is allowed to cool, laid out in cups and moistened.
The seeds of the hymnocalycium are placed shallowly.Crops are kept in a bright place at a temperature of 20 ˚C, the substrate is kept in a slightly moist state by spraying it from a spray bottle.
As for grafting, for this method, completely healthy stock and scion are chosen and the same sections are made on them immediately before grafting with a sharp, sterile instrument. The stock is applied to the scion, trying to match the conductive bundles as much as possible, and fix them in this position for 7-8 days using an elastic band or tape.
How to create optimal conditions for a plant at different times of the year
Rhipsalidopsis is a cactus, but a forest one. It does well in humid and warm climates. But the plant is undemanding to lighting. Unlike distant relatives, desert cacti, Ripsalidopsis in nature lives in partial shade under a canopy, which is formed by intertwining tree branches.
Table: optimal conditions for growing Ripsalidopsis
| From late September to early February (dormant period). | Temperature: no higher than 15-17 ° C. Lighting: bright, diffused. It is best to avoid direct sun. Windows are suitable from the east or west side. Can be placed on the north. Humidity: high. Spray the plant. Avoid drying out and waterlogging of the earthy coma. |
| Second half of February - mid-March (preparation for flowering). | Before the beginning of bud formation: the temperature is cool, watering is poor. With the appearance of buds: increase the temperature, increase the watering. Do not disturb the plant: you cannot move or even turn the pot so that the buds do not die. |
| End of March, April, May (flowering time). | Temperature: 18-22 ° C. Watering: plentiful, as the soil dries, only with soft, rain or melt water. |
| June, July, August, first half of September (active growing season). | Location: Take the plant out into the garden, terrace, or balcony. Shade from direct sun. Watering: moderate, after the soil has dried. Humidity: the higher the better. Spray the plant. Temperature: 17–20 ° C, gradually reduce. Protect from drafts and temperature changes. Watering: Moderate, cut back in October. |
Rhipsalidopsis blooms luxuriantly if it has time to build up a green mass. And for this you need light. In the fall and winter (until February), periodically rotate the pot so that the "crown" is relatively symmetrical. When it's time to set the buds, stop moving the ripsalidopsis so it doesn't get stressed and shed future flowers.
Rebutia miniscula (Rebutia tiny)
These cute little spherical cacti with a diameter of no more than 10 cm. The tiny rebutia differs from other similar species in the placement of flowers - not at the top of the stem, but at its very base.


The flowers, as a rule, have a pink, orange, red hue, and even the golden color of the spines of the rebutia gives it a special decorative effect.
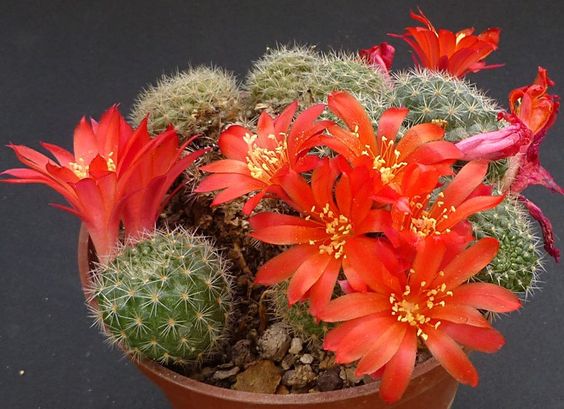


 Such a cactus is very favorable to dry air, but requires mandatory spraying in the morning from a spray bottle. Basically, the plant needs the same conditions as the rest of the indoor cacti.
Such a cactus is very favorable to dry air, but requires mandatory spraying in the morning from a spray bottle. Basically, the plant needs the same conditions as the rest of the indoor cacti.
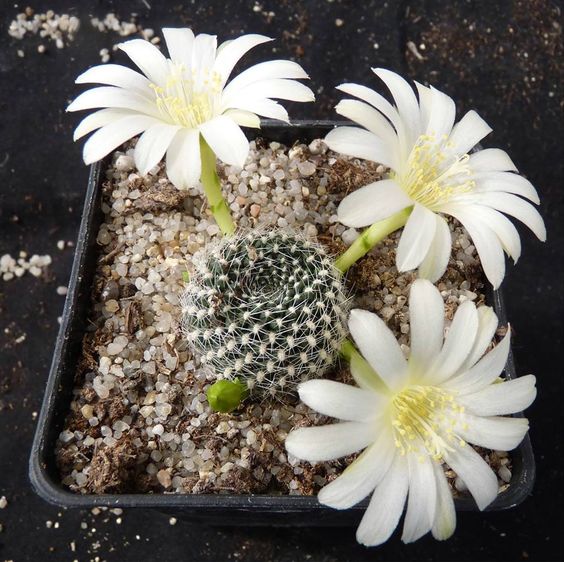

Do you have cacti at home? What are your favorite types?

Peculiarities
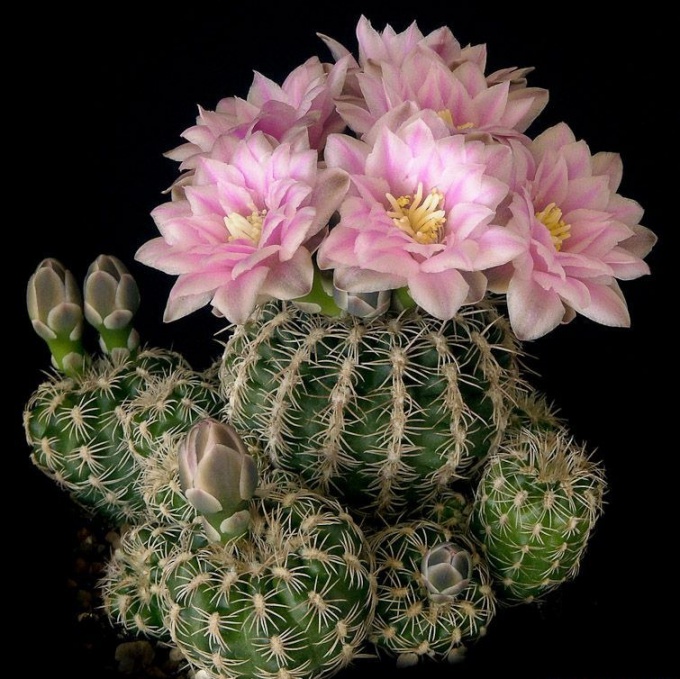
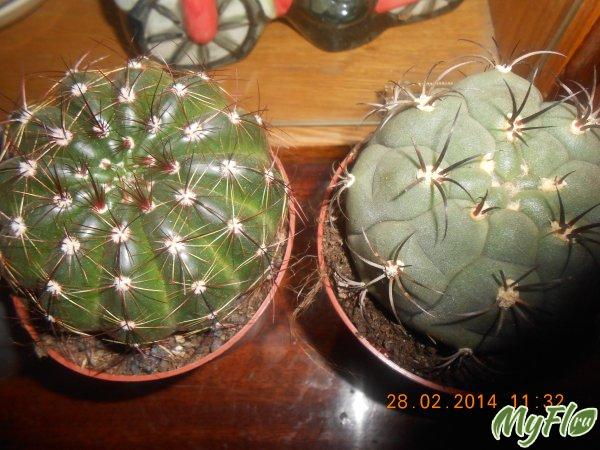
Gymnocalium cactus (Latin Gymnocalium) has about eight dozen species, many of them are found all over the world. Naturally, cacti grow in the tropics, in countries such as Paraguay, Chile and Peru. The plant loves an atmosphere with a high moisture content and temperatures above +20 degrees. These cacti are found in the mountains above sea level up to 1000 meters. The Gymnocalycium cactus was discovered in the 19th century by the naturalist Ludwig Pfeiffer (1844). In the XX century, the hymnocalycium was differentiated into 5 sections according to the characteristics and properties of the seed fund.
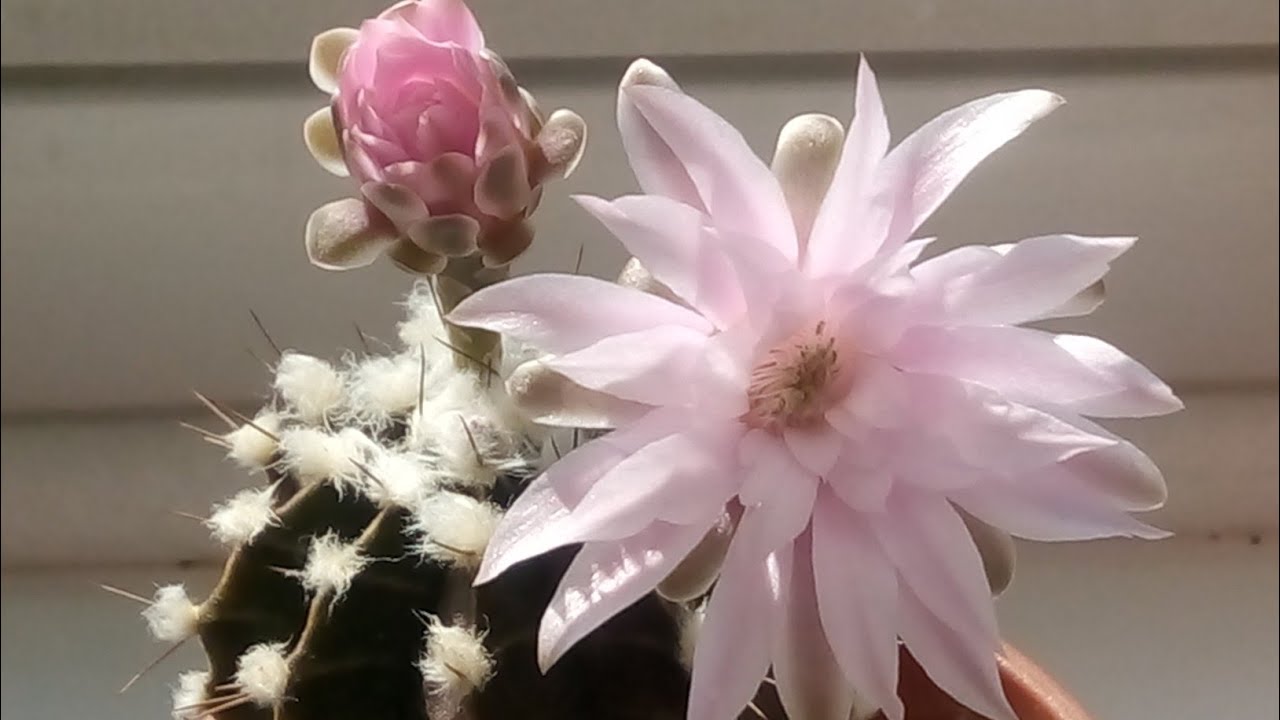
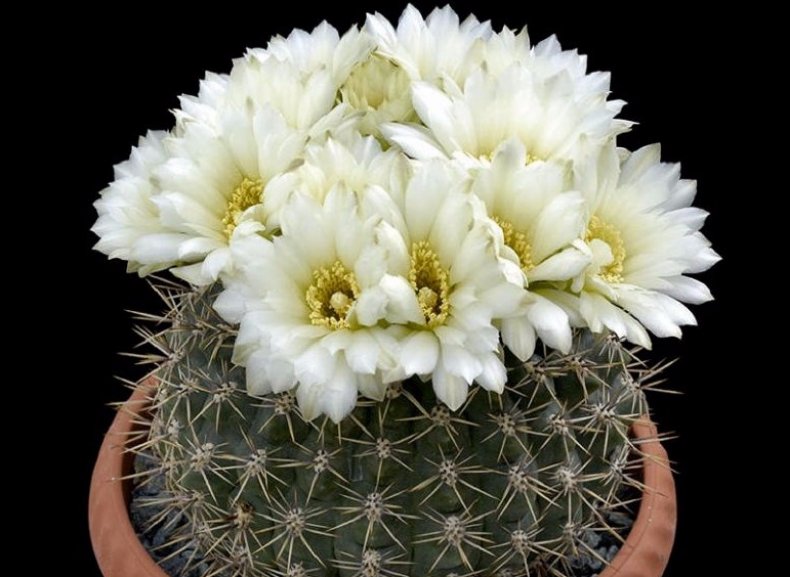
After two years of life, cacti bloom from April to October. The flowers appear at the top and look like small bells up to 7.5 cm in diameter.The appearance is spectacular, while the color scheme can be very different - yellowish red, beige, dark purple, and so on. The maximum parameters of the plant are about 1/3 meter, the stems are spherical. The flowers themselves do not show any thorns or hard villi.
Description of popular species
Gymnocalycium is a plant with a stem in the shape of a flattened ball. Adult specimens reach 15 cm in diameter, and their growth is half that.
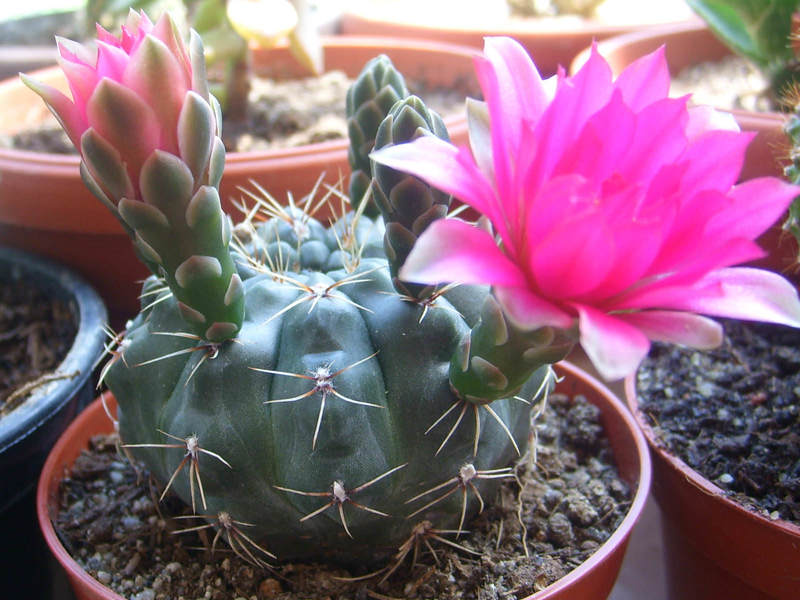

Flowers come in a wide variety of colors:
- pink;
- red;
- yellow;
- white;
- brownish or greenish.
The flowers grow large, with a short tube.
Several varieties are most popular among florists:
- Gymnocalycium mihanovichii or a cactus with a red head resembles a ball in shape. The stem is brownish or gray-green in color. On its surface, 8-10 ribs are formed, covered with spines. The length of the thorns is 1–2 cm. The flowers of this species are yellow, red, white, orange or pink.
- Gymnocalycium of Friedrich is distinguished by a minimum amount of chlorophyll. The stems are colored red-brown or lilac-burgundy.
- Japanese Gymnocalycium is a hybrid variety of Friedrich's Gymnocalycium. It features a brighter cap-shaped top. Chlorophyll is not formed in this part. These flowers only survive when grafted onto a green plant. The Japanese cactus comes in red, pink, burgundy, yellow, or orange.
- Gymnocalycium baldianum or balda has a gray-green stem. A spherical cactus has 9-10 ribs. The thorns of this variety are long and light. The flowers are painted in a variety of shades.
- Gymnocalycium nude - a plant with a shiny green stem and a small number of thorns. On the ribs there are from 5 to 8 transverse stripes.
- Gymnocalycium humpbacked or lumpy reaches 50 cm in height at maturity. The stem is dull green, the ribs are distinctly expressed. The spines are yellowish and long. The flowers are white or cream colored.
- Gymnocalycium stellate is distinguished by large outgrowths (areoles), each of which grows 3-5 spines. The clusters of needles resemble stars in shape.
Description and photo of indoor cactus
Gymnocalycium mix is a mixture of several species that perfectly coexist in one container. The country of origin of the Gymnocalycium is South America, more precisely Argentina and Brazil. An unusual home cactus does not need special care, so it is grown by many growers.
To create compositions, agronomists recommend using several types. They combine perfectly with each other, which makes a beautiful composition of small cacti:
- Gymnokalycium Mikhanovich. It has a greenish stem with a brown or red tint, no more than 5-6 cm in height. The flower is large, funnel-shaped, red, white, orange or yellow occur.
- Japanese species (Friedrich), which does not have chlorophyll - breeders created it on the basis of the previous species. The stem is spherical, produces pink and lilac flowers.
- Andre. Differs in an unusual color, atypical for its species. The stem is dark green, the flowers are formed from bushes and have a bright yellow color.
- Reductum or Humpbacked cactus is a large plant that can grow up to 45-50 cm. Its surface is straight spines, buds are white or beige.
So that the plants do not interfere with each other as they grow, they are planted at a distance of 2 cm from each other. When the cacti grow up and begin to adhere to each other, they are transplanted into a pot larger than the previous one.
See what the plant looks like in the photo.
Gymnokalycium Mikhanovich:
Gymnocalycium of Friedrich:
Gymnocalycium Andre:
Humpback cactus:
Gymnocalycium mix: