Temperature - when the shelter is not yet needed and when it is required to erect it
The plant can easily withstand small drops in temperature. So, frosts down to -5 ̊С are not a threat to the plant. With such a mark on the thermometer, the culture feels fine and even benefits - a light frost hardens the plant and helps the development of the bush. For this reason, it is undesirable to cover the plant until the end of October. Even in the case of capricious and delicate types of hybrid tea roses, it is not recommended to do a shelter for the winter before a more serious drop in temperature.
For reference! When gardeners insulate rose bushes too early, the temperature inside the shelter rises, which is bad given the increasing soil moisture in the early to mid-autumn period. This leads to excess moisture and decay of the bush. It is recommended to start covering the plant after the temperature has been consistently lower than -5 ̊С for 7 days.
Representatives of an ornamental-flowering culture can withstand temperatures down to -7 ̊С without disastrous consequences for their own vitality. Some growers even recommend waiting until the thermometer reaches this limit. Low temperature helps the culture to enter a dormant state correctly, and also increases the immunity of plants by hardening the root system and the ground part of the bush.
The factor that determines the temperature suitable for starting insulation work is the ability to maintain dryness inside the wintering structure for the rose. It is forbidden to cover the bushes with wet soil, wet leaf litter or damp covering materials. The bushes of the plant must also be dry. Following this rule reduces the likelihood of the reproduction of harmful insects, the development of rot and other diseases.

Easy cover
This type of insulation structure for wintering flower bushes is built when the winter season in the region is not very harsh. Often, such a design is performed after a hardening period for a rose, when the air temperature dropped to -7 ° C, but has not yet dropped to a stable -10 or less degrees. In this case, the roses can be covered with the following materials:
- mulch;
- sawdust;
- spruce branches;
- straw;
- foliage.
With a light version of the shelter, the decorative leafy culture is not completely covered. This type of insulation can also be used in the case of regions where a thick snow layer is observed in the winter season, which well protects the delicate plant from the harmful effects of low temperatures (Siberian Territory and the like). And in the southern regions it is not at all possible not to shelter for the winter, since in these regions the temperature rarely lingers for a long time at around -10 ̊С and below.
Capital
The capital type of insulation is erected after the frosts become stable. Often this time in the middle lane and northern regions falls on the end of November or the beginning of December. A thick layer of mulch is poured into the base of the bush, on top of which spruce branches or some other, similar material is laid. After that, 3-8 stakes are hammered along the perimeter - so that it becomes possible to cover the bush with non-woven material.
On top of the non-woven fabric, it is necessary to fix a film that will not be ripped off or damaged by the wind. But, tightly wrapping the plant with foil is not recommended, since during the winter thaws, the material must be lifted from one side to ventilate the bush. This manipulation will also prevent the rose from drying out due to the rise in temperature under the shelter.
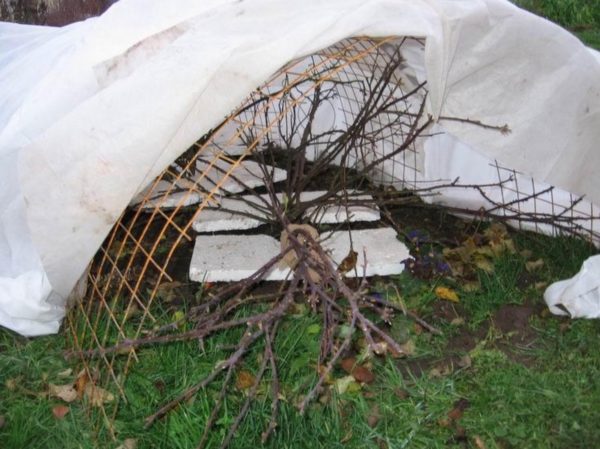

Correct ways to hide a rose
In mid-late autumn, after the completion of watering and trimming, the root system of an ornamental flowering plant must be properly spud. A thick soil layer must be present above the rhizomes. After that, it is necessary to cover the roses with sawdust, dry foliage or grass. Make sure that there are no diseased plant parts or moist mulch under the wintering shelter. To prevent rotting, it is necessary to remove all the foliage from the ground part of the bush.
The type of shelter is determined depending on the mark of the thermometer - when the temperature drops to -40 ̊С, the flower must be provided with a capital shelter. As a preparation, before the bushes are closed with an insulating material, the stems of the plant are bent to the ground and fixed in this position with specialized hooks. It is possible not to bend the shoots, but to cut them off near the ground. Experienced growers believe that there are 3 designs for winter insulation that are better than others:
- frame option;
- embankment and fence;
- sheltering roses with lutrasil.
Attention! The choice of a specific type of insulating structure must be carried out based on the parameters of the rose garden or flower bed, the average winter temperature drop and other climatic and territorial features.
Frame option
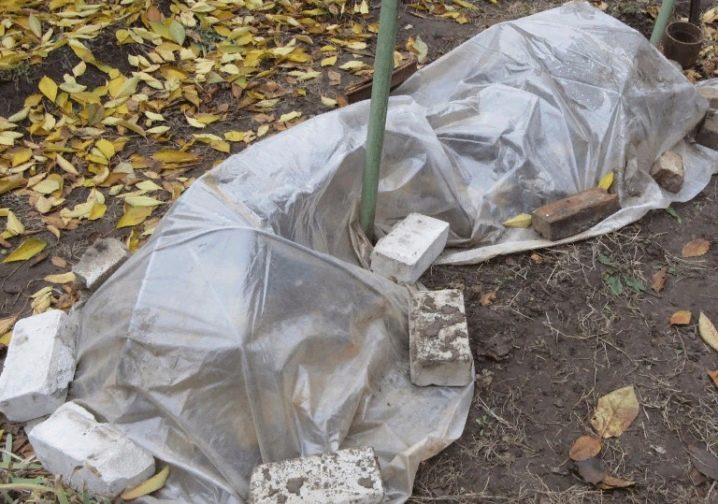
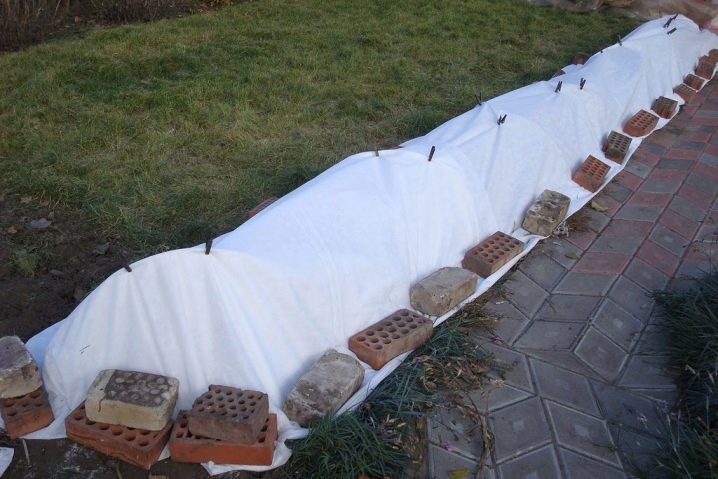
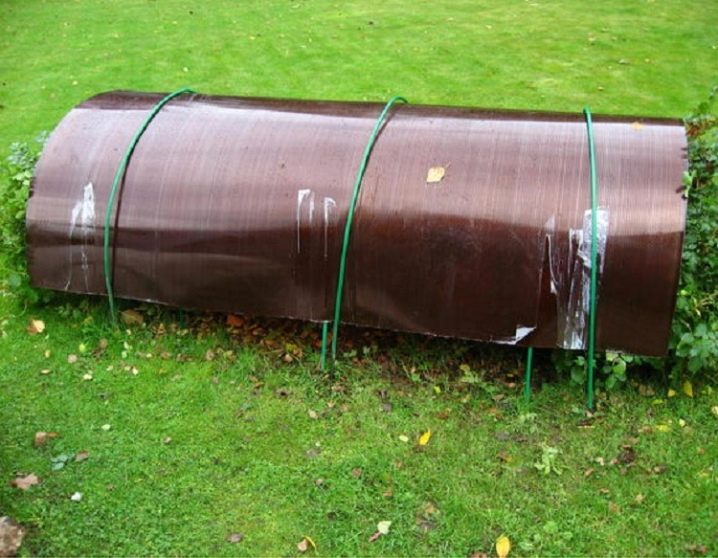
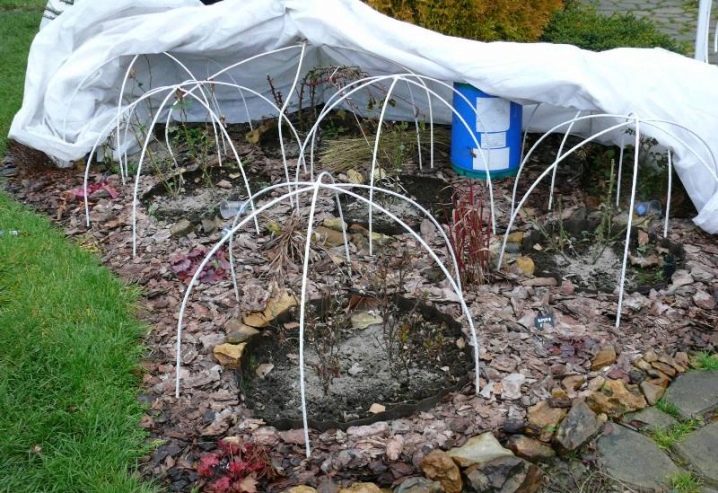
It is possible to build a base for a shelter for rose bushes from several metal strips or rods. In addition to metal for the frame base, it is possible to use plastic sheets, wicker baskets, plastic large flowerpots, wood pallets, boards and the like. Arcs are made of metal, the ends of which are buried in the ground around the plant. The process of erecting a shelter involves the following stages:
- A place is marked around a bent or cut rose.
- The flower grower forms a dome of 2 plates above the bush.
- In a harsh winter, a non-woven covering material is laid on top of the dome, and the rose is additionally sprinkled with leaf litter or needles.
- The edges of the insulation material are pressed against the ground with bricks from all sides - this will allow, if necessary, to raise the corner and ventilate the plant.
It is advisable to fasten the insulating material to the frame after frosts and a stable low temperature outside, which lasts at least a week and a half. The frame option is convenient in the case of large plantings of roses. Depending on the parameters of the plant, it is possible to build shelters of 2 types - a conical frame for undersized varieties and pyramidal / spherical shapes for bush varieties.
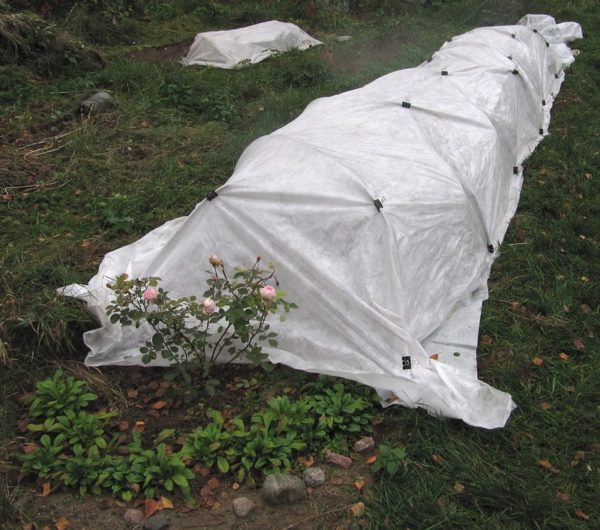

Fence with embankment
The option is to dry backfill the bush in a shape that is set by the breeder around. As a fencing material, it is possible to use a stainless steel mesh, cardboard boxes or thin plywood sheets. A fence made of selected material is erected according to the width and height of a particular plant specimen. Insulation material is poured inside the fenced area:
- leaf litter;
- sawdust;
- hay and the like.
Attention! When the fence is represented by a metal mesh, in order to prevent spilling of the insulation material, it is possible to additionally close it with polyethylene. For a floribunda, a shelter for the winter can be made from mesh bags filled with dry leaf litter.
You need 3 bags, which are placed on the crown of the plant. It is permissible to lay agrofibre on top of the bags. After wintering and such a shelter, there will be no need to clean the rose garden from foliage.
Lutrasil cocoon
Certain tall varietal roses, in particular - standard roses, are wrapped in insulation material for the winter. The material is wound on the crown, and the stem is left on the support. The root is insulated by hilling. To insulate the stem part of the bush, it is wrapped with lutrasil or a similar material. In the lower part, a cocoon is tied so that the frosty air does not penetrate under the insulation.
Pruning and hilling
In climbing plants, pruning in preparation for wintering is characterized by a number of features.So, as the stems are removed from the supports, only the youngest green stems at the top of the shrubs that have not had time to ripen are cut off. All buds and flowers are removed immediately before the start of the shelter.
Rules for pruning a climbing rose.
The foliage of roses most often crumbles on its own as the period of light frost begins. If this does not happen, then the leaves will have to be removed on their own.
This is especially important for the lower part of the plant, where small branches and cuttings are located. Pathogens and pests often hide in these places.
An infection can penetrate the plant through unhealed sections. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary, immediately after removing the stems, to process the cuts with brilliant green or charcoal.
On some varieties of climbing roses, manual foliage removal can be problematic. This is due to the excessive number of thorns on the stems. In such cases, you should resort to using special preparations to remove the leaves. Among them, the most effective are those that belong to the sulfur group.
Before starting to shelter a plant, it is imperative to spud its root collar.... This procedure allows you to save and protect the plant even under the most unfavorable weather conditions in winter.
For hilling, it is recommended to use soil collected between rows. The land must be dried with high quality, which is why it is recommended to prepare it in advance and dry it, sprinkling it under a canopy. 1 bucket per bush will be enough for young plants, 2-3 buckets of soil will have to be spent on old specimens. The earth is poured directly to the central part of the plant, forming a cone-shaped mound. The height of the earth layer should vary from 20 to 30 cm.
Dry sand is a good alternative to earth. Humus, peat and sawdust are not suitable for use in this case, as these materials strongly accumulate moisture. In some cases, it is allowed to use a torus, but it is necessary to mix it with sand so that the material does not cake and can normally let air through. Plants can be overlaid with spruce branches or wooden planks in a circle so that the wind does not destroy the embankment.
Top dressing and processing before the shelter
After pruning and harvesting foliage and branches from under the bushes, it's time to feed the rose before wintering. Top dressing can be root or foliar. Potassium and phosphorus are relevant for autumn. Potassium will make the plant resist diseases, temperature changes in the environment, and will also help to lay the buds of future flowers. And phosphorus will help the ripening of these buds and the growth of the root system.
Phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are produced in the form of granules or in solution. The main thing is that the label indicates that the fertilizer is autumn. In dry weather, the bush is watered with a solution in accordance with the attached instructions. Granules are used in rainy weather, or in the absence of rain, they are scattered under the plant and watered with water. Alternatively, instead of scattering the granules, dissolve them in a bucket of water.


Experienced gardeners recommend using a mixture consisting of 25 g of superphosphate, 10 g of potassium sulfate, 2.5 g of boric acid. All this is dissolved in 10 liters of water and the plant is watered before pruning (no more than 4-5 liters of solution for each bush). For the second time, the rose is fed half a month after pruning with the following composition: 15 g of superphosphate and potassium sulfate are dissolved in 10 liters of water and root feeding is carried out. Foliar spraying is carried out with the same fertilizers, but the dosage of drugs is reduced by 3 times.
The last feeding is carried out when the temperature drops below 0. Phosphorus granules or oven ash are laid out under the bushes.
Experts and amateurs treat the use of manure in autumn differently. Much depends on the region and weather conditions, which are difficult to predict.On the one hand, in the spring, manure will immediately begin to supply the roots with nutrients along with the melt water and stimulate plant growth.
Another autumn procedure is the liming of the rose. Flowers like neutral or slightly acidic, slightly alkaline earth. With increased acidity, the plant has pale foliage, dull petals, weak flowering, and reduced winter hardiness. If these signs are present in the rose garden, then shortly before frost under the bush, dolomite flour is scattered over the width of the crown - a fertilizer belonging to the carbonate class, produced from the dolomite mineral. If the drug is used constantly, then it:
- improves soil structure;
- has a healing effect on it due to the development of colonies of microorganisms;
- the turf is saturated with fertilizers, for the sake of which year-round fertilizing is carried out - nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium;
- cleans plants from radionuclides;
- dissolves the chitinous cover of insects, thereby destroying them, while remaining safe for other living beings.


The next stage of preparing a rose for winter is treatment from diseases and insects. To do this, you need to prepare copper-containing spray preparations, especially if black spots were encountered on the leaves during the season. These drugs include:
copper sulfate;







The last stage before hiding roses is hilling. Many growers abandoned it, citing the fact that its use depends on the climate. Plants are huddled so that the roots do not freeze, but during thaws they often undermine. Therefore, whether or not to huddle your favorite rose is a controversial issue today to protect it from frost.

Required inventory for pruning
 To trim, you need the following set of tools and accessories:
To trim, you need the following set of tools and accessories:
- pruning shears of different sizes and strengths - for large, old branches, a massive one is needed;
- folding saw with the ability to change the angle of the blade;
- secateurs with one cutting end;
- teflon gloves (long);
- folding rake.
For convenience, you can buy knee pads. They are made from different materials. They can be called an indispensable thing for gardening.
Secateurs of different sizes are essential for neat work. It is difficult to grab and chop without damaging a large branch with a small device
Working with young shoots requires caution, therefore it is better to work with a pruner with a thin blade.
Top dressing after autumn pruning
 The last time in a season the rose bush is fed exactly after pruning, but you need to wait about 2 weeks before the plant stabilizes. If in the summer nitrogenous fertilizers are used for regular dressing, then after the buds are dissolved, this component must be removed from the nutrient mass. It stimulates the growth of flowers and shoots. In the fall, it is better to make top dressing with a high content of phosphorus and potassium - such means strengthen existing shoots. But they stop the growth of new ones, do not provoke flowering.
The last time in a season the rose bush is fed exactly after pruning, but you need to wait about 2 weeks before the plant stabilizes. If in the summer nitrogenous fertilizers are used for regular dressing, then after the buds are dissolved, this component must be removed from the nutrient mass. It stimulates the growth of flowers and shoots. In the fall, it is better to make top dressing with a high content of phosphorus and potassium - such means strengthen existing shoots. But they stop the growth of new ones, do not provoke flowering.
Important! After carrying out the last, autumn feeding, the tops of the stems need to be pinched - this will accelerate the process of lignification of the main stem.
Since the plants are weakened in autumn, it is recommended to apply mineral fertilizer to wet soil in the evening after sunset - such conditions will help the queen of the flower garden to go to winter rest smoothly and without injuries.
Which way to hide roses to choose?
It is up to the gardener himself to decide which of the cover methods to use, but for this he needs to keep in mind the following considerations:
- in the cold period (and not only in winter) roses can be damaged by frost, affected by pathogenic fungi, branches can break both during shelter and under the weight of snow;
- a large, well-prepared for winter rose in the middle lane will almost never die, even without shelter (the exception is “black” frosts, when, due to the lack of snow at the beginning of winter, not only the aboveground, but also the underground part of the bush can freeze out);
- a rose that has emerged from wintering with large losses of the aboveground part weakens greatly, and already next winter may be the last for it (the plant does not have time to grow the aboveground part during our short northern summer); the gardener's task is not just to keep the rose alive, but to preserve, if possible, its aboveground part;
- in the fall, roses gradually prepare themselves for frost (according to my observations, the critical temperature for hybrid tea roses in mid-September is -5 ° C, in mid-October -7 ° C, in the first half of November -10 ° C, in the second half of November - about -15 ° C and even -18 ° C);
- pruning roses (not only for the sake of flowers, but also for shelter for the winter), premature wrapping of the bushes not only stop the natural process of preparing roses for frost, but can also completely deprive the plants of the acquired hardening, especially if there are many warm days in the fall; the rose recklessly comes to life, even a light frost can destroy it;
- if you leave the set fruits on the bush after flowering at the end of summer, the plant no longer "thinks" about the new growth of shoots, the buds do not wake up, and such a rose winters better.
How to cover flowers?
There are 3 main methods of insulating rose bushes for the winter.
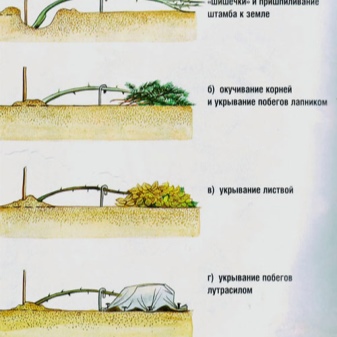
Prikopka. Climbing roses are bent to the ground, non-climbing roses are cut off, after which the shoots are sprinkled with earth, mulch, and spruce branches are thrown over the mound from above. When snow falls, a snowdrift is poured over the spruce branches. The main disadvantage of this method is the overheating of the plant at a warm temperature.



But in severe frosts, when the thermometer drops much below -30, these methods will not save the plant. In these regions, roses are planted in large flower pots, and for the winter they are transferred to cellars, basements, where the temperature does not exceed 4-5 degrees Celsius. In this case, dry watering will be required by putting snow in a pot. In the spring, for some time, the plants are taken out into the street, and when constant positive temperatures are reached, the rose will again take its place in the garden.
But there is another option for using a garden rose: in areas where the summer is very short, rose lovers have made this flower home. Low-sized roses feel great as a house plant. And only on warm days they are on the balcony or in the garden. The roses of the following varieties are suitable for growing both at home and in flowerpots in the garden or in a greenhouse: Fritz Nobis, Louise Odier, Rosa Mundi, Souvenir de la Malmaison and others.




Climbing
For roses with long shoots, there are 2 ways to hide for the winter.
- The earth around the rhizome is laid with spruce branches, sawdust, sand. The lashes are removed from the supports and laid on a coniferous mat. From above, they also fall asleep with spruce branches, after which the entire structure is hidden under the covering material and the edges are tightly fixed. In the spring, the shelter is opened gradually.
- To close the lashes in the second way, you need to tie the shoots in several places on a dry day, bend them to the ground and put them on wire arcs so that the rose does not touch the ground. A frame is installed over the plant, which is subsequently insulated from all sides.


Bush
Shrub roses are not afraid of the first frost. It is necessary to cover the bushes after them. Any method can be used for this.
- Hilling with mulch or spruce branches. The method is suitable for warm winters.
- Frameless or air dry. In this case, either the shoots are cut almost to the root, or each shoot is pinned, as is the case with climbing roses - in both cases, they are insulated from above with any material, and the insulation must be fixed at the edges. If the material does not allow air to pass through, it is recommended to leave air gaps.
- The frame method is logical to use when not one bush grows, but a rose garden. But soft frames for one bush are also possible: several pegs are driven in around the plant, covered with a net and stuffed with mulch.
Stamp
Shelter standard has its own characteristics.
- Young stems overwinter horizontally: the stem is fixed in the ground with staples, spruce branches are poured under the crown and on it, and the rhizome is covered with needles, sawdust, leaves, sand, after which the entire stem is hidden under heat-insulating material.
- Adult specimens will not bend, but only break. A frame made of any material is installed around the stem, insulation is poured inside it, and a cover is put on the plant on top and tied.
- The method used at the University of Minnesota is the overturning method, when a plant, previously very thoroughly watered, is undermined on one side, and very carefully laid in a pre-dug trench along the entire length of the bush.

You need to take care of the wintering of roses during planting.
It is necessary to take into account the dimensions of roses: undersized (miniature and ground cover) are easy to cover, and tall erect (non-spreading) with a height of more than 1.2 - 1.5 m (semi-vine and large-flowered climbing) is much more difficult.
It is also necessary to think about preserving roses in winter when planting roses:
- roses growing in a group are easier to protect from frost than those scattered in different parts of the garden;
- fertilizers must not be applied to the planting pits, which can cause active growth of shoots in late summer and autumn. Nitrogen (in the form of mineral fertilizers and in the composition of humus) is better to apply less than more.
Finally, for the successful wintering of roses, it is very important to prepare them for the next winter:
- flowers should not be cut at the end of summer and in autumn, this leads to the growth of new shoots, which will no longer have time to ripen by winter and will die (sometimes together with branches of the previous order);
- starting from the middle of summer, it is better to stop feeding roses (roses do not need so many nutrients, therefore, spring and early summer feeding with complex mineral or organic fertilizers is enough for the whole season);
- it is necessary in October (for central Russia), gradually, starting from the bottom, to clear the roses from the leaves (they are separated from the branches by a movement from top to bottom and, together with the already fallen leaves, are removed away from the roses; it is best to burn them to prevent the spread of spores of pathogenic fungi) ...
 Protection of roses by hilling. Kevin lee jacobs
Protection of roses by hilling. Kevin lee jacobs
In principle, there are no ways to protect roses ideal for all occasions. Much depends on the capabilities of the gardener and the availability of covering materials, on specific weather conditions, on the frost resistance of roses, their size and the ability to bend to the ground.
Storing roses in the basement
If you do not have time to prepare a winter shelter, you can dig up a rose with a clod of earth and transfer it to a container. In this case, the shoots should be shortened, and the leaves should be cut off. Before planting, such a rose can be stored in the basement at a temperature of 0-2 ° C. Take note that at a temperature of 6-8 ° C, roses are already beginning to germinate.
If necessary, in a dry storage, roses can be watered 2-3 times during the winter. Or you can simply pour snow into the container so that the earthen lump does not dry out
While the roses are at rest, they do not need to be watered, but it is important to remember that they cannot stand even a single strong overdrying.
Do not forget to sign the variety and color of the roses so that when planting in early spring, they will be correctly positioned in the flower garden.
Roses in a container can be taken out early in the spring, cut, composted into the soil and grown in a greenhouse until mid-May.
Recommendations for the selection of materials
Roses can be covered with almost anything at hand, plus special industrial materials that are sold in specialized stores. All materials are divided into natural and artificial.
Several options are natural.
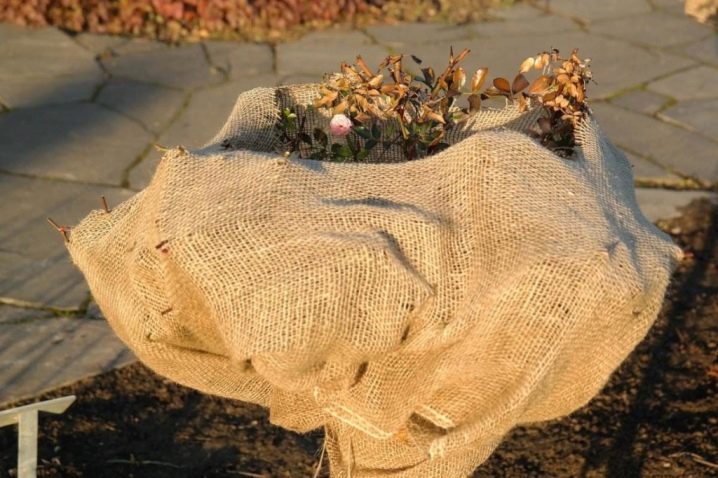
Burlap, which is more often found among real villagers than among summer residents. Natural burlap without a polyethylene lining will provide air exchange, but this is how a single-layer frost protection will not protect much. Moreover, it absorbs moisture and can freeze.
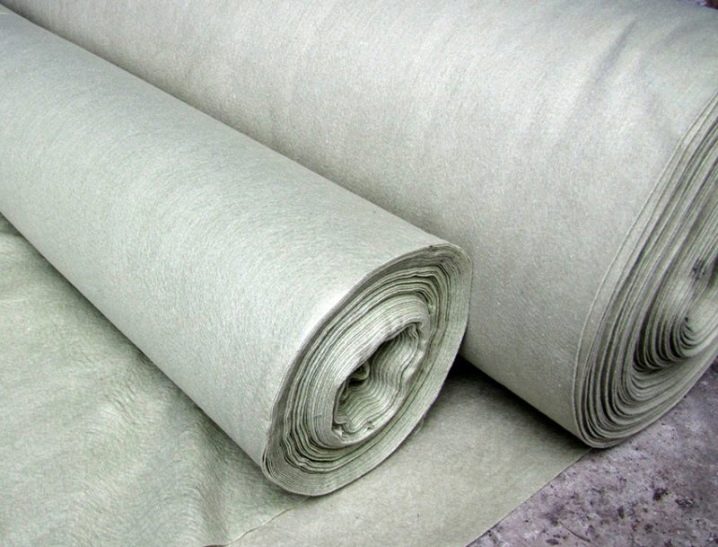





There are many artificial covering materials today.
Polyethylene film is a popular insulation that perfectly protects against wind, precipitation, and cold. But the plant can easily get a burn under it, so there must be an air gap between the film and the branches. The second negative property of the film is the lack of air permeability, which is why condensation accumulates under the film. Excessive moisture can lead to rotting of the branches.






