How to cover roses to preserve them in winter
The next serious step is choosing the right material for winter insulation. In general, if the snow in the region is very heavy and before the first real frosts hit, then you can not puzzle over what is the best way to insulate the flowers. But in many regions of Russia, belonging to the middle lane, the temperature can drop to a dangerous level long before the ground is covered with a thick layer of snow. Therefore, you should think in advance about the best way to cover the bushes in order to protect them from the cold.
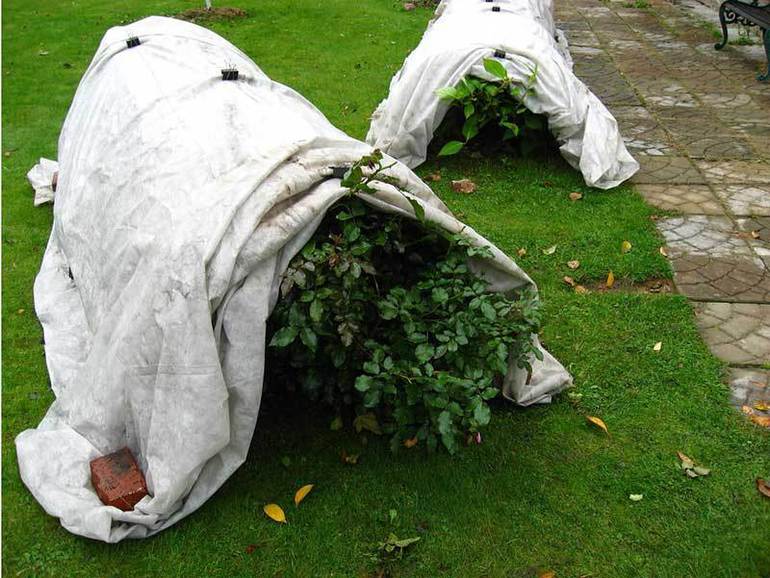
Air dry shelter
This option is suitable for cases where a large number of rose bushes are concentrated in one place, for example, on an area of 10-20 square meters.
On a note! It is undesirable to use polyethylene as a covering material. It does not allow moisture to pass through, which can cause mold and rot on the bushes, which will cause considerable damage to the plants.
A small structure is being erected right above the bushes - a frame about 50-100 cm high made of solid boards, a bar or a slab. From above, the frame is closed with a suitable material - from roofing material to lutrasil. The main function of the structure is to keep the heat coming from the ground and protect it from the cold. At the same time, the shelter remains open from the sides to provide ventilation and remove excess moisture. Only when the air temperature drops to -5-8 degrees, the shelter should be closed from the ends, finally protecting the bushes from the cold. In winter, the entire frame will be covered with snow and the thermal insulation will become even more effective.

The frame can be metal
This rose shelter is simple and reliable. But, of course, if the bushes are scattered throughout the site, then building a shelter over each of them is not only troublesome, but also completely ineffective due to the small area.
Warming with spruce branches
Another way to reliably close bush roses is to use spruce branches. This technology has been effectively used for many decades. In addition, this shelter is perfect for single bushes planted at a great distance from each other. It is enough just to cover the bushes with a thick layer of spruce branches so that they can easily endure even a very harsh winter.
Large armfuls perfectly retain the heat emanating from the ground, and also reliably protect from the cold wind. The needles, or rather the air between them, creates a kind of fur coat that provides good thermal insulation
It is important that it does not interfere with the natural removal of moisture at all - there is no need to be afraid that mold or rotting will appear due to high humidity. The earth and bushes breathe freely and feel great

Simple and reliable way
An additional plus is protection against infections and some parasites. The fact is that needles are a natural antiseptic. Therefore, even during unexpected thaws, in which many bushes are affected by bacteria, roses feel great under spruce branches.
Unfortunately, there is a drawback here as well. Still, it is not always possible to get spruce branches. Not going into the forest to cut down the spruce and chop off its branches - this will certainly be regarded as poaching, and the tree will certainly be a pity for flower lovers. But if there is such an opportunity (for example, when carrying out sanitary felling), then a spruce tree shelter will be an excellent solution.
Use of agrofibre, spunbond and geotextile
Of course, speaking about which rose care is better, one cannot fail to mention modern materials such as geotextiles, spunbond and others.In general, the option is quite effective, but not always and only with the correct use of insulation.

Using a covering material
You can buy the right amount of covering material in almost any specialized store. After that, they only need to cover the area with roses, creating a small air cushion above the soil. At the edges, the material is fixed with bricks, stones, boards or other weighty objects so that it is not blown away by the wind. As in the case of an air-dry shelter, the disadvantage is exactly the same - it is completely unsuitable for free-standing bushes. But for large clusters - quite.
Important! When buying geotextiles and other covering materials, it is advisable to ensure that the density is at least 60 g / sq. m
Of course, less dense counterparts are cheaper, but the quality of thermal insulation is worse.
Alas, some gardeners do not fully understand how such heaters work and simply wrap individual bushes with geotextiles or agrofiber. And then they complain that the material did not work and the bushes froze. This is not surprising - plants do not generate heat by themselves. Therefore, the main task is to keep the heat that comes from the ground. So you need to cover as large a site as possible, and not just the trunk of the plants.
Climbing rose autumn care
Fertilizers and watering
Climbing roses have flexible stems, the length of which, depending on the variety, can reach several meters.
It is clear that such shoots definitely need a support to which the stems of the rose are tied.
A distinctive feature of the climbing rose is that the buds are formed on it constantly, and many varieties bloom until frost.
Nevertheless, in order to properly complete the flowering season, it is necessary to prepare the climbing rose for winter at the end of summer.
In fact, all care for a climbing rose in the fall comes down to preparing for winter.
First you need to stop watering the plant abundantly, loosen the soil under it and apply fertilizers there, which include nitrogen in their constituents.
Therefore, you can only fertilize a rose with phosphorus and potassium, since these components strengthen the roots and trunk of the climbing rose.
Pruning shoots
The health of a climbing rose directly depends on how you care for it. And one of the main components of rose care is proper pruning.
It is pruning that affects the normal growth of the shoots and the flowering of the rose.
Without removing old shoots, you will not be able to form a beautiful crown of a climbing rose.
In addition, a plant that is freed from old stems is simply rejuvenated.
Cutting stems has its own rules:
- when pruning, the growth of developing shoots should be taken into account. In the bulk of varieties of climbing roses, buds are formed on the shoots of last year, so you need to cut the lashes with accuracy;
- it is necessary to use only sharp scissors so that the edges of the shoots do not crack or break - this leads to the possible formation of infection;
- the cut of the shoot must be done at an angle of 45 degrees;
- the cut should be located directly above the kidney, the distance from the kidney to the cut should not be less than 5 mm. In this case, the escape will have enough moisture, otherwise it may simply dry out. In addition, shoots cut well above the bud die off in winter;
- the slices should be protected from infection by treating them with garden varnish.
If you cut the climbing rose incorrectly, it can freeze in winter. Therefore, it is highly discouraged to cut the shoots short.
If the shoots are not cut at all, the rose will lose its decorative appearance, it will bloom poorly and look sloppy.

Autumn pruning rules
The most important rule to remember when pruning climbing roses is that their buds develop from buds located on stems that grow at the top of last year's shoots. And twigs will grow from the lower buds, on which no flowers will appear next year
And twigs will grow from the lower buds, on which flowers will not appear next year.
Therefore, you should not cut the stems of the climbing rose too much.
In the fall, it is generally better to simply remove old dry shoots, and slightly shorten the longest ones. And stop there. In the spring it will be seen.
If you start pruning earlier, then you will stimulate your rose to the appearance of new shoots in it, and they will simply freeze out in winter.
The shoots simply do not have time to woody, they freeze. and then, having thawed in the spring, they will become a source of infection for healthy shoots.
Many novice gardeners are afraid to prune their climbing roses for fear of damaging them with inept actions.
If you still do not know how to cut your rose correctly, I advise you to do it simply:
- halve the height of the climbing rose bush;
- remove all dead and old shoots, cutting them off at the very root.
You can definitely distinguish an old lignified shoot from a young, flexible and green one, and you will not be mistaken.

When is it produced?
It is necessary to start preparing a rose for winter, oddly enough, even in the summer. The type of feeding should be changed in July, and the last feeding is usually done in mid-September. The rest of the preparatory work should be completed by mid-November.
It should also be remembered that cover the plant only in dry weather
and only when the thermometer is at a level above 0.
In the spring and in the first half of summer, it is recommended to feed the plant with nitrogen-containing fertilizers, and closer to autumn - with potash and phosphorus fertilizers. Potassium and phosphorus are elements that help the wood to ripen, lay future buds and buds, and strengthen the root system.
What does it include?
Preparatory work on the preparation of a climbing rose for winter is an integral part of plant care. These include pruning the bush, removing leaves from the plant, cleaning up debris in and around the bush, hilling, and drug treatment.
Watering climbing roses correctly
A climbing rose does not like an abundance of water, but a lack of moisture can easily destroy it.
Water the roses every 7 days. If summers are very hot and dry, double your watering frequency. Use a large 10-liter bucket of warm (preferably rain) water to water a single bush. Try to pour it slowly, at the very root. This will allow the water to penetrate to a sufficient depth (about 30 cm) and the risk of shallow root formation will be reduced. The best time to water is early in the morning.
The next day, shallow (up to 5 cm) loosening the soil. This measure will provide full air access to the roots.
When watering a climbing rose, you need to adhere to the rule of the "golden mean": a lack of moisture can lead to a slowdown in plant growth, while the flowers will become very small. But the abundance of moisture is fraught with trouble: a waterlogged rose is a good target for fungal diseases, its leaves can turn yellow due to the lack of air entering the roots.
Closer to autumn, reduce watering: spend it every 10-12 days. In October, it is no longer necessary to water climbing roses.
Shelters for climbing roses
A florist should know how to lay a climbing rose for the winter
At the same time, he should pay attention to the location of the plants on the site. If the rose bushes are planted in oblong rows, then it is best to cover the roses with shields.
If the plants grow close to each other, it will be preferable to build a frame that covers the entire rose garden.
 Shelter material for climbing roses.
Shelter material for climbing roses.
With a separate arrangement of plants, it is necessary to take into account the weather and climatic conditions of the region. If there is a light frost outside and there is an excess of snow, then plants can be sprinkled on them; how to do it correctly - lay spruce branches on top of the snow
This material will not only warm the roots well, but also reduce the risk of mice and other rodents in the plantings.In all other cases, it is recommended to organize a frame of any size with an air layer.
It is not recommended to lay the stem too low. In low areas, moisture will accumulate, which will cause the development of diseases and rotting of the stems.
Shields for roses
After the plant has been cut for the winter and removed from the supports, it must be carefully but tightly tied in the form of a bundle and, if possible, bent to the ground as much as possible. The ground is lined with spruce branches
To keep the plant better, the branches of the roses are fixed to the soil in several places with a tough and strong wire.
After that, you need to make 2 shields from wood. Their width should be 80 cm, and the length should be equal to the length of the row of plants. Shields are located along the plants at an angle in the form of houses. From the outer sides, it is necessary to fix them with pegs. It is allowed to leave several small gaps and slots in the shields.
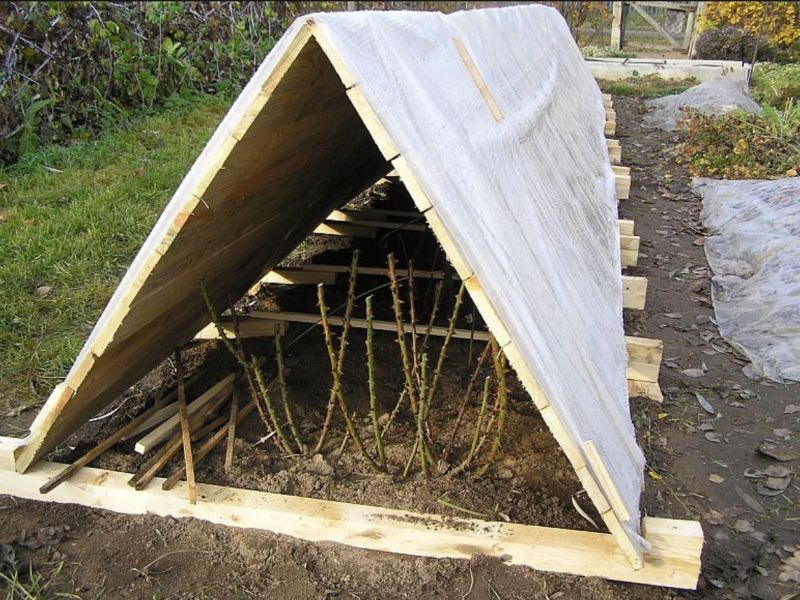 Wooden boards for wintering roses.
Wooden boards for wintering roses.
The upper part of the shields is covered with a polyethylene film so that it can cover them on both sides. The shelter is sprinkled with soil and attached with planks to the shields. Before the onset of frost at -10 ° C and below, the film can be left slightly open, but with the onset of a strong cold snap, the ends should be repaired. With the onset of spring, you need to slightly open the film to prevent the plants from drying out.
Frame shelters
You need to know how to insulate roses with a frame. Such a shelter for a climbing rose for the winter involves the construction of homemade frames in the country. For this, you can use wooden slats or metal wire. Climbing roses are looked after in the same way.
Such a shelter for the winter contains additional supports, to which the branches of plants are tied with a rope. However, they should not come into contact with the frame. When asked how to cover plants, they answer that in this case, fiberglass will be the best material for the frame. It provides good ventilation, but at the same time prevents the climbing rose from suffering from fluid accumulation.
If glass cloth cannot be applied, nonwoven densified material can be used as an alternative. Its upper part can be combined with plastic wrap, which will allow the plants to be protected from snow and other precipitation as best as possible.
It is not necessary to remove the shelter from the plants immediately, but step by step by raising its individual sections in order to ventilate the plants. It is best to start this procedure when the buds on the plant are from 3-4 cm. It is necessary to completely remove the shelter in cloudy weather. This will reduce the risk of sunburn.
After removing the shelter, it is required to inspect the plantings for the presence of sick, injured, shrunken stems. If found, they must be cut, which is what the flower growers do. The bushes should not be straightened right away, they should lie bent to the ground for about 2 more days, otherwise there is a risk that they will break.
Preliminary preparation of climbing roses for wintering
All preparatory activities are completely dependent on the climate of the region where the plant grows. Climbing and hybrid varieties must be protected from frost
It is especially important to do this if in winter the temperature drops below -15 degrees and is kept at this level for a long time.
Preparation for pruning and sheltering climbing roses for the winter begins with the termination of the introduction of nitrogen fertilizer. This usually begins at the end of August. If the bushes are provided with ground cover, then the shoots must be removed from the trellises without fail, these manipulations need to be performed a month before the frost sets in. At the same time, a number of other events are held, namely:
- At the end of August, fertilizers containing nitrogen supplements are stopped. The substance stimulates the growth of new shoots, and this can weaken the flower.In addition, the plant in this state tolerates frost worse. If, upon examination, new shoots are found, then they must be removed with a secateurs, otherwise the bush will simply freeze out.
- If the autumn dressing contains potassium, then this significantly increases the frost resistance of the rose bush.
- After October, they stop cutting the buds, they are given time to bloom on their own and transform into a fruit. These berries help to stiffen the bushes, respectively, in this state, the wintering of climbing roses is more favorable.
- In September, they begin to reduce the number of watering procedures, this also helps to strengthen the stems. Watering is carried out only when the soil dries up, and as soon as the ground begins to freeze, these activities are completely stopped.
When lowered to -3 °, the juice freezes and causes tissue rupture - as a result, longitudinal cracks filled with ice form on the shoots. These are frostbites. They bring the greatest harm to young shoots, because the plant is easily infected with various diseases and rot - in warm weather, they easily enter the internal tissues.
Damping off of the buds, which occurs on the shoots of a wicker rose, when the shelter is untimely removed or when the wintering is illiterate, is also a great danger. To prevent these negative consequences, the climbing rose needs to provide a dry shelter and a sufficient amount of air inside it. Limiting the contact of the stems of the rose with the walls of the shelter will not allow the buds to dry out, and the roses will thaw in it gradually.
Measures to prepare roses for winter begin in August with the replacement of fertilizers: nitrogen fertilizers are excluded from the "diet", it is the turn of potassium-phosphoric ones - they will give the shoots a better ripeness. In early August and September, two root dressings are carried out, and the Osennee fertilizer in granules will be a good addition.
Preparing for winter - pruning roses
When the abundant flowering and development of the rose continues, then in order to slow down the growing season, you need to pinch the runs and bend the stems at the base of the buds.
At the end of September, the roses should be prepared for insulation: the lower leaves should be cut off with petioles, the lashes should be removed from the supports and bent to the ground. Unripe shoots need to be cut off, the wounds should be greased with brilliant green or sprinkled with activated carbon. A day later, a bucket of dry sand for a young plant or 2-3 buckets for an adult is poured into the center of the bush, and after two days, the lashes are treated with a 3% solution of copper sulfate.
In order for the plants to withstand the winter cold well and continue to bloom, you need to start preparing in advance. When growing climbing roses, this process begins at the end of July. At this time, you need to stop fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers, which contribute to the growth of new shoots, and in the cold season this is not necessary at all.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Is it necessary to cut roses in pots
Nitrogen fertilizers must be replaced with potash and phosphorus fertilizers. Such feeding will help the roots and wood to get stronger and will lay the foundation for future buds. Thus, existing bushes are strengthened, and new ones do not grow.
In mid-August, it is necessary to dig up the ground around the climbing rose. This must be done very carefully so as not to damage the root system. After that, you need to fertilize the plants. The last feeding should be carried out no later than mid-September. Before it, you need to water the plant abundantly with water. This is the last watering in the current year, so it should be at least 20 liters.
Climbing roses generally do not require pruning for the winter. But, despite this, it is still recommended to remove dried diseased branches and excess shoots. Thinning helps to maintain the shape of the bushes and improves their flowering.
After cleaning and pruning, the rose is treated with prophylactic agents.
Fungicide solutions help not only fight existing diseases, but also serve as a precaution against future infections.
When is it time to cover the roses
It is also very important to figure out when to start preparing roses for wintering. Of course, this largely depends on the climate in a particular area, as well as the weather.
Therefore, an unambiguous answer cannot be given here.
Dates of the procedure
To protect roses and prepare for winter, pruning and warming in time, you should focus on approximately the following data:
- Moscow region and middle zone - from late October to early November. You should not be afraid of early frosts - most roses (except tropical varieties) can easily withstand a short-term cold snap to -15 degrees. The foliage will, of course, fall off, but the plant itself will not suffer.
- Siberia and the Urals - you should be guided by the beginning to mid-October. In any case, it is advisable to closely monitor the weather. If, according to forecasts, they promise a cold snap to -15 degrees and below, and these are not ordinary frosts, after which warm days will return, but a real onset of cold weather, then it is already worth insulating your favorite flowers.
- Southern regions - in most cases, insulation is not needed at all. This should be done only when forecasters predict a cold winter with frequent cold snaps below -15 degrees.
How to care?
Caring for ground cover roses is simple. The main thing is to water, fertilize, prune bushes on time, as well as prevent diseases and fight pests.
Watering
The first time after planting, ground cover rose bushes need to be watered every 6-7 days. Watering should be done in the morning under the root of the plant and make sure that the water does not stagnate. Matured bushes are watered when the top layer of the earth dries up, making sure that the soil is not waterlogged. You need to water the plants when the soil dries out three to four centimeters deep, using warm water, at the rate of one bucket of water per bush. In autumn, watering is gradually stopped.


Top dressing
During the season, roses that bloom once are fed three times with fertilizers. Fertilizer is applied for the first time a couple of weeks after the appearance of the first leaves, using special multicomponent fertilizers for flowering plants containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. The next feeding is carried out after 4-5 weeks, but before flowering begins. At a time when there is an intensive flowering, the roses are not fed. But if the rose blooms several times during the season, then before each flowering wave it is necessary to carry out additional feeding, removing the wilted flowers.
The last time in the season, the flowers are fertilized in the fall, applying only potash fertilizers for better ripening of the shoots.


Pruning
An important point in caring for a rose is the correct pruning of the bushes. Although it is believed that ground cover roses should grow freely and form a bush on their own, proper pruning of plants will help keep the bush decorative longer and ensure long-term flowering.
For creeping roses, it is important to cut off dead shoots in the spring, and during the summer to remove faded buds if the plant itself does not shed them. If the bushes have drooping branches, then they are pruned in the fall, shortening the shoots for better wintering
Spring pruning allows you to shape the bushes for greater decorativeness. And once every 5 years, rejuvenating pruning is carried out, shortening all shoots to a length of 25-30 cm
If the bushes have drooping branches, then they are pruned in the fall, shortening the shoots for better wintering. Spring pruning allows you to shape the bushes for greater decorativeness. And once every 5 years, rejuvenating pruning is carried out, shortening all shoots to a length of 25-30 cm.


Pruning climbing roses
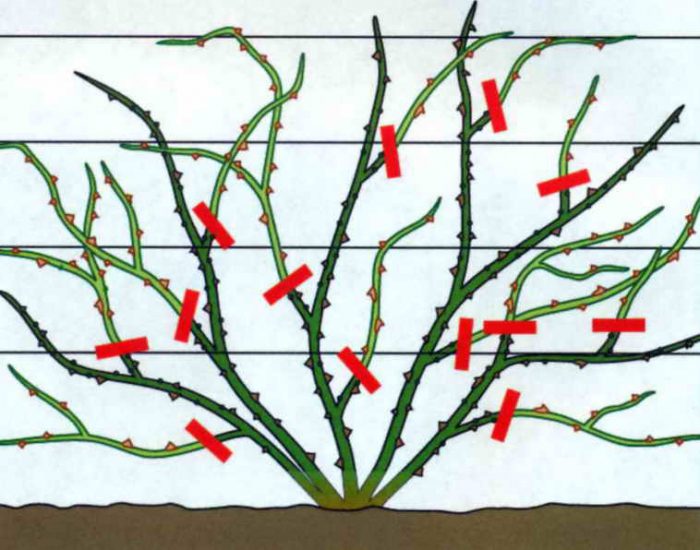
When to prune climbing roses
These plants need pruning, since it is she who allows you to form a beautiful crown, make flowering more abundant, and along the entire height of the bush, improve its decorative qualities. If you cut the plant correctly, then it will delight with its flowering throughout the entire period of intensive growth.Vegetative stems deserve special attention, since most of the flowers are formed on last year's stems. The rose should be pruned in spring or autumn. At the very beginning of the period of intensive growth, absolutely all climbing roses need to remove dead stems, as well as areas that have been frostbitten. And also the ends of the stems should be cut off to the strongest outer bud. The following pruning procedures will be directly related to how many times a particular rose blooms, one or more.
How is pruning done correctly?

Those plants in which flowering occurs 1 time per season, flowers grow on last year's stems. Basal (faded) stems replace regeneration shoots, which can grow up to 10 pieces. Flowers will grow on them only next year. In this regard, faded shoots will need to be removed by cutting them out at the root, while this procedure is recommended to be carried out in the autumn during preparation for wintering. Those climbing roses that bloom several times a season, flowering branches of different orders grow on the main stems for 3 years - from 2 to 5. In the fifth year of life of these stems, their flowering becomes more scarce. In this regard, at the beginning of the spring period, the main shoots must be removed, cut out to the base, and this should be done in the fourth year of their life. The re-flowering bushes should have 3 annual recovery stems and 3-7 flowering stems, which are the main ones. But at the same time, it must be remembered that in most of these roses, flowers are formed on overwintered stems, therefore, in spring, only the upper part with buds, which are underdeveloped, should be cut off from them.
Young roses that have been grafted and planted last or this year need special attention. Until the rose has developed its own root system, you will have to systematically remove the rose hips. After 1-2 years (after the death of the rosehip root system), rose growth will begin to appear.


