Is it possible for tulips to reproduce by scales?
Scales are sometimes called tulip seeds because of their physical resemblance. They ripen by mid-July. But if the flower has not been pollinated, then no seeds are formed on it. When the pod becomes brittle and dry, it is opened and flat, brown, teardrop-shaped seeds are removed. Lay them out to dry on a sheet of paper. Then, until planting, they are stored in a paper bag. Sown in the fall.

Landing technology:
- Choose a pot up to 15 cm high. Fill it 5 cm with a gravel pillow to ensure good drainage.
- Then we add sandy soil. You can also use the cactus mix just short of the edge of the pot.
- We spread the seeds over the surface at a distance of 2 cm between them.
- Sprinkle with a layer of fine sand up to 2 cm deep.
- We take the pot out into the street and dig it in in the garden bed. We cover with agrofibre or polyethylene to protect it from rodents.
- It is necessary to maintain the relative humidity of the soil so that the seeds can germinate in the spring.
- In early summer, these small plants will die off and will remain dormant until next spring, like adult tulips.
- Keep the soil moist as you did last season. And by next year, small bulbs can be transplanted into the soil, at the same time increasing the distance between them, since they will already be cramped in the pot.
All varieties of tulips will look great in your flower garden. But in children, they reproduce much easier, especially if you are not engaged in breeding. It is less labor intensive and blooms many years earlier.
Propagation of angiosperms
Angiosperms are the pinnacle of evolution. For reproduction, they have developed special organs: a flower and a fruit. The bright flower attracts pollinating insects, which facilitate the transfer of pollen between plants. The pericarp fruit protects fragile seeds from adverse effects.
Male and female gametophytes in angiosperms are strongly different:
- Male. The male gametophyte is called pollen and is located on the anther of the stamen. It is a ball with a two-layer shell: the outer one is uneven and the inner one is smooth. Irregularities are needed for better fixation of pollen. There are two cells under the membranes: vegetative and generative.
- Female. The female gametophyte is called the embryo sac and is located in the ovule of the pistil. It has a micropyle inlet for pollen. Opposite the micropyle is the ovum, and in the center is the central cell.
 Male gametophyte:
Male gametophyte:
Female gametophyte:
The process of transferring pollen is called pollination. Pollination of plants happens:
- Self-pollination: pollen falls on the stamens of the same plant organism (peas, beans); the probability of pollination is high, but the diversity of the offspring is low;
- Cross-pollination: pollen falls on the stamens of another plant (corn, watermelon); high diversity of offspring, but low probability of pollination.
By means of pollinating insects (zoophilia) or wind (anemophilia), the pollen is separated from the stamen and flies over the stigma of the pistil. The vegetative cell lengthens and becomes a pollen tube. It grows up and makes its way to the embryo sac. The generative cell is divided into 2 immobile sperm. One of them connects with the egg, forming a zygote. The second unites with the central cell, further forming the endosperm. This process is called double fertilization, that is, two sperm fuse with two cells.
 Double fertilization:
Double fertilization:
Further, an embryo develops from the zygote, which is surrounded by an endosperm with a supply of nutrients.The fetus is gradually formed.
To have more babies
 Woodland bulbs
Woodland bulbs
To stimulate the formation of children in scarious bulbs, the bottom is cut or cut crosswise - most often for the reproduction of hyacinths, since the bulb of this plant lives for many years and gives few children.
When the bottom of the onions is cut, a little is formed, but they are quite large. If the bottom is removed, more bulbs are formed, but they are smaller. Hyacinths grown from a bulb with an incised bottom will bloom in 2-3 years, from a bulb with a cut-out bottom - in 3-4 years. In daffodil bulbs, shallow parallel cuts are made on the bottom.
Professional growers have also come up with a method for propagating daffodils by dividing the bulb. They do it in August. Divide so that parts of two adjacent scales are fixed on a common bottom. The cut sites are thoroughly disinfected.
Delenki are stored at room temperature in plastic bags filled with perlite. They are planted in the ground at the same time as the bulbs (September-October).
Lilies are often propagated by separate scales. Scales in the fall are treated with potassium permanganate (0.3 g per 1 liter of water), dried a little and placed in a plastic bag with peat mixed with sand. Then the bag is inflated, tied and placed in a dark place at a temperature of 21 ° C.
After 2-3 months, after the formation of baby bulbs at the base of the scales, the scales are planted in a pot so that their tip is visible. You can make it easier - immediately plant the scales in sand or a light nutrient mixture. When propagated by scales, flowering plants are obtained in the 3rd, and sometimes - 4-5th year.
In lilies that produce airy bulbs, the formation of these bulbs can be enhanced by the early removal of buds from the mother plants. As they ripen, the bulbs are sown in the ground. Lilies grown from them will bloom in the 3rd year.
Large corms of gladioli and montbrecia form many tubers, so they can be cut into pieces before planting - according to the number of eyes. Each delenka will give a normal corm, sometimes blooming in the same year.
Since the buds of renewal in corms develop unevenly, a division with a central bud will give a larger replacement corm and a greater number of children in the fall than other divisions.
A gladiolus corm (not divided into parts) can also be planted with the bottom up - this is a proven way to get several substitutes from one corm.
How to propagate tulips with bulbs at home
The physiological feature of young bulbs is that they cannot stay idle. In the fall, they are dug up, separated from the old ones and placed in storage. You can store it in a paper bag or net.
The air temperature in the room should be + 20 ° С, humidity 60–70%. At this moment, a flower embryo is formed in the bulb, which will germinate in the spring. With the onset of October, the indoor air temperature is reduced to + 17 ° C.
 For planting, use only healthy specimens and discard any that are damaged or with signs of mold.
For planting, use only healthy specimens and discard any that are damaged or with signs of mold.
Now you need to forcing in order for the tulip to bloom:
- For this, children are placed in soil. It can be pure river sand, pure peat, or a combination of sand and peat. It is allowed to add garden soil and 50 g of ash to the mixture as a source of potash fertilizers.
- Young tulips are planted to a depth equal to two heights of the original bulb so that only its tip is visible above the soil.
- The pots filled with soil mixture are watered with a solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection.
- Containers with tulips are taken out into a room with a temperature of 0 ° C to + 10 ° C and left for 4 weeks.
- After that, the air temperature is lowered to 0 ° C and the container is covered with a film. At this time, rooting of plants takes place.
- After a week or two, the plants are returned back to the room with an air temperature of +10. + 12 ° C.
- The lighting and temperature are gradually increased.At first, the bulbs are shaded so that the sprouts do not stretch out.
- After the sprouts have appeared, they need to be watered regularly - daily or every other day. But this must be done so that the soil is moist, but not wet.
- The temperature is lowered overnight. The entire development cycle will take about 3 months.
- Organize feeding with potash fertilizers 1 time in 7-10 days. You can apply ash or use store-bought fertilizers. They stop adding them when the foliage begins to turn yellow and die off.

When to plant tulip bulbs
Planting tulips can be done:
- in the fall;
- in the spring.
Autumn planting is preferable, since tulips overwinter in natural conditions when used. This ensures timely germination in spring, as well as abundant flowering. When planting buds in spring, you can not wait, since tulips do not always have time to form them before the onset of the summer heat.
Newbie gardeners are often interested in: can these flowers be planted in spring? Of course you can, but you will have to use a certain technology when landing. To do this, put the bulbs in the refrigerator overnight, and then rinse thoroughly with a weak solution of manganese. At the end of these procedures, plant the tulips as close to each other as possible to a depth of about 5 cm.It should be remembered that flowering with this method of planting begins much later.

Vegetative propagation methods
Vegetative or asexual reproduction is carried out using parts of plants that are capable of rooting. Methods for vegetative propagation of indoor plants:
- By dividing the bush;
- By dividing the rhizome;
- Tubers and bulbs;
- Layers;
- Offspring;
- Creeping shoots and whiskers;
- Stem cuttings;
- Leafy cuttings.
But, of course, not all of the listed methods are suitable for every species. Flowers of different species have a different structure, therefore ways of their reproduction are also different. So, bulbous or tuberous plants are propagated only by daughter bulbs or tubers, and only sometimes by leaf cuttings. And with offspring, whiskers and creeping shoots, it is possible to reproduce only those species that form them.
There are indoor flowers for which none of the listed vegetative methods are suitable, since they do not form rooted parts. They are propagated only by seeds. These are the following varieties:
- Palm trees;
- Cacti that do not form children;
- Spherical varieties of milkweed.
It is very difficult to propagate cyclamen in a vegetative way. Its leaves do not take root under any circumstances. It is not recommended to propagate especially valuable specimens of this plant by dividing the tuber or its parts, but only by seeds.
How the tulip reproduces - features
Tulip is a bulbous perennial herb of the Liliaceae family. Initially, plants were found only in the wild.
The zone of the greatest species diversity and the center of origin are mountains in the northern part of Iran, Tien Shan, Pamir-Alai. Thanks to the self-propagation of human breeding, tulips can now be found almost throughout the northern hemisphere. There are about 80 types of them. All species diversity can be divided into 4 groups:
- early flowering;
- medium flowering;
- late flowering;
- prefabricated group of hybrids.

Tulips bloom in May. The entire growing season lasts for a relatively short time, after which a dormant time begins, during which young bulbs are formed. In the fall, they give roots. Bulb generations change every year.
The tulip bulb is a reproductive organ and a source of nutrients for a developing plant. It consists of a bottom (modified stem in the form of a disc), storing scales (leaves), integumentary scales.
In the storage flakes, nutrients are concentrated. Dry leathery integumentary scales protect it from external influences, pests and diseases, excessive moisture evaporation.
Also, the protective function is performed by the unremoved remnants of last year's shoots and scales of a dead mother bulb.
The average life expectancy is two years. For the first year, it is in the form of a bud inside the mother's bulb. In the second year, it turns into an onion.
Between the storing scales of the mother bulb, daughter buds are formed - future bulbs, the central of which is a substitute. In many tulip species, especially wild tulips, it develops faster than other buds. But in cultivated varieties, all buds develop in about the same way.
Also, the buds are laid in the sinuses of the covering scales - these are baby bulbs.
During the summer-autumn period, a stem and flower rudiment and new buds are formed inside the young bulb. After wintering, the bulb sprouts and new generations, then it dies off.
Sun, water ... and depth
It is believed that bulbous plants need to be dug up every year. But in amateur gardens, this rule justifies itself mainly in relation to varietal tulips and hyacinths. Botanical (wild) tulips, as well as most small-bulbous (crocus, snowdrop, white flower, pushkinia, etc.), feel better without annual digging. Usually they are planted every 3-5 years, but if it is necessary to accelerate vegetative reproduction - after 2 years.
In daffodils, lilies, daughter bulbs remain tied for several years by a common perennial bottom, so it is also better not to disturb them every season. In a daffodil, in the second year of cultivation, a single-peaked bulb turns into a two- or three-peaked bulb, then each peak gradually separates into a separate bulb.
By dividing the nest of daffodils in the third year, when the scales that unite it die off, they get stronger planting material than with annual digging, and without unnecessary trouble. In large horticultural farms, the reproduction rate of daffodils (the ratio of the obtained daughter bulbs to the number of nests dug), depending on the variety, is 2.5-3.5. Crocus forms 2-5 new corms, brandy - 2-3.
In general, knowledge of biological characteristics and compliance with the requirements of agricultural technology for a particular crop helps to get as many strong young bulbs as possible. So, for example, a daffodil in most regions of our country does not have enough natural moisture (at least 350 mm of precipitation is needed during the growing season), which means that watering is required.
Or such a moment: it is known that bulbous plants tolerate shading, bloom normally under trees, for which they are especially appreciated by gardeners. However, when shading, fewer daughter bulbs are formed, they become smaller.
Therefore, those varieties that want to multiply quickly are planted only in sunny places. An exception to this rule is ephemera that cannot stand direct sunlight (kandyk, colchicum, hazel grouse).
In addition to daughter bulbs, baby bulbs are also formed. They bloom only after growing for 1–2 years. In a tulip, only bulbs with a diameter of at least 3 cm give full flowering. Smaller ones are children. An adult small onion differs from a child in a more rounded shape (in children, one side is flat).
The bulbs are planted at a depth 3-4 times their height. On heavy soils, the planting depth is reduced by 2–3 cm, on light soils, the same is increased. With a shallow planting of bulbs and corms, more babies are formed, with a deep planting less, but it is larger.
What is asexual reproduction
School biology course defines vegetative reproduction of plants (grade 6, section "Botany") as one of the types of asexual. This means that in the course of its implementation, germ cells are not involved. And, accordingly, the recombination of genetic information is impossible.
This is the most ancient way of reproduction, typical for plants, fungi, bacteria and some animals. Its essence lies in the formation of daughter individuals from maternal ones.

In addition to vegetative reproduction, there are other methods of asexual reproduction. The most primitive of these is cell division in two. This is how unicellular animals and plants, as well as bacteria, multiply.
Another variation of this method is multiple division. It consists in the fact that several daughter cells are simultaneously formed from one mother cell. This happens, for example, in the malarial plasmodium, which parasitizes in blood cells.
A special form of asexual reproduction is the formation of spores. Horsetails, ferns, mosses and moss reproduce in this way.

Seed propagation
It is more difficult to reproduce varietal tulips with the help of seeds, besides, a new plant will be able to bloom only after 4-7 years. However, this method does not require special equipment or laboratory conditions, so it can be tried out at home.
When is used
Seed propagation is used to obtain new varieties: pollination of a tulip with pollen of another variety allows you to get a new glass shape or petal color. Planting tulip seeds just to get a new plant of an existing variety is simply useless - the qualities of the mother plant are lost.
Seed propagation technology
If the parent plants bloom at different times, the pollen should be collected, placed in a paper bag and kept in the refrigerator.
Anthers are carefully removed from the mother flower two days before pollination. The pistil is pollinated 2 times, with a break of 2-3 days
After that, it is advisable to cover the flower with paper in order to protect it from accidental pollination by insects.
The seeds are removed from the capsule when it turns brown and begins to crack. If you are late, they can crumble to the ground. The planting material is stored in a refrigerator at 0 ... + 5 ° C.

Now let's look at how to grow tulips from the obtained seeds.
To begin with, it is recommended to sow them in a box with light nutritious soil to a depth of 1–2 cm. Bulbs will gradually develop from seeds in this box. After 2-3 years, they are planted in a permanent place. Like mature plants, these bulbs need regular rest outside the soil.
For the first time such a tulip blooms in 5-6 years, and the first flowering is weak and inconspicuous. The plant will become truly ornamental only 8–12 years after the seeds have been planted. If its appearance suits the grower, further reproduction is carried out vegetatively.
Vegetative way
Bulb propagation of tulips is not particularly difficult even for novice florists. The vegetative method is also beneficial in that it allows you to completely preserve the characteristics of the mother plant.
How do daughter bulbs appear
Self-renewal and reproduction of tulips occurs with the help of daughter bulbs, which are formed next to the mother. One of them is a substitute. It develops especially rapidly, and two years later - after the main bulb dies off - it takes its place. In fact, it is a clone of the previous plant.
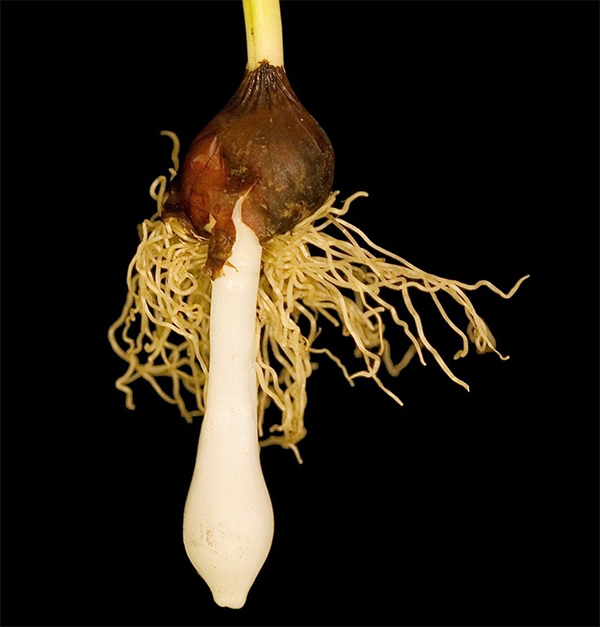
This process can be repeated up to 60 years, but not indefinitely: replacement bulbs inherit from the maternal not only varietal traits, but also gradually accumulating signs of aging. Over time, the plant begins to weaken, lose its decorative effect, and after a certain number of cycles it dies completely.
That is why new tulips need to be grown from lateral young bulbs. Their number depends on the type of plant and the conditions of its cultivation. The annual digging up and separation of children contributes to an increase in their number.
Correct propagation by daughter bulbs.
How to make a full-fledged onion from a daughter
To successfully propagate a tulip in a vegetative way, a number of conditions must be met.
When cutting a flower, be sure to leave a few leaves, with which the bulbs will receive nutrients and can ripen properly.
If you intend to leave the flower in the garden, remove the seed pod from it. Otherwise, the plant will use energy to form seeds and the bulbs will turn out to be smaller.
In any case, after removing the flower, the plant continues to be fully looked after, watering it and loosening the soil as necessary.
Dug out the seed after the leaves have completely wither, but before they decay. For the southern regions, this is the end of June, for the middle zone - the end of July. In the north, excavation is possible at a later date. If the bulbs are removed prematurely, they will be weakened, with poorly developed babies. In addition, after the end of flowering, the plant begins to prepare for the dormant period by building up a protective peel. If it does not have time to coarse, the planting material may suffer during storage from parasites or diseases.
If you miss the moment, the leaves will decay completely and the bulbs may end up being lost. In addition, children begin to crumble from them and may remain in the soil.
Now let's look at what to do with the received children. tulips for their successful cultivation:
- Examine the bulbs for physical damage or rot spots. The skin should be firm, golden yellow.
- Rinse the planting material with water, and then disinfect it for about half an hour in a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Dry the bulbs in the shade for about two days. Then inspect them again and separate the children.
- To prevent the appearance of mites, treat the bottom of the storage boxes with a compound of sulfur and active copper.
- If necessary, sort the planting material into varieties and sign the boxes.
The humidity in the room should be about 80%, otherwise the bulbs may dry out and die.
In the first month of storage, when a flower bud is laid in children, the temperature must be maintained within + 20 ... + 25 ° С. Then it is lowered to + 15 ... + 18 ° С.
The seed should be inspected periodically. Children who are rotten or affected by fungal diseases are immediately discarded.
Planting bulbs outdoors can be done in autumn or spring. In the first case, they should have time to take root a little, but not throw away the shoots. In the middle lane, the optimal time for disembarkation is the second half of September. It is desirable that above-zero temperatures last 20-30 days after planting.

Novice florists sometimes have a question whether tulips of different varieties are pollinated during vegetative propagation. The answer is negative: babies inherit the varietal qualities of the mother bulb, regardless of whether the flower has been pollinated. The persistent myth that bulbs can be pollinated arose for two reasons:
- If you do not dig up the bulbs after the leaves wilt, they often rot and die. Since red varieties are naturally more viable, gradually only they remain in the flower bed.
- There is a variegation virus, due to which spots or strokes of an unusual color appear on the petals. Sometimes the color changes completely. Even if such plants look decorative, they must be removed immediately to avoid contamination of the entire flower garden. The disease is transmitted by thrips or by mass cutting of flowers with a non-sterile knife.
Description and types
Vegetative reproduction refers to asexual reproduction. Another method of asexual reproduction in plants is by spore reproduction.
Vegetative propagation is characteristic of most plant species. For example, strawberries reproduce with whiskers - growing creeping shoots, which are subsequently separated from the mother plant. Trees can reproduce using branches (stems). Vegetative propagation using leaves is also possible.When a leaf of the meadow core touches moist soil, adventitious roots and buds can form.
When a part of a plant capable of living independently forms its own buds, then it is already considered a separate organism.
Thus, vegetative propagation is the reproduction of a plant from roots, stems and leaves (that is, from vegetative organs). However, in algae, vegetative reproduction is the separation of pieces of thallus and even individual cells of the body. During vegetative propagation, the daughter plant possesses the same hereditary material as the parent plant. Such plants are called clones.
Vegetative reproduction allows you to keep the properties of the species unchanged.
Types of vegetative reproduction
Distinguish between natural and artificial vegetative reproduction. These methods are based on the ability of various organs to obtain full-fledged plants under favorable conditions while maintaining the decorative and economic-biological properties of the variety.
Natural
Natural vegetative reproduction occurs with the help of the following organs: rosettes of leaves, whiskers (chlorophytum, saxifrage); rhizomes of underground shoots (lilies of the valley, irises, peonies, calla lilies, etc.); lashes - aerial leafy shoots with a leaf rosette at the end (hawk, tenacious); root shoots - shoots formed from dormant buds of roots (lilac, etc.); bulbs. Bulbous plants are divided into evergreen (pancratium) and deciduous (lilies, daffodils, tulips, etc.).
They reproduce with the help of the following organs: root tubers, which are modified roots-receptacles of nutrients (dahlias); stem tubers with continued growth in subsequent growing seasons (begonia, cyclamen, gloxinia); corms, the reproduction of which occurs by replacing corms, their division and children (gladiolus, saffron)
Artificial
Artificial vegetative propagation is widely used in plant growing, fruit and ornamental gardening. With this method of reproduction, all the characteristics of the mother are transferred to the daughter organisms, which makes it possible to preserve the properties of valuable varieties. Artificial vegetative propagation makes it possible to quickly obtain a large amount of planting material.
There are several ways of such reproduction:
- Cuttings
- Reproduction by layering
- Reproduction by dividing the bush
- Modified organs
- Reproduction by whiskers and root suckers
- Graft
Cutting a leaf
Leaf cuttings are suitable for plants that can take root in this way. For example, Kalanchoe, begonia, violet, ceperomia, fat woman, gloxinia, streptocarpus.
You need to take a healthy leaf of a plant with a shank of 3-5 cm. The cut on the shank is placed at an angle. It is placed in a glass of water to a shallow depth of 4 cm. The period of root formation will take about 2 weeks. After the roots appear, the shoot is transplanted into a prepared pot with soil mixture.

Reproduction by part of a leaf
In addition to water, a light substrate or sphagnum moss is used for rooting. The technology in this case is similar to stem cuttings. The edge of the leaf should be above the ground and not in contact with it. Vegetative stimulants for the rooting of leaves are not recommended.
Plants with large leaves can be divided into pieces and rooted. For example, begonia, aloe, sansivieria or streptocarpus. Pieces with pronounced veins are selected. The end part is not used. Pieces of leaf are laid vertically on a damp, loose substrate (sand can be used) and covered with foil to create a greenhouse effect. During leaf propagation, the pot is in a warm, lighted area.
Bulb propagation of tulips
To grow tulips with bulbs, the latter must be dug out annually in order to get healthy, beautiful flowers next year.Digging is done after the tulip leaves begin to turn yellow (for late varieties) or turn yellow completely (for early varieties).

Tulips in the flowerbed
Before digging up and after the end of flowering, it is necessary to remove the seed pods and part of the leaves from the buds.
It is very important to observe the timing of digging. With early digging, the bulbs may not mature until spring, with late digging, it is difficult to determine the location, as a result of which they can be damaged
After digging them up, they must be examined for damage and disease, selecting only healthy, undamaged specimens for storage.
Then you need to rinse them under running water and stand for half an hour in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Then the bulbs are dried, sorted, the daughter ones are separated from the mother ones and sent for storage.
I have a large garden and vegetable garden, several greenhouses. I love modern methods of plant cultivation and soil mulching, I share my experience.
Bulbs are the material that tulips usually reproduce. For this process to be successful, you should not remove all pouring after flowering. A few need to be left, because they photosynthesize, which means they are able to feed the rhizome. In addition, it is easier to determine the location of the planting material.
It is better to remove the bulbs from the soil using a pitchfork. So the likelihood of damaging them is lower. We do not recommend trying to pull out the bulb by grasping the remains of the aerial part of the plant. So the bulb can be damaged or simply tear off the dried out pour.
If some specimens have minor defects, they can be cut off and then sprinkled with crushed activated carbon or cinnamon.
It is important in winter to keep the planting material so that it is well ventilated and does not rot. Non-solid plastic or wooden boxes are suitable for this.
Sometimes the bulbs are shifted with sawdust, peat, wrapped in paper.
Once a month, you need to sort out the workpieces to make sure that nothing has begun to rot, that fungal lesions have not appeared. After all, one sick specimen is enough to spoil all supplies during the winter.
While watching the video, you will learn about growing a tulip.
Cultivation of tulips is quite a feasible task for amateur gardeners. Reproduction takes place by bulbs. The main thing is to remember the need to dig up the bulbs annually and follow the rules for their selection and storage.
Have you noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter to tell us.
Short description
Tulips are perennial bulbous plants of the lily family. For decorative purposes, they are grown in garden plots by almost all growers.
Specialized floriculture farms are engaged in the cultivation of large quantities of cut for subsequent sale.
The buds have a varied shape and color, among the hybrids there are varieties with variegated petals. During the short growing season, tulips have time to bloom, form seeds and plant new bulbs in the ground, while old bulbs die off.
During the summer dormancy, the rudiments of shoots and buds of the new season are formed in the new bulbs. In the fall, the bulbs will form roots and the shoots will be completed.
Comments (4)
Valeria
04.01.2019 at 05:19 | #
Tulips are very beautiful flowers, I have never had to pollinate them on my own, I mainly germinated bulbs with children, these plants require special attention and care.
Julia Expert Plodogorod
04.01.2019 at 21:15 | #
Hello Valeria! From the described it becomes clear that you are using a vegetative way for reproduction. It is good because it is possible to completely preserve all varietal characteristics, that is, the shape and color will be exactly the same as that of the mother plant. With this method of cultivation, it is imperative to cut the flowers when they have faded so that the plant does not spend energy on ripening the seeds. But, it is necessary to leave the leaves in order to receive nutrients through them.
If you want to experiment with the appearance of your tulips, then you should try seed propagation. Then they just carry out pollination with pollen of another species of this flower. No special effort is required for this, but tulips will delight you with flowering in about five years. To get the effect, it is worth planting next to the bulbs of those varieties that it was decided to cross. If they do not bloom at the same time, then the pollen can be collected and put in a cool and dark place.
It is better to pollinate several times within three days, and then cover the bud with loose paper so that insects do not pollinate it and interfere with your breeding experiments.
Alexander
20.04.2019 at 21:02 | #
Hello Julia! I would like to ask you for advice on the cultivation of tulips, namely wild ones! In short: I accidentally met in the forest a clearing (literally several dozen) of white tulips with a purple vein. I never did this, but there was a monstrous desire to multiply them until they were plucked and presented to someone.
Julia Expert Plodogorod
20.04.2019 at 22:33 | #
Hello, Alexander! As a rule, flowering tulips, like any other plants in this phase, are not recommended to be repotted. But, if there is an urgent need, then we will consider two options.
If the plant, together with the bulb, has already been removed from the soil, then it is not worth removing the peduncle. Rinse the onion carefully and place it in a container with water together with the bud. Next, you should wait until the flowering ends. After, the onion should be dried and put in storage in order to plant it next season on its own site.
If you have not yet taken any action, then the algorithm is as follows. Cut off the peduncle, leaving only part of the stem and the two lower leaves. Next, it is worth digging up the plant using a shovel. If possible, grab as large an earthen ball as possible to avoid injury to the rhizome.
Then you need to dig a hole of the appropriate size on the site and immerse the earthen lump brought from the forest there. After that, watering is required, preferably with settled and not too cold water. You should not feed such a plant after transplanting, this will only be an additional load on it.
If the tulips take root successfully, further care does not differ from caring for domestic ones.
It is important to carefully examine the selected plant so that there are no spots, damage or incomprehensible growths on it. If something like this exists, then there is a high probability of infection of other plants in the garden.
Alternatively, you can mark the spot where you found the flowers and dig up the bulbs in June or July. This is of course a more complicated and time-consuming method, since you will have to monitor the natural cycle of wild flowers, but the likelihood that the bulbs will successfully take root in the future will be higher. You can try both options.
Advantages and disadvantages of growing an apple tree from seed
An apple tree grown from a seed must be transplanted three times during the first four years of life. The first transplant is from a nursery to a tall pot. This is done to ensure the free development of the central taproot. At the second transplant, after a year, into an even larger pot, the central root is trimmed or bent at an angle of 90 degrees. The third transplant is already a landing in the open ground for a permanent residence.
If all these stages are not passed, then fruiting will have to wait for a very long time, about fifteen years. Such a tree can reach eight meters in height - just such apple trees can still be seen in villages and villages. All modern varieties are obtained using the method of grafting on a dwarf stock, so the current apple trees do not grow large.
There is a saying: "Buy a pig in a poke." So, the process of growing an apple tree from seeds is about the same.It is impossible to predict the result in advance! You can become the proud owner of a completely new and delicious variety, or you can grow a completely wild apple tree, the fruits of which are bitter-sour and absolutely inedible, but incredibly beautiful! The saddest thing about this business is that we have to wait for a very long time to see what we will get - from five to fifteen years!
An apple tree grown from a seed is more frost-resistant than the parent tree, from the fruit of which the seeds were taken. Even the great scientist Michurin noticed this feature. The tree grows taller, stronger and very durable - such specimens live up to eighty years. There were cases when in the village gardens apple trees were cut at the age of more than forty years, and after that they began to bear fruit again.


