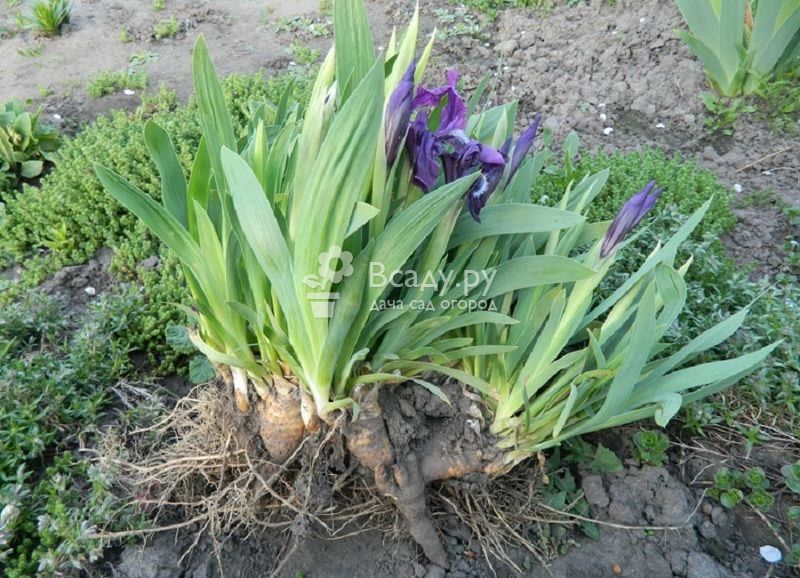
Features of the shelter of irises in different regions
The quality and thickness of the covering material will differ from the region in which the flowers are grown:
- Frost-resistant varieties do not need complete shelter. They tolerate low temperatures well, and it is enough to insulate only the root system. Complete insulation is required only for transplanted irises.
- Iris varieties that are not frost-resistant should be completely covered for the winter. The procedure begins in late autumn, before the onset of frost.
The soil is mulched with a thick layer of peat or spruce branches. The use of dry foliage and sawdust is undesirable. In March, a layer of mulch is removed from each root to prevent rotting.

Middle zone of Russia
The middle zone of Russia is characterized by cold winters. In addition, there is not always enough snowfall.
Moscow suburbs
Cutting the leaves of irises begins 2.5 weeks before the onset of frost. Pine branches or spruces are used to shelter irises in the Moscow region. As soon as the air temperature drops below -1 degrees, the roots of the irises are covered with dry soil. After the ground begins to freeze, spruce branches are laid.
Leningrad region
Winter weather in the Leningrad region is characterized by sharp temperature drops, strong winds and lack of snow. Therefore, the material for the shelter is chosen to be dense. The soil is pre-mulched.

Siberia and the Urals
In cold regions, even frost-resistant varieties of flowers need a thick layer of mulch. It must be dry inside the shelter, so any material is additionally covered from above with a wooden box or bucket. The snow that has fallen on the box or bucket provides additional protection from the cold.

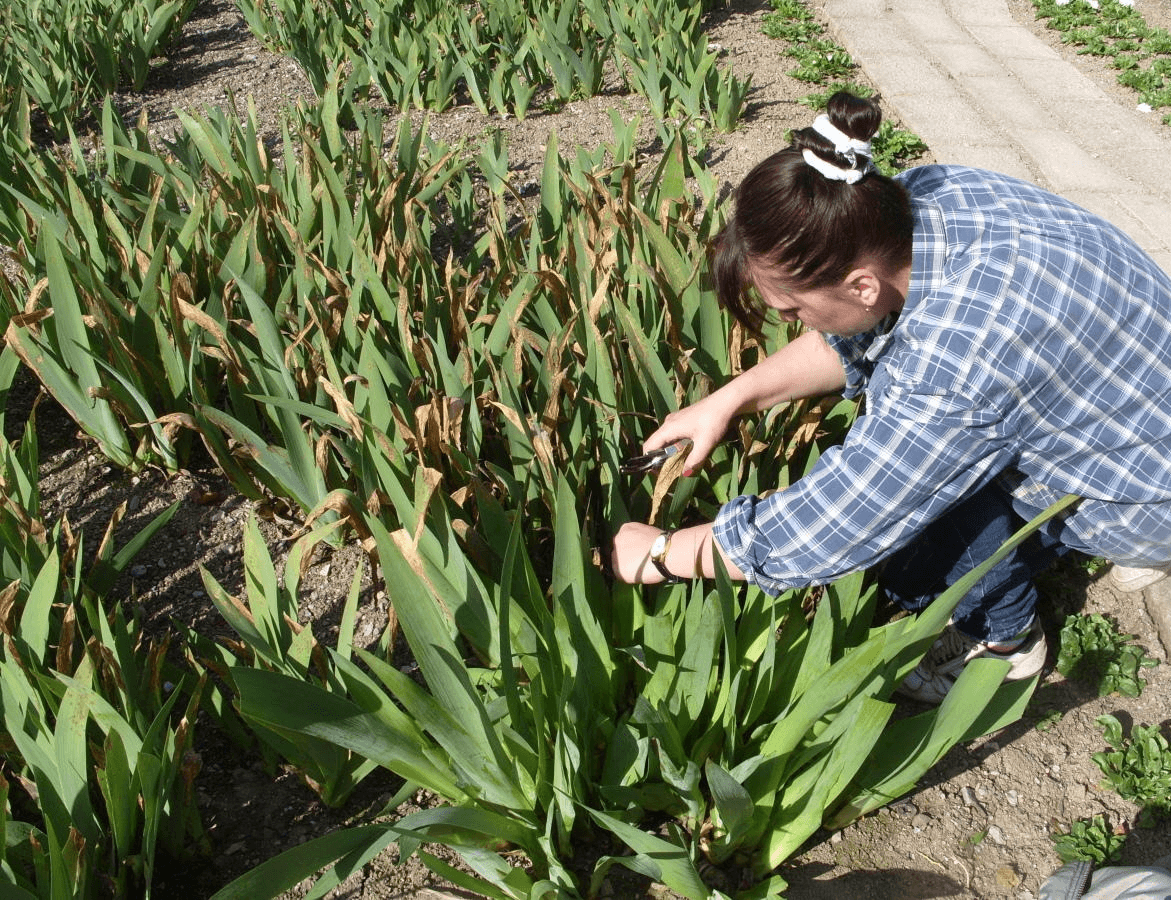
Pruning irises in autumn
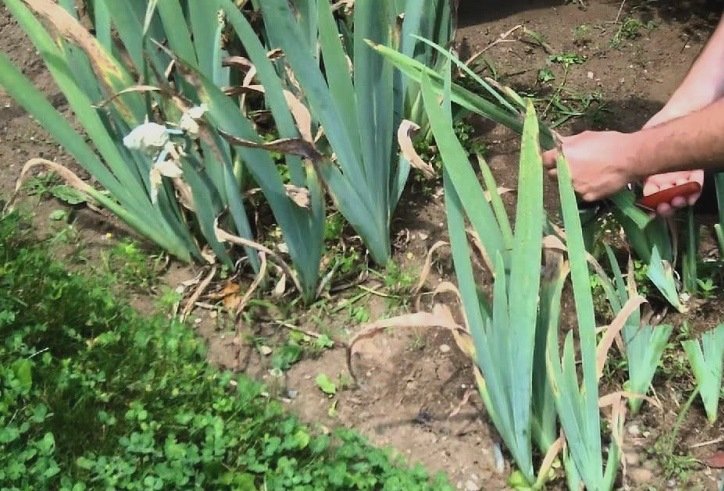
Pruning irises in the fall is an important procedure. It helps to prevent the development of seeds in the plant, their ripening will inhibit the further flowering of these perennials, as it takes away some of the nutrients. In addition, ripe seeds will spontaneously spread throughout the garden, subsequently irises can grow in the most unexpected places. In autumn, dried foliage should also be removed, this preventive measure will protect plants from pests that can winter in it.

Do I need to prune irises in the fall for the winter
Irises must be pruned in autumn so that the plant remains free of dried aerial parts for the winter. The need for this procedure is obvious - dried flowers are removed along with peduncles, withered foliage, in which pests can hide. In this case, it will be easier to cover the irises for the winter.

When is it better to prune irises for the winter
The procedure for pruning irises is carried out in the fall after the plants have completely faded, and the peduncles and leaves are completely dry. It is not recommended to remove green foliage, since in the above-ground part of the plant after flowering, the process of photosynthesis continues, allowing the root system (or bulbs) to recover from active flowering, as well as to stock up on nutrients before the onset of frost. This stock increases the resistance of the root system to frost.

Therefore, the most optimal time for pruning irises for the winter is October, while local climatic conditions should be taken into account, because any plants should be pruned several weeks before the start of frost.

Pruning irises after flowering for the winter
After the irises bloom (ending in early autumn), all dried flowers should be cut off, and all ripening seed pods should be removed. And also the stems and peduncles should be removed after the plants have completely faded. The foliage is removed after it becomes withered and lies on the ground completely.
Video: pruning irises after flowering for the winter
How to properly prune irises for the winter
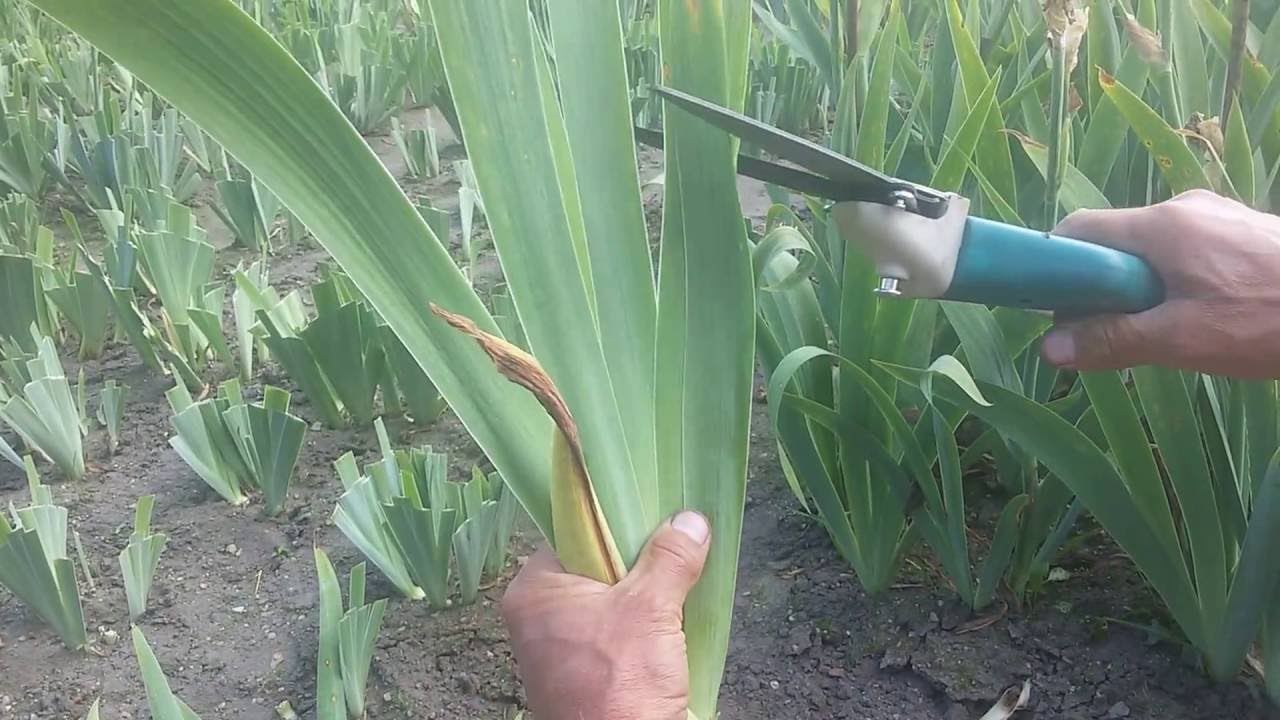
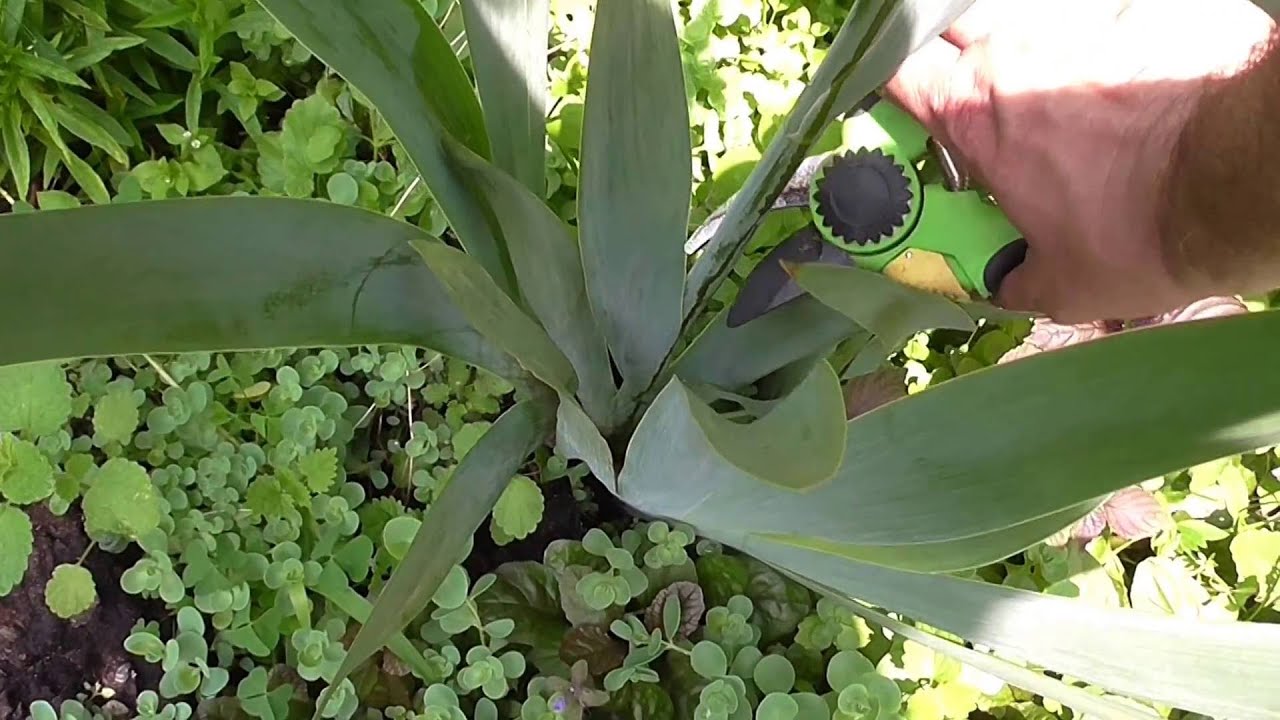
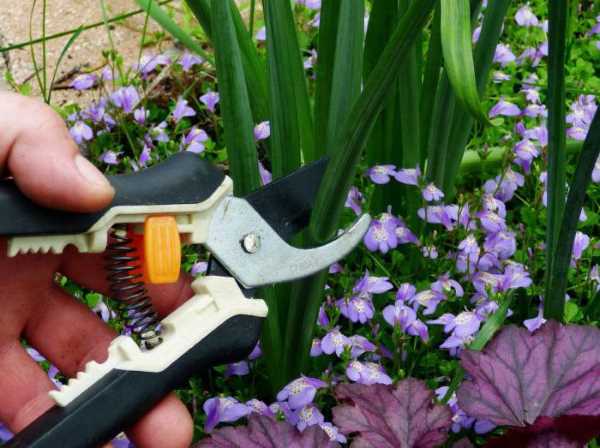
For pruning, you should have sharp garden shears or pruning shears - blunt garden tools can damage the stems, which will rot the remaining aerial parts of these flowers. Dried flowers and ovules can be trimmed or simply pinched off by hand. The flower stalks of plants are cut "at the root".

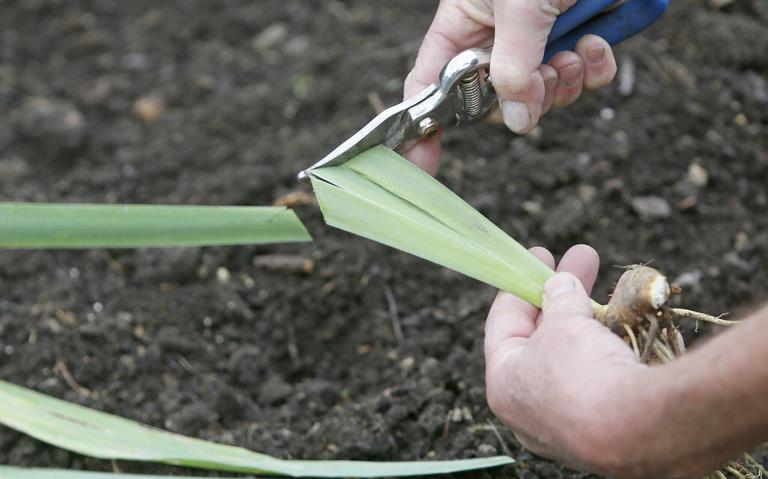
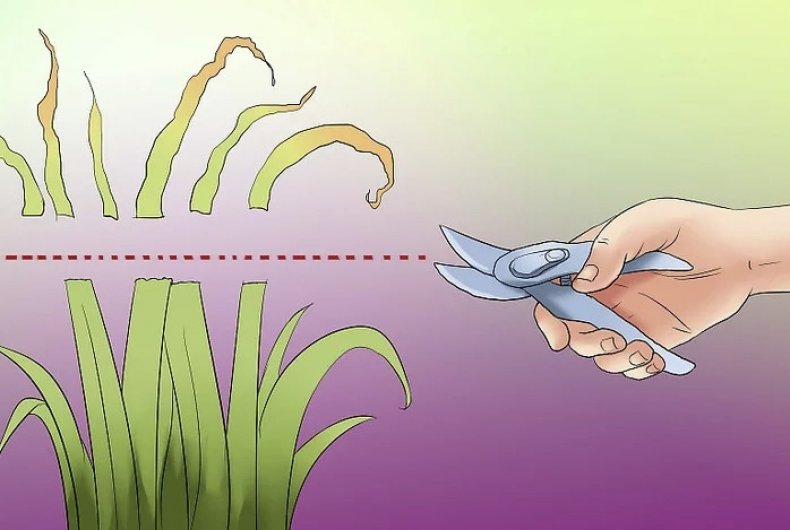
Dried stems and flower stalks are cut with garden shears, leaving stems about 3 cm high.
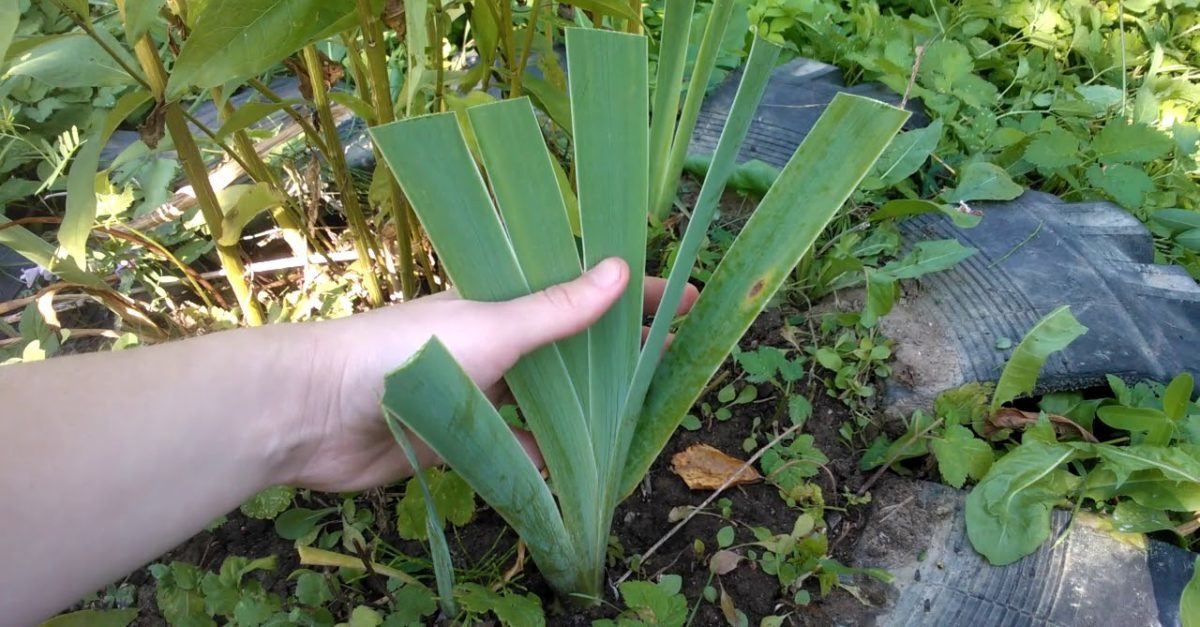
Withered foliage is cut at a height of about 13-15 cm, giving the plant a conical shape. The foliage is cut in the first decade of October.
Care after pruning
Usually, after the end of flowering, such plants should not be watered often, a couple of waterings in the fall season are enough. And if the autumn is rainy, then these perennials should not be additionally watered.

The best fertilizers for irises are mineral fertilizers. However, it should be remembered that nitrogen is applied under these flowers only before flowering begins. But in the fall, two weeks before pruning or two weeks after it, these flowering perennials are fertilized with a complex mineral fertilizer, which includes any potassium salts and superphosphate. However, it should be remembered that if fertilizing is applied after pruning, then at least 14 days must remain before the onset of frost.
Iris care after flowering

Even before the onset of cold weather in early autumn, the irises should be covered to protect them from winter frosts. Young iridescent whales less than a year old especially need it. Adult irises are easier to tolerate frosty weather. To do this, use:
- fallen leaves;
- pine branches (spruce branches).
With the onset of spring, as soon as the snow has melted, the shelter must be removed. After the top layer of soil in the flowerbed has dried, fertilizer must be applied. For this, mineral supplements are used. The soil is loosened to a depth of 1-2 cm so as not to damage the bark color system
In irises, the roots are close to the surface, so it is very important not to catch them.

Irises do not need special care during flowering, however, they require attention. During development, you need to remove flowers that have already begun to fade. After complete drying, they must be completely removed.
Such removal is carried out carefully, without damaging the leaves. From August, you can stop watering plants
Also, you do not need to loosen the soil so that the roots can fully prepare for winter.
When and how to prune irises in the fall?

Pruning irises is a specialty in flower care. There are several types of pruning that take place throughout the year. It depends on the purpose of growing the plant.
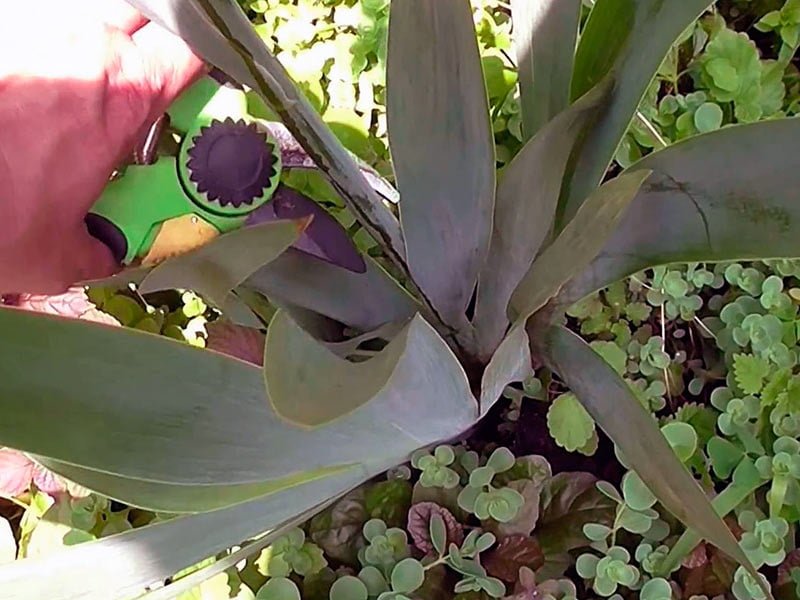
The first pruning is carried out immediately after flowering, removing dried peduncles. To do this, use special garden sharp scissors. You should retreat 2 cm from the buds and cut it off together with the receptacle. Closed buds should not be touched, let them remain. After the final flowering, the entire stem is removed, stepping back 2 cm from the ground.

Leaves should not be cut off, since the plant in this form will lose all nutrients. This will negatively affect the frost resistance of flowers. Be sure to cut the yellowed leaves and check the flowers so that no wilted buds remain on the stems. The leaves should be cut in the fall, shortly before frost, so that the plant does not start up new shoots. Usually, leaf pruning is performed in October with a distance of 15 cm from the ground. Experts advise making a cut in the form of a cone so that moisture does not linger on the foliage.
 Pruning in the fall is a good prevention against plant pests and diseases. Often all insects lay their eggs in foliage. In the spring, the larvae begin to wake up and spread throughout the site. All dry waste must be collected and burned outside the flower bed.
Pruning in the fall is a good prevention against plant pests and diseases. Often all insects lay their eggs in foliage. In the spring, the larvae begin to wake up and spread throughout the site. All dry waste must be collected and burned outside the flower bed.
If you do not prune the cockerels after flowering, their seeds begin to ripen. This will lead to self-seeding and the flowers begin to spread themselves over the site.If there is a desire to collect seeds, then you need to collect them in time. They will be suitable for planting.
Pruning irises is also necessary as an aesthetic component. With cut flowers, the flower bed will look neat and tidy. Such measures are necessary if there is a desire to get healthy and flowering plants next year.
Top dressing and transplanting

mineral dressing with equal proportions of potassium and phosphorus
In summer, when the flowering of irises stops, new links appear on the rhizomes. However, during this period, new buds have not yet had time to set. Shoots are removed from them, but very carefully, without digging a root out of the soil.
Suitable for planting annual plants that have reached a diameter of 1-2 cm and 3 cm in length. You can prepare a sprout as follows:
- cut off 1/3 of the entire length of its leaves and shorten the roots to 8-10 cm;
- choose a sunny site;
- during planting, apply mineral fertilizers and organic matter;
- with an acidic soil composition, add wood ash;
- dig up the area and make holes corresponding to the size of the roots;
- the leaves should be in an upright position, and after planting, press the sprouts lightly to the ground and sprinkle with soil;
- the first time after planting irises are watered only after 3-5 days.
Transplanting and dividing the roots of orcas must be performed once every 4-5 years. If everything is done correctly in the summer, then the irises will be able to get stronger before the onset of cold weather, gain strength and please with bright and large flowers next year.
Preparing irises for winter
Pruning is just one of the activities to prepare plants for winter.
Watering
Irises, like all rhizomes, do not like moisture stagnation. Therefore, watering is stopped by autumn. Experienced flower growers protect flowers from rains with a film in a damp autumn so that the soil does not become waterlogged.
Advice! In the fall, it is not recommended to loosen and weed the plants, so as not to disturb their root system.
Top dressing
These flowers are fed once a month during the growing season using complex fertilizers. But after the middle of summer, nitrogen must be excluded from them. At the very beginning of autumn, fertilizing with phosphorus and potash fertilizers will be beneficial. It will increase the frost resistance of irises. You can use dry fertilizers: 1.5 tbsp. tablespoons of potassium sulfate and 3 - superphosphate. Gently scatter this amount over 1 sq. m and close up with loosening. In dry autumn, it is easier to dilute the fertilizer in water, as indicated in the instructions, and pour it onto the same area.
Features of flowering irises
By choosing different varieties for a flower garden, you can provide a continuous riot of colors for 2.5-3 months. The following factors affect the flowering of iris:
- choice of planting site (here lighting and soil moisture);
- adherence to landing rules;
- fertilization;
- plant age;
- weather conditions and wintering period;
- features of the variety and compliance with the local climate;
- the presence of pests and diseases.

Perennial flower buds are laid after the flowering period (in summer), when the root system is in the phase of active growth.
This stage allows you to transplant and propagate the plant as efficiently as possible. Then, after flowering, plant care includes pruning. Adult plants with poor care and poor soil do not lay flower buds every year, and the annual links of the vegetative shoot become shorter and thinner.
The structural features of the iris flower distinguish it from other representatives of the flora. Single (or in inflorescences) flowers appear on a strong, cylindrical, erect and fairly high (up to 100 cm) peduncle. The perianth is simple, it is not differentiated into a corolla and a calyx, tubular, in most species it has 6 petals. The outer perianth lobes are usually bent downward, while the inner ones are directed upward and often touch. The petals grow together into a tube that contains nectar.
It will also be interesting: When to cut lilies - after flowering, for the winter and whether it is necessary
Do I need to dig the Imperial hazel grouse every year
Fritillaria (this is the biological name of flowers) release buds in early spring. By the middle of summer, the plants enter a dormant period, like many other bulbous crops (tulips, daffodils). The leaves turn yellow, dry out, the stem dries up. This is the moment when the grouse can be pruned after flowering.
Each stalk of the Imperial hazel grouse produces 3 to 7 bells
Blooming "palms" are yellow, white, orange, crimson with a checkerboard pattern.
Withering stems look unaesthetic, but breaking them or twisting them is strictly prohibited, you can damage the delicate bulbs. Those who plant hazel grouse flowers decide for themselves when to dig up the plants. When "babies" are needed, it is better not to disturb the flowers for two or three years, so that the new bulbs grow to medium size. Flowering in this case can not wait. Fritillaria will release a pipe, fluff up the leaves, but there will be no buds on the top of the head.
Important! Faded yellow foliage is a sign that the time has come when they are digging imperial hazel grouse bulbs... Digging is optional, but desirable
Several reasons why it is better to dig up fritillaria:
- for a full-fledged bookmark of flowers, the plant needs to create natural conditions. In the middle of summer, a period of drought and heat sets in in the East. It is noticed that after holding the onions in a warm room, the number of buds on the Imperial hazel grouse increases;
- with seed reproduction of buds, you will have to wait 7 years. Parts of the onions with the remains of the bottom bloom in the second year. Dividing the bulb is the best way to breed flowers;
- by the way, large heads with a diameter of more than 8 mm are cut into 4 parts so that on each lobule there is a piece of the bottom, from which the roots sprout;
- Like all bulbous crops, the rhizome of hazel grouse sinks deeper into the ground every year. The sprout takes longer to germinate, the risk of decay increases. On dry, loose soil, plants are capable of producing a peduncle annually without transplanting. Small-bulb varieties are more resistant to the weather conditions of temperate latitudes, they can not be disturbed for up to three years;
- enrichment of the soil with nutrients. For plants, it is not necessary to look for a new place every year, it is enough to add complex fertilizers, ash, lime to the existing plantation. Then the numerous buds of hazel grouse will delight next spring.
Important! If rotten heads are found during digging, it is better to change the planting site. Grouse grow well after melons, cauliflower, greens
- protection of root bulbs from insects. They do not have a hard peel, a strong smell scares away rodents, but does not prevent the larvae of a bear, sawfly and other insects to feast on juicy pulp;
- prevention of rot. Large-bulb varieties are especially often affected by the disease. Subtropical giants are less sick after summer drying. When hazel grouses are dug up in the summer, the bulbs practically do not rot.
Important! Young annual bulbs are easily damaged when removed. When to dig out hazel grouses after flowering? - Gardeners prefer to do this annually, it is advisable to sift the soil so that there are no plant residues that can rot
Iris transplant
Irises need a transplant so that they bloom beautifully and densely. And this is exactly the procedure that is carried out after the completion of the flowering of these plants. In addition, vegetative reproduction allows new plants to bloom within a year.
It is very important to adhere to the exact dates when transplanting, otherwise you may not wait for flowering next year. The best time for transplanting orcas is considered to be 14 days after flowering has ended.
This period differs in that the plants have already begun to actively store nutrients for the coming winter, their rhizomes are maximally developed, new shoots have already begun to appear on them, but flowering buds are not yet laid.This is when it is best to replant irises.
Selection and preparation of sprouts
For planting, one-year-old sprouts are suitable. Moreover, they should be about 3 centimeters high and about 1 or 2 centimeters in diameter.
To extract a new link for transplanting, the bush must be carefully completely dug out of the ground, gently shaken off and the rhizome must be examined. It consists of individual links that are connected by jumpers. Each individual link usually has its own roots and its own bundle of leaves.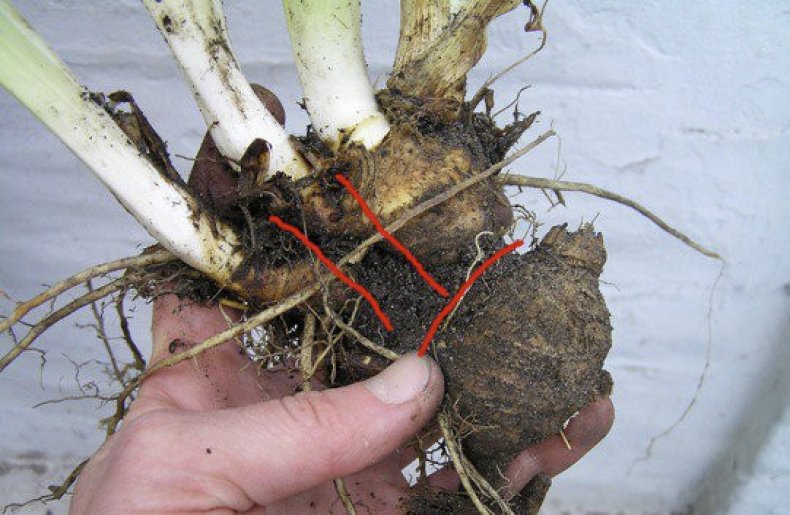  The bush and roots are separated, and each division must contain from 1 to 3 links. Each such share must have a growth point or a bunch of leaves.
The bush and roots are separated, and each division must contain from 1 to 3 links. Each such share must have a growth point or a bunch of leaves.
After division, each plant must be carefully examined and any damage, if any, removed from it. Remove spoiled or rotten roots, dry leaves. In this case, the leaves must be cut off by 2/3 parts, and the rhizomes must be cut by 1/3 part.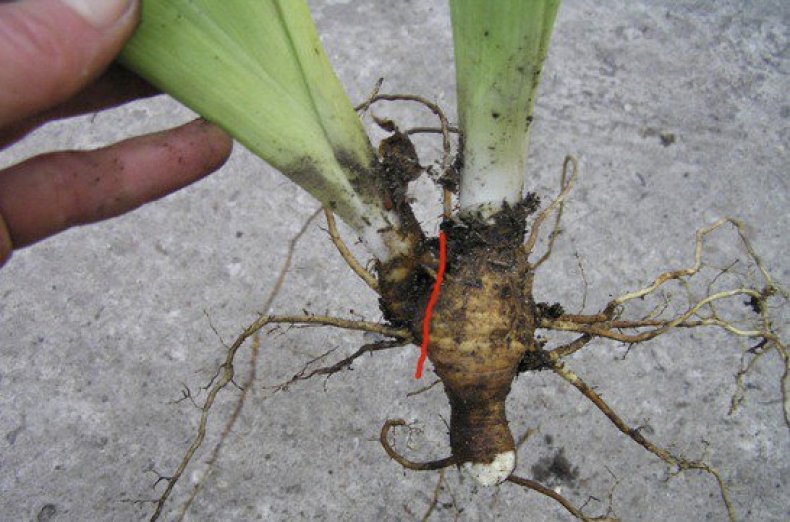  All circumcisions are carried out with very sharp garden tools (scissors, pruning shears, knife). The instrument must be absolutely clean, it can even be sterilized.
All circumcisions are carried out with very sharp garden tools (scissors, pruning shears, knife). The instrument must be absolutely clean, it can even be sterilized.
The cutting sites are disinfected. To do this, the slices are dipped in a solution of potassium permanganate for 15-30 minutes, and then dried in air. The incisions can then be treated with charcoal powder.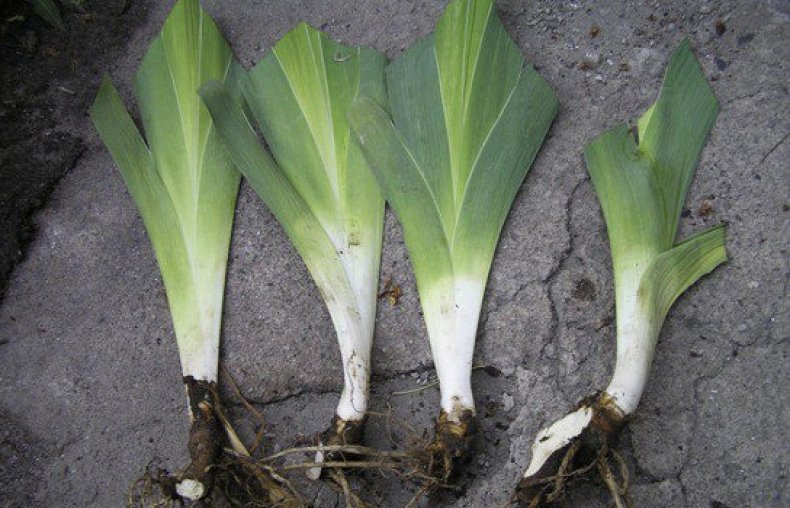 
Growing conditions
It is best to choose a place for growing irises in areas open to the sun. With sufficient sunshine, iris grow well and bloom more abundantly.
It is also desirable that the flower bed is located on some elevation. This is necessary so that melt water in the spring does not flood the rhizomes, otherwise they will rot.
These plants are not very fond of wind and drafts, so try to choose a place that is protected from blowing.
But irises are not too demanding on the soil, although they feel best on neutral and loamy soils.
Transplantation of these flowers is necessary and should be carried out every 5-7 years.
Landing scheme
Before transplanting orcas, you need to prepare the ground for their relocation. To do this, they dig it up, loosen the top layer and enrich it with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. Also, the flower bed can be slightly raised by about 15 centimeters.
Places for planting seedlings should be located at a distance of 30-50 centimeters from each other.
Further landing scheme is as follows:
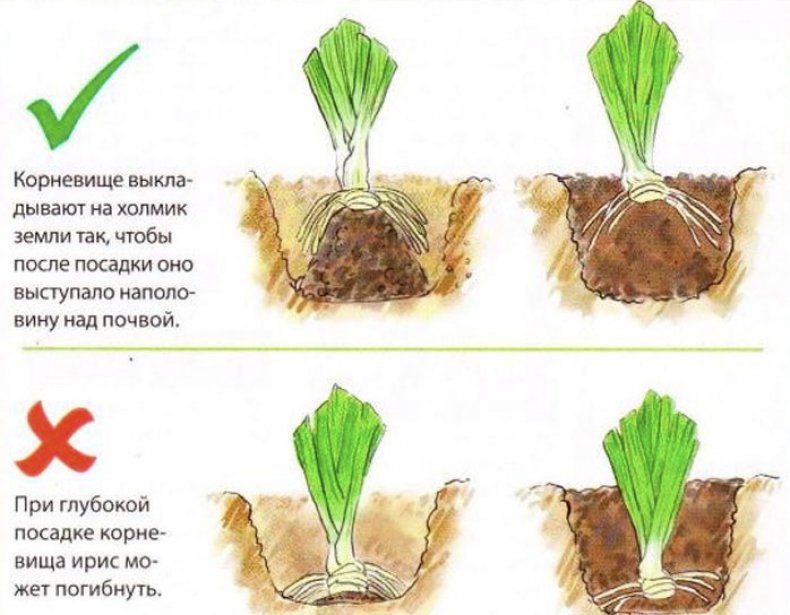
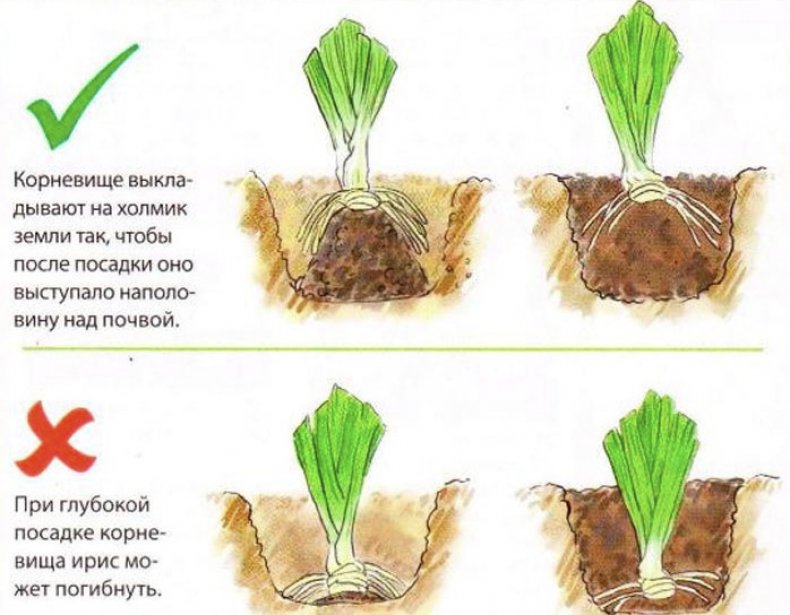
- dig a hole in the ground about 15 centimeters in diameter, and in the middle it should have a slight elevation, and a depression along the perimeter,
- the sprout is placed in the hole so that the rhizomes are flush with the ground, and the leaves are vertical,
- the seedling is immersed in a hole on an elevation, and the roots are laid around in a depression,
- the plant needs to be pressed a little to the ground, covered with soil and lightly tamped so that it holds,
- the planted plant is immediately watered. Re-watering is carried out only 3 or 5 days after planting.