The practice of growing orchids without soil at home
Next, consider the cultivation of orchids without soil: the features of care, how and in what to grow a flower. For example, some growers grow their plants in expanded clay and water. For this:
-
Expanded clay is poured into a closed system and a flower is planted in it;
- Water is poured into the bottom of the container, due to which the roots of the orchid receive nutrients.
IMPORTANT! If the roots have reached the bottom of the container, then the water must be drained completely or the plant must be transplanted into a large container.
Peculiarities
Can orchids grow without soil? A feature of this method can be considered that the roots of the plant need bark only to maintain it in the pot. But in order to transfer a flower to a content completely without earth, it will be necessary to accustom it to a drier content. With this method of growing, plants are fixed in containers using various devices.
What is nutrition in this way?
 Can you grow plants without a substrate? A growing orchid without soil gets its nourishment from the added water during irrigation. In this case, the water must be soft.
Can you grow plants without a substrate? A growing orchid without soil gets its nourishment from the added water during irrigation. In this case, the water must be soft.
Some believe that melt water or rainwater is suitable, but if the grower does not live in the village, then the water collected after the rain, which washed away all the city smog, will simply kill the plant.
Therefore, it is best to spill it with warm boiled water. You can also spray fertilizers on the leaf, but at the same time, the dressing is diluted, increasing the amount of water by 3 times. This is done so that the leaves do not burn.
Advantages and disadvantages
This method has many positive qualities:
- The roots of the flower do not rot from improper watering and improperly selected substrate;
- Transplanting flowers is not required, which means that the roots are not injured;
- It is convenient to feed and monitor the state of the root system;
- While in a glass flask, the roots do not dry out and receive enough light for photosynthesis.
Disadvantages:
-
Sometimes the grower does not feel when to water, and spends it too often. Because of this, the leaves turn yellow and fall;
- Too much sunlight can burn the root mass;
- Cold and draft can quickly destroy the plant.
Air humidity
For good growth and flowering, almost all orchid varieties need to maintain optimal moisture levels at the proper level:
- for phalaenopsis 60-80%;
- for the epidendrum 50-75%;
- for cattleya 60-70%;
- for bulbofillum 40-50%.
Note! Moisture values for intrageneric varieties and hybrids can vary significantly. Therefore, the growing conditions for each specific specimen should be clarified before buying an orchid.
Signs that the plant is not doing well due to extremely dry air:
- the edges of the sheets turn yellow and dry;
- the buds fall off, slightly blossoming;
- long break between flowering phases;
- the elasticity of the leaves decreases;
- the plant is withering away.
Most of the orchid varieties and hybrids grown in home floriculture adapt very well to room conditions and feel fine with a humidity of 40 to 60%. The problem is that in winter, during the heating season, this figure may drop below 20%. There are several ways to increase humidity in a room:
- buy a humidifier or steam generator;
- grow an orchid in a florarium;
- place an aquarium or a small decorative fountain next to the flower;
- constantly irrigate the space near the flower with a spray bottle;
- put wet, clean towels on batteries;
- install the flowerpot in a pallet with wet filler (moss, expanded clay, pebbles).
Orchid substrate components
The substrate can be selected for each specific plant, based on its needs and the climate in which it will grow. The soil can consist of either one pine bark or several components. The most commonly used are bark, sphagnum moss, high peat and fern roots.
Bark
Pine bark is the main substrate for many orchid species. You can either buy it in a store or prepare it yourself, you just need to adhere to a few rules. You can collect bark from the ground, but remove it only from fallen trees. Fresh bark is unusable due to its resinous nature, and removing it from the trunk of a living tree can harm it.
There should be no signs of disease or pests on the bark. It must be boiled before use to remove resin residues and get rid of pathogens.
Pine bark substrates also need acidity adjustment, so dolomite flour is added to them (1-3 g per 1 liter of soil).
Instead of pine, you can use the bark of other conifers: fir, spruce, thuja, juniper, as well as deciduous: oak, willow, etc.
Store the collected material in large pieces, grind only before use.
Moss
Sphagnum moss is usually added to substrates, which is highly hygroscopic and more nutritious for plants than bark. It also acts as a sorbent that absorbs salts harmful to plants. Moss keeps well both dry and frozen.
It is better to collect it in late autumn, after the first frost, when the number of pests decreases. Harvest only the top green part. Store in plastic bags on your balcony, basement, or freezer.
To drive out pests from the moss, soak it in water, then dry it until it is light brown.
Peat
For the preparation of the substrate, it is best to use sphagnum high-moor peat, which has a high moisture capacity, absorbs and retains nutrients well. Another useful property: when fully saturated with water, it can hold up to 40% of the air.
The downside is its acidity. Therefore, a week before preparing the substrate, neutralize it with dolomite flour (7-10 g per 1 kg of peat).
Store-bought peat should have a pH of 5-6.5.
Fern roots
For many years, the roots of the osmunda fern were considered the best substrate for orchids. You can also use other species that grow in our forests. Their plantation can be set up on your site.
In the forest, ferns can be harvested in clearings, clearings and in places intended for involvement in economic circulation. Wash the excavated roots from the ground and dry. For the substrate, both thin roots and thick rhizomes are suitable, which must be cut with a pruner into pieces several centimeters thick.
Such a substrate practically does not cake and retains its properties for a number of years.
Charcoal
Many nutrients useful for orchid nutrition - potassium, calcium, phosphorus and trace elements - are found in charcoal. It is used to neutralize the acidic environment from the bark of coniferous trees and to absorb excess water from the substrate.
Chunks of charcoal that are at least 3 cm in size are best for the substrate.
In addition to these materials, expanded clay, perlite and other leavening agents, coconut fiber and coconut chips are also used in substrates.
Self-cooking

The soil must be disinfected
You can prepare a substrate for an orchid yourself by purchasing separately components, for example, Biomaster kits.
Florists have different recipes.
- 50% pine bark, up to 15-20% polystyrene, up to 15-20% expanded clay, 10% sphagnum, 5% charcoal.
- 95% coniferous bark, 5% charcoal.
- 60% pine bark, 30% sphagnum, 10% charcoal.
During cooking:
- moss and fern rhizomes are poured in water for a day, then dried thoroughly, when soaking, some growers add fertilizers that sphagnum will absorb and, when watering, after planting, will give to the plant;
- the tree bark is crushed into chips of the desired fraction and sterilized in a steam bath for 0.5 hours, completely dried;
- coal and peat are not crushed in fragments up to 2 cm long.
Pre-planting processing
If the majority of ready-made substrates undergo preliminary disinfection treatment against pathogenic microorganisms and pests, then the soil prepared with your own hands must be processed before filling and planting an indoor flower in it.
The components used for its preparation may contain pathogens of infectious diseases (often fungi), and if the rules for storing natural materials are not followed, harmful insects often start.
You can disinfect individual ingredients or a ready-made soil mixture in several thermal ways:
- boiling;
- pouring boiling water;
- oven firing.
After thermal disinfection, the mixture is soaked in cold water and completely dried in natural conditions, spreading in a thin layer and placing in a well-ventilated place. When it dries, you can plant an orchid in it.
Florists often choose furacilin or potassium permanganate as disinfectants.
What are they?
"Garden of Miracles"

Ready-made substrate, suitable for most orchids. It is distinguished by:
- moisture capacity and air permeability;
- macro- and microelements for the growth and development of orchids;
- sterility;
- absence of pathogenic microorganisms.
If you prepare the substrate yourself, then the "Garden of Miracles" is great as a base. The composition is supplemented with long fibers of high-moor peat screening of coarse fractions, which helps to better retain moisture.
"Flower happiness"
Suitable for most orchids. The composition provides good aeration and moisture absorption:
- larch bark;
- charcoal;
- expanded clay.
The ratio of the components contributes to the lush flowering, development and growth of the plant.
"Fasco"

The difference between Fasco and Flower Happiness is in the presence of high-moor peat. It is great not only for phalaenopsis, but also for other varieties - dendrobium, cattleya, etc.
"Peter Peat"

It is a nutritious substrate for most orchids. The composition includes:
- pine bark;
- limestone flour;
- peat of two types - lowland and high-moor;
- complex fertilizer.
This composition allows the orchid to breathe freely, accumulate and receive moisture in a timely manner. When transplanting, the soil provides quick survival, rapid growth and plant health.
"Pokon"

"Pokon" has a completely natural composition, which is guaranteed by the Dutch manufacturer and the RHP standard:
- tree bark;
- limestone;
- complex fertilizer.
The mixture well maintains the balance of moisture and oxygen and, as a result, the health of the flower. The ratio of the components will provide the plant with everything it needs for two months after transplanting.
"Veltorf"

It is recommended to be used for transshipment and transplantation of plants, as well as in the form of mulch or top dressing. The mixture contains peat, pine bark, lime material and complex fertilizer. The presence of all components ensures the health of flowers - their growth, development and flowering.
"Ambulance"

Any orchid in this substrate will feel great. High moor peat and pine bark are added to its composition. The manufacturer guarantees:
- excellent survival rate after transplantation;
- improvement of decorativeness;
- reducing the negative impact of the use of fertilizers;
- excellent microclimate inside the tank;
- increased immunity and resistance to disease;
- suppression of pathogenic microflora.
"Compo sana"

Compo sana nutritional mixture from Germany contains:
- horse milled peat;
- bark;
- limestone;
- nutritional supplements.
Video review of Compo sana orchid soil:
Effect +

In its composition it has the bark of the Angara pine and often serves as the basis for the independent creation of substrates.
EffectBio

It contains environmentally friendly components:
- the bark of the Angara pine - the base;
- sphagnum moss;
- vermicompost is an organic fertilizer.
The substrate is equally effective for growing and propagating orchids. It does not need to be sterilized, the manufacturer has taken care of the composition.
Royal Mix
The composition, in optimal proportions, contains components that provide the necessary air flow to the root part. This includes:
- bark of coniferous trees, heat treated and calibrated;
- coconut fiber and chips;
- charcoal;
- high-moor peat;
- salt supplement;
- mineral compounds;
- trace elements.
The presence of such components will not allow the accumulation of excess moisture, create a thermal layer, thereby providing protection from excess heat and cold.
Ceramis

A feature of the soil is its composition - these are small hollow lumps of clay. They absorb moisture and gradually share it with the flower. They also create good air circulation to keep the root system healthy.
Video review of Seramis orchid soil:
Ceoflora

Consists of light, porous, large-sized granules of fired zeolite 5-9 mm in size. They perfectly absorb moisture and stabilize air circulation in the root system. It is used as an independent soil or as an additive to the traditional composition. It does not contain traces of harmful insects, pathogenic microorganisms, because heat treated.
Over time, it does not compact, thereby maintaining a stable even pressure on the roots. It is suitable for growing orchids in closed systems.
What types of Orchids can be grown without soil?
Only those types of orchids that are considered epiphytic can be grown without soil. Because they have such a content due to nature itself. Therefore, without soil, you can grow varieties:
- Phalaenopsis;
- Dendrobium;
- Cattleya (some of its types).
Actually, if you wish, you can try and decide to grow other types of plants, it already depends on the desire and capabilities of the grower.
Suspended
Such plants are grown on blocks or baskets if they are large enough to be grown on a block. When choosing a material for a block, one must take such that it does not decompose and, at the same time, is a natural piece of wood.
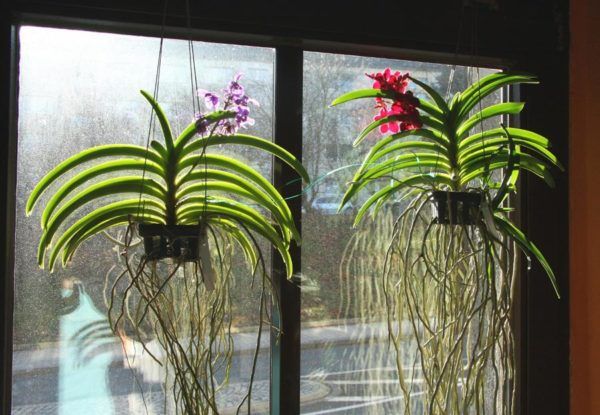

Suspended orchids without soil require constant moisture.
When growing in this way, you must carefully monitor the humidity of the air. It should not fall below 60%.
Basic rules for harvesting
The most important rule is to prepare the ingredients in advance. It is also recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Moss is dried in partial shade, after which they are put in separate bags and stored in a dark, dry place. If the moss is wet, it is placed in the freezer, also packed in separate bags.
- The coals from the fire are collected, crushed into pieces of 3-4 cm. The ash is placed in a bag and stored in a cool place.
- The bark should be dry, but not decayed. With the help of a secateurs, the bark is crushed into pieces of 3-4 cm.
- Fern roots are advised to be stored in a hermetically sealed package.
- Do not forget that all the components collected by the florist on their own are disinfected. Large components are poured with boiling water for half an hour, and then placed in cool water. And small and loose ones are pierced in an oven at a temperature of 220-230 degrees for 5-7 minutes.
Soil acidity
The acidity of the soil affects not so much the plant itself, but the ability to dissolve compounds in the substrate, the decomposition products of which are used by the plant for nutrition. The success of the cultivation of certain plants is determined by which substances better acquire an accessible form in a given soil.
The plant may simply not receive the substances they need, simply because the soil cannot give them them.
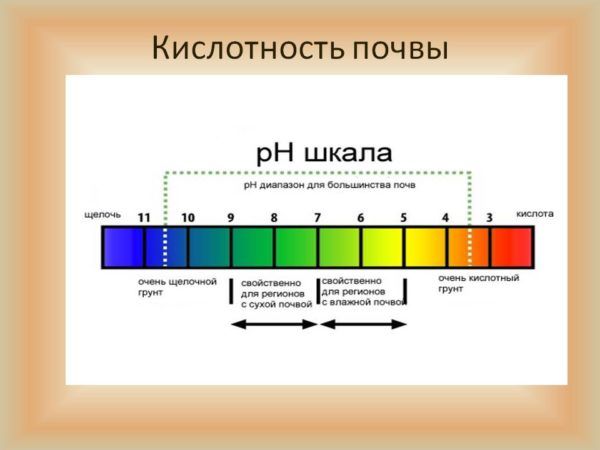
For orchids, soil acidity is used in the pH range from 6 to 8.
For most orchids, a neutral soil reaction is suitable, in the pH range from 6 to 8. However, the genus of orchids is extensive, and there is room for calcephiles, which can grow on steep cliffs above the sea and prefer more alkaline soils.
Advice! Each orchid should be approached individually, taking into account species characteristics and preferences.
The substrate can be checked for acidity using chemical reagents or a special pH meter, but these are quite expensive devices and their purchase is impractical for a small farm. The easiest way is to douse the soil sample with vinegar:
- If the soil does not hiss, then the environment is acidic or slightly acidic;
- Hissing and release of carbon dioxide will begin in an alkaline environment.
What kind of soil to choose in the store? Here the choice is wide - any manufacturer's primer marked "For orchids" will do. On some soils, it is even indicated for which types of orchids this soil will be best suited.
What are the requirements for the substrate
What soil is needed for an orchid is determined depending on the type of flower and the conditions for its maintenance, in particular, on humidity. The drier the indoor air, the more moisture-absorbing the potting soil should be.
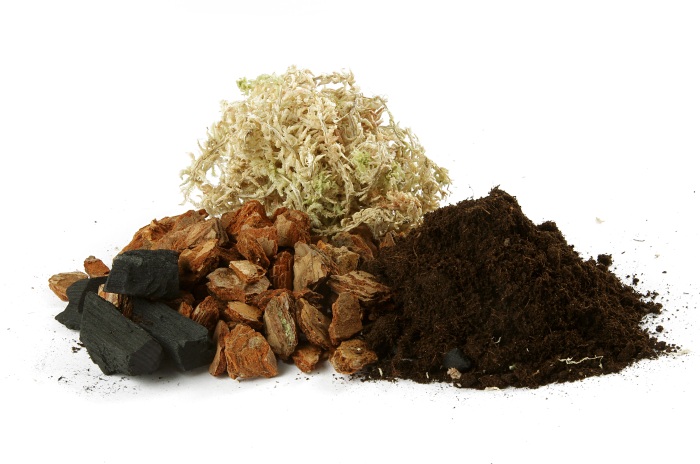

Orchid substrate
Orchid soil must meet the following requirements:
- Sterility. The soil should be free of pathogenic flora and fauna. The less even useful microflora in the substrate, the better for orchids. In living nature, they grow on tree trunks, where practically no such microcosm is formed as in the soil.
- Unchanging structure. The soil should not rot and decompose, this can be fatal to the flower.
- Slightly acidic composition. The most optimal pH level is 5.5-6.0. For some species, it can reach 6.5 pH, but no more. The acidity of the soil is determined using a litmus test. To do this, put a little substrate in a clean vessel and fill it with distilled water. Litmus paper is dipped there for 30 seconds. Depending on the acidity, it will change color. There are also special meters for soil acidity, they are sold in garden supply stores.
- The ability to retain moisture when the air is dry.
- Lightness and friability, the ability to provide easy air access to the roots of the epiphyte.
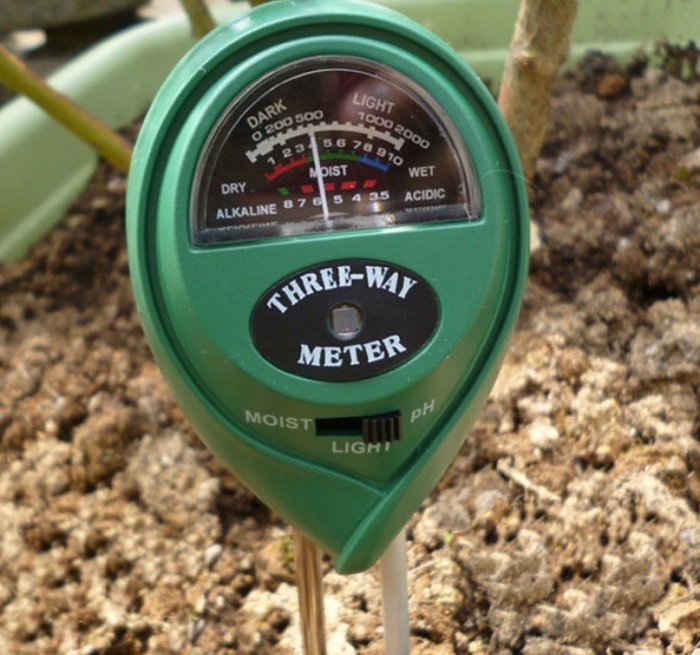

Soil acidity meter
Note! The composition of the soil for an orchid should not contain any toxic elements, it should be safe and environmentally friendly
Can ordinary land be used
This question cannot be answered unequivocally. There are many orchids, and among them there are not only epiphytes growing on trees, but also lithophytes living on bare rocks. Lithophytes include some species of papiopedilum ("Venus shoes"), familiar to all phalaenopsis and lush dendrobiums. All of them can grow as epiphytes.
There are also terrestrial orchid species. These are calante, bletilla, cymbidium, some of the papiopedilum and playone. You can also plant Makodes, Gemaria, Gudaira, Anectochilus in a pot of soil.

Cymbidium
Important! Untreated black soil from a garden plot as a soil for an orchid will not work. Before use, it will have to be sterilized and a number of components added to lighten the structure, since the substrate cannot consist only of earth
The soil
When determining what kind of land is needed for orchids, it is worth remembering that the substrate must be such that the roots of the plant can develop normally and properly anchor in the pot. Traditionally, the composition of the soil for orchids contains a certain amount of ingredients, not only natural, but also of artificial origin. They are selected and mixed so that rotting of the root system is not allowed, the flow of air and light is not limited. The acidity of the soil for an indoor flower should be medium, pH5.5-6.5.
Orchiat, which consists of the bark of New Zealand pine, is considered one of the best commercially available compositions. Many flower growers advise to plant young plants in such a composition, which can quickly become roots for the elements of the substrate. Orchiat retains all beneficial nutrients and microorganisms in its composition.
Note! This porous potting soil is excellent at absorbing, retaining and releasing moisture.
Overview of the substrate on the market
The planting soil market offers not only natural substrates for orchids, but also artificial options, which include mineral fibers and synthetic fillers. But, as a rule, flower growers prefer high-quality natural mixtures, which are not only more affordable, but also environmentally friendly, which is especially important when growing flowers indoors.
Quite high requirements are imposed on such soils. Among them, in the first place is the ability to slow decay, which can trigger a process that is detrimental to the pet's condition.
Novice orchid growers in flower shops can choose ready-made soil such as Flower Happiness, Morris Green, Effect, LandshaftaNET and others.
The table compares the most popular potting mixes for orchids: composition and average cost per liter:
| Substrate name | Manufacturer | Composition | Price per liter |
| Effect | NPO Biotechnology | Pine bark, sphagnum moss | 50,00 |
| EffectBio | NPO BioTechnology | Angarsk pine bark, dolomite | 75,00 |
| LandshaftaNET | LandshaftaNet | Pine bark, sphagnum moss, peat, charcoal, biohumus | 45,00 |
| Orchid | PA "Gardens of Auriki" | Peat, moss, pine bark, charcoal, trace elements | 65,00 |
| Seramis | SERAMIS | Clay granulate seramis, pine bark, trace elements | 250,00 |
| Orchid | Llama peat | Wood bark, peat, agroperlite, fertilizer | 30,00 |
| Flower happiness | Fasco | Larch bark, coal, peat, expanded clay | 35,00 |
| Morrisgreen | "Pelgorskoe-M" | Peat, mineral fertilizer, limestone flour | 20,00 |
| For ORCHID | WELLpeat | Peat, pine bark, limestone, mineral fertilizer | 15,00 |
DIY cooking
All the required components are easy to buy or collect in the forest. When collecting, you must follow some rules:

- Only remove the bark from a dead tree. Check the absence of resin, pests, rot on it. Peel it and cut into small pieces 1x1 cm and larger pieces 2x3 cm. For disinfection, the bark is treated in a water bath or frozen in a freezer. After all the manipulations, it must be dried.
- Moss grows in swampy lowlands of rivers and lakes. The collected moss must be cleaned of fine debris, dried and cut into strips of 10 cm.
- The coal must be clean. The ideal option is to burn birch firewood on your own without adding ignition fluid.
The prepared components are mixed in those proportions that are necessary for a particular type of orchid. Video about the features of making soil for phalaenopsis with your own hands:
Components for different types of flower
Each orchid has an individual need for a certain soil. After all, some grow epiphytes, others settle in the ground.
Phalaenopsis
This orchid requires an excellent aeration soil that is completely devoid of nitrogenous additives. Required components:
- pine bark;
- moss;
- charcoal;
- fern root;
- peat.
The composition prepared in advance before transplantation cannot be pre-mixed.
Dendrobium

Dendrobium requires nutrient-rich soil.
- 3 parts pine bark;
- 1 part charcoal;
- 1 part moss;
- 1 part coconut chips
Wanda
For the health and lush flowering of Wanda, an increased nutritional value of the substrate is required. The composition for Dendrobium is taken as a basis and components are included in it in the following ratio:
- 1 part sand;
- 1 part perlite;
- 1 part peat.
The bark is used in fine fractions.
Cattleya
Cattleya is unpretentious and does not need a rich soil composition and therefore grows well in clean bark.But for a variety of the nutrient medium of the plant, a little moss and coal are added to the substrate. No more than 2-3 pieces.
Miltonia
For Miltonia, harmony in the substrate is mixing the components in equal proportions. The composition includes:
- peat crumb;
- bark of fine fraction;
- sphagnum moss;
- charcoal.
All about soils for orchids
Specialized stores sell substrates for flower cultivation. It should be noted that they are completely ready for use. They contain in the required proportions:
- bark;
- charcoal;
- sphagnum moss;
- coconut fiber.
Photo of the main components of the substrate for orchids.
Common ready-made primers - Flower Happiness, Orchid, Effect soil mixture and many others.
You can find a detailed description of ready-made primers and reviews about them here.
Coconut
It is a natural organic component of brown color and is added to the soil to increase its breathability. At the same time, it is a wonderful moisture regulator that does not cake after prolonged use. It is often used when planting a plant on a block.
You can learn more about coconut soil here.
With your own hands
You can make up a good soil from the components yourself, but then it should be disinfected in any way convenient for the grower. It can be calcined in an oven at 200 degrees Celsius for 20 minutes. Or it is preferable to freeze it in the freezer of the refrigerator for 24 hours.
IMPORTANT! Disinfection is an important step and should not be skipped.
Bark
To grow a flower, the presence of bark is necessary in the soil. It is most often pine, but sometimes it is also oak.
At the same time, before using both barks, they require mandatory heat treatment, where in the first case they get rid of the resin, and in the second case they get rid of tannins.
The main property of the bark is the uniform access of oxygen to the root system of the plant, plus an even distribution of water during irrigation.
Read more about the substrate bark here.
Seramis
This substrate, which appeared quite recently, immediately gained a positive reputation for itself. The soil consists of bark and granules made of clay (70%), the rest (30%) are the necessary components containing Nitrogen, Potassium and Phosphorus.
The soil has:
- breathability;
- regulates the delivery of water to the root system of the plant;
- loose.
A feature of planting in this substrate is that the roots can not be completely cleaned of old soil and Seramis can be used endlessly, just adding the amount of granules needed when transplanting into a larger pot.
Seramis substrate.
Hydrogel
Experienced flower growers do not recommend planting orchid plants in a hydrogel. Because the root system will not live long in this semblance of soil, especially in the cold season: the root system comes into contact with the hydrogel and begins to rot.
IMPORTANT! Experienced growers consider the use of a hydrogel in growing orchids a waste of money, since it not only does not improve the quality of the roots, but can lead to their death due to waterlogging.
You can read more about the content of orchids in a hydrogel here.
Soil
Orchid soil is sold in stores, it is completely ready to use.
It is usually suitable for all types of orchids and consists of:
- bark;
- charcoal;
- sphagnum moss;
- peat;
- pine needles.
Before use, it is soaked for a couple of hours in hot water so that the bark is well wet.
There are a lot of soils, since they are produced by many different manufacturing companies, and it is worth choosing the mixture where the bark is cut into fractions of 1x1 cm.
How often to change?
The soil for the plant is changed in the case of:
- The planned spring transplant due to an increase in the overgrown root system - about once every 2 years;
- After purchasing a flower - one-time after purchase;
- In case of illness - as needed.
IMPORTANT! When starting to transplant an exotic flower, it is necessary to carry it out, adhering to the basic rules.
What is the price?
The rise in prices for substrates depends on the manufacturer and the weight of the bag itself. The soil can be hung in packages from 500 gr. up to 7 kg. Therefore, the price can vary from 32 rubles. up to 150 rubles. At the same time, products brought from abroad will cost more than domestic products, but this does not mean that they are better in quality than those produced in Russia.
How to cook it yourself?
If you are not sure about the quality of the ready-made orchid mixture, it will be better to prepare it yourself. This method has its positive aspects:
- ease of preparation;
- low cost;
- quality assurance;
- selection of components according to the variety of orchids.
There are many recipes for preparing a substrate for exotic flowers. It will not be difficult to complete them, even for an inexperienced florist. The main thing in the process is to observe the specified proportions of the ingredients.
The main components of the substrate:
- Pine bark, you can use the bark of any trees. Grind to a size of 2-3 cm.
- Moss-sphagnum, grows in forests, lowlands. Used fresh and dry.
- Wood ash, about the same size as bark.
- Fern roots are used exclusively in dry form.
- Expanded clay granules are excellent as drainage.
Various variations of mixtures may contain additional components: sand of coarse fractions, pieces of foam, cork material, sod or deciduous soil, gravel, perlite, vermiculite, walnut shells, humus, coconut fiber and others.
We offer you to watch a video about preparing a substrate for orchids:


