Reproduction methods
It is possible to breed paniculate hydrangea using the following methods.
By cuttings
To do this, cuttings are cut during the period of bud swelling. Each instance includes two internodes, the lower cut is made at an angle of 45 degrees, and the upper one is straight. For planting, a mixture of sand and peat is suitable, cuttings are planted into the finished substrate, deepening by 3-4 cm, the container is removed to a warm, lighted place. Some gardeners create a greenhouse effect by covering the container with plastic.
Further care consists of watering and airing. When the cuttings are rooted, they can be planted in the area. Usually, transplantation to a permanent place is carried out 1-2 months after rooting. In winter, these plants require additional shelter.
Air layering
The simplest and most common breeding method
Choose the sturdiest and strongest shoot, gently bend it to the ground and lightly dig in. To secure the layering, you can use staples, stone or brick.
The planting site needs regular watering, but top dressing is not needed. After a year, a new copy can be separated from the parent and planted in a permanent place.


Seeds
The most difficult and time-consuming method, which, moreover, gives little guarantee that the seedling will be promising. In addition, new shoots can make a significant difference compared to the parent bush. Sowing is carried out in the fall. A mixture of peat, leafy earth and sand is suitable as a substrate. Planting is done in a shallow pot. It is not necessary to deeply deepen the planting material, since the seedlings are small in size and may not germinate - you can even just sprinkle the seeds over a moistened surface and lightly tamp them. Next, the seedlings should be covered with foil and removed daily to ventilate the plants and water. Favorable temperature above the surface is +20 degrees. The first shoots can be observed after 1-1.5 months - on this day, the film is removed and re-installed only in the evening.
Seedlings are dived twice and replanted. For the winter, it is better to put them in a room or a greenhouse, where the temperature is kept at 20-25 degrees. At this time, the plants need watering, sometimes they need to be fertilized with nitrogen. Only 1.5-2.5 years after sowing, the seedlings will be ready for transplanting into open ground.


In the next video you will find a presentation of the hydrangea "Samara Lydia".
Landscape use
Hydrangea paniculata looks good both as a tapeworm and planted in groups so as to advantageously present its flowering. White and pink tones of inflorescences stand out brightly against the background of purple-leaved woody forms, gently combined with white-variegated plants.
If the lower part of the bush is bare, you can organize a hydrangea composition by planting species such as oakleaf and serrated hydrangeas in the foreground. These are thermophilic species that need winter shelter.
Oak-leaved hydrangea (Hydrangea quercifolia) - up to 2 m tall, blooms earlier than panicle hydrangea, in June-July, with inflorescences similar to it, but more rare. In the suburbs, it blooms only in warm summer, very modestly. But it has very decorative lobed leaves, similar to oak, which turn purple in autumn. Their color will create a successful combination with the color of panicle hydrangea inflorescences. This ensemble will remind of natural communities where panicle hydrangea often grows in oak forests.
Hydrangea serrata (Hydrangea serrata) blooms almost simultaneously with paniculate hydrangea. Her inflorescences are different - corymbose, consisting mainly of bisexual flowers, surrounded by a few large sterile ones. The color of the inflorescences is white or blue.
English landscape designers recommend planting a panicle anemone to the hydrangea. The spring decorative effect will be given by the anemone oak, mountain weevils, hellebores, autumn - the compatriot of our heroine the Japanese anemone or her hybrids, as well as blooming at the same time astilbe.

Photo: Maxim Minin, Rita Brilliantova, Galina Vlasenok, Lada Anoshina
Description
Hydrangea is a plant from the hydrangea family of the same name. In the genus of culture, there are about a hundred species and even more varieties. These plants in their natural environment and in gardens are represented by small trees, shrubs and vines. Most of the species of the genus Hydrangea are found in the wild in North America and the Far East, however, the perennial culture is widespread throughout the world.
The beautiful plant got its name from the princess of the Holy Roman Empire. Later, botanists gave the scientific name Hydrangea, translated from Latin meaning "a vessel with water". A similar analogy of the botanical name is due to the high moisture-loving nature of the ornamental culture. In Asian countries, you can find another unofficial name for hydrangea - "adzisai", which means "purple sun".
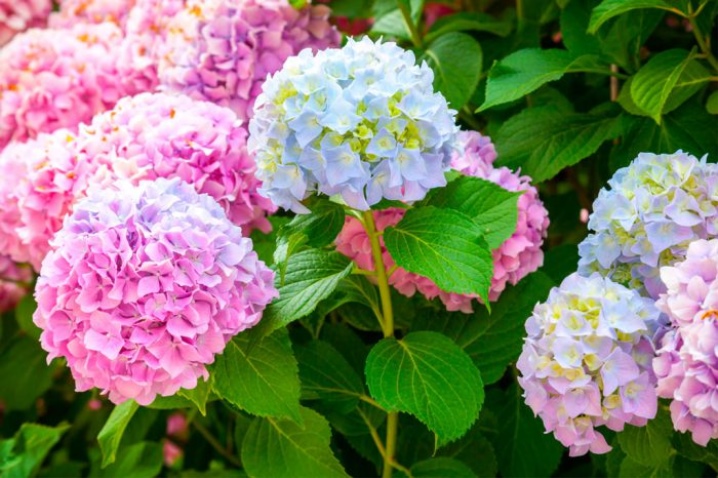

In its natural environment, hydrangea can grow up to 3-meter marks, resembling a compact and spreading tree. And also in the wild, liana-like varieties grow that stretch up the trunks of other tall crops growing nearby, such hydrangeas can grow up to 30 meters. Today, hydrangea is represented by evergreen and deciduous species, the latter are more in demand in latitudes with a mild climate.
As for the appearance, the flower has opposite large leaves, which in most cases are oval in shape with a pointed top edge. Along the edge of the leaves, they have small denticles, in addition, veins are visualized on them.
The culture enters the flowering phase in the spring, continuing to delight the eye of gardeners with inflorescences of various colors until the arrival of the first frost. Hydrangea inflorescences can be in the form of a ball or shield, paniculate varieties are found, combined into a separate species. The inflorescences have 2 types of flowers. The first group includes fertile specimens, the second group is represented by sterile flowers, which are usually located at the edges. However, there are varieties of this culture that will have exceptionally fertile flowers.
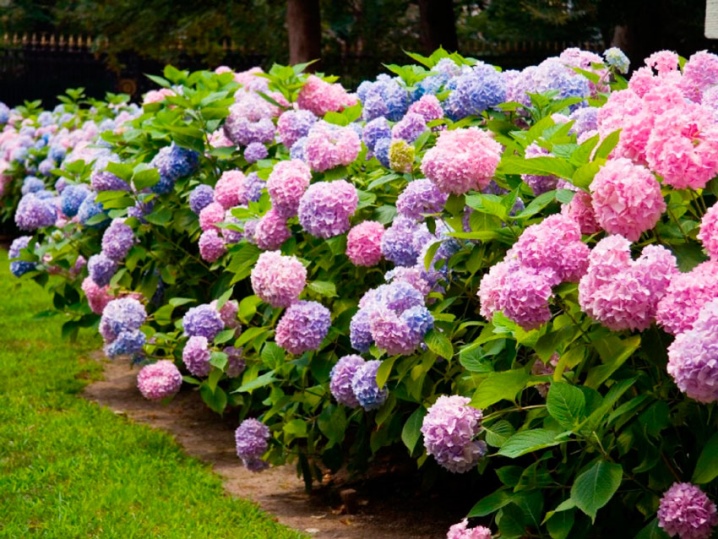

As for the color, a wide color palette of plants is provided for gardeners that can be grown at home and in the garden. Among the most popular are lilac, white, pink, red, crimson and burgundy variations.
Hydrangea is a fruiting crop. In this case, the fruit is a box with chambers located inside, there can be from 2 to 5. Small seeds ripen inside each of them.

Follow-up care
"Polar Bear" is a very beautiful, but demanding plant to care for. Consider the mandatory rules that the gardener will have to follow.
Watering
Polar bear is incredibly fond of moisture and, with a lack of it, quickly begins to fade. Therefore, watering should be systematic. If the summer is hot, you need to supply water at least three times a week, 15 liters will be enough. In cool seasons, the plant needs watering once every one and a half weeks, the amount of water is the same. But when the summer is rainy, watered according to the situation, it is quite possible that 5 times per season will be enough.
Every third watering, many gardeners use potassium permanganate, adding about 2 g per bucket of water. This simple remedy will be an excellent prevention of fungal diseases. Water is poured into the trunk circle, avoiding contact with leaves and stems. The liquid is served early in the morning or in the evening, only warm, settled water is used.

Top dressing
In the first two years, you do not need to give any additional fertilizing, the hydrangea is quite enough of those substances that it receives from the soil. Everything changes with the beginning of the first flowering. Here, top dressing becomes a mandatory step in crop care. Panicle hydrangea is an unusual plant, and this is manifested in the fact that the saturation of the color of the petals is directly proportional to the acidity of the soil. The most beautiful and brightest flowers grow on acidic soil. That is why, before flowering, gardeners use acidifying drugs. After flowering, potassium and phosphorus are preferred.
The very first fertilizer feed takes place in May. To do this, choose complex preparations that will help the plant recover after the winter months. The fertilizer is dissolved in water, following the instructions. As a rule, there are two such dressings, the second follows 14 days after the first. In addition, it is possible to accompany complex fertilization with organic matter, it will not harm the plant.


In early June, it is important not to miss the time of acidic dressings, which will help the hydrangea bloom more beautifully and more magnificently. The fertilizer is prepared as follows: 45 grams of potassium sulfate and 70 grams of superphosphate are dissolved in one and a half buckets of water
Also, such feeding is carried out in July, thanks to it, next year it is possible to achieve excellent flowering. In mid or late October, panicle hydrangea is fertilized for the last time. This top dressing is designed to facilitate wintering. For her, they take fertilizers for hydrangeas.
What can not be used in dressing:
- chalk;
- ash;
- dolomite flour.
All these substances do not contribute to soil oxidation, in addition, they are harmful to hydrangeas.


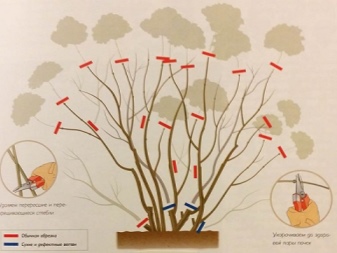
Pruning
There are two types of pruning hydrangea paniculata: thinning and rejuvenating. The first type is used so that the culture does not grow too much. Such pruning will be needed in the fourth year, it is done in March and just before the onset of frost. In March, all frozen and weakened branches are removed. Shoots are cut by 2/3. As for the autumn pruning, it is needed to prevent the shoots from breaking off under the weight of the snow. At the same time, brown inflorescences and shoots are removed, which are most knocked out of the general range of the bush. If you do not carry out thinning pruning, then over the years this will lead to shredding of flowers, thickening of bushes and various diseases.
Rejuvenating pruning is done only in the spring. This type of pruning is necessary for old plants, which are cut so that only a stump remains. In a year or two, such a plant will acquire new, succulent shoots.

Description and characteristics
Japan is considered the native country of the shrub, although the plant has long been found in the regions of China and Sakhalin, hence its frost-resistant abilities. Hydrangea Tardiva is one of the paniculate varieties, notable for the peculiar shape of the flowers and their sweet honey smell. The plant is a rounded shrub with an average height of 2 m, although with proper care and good conditions it is quite capable of reaching 3 m. The shoots are rather large in size, their texture quickly becomes woody. This feature of the stems serves as their protection from the cold.
The flowers are narrowed, conical and white-pink in color. At the very beginning of flowering, the formed small buds with stamens acquire a creamy hue, but as they grow, they become a delicate pale pink color. The flowering shrub is distinguished by its density. Paniculate inflorescences begin to form at the ends of the shoots around the third year of the plant's life, their length can vary from 40 to 55 cm. The buds appear in August-September and bloom until November.
The bush grows quite quickly and can significantly increase in size in one season. The shrub, despite its demanding care, is quite amenable to cultivation on the territory of Russia, even in areas with a difficult climate.But due to its late flowering, it is still worth growing in regions with a warm climate in order to fully enjoy the beauty of flowering. The characteristic features of the Tardiva hydrangea include:
- rather high resistance to diseases of the root system;
- winter hardiness;
- fast renewal of damaged parts;
- the possibility of growing in the same place for quite a long time;
- long flowering period.


