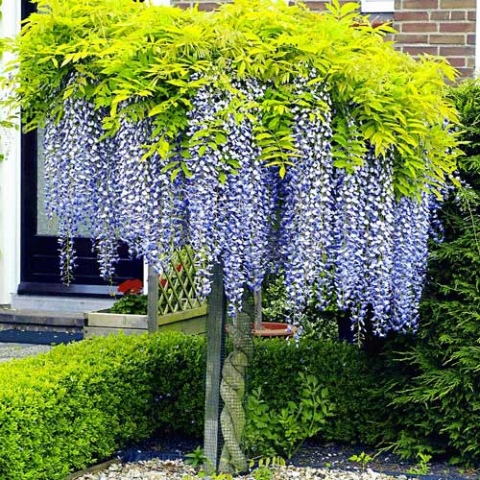
How to take care at home?
Wisteria loves heat very much, so it can only be grown in warm regions.
The flower is planted in tubs and exposed to fresh air, and in the cold season it is brought into a warm room.
Temperature
In summer, the temperature is 20-30 ° C, in winter the plant is indoors at a temperature of 5-10 ° C. There are frost-resistant varieties that can withstand up to -20 ° C. At the onset of the first frost, wisteria is prepared for wintering.
Watering
The plant loves moderate watering. A large amount of water will lead to loss of leaves and buds. If the spring is dry, the flower is watered abundantly.
From the beginning of flowering to the end of summer, the soil is kept moist. In the last days of September, watering becomes scarce. In the cold season, watered once a week.
Light
For abundant flowering, bright light is needed. Wisteria should receive 3-4 hours of sunbathing daily, morning and evening.
Important! In the warm season, in spring and summer, on a particularly hot day, the plant needs to provide shade.
Soil composition
Wisteria should be planted in a moist and light substrate that is moderately fertile. The soil must be breathable and not retain water. It is best to prepare the soil yourself by mixing peat, sand and humus with turf soil, in a ratio of 1: 1: 1: 3. This mixture will help the plant to take root and grow vigorously.
Pruning
This procedure is necessary to stimulate flowering and branch formation. It is carried out at different stages of development.
First time
- One strong shoot is chosen, the rest are removed.
- Upon reaching the required height, the shoot is cut to a strong bud, by about a third. The stem should be thick enough at the cut.
- Then the shoot is tied to the pole in an upright position. Garters should not injure the plant.
- All side shoots must be cut off.
In the summer after 1 year
- Shorten the strong shoot again.
- Side branches at a height of less than 30 cm are removed.
- The middle ones are shortened by a third, and the upper ones are left unchanged.
- The garters are then checked and, if necessary, made weaker.
Top dressing
They are fed once a week during the period of active maturation. Top dressing contains phosphorus and potassium. Organic dressings are added alternately with liquid minerals.
Reference! Organic fertilizers include chicken manure, egg shells, manure, or wood ash.
Pot
At home, wisteria is best planted in a clay pot. The container is disinfected before planting. When transplanting, the pot is selected larger and deeper than the previous one.
Transfer
Once a year in the middle of summer, a young plant is transplanted, an adult plant - once every 3 years. To do this, you need a pot larger than the previous one.
Before transplanting, the pots must be washed and scalded with boiling water.
- Close the holes at the bottom of the pot and lay out a layer of expanded clay.
- Pour in previously prepared or purchased soil.
- Carefully remove the wisteria from the old pot, separate the excess soil and place in a new pot.
- After transplanting, water and place in a dark room.
- After a while, return the vine to its original place and maintain the conditions in which it grew.
Wintering
- Dry shoots are cut, flower brushes are removed.
- The plant is untied from the support and the vine is placed around the trunk.
- The top is covered with agrofiber, a bag or thick paper.
- Young shoots can be additionally insulated by sprinkling them with needles, leaves or mulch.
It is undesirable to use the film, it can cause rotting.
Description of wisteria
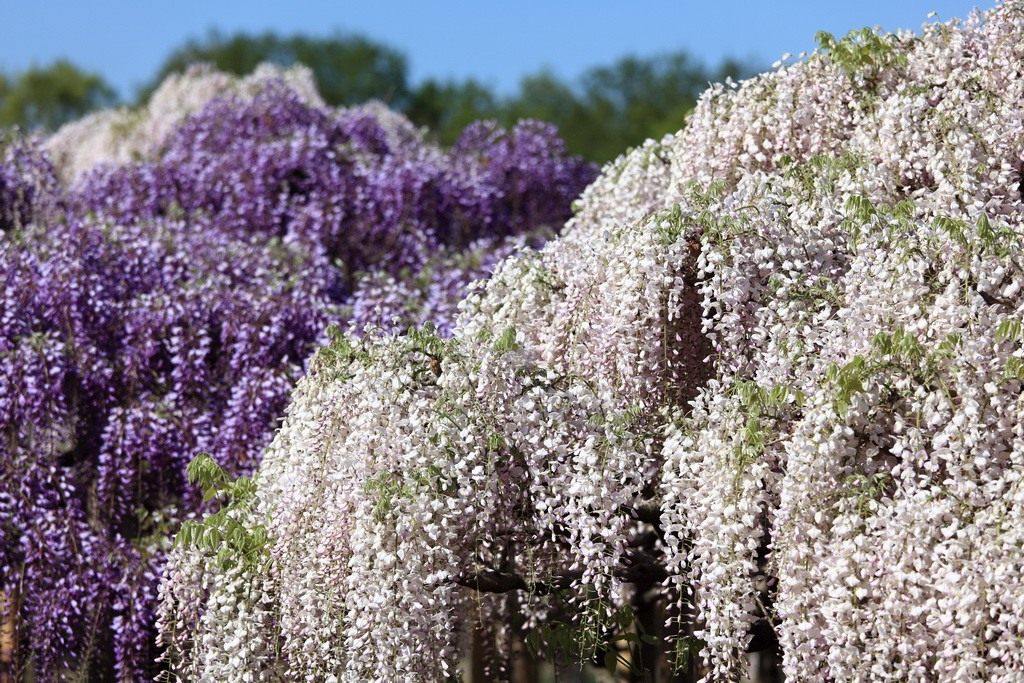
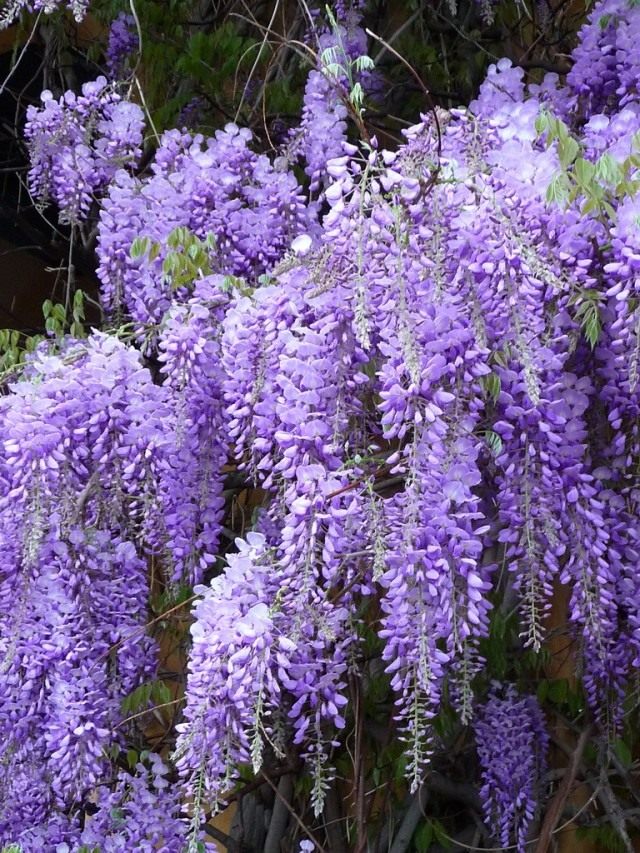
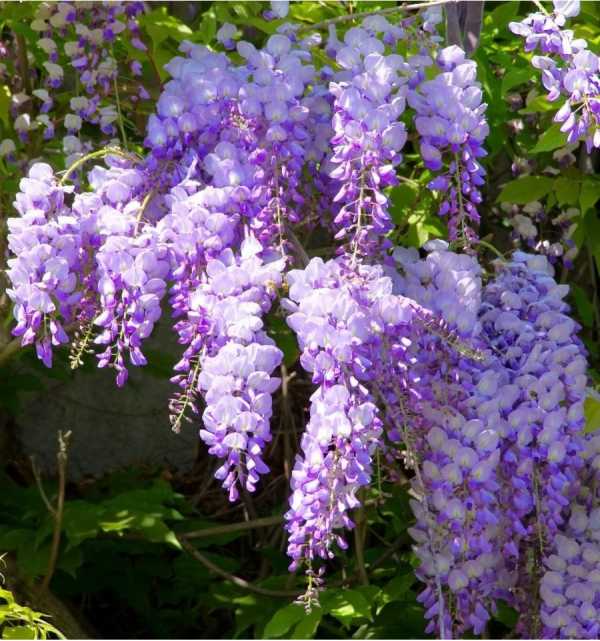
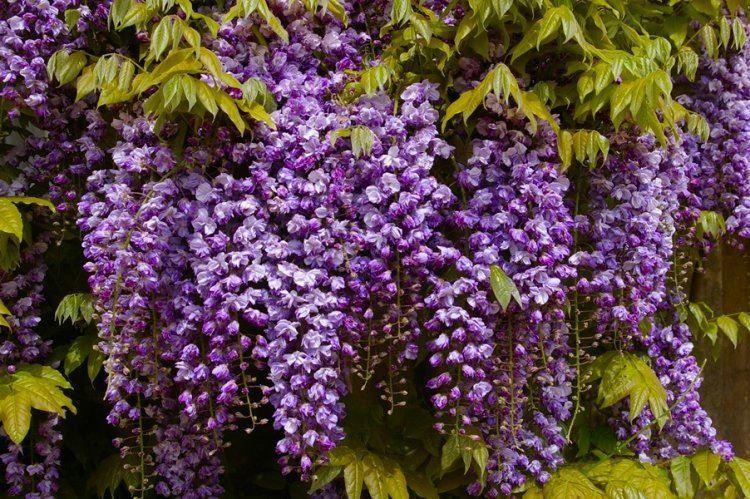
Wisteria (from the Greek γλυκός - sweet), or wisteria (lat.Wisteria) is a genus of tall, treelike climbing subtropical plants from the Legume family with large, pinnate leaves, pubescent in youth, later naked, spectacular light purple, less often white, flowers, in hanging, loose racemes up to 30 cm long.Flowering in spring , retains individual flowering clusters throughout the summer. It is widely used in landscape design.
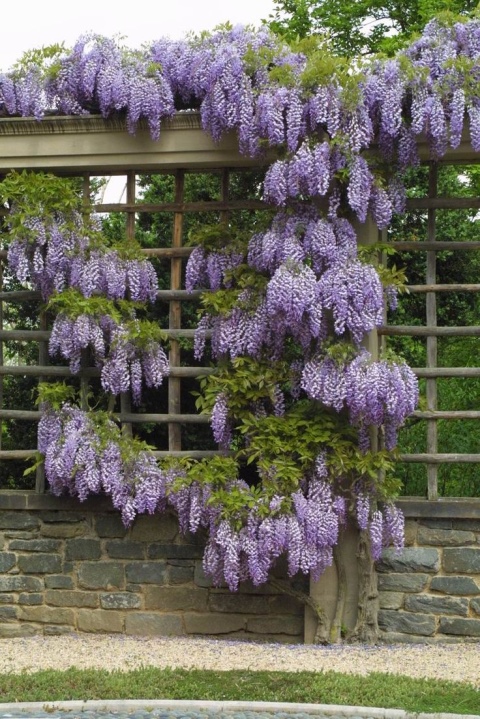
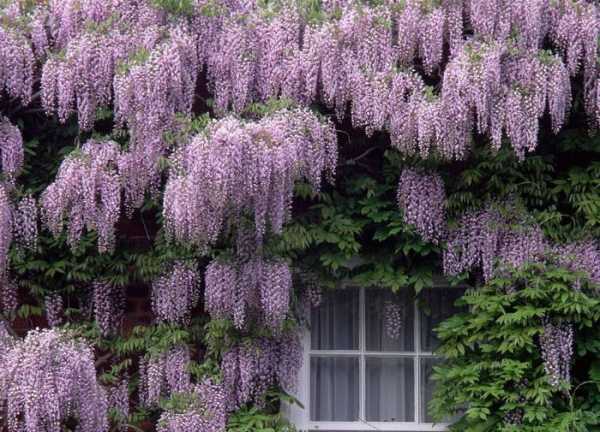
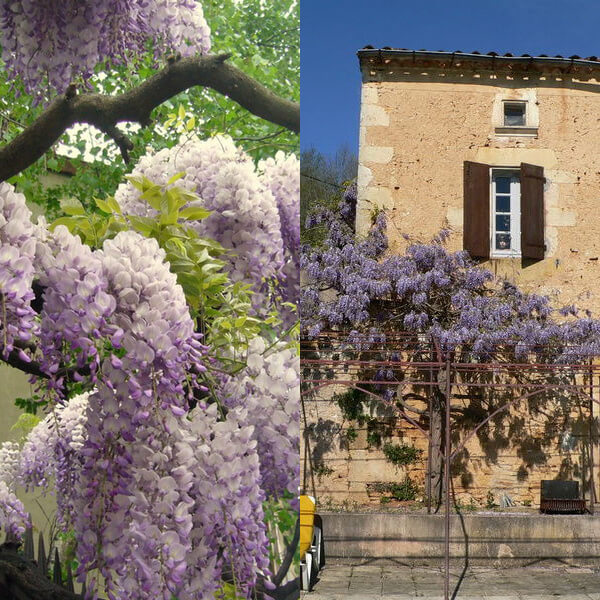
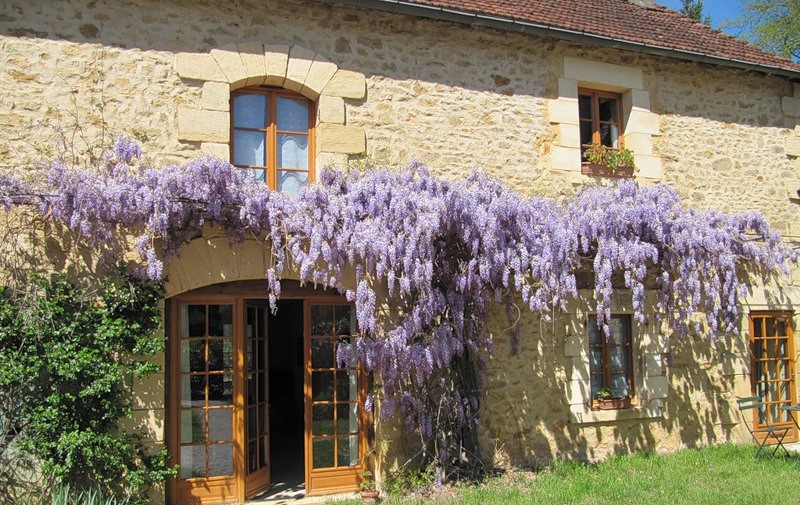
Wisteria is a common climbing plant that needs good conditions - fertile nutritious soil and bright sun. Install strong supports, as wisteria grows over time and covers a large area. Wisteria can be planted in front of the house or on the terrace. Soon this magnificent plant will decorate the territory with its beautiful clusters of fragrant inflorescences.
Wisteria can be planted by a pergola or garden pavilion. It can be used to drape bare walls. Liana blooms when there are no leaves on the branches yet. They appear already during flowering.
Varieties of wisteria amaze with the splendor of the numerous flowers collected in cluster inflorescences, which can reach up to 80 cm in length. Flowers bloom either simultaneously with the appearance of leaves, or a little earlier. Wisteria as a tub plant is grown to decorate south-facing balconies where there is a lot of light and warmth. With good care, plants bloom profusely in spring and again in the second half of summer, but weaker.
 Wisteria abundantly flowering, cultivar 'Violacea Plena'. Cliff
Wisteria abundantly flowering, cultivar 'Violacea Plena'. Cliff
Wisteria - care

With further care, wisteria is watered carefully: it loves moisture, but does not grow well in wet, ripe soil. With long breaks and dryness of the soil, it can stop flowering
Also, this fast growing vine should be fed regularly to provide nourishment during growth. For fertilization, use a solution of Kemira-Lux, organic fertilizers and once a season watered with chalk water (for 1 bucket of water + 100 grams of chalk).
During the season:
- cut dry shoots,
- remove faded brushes,
- tie up and guide the shoots along the support.
- before winter, like climbing roses, the liana is huddled high, shoots are removed from the supports and covered with a covering material, or covered with dry leaves.
Wisteria requires shelter only at a young age. In the future, an adult bush can no longer be covered. Frost-resistant wisteria can withstand frost down to -20-25˚C.
Features of growing Deytsia
Beautiful flower garden ideas
Unpretentious perennials, names and care features
How wisteria reproduces
If you become the proud owner of a delicate wisteria, you will no doubt want to propagate this beautiful plant. Standard trees will give your garden an exotic look, and vines will allow you to hide imperfections in buildings, decorate gazebos or create an incredible "living" fence. There are several breeding methods, we will consider each of them in more detail so that you can choose the right one for yourself.
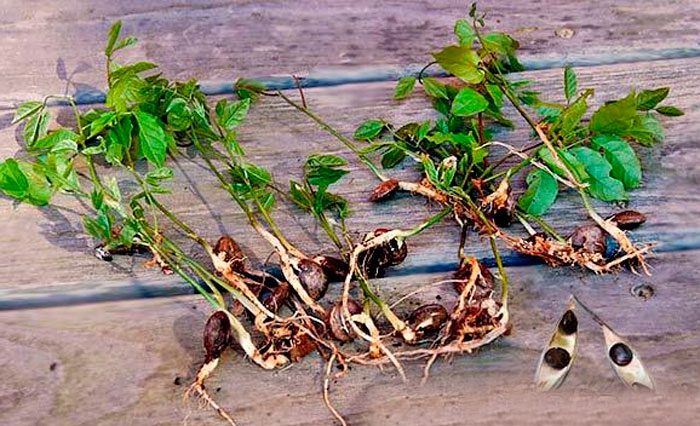
Stem and root cuttings
This is the simplest method that even novice gardeners can easily perform. In October or November, carefully cut the vines from the creeper and divide into small cuttings using a pruner. Then put them in a container with a damp substrate and place in a cool place, such as a basement. In March, cuttings can be planted in a school or placed in a permanent place in the garden, covered with plastic bottles. This method practically does not differ from grape propagation, but the success rate is only 50%. Winter cuttings are carried out from February to March.
The prepared stems are carefully cut in half along the axis, and then the resulting halves are divided into small cuttings 5 centimeters in length
Next, the seedlings are rooted in boxes with a substrate at a distance of 5 centimeters from each other and sprinkled with a small amount of sand. When placing the cuttings, make sure that the bud is at the top.Propagation by root cuttings is also possible, but this method requires a lot of time and effort. In March, the plant is dug up, the young roots are significantly cut off, and part of the large roots at the root collar is also cut off. After all the manipulations, the tree is planted in its usual place. The procedure stimulates the emergence of many new roots that can quickly form adventitious buds, from which stems soon appear. It is these roots that you will need for grafting.

Reproduction scheme of wisteria by cuttings
In the fall, the wisteria is dug up again, inspected for the presence of young roots and a transverse incision is made with the help of a pruner near the root collar, removing them. The thickness of the root cuttings should be between 5 and 15 centimeters, so you can immediately get rid of the thin tips of the roots and lateral roots. To avoid the occurrence of diseases, treat the seedlings with a fungicide. Next, they should be planted in a prepared, moistened substrate and placed in a warm, bright room. Within a month you will be able to notice the appearance of the first stems, and in the fall the plant will be ready for planting in open ground.
Layers
This is perhaps the most effective method. It is carried out in late autumn, after the foliage has completely fallen off. Examine the vine, select a few powerful lower shoots, cut them slightly, bend them down, and then attach them to the ground using a special hairpin. The resulting layers must be sprinkled with earth so that only their tops remain on the surface. In April, the stems must be looped from the side of the mother plant. By the fall, the plant will take root, and you can transplant it to the desired area. If the stalk develops very slowly, then it is better to postpone the transplant until the next season.
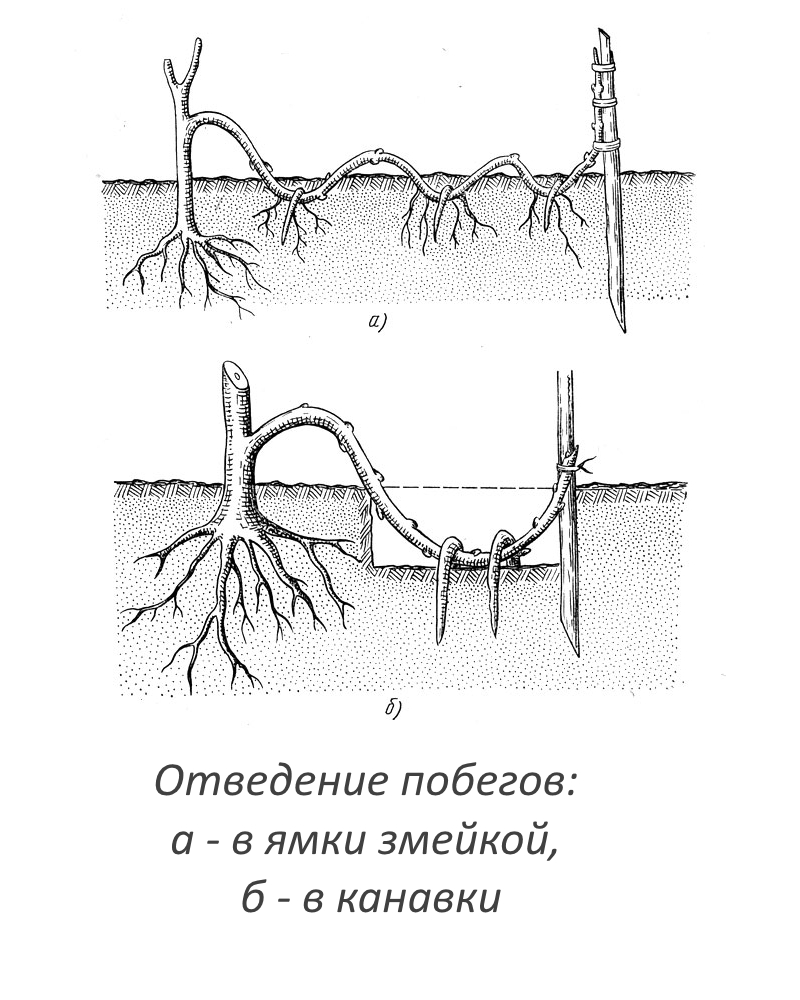
Wisteria propagation scheme by layering
Seeds
Experts do not recommend propagating wisteria by seeds, since some seedlings grown in this way do not bloom. Planting material is sown in special containers with a substrate in December or January. If you want to sow seeds directly into open ground, then do it in March or April. Wisteria is characterized by late germination, and seed germination lasts up to 3 years. Seeds planted in a container must be germinated at a temperature of 22-25 ° C, regularly moistening the soil. The first shoots will appear 3-4 weeks after planting, and starting from 5 weeks they can be taken out in the sun. As soon as the seedlings form the first pair of true leaves, dive them into individual pots. From this moment on, the seedlings must be prepared for planting in open ground. Take them out to the balcony or to an unheated room every day. By April, young wisterias will be ready to move to their summer cottage.

Wisteria seedlings can be grown from seeds
Varieties
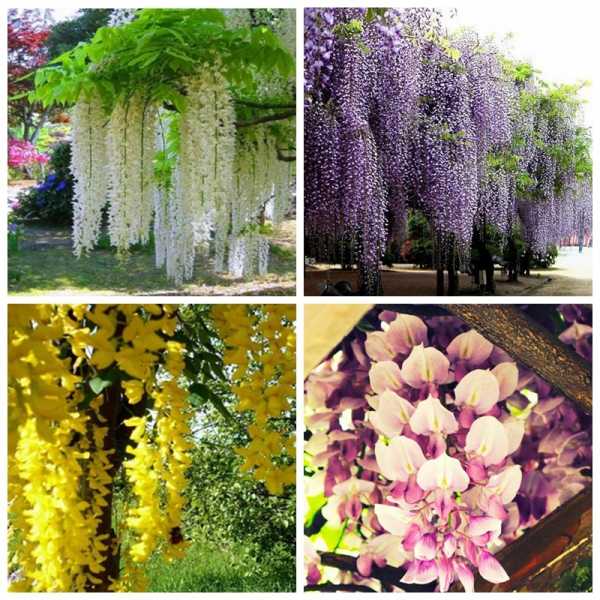
- The following types of wisteria are distinguished:
- Short-crested. A shrub species that grows up to 8 meters in height. Blooms in early summer. Very thermophilic. The flowers are often violet-blue, less often white, the length of the inflorescences is up to 21 cm.
Wisteria brachybotrys
Short-toothed. Liana with purple inflorescences up to 18 cm.
Abundantly flowering (multi-flowered). The flowering period is from mid-April to early June. Reaches 10 meters. The flowering period is early summer. Flowers - purple, white, pink or blue cluster-inflorescences up to 30 cm long. Quite resistant to temperature changes.
Wisteria floribunda
Shrub. The smallest (no higher than 3 meters) and slow-growing species. The flowers are large enough, usually lilac in color.
Wisteria frutescens
American. A very thermophilic plant. It can reach a size of 15 meters. The flowers are blue-violet, odorless, the inflorescences are not large.
Macrostachia (Kentucky) - differs from the American only in the presence of aroma and the large size of the inflorescences.
Wisteria macrostachya
Chinese. One of the most beautiful species. It can grow up to 20 meters in height.Inflorescences are usually white and light purple in color. It tolerates light frosts well, quickly adapts. Blooms from April to June. There are three varieties - "Alba", "Prolific" and "Sierra Madre". You can find more information about Chinese wisteria here.
Wisteria sinensis
Fluffy. A beautiful relatively small wisteria with large and fragrant purple flowers.
Wisteria villosa
Japanese. The most thermophilic species. The decorative properties are the least pronounced. Flowers only white, small, short inflorescences.
Beautiful. Deciduous liana, reaching 5 meters. The flowering period is May-June. It is thermophilic, for the winter it is required to additionally insulate or keep in a greenhouse. It is considered the most beautiful view.
Wisteria ventusa
All plant species are thermophilic and grow in their natural environment mainly in areas with tropical and subtropical climates. Short frosts (up to 20 degrees) for several days can be tolerated by any type of this plant, but there are also specially bred frost-resistant varieties.
Frost-resistant varieties of Wisteria are only some varieties of American wisteria - "Blue Moon", "Clara Mac", "Pink Ice" - they can withstand frosts down to -35C.
The most common and suitable for mid-latitude cultivation is the Blue Moon variety. This variety, artificially bred in Minnesota, can withstand frosts up to 40 ° C. Flowers are large, blue with a yellow center, collected in bunches of 15 - 30 cm.The flowering period is long, throughout the summer - from June to August, with varying intensities ...
Wisteria Blue Moon
You can grow Blue Moon and other varieties of wisteria and at home as an indoor standard or semi-stem plant. Recently, the use of wisteria to create bonsai has been common. Since most varieties are thermophilic and are recommended to be transferred indoors for the winter, all of them can be used as indoor plants. Shrub, American, Japanese and fine wisteria are most suitable for use as potting plants.
When growing wisteria as a houseplant for the winter, it must be transferred to a cool room!
In the climatic conditions of the middle lane, wisteria is best grown indoors. If you use it for planting in the ground, then you should choose the varieties and species that are most resistant to frost. With proper care, this beauty will delight you for years to come.
How to plant wisteria
Now that you have learned about all possible breeding methods, you should talk about planting a plant in open ground. Whether the wisteria will take root in a new place depends on the quality of the soil, the correct placement and planting.
The soil
Wisteria is not very demanding on the soil, but prefers to grow on loose, fertile, well-drained soils. If you decide to grow it in a flowerpot, we recommend purchasing a suitable substrate in a specialized flower shop. You can cook it yourself by mixing 4 parts of leafy soil with 1 part of turf and 1 part of sand. To protect the plant from pest infestation and the occurrence of fungal infections, pre-calcine the soil in the oven or treat it with fungicides.
Growing wisteria in a pot
Container growing involves the formation of a standard tree. It will serve as an unusual decor for a hall or winter garden. Such a plant can be taken out into the fresh air no earlier than June. Note that indoor species have a rather small root system, so it is better to give preference to small containers. In spacious flowerpots, the flower will rapidly increase the green mass, which will negatively affect flowering. In summer, it is better to keep wisteria outdoors, but in winter it should be transferred to a room where the air temperature ranges from 8 to 10 ° C.Please note that keeping in a well-heated room in winter will lead to the death of the tree. You can even send the plant to the basement, but from mid-January it needs to be gradually adapted to higher temperatures. By the beginning of March, wisteria is transferred to a room or to a glazed balcony.
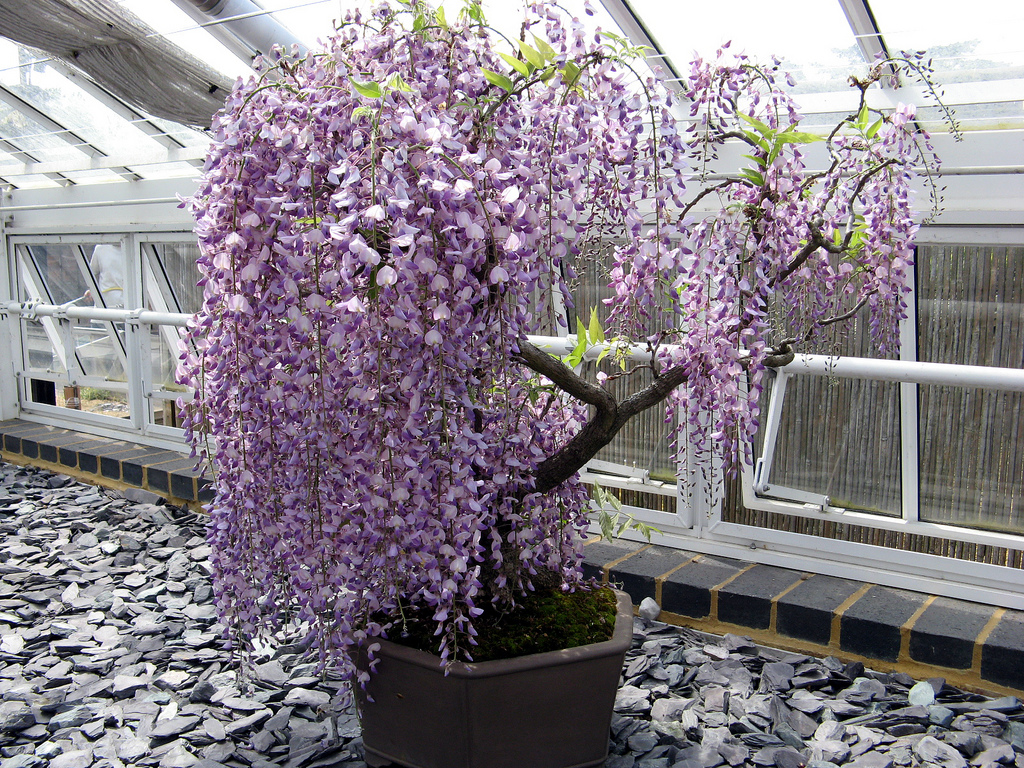

Wisteria can be grown in a pot indoors almost all year round, but in winter it is taken to a cooler place.
Planting wisteria in open ground
In early spring, as soon as the last frosts have passed, seedlings can be planted. Even if you prefer frost-resistant wisteria, you should not expose a fragile plant to the risk of frostbite. Wisteria is a perennial, so immediately decide on its location. The selected area should be protected from drafts and at least 5-6 hours a day in the sun. Next, consider a step-by-step algorithm for planting a plant.
- Dig holes 60x60x50 centimeters in size.
- Apply complex mineral fertilizers to the soil. As a rule, it is enough to take 20-30 grams per 1 square meter, but it is better to use the mixture according to the dosages indicated on the package.
- Place the seedlings vertically in the holes, and then fill them with soil so that the growth points or leaves are on the surface.
- Moisten the soil well, sprinkle it with sand on top.

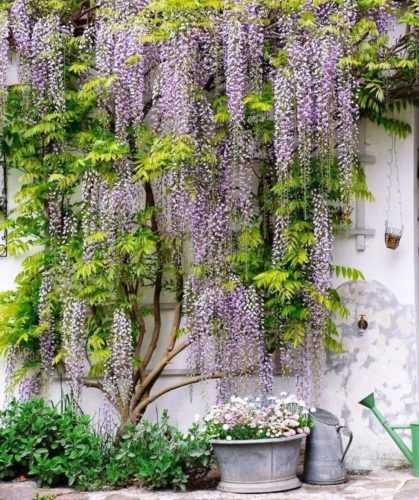
Wisteria is mainly planted in open ground, where it can reach its full growth.
Care after landing
After planting, the first step is to mulch the young wisteria 10 centimeters above the neck. For these purposes, peat or dry composted grass can be used. Spread the mulch in an even layer and leave it on throughout the year. In summer, it will protect the root system from overheating, and in winter, on the contrary, it will help to avoid frostbite. By the way, in winter, you need to take care of the shelter. This is especially true for species that do not tolerate low temperatures. After planting a plant, your main task is to carry out timely watering, feeding and loosening the soil. If you follow the recommendations carefully, next year the seedling will delight you with bright shoots.

In order for the wisteria to be comfortable in summer and warm in winter, you can mulch the soil around the trunk
Care
To form a hedge, the liana must be provided with good support. The structure must be strong enough to support the weight of the overgrown specimen.
It is recommended to cover frost-resistant wisteria in the first year for the winter. The plant is tilted to the ground and covered with spruce branches. Spunbond can also be used as a covering material. Overgrown shoots are not removed from the supports for the winter.
For normal growth of vines, you need to choose a good place for planting, water and cut wisteria correctly, and fertilize on time.
Landing

Saplings are planted in spring. A few months before it, organic and mineral fertilizers are applied to the soil. Then they dig holes 30-50 cm deep. Crushed stone or broken brick is laid out on the bottom.
After planting, the plant can be treated with any growth regulator for better survival. To maintain optimal humidity, wisteria is watered daily. Each seedling takes 2 liters of water.
Pick-up location
Wisteria Blue Moon is thermophilic. Therefore, it must be planted in an open, sunny place. In the shade and partial shade, the culture is not grown, because it begins to stretch and bloom later. Wisteria will grow best on the south side. At the same time, the site must be well protected from the wind.
This variety of wisteria grows actively on slightly acidic loamy and sandy soils with good drainage properties. Acidic peat soils are not suitable for the plant.
For vines, it is recommended to immediately select a permanent place, since it does not tolerate transplantation well. Experienced gardeners grow it near the house or fence, since in this case additional support is not required.
Fertilizer and feeding

Top dressing is not performed on fertile soils. In other cases, potassium, phosphorus, rotted manure are used. Fertilizer is diluted in water. Top dressing is applied during the formation of the first buds every 3 days.
Transfer
It is not recommended to transplant wisteria. If there is an urgent need to change the place of growth of the plant, then you need to dig out the wisteria with a large clod of earth. You should first cut off too long shoots. The best survival rate after transplantation is shown by young plants that are not one year old.
Watering
In hot weather, vines require abundant watering. With a lack of moisture, wisteria blooms poorly. The soil under the wisteria should always be moderately moist. Excess moisture is contraindicated for the plant, since the roots can rot. Watering begins to be reduced closer to autumn.
So that the soil does not dry out during the heat, it is mulched with cut grass. The plant also needs periodic spraying. The procedure should be performed early in the morning or late in the evening.
Pruning
In the spring, the shoots are shortened by 4 upper buds. After winter, you need to remove the frozen parts of the plant. In the second year, the main stem is shortened to 80 cm. The distance is measured from the upper shoot located on the side. The remaining side branches are cut off by 30%. A similar procedure is performed annually.
At the end of summer, the lateral shoots of wisteria are shortened to 20 cm. At the same time, new basal processes are eliminated.
Pruning is also carried out for better flowering. During the summer, the increments are shortened to 17 cm every 14 days.




















































