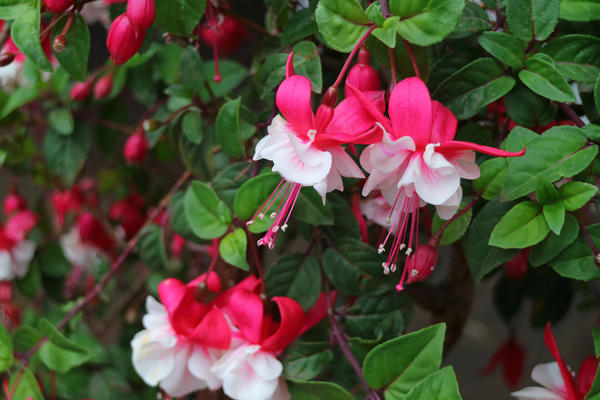
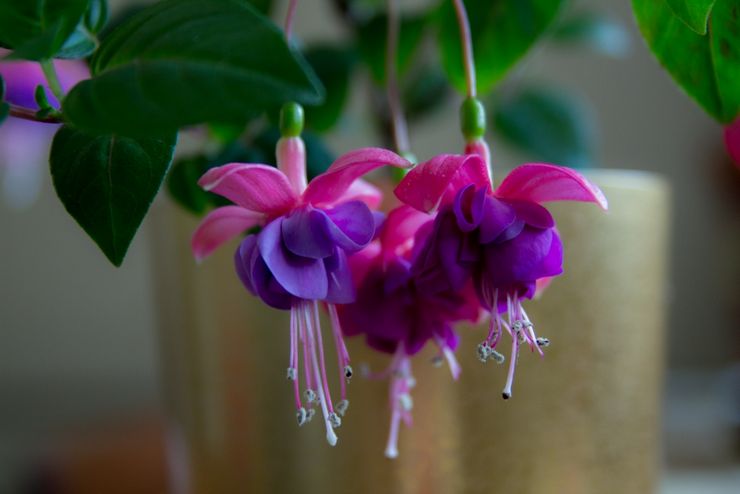
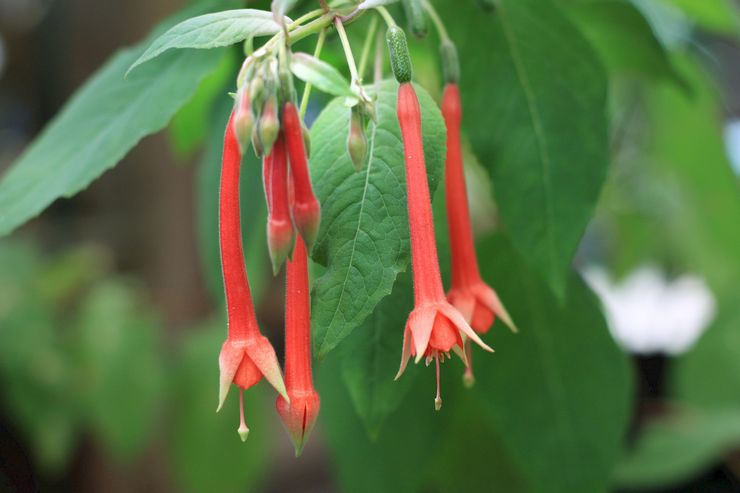
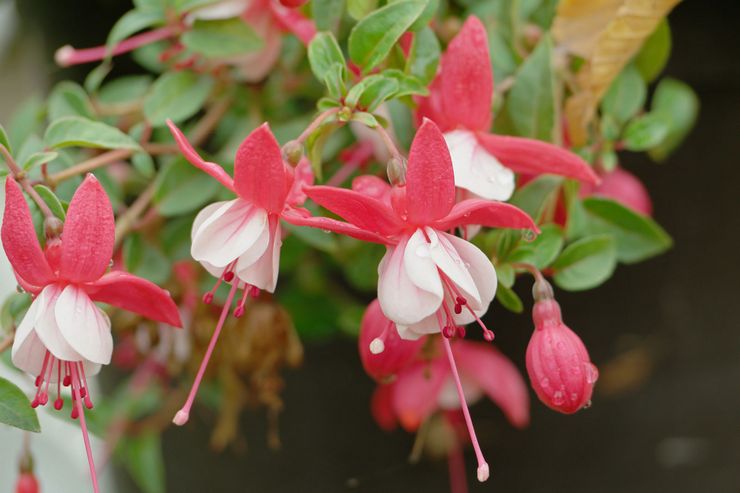
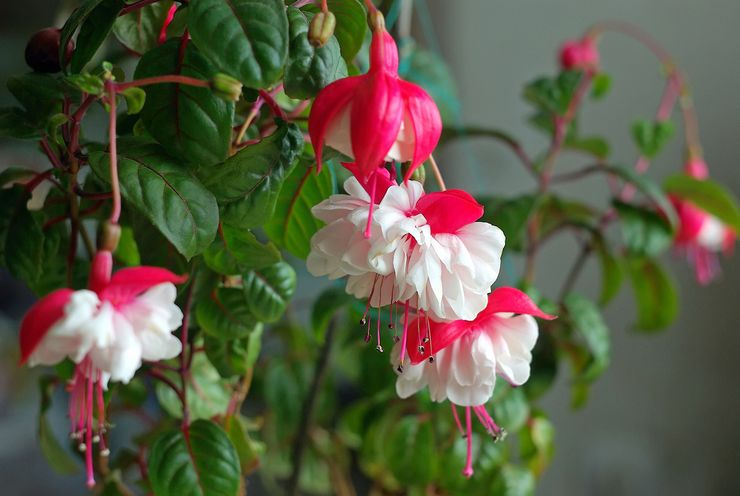
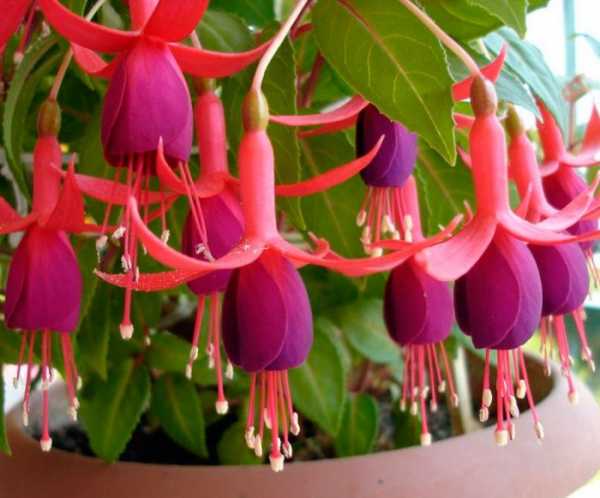
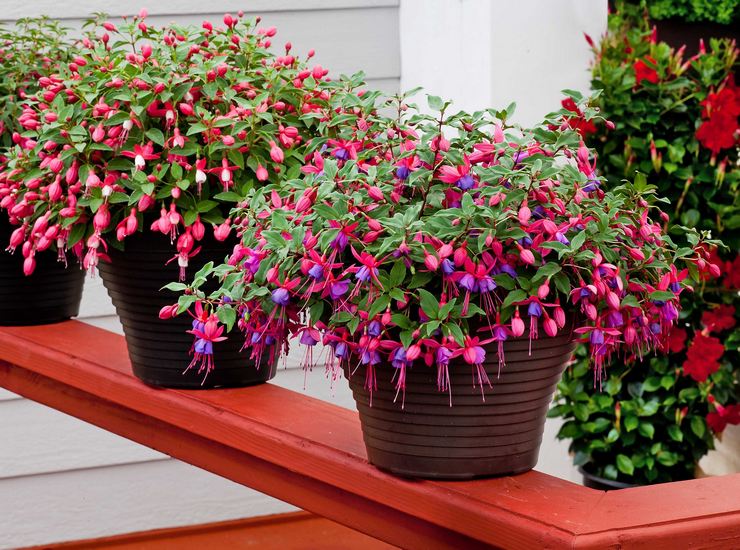
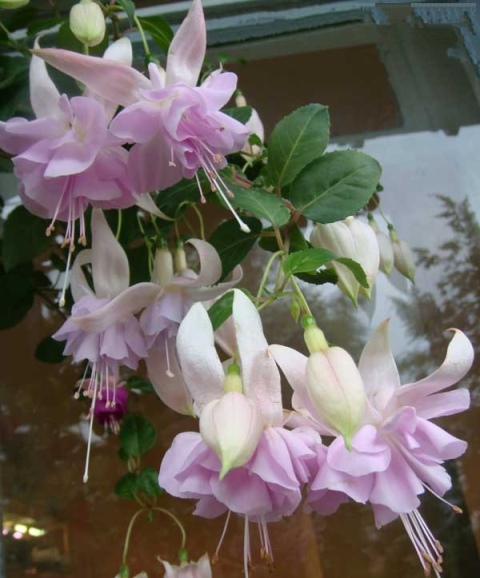
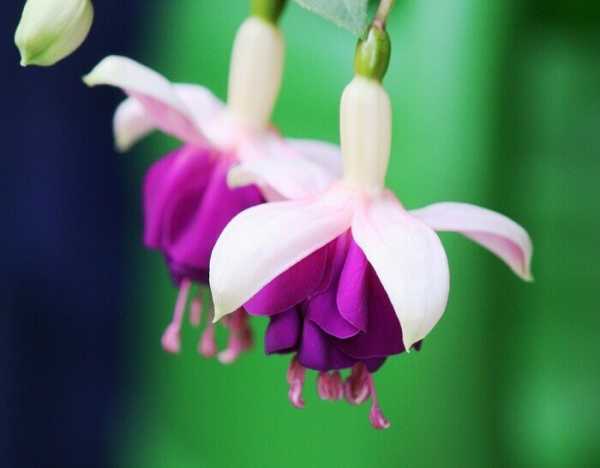
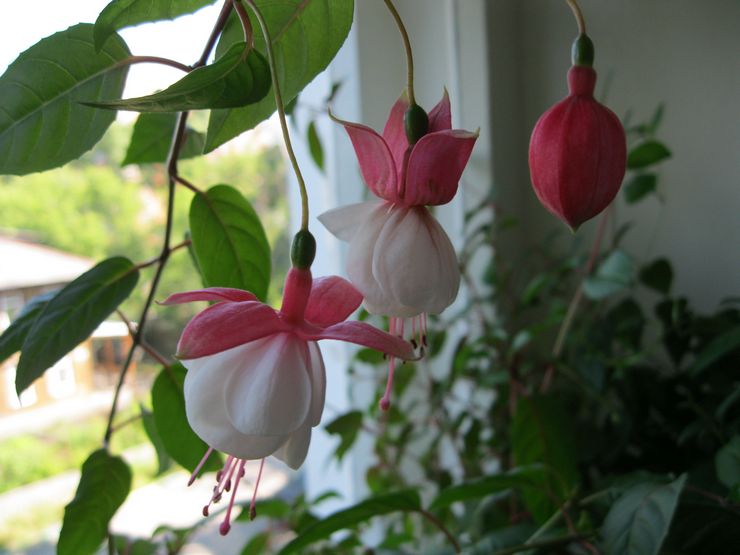
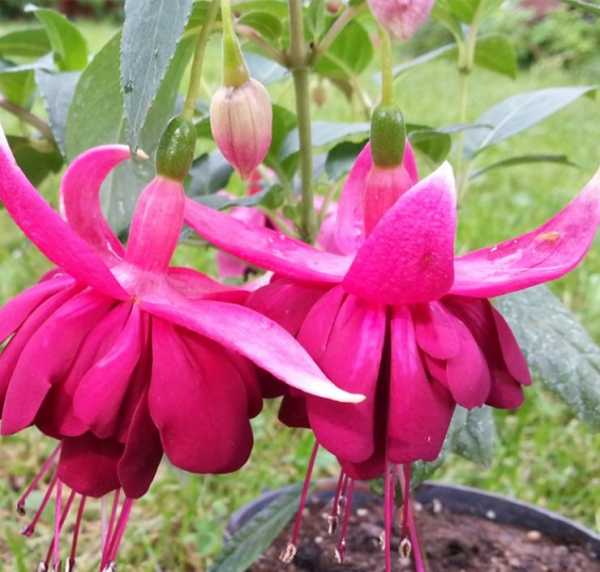
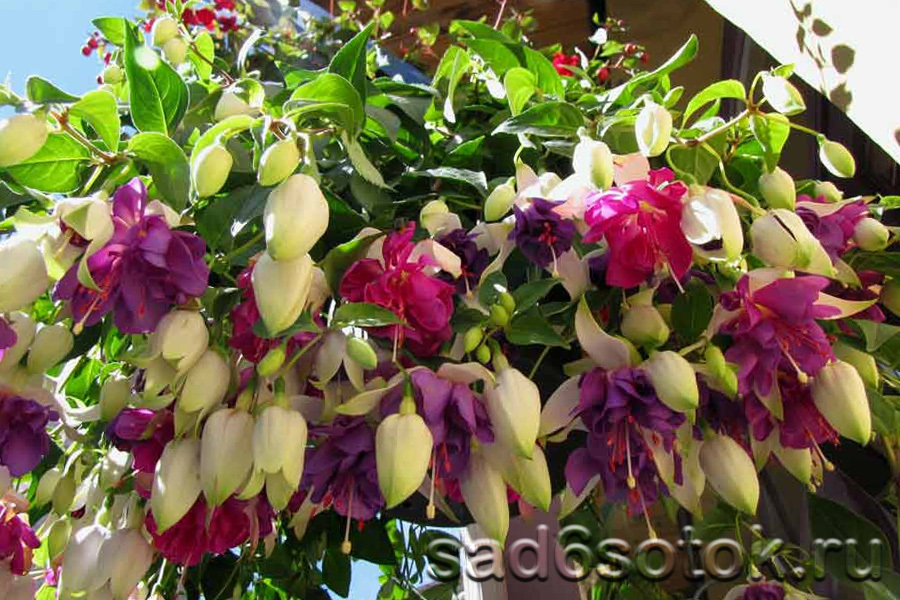
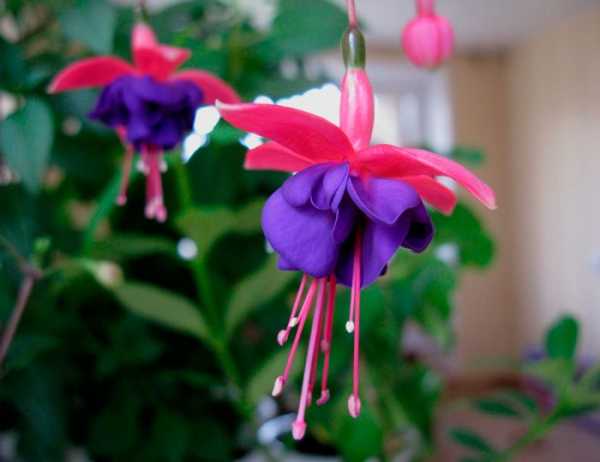
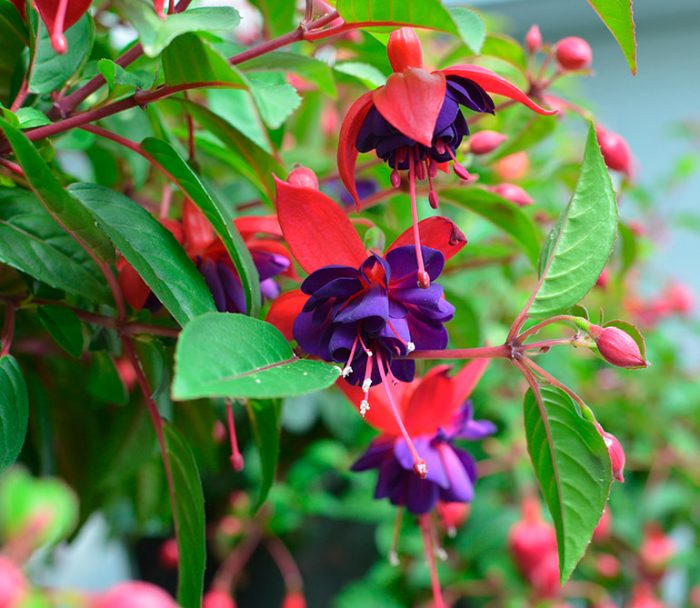
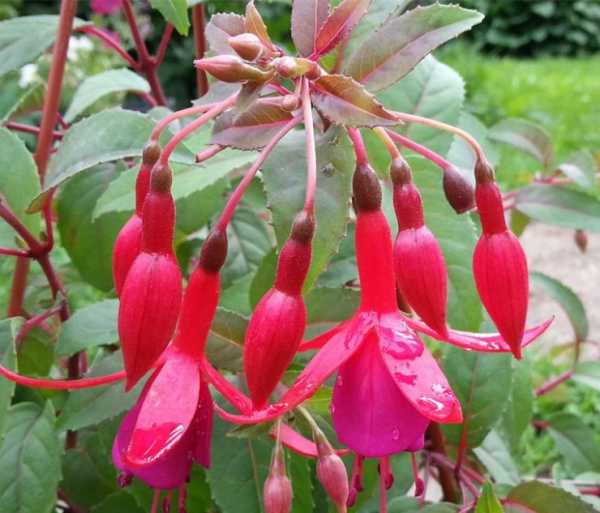
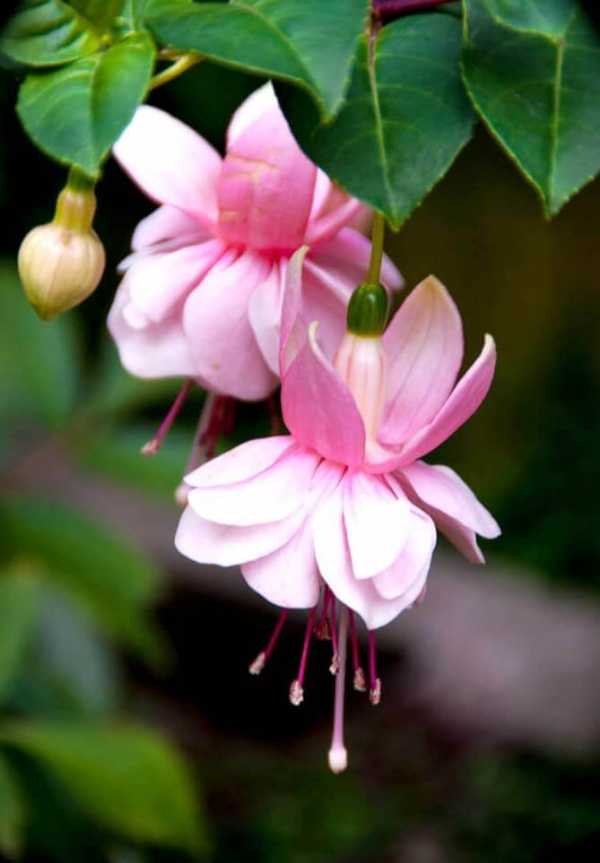
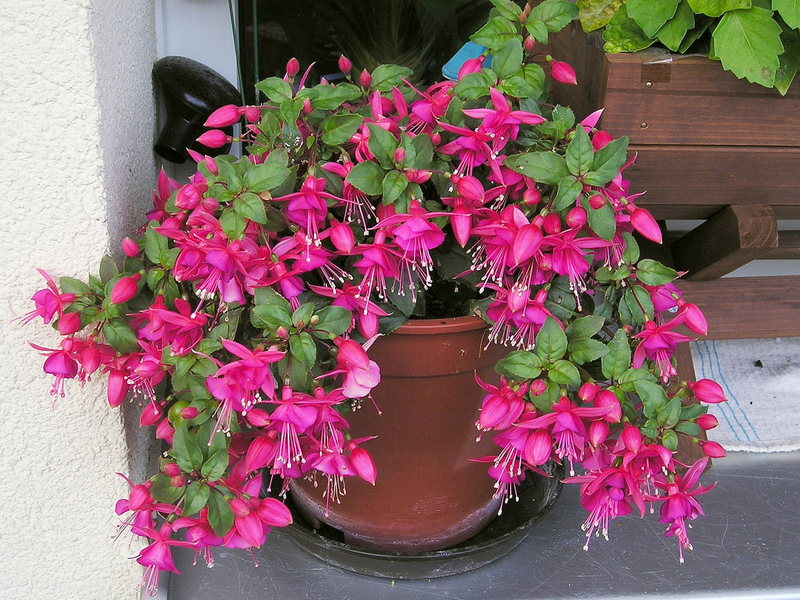
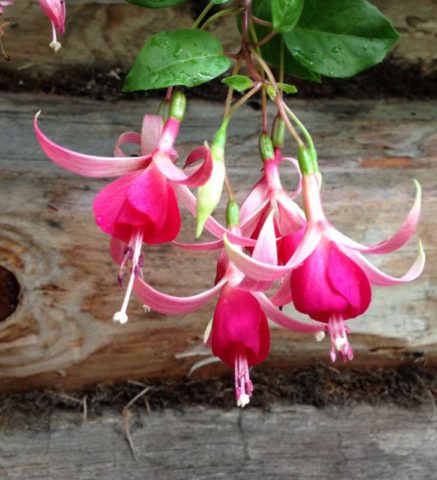
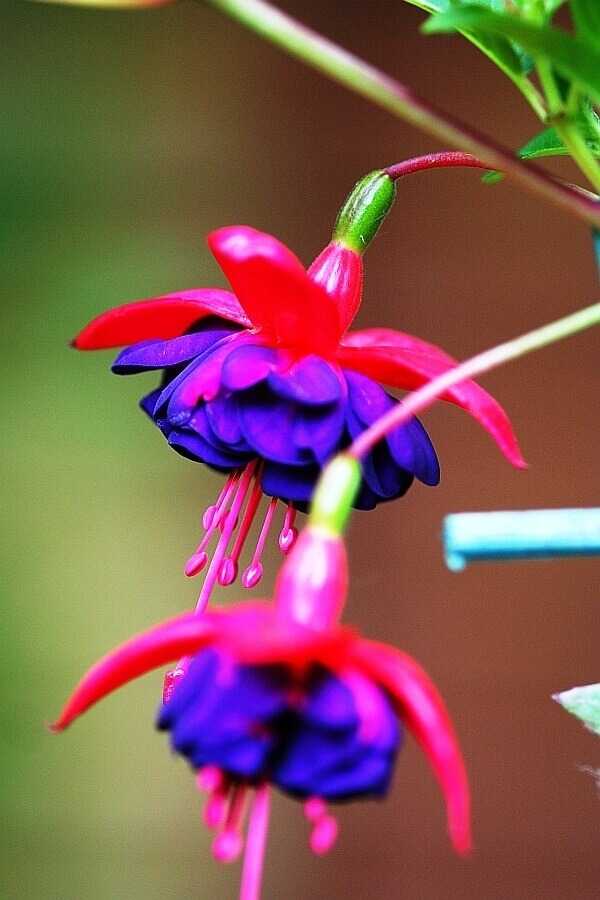
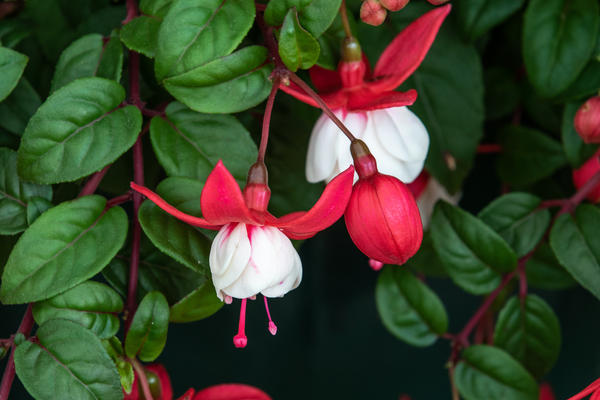
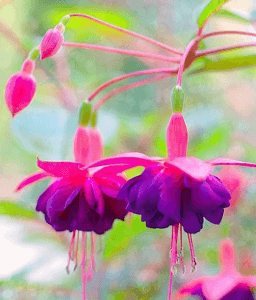
How to grow and care for an indoor flower?
The plant is very unpretentious to care for, so it is perfect for novice flower growers.
Selection of a place and soil for growing
The most important condition for planting a shrub is the presence of sunlight, while it should be protected from direct exposure to rays. The soil should be slightly acidic; a mixture of earth, sand and peat in a ratio of 3: 2: 1 is suitable for the substrate.
For home growing, it is better to choose a place near the west or east window. Be sure to protect the flower from drafts.
Important care procedures: watering and feeding

Watering should be abundant and infrequent.
Transfusion should not be allowed, this will provoke rotting of the roots. During the period of growth and flowering, it is better to water the flowers once every 3 days, and in hot weather, it is possible every other day.
On hot days, fuchsia should be regularly sprayed with settled water. Closer to the dormant period, watering is reduced to once a week, and even less often in winter.
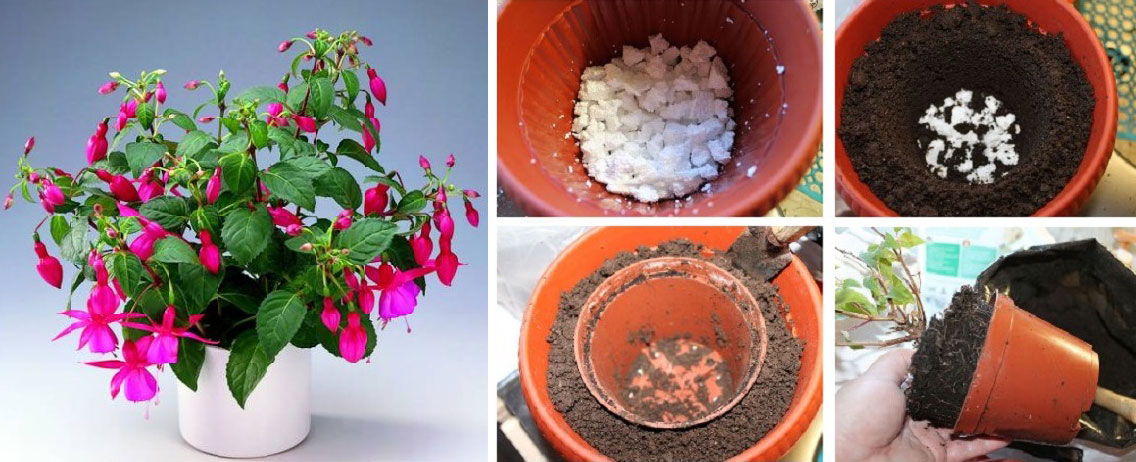
In the first month after transplanting, there is no need to feed the plant, since the fresh soil must be sufficiently nutritious. After feeding, they are carried out every 2-3 weeks, for this they use various fertilizers for flowering plants with minerals.
Excessive feeding will harm the plant, because the perennial will grow foliage, but will not be able to actively bloom. In autumn and winter, the flower is not fertilized.
Cutting and shaping rules
Pruning must be done twice: in early spring and in autumn after flowering. Pruning in spring is carried out before the flowering period has begun: old branches need to be cut off, and young ones should be pinched. Pruning helps shape the shrub. Also, after winter, it is necessary to remove the thin formed shoots, because they will not be able to bloom luxuriantly.
In the fall, it is necessary to remove the faded branches, keeping 2 cm to the buds, and also to cut off the dead peduncles. If diseases or pests are found, then it is necessary to cut off the damaged parts and process the plant.
It is important to remember that flowers bloom on young shoots and it is they who form a beautiful bush.
Cultivation and features of places
So, we already have quality seeds. Growing aster seedlings should be started in the spring. We begin to sow seeds in the soil when the sun is already warming well outside the window - in the last decade of March or early April.
First, decide on a place. You can use regular flower pots, which are more spacious. Drawers will also work. And some artisan flower growers build miniature greenhouses on the windowsills especially for timid seedlings.
If you have a large greenhouse at your dacha, then you can arrange a nursery garden for future asters there too. In principle, the place of planting seeds for seedlings does not particularly affect the germination rates. At the preparatory stage, I advise you to treat the seed material with fungicide powder, and water the soil with a solution.
This is necessary for the prevention of a disease like a black leg, which can very much harm the plant. Do not be lazy at this stage to take care of healthy seedlings in order to subsequently get strong "stars" in the autumn flower bed.
Seeds are sown into the ground to a depth of half a centimeter. It is recommended to water them with manganese solution immediately after sowing. In order not to blur the grooves, I use a strainer. I just gradually pour water with potassium permanganate through it, as if sifting. Then I cover the pots with paper, and if you are building a mini-greenhouse, then use plastic. After about a week, shoots should appear.
We move the seedlings to a place in the apartment well lit by sunlight, and remove the film from the greenhouse. Then we are waiting for the appearance of the first leaf.This significant event suggests that it is time to start a dive. As a child, I always helped my grandmother in this matter.
We carefully transplanted small sprouts. At the same time, you feel with your heart how life is being born
And even if these are just plants, they also strive for the sun and fight for their existence.
The day flashes by with unfamiliar faces.
In the twilight, the last lightning will break out
Blue asters, burgundy, white ...
Asters tolerate picking well. Each individual plant must be planted from its "relatives" at a distance of more than 5 cm. Do you want a proprietary secret? I use egg trays to give the seedlings the freedom they want. It is convenient to transplant flowers from these cells into open ground.
The first feeding is carried out a week after the dissection. Further, this procedure should become regular. When planting asters for seedlings, a complex fertilizer is used for these purposes, which can be purchased at the store.
Plan to relocate sprouts to open areas for May. During this period, frosts are still possible, but you should not worry - the seedlings will withstand a cold snap to -4 degrees. Better to choose a warm May evening for planting seedlings in the ground. Maintain a distance of 25-30 cm between plants. In the early days, you can cover the asters with foil so that they can more easily survive the change of residence.
If, when diving, you notice that the seedlings are very elongated, plant them in the soil deeper. You can even almost to the level of a leaf.
Aster seedlings need moderate watering. Remember: it is better to give the seedlings less water. Excessive moisture can be harmful.
The watering procedure is recommended to be carried out in the first half of the day, so that the soil dries out a little before dusk.
For aster seedlings, temperature differences are useful. During the day, ensure the temperature regime is within 20-25 degrees, and at night a cold snap should come up to +12.
I strongly advise against planting aster seedlings in the beds that were occupied with tomatoes or potatoes last year. The principle of beneficial symbiosis does not apply here. The fact is that tomatoes and nightshades often suffer from fusarium. Dangerous pathogens of this plant disease feel great and multiply in the soil. And cute humble asters can adopt this disease.
Motley autumn lives with carnivals,
Extending summer into rainy weeks,
Pampering with bright days and colors -
Purple, yellow, red asters ...
.
Diseases and pests
Fuchsia ampelous, like many other ornamental plants, faces diseases and pests. More often than others, there are several problems.
- Whiteflies are small whitish midges, visually they resemble a microscopic moth. They live on the back of the leaf blade, when shaken they fly in different directions. These parasites suck the sap from the plants, as a result they turn yellow and begin to wilt. Treatment with Actellik or Aktara will help to get rid of the whitefly. Spraying is carried out 1 time in 3-4 days, if necessary, the funds are alternated.
- With excessive moisture, the plant often encounters powdery mildew. In the fight against it, treatment with Fundazol or Topaz will help.
- Short and shallow flowering is most often associated with a lack of minerals, a lack of light, or keeping the plant in a too warm place - if such signs appear, care should be adjusted.
- Very often, a spider mite appears on fuchsia leaves. The parasite itself is so small that it is impossible to see it. However, a whitish web can tell about the problem. If processing is not done in time, the leaves die off quickly. Means "Fitoverm", "Confidor" or "Agravertin" will help to cope with the problem.


How to grow ampelous fuchsia, see below.
Bush varieties

Fuchsia bush variety Rohees New Millennium
Rohees New Millennium
A compact bush with erect shoots up to 40 cm high, all covered with medium-sized double flowers with black cherry skirts and light purple sepals. This unusual combination gives an attractive contrast and looks exotic. One of the best dark-colored varieties is easily propagated by cuttings, and woody, strong shoots make it suitable for tree formation.
Andromeda
The tall, strong bush is characterized by long, frequent shoots up to 90 cm tall, covered with beautiful dense light green leaves with red veins.
Early flowering, profuse, simple, small flowers with scarlet sepals and a crimson skirt.
The bush grows quickly, the shoots are lignified and suitable for the formation of a trunk, but Andromeda is very decorative and in a bushy natural form. Cuttings root well, the variety is easy to care for and can be grown in the garden.
Hanna
A powerful shrub with shoots up to 50-60 cm long, fast growing and luxurious flowering throughout the season. The flowers are simple, rarely double. The sepals are scarlet, raised up, the skirt is creamy with crimson veins at the base. The leaves are green, elongated.
Stems woody rapidly - this is one of the best varieties for growing in standard form. Cuttings quickly form roots, cultivation and reproduction is available to a novice grower.
Fuchsia propagation
Three methods of propagation are used: seeds, leaves and cuttings. The first two methods are used much less frequently. But this does not mean that they are less effective. They are just more laborious and the result will take much longer. Novice growers (and experienced ones too ...) prefer propagation by cuttings. Let's start with him.
Propagation of fuchsia by cuttings
This can be done both in spring and autumn. Autumn breeding (August-September) is mainly used for slow-growing varieties. Most often, cuttings are taken in February-March, in which case flowering may occur in the same year.
- Cuttings for propagation are taken small (6-10 centimeters long) from the top of the plant, cutting them off under the lower bud.
- The lower leaves must be removed, leaving 3, maximum 4 pairs.
- Cuttings can be rooted in loose (peat) soil, in wet sand, and in water. For beginner flower growers, I would recommend the latter method, for clarity.
- After about 20-25 days (possibly even earlier), the stalk will give enough roots to be planted in a pot. For young fuchsias, the composition of the earth should be as nutritious as possible. A mixture (in equal parts) of leaf, turf, humus and sand is recommended.
Fuchsia leaf propagation
- In this case, you need to take not just a separate leaf, but cut it off with a small piece of the stem.
- The petiole with a piece of stem is buried in the ground (about 1 cm). To do this, you can use the formula above.
- The earth and the leaf are moistened and covered with a transparent cap (jar, PE bag, etc.).
- For better rooting, the leaf must be sprayed daily.
- After the appearance of young plant rosettes, they can be transplanted.
Fuchsia seed propagation
This process is quite complicated, so I would not recommend it to beginner growers. Is that as an experiment. The difficulty lies in properly pollinating the flowers of the plant. Self-pollination of the mother plant is unacceptable! Artificial pollination is required. If not all flowers are pollinated, then the pollinated one must be isolated from the rest by putting on a protective cap made of film. After the flower bears fruit and it ripens, you can collect the seeds and start sowing.
This procedure is simple and not much different from obtaining plants from seeds. The only thing I would like to note is that you do not need to bury the seeds in the ground, it is enough to scatter them over the surface of the moistened earth.
This method, for all its complexity and laboriousness, is quite interesting.Indeed, in its process, you can truly get YOUR flower, with a unique color. So, even novice flower growers can feel like real breeders.

Reproduction methods
Cuttings

Fuchsia semi-ampelous grade Golden Monique
The most common and available in home breeding method for fuchsias - grafting. Shoots with two or three internodes are used as cuttings. To prevent the cutting from fading and retaining moisture, large leaves are cut to half the size. Large healthy leaves, cut along with the adjacent bud, can also be used for propagation.
The prepared cuttings are treated with the Kornevin stimulator and planted in pots with a diameter of 5–7 cm, in a moist substrate, for the preparation of which up to half the volume of sand or vermiculite is added to the mixture for adult plants.
The seedlings are placed in a warm place with diffused light and a temperature of 18-22 ° C. To maintain air humidity, they are covered with cans or plastic bags. From time to time, the plants are sprayed, but do not forget to ventilate. In most cases, cuttings root easily with the yield of full-fledged seedlings up to 85-100%. After rooting, the plants are transferred to a permanent place and looked after as if they were mature shrubs.
Seed propagation
Seed reproduction is also available to amateurs, the way to develop a new variety is especially relevant if desired. For this, the seeds are sown in small bowls with a small amount of sterile soil, lightly covered with vermiculite and covered with glass. Seedlings appear in 1.5–2 months, they are regularly watered by spraying and ventilated. When two true leaves appear, the seedlings are transplanted into pots and looked after like cuttings obtained by cuttings.
How to care for fuchsia outdoors
Watering
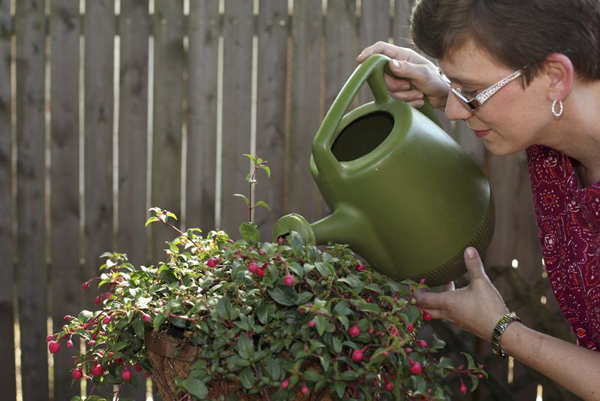

Fuchsia belongs to plants that love moisture very much. It can be either watered or sprayed. But, the main thing here is not to overdo it, and to exercise moderation. Fuchsia should be watered every day, but you need to do this with a little water. Otherwise, root decay will threaten your plant. Assess the topsoil before watering. If fuchsia is dry at a depth of one centimeter, then watering is very necessary.
Top dressing

Fuchsia will develop correctly only if there is a sufficient amount of humus and useful fertilizers in the soil mixture.
Therefore, it is very important to make sure that you have applied a sufficient amount of phosphate fertilizer to the soil before planting it in open soil. But it doesn't end there
Pruning

Pruning is carried out in late winter - early spring
It is very important to remove 2/3 of the bottom of the plant. This includes the dead and diseased parts of fuchsia.
Pruning will significantly rejuvenate the plant, and promote abundant flowering in summer and fall. Pruning rules:
- Water the plant twelve hours before pruning.
- Remove all bad branches. That is, damaged or dead, thin or intersecting.
- Cut out damaged or weak branches almost all the way to the stem.
- Prune the vertical branches.
- Prune healthy branches. The result should be a branch with three buds.
- Remove all old leaves.
Garter
To make the fuchsia bush beautiful, its central part can be tied to small pegs, and left to grow further, periodically cutting off the side shoots.
Forms and varieties
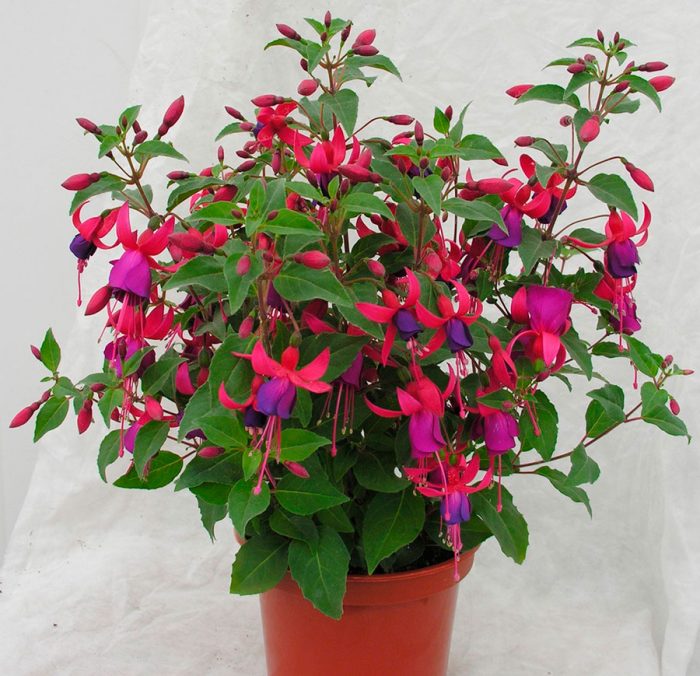
In home floriculture, hybrid fuchsia is most often grown - a group that includes more than two thousand varieties of delicious shades, each of which deserves the attention of a florist and will wonderfully decorate a room, balcony or veranda.
According to the shape of the bush and the type of growth, bush, ampel and semi-ampel types are distinguished. This division is rather arbitrary, since in many respects the appearance depends on the formation and growing conditions.
Shrub fuchsia (erect)

Shrub fuchsia (erect)
The most common form, which is characterized by erect, frequent branches from 35 to 90 cm in length. Oblong-oval, serrated leaves opposite on long petioles. The flowers are collected in loose clusters or single, located in the axils of the leaves and hang down like luminous lanterns.
It is the bush type that is most often used to create standard forms, breaking off all lateral shoots and allowing fuchsia to grow only at the top or, for greater effect, grafting one of the ampel varieties onto the stem.
How to grow a rose in the form of a stem, read in the article "Standard roses - planting".
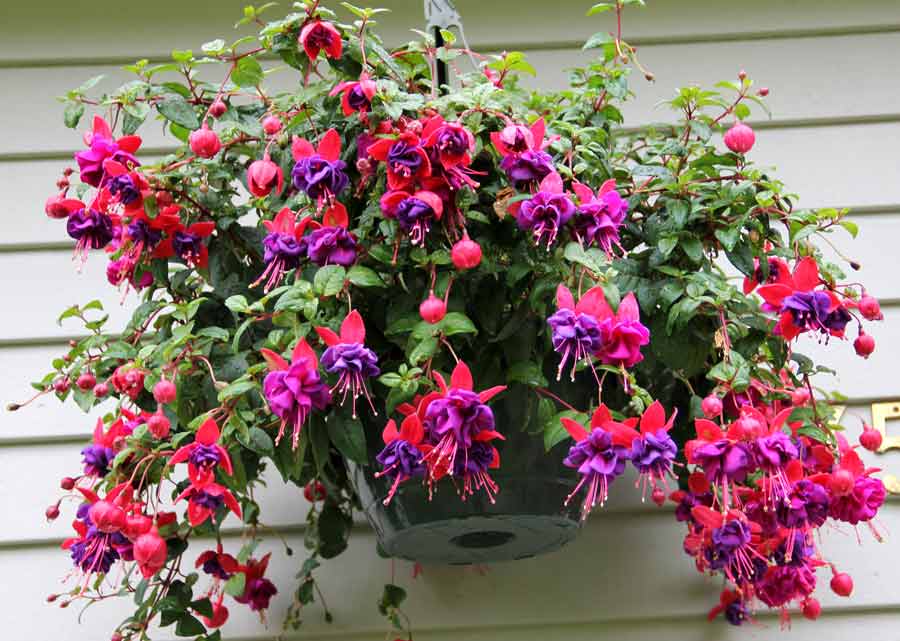
Ampel fuchsia

Ampel fuchsia
Long flexible stems of ampelous fuchsia fall freely, which makes it possible to plant plants in pots, decorate verandas and terraces with them. The flowers are medium to very large, of various shades, double, semi-double and bicolor. For more lush flowering, several cuttings are planted in one pot.
Semi-ample fuchsia

Semi-ample fuchsia
At the initial stage, semi-ampelous varieties look like typical bush forms with erect shoots, which eventually droop, hanging under a load of heavy flowers, and the bush takes on an ampelous appearance. Lush flowers can break off shoots, so they are tied to supports. The appearance and development of such fuchsia largely depends not only on the variety, but also on the formation, and some species can be successfully grown as trees.
Description of fuchsia garden perennial
Fuchsia owes its name to a German doctor L. von Fuchs, who is considered the "father of botany".
Fuchsia branches are distinguished by their flexibility, the aspiration of the crown downward.
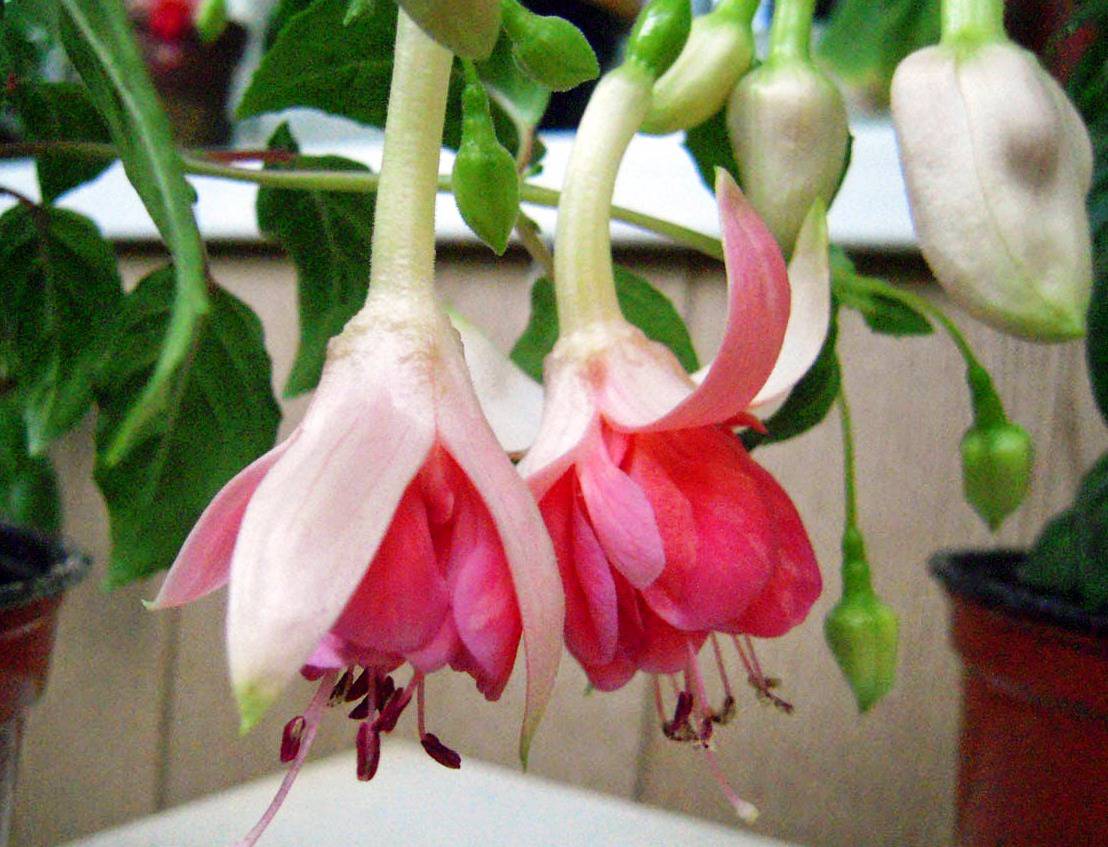
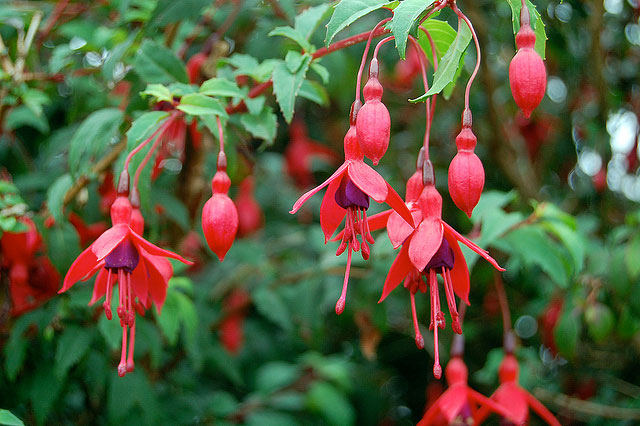
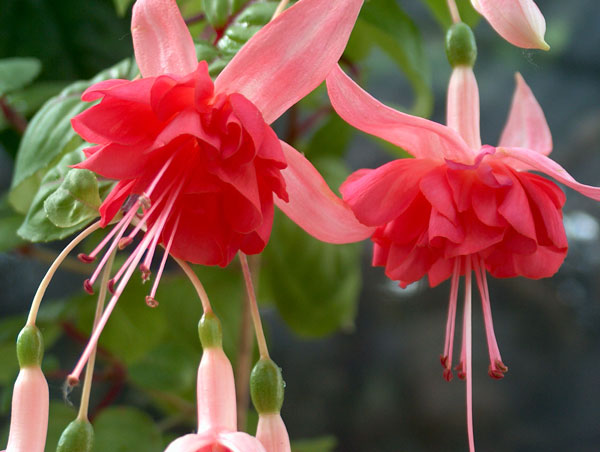
What does a flower look like
The leaves are bright green, oval in shape. Their length is about 5 cm. The ends are pointed, and the edges of the leaves have a serrated border. The stems are light reddish in color. Sometimes foliage also takes on this shade.
The flowers of the plant are single, directed downward. They are shaped like a bowl. Flowers are double, simple and semi-double. Their color varies: orange, lilac, cream, white, pink, blue and purple.

Terry flowers
Flowering continues for a long period of time. Flowers at this time more and more rush down and wither by the end of flowering.
Fuchsia is an annual or perennial plant
Fuchsia belongs to the genus of exotic perennial plants. But since this is a thermophilic flower, in northern latitudes it is one of the annuals.
Types of room fuchsia by structure
All fuchsias are divided into two types depending on the type of shoots and buds. The following groups of these plants are distinguished - bushy and ampelous. Each variety has its own characteristics.
Ampelny
The main feature of the ampelous species is the active growth of lateral shoots, therefore the flowers are placed in hanging pots and decorate the balconies and facades of private houses with them in the warm season.
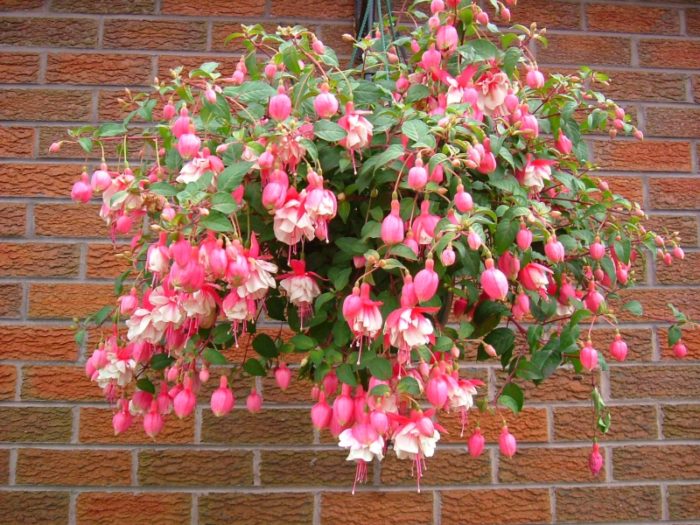

The most popular varieties of ampel fuchsia:
- Imperial Crown has beautiful reddish flowers and elongated shoots;
- A ballerina can be easily distinguished by voluminous buds with a characteristic two-tone color;
- Blue Angel is distinguished by flowers of white and purple color;
- Annabelle boasts snow-white inflorescences;
- Hollis Beauty cannot be confused with another variety due to the presence of large purple-white buds;
- Prince of Peace has white and red inflorescences.
Bushy
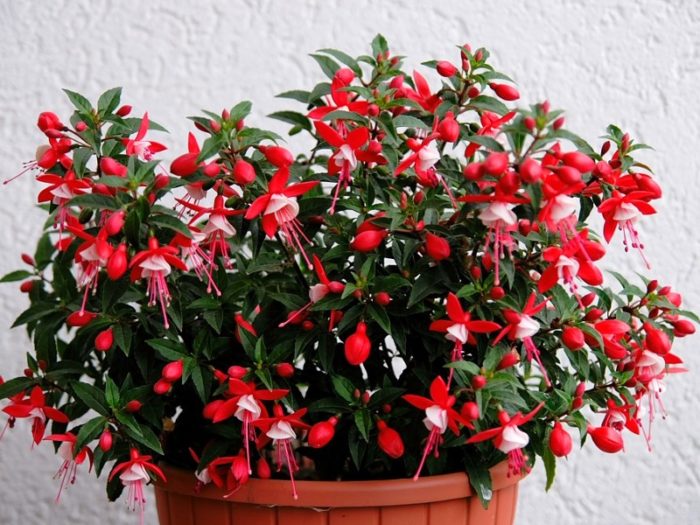

This variety is the most popular when choosing plants for the garden, as it feels good outdoors. Skilled gardeners grow a whole tree from a small bush without unnecessary branches. But bushy fuchsias grow well even in indoor conditions.
Florists love the following varieties most of all:
- Gotu is easily recognizable by its burgundy flowers and dense stamens at the end;
- Alisson Bell has reddish-purple flowers with a pleasant texture;
- Waist is popular for its rich orange color and unusual shape of the inflorescences;
- Henriette Ernst stands out for its reddish colors with a silvery sheen.
Fuchsia how to pinch

Fuchsia grows up to 5 meters in height. The height of the plant depends on the Fuchsia variety. It is difficult to grow such a giant in indoor conditions. If you pinch the plant in time, it will form into a beautiful and strong bush. Fuchsia grows, how to pinch so as not to harm?
When Fuchsia hibernates in the basement, the plant is pruned in the fall. In the spring, you will have to select dry shoots and leaves. If the plant has overwintered in the room, it must be pruned. All long and thin shoots are carefully removed with pruning shears. There is little benefit from such branches. They will not bloom richly, your bush will not become more beautiful from them. You can use garden shears for pruning.
If the plant is pruned periodically, it will grow in breadth instead of in height. A strong and beautiful bush will form soon.
Pay attention to woody shoots. They break down, pull a lot of nutrients from the soil, but bloom poorly
They also try to cut them off.
Fuchsia grows as a tree, how to pinch in this case? Plucking Fuchsia is carried out in winter, when the life processes of the plant slow down. In the spring, you get a lush bush. If the crown of the flower is not formed, it is pruned in the spring. You can cut the plant to the very stump.
In this case, Fuchsia will wake up longer and bloom later, but a wide bush will form. If the shoots are cut only a third, Fuchsia will turn into a tree and can take up a lot of space.
Special attention is paid to shoots that grow in the place of old branches. These cuttings are the best propagation material.
Any species of this plant propagates by cuttings. As the shoots grow back, 1-2 pinches are carried out. As a result, the plant blooms profusely and has a lush crown.
Young twigs are pinched over the third pair of leaves. In this case, more tillering occurs. If the density of the bush does not suit, the overgrown branches are pinched again. This time it is done near the second pair of leaves.
Do not forget that before the color period, the plant needs 2 months to develop the buds. Small-flowered fuchsia varieties with non-double flowers bloom faster than plants with large inflorescences and large double flowers.
Growing a tree or making a bush out of fuchsia? You decide
Diseases and pests
The flower has a fairly good immunity, but there are hardly any pests that can cause problems for gardeners:
- Whitefly is a small insect that often infects plants located on balconies. The main feature is a whitish bloom on the leaves. With severe damage, they turn yellow and fall off. You can cure it by washing with soapy water, but this will only help if the fuchsia is still green. If the defeat has gone further, then only chemical treatment with special preparations will cope.
- Spider mite - affects the plant in dry and warm air. A sign of infection is yellowness on the leaf and yellowish-gray bloom on the underside. To prevent infection with this pest in hot weather, the plant should be sprayed regularly.
Other diseases are most often caused by improper care and inadequate nutrition. So, with excessive moisture in the soil, powdery mildew appears, and with a deficiency of manganese, yellowing of the leaf veins.
Description of fuchsia with photo

First of all, I would like to say that the Fuchsia genus has about a hundred species of plants that belong to the Cyprus family. Its representatives live in the mountain forests of America, and are also found in Mexico, Argentina, Tahiti, New Zealand, Chile, Peru and the Falkland Islands. Under natural conditions, the plant always lives in partial shade, under the canopy of trees.
The leaves of the plant are opposite, in shape they can be either lanceolate, ovate, serrate, or crenate or entire. The fruits of the plant are quite juicy, and somewhat resemble a berry.Fuchsia's appearance is either bushy or creeping. It has graceful flowers on thin pedicels, which differ in different colors.
The main feature of fuchsia, which gives it the greatest grace, is the long, brightly colored stamens that protrude outward, and the prominent column of the pistil. All this makes the plant a unique creation.
Types and popular varieties
Over a fairly long period, many types of fuchsia have been bred. This article will only talk about a few.
Fuchsia hybrid
Upright or ampelous shrub. It has quite bright flowers, which are distinguished by their large size. A distinctive feature of this variety of fuchsia is the multi-colored cups and petals. This species has a large number of varieties. Among which there are:
- Litte Bell, since the flowers of this variety are somewhat reminiscent of bells;
- Cecile - the shape of the flowers resembles the skirts worn in the fifties;
- Swingtime - flowers resemble some unknown overseas birds.
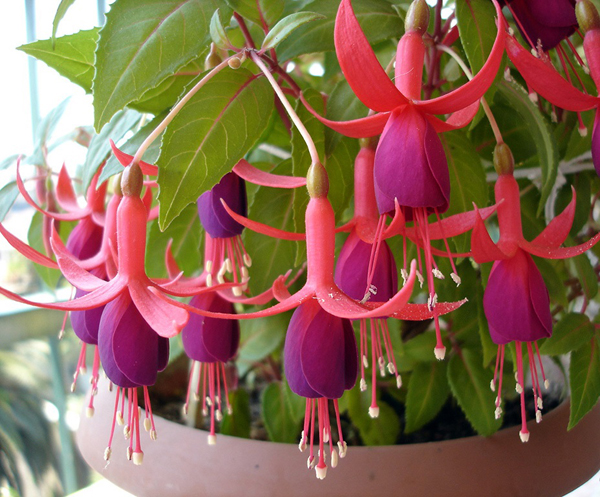 Fuchsia hybrid
Fuchsia hybrid
Fuchsia three-leafed
It is considered a rare type of fuchsia. A distinctive feature is the presence of rhizomes, elegant large foliage with a reddish-green color, short inflorescences, and finally, bright coral flowers. The fuchsia variety is quite hardy. Varieties: Bacon, Constance, Garden News. These varieties are resistant to winter, and can be either in a small shelter, or without it at all, or under the snow.
 Fuchsia three-leafed
Fuchsia three-leafed