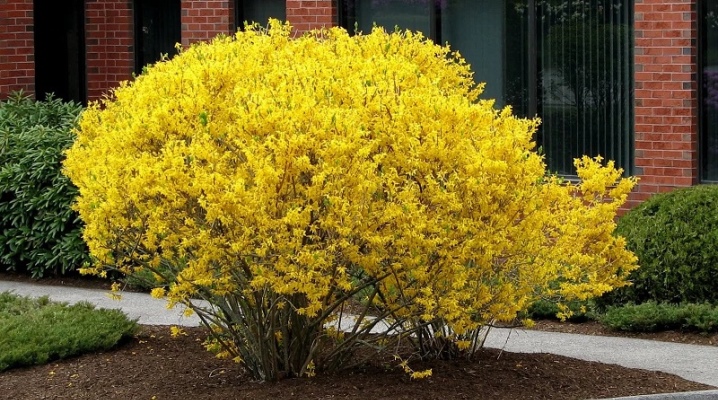
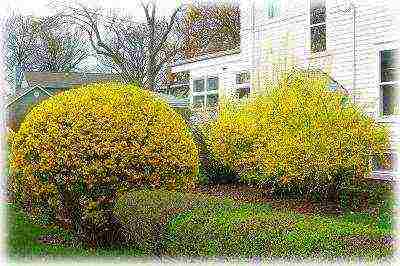Forsythia care
Caring for this plant is not much different from caring for other shrubs in the garden.
Watering conditions
If it rains a lot in summer, then forsythia is not watered. In a dry summer, the bush needs to be watered 2 times a month. Pour at least 12 liters of water under each plant.
After watering, the soil is necessarily loosened. Weeds need to be removed. It is necessary to loosen it so as to ensure the flow of air to the roots (approximately to the depth of the shovel). After loosening, the area near the trunk should be mulched with a compost mixture.
Top dressing
The shrub should be fertilized 3 times. In early spring (early March) a layer of manure is placed near the trunk. Then it is watered. During this time, manure acts as mulch and fertilizer.
In April, a combined mineral fertilizer is applied. You need about 70 g per square meter.
Finally, the soil should be fertilized after flowering. At this time, buds are laid for future flowers. Optimal fertilization - Kemira-universal (about 120 g per 1 sq. M of soil).
During the rest period
During the rest period, sanitary pruning is carried out. Dried and old shoots are removed. The main pruning is done in the summer when flowering stops.
Note! Branches that have finished flowering are shortened by about half. Dry stems are left about 4-6 centimeters to grow
To rejuvenate the tree, you need to cut off all the stems, leaving about 6 cm. This stimulates the growth of young shoots. You cannot do such pruning too often - the bush will grow well, but it will not bloom completely.
Important! The optimal frequency of forsythia rejuvenation is no more than once every 3 years
Preparing for winter
To protect the plant from low temperatures, you need to cover the area around the trunk with foliage. Its optimal layer is at least 10 cm. Bend the branches, sprinkling them with spruce branches on top. This shelter is removed in early March.

Preparing forsythia for winter
You can cover young bushes with spruce branches. If a lot of snow has fallen in winter, then the plant will overwinter perfectly without covering.
Forsythia is a beautiful, unpretentious plant that can decorate any garden or personal plot, if looked after. Care does not require any special skills. Any gardeners can use forsythia to turn their garden, house into a real work of art.
Reproduction of forsythia by cuttings and dividing the bush (with video)
Reproduction of forsythia is most often done vegetatively: by dividing the bush, layering and green cuttings. In the first case, an adult plant is dug out, keeping the root system. Then, with a sharply sharpened pruner, they are carefully divided into 3-4 parts, the resulting plants are immediately planted in the ground and watered abundantly.

In autumn, forsythia is best propagated by root suckers. They are dug up, separated from the mother plant and planted. Then the new plants are pruned, leaving no more than 2-3 buds above the soil level: this promotes tillering of the plant.
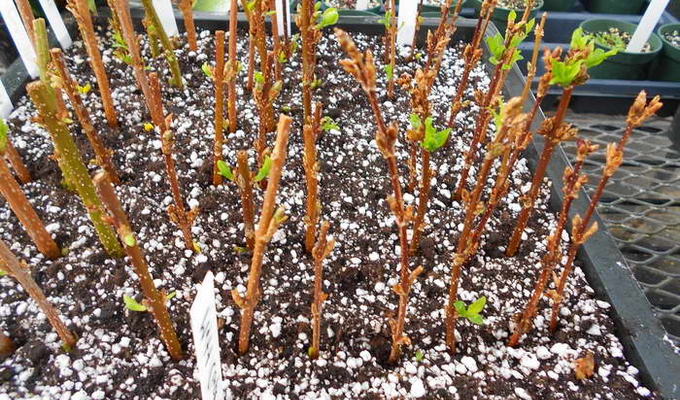
Propagation of forsythia by cuttings - the most difficult method of propagation, it is called green cuttings. Unlignified shoots are cut in June and divided into cuttings 10-12 cm long. All leaves, with the exception of the apical ones, are removed. The cuttings are planted in a greenhouse in a special soil mixture consisting of river sand, humus and drainage, which is taken as expanded clay. The latter is laid on the bottom of the garden bed and covered with a mixture of humus and river sand. Cuttings are planted in this soil, deepening them no more than 2-3 cm.

For full-fledged root formation, cuttings need timely watering. In nurseries, this is achieved by installing special devices with timers in the greenhouse, which supply water at a strictly defined time through spray nozzles.
In summer cottages, the "fog" effect can be achieved if you build a small greenhouse and cover it with a film that practically does not allow sunlight to pass through. In hot weather, you will have to water the cuttings every 2-3 hours. Rooted cuttings in the fall are carefully dug up and immediately planted in a garden bed with well-prepared, loose and fertilized soil for growing.Next fall, the seedlings are ready for digging and transplanting to a permanent place or for sale.
Sowing seeds is carried out in autumn or spring after a mandatory two-month stratification at a temperature of 2-5 ° C. After a year, the seedlings are planted at a slightly greater distance, and at the age of four years, the plants are planted in a permanent place. With seed propagation, forsythia bloom in the fourth year.
Finally, watch a video about forsythia, from which you can learn a lot more interesting things about growing this shrub:
Chubushnik (garden jasmine)
This deciduous shrub is especially decorative in spring and summer in a cloud of incredibly fragrant flowers. For a small garden area, it is better to choose undersized varieties of chubushnik - Dwarf, Gnome, Pompon, Snowstorm, Komsomolets, Enchantement, Manteau d'Hermine, Bouquet Blanche.
The most beautiful varieties of chubushnik - photo and description
A selection of the best types and varieties of chubushnik for the Moscow region and the middle lane.
This plant can be planted as a hedge near your home or as a tapeworm. It grows well next to other shrubs - lilac, weigela, spirea, hydrangea, etc. If you dream of creating a spectacular mixborder, then plant a chubushnik in the background, and bright flowering perennials (peonies, lilies, etc.) in the foreground.
Varieties of decorative chubushniks are relatively unpretentious and mostly frost-resistant, can be grown both in open areas and in partial shade. They can not stand only waterlogging and droughts, in which they quickly fade. Over time, in addition to fertilizing and watering, in the care of the chubushnik, it is imperative to include thinning, because these bushes are usually prone to thickening.
Of course, we have not listed all types of plants suitable for a small area. Depending on the size of the site and the conditions of your climatic region, you can consider as "candidates" for a mini-garden dwarf apple and pear trees, Japanese maple, juniper, magnolia star or large-flowered, weeping willow, heuchera, clematis, cotoneaster, forsythia, ferns , peonies, irises ...
The main thing is not to chase the abundance of species and varieties on one small site, but to competently approach the planning of the space and think over its design in advance.
And if you have already laid out a miniature garden on your site, maybe you will also be interested in a mini-garden in your apartment? Yes, this is also possible!
6 trees for a mini-garden in the apartment
You don't need a large plot to grow a tree. If you wish, you can arrange an orchard even on the windowsill.
Types and varieties of forsythia
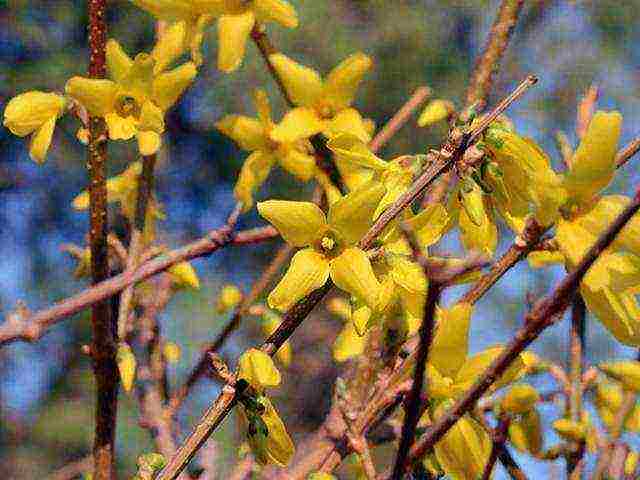
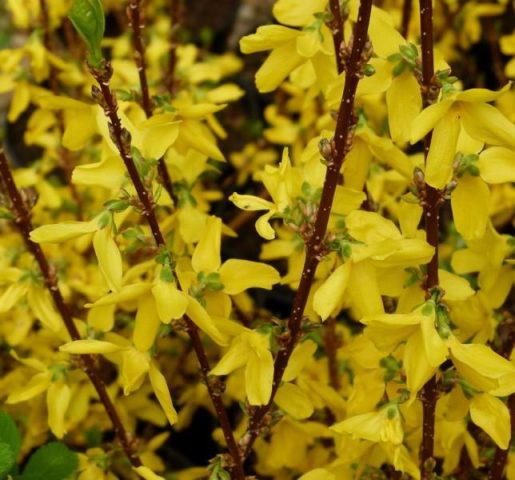
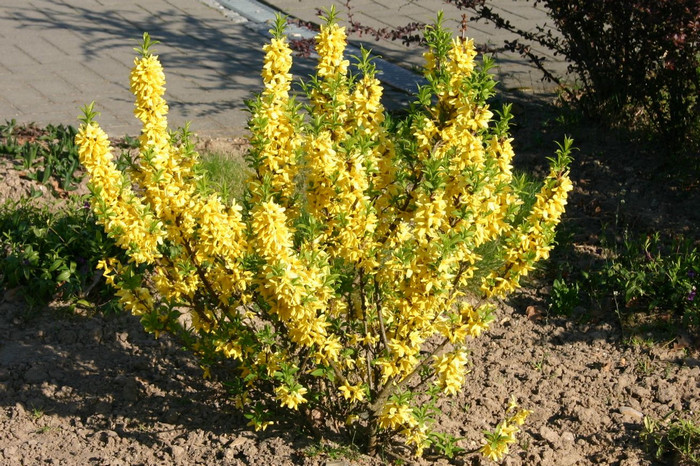
The most common species in culture in our latitudes is European forsythia (Forsythia europaea). It is a low (up to two meters) upright shrub with entire oblong leaves up to 7 cm long. Its flowers are single, bell-shaped, golden yellow in color.
Forsythia giraldiana
Very similar to European, but more sensitive to low temperatures. She is the same height, her stems are also mostly straight, but tetrahedral, yellow-brown in color. Leaves are elliptical, dark green, up to 10 cm long. Blossoms in May with large graceful light yellow flowers with twisted petals.
Photo: Forsythia giraldiana
Forsythia hanging, or drooping, or drooping (Forsythia suspensa)
A taller shrub - up to three meters tall, with a spreading crown, arched, drooping, thin tetrahedral branches of a reddish-brown or olive color. Leaves on old shoots are simple, on growth ones - trifoliate. The flowers are large, up to 2.5 cm in diameter, golden yellow, collected in bunches of several pieces. Several forms of hanging forsythia are grown in culture:
- variegated (forsythia variegata) - bright yellow flowers, yellowish variegated leaves;
- Fortune (forsythia fortunei) with narrow trifoliate leaves, dark yellow flowers, collected in bunches;
- purple-stemmed (forsythia artocaulis) - with dark red shoots and leaves at the time of disclosure;
- and others: forsythia of Zimbold, forsythia deceiving, forsythia hanging from Fortune.
In the photo: Forsythia suspensa
Forsythia dark green (Forsythia viridissima)
High, up to three meters high, shrub with green branches directed upwards. Leaves are dense, simple, oblong-lanceolate, serrated in the upper part, very dark green shade, up to 15 cm long, up to 4 cm wide. Bright greenish-yellow flowers are collected in few bunches. Drought-resistant.
In the photo: Forsythia dark green (Forsythia viridissima)
Intermediate forsythia (Forsythia x intermedia)
It is a hybrid of drooping forsythia and dark green forsythia. It grows up to three meters in height, blooms in the fourth year of life. Its leaves are oblong with a jagged edge, but there are also trifoliate, up to 10 cm long. The dark green color of the leaves remains until late autumn. Bright yellow flowers are collected in bunches of several pieces. Blooms in April-May. Hardy, drought-resistant, growing very quickly. Varieties:
- Beatrix Farrand - bush height up to 4 m, bright yellow flowers with dark yellow stripes at the base;
- Denziflora is a low bush up to one and a half meters high and about the same in volume, the flowers are pale yellow, twisted. Blooms in May for two to three weeks. Afraid of frost;
- Spectabilis is one of the most beautiful varieties: a bush of only one meter in height, but the crown reaches 120 cm in diameter. The leaves are green in warm weather, in autumn they are purple and bright yellow. The flowers are dark yellow up to 4.5 cm in diameter and bloom at the end of April.
In the photo: Forsythia intermediate (Forsythia x intermedia)
Forsythia snow, or white (Forsythia abeliophyllum)
Reaches a height of 1.5-2 m. Leaves are oval, up to 8 cm long; in summer, the underside of the leaves acquires a purple hue. The flowers, as the name implies, are white, with a yellow throat, pale pinkish in buds.
In the photo: Forsythia snow, or white (Forsythia abeliophyllum)
Forsythia ovoid (Forsythia ovata)
Low shrub - from one and a half to two meters in height. Branches are spreading, grayish-yellow in color. Leaves up to 7 cm long, bright green in summer, acquire a purple hue in autumn. Single bright yellow flowers up to two centimeters in diameter. It blooms earlier than all other types of forsythia, grows rapidly, hardy and drought-resistant. Popular varieties:
In the photo: Forsythia ovate (Forsythia ovata)
- Spring Glory - up to three meters high, green leaves in summer become variegated in autumn - from pale yellow to dark purple. Blooms profusely in May with bright yellow large flowers;
- Tetragold is a bush up to one meter tall, dark yellow flowers up to three centimeters in diameter. Blooms from mid-April;
- Goldsauber is a valuable and very popular variety with large golden yellow flowers. Frost resistant. Blooms from mid-April for about three weeks.
Phlox: a description of growing from seeds Freesia: growing in the garden and at home
After this article, they usually read
Add a comment
The use of forsythia in garden design
Forsythia in landscape design has found its application as an element of mixborders, where it is planted in the back rows. This bright yellow plant looks good in combination with other ornamental shrubs, especially those with dark foliage. Forsythia is used both in single plantings and in complex plant compositions. Due to the fact that the shrub blooms early, it can be planted next to later flowering species.
Forsythia bushes often have a very dense and dense crown, in addition, they grow quickly and tolerate pruning well. Due to these qualities, the culture is often used to create curbs and hedges.
As for single plantings, forsythia look great in wild natural gardens, as well as in rockeries and rock gardens. The advantage of culture is that it grows well in a gas-polluted atmosphere and is capable of purifying the air from harmful emissions. Due to this property, the plant can be used in urban landscaping.
In conclusion, I would like to remind once again that forsythia came to us from rather warm places and even the most winter-hardy of them can suffer in severe winters - part of the annual growth or flower buds die if they turn out to be above the level of snow cover. However, the extraordinary decorative qualities of these shrubs are worth patiently waiting for the next, more favorable year and again to see forsythia in lush bloom.
Features of growing outdoors in the Moscow region
Forsythia is incredibly popular with gardeners and landscape designers around the world, not only for its exceptional aesthetic appearance, but also for its ease of growing. Next, about all the intricacies of this process.
Site selection and planting in the ground
The place for planting the plant should be chosen very carefully, since forsythia does not like drafts, strong winds, and also shade. This means that the landing site must be necessarily sunny, quiet, warm.
 Young forsythia bush
Young forsythia bush
Just as carefully should be approached and the choice of the optimal soil for planting a plant. It must be necessarily light, nutritious and perfectly permeable to moisture. A mixture of leafy soil with sand and humus is ideal for growing forsythia. All components are taken in equal proportions.
Before planting seedlings, it is necessary to prepare planting pits on the site with a size of 0.5x0.5x0.6 m.A strict distance of 1.5-2 m must be observed between the pits (keep in mind that the plant is very spreading and requires a lot of free space).
So, first of all, we pour a drainage layer into the pit, consisting of crushed stone or broken brick (the layer thickness is about 20 cm). Pour coarse river sand from above in a layer 2 times less than the drainage layer. After that, pour out the previously prepared soil mixture. Now you can lower the seedling. Make sure that the root collar remains on the surface. Pour the rest of the potting mix on top and be sure to water the young forsythia.
Subtleties of care
Caring for forsythia is fairly simple, but should be done on a regular basis. The plant must be provided with moisture, top dressing, and the soil must be loose. It is also necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the bush and, if necessary, carry out pruning.
 Forsythia bloom
Forsythia bloom
Watering should not be frequent, but during the onset of drought, at least once or twice a month indulge forsythia bushes with water (1 bucket of water per 1 bush), and after watering, be sure to loosen the soil and, if desired, mulch it.
Advice. During the rainy season, you should refrain from watering the plant: forsythia will have enough moisture that it will receive from precipitation.
The plant should be fed 3 times during the whole season. Fertilizers are applied for the first time in early spring. Spread the rotted manure around the trunk circle and gently pour water (try not to catch the plant itself). Such feeding will become a "catalyst" for active growth and lush flowering in the future.
By the middle of spring, you can apply a complex mineral fertilizer, and with the end of flowering, be sure to please the plant with a universal kemira. This will help ensure that the buds are laid on time for the next year.
 Forsythia needs a sunny spot
Forsythia needs a sunny spot
Pruning a plant is an important stage of care, on the correct implementation of which its vitality and abundance of flowering will directly depend. It is advisable to prune forsythia in the autumn after flowering. All old branches should be pruned, leaving only a small stump, while young ones should be pruned only by a third. Be sure to also regularly prune the branches that reach the ground, as they tend to sprout.
Well, and finally, a few words about the "wintering" of the plant. Certainly some varieties of forsythia are cold-resistant.Nevertheless, it is better to protect the plant from its effects by feeding the soil in the autumn period with potash-phosphorus fertilizer, and then mulching it with a layer of soil containing sawdust. It is better to cover the bush itself with spruce branches, branches, etc.
That's all you need to know about forsythia in order to successfully grow it outdoors in the Moscow region. Good luck!
Reproduction of a yellow blooming beauty
Forsythia propagation works are carried out mainly in autumn. Let's make a reservation right away that seed reproduction, although possible, is "not worth the candle", leave these experiments to the breeders.
Like all shrubs in private gardening, forsythia reproduces vegetatively: by cuttings and layering. Reproduction by layering is the easiest and fastest way to get a new seedling. In the fall, the flexible falling branches are bent to the ground, a shallow incision in the bark is made at the place of the trench, pinned for fixation and added with moist, loose fertile soil.
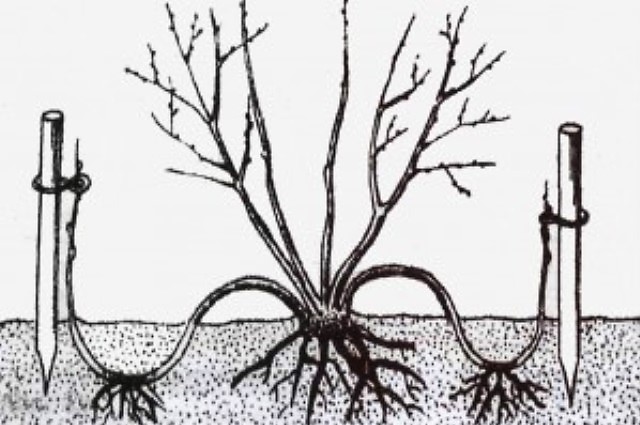
Already next spring you will have a ready-made seedling, which must be separated from the mother plant. Over the summer, the young plant will form a powerful root system, and in the fall it can be transplanted to a permanent place. With this method, the flowering of the shrub will begin already at 2 - 3 years of age.
Also in the fall (September - October), propagation is carried out by lignified cuttings. To do this, the ripened shoots of the new year are cut into cuttings 15 cm long and planted in a school in the open ground or a greenhouse, burying 10 cm into the substrate so that 2 - 3 buds remain. For winter, cuttings are covered with dry leaves and covered with snow during winter.
Rooting and growth of planting material will take place for the entire growing season, and only in autumn the grown seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place. They will bloom a little later than with the first method, but cuttings allow you to get a large yield of planting material. This method is convenient if you want to plant a hedge and arrange an alley.
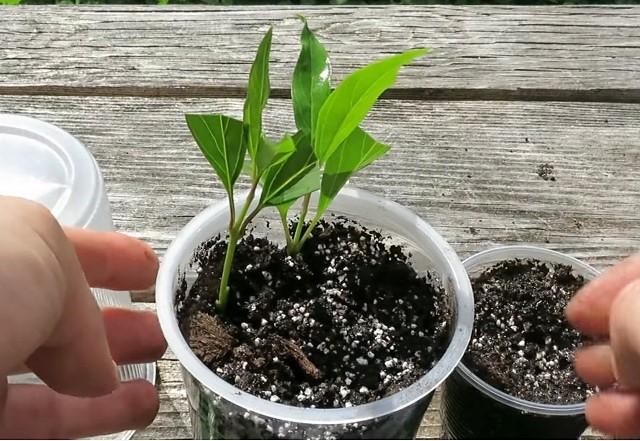

In summer (June), forsythia can be propagated by green cuttings. They are cut from the young growth, the lower leaves are removed, and the upper ones are shortened in two. In this case, it will be necessary to treat the cuttings with growth stimulants and cover the plantings in the school with a film to retain moisture. The amount of maintenance work will also increase: spraying, watering, airing.
The best plants and shrubs
Evergreen
Serbian spruce
Having a height up to 5 meters and crown diameter up to 8m, the spruce feels great in the city. Not whimsical and does not need a haircut, frost-resistant and resistant to pests.

Basic care: it is worth carrying out sanitary pruning and feeding.
Thuja western Brabant
This plant is very popular and for good reason, because it is the most unpretentious, fast-growing, it quickly recovers after cutting and a plant that is undemanding to the composition of the soil. Its fast-growing needles live up to 150 years. It grows in two forms, like a tree and like a bush, depending on your preference.
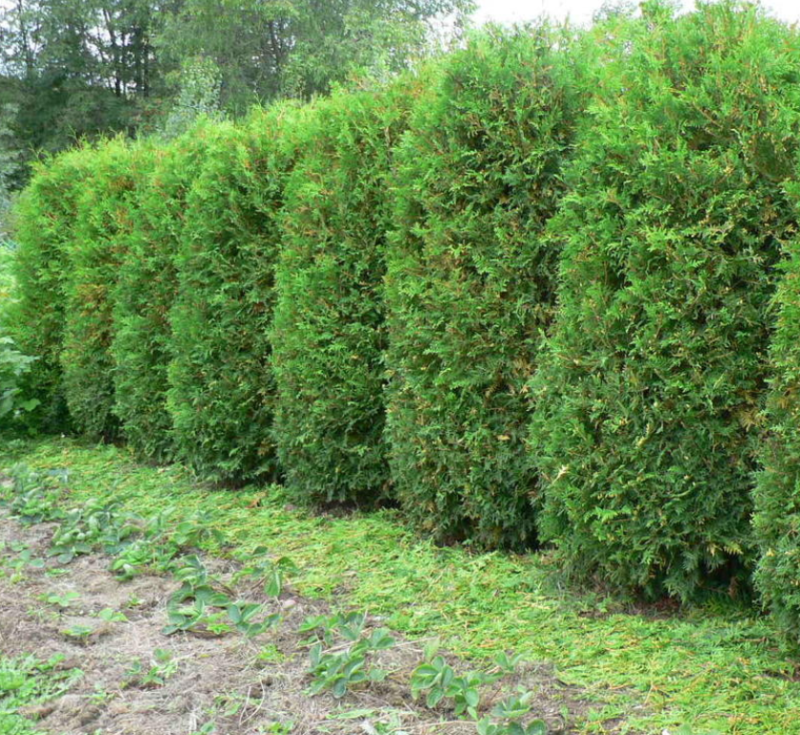

Care: evergreen needles are unpretentious, but in drought it should be watered abundantly, and in frost, cover the soil and, if possible, wrap the bush itself for the first two years of life in frost. Conduct sanitary pruning. Three years after planting, you can trim to size.
Trees
Apple tree of Nedzvetsky
An unpretentious tree with a good growth rate and resistance to pests, diseases and frost. A tree that will delight you for a long time with its unusual crown painted greenish on top and purple below. Beautiful blooming with purple flowers and fruiting with small apples.

Hornbeam
It will help create an impenetrable hedge that keeps you out of wind, dust and noise. Unpretentious, tolerates shaping well and is not afraid of cold weather. Resistant to diseases and pests. In the second half of spring, it is covered with flowering catkins. Prefers moderately moist soil and lighted areas.

Shrubs
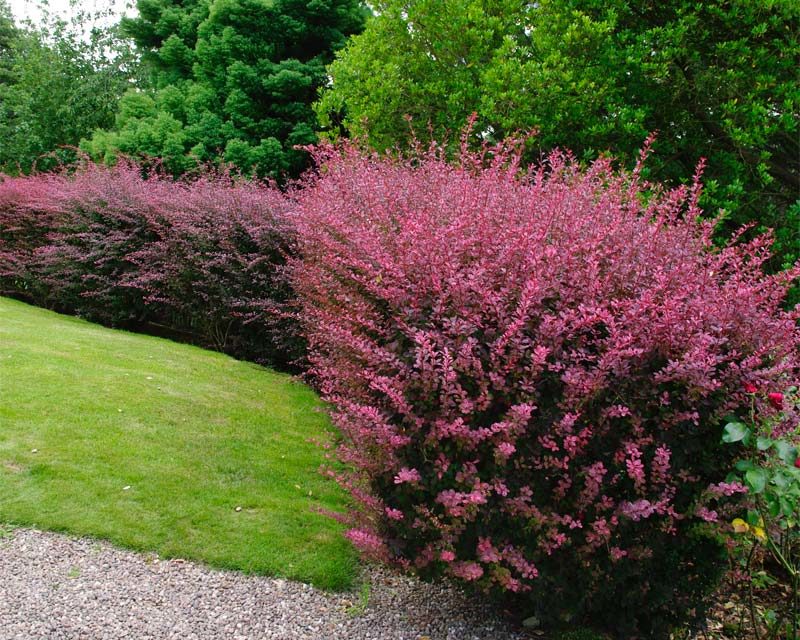
Barberry Thunberg
Any barberry can suit you, but this one stands out for its decorative qualities, its small leaves can have many colors, including: yellow, red, brown, pink. Has resistance to fungi. This barberry is long-growing and its fruits are not edible.

Hawthorn Green Meat
Valued for its dense and dark greenery, it has powerful thorns up to 1.5 cm in length and an oval crown, it can also reach 8 meters in diameter. It blooms in May, and begins to bear fruit in September, but it should be said that it begins to bear fruit after 9 years. Distributed throughout Russia for its unpretentiousness and the quality of an impregnable fence.
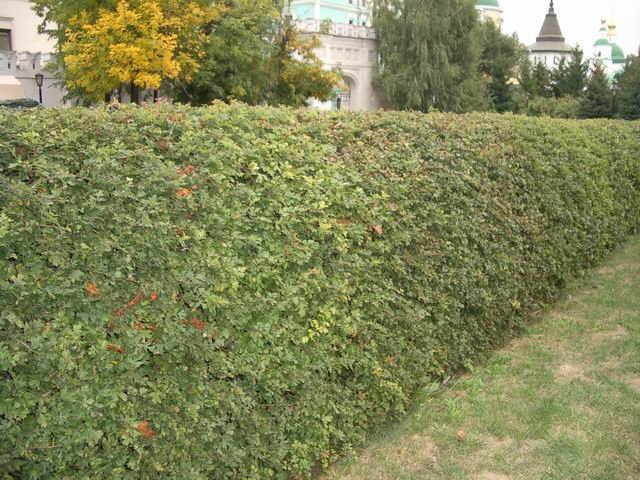

Basic care: sanitary pruning should be done.
Common privet
Unpretentious shrub resistant to bad weather. It grows up to 5 meters in diameter and has small dark green leaves. In spring it blooms with small flowers with a pleasant aroma, the fruits ripen in early autumn and are black in color. It tolerates molding well, which is not necessary, since the shrub also looks great in the wild.
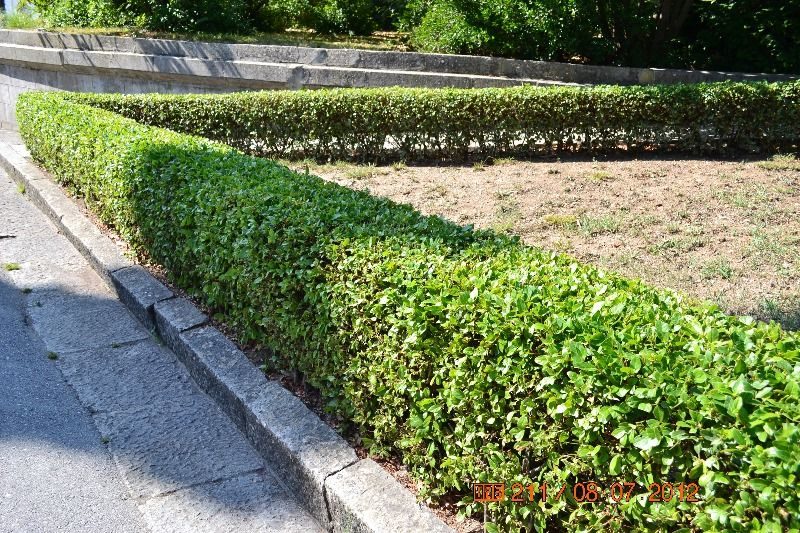

Basic Care: Requires standard care, which includes sanitary pruning and watering.
Alpine currant
Suitable for small meter structures, as well as for the formation of complex shapes. It is resistant to wind and frost, but it does not tolerate heat well. It is susceptible to attacks by aphids, spider mites and rust. It has red fruits that ripen in the middle of summer. Leaves are small and large toothed.
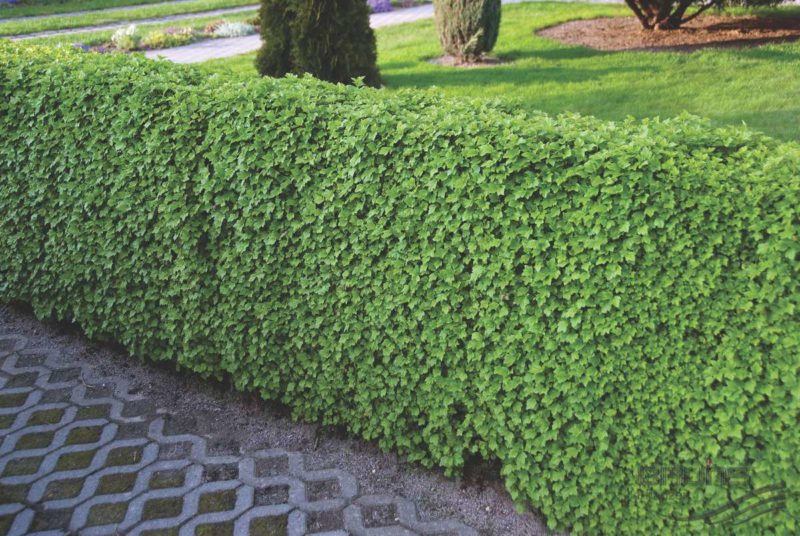

Basic care: attention should be paid to pest control by spraying with special products. It is also necessary to feed in spring and autumn and remove damaged branches.
Action
A shrub with a lush blooming crown and good growing times. Does not like cold and wind, in winter it should be sheltered from frost, and planted in areas well-lit by the sun. He does not like drought, but he also does not like waterlogging; in the fall, watering stops altogether. It is planted at a distance of 2 meters from each other. Loves top dressing that is best absorbed during flowering.
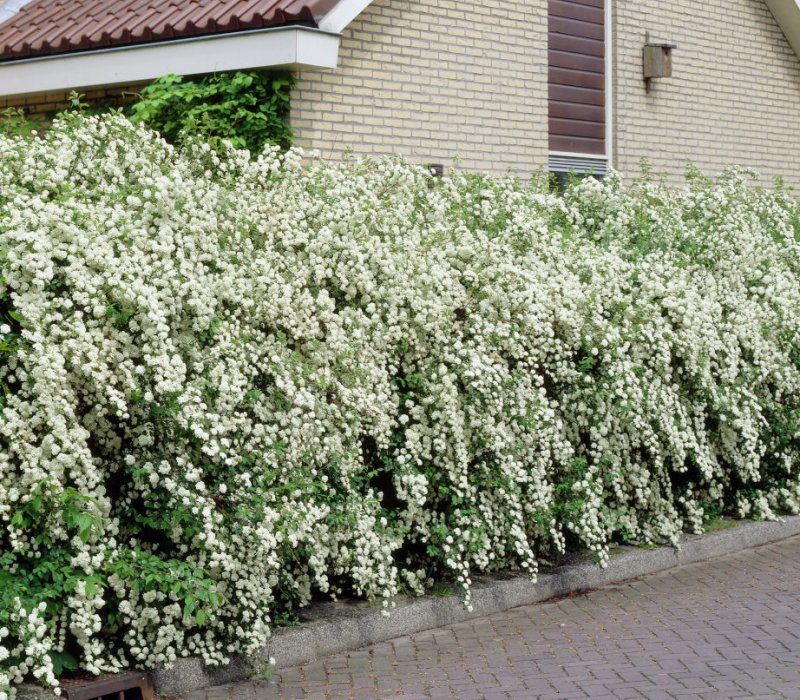

Spirea Japanese
Slowly growing shrub no more than a meter in height and 2 meters in diameter, there are Spireas and up to 2 meters. It has a lush dark green crown and blooms magnificently in the middle of summer with pink flowers. Resistant to frost and shade, but should be covered for the winter. Having short roots, it does not tolerate drought very well and dries quickly. In the dry season, 15 liters of water should be poured under one bush 2 times a month.

Hydrangea
This bush is not tall, has a lush crown and beautiful buds that bloom for up to two and a half months. The plant is hardy and not whimsical, but susceptible to disease. Sanitary pruning and prophylaxis against diseases and pests should be carried out. Having a height of up to a meter and possessing a lush crown, it should be planted from each other at a distance of 1.5 to 2 meters.
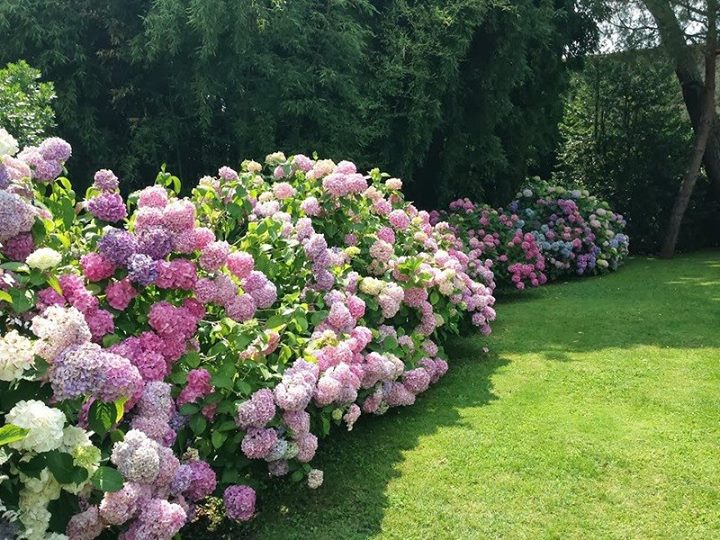

As you already understood, there are quite a lot of plants suitable for growing hedges in the Moscow region. They all have their own characteristics when planting and leaving, and their appearance can be very diverse. Therefore, choosing the best plant for a living fence, which will suit you!
Types and varieties of forsythia
There are 6 main types of shrubs: drooping, dark green, intermediate, ovoid, middle and European forsythia. Of these plants in our country, drooping, intermediate and ovoid forsythia are most often grown. Let us consider in more detail the characteristic features and varieties of each of these species.
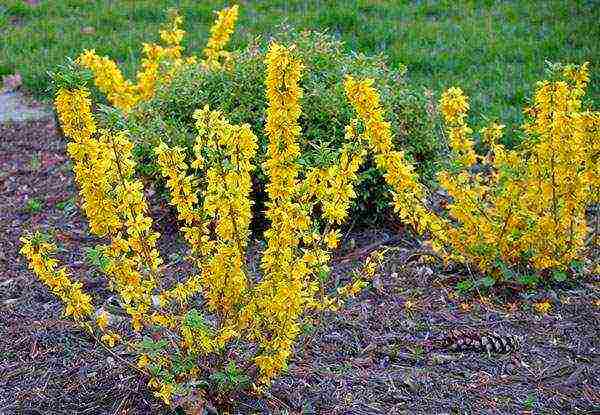
Forsythia drooping
This plant is a medium-sized shrub, reaching 3 m in height. The culture begins to bloom about 5-6 years after planting. Forsythia drooping is called so because of the characteristic type of bush, from the main branches of which long thin shoots hang.
Young branches are decorated with small trifoliate leaves, while on older branches the foliage is ovoid. Culture buds are collected in small inflorescences of 5-6 pieces. The flowering period of forsythia drooping falls in May and is approximately 18 days
When growing this type of shrub, it is important to remember that thin young shoots are very unstable to low temperatures, therefore, with the onset of winter, they should be bent in the ground and covered
The most common varieties of such a plant are the following:
- Forsythia "Variegata" is distinguished not only by magnificent bright yellow flowers, but also by decorative foliage. Delicate green leaves have a light, yellowish-white edging along the edge.
- Forsythia "Fortune" has narrow trifoliate leaves and blooms with rich yellow buds.
- The "Artokaulis" variety is distinguished by the unusual color of the bark and leaves, which are painted in a burgundy shade.
- Forsythia "Siebold" is a low-growing shrub whose branches spread along the ground. The flowers of this variety are rich yellow, bell-shaped, and their petals are beautifully curved outward.

Diseases of forsythia
Forsythia is quite resistant to disease, but does not tolerate stagnant water and long periods of rain. From an excess of moisture in the soil, root rot can begin, this trouble is quite difficult to cure, but it is easy to prevent it during planting of a seedling, choosing higher places and providing a good drainage layer.
Loosening the soil of the near-trunk circle after abundant watering is also a good prevention of this disease. But if root rot has begun, you can get rid of it only by digging out the bush and removing the damaged areas. After that, large cuts must be treated with garden pitch and the healthy part must be planted on another, whiter, higher and dry place in the garden. It will also be useful to water the planting with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
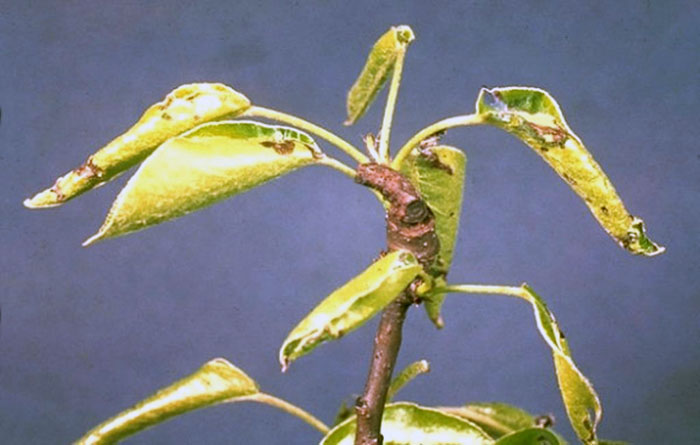

Another serious disease of forsythia is bacteriosis, the main symptom of which is early yellowing of foliage. On the cut of the shoot, dark veins of blood vessels become noticeable. This disease is not cured and leads to the rapid death of the plant, moreover, it is extremely infectious and can affect other plantings on the site. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary to dispose of the diseased plant by burning, without further using its ash. The place where the bush was sitting must also be disinfected with any available drugs or a solution of potassium permanganate.
Moniliosis is a fungal disease of shrubs, it also carries a danger for planting forsythia, dry spots appear on the leaves, prone to overgrowth. To avoid the spread of the fungus, the affected shoots are cut out, the sections are treated with garden varnish, and the whole plant is sprayed with antifungal fungicides. It is better not to leave diseased shoots on the site, the most reliable way to destroy fungal spores is fire.
Forsythia care
How to care for forsythia
Caring for forsythia is not much different from caring for any garden bush. With a sufficient rate of precipitation in the summer, the plant does not need watering, but if the summer turns out to be dry, then forsythia will have to be watered at least once or twice a month at the rate of 10-12 liters for each bush. After watering, you need to loosen the soil and remove the weeds, and you need to loosen it to the depth of the bayonet of the shovel in order to provide air access to the roots of the plant. After loosening, the trunk circle is mulched with compost or dry soil.
Planting and caring for lilacs - detailed information
Forsythia is fertilized three times per season: in early spring, a thick layer of rotted manure is laid out in the near-trunk circle, but not close to the branches and trunk, and then watered abundantly. Manure will become both mulch and organic food for the plant. In April, a complete mineral fertilizer is applied to the soil at the rate of 60-70 g per 1 m².After flowering, when the plant lays flower buds for the next year, forsythia is fed with a universal kemira at the rate of 100-120 g per 1 m².
In the photo: Spring flowering forsythia
Reproduction of forsythia
Forsythia is propagated most often vegetatively. For example, green cuttings about 15 cm long, which are best cut in June. The lower leaves are removed, and the cuttings, having previously been treated with a root stimulator (root, epin or heteroauxin), are planted under a greenhouse in perlite or sand.
Lignified cuttings cut in October can also be rooted, and they are planted directly in the ground in the garden, leaving two or three buds above the surface. You just need to cover the cuttings for the winter with dry leaves. In the spring, when you remove the cover, the cuttings that have taken hold will grow, and by the fall you will have beautiful seedlings.
Growing barberry Thunberg is a decoration of any garden
Forsythia is also propagated by layering: in summer or autumn, bend the lower young shoot to the ground, after pulling it at the base with a wire and cutting the bark on the side that lies on the ground, fix it, sprinkle it with fertile soil, and the shoot will very soon form roots. In the spring, cut this branch from the bush, and the next year the young plant will bloom.
Forsythia also reproduces in a generative way, that is, by seeds, but this is already a conversation for specialists.
Pruning forsythia
Young forsythia bushes are subjected only to sanitary pruning - they remove frozen, shriveled or broken shoots. In adult plants, the frozen ends of the branches are cut off in the spring, while the main pruning is carried out in the summer, when the flowering ends: the faded branches are shortened by half, the old and dried ones are cut at a height of 4-6 cm from the soil level, and then lateral shoots will go from them. Pruning also helps to regulate the density, height and shape of the shrub - cupped or globular.
If you need to rejuvenate your mature forsythia, it is best to cut all branches to a height of 4-6 cm, or at least 2/3, in order to activate the growth of young shoots. But do not abuse such haircuts, because as a result, the bush will grow stronger, but it will stop blooming. It is necessary to rejuvenate forsythia so that it does not lose its decorative qualities, no more than once every 3-4 years.
Pests and diseases of forsythia
This shrub is resistant to both pests and diseases, but sometimes it is affected by wilting, moniliosis and bacteriosis. Withering is treated by spraying with a two to five percent solution Planting a white turf, but there is no salvation from bacteriosis, and the bush will have to be dug up along with the roots and destroyed. Moniliosis is expressed by the appearance of brown spots on the leaves. In case of illness, you need to cut and clean all the affected areas to healthy tissue.
Forsythia has trouble due to nematodes, then you have to disinfect the soil with carbation.
How to propagate forsythia?
- The breeding process takes place mainly in the autumn. It should be noted right away that the seed method of reproduction, of course, can be used, but it is not worth the efforts of the grower. This breeding method should be left to the breeders.
- Like other types of shrubs in private gardening, forsythia is most often propagated by vegetation: cuttings, as well as layering. Propagating a culture by layering is the easiest way of all. In this way, you can easily and quickly get a new seedling. In the autumn, the plastic and falling branches bend down to the soil itself, you need to make a small cut in the bark area, for reliable fixation of the branches it is worth digging in moist, loose, fertile soil.
- Already with the coming of next spring, the grower will have a new seedling, which should be separated from the main mother plant. During the summer season, the plant will create powerful rhizomes, and by autumn it can already be transplanted to a permanent growing area.With this method of cultivation, the flowering of the bush will occur as early as 2-3 years of its existence.
- Also in the autumn (September - October), the plant should be propagated using lignified cuttings. For this process, it is worth collecting ripe shoots from the new year and cut into cuttings 15 centimeters long, and then planted in open ground or in a special greenhouse, deepening the cutting into the soil to a depth of 10 centimeters, so that there is still room for the development of two or three buds ... For the winter, cuttings should be covered with dry leaves, creating a layer of protection, and sprinkled with snow throughout the winter.