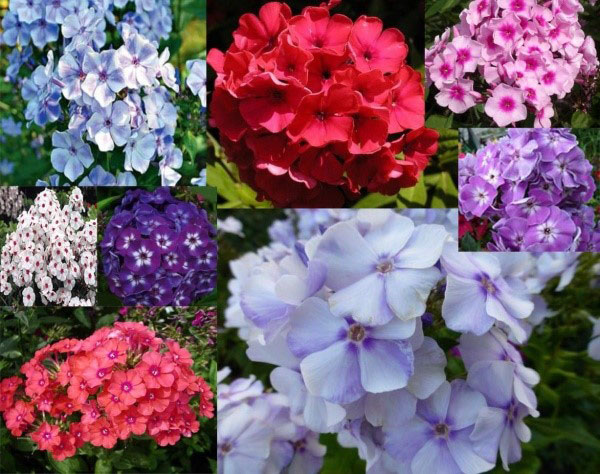
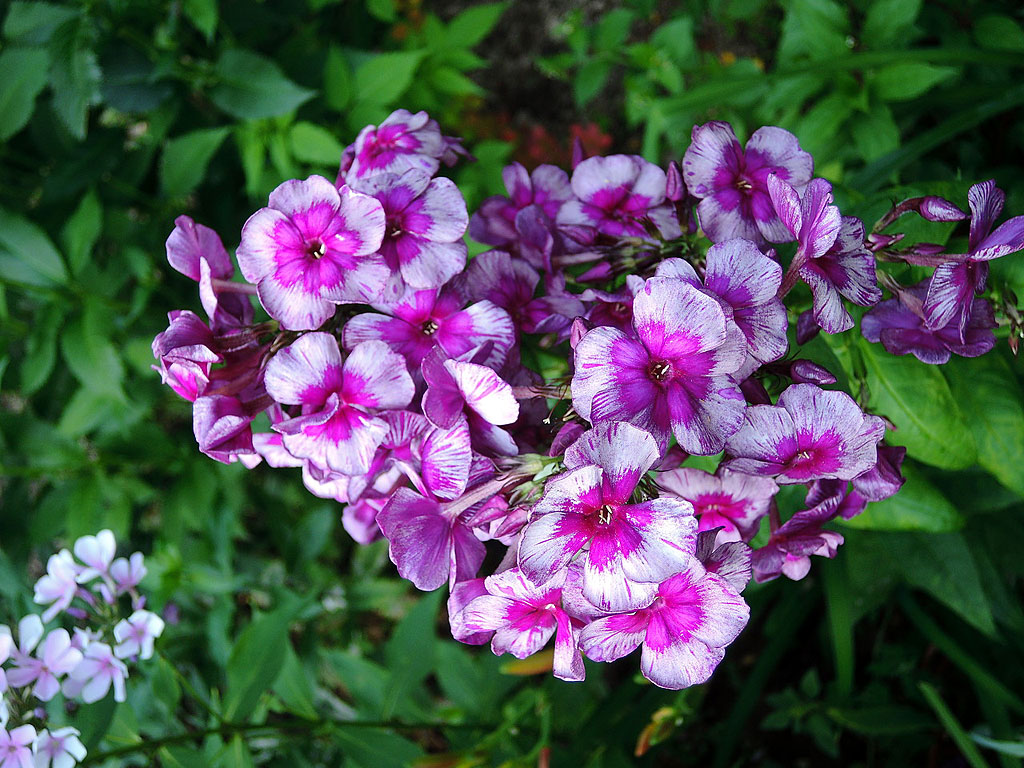
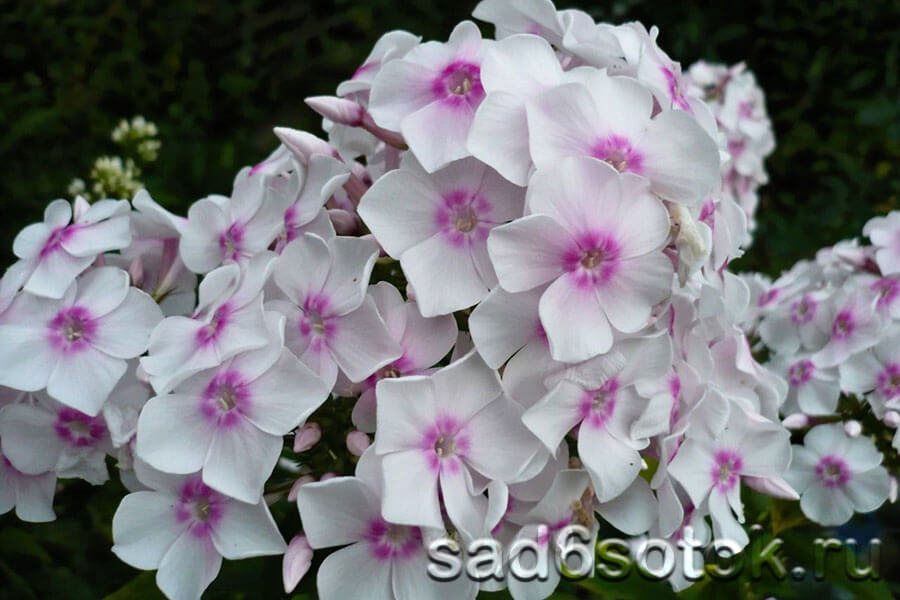
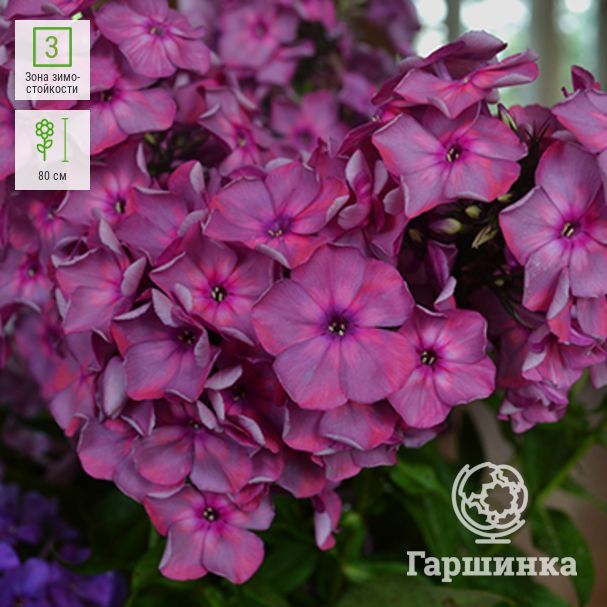
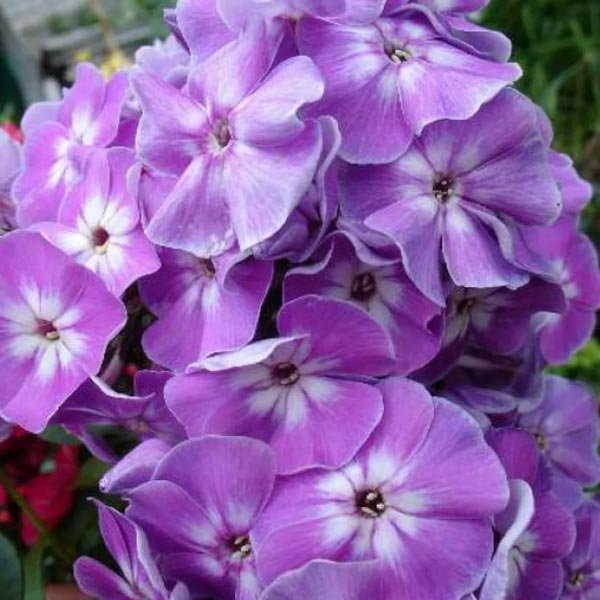
Description of the variety and its characteristics
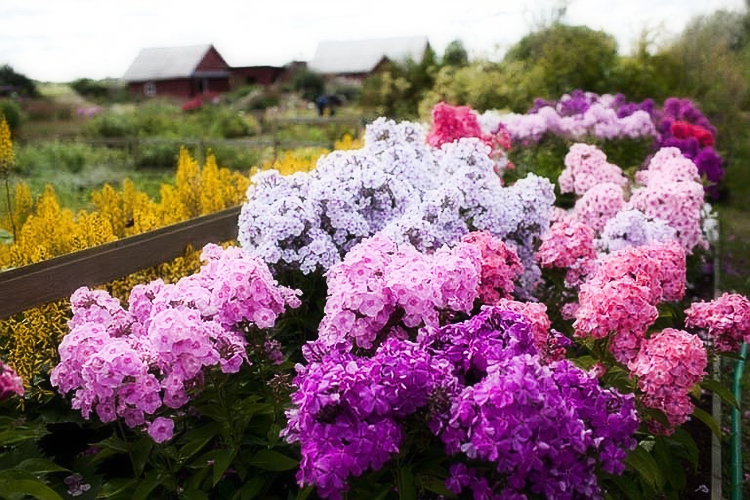
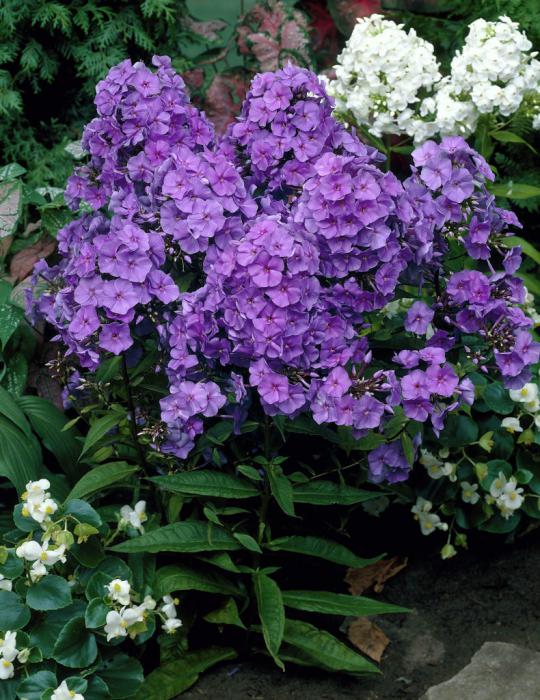
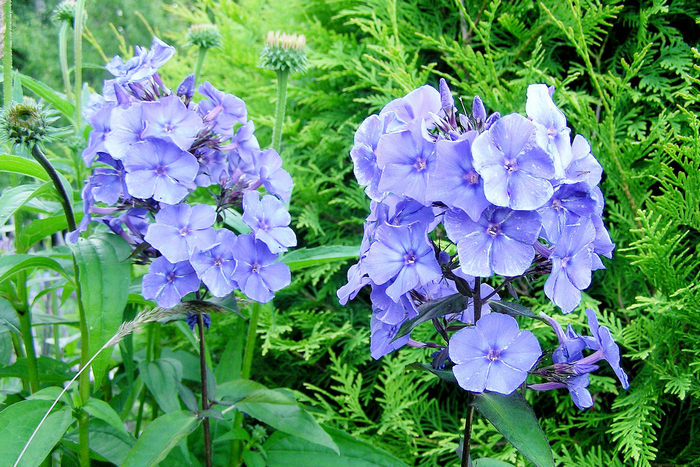
"Blue Paradise" is a highly decorative variety of frost-resistant paniculate phlox of Dutch selection. In landscape design, phloxes of this variety are widespread due to their very colorful and unusual flowering. The height of the bushes varies from 0.6 to 1.2 meters. The diameter of the aboveground part can be 0.3-0.6 meters.
Plants are semi-spreading, multi-stemmed, erect bushes. Stems are well branched, strong, dark green. Flowering shoots are strong, elastic, dark purple or purple-burgundy in color. Leaves - dark green, elongated, lanceolate, with a pointed apex.


Plants have a strong, well-developed root system that is shallow in the ground. With the arrival of cold weather, the aerial part of the phlox dies off, and the root system plunges into a state of dormancy. Phloxes of this variety belong to the group of plants with medium early and medium flowering periods. Under favorable conditions, flowering occurs in the second half of summer and continues until autumn. During this period, spherical or conical inflorescences of medium size are formed on the flowering shoots of the plant.
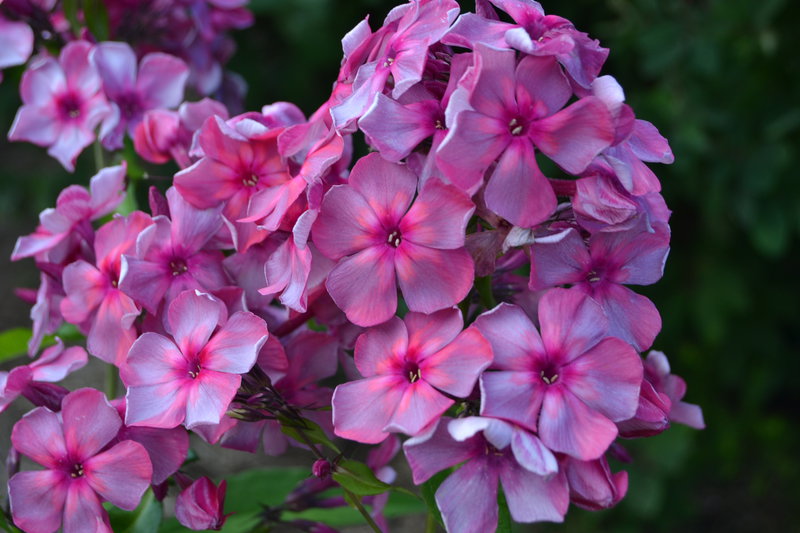
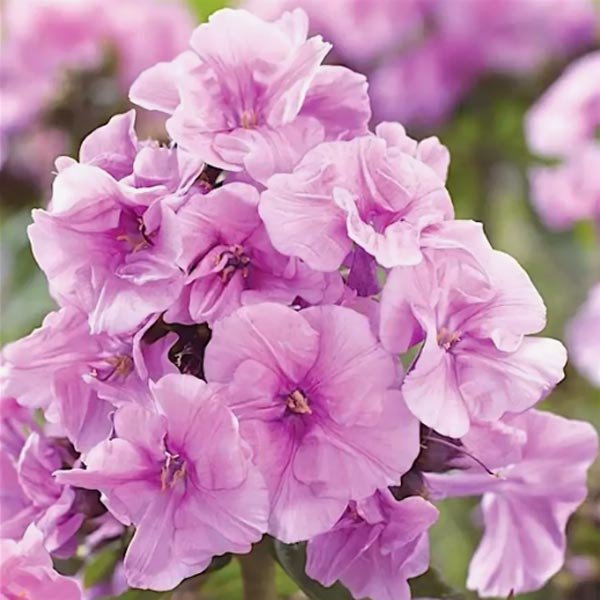
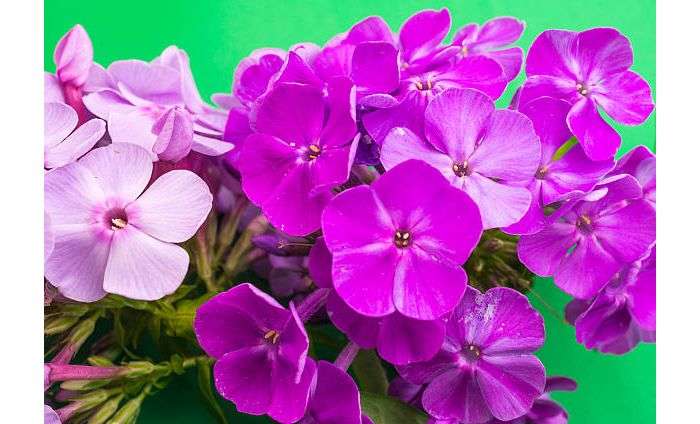
Initially, Blue Paradise phlox buds have a deep dark blue color, which gradually acquires a purple hue. The color of the opened flowers is blue-violet or lilac-purple. The flowers are round, symmetrical, five-petal, reaching 4 or more centimeters in diameter. A notable feature of flower color is its variability during the day. So, with the arrival of twilight, the flowers of phlox of this variety begin to darken, acquiring a deep ink shade.
Phloxes of this variety tend to grow rapidly. With proper care and favorable external conditions, plants actively grow green and root mass, forming beautiful bushes
Another important feature of this variety of phlox is their resistance to fungal diseases. So, observations show that these perennials demonstrate high resistance to powdery mildew pathogens.
Rules for planting varieties of phlox paniculata and caring for them
The order of planting and caring for a plant is formed depending on the region in which the cultivation is carried out. So, in the southern regions, mulching performs the function of retaining moisture, and in the northern regions, protecting the roots from freezing.
Attention: varieties of foreign selection have a significantly lower frost resistance in comparison with domestic ones, therefore they often freeze out in winter in the Moscow region
Reproduction
The easiest way to get a new bush is by cutting off some of the roots of the mother plant. This is done in early autumn or spring, when new shoots appear above the soil level. A good cut has 2-3 well-formed stems, and when planting, they are deepened by only 3-4 cm. Young cuttings, which are dug up in early June, take root perfectly. Usually it takes no more than a month to settle down in a new place. The method of rooting layers is also used. The stems are bent and attached to the ground, spudding with a mixture of humus and peat. By the fall, an independent bush will grow from such a layer.
If planting is carried out by seeds, then stratification is required. Sowing in seedling boxes is carried out a month before the expected date of disembarkation in open ground. Usually the end of May is chosen for this. It is advisable to prepare the soil in advance, clearing weeds, carefully digging up and adding a large amount of organic matter. The plant is very sensitive to abundant watering and soil fertility.
The place for planting is chosen so that a light partial shade falls on the bushes. This technique allows you to achieve brighter shades of inflorescences. The soil is suitable for sandy loam, slightly acidic. The flowerbeds are formed in such a way that the soil forms a light slope along which melt water and rains will flow freely. Planting scheme from 35x35 cm to 50x50 cm, depending on the height of the variety. In one place, the bush feels good for 4-6 years.
Lack of moisture in the soil is the most destructive for phlox. Thin shoots of the main roots are located at a depth of only 15 cm. Therefore, the soil under the bushes must not be allowed to completely dry out. Lack of water affects the abundance of flowering, and the flowers themselves are much smaller. Normally, 1.5-2 buckets of water are poured under one bush in the morning. If tall varieties are selected, then by the end of July they will need support.
Important: do not allow weeds to appear on the flower bed, as many different diseases come with them. Before frosts come to the site, the bush must be completely cut off at the root.
The center must be powdered with copper sulfate. All cut off parts must be burned. In order to avoid damage by powdery mildew, the bushes are not recommended to thicken, and also to be planted in depressions where puddles can form.
Before frosts come to the site, the bush must be completely cut off at the root. The center must be powdered with copper sulfate. All cut off parts must be burned. In order to avoid damage by powdery mildew, it is not recommended to thicken the bushes, and also to plant them in depressions where puddles can form.
Top dressing
For the entire season, phlox will have to be fed only 3 times. For the first time, when young shoots grow back, nitrogen and complex fertilizers are applied. During the formation of buds, phosphorus-potassium mixtures are introduced. The same fertilizer must be applied after flowering is completed to prepare the bush for wintering. Manure is applied at the first planting, or in the spring when the soil thaws.
Phlox diseases.
For example, a disease such as variegation covers the phlox petals with an unusual pattern, disfiguring the appearance of the plant. There is no cure for this disease, so the bush is dug up and destroyed in order to avoid contamination of other plants. The same sentence will have to be carried out if it is found that the plant has been struck by a fungal disease called powdery mildew, which manifests itself as a whitish dull bloom on the leaves and stems.
Phloxes suffer from another fungal disease - phomosis, which makes the shoots fragile and the leaves dry. As a preventive measure, it is suggested to spray colloidal sulfur on the leaves and stems of phlox (but not on the inflorescences), but the air temperature should be at least 18 ºC. Septoria disease manifests itself as dark brown dots on the leaves of plants, which increase in size with the development of the disease. At the first sign, spray the bush and the soil around it with Bordeaux liquid, and after two weeks, repeat the treatment. Another disease, verticillary wilting, destroys the root system of phloxes, but only phloxes growing on acidic soils are ill with them.
Annual phlox - planting and care
Planting annual phlox.
We have already talked about how to plant phlox from seeds. But some growers do not want to put the seeds at risk for fear of severe spring frosts, so they plant phlox seedlings in spring. On seedlings seeds of phlox annual sown in March, shoots appear in a week. The sprouts that appear need light, watering and a moderate temperature. After two to three weeks, the seedlings dive. In the first days after the dive, try to protect the seedlings from direct sunlight to avoid burns. Cover them with newspaper or opaque plastic wrap. Before planting phlox in open ground, you can feed the seedlings with mineral fertilizers two or three times.The concentration of top dressing should be half that for an adult plant. To achieve the splendor of the bush, the seedlings in the phase of 4-5 leaves are pinched.
In May, grown phlox seedlings are planted in a flower bed at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other
It is very important to choose the right landing site. Annual phlox are cold-resistant, drought-resistant, love light, but do not tolerate overheating of the root system
The most beautiful phlox grow in partial shade, and the thicker the shade, the less abundant but longer flowering phlox will have. In the sun, the flowers of phlox quickly fade, in partial shade they retain their color saturation for a long time, and if you planted the so-called "blue" varieties, the flowers of which in twilight light become almost blue, you will have an incomparable aesthetic pleasure from the flowering of phlox grown in partial shade. guaranteed. It is best to plant phlox in high beds, away from trees and shrubs with a highly branched root system.
The garden soil for phlox should contain a large amount of humus. Heavy soils with poor drainage are detrimental to phlox. They also do not like acidified areas, in this case lime will need to be added to the soil. The best soil composition for phlox is fertile sand without clay admixtures - provided it is well watered, it will allow to grow powerful flowering bushes. Sand, organic fertilizers and peat will have to be added to heavy loams. Seedlings are planted in a shallow hole, into which vermicompost or compost (or two handfuls of ash) is added before planting, the roots are straightened horizontally.
Reproduction
Perennial paniculate phloxes reproduce quite simply. To do this, you can use 4 methods of preparing a new planting material. The simplest ones are grafting and dividing the rhizome. Also, the method of dropping is not difficult, but in this case, the plant is not recommended to be transplanted to another place. Phlox seedlings can also be purchased at the nursery.
Note! The phlox seed propagation method is used to develop a new shade. The process of preparing and germinating seeds is more complicated than others, therefore it is rarely used.
Cuttings
Cutting is best done in early summer, before the plant has bloomed. To prepare the cuttings, you need to choose a young and juicy shoot. You need to cut at an acute angle at a height of 2-3 cm from the ground. Cut off the top of the shoot and remove the leaves.
Next, you should leave the twig to soak in the root solution for several hours. After that, the cutting should be placed in the prepared nutrient soil to a depth of 5 cm, moistened and covered with a glass or plastic cap. After about 30 days, phloxes take root and can be replanted to their planned location.
Important! All sections should be done with a clean instrument to avoid infection.
Rhizome division
The optimal time for phlox reproduction by dividing the root system is autumn or early spring. To do this, the bush must be carefully poured in without damaging the root system, and divided into several parts. Each lobe should contain 2-3 strong adult shoots. After complete separation, phlox can be planted in open ground.
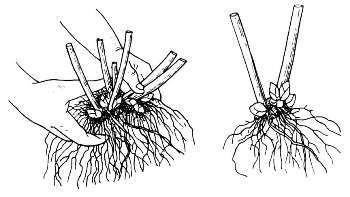
Reproduction by dividing the roots must be done very carefully.
Digging in layers
This method is ideal if you want to enlarge the shrub in diameter and make it lush. For digging, a young shoot is selected, pressed to the ground and covered with a layer of nutrient soil. By the end of summer, an independent shoot grows from the cut.
Top dressing for beautiful flowering
Due to the fact that flowers grow in one place for several years in a row, phlox fertilization is simply necessary if you want to see beautiful, healthy and lush plants. It is customary to divide the timing of top dressing into several stages:
the first feeding of phlox is carried out after May 10-15 with liquid mullein (1:15, 10 l / m²) or ammonium nitrate (3/4 tablespoons per bucket);
the second fertilization is carried out in early June, using mullein or chicken droppings, and superphosphate (1/2 tablespoon) and potassium salt (15 g) are added;
the third feeding usually occurs at the beginning of July. You can use all the mineral components listed above and organic fertilizers. The only condition in this period is the need to reduce the nitrogen dose by 1.5-2 times.
Subsequent feeding is carried out depending on the state of the plants - usually late-flowering phloxes are fed at the beginning of August, excluding nitrogen, only potassium salt (15-20 g) and phosphorus (1/2 tbsp) are added.
In addition to the above recommendations, you can purchase special complex fertilizers in stores and feed them according to the instructions on the package. Some summer residents and gardeners quite often use humic fertilizers and preparations to achieve lush flowering of phlox.



















































