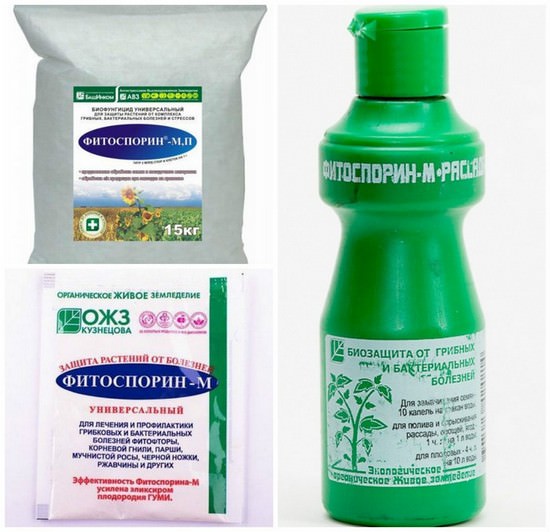
Form of release and characteristics of Fitosporin
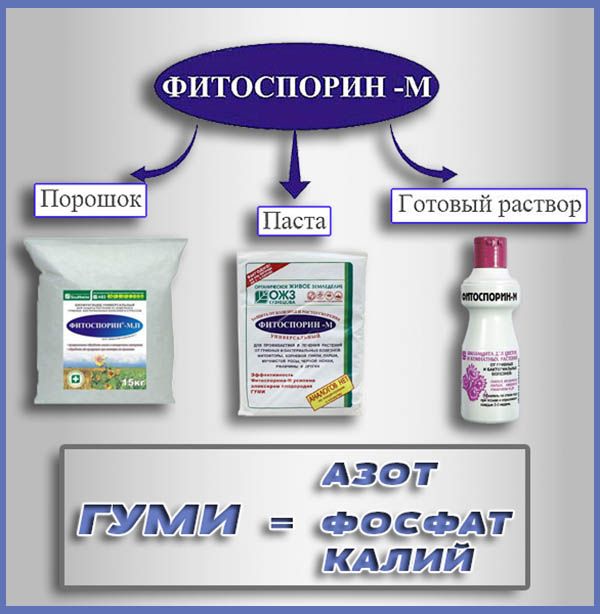
There are 3 types of Fitosporin. These are powder, paste and ready-made solution of the drug. And each of these types has its own characteristics.
Powder
It is used both for the treatment and prevention of phytopathologies. Before use, a solution is prepared from it.
The advantage of the product is the possibility of its long-term storage. Even after opening the package, the drug is able to retain its fungicidal properties for a long time.
Paste
The paste contains a high concentration of humic substances. This makes it possible to achieve a prolonged action of the agent in comparison with the powder. However, the paste is used more to stimulate the immune system of plants and prevent their fungal and bacterial lesions than for their treatment.
Liquid
Liquid concentrate is a ready-made product that is distinguished by a high dose of the active ingredient. Therefore, before use, it must be mixed with clean water. It is used mainly for spraying crops on the leaves. With its help, you can process not only garden or garden plants, but also indoor, ornamental ones. It is also allowed to spray the fruit crop with a solution before storing it.
How to use phytosporin for the protection and treatment of plants in the garden and vegetable garden
The phytosporin instruction for tomatoes indicates that the treatment should be carried out with the following frequency:
- for vegetative and fruiting plants - once a week during rains and once every 2 weeks in dry weather, it is best to spray 2-3 hours before or immediately after rain;
- for watering the soil under the root, the frequency is 1 time per month;
- for spraying shrubs and fruit trees, apply 2 times a month;
- water indoor plants once a month in cold weather and 2 times in summer.
Dosage and dilution depends on the form of phytosporin.
Powder instructions for use
It is necessary to prepare the solution no earlier than an hour or two before use.
It is important to know how to properly dilute phytosporin powder and observe the proportions for each crop indicated on the package.
Since the drug is a live bacterial culture, the temperature of the water for the solution should not exceed 25-28 degrees, otherwise beneficial microorganisms will die. The dosage is as follows:
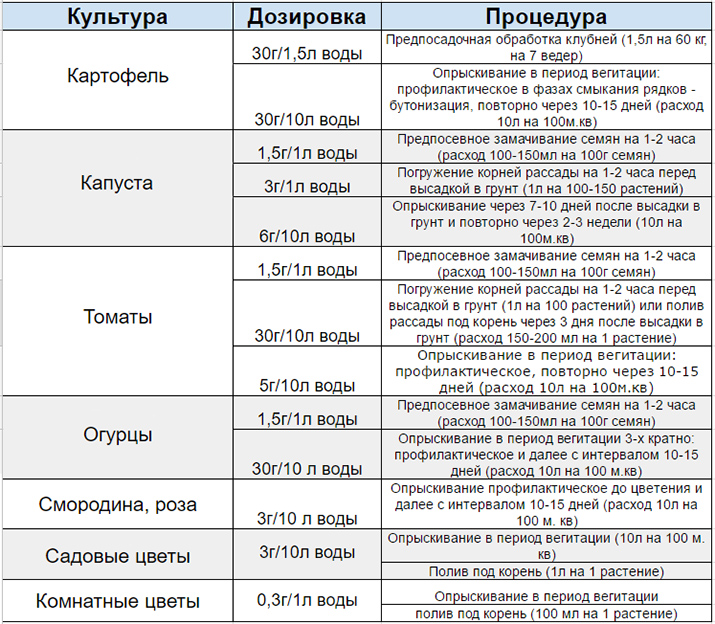
- To soak seeds of tomatoes, peppers, eggplants and other crops, you need 0.5 tsp. Dissolve the powder in 100 ml of water and let the seeds stand for 2 hours, then dry.
- To process potato tubers before planting, stir 10 g of powder (3 tablespoons) in 0.5 liters of water and spray the planting material with this solution. Enough for 20-25 kg of potatoes.
- Before planting seedlings and bushes with a bare root system, it is necessary to dilute 10 g of powder in 5 liters of water and soak the roots for 2 hours, and after planting, water the soil with this solution.
- Preventive feeding of tomatoes with phytosporin is carried out by spraying the leaves and watering every 10-14 days with this solution: for potatoes and cucumbers 10 g per 5 liters of water, for tomatoes and other nightshades - 5 g per 10 liters, for cabbage and legumes - 6 g per 10 l.
- To treat tomatoes with phytosporin, the powder must be diluted at the rate of 10 g per 10 liters, processed 3 times after 1 week along the top and bottom of the leaves, with watering of the soil.
- For indoor plants, the dosage is 1.5 g of powder per 2 liters of water. From mold on violets - 1.5 g per 1 liter of water.
- Soil processing in the beds in greenhouses in autumn and spring is carried out by watering with such a mixture - 5 g of powder per bucket of water, consumption per square meter of beds is at least 3 liters, in a greenhouse - 5 liters.
- To stimulate the growth of the plant, it is necessary to make a mixture of phytosporin and zircon - take 5 g of powder and 1 ml of zircon for 10 liters of water. How many times to process? Processing is carried out twice - a week after planting the seedlings and when the ovary reaches the size of a quail egg.
Phytosporin paste - how to dilute and apply
This form of the drug is a concentrate with the addition of Gumi - an extract from the mood of organic fertilizers. You don't need to add anything to it. In the instructions for using paste for tomatoes and other garden crops, it is recommended to dilute phytosporin in a concentrated solution in a proportion of 1 part of the paste and 2 parts of water.
It turns out a ready-made brown solution that can be stored all season. This phytosporin solution should be used like this:
- For soaking bulbs and tubers 3 tbsp. dilute the concentrate in a glass of water.
- For seed treatment - 2 drops of concentrate per glass of water, holding time - 2 hours.
- When rooting cuttings and soaking roots - 4 drops per glass.
- Foliar prophylactic spraying of leaves - 3 tsp. 10 liters.
- To feed an adult tomato plant at the root of 5 tbsp. on a bucket of water.
- Indoor plants are watered with a solution of 15 drops per 1 liter, and sprayed with 10 k / l.
Ready phytosporin solution
The description in the instructions says that this liquid is intended for spraying plants on the leaf, as well as for processing vegetables, fruits and berries before storage. Several options for the ready-made solution are on sale:
- Fitosporin-M Biosecurity for flowers and indoor plants - protects and treats indoor plants from fungi, mold, powdery mildew, spotting;
- Fitosporin-M Storage should be used for spraying before laying apples, pears, plums, grapes for long-term storage;
- It is recommended to treat plants with Fitosporin-M Golden Autumn, starting from the second half of August - this will save them at the very peak of the development of diseases.
The dosage for the dilution of liquid concentrates is 100 drops per 2 liters of water.
Fitosporin-M Reanimator is the most powerful concentrate, it is used for infection of tomatoes and other vegetables with late blight and other mycoinfections, it not only stops the development of the disease, but also helps plants to recover. It is used according to the following scheme: the first treatment is 1 part of the concentrate for 2 parts of water, the second and third treatment is every 10 days at the rate of 1 part of the concentrate for 5 parts of water.
Marianna Pavley
Fitosporin instruction
Fitosporin is used for treating seeds, cuttings, preparing the ground before sowing and planting, for spraying vegetative and fruiting plants. Treatments can be carried out in any weather, but after rains, the protective film formed from spraying is partially washed off, so re-spraying is necessary. Frequency 7-14 days depending on the weather. In the period of long, lingering rains, it makes sense to spray 2 - 3 hours before rain or immediately after rain. If Fitosporin is used for irrigation, then the frequency of treatments is 1 month for vegetables and 2 times a month for fruit trees and shrubs. Indoor plants once a month.
Phytosporin can be sprayed on fruit trees and shrubs from scab. 5 g of powder per 10 liters of water can be sprayed as much as you can get from the stairs along the crown. It is best to combine spraying with phytosporin with a growth stimulator - zircon 1 ml per 10 l of water. Spray the first time at the spread of the leaves, the second when the ovary is slightly smaller than a quail egg. Watering fruit trees is probably not justified - too much solution needs to be prepared and not everything will be absorbed by the roots.
Fitosporin powder
Dilute 1-2 hours before processing.
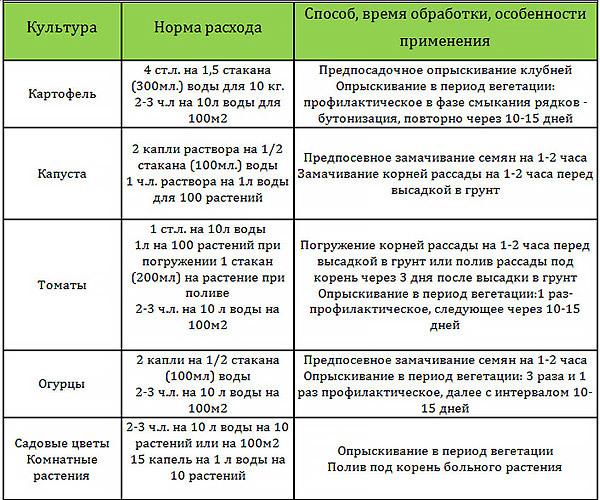
- For soaking tubers and bulbs: 10 g of powder per 500 ml of water, spray with this solution, enough for 20 kg of pre-planting material processing.
- For soaking seeds for 2 hours before planting: 1.5 g of powder (0.5 tsp) per 100 ml of water.
- To soak the root system for the prevention and treatment of rot, before planting seedlings: 10 g of Fitosporin per 5 liters of water, soak for 1-2 hours. After planting or transplanting, you can water the soil with this solution (like regular watering).
- For the prevention and treatment of fungal and bacterial diseases, spraying on the leaf:
- potatoes - 10 g of powder per 5 liters of water, again after 10-14 days,
- cabbage - 6 g per 10 l of water, again after 2-3 weeks,
- tomatoes, peppers, eggplants - 5 g per 10 liters of water, again after 10-14 days,
- cucumbers - 10 g per 5 liters of water, spray three times with an interval of 10-15 days.
- For spraying indoor and garden flowers: as a prophylaxis, 1.5 g (1/2 teaspoon) per 2 liters of water; for the treatment of diseased flowers 1.5 g per 1 liter of water.
- To prepare greenhouses and soil before planting vegetables and berries: 5 g of powder per 10 liters of water spray the surfaces of greenhouses and greenhouses, water the soil, a week before planting.
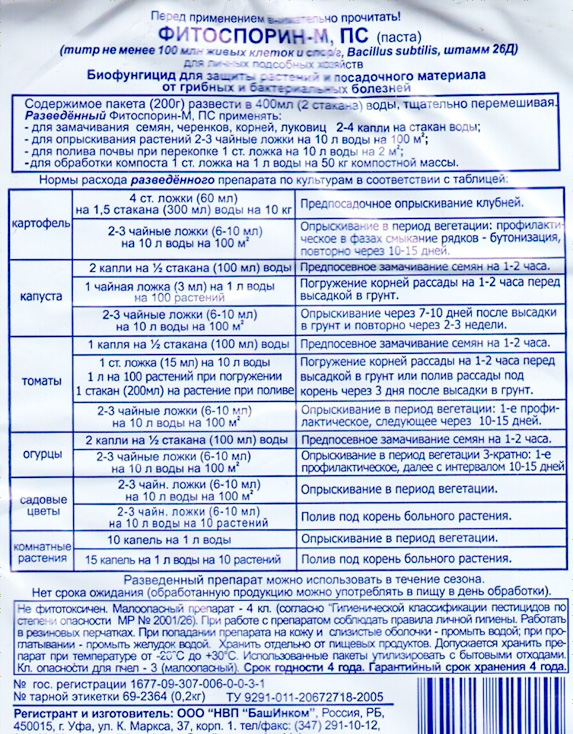
Fitosporin paste
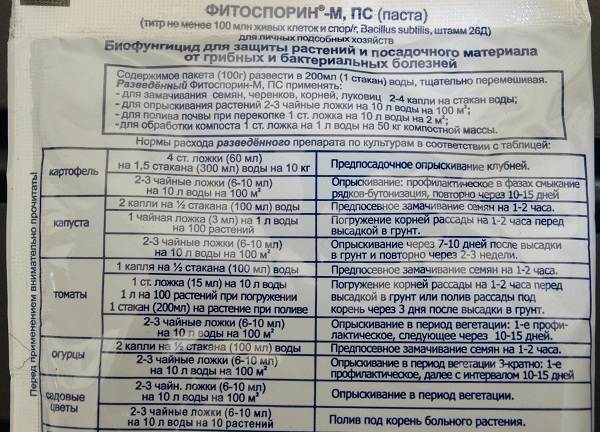
Fitosporin-M paste contains GUMI, so you do not need to add anything to it. Preparation of the solution concentrate: dilute 100 g of phytosporin-m paste in 200 ml of water, or in any other amount in a 1: 2 ratio. The resulting concentrated solution can be stored, and before use, dilute again with water at the rate of:
- Tubers and bulbs before storage or planting, spraying at the rate of 3 tbsp. tablespoons of the solution concentrate in 1 glass of water.
- For soaking the seeds of vegetables, garden and indoor flowers - 2 drops of a concentrated solution in half a glass of water, soak for 2 hours.
- For rooted cuttings: 4 drops of working solution in 1 glass of water (200 ml).
- Spraying vegetables, berries, fruit trees and flowers on a leaf for the prevention and treatment of various diseases - 3 teaspoons of concentrate per 10 liters of water or 4 drops of concentrate per 200 ml of water, watering and spraying.
- Houseplants: 10 drops per liter of water for spraying and 15 drops per liter of water for potting soil.
Fitosporin liquid
Liquid phytosporin (in a ready-made solution) is intended, first of all, for spraying vegetative plants on the leaf (including indoor plants), as well as for spraying vegetables, fruits, berries, tubers before storage. At the same time, the manufacturer offers the same solution in different versions: you can see a bottle with the inscription "Fitosporin - M Biosecurity for flowers and indoor plants", "Fitosporin - M Golden Autumn", Fitosporin - M Storage "- these are identical solutions in terms of quantity beneficial bacteria and used in the same way: at the rate of 10 drops per 1 glass of water (200 ml). You can root the cuttings in the same solution, or soak the seeds.
Consumption rates
The amount of biofungicidal powder and the concentration of its dilution depend on the purpose of use and on the planting crops. To begin with, a working solution (PP) is made. If it is a paste, the 200g sachet is diluted with 2 cups of water. If there are no specific guidelines for a given crop, general recommended guidelines should be followed. PP is prepared at least 1-2 hours before use.
For soaking seeds, cuttings, bulbs and tubers
2-3 drops of the finished composition are added to 1 glass of water.

Tubers and bulbous plants are soaked just before planting for 2-3 hours. After the procedure, small seeds should be dried until the free-flowing state is restored, otherwise their planting will be difficult, and subsequently thickened.
For spraying plants on a leaf
For a large (10L) bucket of water - 2-3 tsp. This amount is enough to process 100 sq.m. landings. This figure is arbitrary, since it depends on the height of the plants, the degree of their foliage, etc.
For a 10-liter bucket, 1 tbsp is taken. solution. Distribute over 2 sq.m. beds.

For the compost pit
1 tbsp is added to 1 liter of water. working solution. This is enough for about 50 kg of the contents of the compost pit. It is recommended to take for this case "Fitosporin" enriched with "gum".

Despite the spread of mineral-based fertilizers, pesticides and fungicides, the effectiveness of the respective preparations is still controversial among flower growers: "chemistry", depending on its purpose, really enriches the soil, removes diseases and pests, but this does not happen without destroying the natural microflora. As a result, plant care deserves the use of exclusively biological agents, and Fitosporin for flowers is one of them.
Phytophthora, powdery mildew, black leg - no matter what ailments the greenhouse is exposed to, fungi and bacteria are always the causative agents of an unpleasant misfortune. Accordingly, using a fungicide to control them makes a lot of sense.
On a note
The drug from Ufa has a low 4th class of toxicity. The threat to living organisms, including humans, animals and beneficial insects (eg bees, ants), is minimized. Poisoning and irritation can occur only if the elementary rules for the operation and storage of the product are not followed: it is necessary to process the plants with rubber gloves, and after that, it is imperative to wash your hands with soap, hide the biofungicide in a place inaccessible to children and animals
Forms of phytosporin release

Forms of production of Fitosporin - paste and powder
Fitosporin is produced-supplied in the form of powder, thick paste, and liquid. The drug has the same positive effect on flowers, regardless of its consistency. The latter affects the convenience of preparation and storage of the biological product: if the liquid consistency is quickly diluted in water, then the pasty phytosporin is easy to freeze, and the powdery one, being packaged, does not take up much space.
On a note
The insert "M" in the name of phytosporin indicates that its composition, in addition to hay bacteria, provides for the immunomodulator "Gumi", which contributes to soil fertility. Following the "M" there may be other letters that serve as markers of the consistency of the substance: "P" - powder, "Zh" - liquid, "PS" - paste, "K" - nanotechnological gel. Since today the manufacturer uses humate in almost every type of phytosporin, many are used to calling the hero of the topic in abbreviated form - "phytosporin"
Phytosporin for orchids: how to breed and apply
The method of application, as a rule, depends on the form in which the drug was purchased. It should be noted that liquid phytosporin is the most practical for home use on indoor plants.
It is best to process in the evening, after sunset, or during the day, while the treated plants should be placed in a dark place (in the bathroom). The frequency of treatments is 1 time per month.
Liquid
Designed for spraying plants on the leaf. In this case, the recommended concentration of the drug is:
- 10 drops per 200 ml of water - for prophylaxis;
- 20 drops per 200 ml of water - for the treatment of an infected plant.
Orchid roots or seeds can also be soaked in the solution.

There is also a variety - Fitosporin-M Reanimator, the appearance of which is shown in the figure below.

Powdery
In this form, phytosporin is most commonly found. It should be diluted 1-2 hours before use in order to awaken dormant bacteria. The amount of powder required for the solution is different and depends on the method and purpose of use:
- Soaking seeds: dilute 1.5 g of powder in 100 ml of water - 2 hours;
- Soaking roots, watering for prevention and treatment: 2 g per 1 liter of water - 1-2 hours;
- Spraying on a leaf for prophylaxis: 1.5 g per 2 liters of water;
- Spraying on a leaf to treat bacterial and fungal infections: 1.5 g per 1 liter of water;
- Substrate treatment: 1 g per 2 liters of water.
Important! 1 teaspoon contains 3 g of powder.

Paste
The paste is the least suitable for home use.It is designed to prepare a large amount of solution and use it in the household (in the country, for example).
Also, the paste includes GUMI - an additive for enriching the solution with microelements (top dressing). This phytosporin is better suited for tomatoes or cucumbers, but not for orchids. A concentrated solution is prepared in a 1: 2 ratio (100 g of paste per 200 ml of water), and then diluted depending on the purpose and method of application:
- Spraying on the leaf: 10 drops of concentrated solution per 1 liter of water;
- Watering the substrate: 15 drops per 1 liter of water;
- Seed soaking: 2 drops per 100 ml - 1 hour;


Compatibility with other drugs and fertilizers
Fitosporin is compatible with many chemicals: fertilizers, insecticides, fungicides, growth regulators, antibiotics. The most important thing is not to combine phytosporin with drugs that have an alkaline reaction - this will destroy beneficial microorganisms.
Advice! Fitosporin with the addition of GUMI is inappropriate to combine with growth stimulants.
Precautionary measures
Fitosporin belongs to the 4th hazard class. The bacterium, which is the main component, is absolutely harmless to humans
However, with all this, the solution can cause slight irritation of the mucous membrane, therefore, general precautions must be followed.
Treatment should be carried out using personal protective equipment, while smoking, eating and drinking should not be. If the solution gets on the skin or mucous membranes, wash it off with plenty of water.
In case of accidental ingestion, drink a few glasses of water, induce vomiting and swallow 2-3 tablets of activated charcoal.
Store the drug out of the reach of children and animals, in a dry place at room temperature. Keep away from food and medicine. It is necessary to store the working solution at room temperature, in a dark place, protected from sunlight.
The water for preparing the solution must be clean, preferably settled or boiled, have a slightly acidic or neutral reaction.
You can check the pH of the water used using indicator paper or special pH tests, which are sold in a pharmacy or pet supplies in the aquarium department. Use water at room temperature.
Important! It is unacceptable to use chlorinated or alkaline water - such water is detrimental to the bacteria Bacillus subtilis.
It is necessary to store the solution at a temperature of 5-20 ° C, while over time, the activity of bacteria decreases and the effectiveness of the drug decreases. Shelf life up to 4 years.
Overdose is not dangerous, however, it leads to excessive overspending of the drug.
Advantages
The fungicide in question is a universal means of fighting infections, therefore it is used on all garden, garden and indoor plants. The product is used for spraying green mass, soaking seeds and cuttings before planting, watering the root system and preparing plants for transplanting. The drug is economical, easy to dilute and you don't have to worry too much about safety at this time.
The product can be used at any stage of the vegetation of plants, even during flowering and ripening of fruits, since the drug has minimal toxicity. For the same reason, it can be safely used right in the apartment, if necessary, to process indoor flowers.
Fungicide has the ability to increase the plant's own immunity, reduce their susceptibility to stress and improve metabolism.
Learn more about how to use and what "Fitosporin" is needed for, you can from the instructions that are attached to each package.
Drug action
How does this drug work? Why is it so effective? Let me remind you again, it consists of hay bacillus bacteria that live in the soil. It is worth noting that this drug is completely safe.These bacteria are used to treat gastrointestinal diseases in infants. With active reproduction, they secrete substances that kill most types of pathogenic fungi and bacteria, such as black leg, late blight.
The drug is used at all stages of cultivation for:
- preparing the soil or soil in the greenhouse before planting;
- for soaking seeds and roots of seedlings;
- for spraying foliage during growth;
- spraying the greenhouse for decontamination;
- decomposition of compost.
I met negative reviews on the network that Fitosporin does not help. I’m sure it doesn’t help because it’s not being used correctly or not for long enough.
Advantages
- Security. As I wrote earlier, these bacteria are completely safe, both for plants and for humans and animals. Therefore, the preparation can be used to treat fruits and root crops, for example, potatoes for the prevention of putrefactive bacteria.
- Anti-stress effect. During transplantation, drought, heavy rains, plants are stressed. Phytosporin helps crops to quickly survive these weather disasters and strengthen immunity.
- Increased productivity. I have been keeping records of the entire harvest for several years and noticed that since the application of the product, the yield of such capricious crops as cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants has increased by 25-30%.
- Efficiency. With proper use, the plant can be saved (you will have to use Fitosporin Reanimator), but it is better to use this remedy as a prophylactic one. Eminent gardeners and gardeners consider it the most effective in the environment of similar bacteriological preparations.
Solution "Fitosporin Reanimator"
In addition to the main components, it contains vitamins and other useful enzymes. Judging by user reviews, this drug saves from many diseases that are usually considered incurable. It is diluted in a ratio of one to twenty at the initial stage of the disease, and in a ratio of 1: 2 in the acute phase. In order to save the plant, the soil and the top should be cultivated every forty-eight hours. Water for dilution of the concentrated composition should be taken boiled and cooled. Its temperature should not be below twenty degrees.
In order for the bacteria to wake up and activate, they need at least two hours. Only after the allotted time can you start using the composition
It is very important when processing the plant to spray the lower part of the leaf plates. The fact is that bacteria and fungi are very often located precisely at the bottom or at the base of the leaf.
The work is carried out after sunset, since beneficial bacteria die in direct sunlight and in the heat.
Ways to use the drug
The tool is used at various stages of flower development. They can work the soil, spill it. By soaking orchid seeds in a solution of "Fitosporin", it becomes possible to prevent the ingress of infection, from which it is not always possible to protect yourself. It can penetrate the cookware.
A solution of "Fitosporin" is used to soak orchid roots. This is done as a preventive measure during transplantation or during the complete or partial revitalization of the plant. During the procedure, the living roots are washed, and the outlived ones are cut with a disinfected instrument, after which the plant must be kept in the Fitosporin solution. Be sure to sprinkle the cut points with cinnamon or crushed coal, and then dry.
For processing, it is effective to spray the leaf mass from a finely dispersed spray gun. For this, it is best to use the liquid form of the drug. Spillage can be done if the plant is in heavy soil.
What is it?

What is Fitosporin and what is the principle of its action based on? The composition of Fitosporin can be quite rich, but the main active ingredient is the bacteria Bacillus subtilis or hay bacillus, which is very widespread in nature.
An uninitiated person may think that its use for growing vegetables and fruits may be inappropriate and dangerous to human health, but this is not the case. Scientists have long proven that these bacteria are not harmful to us, but, on the contrary, are useful. Their ability to suppress the development of pathogenic fungal microorganisms is widely used in cooking, medicine and other areas of human activity.

In particular, in Japan, hay sticks are used to ferment soybeans, and in medicine in different countries they are used to obtain medicines designed to treat digestive disorders.
Benefits of the drug:
- Protection and treatment of a wide variety of fungal and bacterial diseases - scab, dry and wet rot, mold, rust, bacteriosis, Alternaria. The drug is effective against powdery mildew, phytophthora and rot. What other infections and diseases does it help against? From a monolial burn, as well as a wide variety of pests.
- Stimulating plant growth, increasing its immunity.
- High environmental friendliness and safety. The use of the drug Fitosporin-M is also possible during the fruiting period. Moreover, the berries can be harvested and eaten the next day after processing.
- The ability to use throughout the entire growing season.
- Increasing the yield of agricultural crops.
- Compatibility of Fitosporin with insecticides, fungicides and other chemical agents. In addition, the fungal agent reduces their negative effects on plants.
- Possibility of application for processing greenhouses in spring.
- The peculiarity of the use of phytosporin is that it can be used to increase the safety and keeping quality of fruits.
The use of phytosporin
Fitosporin-M refers to systemic drugs that can spread through the vascular system of plants. Its basis is a spore culture, by the products of its vital activity (it produces fungicidal oligopeptides) suppresses the reproduction of pathogens of fungal and bacterial plant diseases:

- alternaria,
- powdery mildew
- bacteriosis,
- bacterial spot (black rot),
- bacterial cancer,
- white spot (septoria),
- brown rust,
- root rot,
- monolithic burn,
- powdery mildew,
- scab,
- peronosporosis (downy mildew),
- penile rot,
- rust,
- rhizoctonia,
- snow mold,
- dry and wet rot of tubers,
- tracheomycosis (tracheomycotic wilting),
- phytophthora,
- phomosis,
- fusarium rot,
- cercosporosis, etc.
And also rot during storage of tubers and bulbs: white rot, gray rot, black dry rot, fruit rot, dry fusarium rot, etc. Fitosporin is not a panacea for all diseases of garden crops and indoor (tropical) flowers, its effectiveness may differ in different plants and depending on the disease ranges from 65 to 95%. These are very good indicators, considering that the drug is low-toxic, and can be safely used even in an apartment.
The great advantage of this preparation is the preservation of living cultures in a wide temperature range from -50 to + 40 ° C. The biological product retains its properties even after freezing and thawing. Under unfavorable conditions for it, the bacterial culture of Bacillus subtilis turns into a spore state, vital activity is suspended, but as soon as the conditions are restored (for example, after thawing), the bacteria become active, inhibiting pathogenic fungi and bacteria. In addition, the biofungicide Fitosporin-M can be enriched with humic bioactive fertilizer GUMI (this should be indicated on the package).Humic acids are needed only for the roots; there is no need to add humic acids for spraying vegetables and fruits, including before storage.
The main advantage of phytosporin-M is the ability to use it at any time at any stage of plant development - during the growing season, flowering, fruiting. The manufacturer guarantees the safety of the crop even on the day of phytosporin treatment. However, there is a significant drawback: the bacteria of the hay bacillus (any of its strains) die in bright sunlight. If you want to apply phytosporin spraying for diseases, do it exclusively in cloudy weather, or at the end of the day, when it is already getting dark. This is how the wife recalls: do not forget to wash fruits and vegetables with hot water, and berries - with cold running and boiled water, before eating and preparing meals.
If you need a fungicide to protect your garden, vegetable garden and home flowers from the group of biological products, pay attention to another drug in this group - Trichophyte