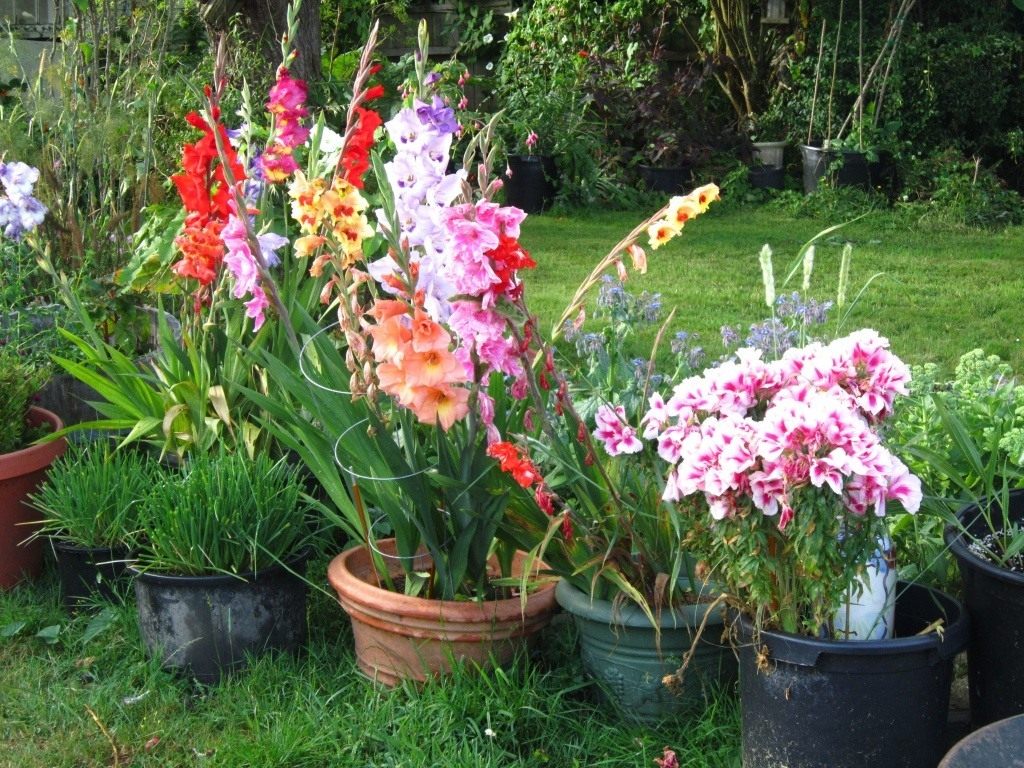
Necessary conditions and proper care
In order for the plant to successfully form buds, and then bloom for a long time, it needs to provide optimal conditions
Next, we will consider the main points that you should pay attention to if you want to enjoy the abundant flowering of gardenia.
Read about the rules for caring for a gardenia at home and what to do with it after purchase in our material.
Temperature
The air temperature in the room should be in the range of + 22-24 degrees in summer, and + 18 + 20 degrees in winter. Such conditions are optimal for a southern flower.
Humidity
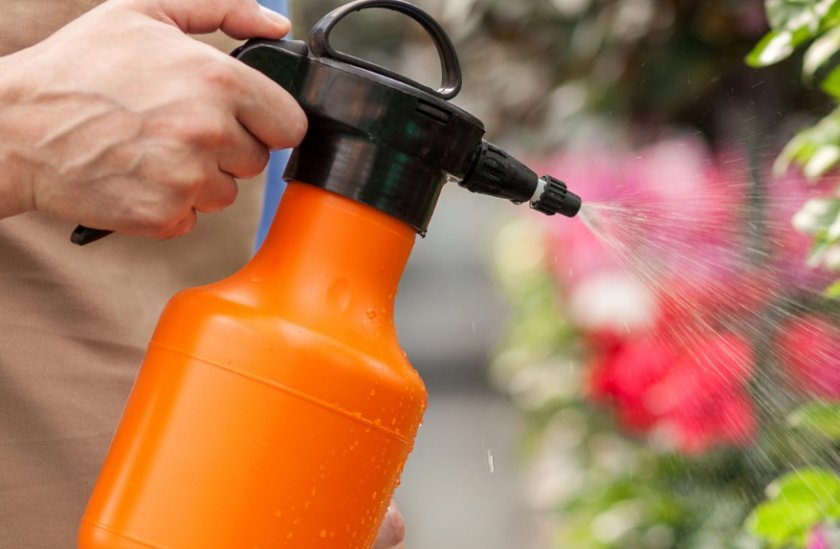
Gardenia needs sufficient air humidity: for this, it is necessary to regularly spray it with gardenia. Use a fine spray for spraying.
If there is a lack of moisture in the soil and air, the gardenia will respond by dropping the buds. You yourself understand that in this case there can be no talk of any rapid flowering.
Important! As soon as the buds bloom, spraying must be stopped so that drops of water do not leave brown spots on the petals.
Top dressing
In order for the gardenia to bloom profusely and for a long time, it needs additional nutrition. It is better to use both organic and mineral compositions. Complex dressings are suitable in the most optimal way - choose a suitable ready-made composition in the store.
Note that with correctly selected and made feeding, gardenia forms abundant lush buds that do not fall off for a long time.
Top dressing should be carried out throughout the entire period of the active growing season: that is, from March to October. The frequency of fertilization is every 7-10 days. For some experienced gardeners, gardenia can bloom almost all year round - in this case, feeding is required to be done all the time while the shrub is blooming.
The plant thrives and looks best if there is enough iron in the soil. This mineral is also reflected in flowering in the most direct way. It is best to use chelated iron salt solutions as a valuable mineral source for gardenia.
On a note! When feeding, exclude formulations containing magnesium and calcium: these trace elements of gardenia are not suitable, and can even destroy the plant.
During the period of active growth and flowering of gardenia, phosphorus and potassium are needed - be sure to feed the shrub with such compositions. Thanks to potassium phosphate dressing, gardenia will begin to bloom more abundantly, more luxuriant and longer.
Transplants
You should know that flowering and transplanting gardenia are incompatible concepts. The shrub reacts to the dropping of peduncles even to a simple overturning of the pot, let alone a transplant. Therefore, the gardenia is transplanted only before the beginning of the growing season, in early spring.
You can find out how to transplant a gardenia at home here.
The soil
The plant loves acidic soil. If you originally planted it in acidic soil, then over time, due to watering, the acidity will decrease.
Therefore, periodically irrigate with the addition of citric acid to the water - this measure will help provide the soil with the necessary acidity. The optimal acidity of the soil will help make the aroma of the blooming beauty the most pleasant and intense.
Read more about what soil is needed for gardenia here.
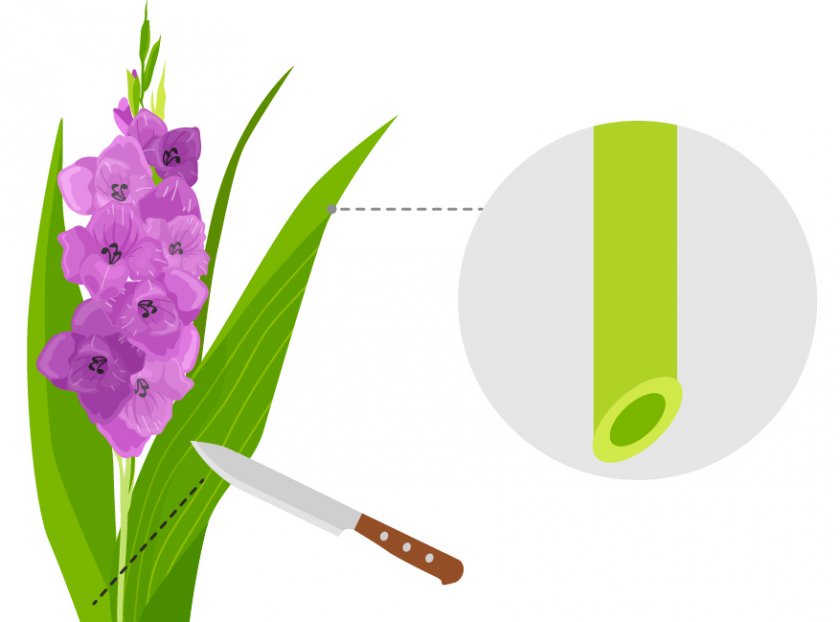
Preparing the bulbs for germination
This blooming culture is very popular throughout Russia, even in the Urals and Siberia. But it does not tolerate winter frosts - corms die when the soil horizon freezes deep. In this regard, they are dug up and stored in the cellars in the autumn-winter period.And with the approach of spring, about a month before disembarkation, they are taken out for further preparation.
So, in central Russia, gladioli are planted in open ground from mid-April to early May. At the same time, there is no need to be afraid of small spring frosts, they are not afraid of gladioli. Accordingly, the corms are taken out of storage in late March - early April. Just at this moment, root tubercles and buds begin to appear, which signal that the bulb is alive and ready to wake up.

Each corm must be carefully examined for the presence of rotten and damaged areas, traces of diseases and pests. To do this, you need to be very careful so as not to damage the sprouts, to clean each of the integumentary scales. All diseased material is disposed of. In the case of the value of the variety or the inability to throw out even one onion, some remedial measures can be applied. Select the least damaged corms, clean them to healthy tissue, treat the cut with brilliant green. After 7-10 days, a protective cork layer forms at this place. Instead of brilliant green, you can use a specialized pesticide or wood dust. How to do it right in this case, it is up to the summer resident himself to decide.
Diseases and pests during storage
Most often, gardeners are faced with gladioli diseases caused by bacteria, viruses and harmful fungi. A lot of troubles are brought about by pests dangerous for bulbs. If we talk about diseases that develop during storage, then they are almost always associated with rotting of the bulbs. The infection gets from the soil during the growing season, it is often transmitted in a latent form from the mother bulb to the young substitute and children. Various types of rot are most common in seasons when heavy rainfall and stagnation of water in the soil were observed.
Fusarium, septoria, sclerotinia, scab, penicillous rot - these are all diseases that lead to massive rotting of the bulbs both during growth and during storage.
Diseases can be noticed by the appearance of the plant and by the condition of the bulbs. If the leaves begin to lighten and rot, then the plant is probably affected by furasiosis. The brown color of the leaves and decay at the base of the stem indicates a lesion with dry rot. The presence of infection in only one plant does not mean that the rest of the gladioli are not affected. Most likely, they are also infected. Diseases often appear in a complex, and several pathogens of various infections may be present on one bulb.
Some pathogens get on the bulb during the growing season, but are invisible when dug up and develop on the planting material if stored improperly.
Pests
In addition to diseases, gladioli can suffer from pests. The greatest harm is caused by thrips - a small sucking insect that feeds on the juice of gladioli. As a result of thrips activity, plants weaken, lose their attractive appearance, and also become carriers of various viral diseases. In autumn, at a temperature of about 10 ° C, thrips migrates to the bulb. If, after digging up, the tubers are not treated with insecticidal solutions and stored in a warm room, then the gardener risks losing the entire collection, as ideal conditions for the development of thrips will be created. To combat the pest, plantings of gladioli are sprayed with insecticides at least three times per season. After digging, the bulbs are processed.
For gladioli, a wireworm is a danger. It bites into tubers, eating away their contents, which can lead to the death of the plant. In addition, fungi can enter the wounds inflicted by insects. To prevent this situation, it is not necessary to plant gladioli after potatoes and carrots and in areas clogged with wheatgrass.
Fertilizers for gladioli when planting in spring and summer
The landing of gladioli occurs in central Russia at the end of April and the first ten days of May.For the first time, a flower is fed when preparing the soil.
Before planting corms for 2 weeks, when digging on 1 square of a flower garden, urea is closed up (20-30 g). Organic matter (compost or humus) is also introduced when planting.
The main recharge is applied when 2-3 leaves appear, when the gladiolus needs nitrogen. Water the plants under the root with a solution (3 tbsp. L. Nitrate per 10 l of liquid).
The flower is fed at least 5 times during the flowering period. In summer, microfertilizers feed on the leaves are effective using:
- copper sulfate;
- potassium permanganate;
- magnesium;
- boric acid;
- gland.
The main crop needs in the summer season are potash salts. Plant nutrition for abundant flowering is a combination of potassium with phosphorus and nitrogen. Fertilize plants at the end of summer after flowering with potassium and superphosphate.
On a note. When using double superphosphate, the agent is poured with boiling water and wait until it is completely dissolved.
Then 200 g of the solution is diluted in 10 liters of liquid and the gladioli are watered.
The substances in demand for plant nutrition in August-September include potassium sulfate or potassium magnesium.

How to feed
Gladioli in the Moscow Region, Siberia and the Urals
Growing gladioli is popular in many regions of Russia. In Moscow and the Moscow region, the planting of the bulbs begins on the twenty-fifth of April and ends on the tenth of May. At this time, the soil has time to warm up to ten degrees, which is very favorable for the development of culture.
In the Urals and Siberia, a favorable time for planting flowers is the second decade of May. If planted earlier, the flowers will not germinate for a long time, since the soil is not yet warmed up enough.
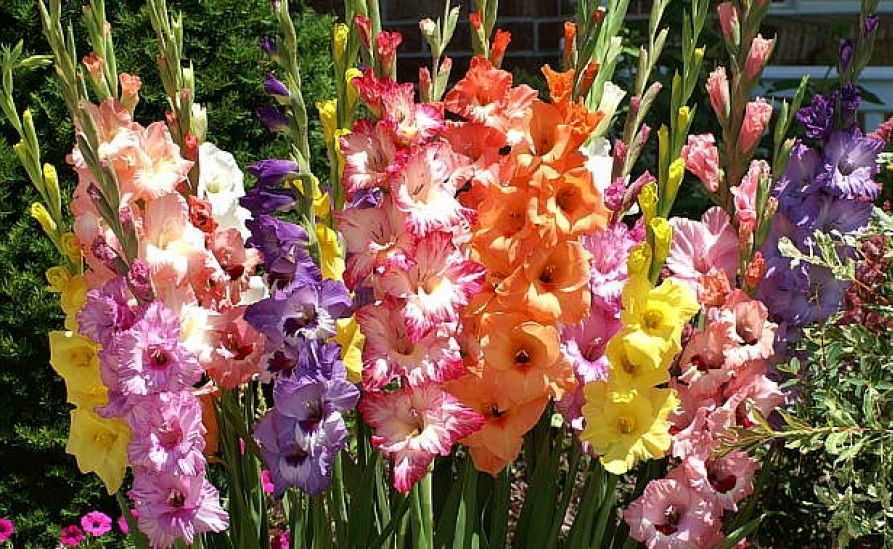
In order for gladioli to bloom magnificently on a flower bed, they must be properly grown. First of all, you need to remember about the timing of planting, then do not forget about the rules for caring for plants. At the same time, top dressing takes the first place in the care of flower queens.
vote
Article Rating
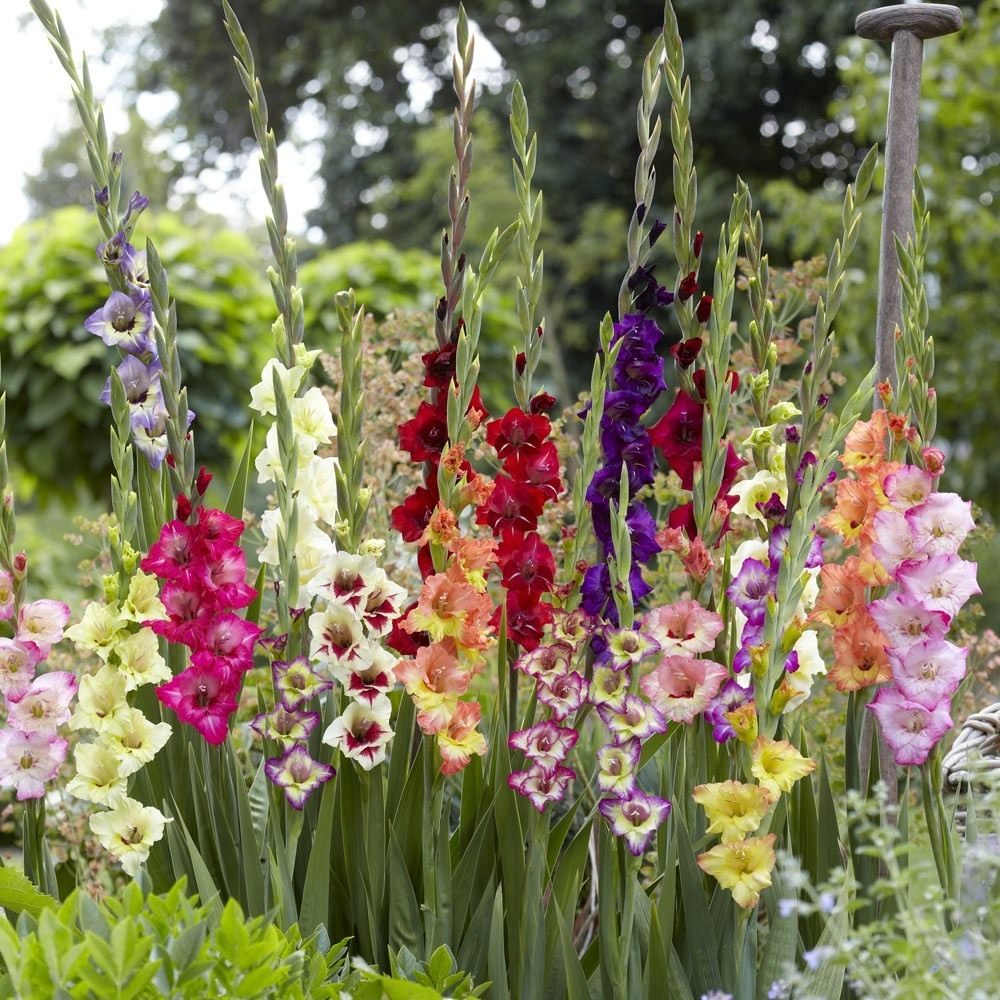
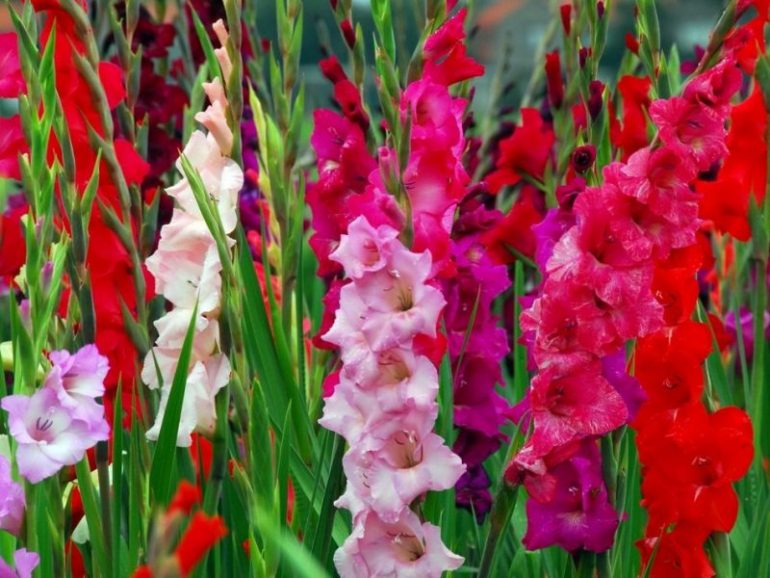
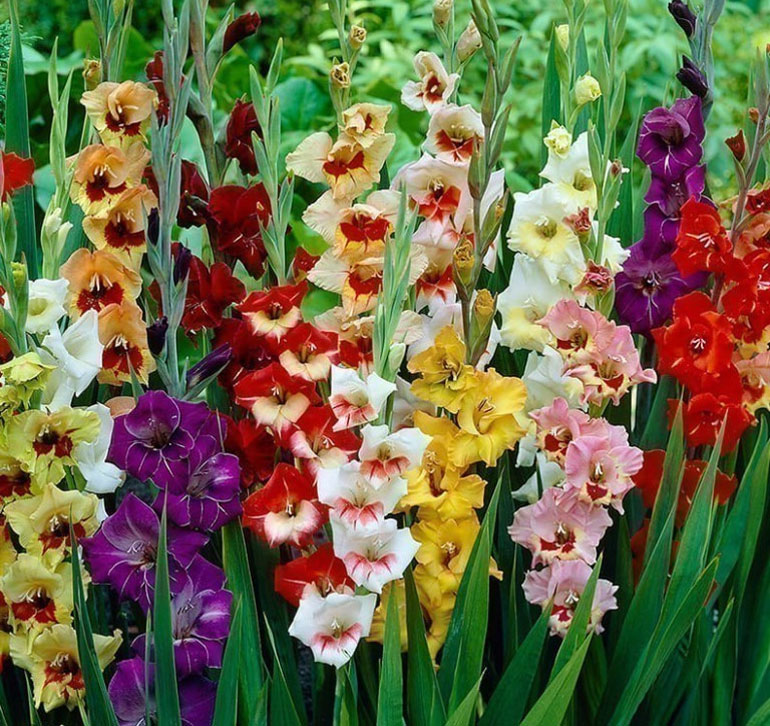
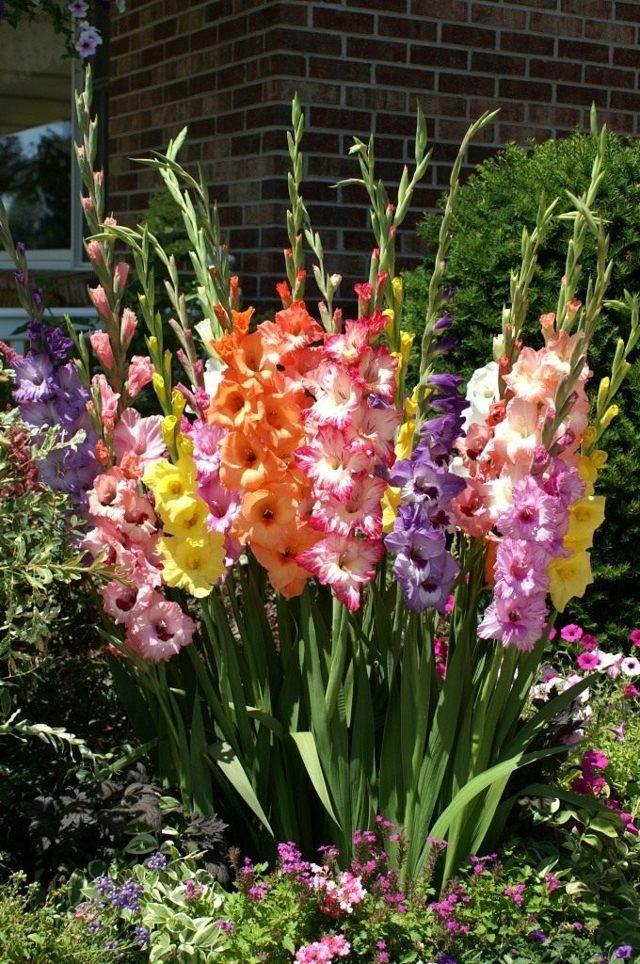
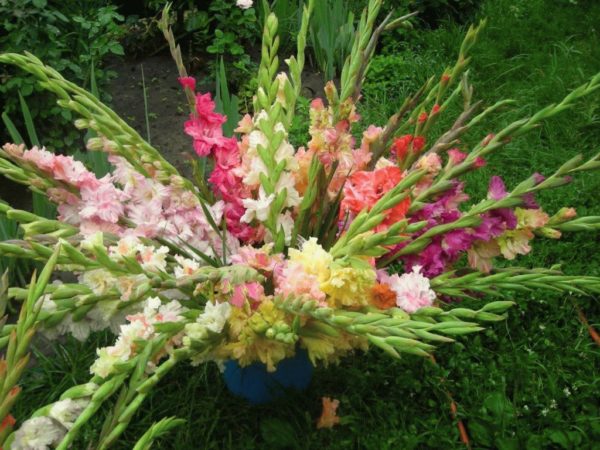
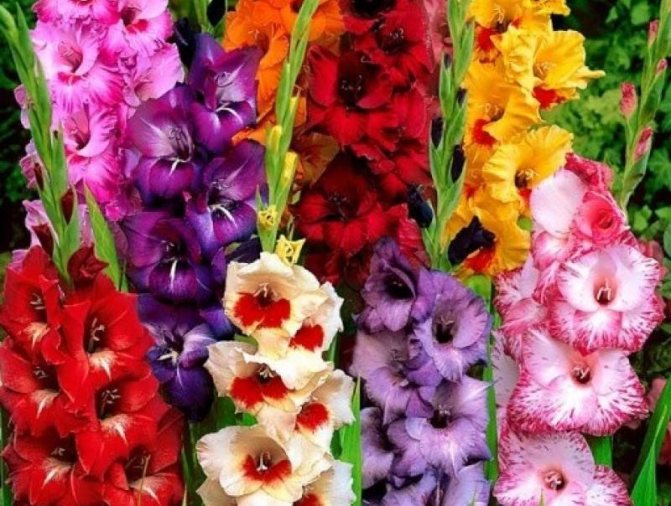
Description of gladioli
The flower is legendary. According to legend, the flowers grew from the swords of captured Thracian warriors, whom the Romans turned into gladiators. 2 captives: Sevt and Teres, made friends in captivity. By order of the Roman military commander, in order to entertain the public, they were to fight with each other. The winner was promised freedom and return home as a reward.

Top dressing for a luxurious bloom of gladioli
But the young men abandoned the fight, at the same time driving their swords into the ground. They were put to death for disobedience. When the bodies of the soldiers touched the ground, a miracle happened: the swords released their roots and blossomed. In honor of the brave gladiators, the plants got the name gladioli. They symbolize friendship, loyalty, selflessness.
The plant is highly prized for its decorative properties. Distinctive features of the flower:
- the form;
- dimensions;
- coloring;
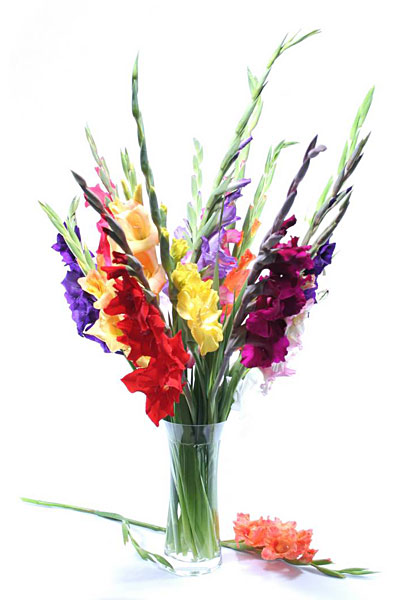
- flowering duration;
- long preservation in the cut.
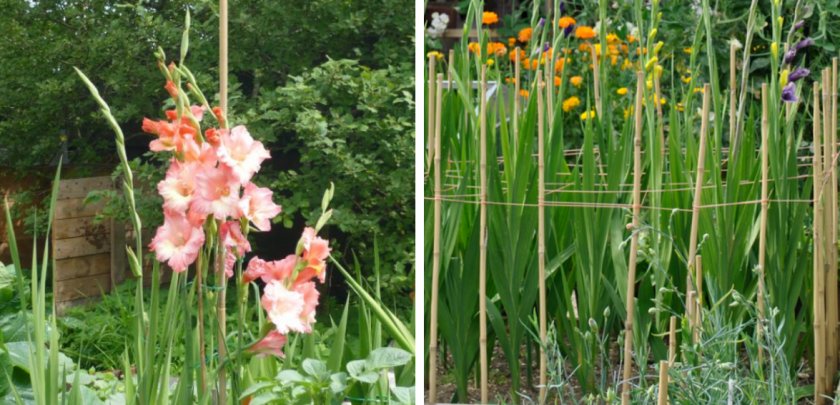
Peduncle height varies from 0.5 to 1.3 m.
The word is translated from Latin as a sword. Gladiolus is like a sword. The inflorescence of the culture is a loose 1- or 2-sided ear. The dimensions of the inflorescence of dwarf varieties reach 25 cm, up to 120 cm in large-flowered ones.

Varietal variety of gladioli
Gladioli amaze with varietal diversity - there are 5000. The variety lives on average for about 10 years.
The leaves are alternate, sessile, linear or xiphoid, up to 80 cm long. The roots of gladiolus are corms.
On a note. With the blooming of new flowers, there is a rapid increase in the size of the peduncle. The dimensions of the flowers range from 3.5 to 26 cm.
The membranous capsule filled with winged seeds is the fruit of the flower. Their number is 250. The seeds do not have a dormant period. Sowing seed material after harvesting is accompanied by germination after 2-3 weeks.
Terms of feeding
During the period of active growth, when 2-3 leaves appear, gladioli begin to feed. At this time, it is desirable to apply nitrogen fertilizers. For 1 sq.m of soil, 30 g of urea diluted in a bucket of water is enough.
From folk recipes during this period, green dressing is suitable. For its preparation, 1/3 of a large container is filled with chopped grass (weeds). Then water is added to the container to the brim and cover it tightly with a lid. Infuse the herb for 3 days. For gladioli, 1 liter of the finished infusion is dissolved in a bucket of water (10 liters) to which 1 cup of wood ash powder is added.
Simultaneously with root dressing, it is recommended to spray the plants with Zircon, which accelerates growth and stimulates lush flowering. It is recommended to spray flowers after sunset in dry weather. The drug is carefully diluted in cold water according to the instructions that come with it.
After the appearance of 4 leaves, fertilizers are re-applied. For 10 liters of water, 35 g of nitrate and 25 g of sulfate are required. One bucket of solution is enough for watering 1 sq. m of a flower bed.
The third feeding should be carried out after at least 6 leaves appear on the plant. At this time, potassium fertilizer should be applied, which is required for normal metabolism. Dissolve 30 g of the drug in a bucket of water, if desired, add 15 g of urea there.
Gladiolus
Immediately before the appearance of flowers, various complex fertilizers with microelements are applied.
When the gladioli have completely faded, 5 feeding is carried out. In 10 l of water, 30 g of potassium sulfate and superphosphate are dissolved. The ready-made solution is designed for watering 1 sq. m of soil.
In early autumn, gladioli are recommended to be watered with a solution of potassium permanganate (5 g of crystals per 10 liters of water). In addition to nutrition, such a final watering is necessary to disinfect the soil and flower bulbs.
The most difficult thing in caring for gladioli is feeding
Top dressing is the key to success in growing these plants. For the same reasons that gladioli cannot endure drought on their own for a long time and need systemic irrigation, they are also dependent on the constant replenishment of the level of nutrients in the soil.
Unlike many other garden plants, there are no simplified feeding schemes for gladioli. The fertilization schedule for gladioli should correspond to the stages of development, because without feeding the plant it is difficult to move to the next stage and grow and develop normally.
The first feeding for gladioli is applied at the very beginning of their development, it is necessary for the active growth of shoots from the tuber, the formation of a high-quality leaf mass and the establishment of peduncles.
- In the initial phase, gladioli most of all need nitrogen, but its amount should not be excessive, because an excess of this nutrient can lead to a delay in flowering.
- The greatest amount of nitrogen in gladioli is pulled from the soil at the stage of the appearance of the first true leaf, but feeding is best done only at the stage of 2-3 leaves. Accordingly, with these requirements, the first top dressing is applied in the form of nitrogen fertilizers in a standard dose or complete mineral mixtures with a low potassium content are applied (25-30 g of nitrogen fertilizers 15-20 g of potassium 30-40 g of superphosphate).
- The mineral mixture can be replaced with a combination of organic fertilizers, such as mullein or chicken manure, with the addition of half the dose of superphosphate and potassium permanganate.
- If you planted late varieties or carried out planting at the end of May-June, then it is better to postpone nitrogen fertilization until 4 leaves appear, and in unfavorable weather or an excess of organic matter in the soil, carry out the first fertilizing only in June.

When 5-6 leaves appear on the plant, the use of nitrogen in gladioli practically stops, and access to phosphorus is of greater importance for flowering and fruiting, especially before the beginning of budding and at the entire stage of preparation for flowering. The second dressing should also consist of three elements, but with a different ratio of elements.At this time, for gladioli, a standard dose of a phosphorus-potassium mixture or 10-20 g of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers and about 20 g of phosphate fertilizers are applied.
Before the start of flowering itself, the third period of development begins, during which gladioli most of all need potassium. The third feeding is carried out exclusively with potassium-phosphorus mixtures during the budding period or at the beginning of the peduncle's movement, adding about 30-40 g of phosphate and 15-20 g of potassium fertilizers. Since mid-August, gladioli cannot be fed.
There is another feeding strategy, consisting of 6 procedures, which is often used when growing gladioli for cutting:
- After the appearance of the first true leaf, gladioli are fed with nitrogen fertilizers in an amount of 25-30 g with an addition of 20-25 g of potash per 1 m2 of soil.
- In the phase of 3-4 leaves, 10-20 g of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers and about 2 g of boric acid are applied.
- After the release of the sixth leaf, 15 g of nitrogen and 30 g of potash fertilizers are applied.
- During the appearance of the peduncle and the beginning of flowering, a full mineral fertilizer is used in the amount of 30 g.
- After the end of flowering, 15 g of phosphate and 30 g of potash fertilizers are applied.
- In late August or early September, gladioli are watered with a solution of 5 g of potassium permanganate per 10 liters of water.
Fertilizers for gladioli should preferably be applied in liquid form; dry dressings are practically ineffective for them. If you have too much time, it is better to halve the standard dose of fertilizer and carry out two fertilizing with an interval of a week at each stage.
In addition to conventional dressings to accelerate flowering and improve decorative qualities, you can carry out up to 3 foliar dressings for all plantings of gladioli, in particular at the budding stage, using aqueous solutions of potassium permanganate, copper sulfate, boric acid or special mixtures of trace elements. Foliar top dressing can be carried out only in the evenings or on cloudy days, using the smallest possible spraying method, trying to apply the mixture in such a way that fertilizers fall on both sides of the leaves.
The subtleties of germination
How to prepare the bulbs further so as to get guaranteed friendly and strong sprouts? To do this, gladioli are laid out in one layer on trays (trays) lined with dry sawdust, sphagnum, gauze folded in several layers, paper. This is necessary in order to avoid premature root development and their unwanted damage during planting in the ground. Containers with prepared bulbs must be placed in a dry, warm, bright place for enhanced bud growth and swelling on the bottoms of the root tubercles. Leave them to germinate for 2 weeks, after which you can hear light clicks. This is how the process of pecking young shoots proceeds, which in the light, depending on the variety, quickly acquire a rich greenish or reddish color.

It happens that 3-4 strong, equivalent sprouts are formed on a large onion at once. In this case, it can be cut into 2 or 4 parts with a cooled knife calcined on a fire, and the cut can be immediately processed with brilliant green. After cutting, a sprout and an equivalent part of the bottom with root tubercles should remain on each lobe
It is important to do this no later than a week before disembarkation. After the sections are tightened, further actions will be no different from the preparation of the rest of the planting material.
If one sprout clearly dominates on the bulb, then you should not be sorry, just remove the weak ones to allow one powerful peduncle to develop. At the same time, corms should not be moistened until they are planted in peat pots or soil.
Babies, or tubers, of gladioli differ from adult bulbs in a strong integumentary membrane, through which it is difficult for a sprout to break through. Therefore, it must be carefully removed by pressing on the bulb from both sides until a characteristic click. Without this procedure, the percentage of germinating tubers will be very low, it may not even reach 30.
It is advisable to get the material out of the cellar no earlier than 7-10 days before disembarkation in order to protect it from drying out. Unlike adult bulbs, babies are very small in size and, accordingly, a smaller supply of moisture and nutrients.
What and when to water after?
Watering should be started after the first shoots appear. Remember to loosen and weed the soil systematically. Gladioli cannot stand watering with cold water, so stand the water in buckets in the sun. Watering should also be done before each top dressing. When the second leaf appears, it is worth feeding the plant with saltpeter (dilute 15-20 g of calcium nitrate in 10 liters of water). To make gladioli bloom earlier, then a week after the first feeding we water the plant with a solution consisting of the following microelements:
- potassium permanganate - 2-3 g;
- boric acid - 2-3 g;
- magnesium sulfate - 4-5 g;
- zinc sulfate - 1-1.5 g;
- ammonium molybdate - 1.5-2 g;
- cobalt nitrate - 1-1.5 g;

The second watering with this composition should be done after 21 days and a total of 4 times. When 4 leaves appear, you need to water it with urea and potassium sulfate, each 30 g per 10 liters of water per 1 sq. m. When the following sheets appear, organic fertilizer can be added to this composition, diluted in a ratio of 1: 20. During the growth of the arrow of the peduncle and the blooming of the buds, it is worth watering with nitrophosphate, diluting 30 g per 10 liters of water. It is also calculated for 1 sq. m. soil.
To make the bulbs larger for planting next year, when the gladiolus blooms, water the plant with boric acid diluted in water at a rate of 2: 10. At the beginning of September, all plantings can be watered with potassium permanganate in a proportion of 5 g per 10 liters of water. And after that, all feeding should be completely stopped.

Organics that may come in handy
Waste products, plant parts are suitable for additional feeding. They improve the composition of the soil, normalize water and air conditions. This method is suitable for those gardeners who have many other crops in addition to flowers on the site.
Chicken droppings

The tool is used to prepare a solution, less often it is scattered dry. The tool is suitable not only for gladioli, but also improves the condition of the soil. It replenishes potassium reserves, restores acidity. In addition, the composition of microflora is normalized, the flower quickly builds up its green mass, and flowering is accelerated.
Chicken droppings are never poured in pure form (!): An extract is made from it or repeatedly diluted with water.
- One part of the waste takes 20 parts of water, insisted for 2-3 days.
- In order not to damage the roots, the solution is poured between the rows, retreating 15-20 cm.
- Make sure that the soil is well moistened before and after fertilizing.
Mullein

Diluted mullein is also suitable for fertilizing gladioli. It contains all the essential elements for plant nutrition. An infusion is prepared from the cakes, diluted with water in a ratio of 1:15. They also make a manure extract: a bag with a mullein is suspended in a barrel of water, insisted for a week. After 7 days, the bag is removed, and the hood is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 4. For 1 sq. requires 10 liters of solution.
Cow cakes reduce the acidity of the soil, making it porous and light. When they decompose, carbon dioxide is released, heat is released. Beneficial microorganisms and earthworms multiply in the soil, and there are more microelements. This creates optimal conditions for root development.
Horse dung

Horse dung is also called rose jelly. Its beneficial properties are known not only for flowering shrubs, but also for bulbous ones. For gladioli, semi-mature and dry manure is suitable. Half-ripe cakes in the amount of 1 kg are mixed with a bucket of water, insisted for 1 day. Then it is again diluted by half with water and used for watering.
Slurry mixture
The manure mixture is made from cow, horse manure, chicken manure in a ratio of 1: 1: 0.5. For 1 liter of such a mixture, 10 liters of water are needed.The solution is insisted in a warm place for 3-4 days. After that, the aisles are watered with it.
Rabbit dung

If there are rabbits in the country, their waste is used to fertilize a small area. They contain all the necessary substances for flower crops - potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus. The indisputable advantage of rabbit manure is the absence of weed seeds. Animals eat plucked leaves.
Irrigation solution is prepared from one part of droppings and one part of wood ash. Add a bucket of water and let it ferment. After fermentation, dilute again with water in a ratio of 1:10 and use for watering.
Nettle infusion

Nettle contains a lot of nitrogen, iron and potassium, easily digestible vitamins A, E, K. An infusion is prepared from the stems and leaves. To do this, the grass is poured into a large container, filling the space by 1/3. The remaining space is topped up with water, leaving a little free space on top for fermentation. The agent is insisted for 7 days, after which it is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. A glass of liquid is enough for one plant.
If it is difficult to follow the growth phases of a gladiolus, there is a simplified diagram. Instead of one-time fertilizers, they are applied regularly, every 2 weeks, in small doses. In such cases, a universal fertilizer for flowering plants is used.
Why is it not dismissed?
We will find out why gardenia blooms for a long time or does not bloom at all, what to do and how to deal with it correctly.
The reasons for the lack of flowering of this tropical beauty may be the following factors:
- lack of soil acidity;
- hard water when watering;
- temperature drops;
- lack of lighting;
- dry air;
- mineral deficiency (or overabundance).
So what if the shrub is not blooming?
It is necessary to provide the flower with optimal living conditions for it.
It is important that the pot is fully lit all the time, except at night. At the same time, in summer, from the direct sun, the flower must be shaded, and in winter, on the contrary, it should be placed on the sunniest window sill in the apartment.If the apartment is located on the north side of the house, and there are no sunny windowsills, as a fact, the shrub will need additional lighting
Use ordinary fluorescent lamps to create an artificial "sun", located at a distance of 60-70 cm from the pot.
The plant needs constantly moist air and soil. At the same time, neither excessive waterlogging nor drying out should be allowed. Watering is necessary regularly - water should be used only soft, settled, slightly acidified with lemon juice
In summer, watering should be more abundant, in winter more rare.
Note! To ensure constant air humidity, place the gardenia pot on a pallet of expanded clay or sphagnum.
Spraying should be done regularly. But during the budding period, spraying should be stopped in order to avoid the appearance of spots on delicate petals.
Important for flowering and temperature conditions
The plant feels best in winter at + 18-22 degrees, and in summer at + 22-24 degrees. The temperature in the room should not fall below +16 degrees - the tropical beauty does not tolerate cold weather. Overcoming any of these limits will lead to the absence (temporary or permanent) of flowering. Moreover, if the shrub is placed in a room with an air temperature that is too low for it, the buds will not open at all.
Also, make sure that the soil temperature corresponds to the air temperature - there should be no difference between these two values.
To stimulate the plant to bloom for a long time, you can pamper it with a "steam bath". To do this, bring the pot to the bathroom, fill the tub with hot water to the brim, and leave the gardenia in this humid, warm atmosphere for 2-3 hours. Until the buds are blooming, you can repeat the procedure every week.