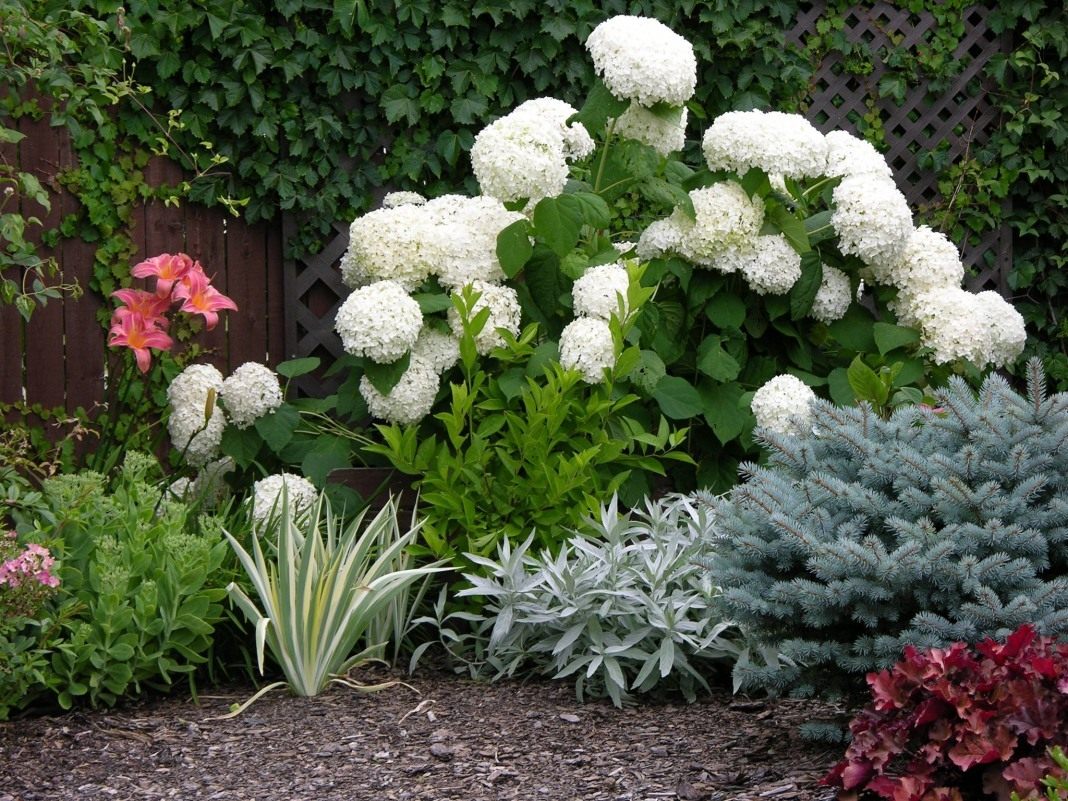
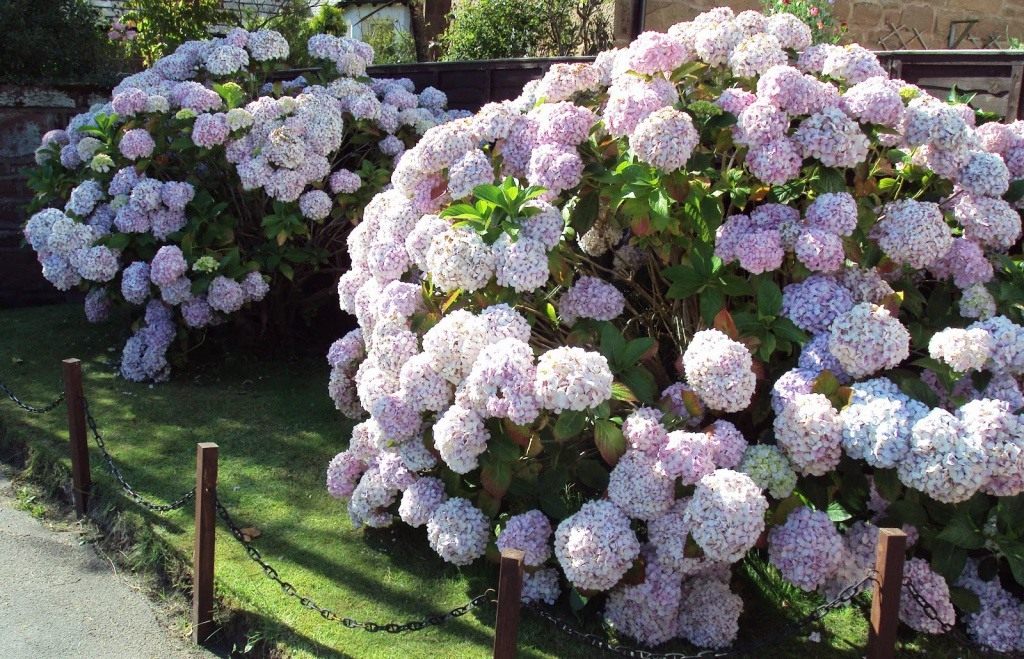
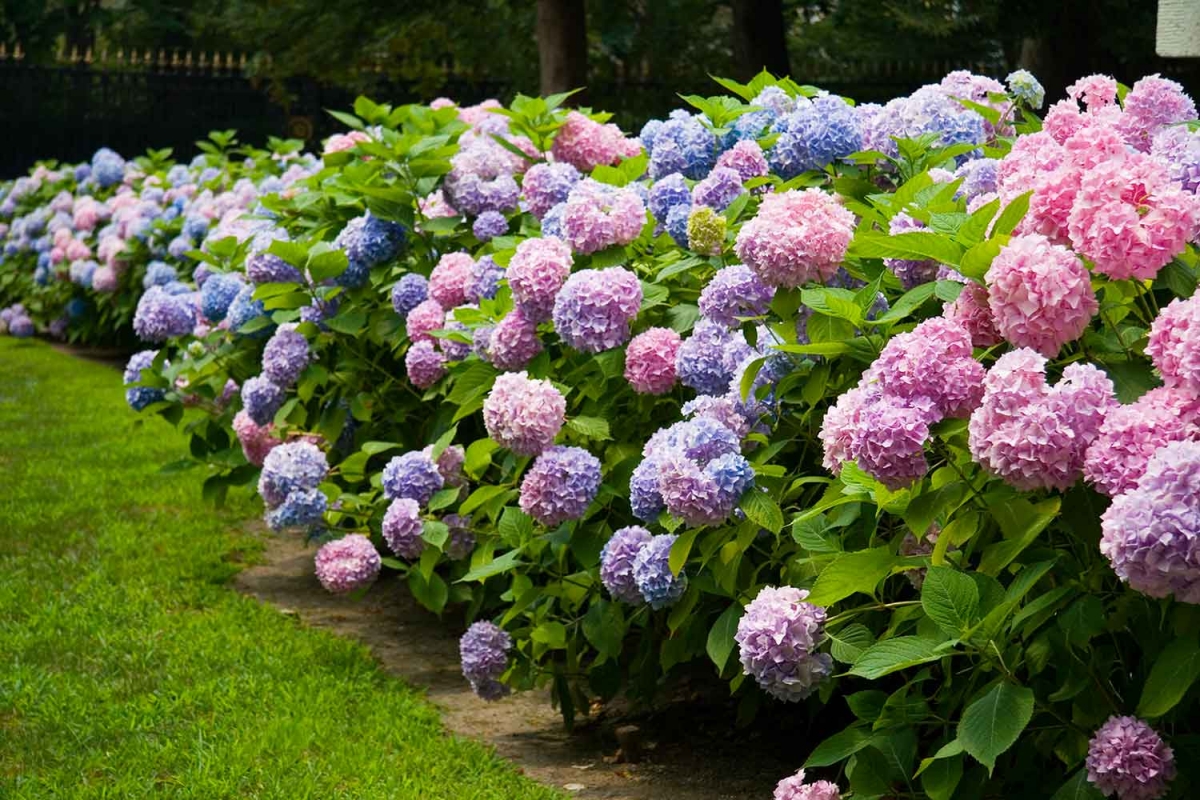
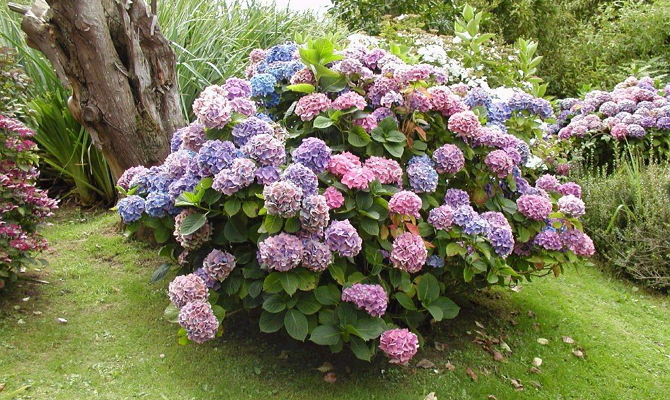
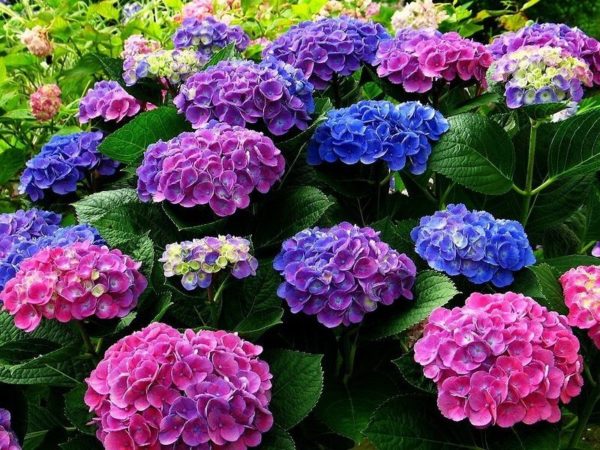
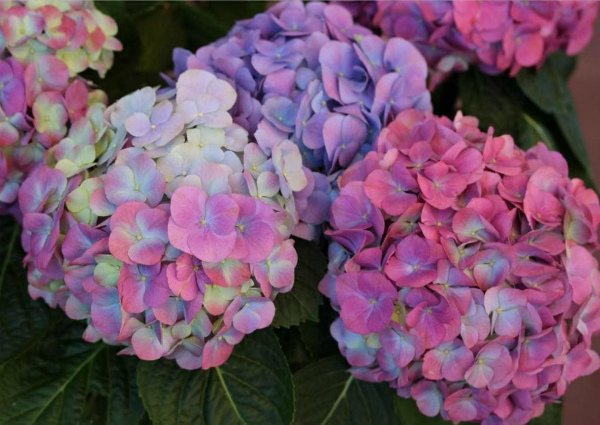
How to feed hydrangea in spring
Awakening from winter sleep for a plant is due to the active growth of green mass. Nitrogen is responsible for the growth of foliage, the growth of shoots and the laying of buds. As part of the spring fertilizer for hydrangea, it plays a central role.
Spring feeding of the plant is carried out when the soil has dried out and the leaves of the hydrangea have blossomed. Prepare a mixture from:
- urea,
- potassium sulfate.
A bucket of water is poured over a matchbox of fertilizers of each type. For each adult bush, half a bucket is spent, watering the shrub at the root.
Important! Root feeding of plants is carried out only on wet soil! Otherwise, you can burn the roots. In early spring, hydrangeas can be fed:
In early spring, hydrangeas can be fed:
- infusion of mullein (for 1 part of manure 10 parts of water),
- chicken droppings (1 part fertilizer and 14 parts water).
The solution is prepared by pouring water over the manure or dung. The mixture is infused for a day. The consumption rate is 5 liters per adult plant, 1-2 liters are enough for young seedlings.
Treelike hydrangea and large-flowered hydrangea respond especially well to this feeding.
Experienced growers often use Pokon fertilizer for rhododendrons and azaleas. In the composition of top dressing, the main share is occupied by nitrogen and potassium. This is a long-lasting fertilizer, which is enough to sprinkle under the bushes in spring, its effect on the plant will not subside until autumn.
The topical fertilizer for the spring feeding of hydrangeas is the Russian Flower Paradise fertilizer. In addition to accelerating foliage growth and increasing the number of buds, the drug strengthens the plant's immunity, protects it from the negative effects of frost.
During budding, formulations with the presence of potassium and phosphorus are prepared for hydrangeas. It can be superphosphate, in the amount of 20 g per 10 liters of water; or a ready-made mineral fertilizer with a predominance of the necessary substances in the composition (Agricola, Kristalon).
To give flexibility to the shoots of an ornamental shrub, the plant is sprayed three times in the spring with a pink solution of potassium permanganate. Treatment with potassium permanganate will protect the hydrangea from a number of fungal diseases.
If the leaves turn yellow
Often, hydrangea leaves winter sleep weakened, it grows poorly, leaves turn yellow and shrink. The most common cause of this plant condition is a lack of nitrogen. "First aid" for the bush will be spraying the crown of the hydrangea with ammonia. Ammonia is an ammonia solution, that is, nitrogen fertilizer. 2 tablespoons of ammonia are added to a bucket of clean water, and the shrub is sprayed from top to bottom. Enough 1 - 2 treatments of the plant.
Another reason for the yellowing of leaves in hydrangea may be a disease - chlorosis. The plant is treated by leaf treatment with iron sulfate and iron sulfate - 5 g of powder per 1 liter of water.
Now read:
- Hydrangea
- How to feed dahlias throughout the season
- What do peonies love and how to feed them in spring (+ ...
- Pruning tree, paniculate and large-leaved ...
- Hydrangea tree (white) at their summer cottage
What organics can not be used for hydrangea
Wood ash is considered to be the richest source of micro and macro elements. But as a top dressing for hydrangeas, it is not good. Wood ash contains a lot of carbonates. These are carbonic acid salts that alkalize the soil.
For some plants, such an event is threatened with extinction at the site. Hydrangeas, rhododendrons (azaleas) among them. Even feeding the hydrangea with kefir or sour whey is practiced in order to increase the acidity in the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe roots.
Do not add lime, chalk, phosphate rock as a phosphorus fertilizer for hydrangeas.An excess of the alkaline component in the soil will immediately affect the condition of the foliage and peduncles.
The latter may not form at all, and the leaves will be affected by chlorosis. This is due to poor metabolism: hydrangeas consume a lot of phosphorus, which dissolves fully only in an acidic environment.
Phosphorus is needed to feed the lushly flowering shrubs every day throughout the growing season. If its intake is disrupted, metabolic failure occurs in the tissues. This affects the immune system - it weakens, and the culture starts to get sick.
New varieties of hydrangeas for 2020
Hydrangea paniculata Hercules
When you see huge powerful inflorescences on a relatively low (height and width 100-150 cm) bush, you understand that this hydrangea fully justifies its name given to it in honor of the mythical hero.
Strong, thick, straight shoots allow the plant to withstand inflorescences that amaze with their magnificence: very large (up to 40 cm long), conical, at first greenish, in full bloom - snow-white with greenish tips, and turning pink at the end of summer. With good care and proper pruning, Hercules panicle hydrangea will delight you and your garden guests with giant inflorescences from July to September. The variety is resistant to diseases, pests and frost.
Arboreal candibel marshmallow
The bush is compact, 80 cm high and 90 cm in diameter, with strong shoots. The inflorescences are dense, pale pink, the original "marshmallow" shade. The flowers are pink, gradually turning white.
Flowering period: from July to September on the shoots of the current and last year. Disease resistant foliage. Pruning this hydrangea is recommended in early spring. Hydrangea tree Candibel Marshmallow has good frost resistance. The variety was awarded a bronze medal at Plantarium 2019 (Holland).
Pinky Promis
An interesting variety, the peculiarity of which is the original combination of pink, white and creamy yellow flowers in the middle of flowering. During the season, they gradually change color from white to dark pink.
The flowers of the Pinky Promis paniculata hydrangea are collected in dense inflorescences that look great against the background of dark green leaves. The bush is low: 70 cm high and 80 cm wide.
Hydrangea paniculata Polstar
Panicle hydrangea for balconies and terraces. Ultra compact variety 50 cm high and 50 cm wide. Abundant flowering in late June - September. The flowers are very elegant, at first greenish-white, then they turn salmon-pink, closer to September - dark pink. The leaves are small, dark green.
For panicle hydrangea Polstar, you should choose a sunny or semi-shady place with moist, drained soil.
Samara Lydia
At the beginning of flowering, the flowers are creamy white, and by the end of the season the color acquires a rich crimson tone, while the top of the inflorescence remains white. The bush of hydrangea paniculata Samara Lydia is low - 100 cm, 100-120 cm wide. The shoots are strong and durable.
Hydrangea paniculata Samme lava
Compact, low variety with very dense, lush inflorescences. This hydrangea changes its color several times per season. The inflorescences are white at the beginning of the dissolution, then the color changes to pale pink and, finally, dark pink.
The bush of hydrangea paniculata Samme Love is perfectly branched, so it looks lush, and in bloom - just a feast for the eyes! Inflorescences are very dense, pyramidal with a rounded top.
Strawberry Blossom
An excellent variety with very large, dense inflorescences, the length of which reaches 30 cm. The flowers at the beginning of flowering are creamy white, then pink with a white top. In the future, the pink tone thickens to raspberry, and the top of the inflorescence remains white.
The bush of the panicle Strawberry Blossom hydrangea is low - about 100 cm, width 100-120 cm, with strong, durable shoots. It deserves a better place in your garden!
Useful articles from the "Floral" section:
Useful articles for the gardener:
- Savoy cabbage
- Harvesting peas: when to harvest, storage methods
- Auspicious days for planting pumpkins in 2020
- Apricot compote for the winter: delicious and simple recipes
- Planting garlic before winter in 2020: when to plant, favorable days
- When to harvest walnuts: timing, storage
- Mushroom picker calendar 2020: when to collect, auspicious days
- Autumn work in the garden and garden: what needs to be done
- Do I need to dig a garden before winter: timing, what fertilizers to apply
- Apricot compote for the winter: delicious and simple recipes
Top dressing hydrangeas in June
In early summer, shrubs grow intensively and form ovaries. At this time, they need nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
You can feed hydrangea in June with folk remedies and special fertilizers.
From folk remedies for feeding, an infusion of nettle or a solution of a mullein is suitable:
- Nettle infusion is prepared within 10 days. Before that, the greens of the plant are crushed and poured with 10 liters of water. You get a saturated infusion, which is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:15 before use. Three to five liters are poured under each bush. This fertilizer contains a lot of nitrogen, which hydrangeas need in spring and early summer. If you add a glass of wood ash to 10 liters of solution, the fertilizer will be enriched with phosphorus and potassium.
- The mullein is diluted with water 1:15, insisted for three days and each plant is watered with two to three liters. Instead of mullein, you can use slurry, diluting it with water in a ratio of 1:10. Such fertilizers will saturate the soil in the flower garden with nitrogen, humic substances and trace elements.
It is recommended to alternate organics with mineral fertilizers. To increase the number of ovaries, Agricola and nitrophoska are used. A tablespoon of each fertilizer is diluted in 10 liters of water and the bushes are watered.
Whether to feed the hydrangea in spring
For lush flowering, regular feeding of hydrangeas is necessary. One of the most important dressings is spring dressing, which helps to ripen beautiful flower stalks, make the shrub more lush, with strong shoots.
Hydrangea in the garden
At the same time, flowering becomes longer and more abundant. Top dressing helps to protect the plant from pests and various diseases.
Important! The lack of dressings, as well as their incorrect introduction, can cause hydrangea disease and shorten the flowering period. Hydrangea is rightfully considered one of the best decorations in any garden, but it is good with abundant flowering.
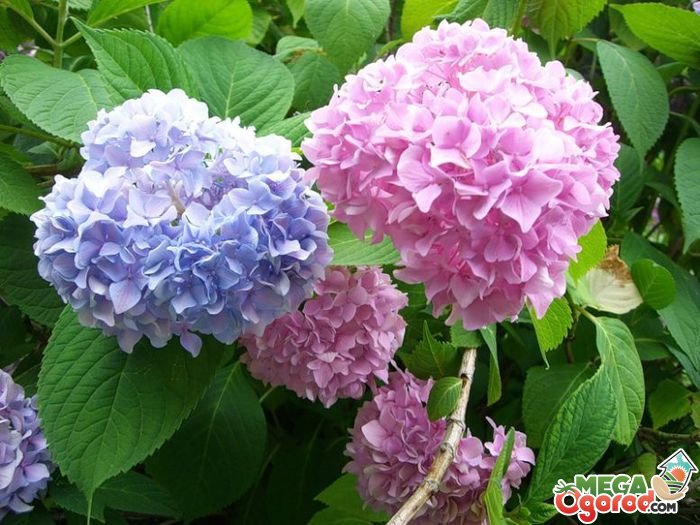
On some shrubs, you can see colorful blooms.
Hydrangea is rightfully considered one of the best decorations in any garden, but it is good when it blooms abundantly. On some shrubs, multi-colored blooms can be seen.
The result of the lack of dressing
This is achieved with the help of different acidity of the soil, while the shades change from blue and lilac to pink and raspberry.
Timing
Each feeding has its own specific time. This is due to the fact that the different elements contained in the supplements are responsible for the different life processes of the hydrangea. And also, having received all the necessary substances, the hydrangea will be more resistant to the variability of weather conditions, diseases, pests and other stresses (for example, transplanting). Before feeding the plant, you need to remember if you added any fertilizer to the hole when planting the plant. If so, then the hydrangea does not need additional feeding for the next couple of years.
In the spring, it is necessary to feed the plant with those trace elements that are needed for the phase of active growth. These include: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, iron. Nitrogen is responsible for the set of vegetative mass. Lack of phosphorus will be expressed in frail and expressionless flowering. Potassium is a versatile element that can be added to complementary foods in both spring and fall. In spring feeding, it is responsible for high-quality flowering.The brightness of the inflorescences and the formation of buds depend on magnesium.
The first feeding of the plant occurs when the snow melts and the first shoots of grass appear. This usually happens in May or late April. The first feeding should consist of nitrogen-containing fertilizers. This is ammonium nitrate or urea. If you wish, you can use organic fertilizers, but their effectiveness is much lower. Potassium and phosphorus can be used with nitrogen supplements.
It happens that you forgot or missed the first feeding. There is nothing wrong with that, the main thing is to add a little more nitrogen during the second feeding. If you missed the second feeding, this is also not a reason to be upset. Some summer residents do not feed hydrangeas at all and, despite this, they grow well. You should not completely exclude nitrogen from feeding - it is he who helps the plant in the formation of new stems and leaves.
The second feeding should be in July, during the budding period. Most often, most gardeners only do one top dressing - just when the buds are forming. They immediately provide the plant with a full range of essential nutrients and trace elements. However, the main thing here is not to overdo it, so such things should be left to more experienced gardeners.
During the second feeding, the emphasis, on the contrary, shifts towards phosphorus and potassium, since they affect the state of the buds. Very little nitrogen is required to maintain the overall appearance of the plant. Excess nitrogen can lead to the fact that the vegetative mass will pull over most of the nutrients, preventing the buds from forming and opening properly. And also, an excessive amount of nitrogen will lead to the fact that the hydrangea will simply "drive the foliage", not allowing the leaves to fully live their life cycle, forming new ones all the time. As a result, the leaves will become weaker, and the plant itself will begin to wither.
The very last feeding takes place in the fall to prepare the hydrangea for the long wintering period. Its goal is to allow the plant to accumulate as much nutrients as possible so that next year the awakening and formation of new buds will occur as soon as possible. In this regard, potassium comes out on top, followed by phosphorus. We begin to gradually remove nitrogen from the dressings immediately from the beginning of August and completely remove it from the composition by the fall, since it is responsible for the formation of new branches, which is absolutely not useful in winter. Conversely, the amount of potassium increases, since it is responsible for the formation of a strong root system, and the stronger and longer the roots of the plant, the better the plant will survive the winter when the amount of nutrients in the soil is minimal.
Top dressing for roses in summer - folk remedies
There are many safe folk remedies you can use to fertilize flowers.
If you don't know how to feed roses in June, then pay attention to the following means:
- Onion. For spraying, you can use a solution prepared on the basis of a husk. With its help, you can not only saturate the plant with useful substances, but also protect them from diseases and pests. To prepare the infusion, mix 4 liters of water and 100 g of husks. Put on the stove and boil for 10 minutes, and then leave for another 4 hours. After that, you can start spraying.
- Bird droppings. A good fertilizer for roses in June, which contains nutrients for growth and lush bloom. Please note that you cannot use litter in its pure form, as it contains a lot of uric acid, which will burn the roots. To prepare the solution, combine part of the droppings and 20 parts of water. Insist for 10 days, stirring regularly. Apply the finished solution not under the bushes, but between the rows.
- Weeds. To prepare a useful infusion, you need to fill 3-4 buckets with chopped grass, and fill the rest of the volume with water. Leave everything to ferment for 3-5 days.As a result, you get a concentrated mixture, which should be diluted with water, taking into account the ratio of 1:10.
Top dressing of roses with ash in summer
Gardeners consider ash to be a complex additive, since it contains all the substances necessary for a plant. Ash for roses in June is good because it stimulates growth and development, and also helps fight pests. It is recommended to alternate its application with organic fertilizers. Thinking about what to feed the roses in June, then use this solution: 1 tbsp. ash per 10 liters of water. You can combine ash with compost or herbal decoction.

Feeding roses in June with yeast
It is recommended to combine this option with the addition of ash, which will prevent the absorption of potassium by this additive. Thanks to yeast cultures, it will be possible to saturate plants with useful substances, strengthen immunity and stimulate growth. Feeding roses in summer with yeast will improve root formation and soil condition.
- To prepare the working solution, mix 10 dry yeast, 2 tbsp. tablespoons of granulated sugar and 1 tbsp. warm water. Place in a warm place to ferment, and then dilute all 10 liters of warm water.
- For feeding in June, part of the infusion must be taken in five parts of water. There should be 1 liter of solution per bush. The result will be visible in a few days. After 2-3 days, feed with ash.
Feeding roses with manure in summer
You can saturate the bushes with useful substances with the help of manure, only it should not be fermented. To prepare the solution, combine part of the fertilizer and ten parts of water, and then leave for a week. It is recommended to stir the composition from time to time. Feeding roses with manure in June is carried out with the calculation of 3 liters for each bush. As for the rotted manure, it can be used for mulching the soil under the bushes.
How to deal with disease?
Hydrangea is a plant that is quite resistant to diseases and pests. However, a lack of nutrients, non-compliance with watering rules can lead to the fact that your favorite shrub is attacked by diseases such as chlorosis or gray rot; aphids or spider mites are often found among pests. If we are talking about a spider mite, then first spray the plant with soapy water, and then treat it with Acrine. Common karbofos helps from aphids: dilute and process the shrubs according to the instructions.
There are also some diseases that can ruin a beautiful hydrangea. Let's take a closer look at their symptoms and methods of struggle:
- Chlorosis. The main symptom is leaf discoloration. Here, ferrous sulfate and iron sulfate will help you (dilute 5 g of the product in a liter of water). Just pour the mixture over the plant. If after 3-5 days the green color of the leaves does not return, repeat the treatment again.
- Powdery mildew, which is manifested by the appearance of yellow specks on the leaves of the shrub. The main cause of the disease is high soil moisture. Green soap (mix 150 g of the product in a liter of water) or copper sulfate will help get rid of powdery mildew, prepare a solution from a liter of water and 20 g of the product.
- Also, hydrangea can be attacked by gray rot, which is characterized by the appearance of brown spots on the shoots. If the fight is not started in time, the rot will move to the flowers, and the plant will die as a result. The main reasons for gray rot are too close planting of shrubs and high humidity. It is best to use Bordeaux liquid. Damaged stems or leaves are best removed and burned before processing to prevent gray mold from spreading to other garden crops.
What is missing
The main rule of plant feeding is that it is better to underfeed a little than to overfeed. Overfeeding affects not only the quality of the crop, but also the plants wither, and the soil loses its fertility.
In the phases before fruit set in garden annuals, the deficiency / excess of a particular nutrient is determined mainly by the leaves:
- A yellow border appears on old leaves, then they turn yellow between the veins from the edge to the center - potassium deficiency. If there are still green areas near the veins, an urgent potash fertilization is needed, for example. 1 tbsp. l with a top of potassium sulfate in a bucket of water, and watering with this solution, 0.5 liters per bush. Suddenly leaves with signs of potassium starvation curl downward and wrinkle - there is also not enough nitrogen. Then, instead of sulfate, potassium nitrate is diluted, 2-3 tbsp. l per bucket, and watered the same way. If brown burns have gone between the veins - that's all, it's useless to feed.
- The leaves turn pale, the ends brighten and sharpen - there is not enough nitrogen, you need to feed with a solution of carbamide (urea), 1 tbsp. l. on a bucket of water, 0.5 liters per bush. If the moment is missed and the leaves began to turn yellow over the area, you need to dig in a bush or two and see if the roots are brown. Suddenly yes - there is no need to feed, the dead will have a poultice.
- A light green spot appears on the pulp of the leaves, then the leaves turn yellow to the veins (chlorosis has begun), become brittle, fall off. If the color of the remaining green areas is even - there is a lack of magnesium, you need to pour 0.01% (1 g per bucket of water) with a solution of sodium humate with magnesium or mark +7. If the affected areas are not reddish, purple or pinkish - overfeeding with potassium, shade with a net, intensify watering and hope that the plant will recover.
- Young leaves with yellow spots, deformed (fringe at the edges). Turn the sheet over, look - the underside is lilac or with a purple glow. Calcium deficiency, we do urgent liming: we spray the soil between the plants with lime milk.
- Leaves bend into spoons and become brittle, growth points die off, flowers known to be pollinated fall off without mating - boron deficiency. We spray the plants with 0.1% boric solution, 0.5 liters per bush.
- The leaves are small, dense, curled down, bluish or purple; veins with a purple tint or reddish. Torn off drying leaves darken to almost black. Phosphorus deficiency, watering with solution of 1 tbsp. l. superphosphate in a bucket of water, 0.5 liters per bush. Suddenly, watery spots appear on the leaves - a concomitant starvation for nitrogen. Then we replace superphosphate with ammophos or diammophos.
- Chlorosis, as with a lack of magnesium, but the veins also turn pale, and the leaves curl up in a tube - overfeeding with strong nitrogen fertilizers: mullein, urea, ammonium nitrate. We intensify watering, give microfertilizer with molybdenum according to the instructions for it (it is better to separately molybdenate with neutral ballast, for example, sulfate).
- The leaves brighten to lemon color, but do not noticeably turn yellow, then turn slightly yellowish. Growth points do not die off, but they do not develop either - iron deficiency. We give microfertilizer with iron (iron chelate, for example). Sometimes it is possible to fix the matter by sprinkling with water from a rusty iron tank, but this depends on the properties of the local water, tk. not all iron ions are active for plants.
- Chlorous spots on young leaves, then the leaves turn yellow, turn brown and fall off - manganese deficiency. Watering 0.5 liters per bush with a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
- On young leaves, brown spots at the petioles, then the browning spreads along the leaf, it becomes translucent and falls off - zinc deficiency, spraying with 0.02% zinc sulfate solution, 0.5 liters per bush.
- The tips of the leaves turn white, starting with young ones. The color of the leaves is blue, the edges are wrapped in a tube, the internodes are shortened - copper deficiency. Spraying with 0.01% solution of copper sulfate as before. case.
it is sometimes possible to clarify the diagnosis in accordance with the properties of the soil:
- Unkempt garden land, gray forest, podzolic, sod-podzolic - a lack of nitrogen, then phosphorus is likely.
- Sands, sandy loams, light loams - most likely, there is not enough potassium, boron or copper.
- Alkaline and carbonate (chernozem, chestnut) - they have a chronic manganese deficiency.
- Peaty, silty (for example, a drained swamp), meadow - besides manganese, copper is probably not enough.
Top dressing for chlorosis
Hydrangea is very often affected by chlorosis. It occurs when there is a lack of iron. Soils are usually rich in iron, but it is in a state that is not available to plants. The introduction of iron in the form of dressings does not give a result, since iron is a sedentary compound, it is practically not absorbed by plants.
Modern industry offers a smart way to feed plants with iron. Ferovit will help to avoid leaf chlorosis and replenish iron deficiency. For spraying the bushes, a solution is prepared from one liter of water and 1.5 ml of the drug. Processing is carried out twice with a break of 2 weeks. If signs of chlorosis appear, the drug should be applied weekly until the hydrangea is completely healed.
Rules for making fertilizers for hydrangeas in the spring
 When feeding hydrangeas, the same rules apply as when fertilizing other garden plants.
When feeding hydrangeas, the same rules apply as when fertilizing other garden plants.
- The first feeding after the snow melts is given when the above zero temperature is established. Only when the soil warms up to +4 +6 degrees, the roots are able to assimilate nutrients from the environment.
- Watering the plant with a nutrient solution under the root is carried out only on wet soil (the bush is watered abundantly on the eve of feeding with plain water). Moisture-infused roots will better absorb food and will not get burned.
- The introduction of solid fractions of fertilizers on the soil surface should be accompanied by shallow loosening, by 4-5 cm, and subsequent irrigation with clean water.
- A solution for foliar dressing (spraying on a leaf) is prepared 2 times weaker than a liquid for watering hydrangeas at the root.
- The bushes should be sprayed in cloudy weather or in the evening, so as not to provoke burns on the foliage due to droplets of moisture.
- It is necessary to prepare nutrient solutions for plant fertilization by accurately measuring the doses of fertilizers. At a high concentration of the active substance, there is a high risk of burning the roots or foliage of the plant.
The specificity of hydrangea cultivation is that it prefers acidic soils for growth. Fertilizers that reduce acidity are not used for it: ash, manure.
Hydrangea dressing options and their dosage
The market is oversaturated with all kinds of fertilizers and dressings. The offered preparations are divided into mineral and organic, intended for the care and protection of the flower. Folk remedies that have been successfully used to grow hydrangeas have proven themselves perfectly.
Organic
Fertilizers based on natural or natural remedies are called organic. For many years, they not only feed, but also warm plantings in the winter season.
Kefir, whey, sour milk
For many years, summer residents have been using dairy products to maintain flower crops growing in their personal plot. Any fermented milk product is perfect for these purposes. Feeding hydrangeas with kefir is carried out only in a diluted form, the optimal ratio is 1: 4.
Cow dung and bird droppings
When using organic matter, you can use rotted manure and droppings. They are divorced in a ratio of 1:10 and alternate with mineral products.
Bread or yeast feeding
Soaked black bread or dry yeast previously diluted in warm water promotes the growth of green mass. In this case, 1 loaf of black bread is soaked in 10 liters of warm water for 2-3 days. The fermentation process takes place in the sun or in a warm room. Before applying fertilizer under the bush, the composition is thoroughly filtered.
Potassium permanganate
The use of potassium permanganate in a diluted form not only improves the formation of buds, but also behaves perfectly in the care and protection of the plant from all kinds of pests. Potassium permanganate is watered and sprayed with hydrangea.
Ash
Feeding with ash is not recommended due to the fact that hydrangea is sensitive to soil acidity. The introduction of ash into the soil significantly lowers the pH, which can lead to the rapid death of the flower.
Urea
For feeding with a mineral composition, it is preliminarily diluted in water. 25-30 g of urea is added to 1 bucket. When applying, observe the rate: 1 bucket of the resulting composition is introduced per 1 square meter of planting.
Vinegar and other acidulants
The bush is not able to fully receive nutrients from the substrate if its pH does not correspond to the required one. How to fertilize hydrangea to increase acidity? Citric acid, diluted in an amount of 40 g of the drug per bucket of water, is successfully used.
Additional Information! You can use lemon only after it is completely dissolved.
Experienced growers advise using apple cider vinegar diluted with water. Optimal proportion: 100 grams per 10 liters of water at room temperature.
Chemical
Mineral dressings can consist of individual substances or whole complex compounds. In floriculture, it is permissible to use complex options, since it is not required to carry out calculations and observe dosages.
Agricola
The drug belongs to special agents designed to fertilize hydrangeas. It initially contains all the necessary trace elements. A liquid preparation is a product consisting of humates.

Agricola yellow
Nitrofoska
Complex mineral dressing. It has proven itself to be perfect for summer use. The use of nitrophoska during the formation of inflorescences not only protects the flower from harmful insects, but also protects the flowers from premature falling off.
How to fertilize hydrangea after flowering
Panicle hydrangea is decorative in throughout the season, and if you do not cut the inflorescences, they can stay on the bushes all winter. Therefore, the hydrangea will "bloom" when you cut off its shoots - this plant is very fond of pruning, blooms on the shoots of the current year, so towards the end of autumn you can safely cut your bush, leaving no more than a third of the shoots' length. It is not necessary to cover the panicle hydrangea for the winter.
To prepare the plant for wintering, you need to fertilize it with a prepared solution in late summer or early autumn, which is done as follows:
- 2 teaspoons of potassium sulfate is diluted in 10 liters of warm water;
- add 1 tablespoon of superphosphate there;
- let the solution brew for several hours, after which the bush is plentifully spilled on it.
From the middle of summer, stop using nitrogen fertilizers, the plant no longer needs them. And you should not at all add them to the soil in the fall - the plant will react to nitrogen fertilization with active growth of shoots, and they will freeze at the very first frost that comes, because of which later they will simply begin to rot. To save your plant from the need to winter with rotting shoots, you should abandon the introduction of nitrogen into the soil, starting in the middle of summer.

In addition, in the fall, you can mulch the bush with organic compounds - peat, manure, humus. The bush of paniculate hydrangea, the roots of which are covered with a warm layer of organic fertilizers, will perfectly endure winter, and in spring, as it thaws, nutrients will begin to penetrate into the soil, feeding the underground part of the plant.