Reason 1. The peony grows "in the wrong" place
The first reason for the lack of flowering of a peony is the wrong choice of a place for its planting. If the plant is, in principle, uncomfortable, and it spends all its energy on survival, you must admit that there is no time for flowering.
So before starting this culture on the site (in principle, like any other), find out more about its preferences. In the case of a peony, the choice of a landing site should also be carefully chosen because it will "live" in one place for many years.
What place would a peony prefer to grow well and bloom luxuriantly? First of all, it is sunny - even a couple of hours of regular daily shading can lead to a sharp deterioration in the flowering quality of this crop. You also need to ensure that the area with peonies is protected from constant winds and drafts.
Secondly, it must be remembered that the soil for the peony must be slightly alkaline and necessarily well-drained - stagnant water in swampy areas or the close occurrence of groundwater also negatively affects the plants - their roots quickly rot.
It is not necessary to place peonies in the zone of the root system of trees and large shrubs, because their development can be affected by a lack of moisture and nutrition.
Planted against the wall of a building (closer than 1.5 m), peony bushes in the heat can suffer from overheating, in winter and spring - from snow blockages or drops.
How to plant peonies in spring - a step-by-step master class with a photo
The spring planting of peonies is not much different from the autumn planting. Although there are still some features ...
How to fertilize correctly?
It is important not only to apply the correct fertilizers intended specifically for the lily, but also to observe the regime. Each season requires its own feeding
The following rules are recommended by experienced florists.
The first fertilizers are applied immediately during the planting of the flower in the spring. In this case, the condition of the soil is of great importance - if it is fertile and well rested, then you can do without additives. Otherwise, fresh manure (about 8 kilograms per 1 m²) or wood ash in the amount of 100 grams per 1 m² must be added to the soil. You can also apply mineral fertilizers: before planting, those rich in potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus are well suited.
Lilies need nitrogen supplements, which promote the development of the ground part of the plant and abundant flowering. As the first top dressing, ammonium nitrate is used - about 2 tablespoons per 1 m². You can also feed with urea - just prepare a solution of 10 liters of water and 1 tablespoon of the drug
It is poured into the ground.
It is very important to feed the lily in late May-early June before flowering, when the first buds are just beginning to form. During this period, the flower needs nitrogen, phosphate and potassium.
Supplements with such a composition form a full and beautiful bud. The next summer dressing should be done during the period of rapid flowering. The flower needs to be pleased with complex fertilizers and microelements. Experts also advise using wood ash.
In order for the lily to bloom profusely and for a long time, it is advisable to feed it with Azophos or nitroammophos in the summer. These substances must be soaked in water in a proportion of 2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water.
In the fall, when the plant has already bloomed, it also needs to be fed and thereby prepared for winter. The bulb is filled with nutrients that will help it cope with frost. With the arrival of late autumn, the soil is covered with compost.

A few more tips are sure to come in handy for lily fans who grow these gorgeous flowers with love and special care.
- To prevent the lily from freezing with the arrival of frost, the soil around it needs to be insulated. To do this, use fallen leaves or humus. Before planting a lily and adding mineral supplements, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with the condition of the soil. If the acidity index is high, then it must be reduced before fertilization. This can be done with slaked lime.
- It is necessary to apply fertilizers to the soil for feeding the lily only when the outside air temperature is not less than + 8C.
- When choosing a fertilizer, also carefully study its composition. There are certain supplements for each season.
If you adhere to all of the above rules of care and feeding, lilies will be strong, healthy, richly and beautifully blooming. These beautiful plants will be able to please the eye for a long time, decorating flower beds, front gardens, complementing landscape design
For information on how to feed lilies before flowering, see below.
Step 5. Protecting clematis from diseases and pests
Clematis most commonly affects diseases such as gray mold, rust, powdery mildew and wilt (wilting). The best way to protect clematis from these diseases is to take timely preventive measures:
- do not allow the soil to become waterlogged;
- remove weeds in time;
- inspect the bushes regularly and immediately cut off all infected shoots to prevent the spread of the disease;
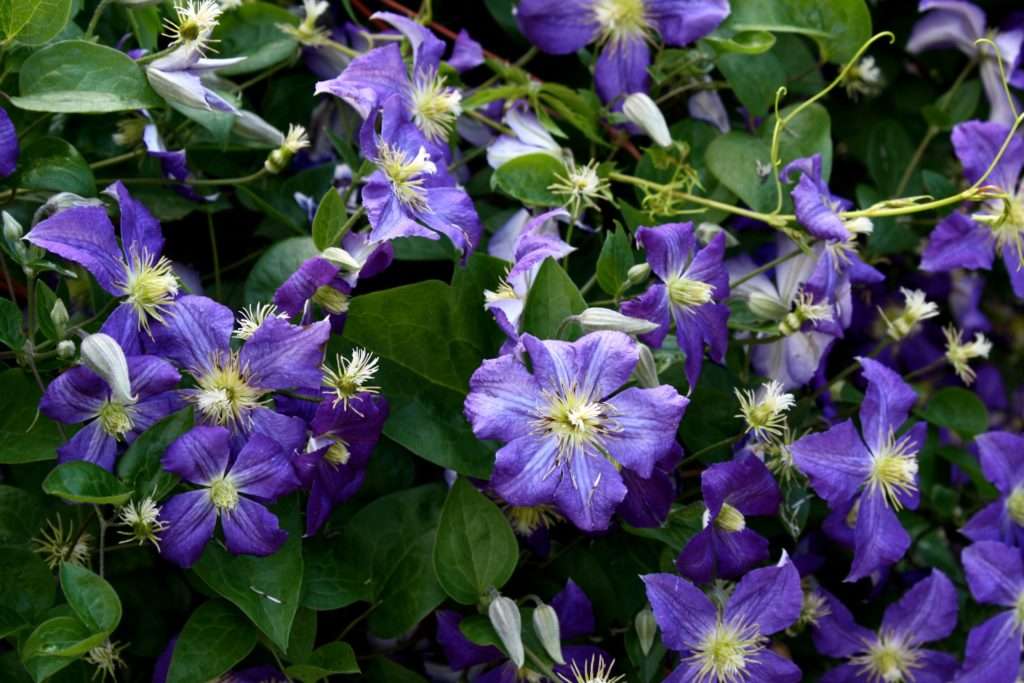
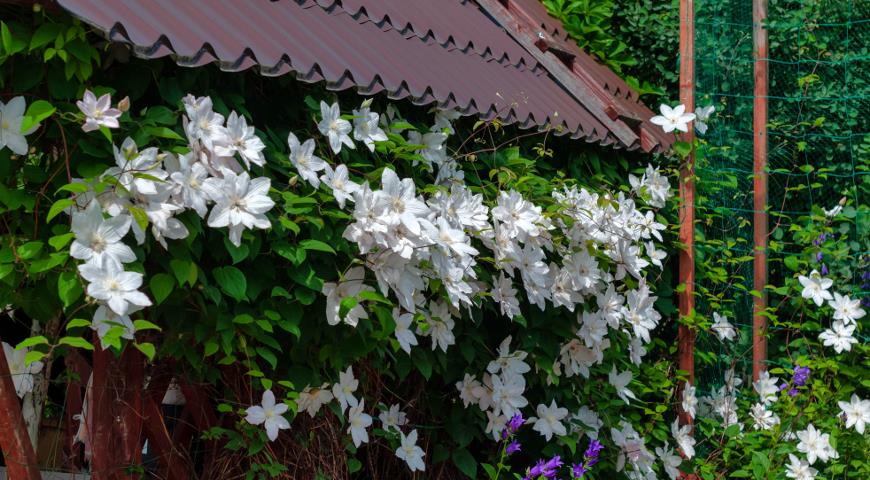
- choose suitable growing conditions: sunny dry place, slightly alkaline soil, light soil.
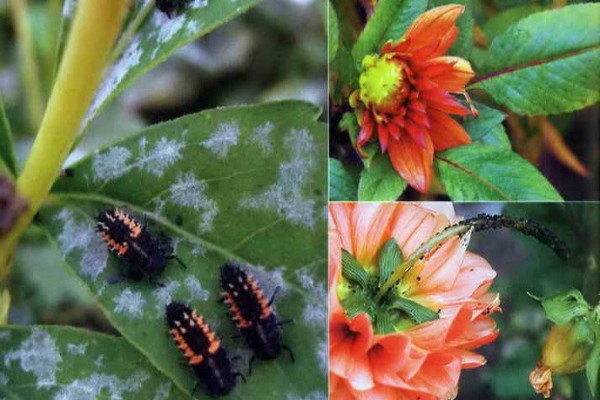
5 most dangerous diseases and pests of clematis (photo, description, treatment)
We will not give offense to clematis!
The most important pest of clematis is the rootworm nematode. It is almost impossible to defeat it, so the only thing that can be done is to prevent it from appearing. To do this, mulch the soil near the bush with wormwood and mint. These herbs, with their strong odors, will scare away the pest and save clematis.
How to get rid of a nematode on the site: chemical and folk remedies
Roundworms in the area destroy all plants indiscriminately? It's time to start a serious pest control!
Another attack that can lie in wait for clematis is slugs. One way to deal with them is to spread the boards at some distance. Slugs, who are very fond of shade and dampness, crawl under the shelters prepared for them. After that, it remains only to collect them and destroy. About other ways to deal with slugs - in our article:
How to deal with slugs on the site: folk remedies and chemicals
Spring has come, which means that numerous pests are awakening. Some of the most unpleasant are slugs, which can destroy almost all plantings.
Clematis love grooming
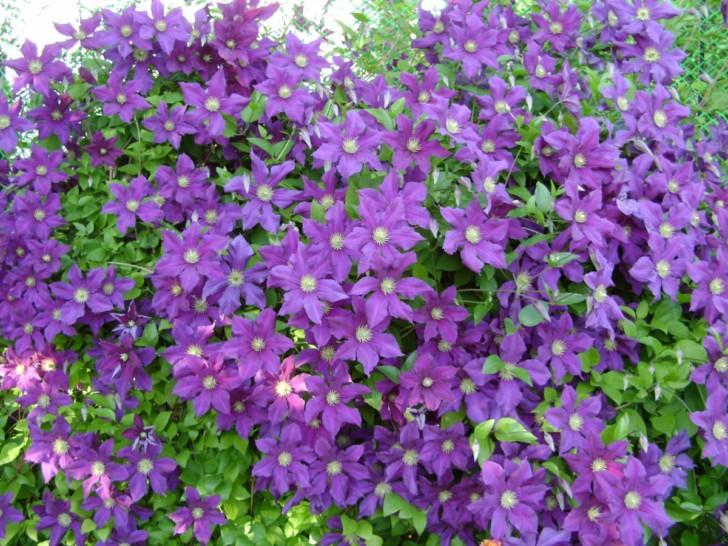
In gratitude for your attention, you will receive incredibly beautiful huge flowers that will decorate your summer cottage
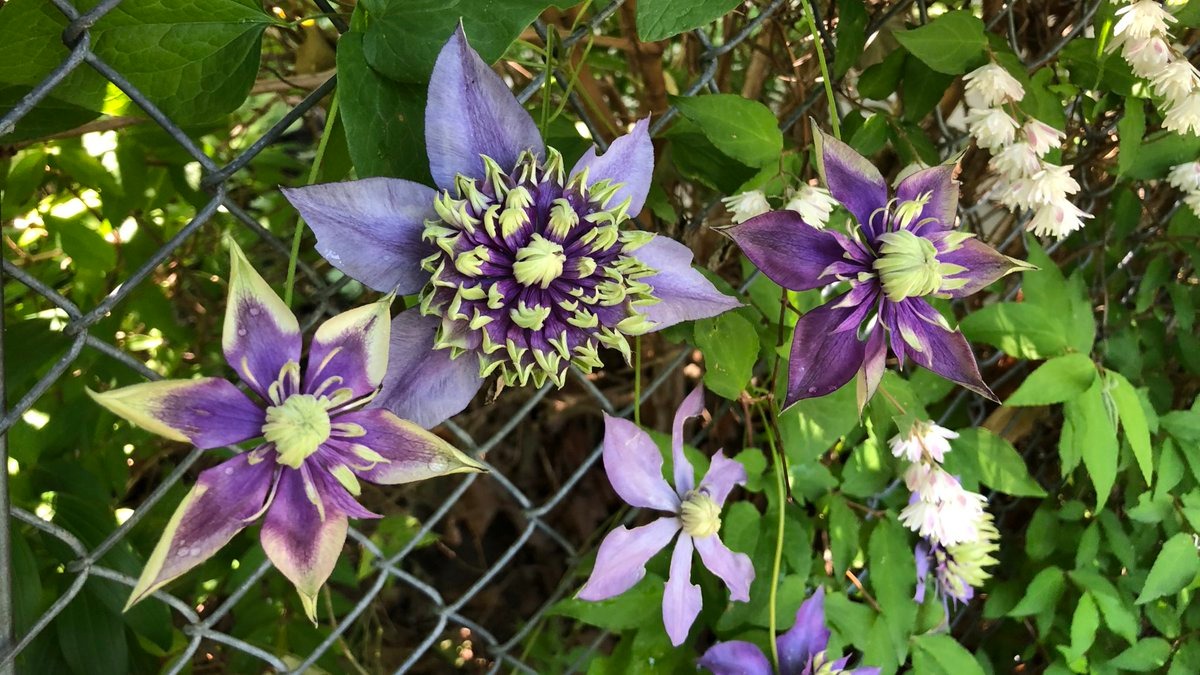
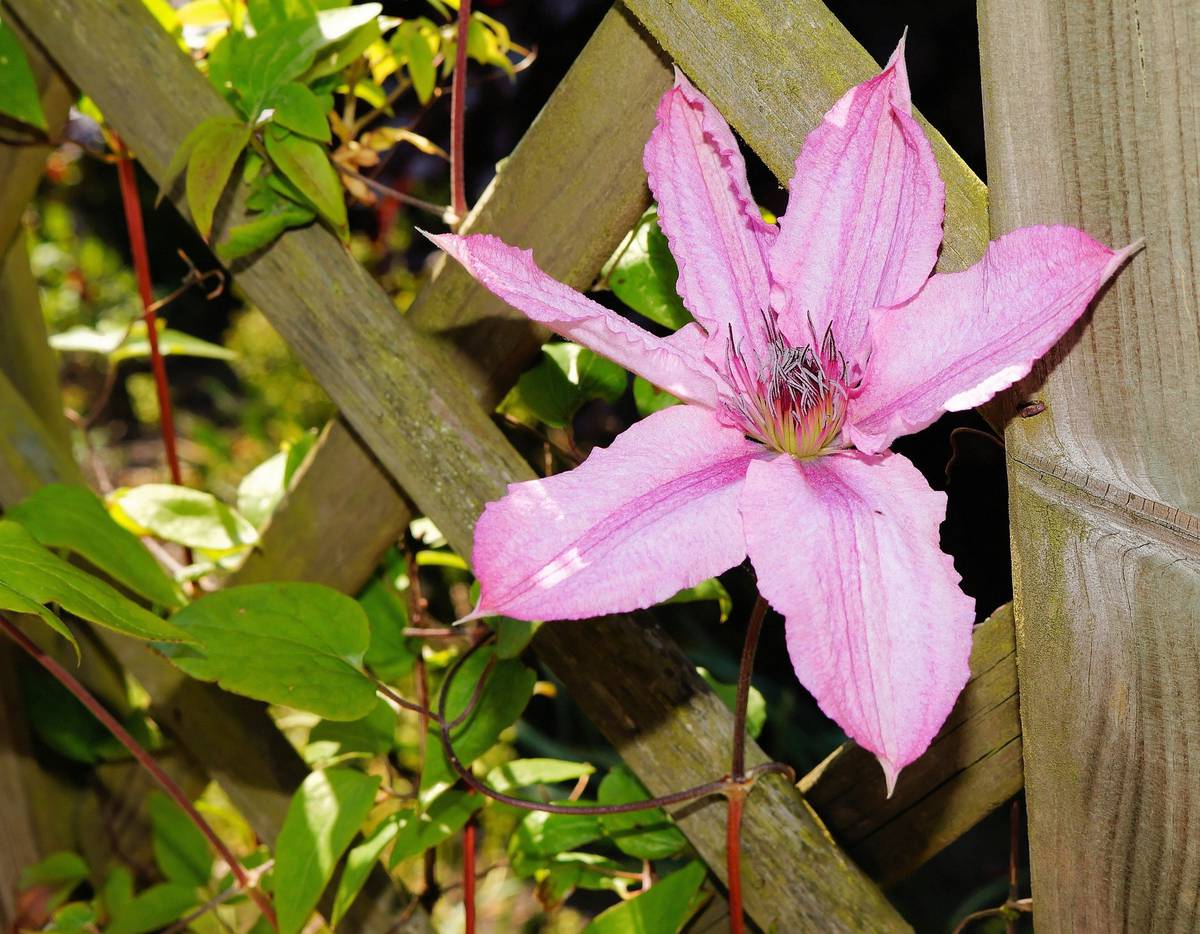
The most unpretentious varieties of clematis with photos and descriptions
A selection of varieties of clematis, which are worth looking at for novice growers.
Reproduction of clematis
There are two main ways of reproduction of all plants: seed and vegetative. Seed is the sowing of seeds, with the vegetative method, parts of plants are used: roots, cuttings of stems, green and lignified cuttings.
Seeds
It is impossible to propagate hybrid large-flowered clematis by seeds, because the grown seedlings do not repeat the properties and varietal characteristics of the parent plant, the method is suitable only for the reproduction of species small-flowered clematis.
By dividing the bush
This is the easiest way of breeding clematis available to every flower lover. You can divide the bushes 5-6 years after planting, in autumn or spring. Dig up the bush, divide it into several parts, plant each part according to the rules set out in the landing section.
If the bush is very large and it is not possible to dig it up, then you need to dig it up on one side and separate part of the plant with a shovel.
- Advantages of the method: the resulting plants bloom quickly.
- Disadvantages: all diseases of the mother bush are transmitted, in some cases the plants do not take root well due to a violation of the balance of roots and shoots.
Reproduction by layering
In spring or autumn, grooves are dug radially from the bush, 5-10 cm deep. Lateral shoots are laid in these grooves, pressed with wire brackets, covered with earth or peat.
After a year, the rooted shoots can be separated from the plant and planted on their own.
- Advantages of the method: easy to use, does not reduce the decorative effect of the mother bushes.
- Disadvantages: diseases of mother plants can be transmitted, not suitable for industrial use.
Cuttings
The method of obtaining a large number of clematis seedlings under industrial conditions is also used by amateurs.
Cutting by timing is divided into winter, spring and summer.
Planting material - clematis cuttings, green or lignified are used. To improve the result, growth stimulants are used: heteroauxin, beta-indolylbutyric acid, anaphthylacetic acid, ready-made preparations such as epin, root, etc.
It is very important to maintain a temperature regime, 18-20 degrees, constant air humidity
Cuttings root best when using a fogging machine. Plants must be protected from direct sunlight, overheating, drying out and high humidity.
The main advantage of the method is to obtain healthy seedlings without hereditary diseases, developing on their own roots.
Work calendar
Necessary measures and approximate terms of work for the care of clematis.
The time of one or another agrotechnical reception depends on the geographical location of the site and weather conditions. Your personal observations of the growth and development of plants will make adjustments to the timing of the work.
Work on the care of adult clematis begins in April
April. From the middle of the month, the winter shelters should be removed very gradually. There is no need to rush. If you remove all the shelter, clematis sprouts will appear above the ground, and quite likely frost will destroy the root collar, the most vulnerable part of the plant. Splitting of the root collar from spring frosts is the most common cause of the death of clematis.
May. Time of spring revision of plants. You can transplant young seedlings to a permanent place and divide old bushes. Loosening, weeding. It is necessary to install new supports under the clematis or check the reliability of the old ones. As the shoots grow, they are attached to the supports.
If the sprouts of some plants do not appear, then it is still premature to talk about death.
It is necessary to carefully excavate and see the condition of the kidneys and root system. Sometimes it is useful to dig up the plant, rinse in water, divide by the number of living buds and plant in a new place.
And sometimes - just wait for the start of growth.
June. Time of active growth of clematis. Weeding, loosening, tying stitches to supports. It is useful to spill clematis with milk of lime and feed them with slurry.
July. Lush bloom of all clematis in your garden. Watering is necessary in dry weather. Watering is necessary rarely, but abundantly enough. Once every 2 weeks, you can feed it with slurry and mineral fertilizers.
August. It is advisable to add ash to the top dressing. This promotes better ripening of the whips and improves the winter hardiness of plants. Feeding with organic fertilizers and nitrogen is gradually stopped
In August, it is important to monitor the health of the bushes. A disease such as wilting clematis most often manifests itself in August.
September. Loosening the soil, weeding. Top dressing is stopped. Plants can be transplanted to better locations.
October. Autumn pruning of clematis begins in the middle of the month
It is important to make sure that the root collar is covered with earth. If it is on the surface, then sprinkle it with humus or compost.
When the air temperature drops, plants begin to gradually cover.
November. With the onset of stable frosts, in dry weather, the clematis ends up sheltering for the winter. One of the serious dangers is the onset of frost before snow falls. With a constant snow cover, clematis do not need shelter at all, but frosts after a thaw can damage the plant.
Covering clematis on winter, you can safely part with your favorites until spring.
Phomopsis wilt of clematis
Withering of clematis is caused by two kinds of fungi - phomopsis and fusarium. The wilting caused by a fungus of the genus Phomopsis can usually be observed in late spring - early summer: yellowish-brown spots appear on the leaves of clematis, which are closest to the ground. Over time, the leaves die off and fall off. An insidious disease affects not only leaves, but also shoots and stems. This fungus is able to completely destroy the terrestrial part of large-flowered hybrids. It is easier for the original species - in their case, the disease does not pose a great danger, except that the leaves will be covered with small spots, but this is unlikely to lead to serious consequences.
In order not to lose the plant, it is important to diagnose the disease as early as possible. To do this, you need to periodically check the clematis for spots on the leaves.
Examine the older leaves in the lower third of the plant's shoots most closely. Inspections should begin in mid-May.
It is important to remove fallen leaves and dry last year's leaves in time. The tool with which you cut off diseased shoots and leaves must be treated with boiling water or disinfected with alcohol
The fungus of the genus Phomopsis actively develops in a humid environment, when moisture from dew or rain lingers on the leaves. Therefore, clematis is best planted in places with good air circulation.
Keep in mind that diseased shoots can die completely in just two weeks, so review the leaves regularly. Burn affected leaves and shoots, treat healthy stems with fungicide.
Never put cut diseased shoots and leaves in compost, so as not to infect other plants!
If you found signs of the disease in time, and the fungus did not have time to penetrate all parts of clematis, then the plant will quickly recover. If you discovered Phomopsis wilting late, then clematis can hardly be saved.
Reproduction of clematis
There are several possible options for breeding a plant:
- cuttings;
- layering;
- dividing the bush;
- germination from seeds.
Let's consider in more detail each of the methods.
How to propagate clematis by cuttings
Cutting clematis is the most famous method for breeding shrubs that are more than three years old. Such a procedure should be carried out in early summer (May, early July), when the flower is in the active phase of germination, but in order for it to take root, it is necessary to have time before the flowering stage.

Experienced gardeners advise you to follow a number of rules for successful plant propagation:
- It is better to cut off cuttings in the morning or late evening to protect the plant from dehydration. The best option for the procedure is cloudy weather.
- It is better to cut off the middle part of the shoot, so that one internode and two fully developed buds in the leaf axils are obtained. You need to leave 3-4 cm of the stem under the knot, and 1-2 cm above it.
- The upper cut of the shoot should be straight, and the lower cut obliquely (at an angle of 45 degrees).
- It is not recommended to cut off many shoots at the same time, in one procedure they should be no more than 1/3 of the bush.
- In order for the plant to take root better, it is necessary to treat it with a solution that biostimulates growth, and root it into a soil prepared in advance treated with "hot steam" with peat substrate and sand.
- The knot should be deepened approximately 5 mm into the soil. It should be planted keeping a distance of 5 cm between cuttings, and 10 cm between rows. To protect the buds from drought, the stalk must be buried 1-2 cm into the ground.
- The ideal place for rooting would be a greenhouse, pot or greenhouse, since the plant requires a constant temperature regime within 17-23 degrees.
- The main thing in the process of survival is to maintain uniform moisture in the soil and air. Daily watering is required, and after 30 days it can be reduced to 2 times a week. The rooting process takes approximately 50 days.
- Peat can be used as a top dressing for clematis.
- Until spring, the plants are left in a greenhouse, covered with sawdust, and then planted.
Reproduction by layering
It takes a considerable amount of time to grow a flower from a cut, but the process itself is very simple. It is better to carry out the germination stage in late spring or autumn. For the best result, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Small grooves with a depth of no more than 8-10 cm should be prepared near the plant and young shoots with at least 5 nodes should be laid in them.
- Then sprinkle the shoots with soil.
- Make sure that the top of the layers is always above the ground. They can be tied up, if necessary.
- A plot with layering requires daily watering and periodic loosening of the soil.
- The next spring, young bushes can be detached from the old plant and planted elsewhere.
Breeding a flower by dividing a bush
This method is used for plants that are more than 5-6 years old. It is advisable to divide the bush a month before frost or in early spring, even before the first buds appear. Since the divided bush does not take root well, it is required to fertilize the plant a year before so that new young roots germinate.
To divide the bush, you must:
- Dig out the bush carefully and shake it off the ground.
- Divide the bush into several parts with good root system and buds.
- Plant the resulting bushes.
Growing clematis flowers from seeds

Clematis seeds
This growing method is used for small-flowered, wild-growing flower species. The best period for sowing seeds is spring.
Seed growing methods:
- Seeds must be stratified before planting. You will need to soak them in water for about a week, and then cover them with wet sand and place them in a refrigerator with a temperature of 1-6 degrees for two months. Disembarkation can be done at the end of April directly into the ground. The soil needs to be moistened periodically.
- Plant the seeds directly into the ground in the fall and sprinkle with sand. During the winter, they will go through the process of natural stratification, and in the spring they will germinate.
Viral diseases of clematis and the fight against them
Much less often, clematis are affected by viral diseases, as a rule, they are not treated, and the affected plants must be destroyed outside the territory of the site. Sucking insects spread.
Yellow mosaic of leaves
Contrary to the name, the leaves do not turn yellow, but discolor and become brittle. There are no means to combat this virus yet.
As a preventive measure, plantings should be treated with preparations from sucking insects, which are its carriers. Carbofos, colloidal sulfur, potassium soap will do.
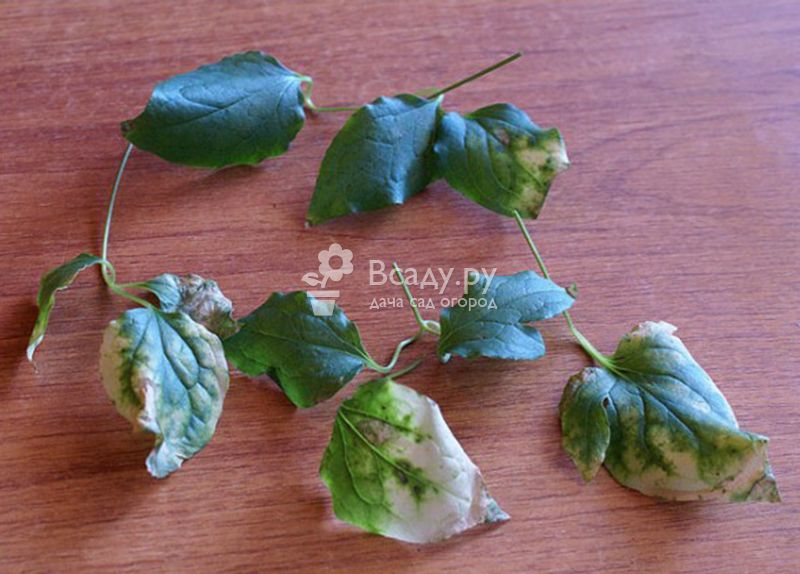

Also, peonies, phloxes, delphiniums, hosts should not be planted in the immediate vicinity of clematis - plants that are susceptible to this disease and can cause infection.
If the vine is severely affected, but not completely, remove it, but to preserve the variety, prepare cuttings from healthy parts. They can be rooted in the quarantine area and monitored for the manifestation of the disease. Read about how to do this in our article: Clematis - propagation by seeds, green cuttings and layering.
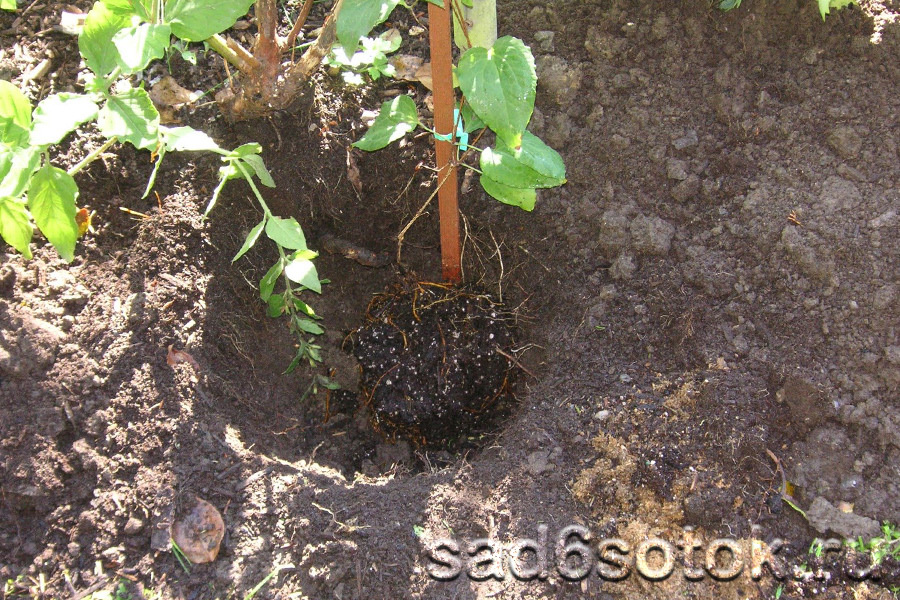
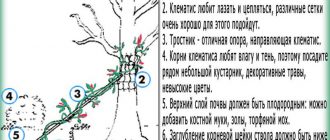
Planting clematis
Since clematis can grow in one place for more than 20 years, they prepare the ground very deeply in advance.Usually, holes are dug with a size of at least 60x60x60 cm, and for group plantings, the site is prepared over the entire area.
2-3 buckets of humus or compost, 1 bucket of peat and sand, 100-150 g of superphosphate, 200 g of complete mineral fertilizer, preferably 100 g of bone meal, 150 -200 g of lime or chalk, 200 g of ash. On light soils, more peat, leaf humus and clay are added.
If the soil on the site is wet, dense or clayey, then a 10-1 5-cm layer of crushed stone, broken brick or coarse sand is poured onto the bottom of the pit. Thoroughly mixed earthen mixture is poured into the pit and compacted. In the southern regions, it is preferable to do this in autumn (from late September to early November; in the middle lane, the best time is September (in warm weather and later); even further north, clematis are planted in spring (late April-May) or early autumn. Plants in containers can be plant whenever you want (except for winter, of course).
A solid, rigid support is installed in the center of the pit. A stretched rope is not suitable here, it will not protect young fragile whips from gusts of wind. Having covered the hole with soil about half, they make a mound on which the roots of clematis are spread to the sides and down.
Holding the plant with your hand, pour the mixture to the roots, making sure that the clematis is planted deeply. Only then will he develop a tillering center, on which new buds are subsequently laid, shoots and roots are formed. Such bushes are better able to withstand severe winters and suffer less from heat.
Clematis planted flush with the surface are short-lived: they do not bush, grow in 1-2 stems, their root system suffers from soaking. The larger the seedling, the deeper the planting should be. Young one-two-year-old plants are buried by 8-12 cm and the lower pair of buds, more mature and divided bushes - by 12-18 cm.
If clematis is planted in the spring, then the planting pit is not filled with earth to the brim, but left 5-8 cm uncovered so that the “newcomer” does not “suffocate”. As the shoots become lignified, this space is gradually filled with soil. After planting, clematis is watered abundantly, shaded from the sun, and the surface of the earth around the plant is mulched with peat. When planting in the fall, the earth is poured to the edges, the entire aboveground part is cut off to the soil level or slightly higher.
Pests of clematis
Clematis can be attacked by pests.
1. Nematodes are found on the roots or leaves of clematis.
If, when digging up the plant, they are found on the roots, then new clematis should not be planted in this place for several years.
The worms infecting the leaves cause them to dry out and die.
Pests enter the damaged plant from weeds or from the soil.
For prevention, it is recommended to use only healthy plants for reproduction, and regularly fight weeds. With a strong infection, clematis is better to destroy and disinfect the soil.
Sometimes marigolds, garlic, parsley, dill, coriander, calendula planted nearby give a good result in the fight against a nematode.
2. A fenestrated moth is a butterfly with brown wings and golden spots. Breeds small yellow caterpillars with warts on their bodies. Caterpillars feed on clematis leaves by cutting and twisting them into a tube.
When disturbed, they release a fluid that resembles the smell of a bug. To combat moths, you need to spray the plant with insecticidal preparations.
3. Butterfly - moth has greenish wings, appears in June-July. Lays green pupae between clematis leaves. You need to collect caterpillars with your hands and destroy them, spray clematis before flowering with "Agravertine".
4. Beet aphids accumulate on the underside of clematis leaves, sucking out nutrients from them. To fight, you need to spray with any insecticide.
5. When attacked by a spider mite, the leaves turn yellow, the buds dry up, and a cobweb appears on the plant.
Good for getting rid of the parasite helps infusion of garlic - 200 grams per 10 liters of water. You can use a solution of colloidal sulfur, actelik for spraying.
6. Slugs and snails destroy young shoots, they are especially dangerous in spring, when the plant is just awakening.
To collect parasites, cabbage leaves are laid out as baits, and ash is sprinkled on their places of movement.
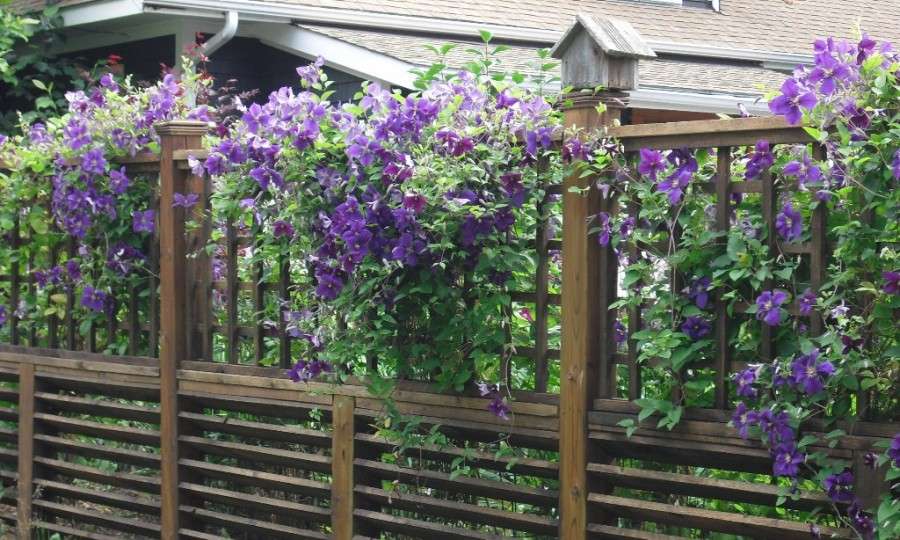
Clematis: classification
There are several types of classification of clematis and they are usually divided:
By types:
- Zhakman;
- Purple;
- Woolly;
- Flowery;
- Spreading.
By flower size (from 5 to 7 cm and 15 - 20 cm). By pruning type (those that do not need pruning and those that are cut almost completely).
By flowering:
- on last year's shoots;
- on last year and current;
- on this year's vine.
Group 1
Alpine, varieties:
- Albina Plena - white, double flowers on three-meter shoots;
- Atragena Frank is a winter-hardy plant, 2.5 meters in height with flowers in the form of blue bells;
- Pamela Jackman - blooms with medium-sized blue petals.
Flowery, varieties:
- Vivien Pennel is a three-meter plant with large, purple-blue flowers;
- Kid is a small plant with blue flowers, not exceeding a meter;
- Jeanne d'Aarc is a large white flower that grows 2, 5 m.
Mountain, varieties:
- Rubens - has bronze leaves and a vine, reaching up to 6 meters, with pink petals;
- Montana Grandiflora - has medium-sized pink and white buds and a five-meter vine;
- Tetrarose - the diameter of purple flowers reaches 8 cm.
Group 2
Woolly, varieties:
- Madame de Cultre - has large, white inflorescences, liana grows up to 3 meters;
- Lawsoniana - blooms with large purple flowers, the vine reaches 3 meters;
- HybridaSieboldii - large lilac flowers on a three-meter liana.
Sprawling, varieties:
- John Picton is a three-meter plant with purple-lilac flowers;
- Multi Blue - violet-blue flowers and vines up to 2.5 meters;
- Arctic Queen - 2.5 meters, with large white petals of the buds.
Group 3
Zhakman, varieties:
- Rouge Cardinal - 2.5 meters, with dark petals;
- Star of India - 3 meters, with large purple flowers and a red stripe;
- Bella is 2 meters with flowers in the shape of stars and changing color from white to pleasant yellow.
Viticella, varieties:
- Ville de Lyon - reaching 3.5 m in height, deep red flower;
- Viola - 2.5 m vine, with large purple flowers;
- Polish Spirit - blue and dark blue petals unfold along a 4-meter liana.
Whole-leaved, varieties:
- Durana is a low liana (up to 2 m), with oval leaves and purple flowers;
- Vyarava - 2.5 m in length, with purple petals expelled from the inside in dark blue;
- The memory of the heart - it can be one meter or two meters, it blooms with bells with flower sizes varying from 5 to 9 cm.
Tangut, varieties (four-meter vines):
- Anita - white petals;
- Love locator - bright yellow;
- Aureolin is yellow.
Description of diseases of the clematis plant and their treatment at home
Plants infect fungal and viral diseases.
On the video, a description of diseases and pests:
Fungal diseases
The most common fungal diseases are:
Withering. It is dangerous for clematis, since their root system goes into the ground by one meter. The shoots begin to wither, and then dry up completely. Basically, the disease manifests itself in early spring after a warm winter. The disease more often occurs during intensive growth, since the plant tissues work rather quickly, the plant withers in a few hours. If a disease is detected, all infected shoots are removed and the plant is watered with foundation. Effectively spray in early spring with a solution of copper sulfate. Top dressing and timely removal of weeds will help prevent the disease;
REFERENCE: The cause of the disease is the spores of a fungus that lives deep in the ground.It leads to blockage of blood vessels, which causes metabolic disorders and subsequent wilting of the shoot.
- Gray rot. Its appearance is evidenced by brown spots on shoots and leaves. Spores spread rapidly, which leads to infection of neighboring plants. Most often, gray rot can be observed in rainy years. As a preventive measure, as well as for treatment, spraying and watering the bushes with a solution of foundationol is carried out;
- Leaf spot. On the affected plant, brown spots appear with a well-defined edge on the leaves. The disease disrupts photosynthesis and weakens the plant, resulting in a shorter flowering period. The infected leaves are cut off and the plant is sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate;
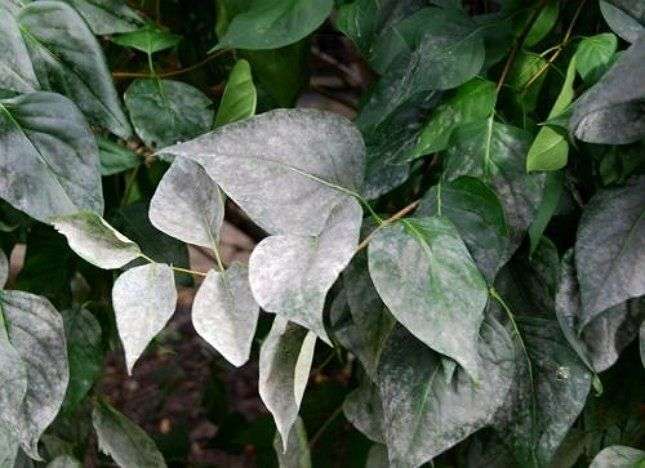
- Powdery mildew. The disease leads to damage to shoots, leaves, flowers. A white bloom appears on the clematis, which causes tissue death. Clematis stops growing and blooming. Powdery mildew occurs more frequently during the hot summer months, especially in the southern regions;
Preventive measures include cutting off damaged shoots and spraying with a solution containing 30 grams of copper sulfate and 300 grams of soap diluted in a bucket of water. It is also effective to spray with a solution of soda ash.
- Rust. Red pads appear on the leaves and shoots, in which fungal spores live. The disease causes wilting of the leaves. When the first signs are found, the infected leaves and shoots are cut out, and the clematis itself is sprayed with a solution of 2% Bordeaux liquid;
- Alternaria As a result of the disease, weakened leaves die off. Most often it appears in August-September. The cause is a fungus that lives on the old parts of the plant, which leads to necrosis. Severe damage causes infection of healthy leaves and shoots. Efficiency will give the use of all copper-containing preparations;
- Septoria. If gray spots with a reddish edge appear, then the plant has been struck by septoria. Since photosynthesis is impaired in damaged leaves, clematis weakens. To cure the plant, spraying with a 1% solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid is carried out.
Viral
Rarely enough, plants also infect viral diseases. The yellow mosaic is caused by viruses carried by sucking insects.
ATTENTION: Since there are no effective treatments, the infected plants are destroyed.
As a preventive measure, do not plant clematis near the delphinium, hosts, peony, bulbous. After the procedure for pruning plants in the garden, the instruments must be treated with a disinfectant solution. The appearance of colorless flowers is caused by improperly selected fertilizers, a lack of light and heat.
Conditions for growing clematis
Clematis are light-loving plants. If there is not enough light, not only will you not achieve good flowering, you may not even wait for it at all. Therefore, in the middle lane, it is best to plant them in sunny or slightly shaded areas at midday. Only in the southern regions, where clematis often suffer from overheating of the soil, are they planted in partial shade. For group plantings, each plant should receive enough light, and the distance between the bushes should be at least 1 meter.
The wind is a terrible enemy of clematis not only in summer, but also in winter: it breaks and confuses shoots, damages flowers. Where snow is blown off in winter, planting clematis is not a good idea. And in the lowlands, where cold air accumulates, clematis feel uncomfortable.
Clematis are very demanding on moisture: during their growth, they need abundant watering. At the same time, wet, swampy areas with a high groundwater table (less than 1.2 m) are not suitable for them, even if the water stagnates only for a short time. Waterlogging of the soil is dangerous not only in summer, but also in early spring during and after the snow melts.When planning the planting of clematis, you need to consider the natural outflow of water from the bush: add earth, plant bushes on ridges or dig slopes with a slope.
 Clematis. Colin
Clematis. Colin
Wilt: Clematis Disease
Wilt is the second name for wilting. It is very simple to define the disease: shoots on an outwardly healthy shrub suddenly lose their elasticity, begin to wither and dry (Figure 3).
Wilt is considered a dangerous disease, as it spreads quickly, and inexperienced gardeners often confuse its symptoms with insufficient watering and as a result the plant dies.
Causes
Most often, wilting occurs when the bush reaches a period of maximum growth and budding. Since during this period the root system of the plant works under a heavy load, it becomes more vulnerable to disease.
It is important that at the initial stages it is difficult to determine the disease, but improper watering and non-compliance with the rules of cultivation can be provoking factors.
Symptoms
During weeding of the plant, damage to the lower parts of the shoots can occur, which leads to mechanical wilting. In a strong wind, when the cords on the supports are not stretched, the wind twists the shoots. This causes tissue damage similar to contagious wilting.
Common care mistakes
|
Violation of watering rules
Peculiarities:
|
|
 |
Incorrectly selected soil
Peculiarities:
|
 |
Lack of nutritional components
Peculiarities:
|
 |
Failure to comply with the rules of pruning
Peculiarities:
|